5d4768f31576eece619730c3099ea21b.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 20
 Adaptive Data Refinement for Parallel Dynamic Programming Applications Shanjiang Tang 1, 2, Ce Yu 1, Bu-Sung Lee 2, 3, Chao Sun 1, Jizhou Sun 1 1 Tianjin 2 Nanyang University, China Technological University, Singapore 3 HP Labs, Singapore 25 th May 2012
Adaptive Data Refinement for Parallel Dynamic Programming Applications Shanjiang Tang 1, 2, Ce Yu 1, Bu-Sung Lee 2, 3, Chao Sun 1, Jizhou Sun 1 1 Tianjin 2 Nanyang University, China Technological University, Singapore 3 HP Labs, Singapore 25 th May 2012
 Out. Line • • 2 Background & Motivation Adaptive Data Refinement Approach Evaluation Conclusion Tianjin University
Out. Line • • 2 Background & Motivation Adaptive Data Refinement Approach Evaluation Conclusion Tianjin University
 Dynamic Programming (DP) Ø What is Dynamic Programming (DP) ? DP is a popular algorithm design technique for the solution of many decision and optimization problems by decomposing the problem at hand into a sequence of interrelated decision or optimization steps that are solved one after the others. Generally, if r represents the cost of a solution composed of sub-problems x 1, x 2…xl, then r can be written as: r = g(f(x 1), f(x 2), f(x 3), … , f(xl)). Examples: 3 Tianjin University
Dynamic Programming (DP) Ø What is Dynamic Programming (DP) ? DP is a popular algorithm design technique for the solution of many decision and optimization problems by decomposing the problem at hand into a sequence of interrelated decision or optimization steps that are solved one after the others. Generally, if r represents the cost of a solution composed of sub-problems x 1, x 2…xl, then r can be written as: r = g(f(x 1), f(x 2), f(x 3), … , f(xl)). Examples: 3 Tianjin University
