61286e975bb2eb4d23843c4c9b66f530.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 26

ADAPTIVE LEARNING IN THE LIBRARY DESIGNING A SUSTAINABLE AND EFFECTIVE ONLINE INSTRUCTION PROGRAM Joelle Pitts Assistant Professor | Instructional Design Librarian Kansas State University

OVERVIEW • Distance Student Behaviors and Expectations • Adaptive Learning • Library Applications

BACKGROUND • SLIM • Great Plains IDEA • • • Distance Education Consortium Fully online degree programs/course sharing Faculty and student interaction Program building Assessment Research

GREAT PLAINS IDEA FACULTY • Most teach on campus • Most are under pressure • Most completed their graduate work using outdated technologies • Focus is getting content online • Most assume their audience is nontraditional • And knows how to conduct research • Information literacy gaps • More training needed

ONLINE = NON-TRADITIONAL?

NON-TRADITIONAL?

NON-TRADITIONAL?

NON-TRADITIONAL GPIDEA STUDENTS • Demographics • Mostly female • Avg. age 33 • Non traditional • Work at least part time • Family responsibilities • Financial restrictions

NON-TRADITIONAL GPIDEA STUDENTS Behavior • 10+ years since undergraduate work • Technology learning curve • Wikis • Google applications • Multimedia/collaborative platforms • Library use • Aren’t aware they are able to access it as a distance student • Perception of the library is print based Expectations • • Consistency Format Efficiency Cost

TRADITIONAL GPIDEA STUDENTS • Fastest growing population in online education • Demographics • Millennial (18 -30) • Work part time • Some family obligations
TRADITIONAL GPIDEA STUDENTS Behavior • Technology • Wired • Social Media • Multimedia/collaborative platforms • Mobile • Gaming Expectations • • Consistency Format Efficiency Cost • Library use • Aren’t aware they are able to access it as a distance student • Perception of the library is print based Pew Research Center (2010)

GPIDEA COMMON STUDENT BEHAVIORS AND EXPECTATIONS Behavior Expectations • Library use • Aren’t aware they are able to access it as a distance student • Perception of the library is print based • • Consistency Format Efficiency Cost Information Literacy Level? Online ≠ non-traditional

ADAPTIVE LEARNING
ADAPTIVE LEARNING BASICS • A system which collects user information and behavioral data to customize a learning experience for an individual • Encourages active participation rather than passive receptacle • Moves away from static hypermedia (same page content and links for all users) • Artificial Intelligence movement Brusilovsky (2001)

THIS…

NOT THIS…
MACHINE LEARNING • Machine collects data and recognizes patterns in the data • Algorithms – sequence of instructions to transform the input into output • Intelligent systems have the ability to learn in a changing environment Alpaydin (2010)
ADAPTATION PROCESS • Data collection • User interaction • Direct input • • • Interpret data using models Infer user requirements and preferences Tailored aggregation Presentation of tailored content (adaptive effect) Synthesis with population data Paramythis & Liodl. Reisinger, (2003)
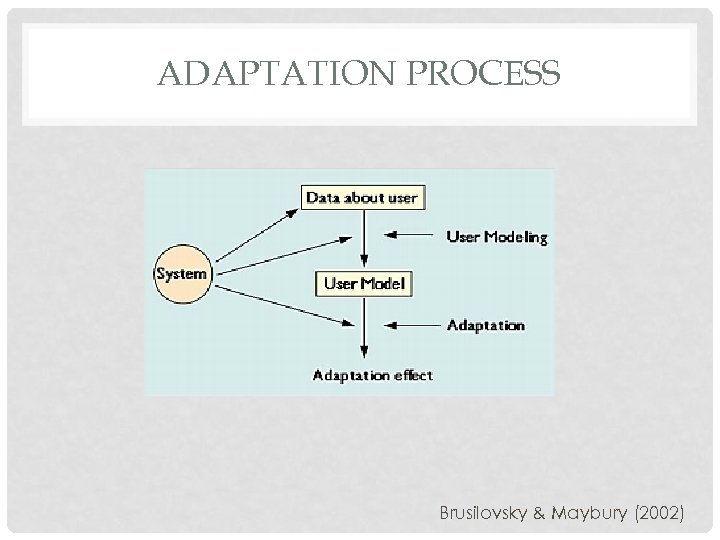
ADAPTATION PROCESS Brusilovsky & Maybury (2002)
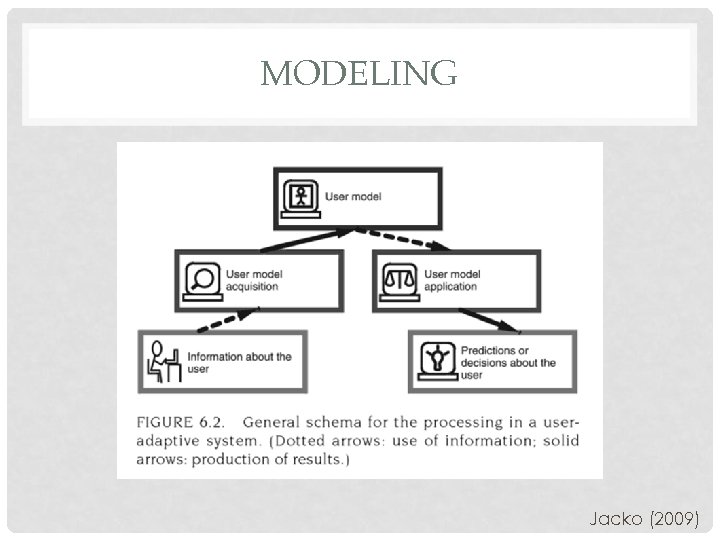
MODELING Jacko (2009)

