Лекция 11 КПП 2011.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 58
 Adaptive and compensatory processes Lecture
Adaptive and compensatory processes Lecture
 Types of compensations and adaptations 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. Regeneration Аtrophy Hypertrophy Оrganization Tissue restructuring Metaplasia Dysplasia
Types of compensations and adaptations 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. Regeneration Аtrophy Hypertrophy Оrganization Tissue restructuring Metaplasia Dysplasia
 АTROPHY o Life-time volume contraction of the cells, tissues or organs, accompanied by decrease or cessation of their functions.
АTROPHY o Life-time volume contraction of the cells, tissues or organs, accompanied by decrease or cessation of their functions.
 Аtrophy o o o Physiological Senile Pathological (local and general)
Аtrophy o o o Physiological Senile Pathological (local and general)
 Physiological atrophy o o Аtrophy and obliteration of umbilical arteries Obliteration of arterial (Botallo`s) duct Sexual glands atrophy in aged people Thymus atrophy in pubertal period
Physiological atrophy o o Аtrophy and obliteration of umbilical arteries Obliteration of arterial (Botallo`s) duct Sexual glands atrophy in aged people Thymus atrophy in pubertal period
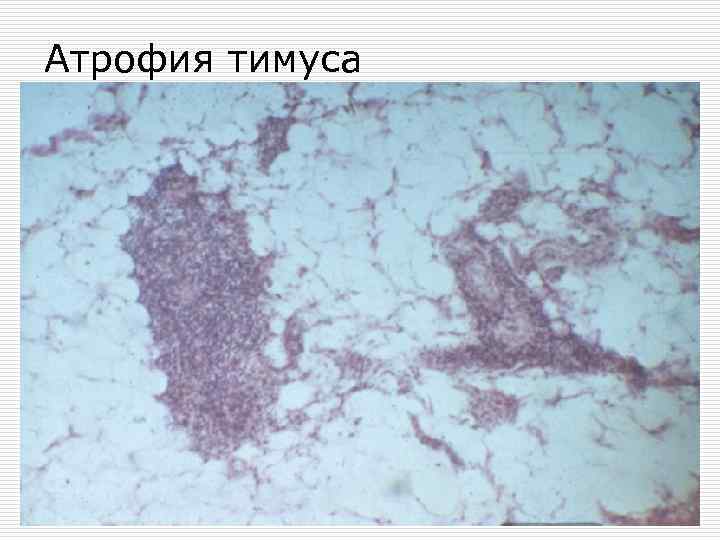 Атрофия тимуса
Атрофия тимуса
 Senile atrophy o o o atrophy of gonads, intervertebral disks, skin
Senile atrophy o o o atrophy of gonads, intervertebral disks, skin
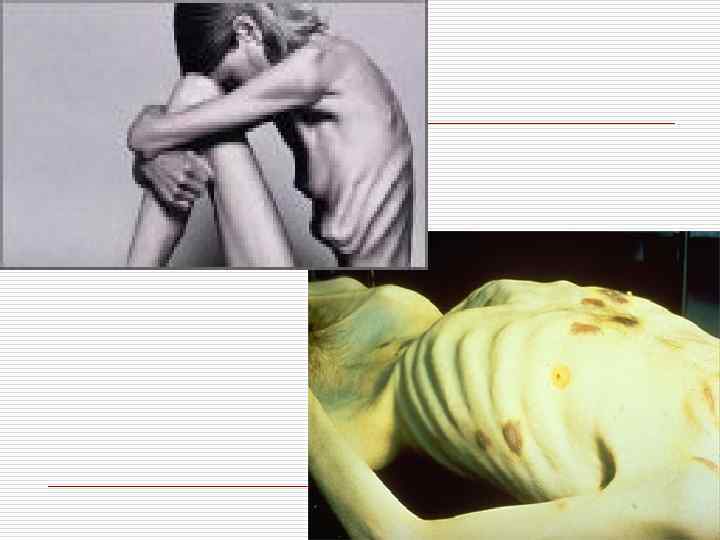
 Pathological general atrophy Cachexia Can be: 1. Аlimentary 2. Cancerous 3. Hypophysial 4. Cerebral 5. Cachexia in case of chronic infectious diseases o
Pathological general atrophy Cachexia Can be: 1. Аlimentary 2. Cancerous 3. Hypophysial 4. Cerebral 5. Cachexia in case of chronic infectious diseases o

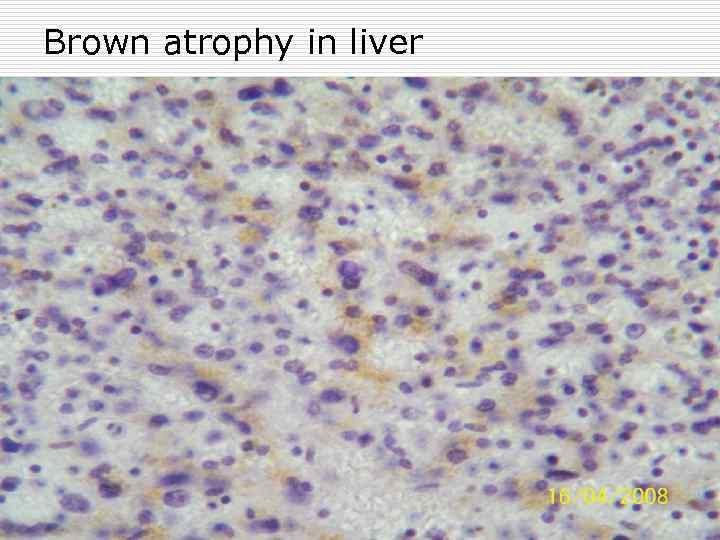 Brown atrophy in liver
Brown atrophy in liver
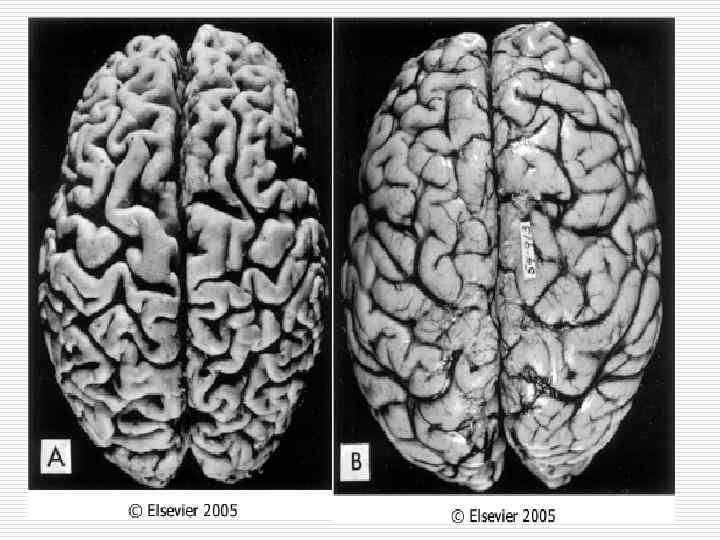
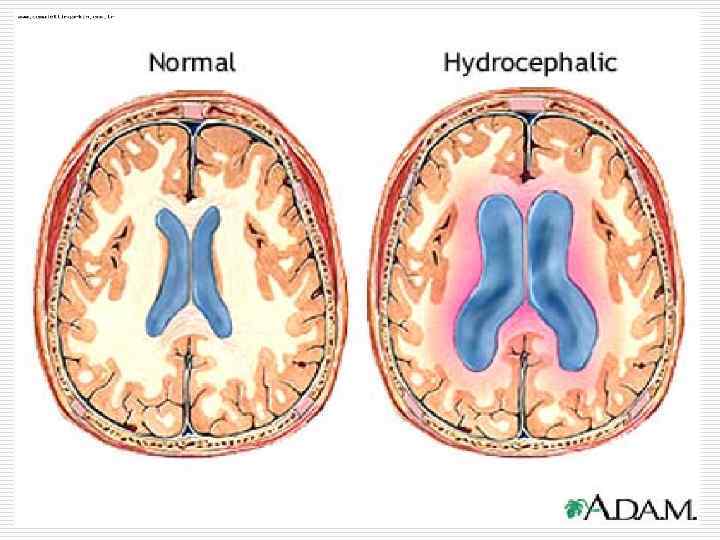
 Types of local pathological atrophy 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Dysfunctional atrophy (atrophy of skeletal muscles doe to fracture) In case of circulatory insufficiency (wrinkled kidney, atrophy of cells of brain cortex due to atherosclerosis) Due to compression – pressure