Лекция 10 Регенерация 2011.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 55
 Adaptive and compensatory processes Lecture
Adaptive and compensatory processes Lecture
 Adaptation It is a wide biological concept, including phylogenesis, ontogenesis, evolution, heredity and all forms of an organism functions regulations both in a normal and pathological states, that is an adaptation to the changing living conditions and the ability to survive.
Adaptation It is a wide biological concept, including phylogenesis, ontogenesis, evolution, heredity and all forms of an organism functions regulations both in a normal and pathological states, that is an adaptation to the changing living conditions and the ability to survive.
 Compensation It is a more particular concept, an example of adaptation. A combination of an organism reactions, appearing in case of injuries or diseases and directed at the restoration of the impaired functions.
Compensation It is a more particular concept, an example of adaptation. A combination of an organism reactions, appearing in case of injuries or diseases and directed at the restoration of the impaired functions.
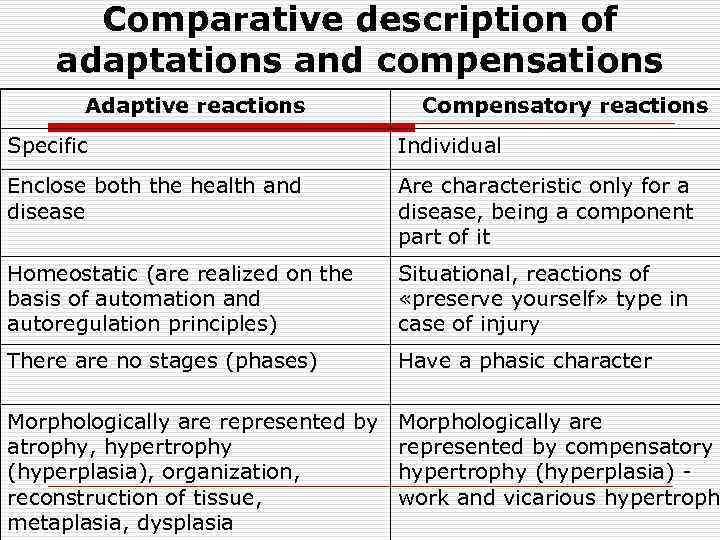 Comparative description of adaptations and compensations Adaptive reactions Compensatory reactions Specific Individual Enclose both the health and disease Are characteristic only for a disease, being a component part of it Homeostatic (are realized on the basis of automation and autoregulation principles) Situational, reactions of «preserve yourself» type in case of injury There are no stages (phases) Have a phasic character Morphologically are represented by Morphologically are atrophy, hypertrophy represented by compensatory (hyperplasia), organization, hypertrophy (hyperplasia) reconstruction of tissue, work and vicarious hypertroph metaplasia, dysplasia
Comparative description of adaptations and compensations Adaptive reactions Compensatory reactions Specific Individual Enclose both the health and disease Are characteristic only for a disease, being a component part of it Homeostatic (are realized on the basis of automation and autoregulation principles) Situational, reactions of «preserve yourself» type in case of injury There are no stages (phases) Have a phasic character Morphologically are represented by Morphologically are atrophy, hypertrophy represented by compensatory (hyperplasia), organization, hypertrophy (hyperplasia) reconstruction of tissue, work and vicarious hypertroph metaplasia, dysplasia
 Stages of compensatory reactions Formation II. Fixation (compensations) III. Decompensations (energy exhaustion) I.
Stages of compensatory reactions Formation II. Fixation (compensations) III. Decompensations (energy exhaustion) I.