CATEGORIES OF ADAPTATION • Interaction with the system • Course/object delivery • Content adaptation • Collaborative/social support Paramythis & Liodl. Reisinger (2003)

CONTENT ADAPTATION • Adaptive presentation • content of a hypermedia page adapted to the user’s goals, knowledge and other information • Adaptive navigation • link presentation and functionality adapted to the goals, knowledge and characteristics of the user • • Direct guidance Link sorting Link annotation Link hiding Brusilovsky (2000)

ASSESSMENT • System feedback • Embedded assessment • Adaptive • Timing/architecture • Question level

EXAMPLES • • • Adaptive e. Learning Research Group AHA! Andes Physics Tutor ELM-ART GRE i. Know! Learnthat Khan Academy Knewton • More…

REFERENCES • Alpaydin, E. (2010). Introduction to machine learning, ch. 1. MIT Press • De Bra, P. , et al. (2003) AHA! The Adaptive Hypermedia Architecture. In Proceedings of the fourteenth ACM conference on Hypertext and Hypermedia, Nottingham, August, pp. 81 -84 • De Bra, P. , Aroyo, L. , & Chepegin, V. (2004). The next big thing: adaptive web-based systems. Journal of Digital Information, 5(1). • Brusilovsky, P. (2000). Adaptive hypermedia: from intelligent tutoring systems to webbased education. Intelligent Tutoring Systems: 5 th International Conference. • Brusilovsky, P. (2001). Adaptive hypermedia. User modeling and user-adapted interaction. 11: 87 -110. • Brusilovsky, P. , & Maybury, M. T. (2002). From adaptive hypermedia to the adaptive web. Communications of the ACM, vol. 45, No. 5. • Brusilovsky, P. , & Peylo, C. (2003). Adaptive and intelligent web-based educational systems. International Journal of Artificial intelligence in Education 13, 159 -172. • Great Plains Interactive Distance Education Alliance. (2009). New student survey • Jacko, J. A. (2009). Human-computer interaction: design issues, solutions, and applications. Taylor & Francis. • Paramythis, A. , & Liodl-Reisinger, S. (2003). Adaptive learning environments and e-learning standards. European conference on E-Learning. • Pew Research Center. (2010). Millennials: a portrait of generation next. http: //pewsocialtrends. org/files/2010/10/millennials-confident-connected-open-tochange. pdf

IMAGE CREDITS • http: //web. mit. edu/newsoffice/2009/ai-overview 1207. html • http: //s 425. photobucket. com/albums/pp 339/ridizle 4/? action=view¤t=terminator. png&newest=1 • http: //www. llift. com/pages/platform. htm • http: //www. gw. edu/academics/off/online/ • http: //www. braintrack. com/college-and-worknews/articles/non-traditional-students-becomingthe-norm-10082502 • http: //www. drexel. edu/univrel/digest/archive/1103 06/index. html
61286e975bb2eb4d23843c4c9b66f530.ppt