atrophy (hydronephrosis, hydrocephaly, emphysema of lungs) Neurotic (atrophy of skeletal muscles) Under the influence of physical or chemical factors (atrophy of gonads, medullary hemopoiesis)
Types of local pathological atrophy 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Dysfunctional atrophy (atrophy of skeletal muscles doe to fracture) In case of circulatory insufficiency (wrinkled kidney, atrophy of cells of brain cortex due to atherosclerosis) Due to compression – pressure atrophy (hydronephrosis, hydrocephaly, emphysema of lungs) Neurotic (atrophy of skeletal muscles) Under the influence of physical or chemical factors (atrophy of gonads, medullary hemopoiesis)
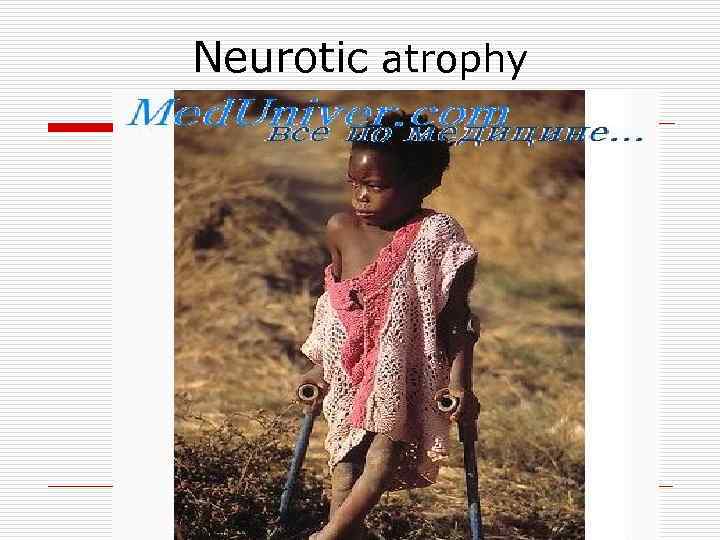 Neurotic atrophy
Neurotic atrophy
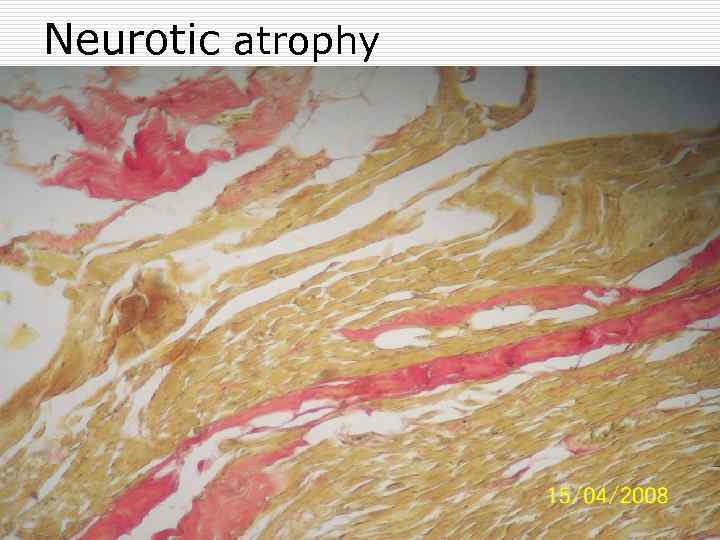 Neurotic atrophy
Neurotic atrophy
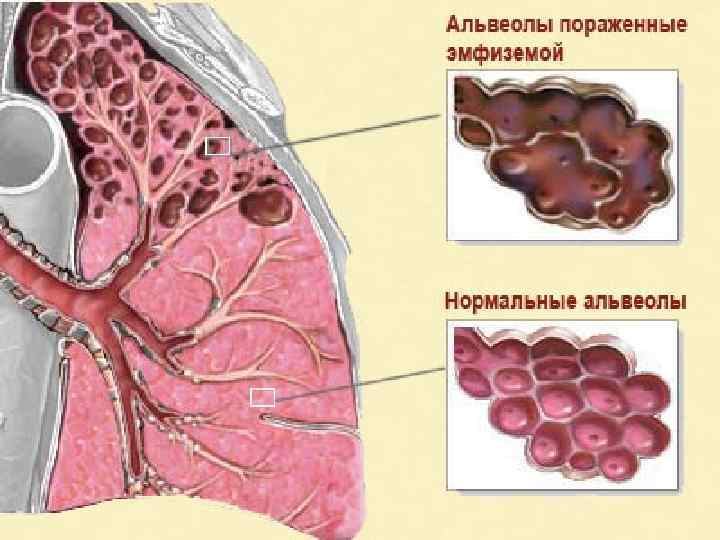
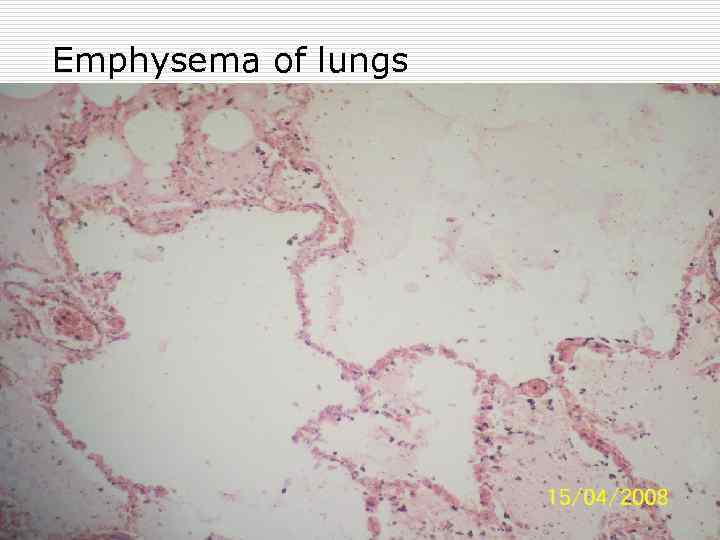 Emphysema of lungs
Emphysema of lungs
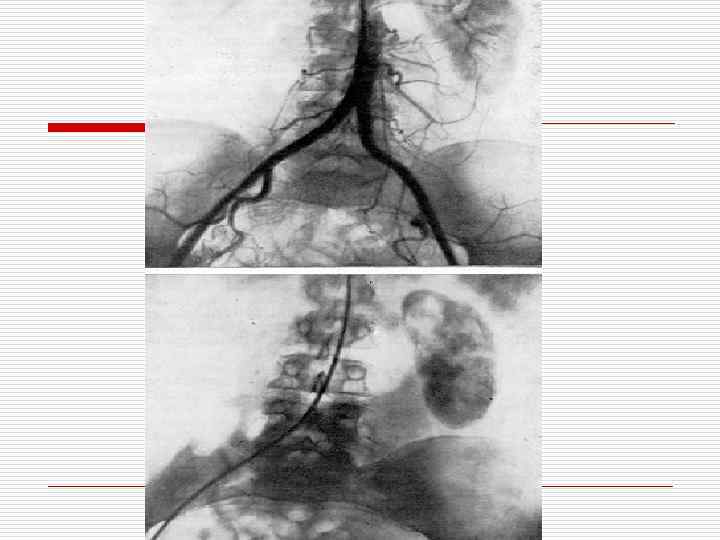
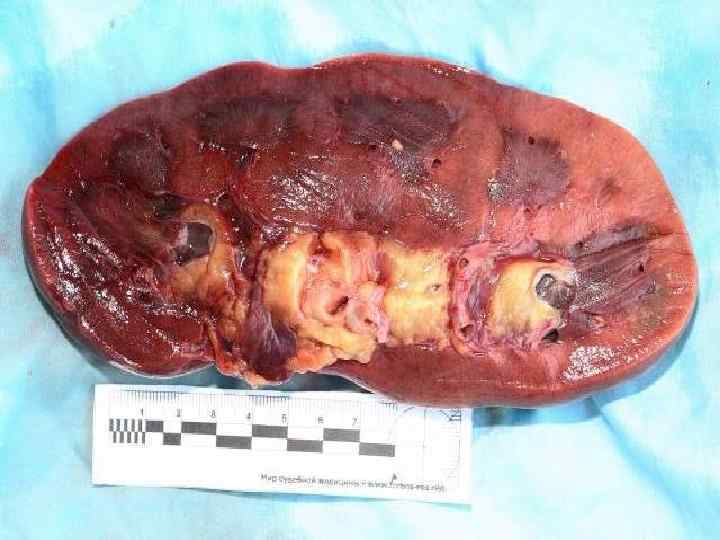
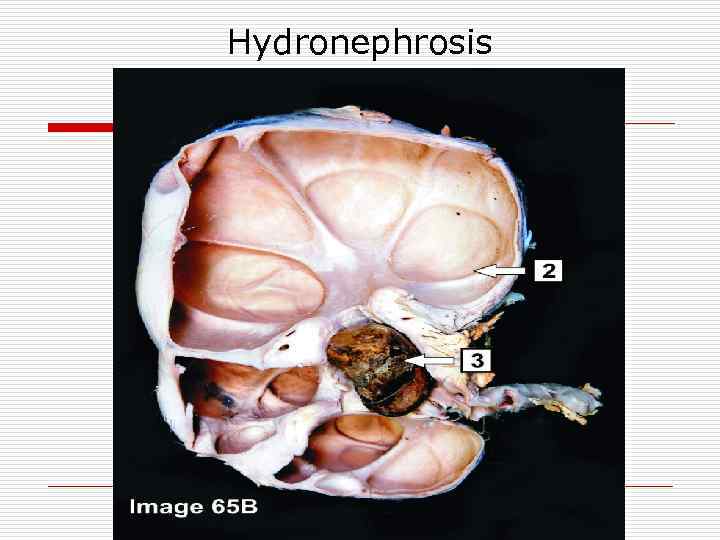 Hydronephrosis
Hydronephrosis
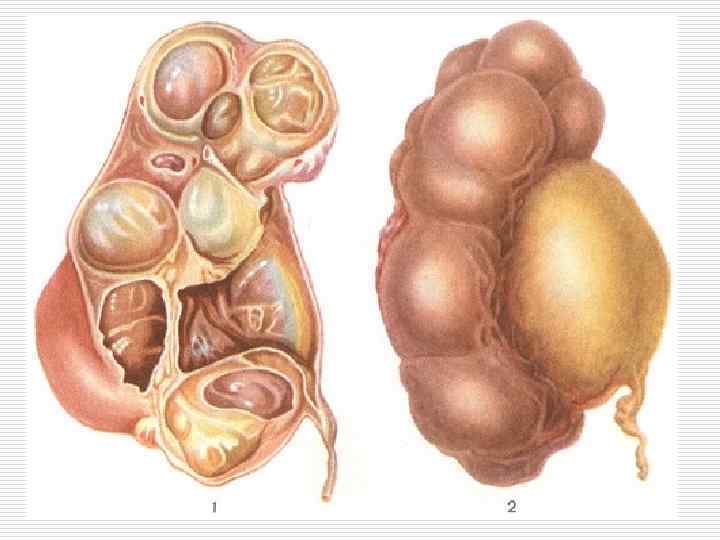