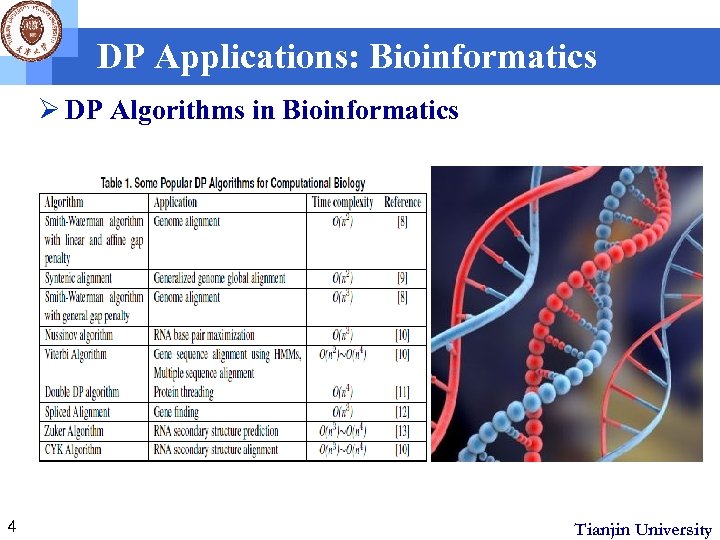 DP Applications: Bioinformatics Ø DP Algorithms in Bioinformatics 4 Tianjin University
DP Applications: Bioinformatics Ø DP Algorithms in Bioinformatics 4 Tianjin University
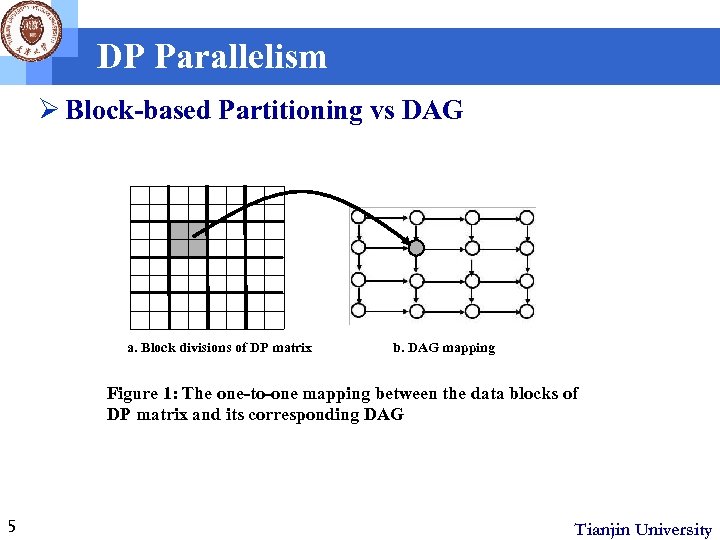 DP Parallelism Ø Block-based Partitioning vs DAG a. Block divisions of DP matrix b. DAG mapping Figure 1: The one-to-one mapping between the data blocks of DP matrix and its corresponding DAG 5 Tianjin University
DP Parallelism Ø Block-based Partitioning vs DAG a. Block divisions of DP matrix b. DAG mapping Figure 1: The one-to-one mapping between the data blocks of DP matrix and its corresponding DAG 5 Tianjin University
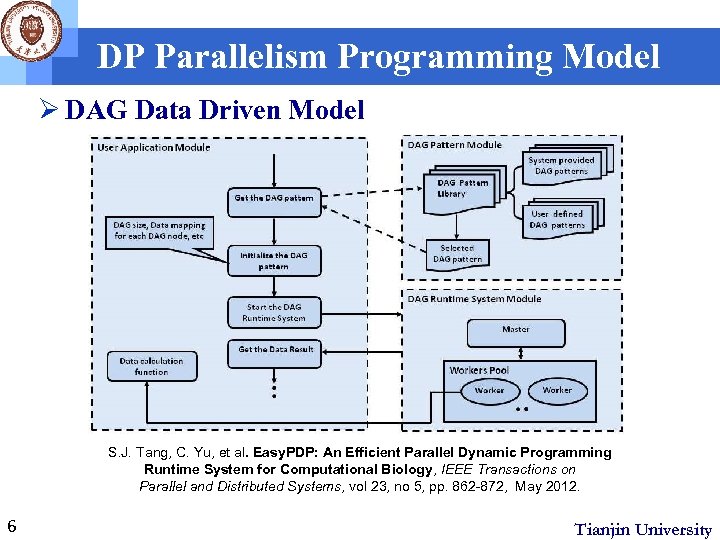 DP Parallelism Programming Model Ø DAG Data Driven Model S. J. Tang, C. Yu, et al. Easy. PDP: An Efficient Parallel Dynamic Programming Runtime System for Computational Biology, IEEE Transactions on Parallel and Distributed Systems, vol 23, no 5, pp. 862 -872, May 2012. 6 Tianjin University
DP Parallelism Programming Model Ø DAG Data Driven Model S. J. Tang, C. Yu, et al. Easy. PDP: An Efficient Parallel Dynamic Programming Runtime System for Computational Biology, IEEE Transactions on Parallel and Distributed Systems, vol 23, no 5, pp. 862 -872, May 2012. 6 Tianjin University
 DP Parallelism Framework: Easy. PDP Ø Easy. PDP Framework v A shared-memory system implementation of DAG Data Driven Model for DP applications v Adopt the dynamic workers pool v Current version works with C/C++ and use P-threads Ø Source code (open-source now) downloading at: v http: //easypdp. sourceforge. net/ v http: //cs. tju. edu. cn/orgs/hpclab/release/Easy. PDP/ 7 Tianjin University