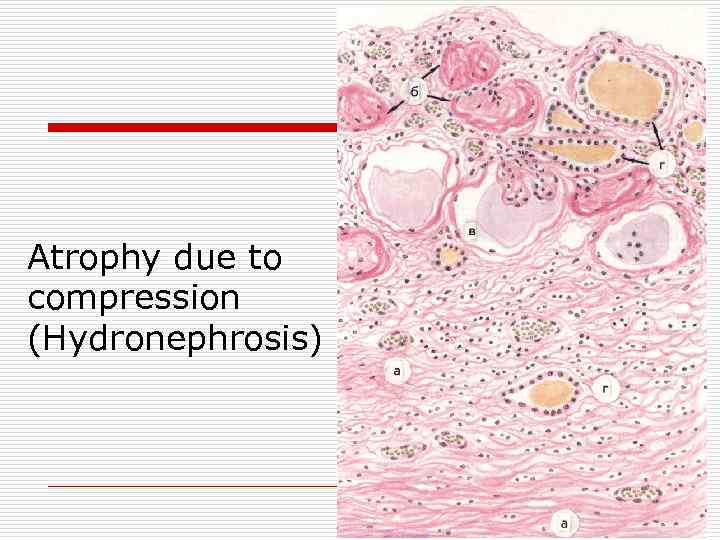 Аtrophy due to compression (Hydronephrosis)
Аtrophy due to compression (Hydronephrosis)
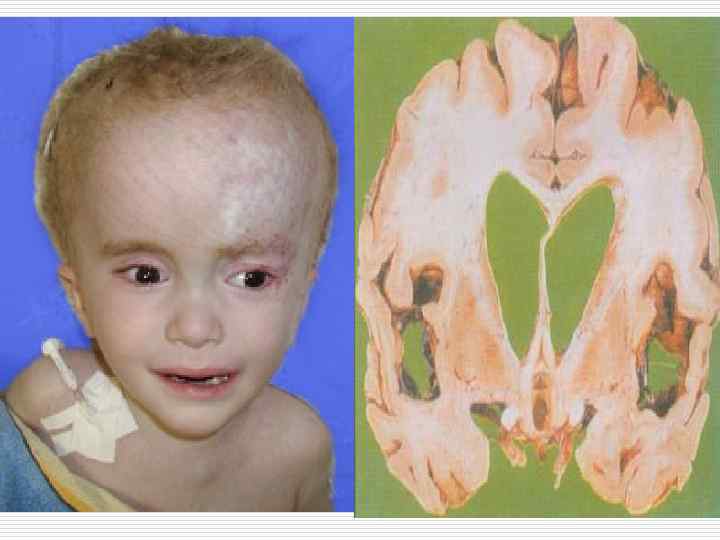
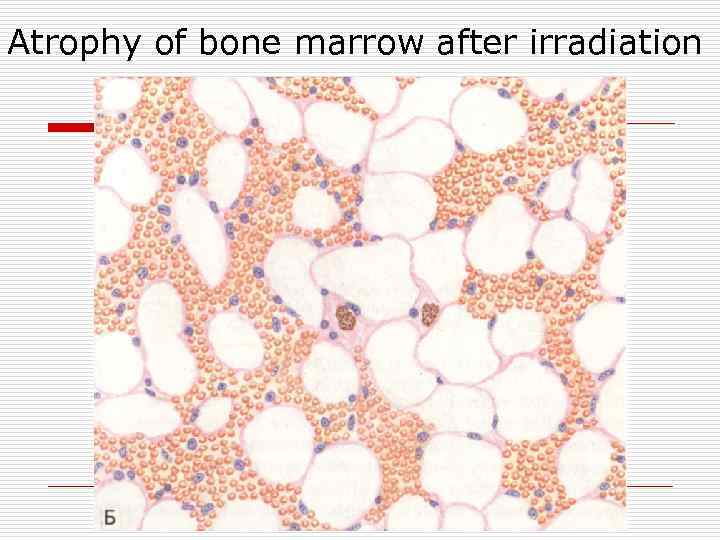 Аtrophy of bone marrow after irradiation
Аtrophy of bone marrow after irradiation
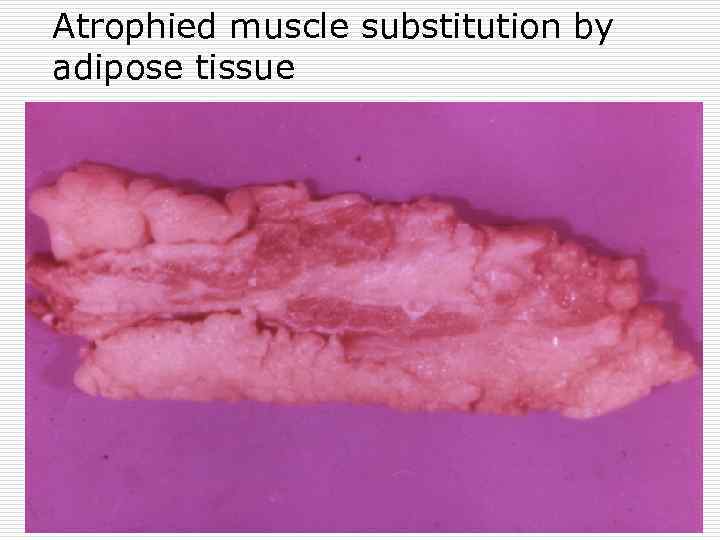 Atrophied muscle substitution by adipose tissue
Atrophied muscle substitution by adipose tissue
 Atrophy morphology 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. Consolidation of tissue structure Dehydration Decrease of cellular mass Cells volume contraction Destruction of collagenic fibers Accumulation of acidic products Appearance of lipofuscin (brown atrophy)
Atrophy morphology 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. Consolidation of tissue structure Dehydration Decrease of cellular mass Cells volume contraction Destruction of collagenic fibers Accumulation of acidic products Appearance of lipofuscin (brown atrophy)
 Hypertrophy Volume increase of the functioning tissue, ensuring the organ hyperfunction. Hyperplasia – quantity increase of the cells, intracellular structures, vessels, stroma components.
Hypertrophy Volume increase of the functioning tissue, ensuring the organ hyperfunction. Hyperplasia – quantity increase of the cells, intracellular structures, vessels, stroma components.
 Types of hypertrophy o o Physiological Pathological Types of pathological hypertrophy o o Neurohumoral Hypertrophic overgrowth (false) Work, compensatory Vicarious (substitutional)
Types of hypertrophy o o Physiological Pathological Types of pathological hypertrophy o o Neurohumoral Hypertrophic overgrowth (false) Work, compensatory Vicarious (substitutional)
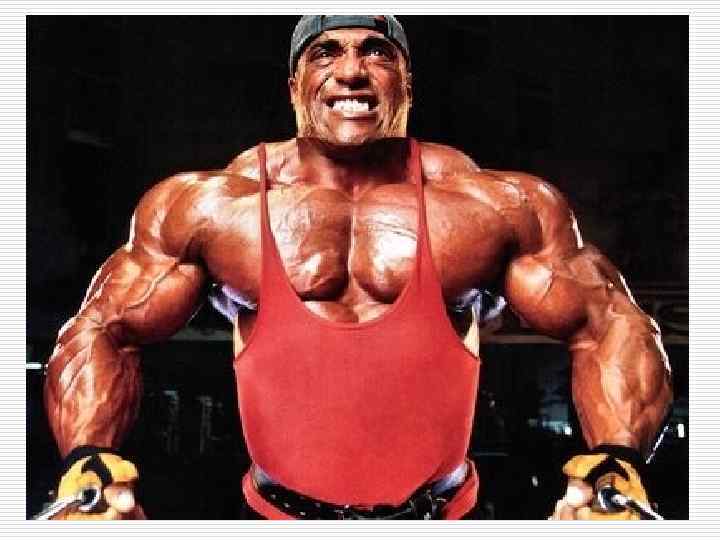

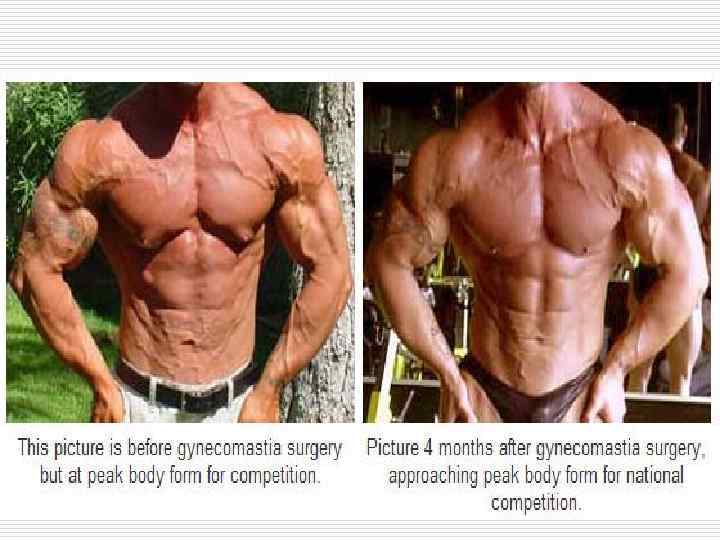
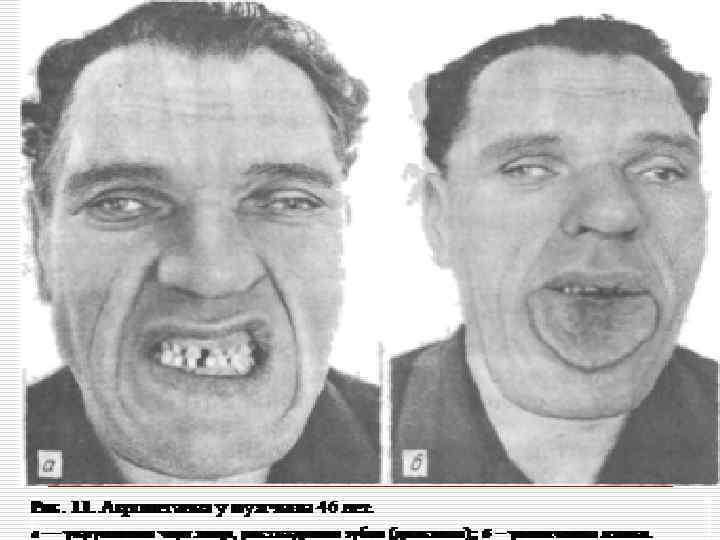
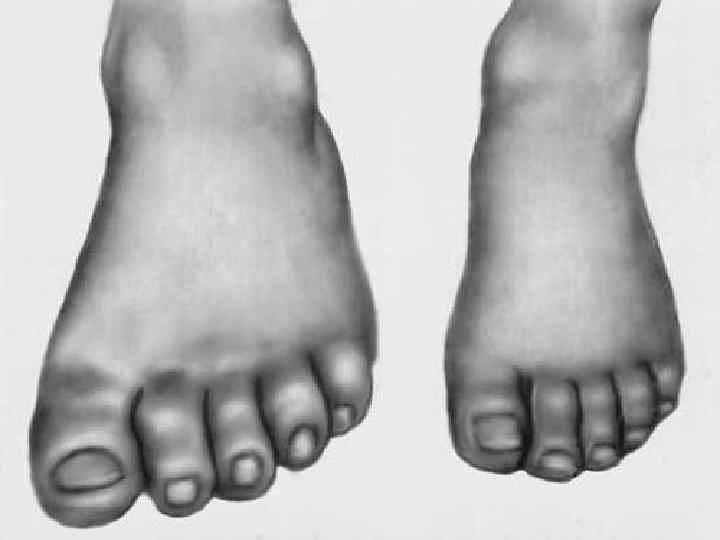
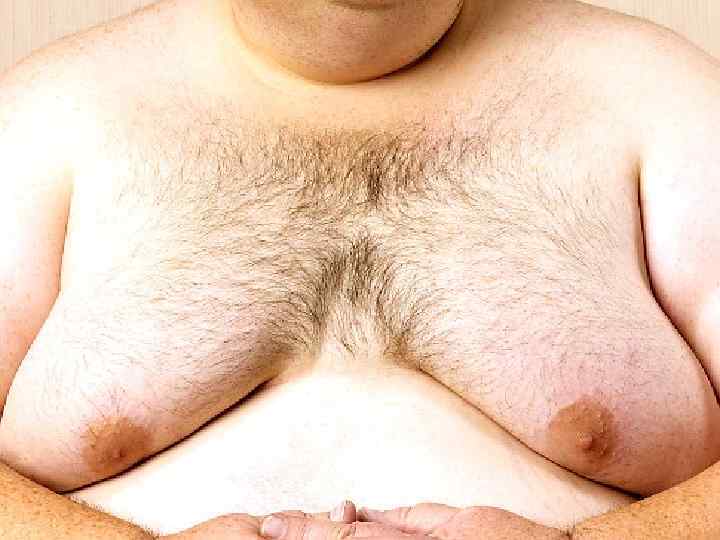
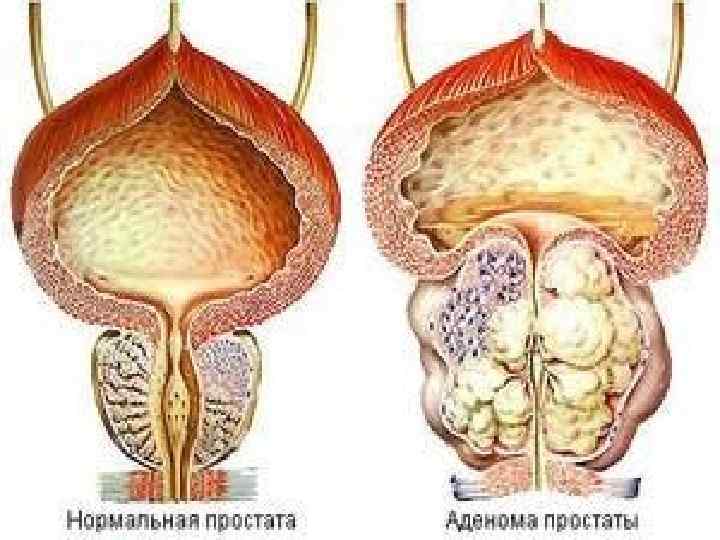
 Neurohumoral hypertrophy (hyperplasia) appear due to endocrine glands dysfunction. o In case of ovarian dysfunction in the endometrium glands hyperplasia develops. o In case of atrophic processes in oothecas in the mammary glands of men hyperplasia of gland lobes develops (gynecomastia). o Adenohypophysis hyperactivity usually appearing due to adenoid tumor (adenoma) is accompanied by enlargement of organs and protruding skeleton (acromegalia).