DP Parallelism Framework: Easy. PDP Ø Easy. PDP Framework v A shared-memory system implementation of DAG Data Driven Model for DP applications v Adopt the dynamic workers pool v Current version works with C/C++ and use P-threads Ø Source code (open-source now) downloading at: v http: //easypdp. sourceforge. net/ v http: //cs. tju. edu. cn/orgs/hpclab/release/Easy. PDP/ 7 Tianjin University
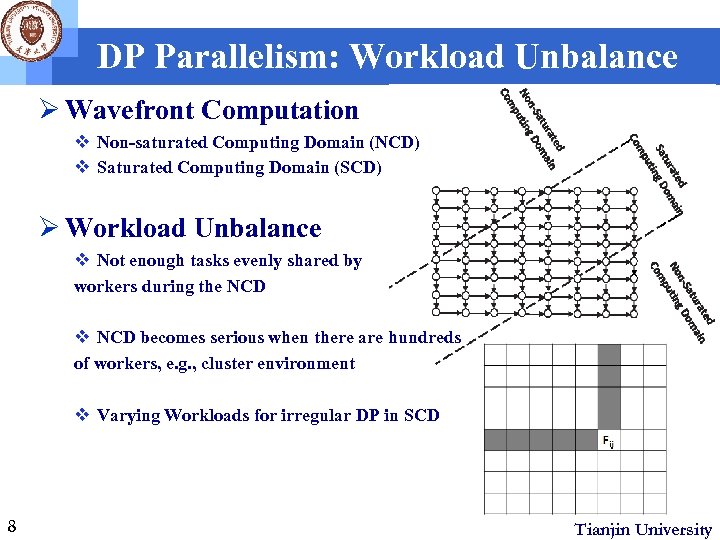 DP Parallelism: Workload Unbalance Ø Wavefront Computation v Non-saturated Computing Domain (NCD) v Saturated Computing Domain (SCD) Ø Workload Unbalance v Not enough tasks evenly shared by workers during the NCD v NCD becomes serious when there are hundreds of workers, e. g. , cluster environment v Varying Workloads for irregular DP in SCD 8 Tianjin University
DP Parallelism: Workload Unbalance Ø Wavefront Computation v Non-saturated Computing Domain (NCD) v Saturated Computing Domain (SCD) Ø Workload Unbalance v Not enough tasks evenly shared by workers during the NCD v NCD becomes serious when there are hundreds of workers, e. g. , cluster environment v Varying Workloads for irregular DP in SCD 8 Tianjin University
 Out. Line • • 9 Background & Motivation Adaptive Data Refinement Approach Evaluation Conclusion Tianjin University
Out. Line • • 9 Background & Motivation Adaptive Data Refinement Approach Evaluation Conclusion Tianjin University
 Adaptive Data Refinement Approach Ø Dynamic Data Repartitioning v Re-partition the data block into smaller ones whenever detecting workload unbalanced (i. e. , there are idle workers) Ø Challenging Issues: v How to keep the data dependency for repartitioned block data? v How to detect the workload unbalance during runtime? v How many partitions are suitable for a data repartitioning? 10 Tianjin University