Neurohumoral hypertrophy (hyperplasia) appear due to endocrine glands dysfunction. o In case of ovarian dysfunction in the endometrium glands hyperplasia develops. o In case of atrophic processes in oothecas in the mammary glands of men hyperplasia of gland lobes develops (gynecomastia). o Adenohypophysis hyperactivity usually appearing due to adenoid tumor (adenoma) is accompanied by enlargement of organs and protruding skeleton (acromegalia).

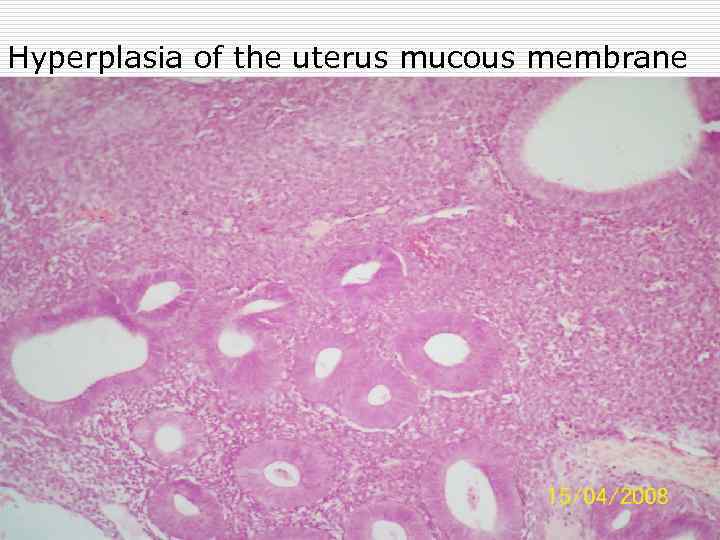 Hyperplasia of the uterus mucous membrane
Hyperplasia of the uterus mucous membrane
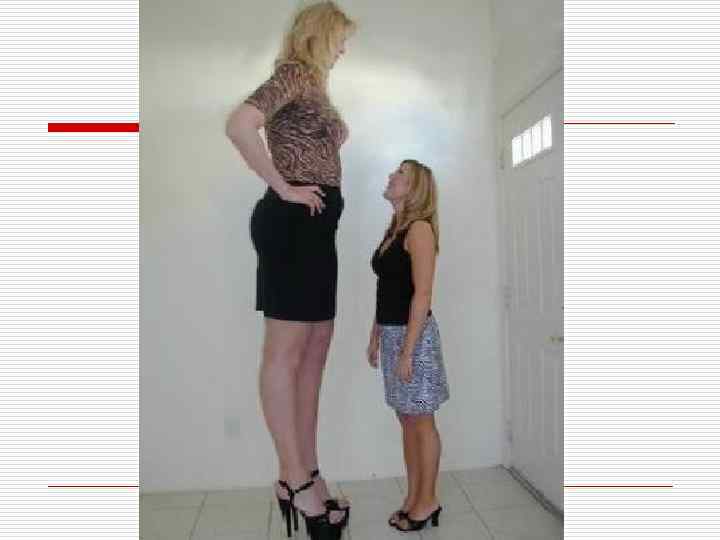
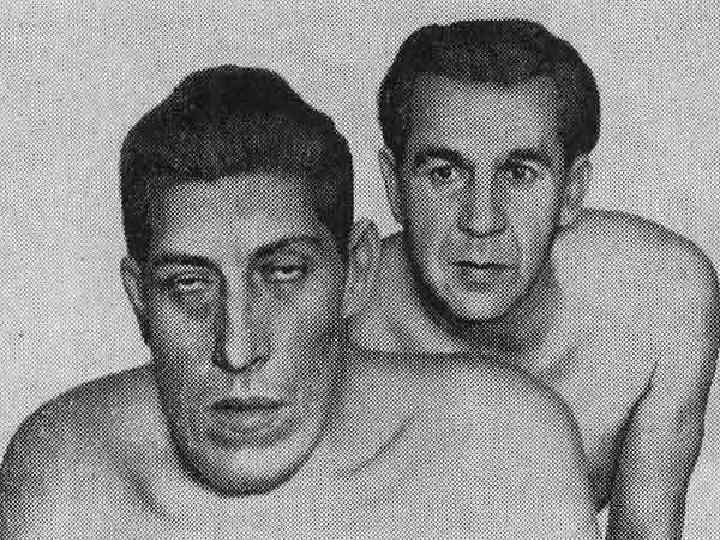






 Hypertrophic overgrowth (false hypertrophy) o o It is very often observed in case of a chronic inflammation (for example on mucosas with polyps formation) and in case of limphokinesis breaks in legs and lymph congestion, leading to the connective tissue overgrowth (development of elephantiasis).
Hypertrophic overgrowth (false hypertrophy) o o It is very often observed in case of a chronic inflammation (for example on mucosas with polyps formation) and in case of limphokinesis breaks in legs and lymph congestion, leading to the connective tissue overgrowth (development of elephantiasis).
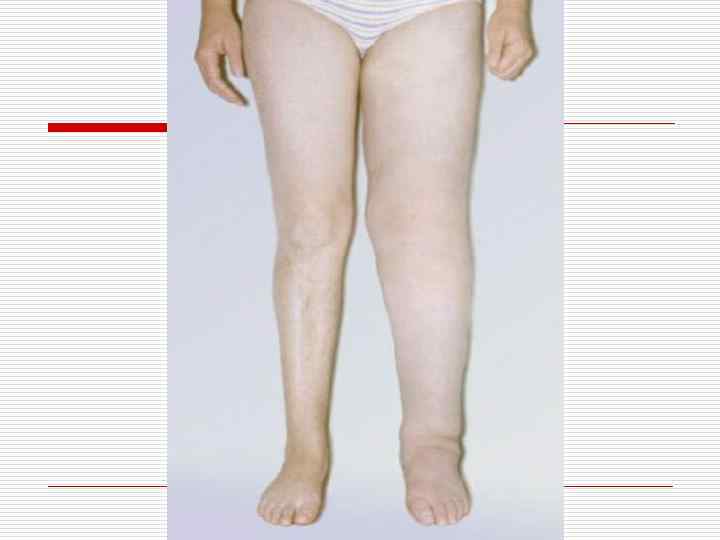
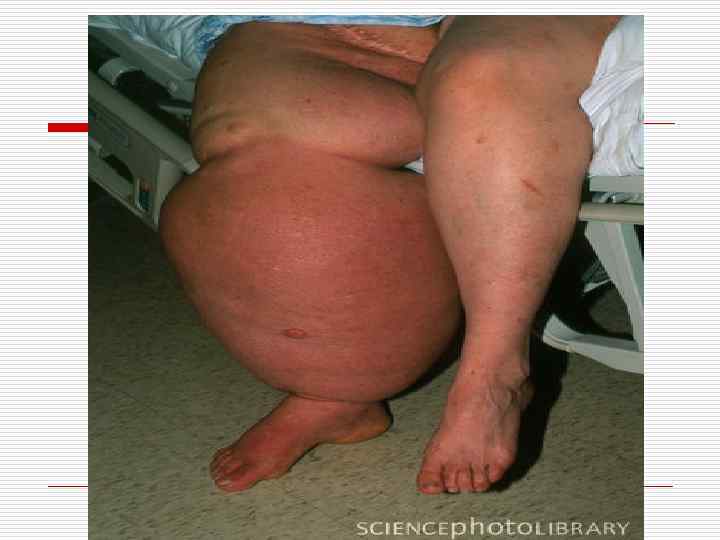
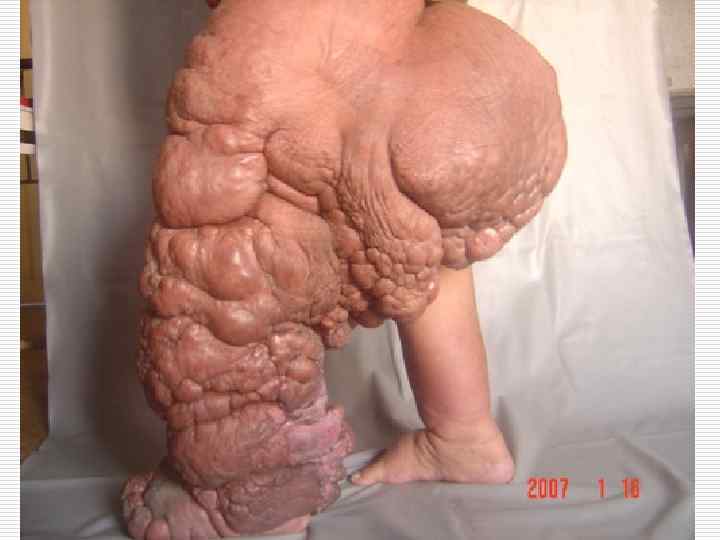
 Work (compensatory) hypertrophy takes place in the heart, gastrointestinal (G. I. ) tract, urinary and other organs. o Hypertrophy in the heart develops in case of birth and acquired valvular affections, accompanied by stenosis of atrioventricular openings, in case of arterial hypertension, coarctation of aorta, lungs vessels sclerosis, etc.
Work (compensatory) hypertrophy takes place in the heart, gastrointestinal (G. I. ) tract, urinary and other organs. o Hypertrophy in the heart develops in case of birth and acquired valvular affections, accompanied by stenosis of atrioventricular openings, in case of arterial hypertension, coarctation of aorta, lungs vessels sclerosis, etc.