Adaptive Data Refinement Approach Ø Dynamic Data Repartitioning v Re-partition the data block into smaller ones whenever detecting workload unbalanced (i. e. , there are idle workers) Ø Challenging Issues: v How to keep the data dependency for repartitioned block data? v How to detect the workload unbalance during runtime? v How many partitions are suitable for a data repartitioning? 10 Tianjin University
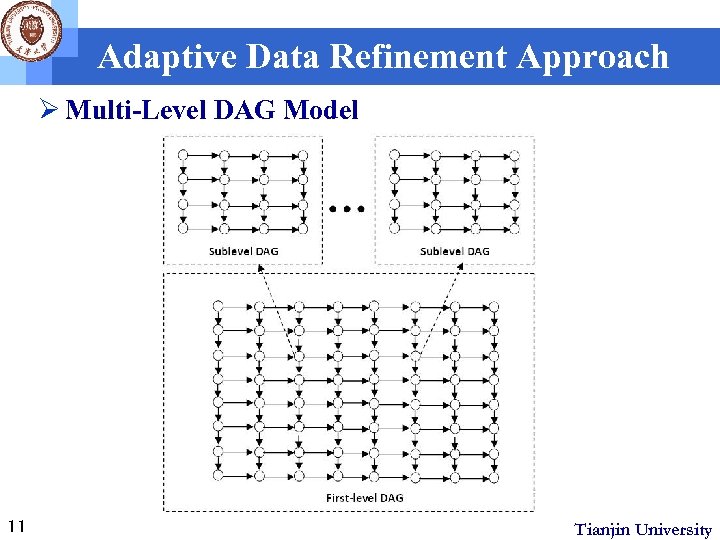 Adaptive Data Refinement Approach Ø Multi-Level DAG Model 11 Tianjin University
Adaptive Data Refinement Approach Ø Multi-Level DAG Model 11 Tianjin University
 Adaptive Data Refinement Approach Ø Workload Unbalanced Detection v Based on the principle that the load unbalanced is assumed whenever there are idle workers before the whole computation finishes. Our system just need to periodically check the status of workers in the pool. Ø Size of Partitions for a data block v Give an empirical result by experiment. v It’s fine when set the number of partitions to the square of the number of workers. 12 Tianjin University
Adaptive Data Refinement Approach Ø Workload Unbalanced Detection v Based on the principle that the load unbalanced is assumed whenever there are idle workers before the whole computation finishes. Our system just need to periodically check the status of workers in the pool. Ø Size of Partitions for a data block v Give an empirical result by experiment. v It’s fine when set the number of partitions to the square of the number of workers. 12 Tianjin University
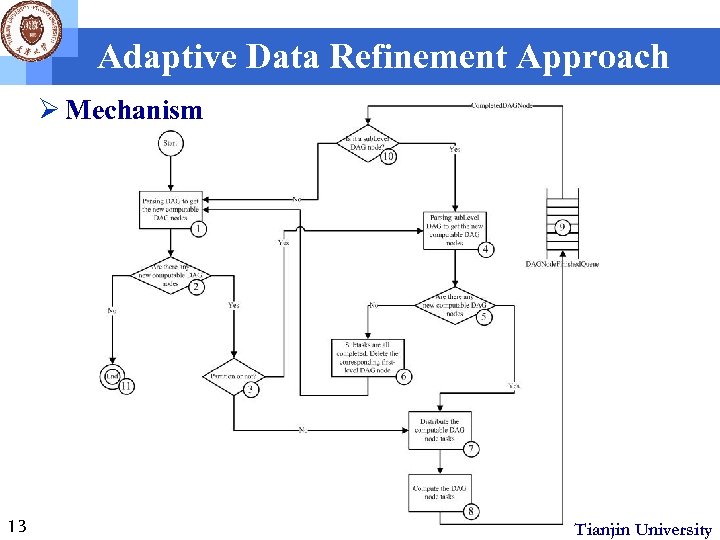 Adaptive Data Refinement Approach Ø Mechanism 13 Tianjin University
Adaptive Data Refinement Approach Ø Mechanism 13 Tianjin University
 Out. Line • • 14 Background & Motivation Adaptive Data Refinement Approach Evaluation Conclusion Tianjin University
Out. Line • • 14 Background & Motivation Adaptive Data Refinement Approach Evaluation Conclusion Tianjin University
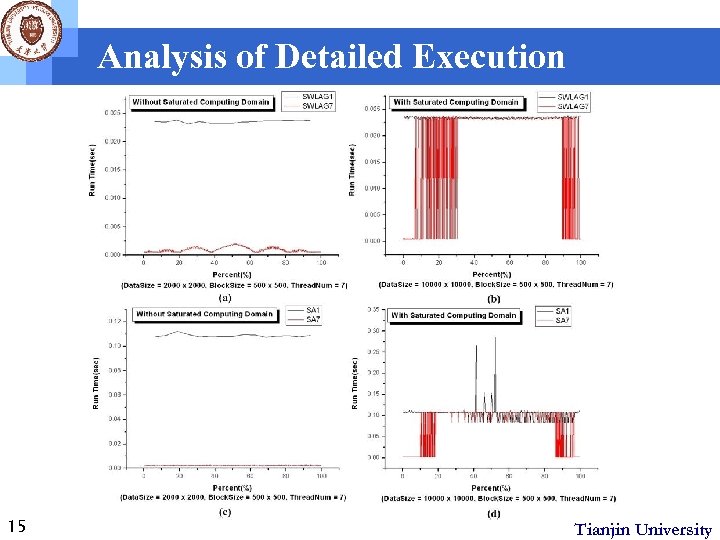 Analysis of Detailed Execution 15 Tianjin University