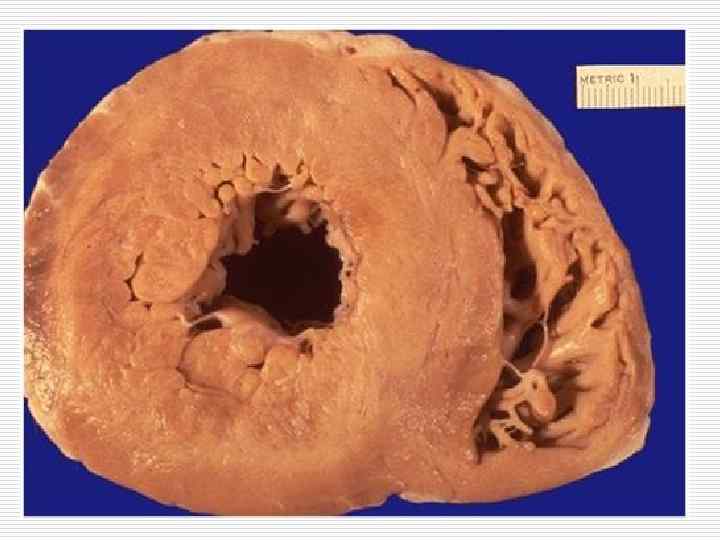
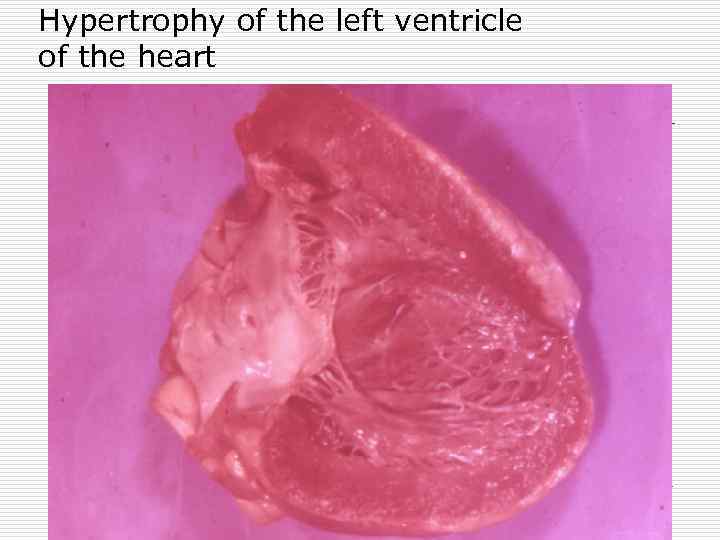 Hypertrophy of the left ventricle of the heart
Hypertrophy of the left ventricle of the heart
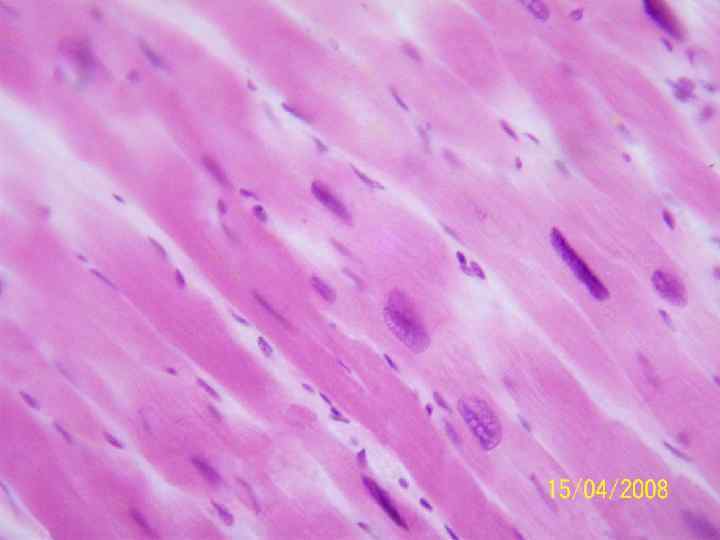
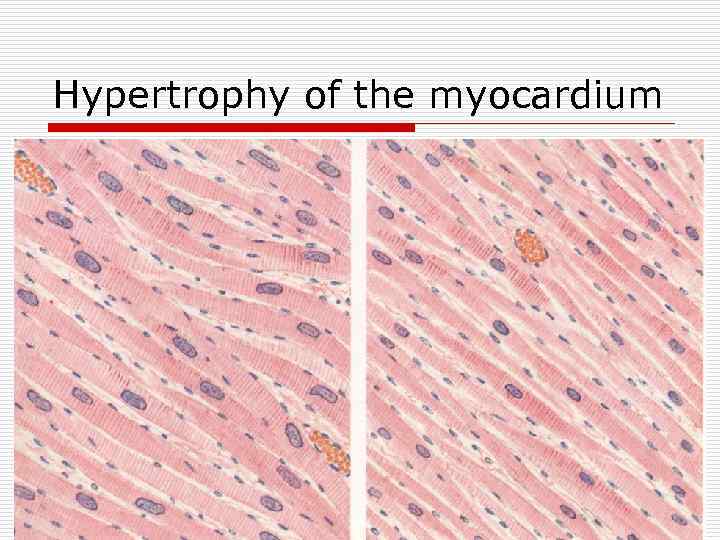 Hypertrophy of the myocardium
Hypertrophy of the myocardium

 Vicarious hypertrophy is observed in case of the death of one of the pair organs (lungs, kidneys, etc. ) due to some disease or operation. Compensation of the failed function is provided by an increased work of the remaining organ that is subject to hypertrophy.
Vicarious hypertrophy is observed in case of the death of one of the pair organs (lungs, kidneys, etc. ) due to some disease or operation. Compensation of the failed function is provided by an increased work of the remaining organ that is subject to hypertrophy.
 As is obvious from the above-stated, the compensatory and adaptive reactions are the major reactions of the entire organism, ensuring homeostasis preservation both in the normal and pathological states. These reactions are the basis of reliability of biological systems.
As is obvious from the above-stated, the compensatory and adaptive reactions are the major reactions of the entire organism, ensuring homeostasis preservation both in the normal and pathological states. These reactions are the basis of reliability of biological systems.
 Regeneration, hyperplasia, restructuring, functions doubling, changing of biological reactions speed depend on environmental factors influence rhythm
Regeneration, hyperplasia, restructuring, functions doubling, changing of biological reactions speed depend on environmental factors influence rhythm
 Therefore, adaptation and compensation are directed only at disease containment and prolongation of the patients life
Therefore, adaptation and compensation are directed only at disease containment and prolongation of the patients life