Analysis of Detailed Execution 15 Tianjin University
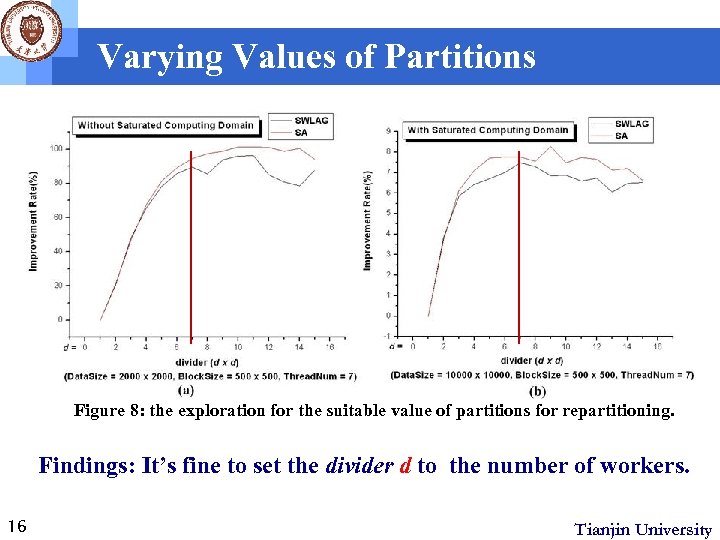 Varying Values of Partitions Figure 8: the exploration for the suitable value of partitions for repartitioning. Findings: It’s fine to set the divider d to the number of workers. 16 Tianjin University
Varying Values of Partitions Figure 8: the exploration for the suitable value of partitions for repartitioning. Findings: It’s fine to set the divider d to the number of workers. 16 Tianjin University
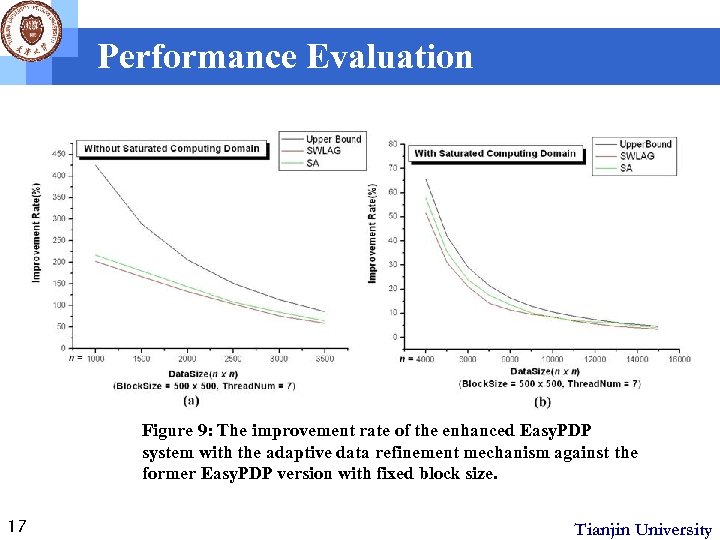 Performance Evaluation Figure 9: The improvement rate of the enhanced Easy. PDP system with the adaptive data refinement mechanism against the former Easy. PDP version with fixed block size. 17 Tianjin University
Performance Evaluation Figure 9: The improvement rate of the enhanced Easy. PDP system with the adaptive data refinement mechanism against the former Easy. PDP version with fixed block size. 17 Tianjin University
 Out. Line • • 18 Background & Motivation Adaptive Data Refinement Approach Evaluation Conclusion Tianjin University
Out. Line • • 18 Background & Motivation Adaptive Data Refinement Approach Evaluation Conclusion Tianjin University
 Conclusion Ø Adaptive Data Refinement Mechanism v Currently, we implement it in our Easy. PDP framework. In future, we will add it to our distributed framework (Easy. HPS). v The idea is not limited to DP applications, it can be used in other applications whose dependency can be modeled as DAG. 19 Tianjin University
Conclusion Ø Adaptive Data Refinement Mechanism v Currently, we implement it in our Easy. PDP framework. In future, we will add it to our distributed framework (Easy. HPS). v The idea is not limited to DP applications, it can be used in other applications whose dependency can be modeled as DAG. 19 Tianjin University