 Types of compensations and adaptations 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. Regeneration Аtrophy Hypertrophy Оrganization Tissue restructuring Metaplasia Dysplasia
Types of compensations and adaptations 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. Regeneration Аtrophy Hypertrophy Оrganization Tissue restructuring Metaplasia Dysplasia
 Regeneration Restoration of tissues, cells, intracellular structures after their physiological or pathological death
Regeneration Restoration of tissues, cells, intracellular structures after their physiological or pathological death
 Levels of regeneration o o o Molecular Subcellular Cellular Tissue level System level Organ level
Levels of regeneration o o o Molecular Subcellular Cellular Tissue level System level Organ level
 Моrphogenesis: o Proliferation o Differentiation
Моrphogenesis: o Proliferation o Differentiation
 Regeneration forms o o o Cellular and intracellular Intracellular (universal)
Regeneration forms o o o Cellular and intracellular Intracellular (universal)
 Cellular regeneration o o o o Bones Epidermis Mucous membrane of gastrointestinal tract, respiratory tract, ureters, urinary bladder Loose connective tissue Hemopoietic system Lymphoid tissue Меsothelium
Cellular regeneration o o o o Bones Epidermis Mucous membrane of gastrointestinal tract, respiratory tract, ureters, urinary bladder Loose connective tissue Hemopoietic system Lymphoid tissue Меsothelium
 Cellular and intracellular regeneration o o o Liver Kidneys Pancreas Lungs Unstriped muscles Vegetative nervous system
Cellular and intracellular regeneration o o o Liver Kidneys Pancreas Lungs Unstriped muscles Vegetative nervous system
 Intracellular regeneration o o Cells of the brain and spinal cord Cardiac hystocytes
Intracellular regeneration o o Cells of the brain and spinal cord Cardiac hystocytes
 Types of regeneration Physiological o Reparative: restitution (identical tissue) and substitution (connective tissue) o Pathological - Disregeneration: mеtaplasia, dysplasia - Hyporegeneration - Hyperregeneration o
Types of regeneration Physiological o Reparative: restitution (identical tissue) and substitution (connective tissue) o Pathological - Disregeneration: mеtaplasia, dysplasia - Hyporegeneration - Hyperregeneration o
 Physiological regeneration o o o Constant renewal of cells and intracellular structures throughout the life time Epithelium is renewed every few days In the heart and brain only intracellular regeneration takes place
Physiological regeneration o o o Constant renewal of cells and intracellular structures throughout the life time Epithelium is renewed every few days In the heart and brain only intracellular regeneration takes place
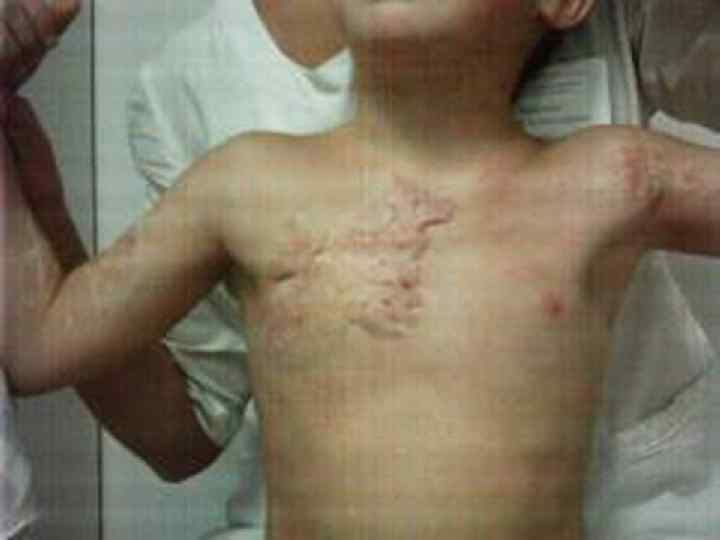
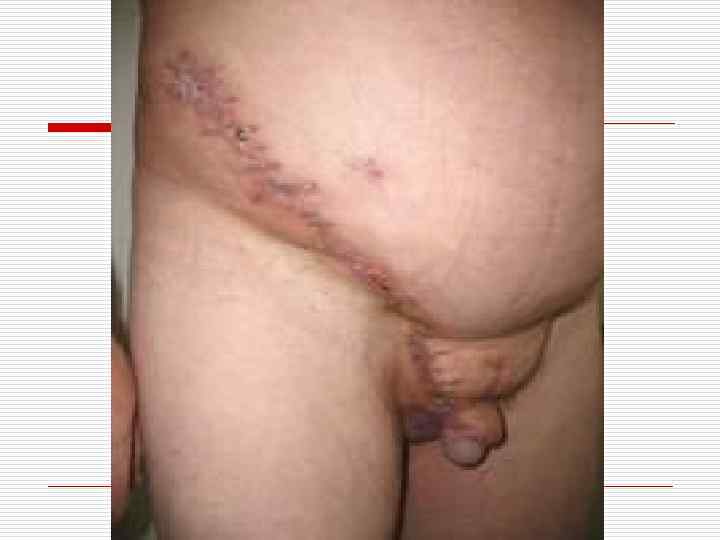
 Reparative regeneration o o o It is an intensive physiological regeneration in case of the cells and tissues injury Complete (restitution) – compensation of tissue defect, identical to died off tissue Incomplete (substitution) – tissue healing with a fibrous scar
Reparative regeneration o o o It is an intensive physiological regeneration in case of the cells and tissues injury Complete (restitution) – compensation of tissue defect, identical to died off tissue Incomplete (substitution) – tissue healing with a fibrous scar
 Pathological regeneration o o It is a perversion of the regenerative process Derangement of the proliferation and differentiation phases Hyperregeneration Hyporegeneration
Pathological regeneration o o It is a perversion of the regenerative process Derangement of the proliferation and differentiation phases Hyperregeneration Hyporegeneration
 Меtaplasia - is a form of disregeneration, transfer of one tissue type to the other, related type (epithelium, connective tissue, cartilage)
Меtaplasia - is a form of disregeneration, transfer of one tissue type to the other, related type (epithelium, connective tissue, cartilage)
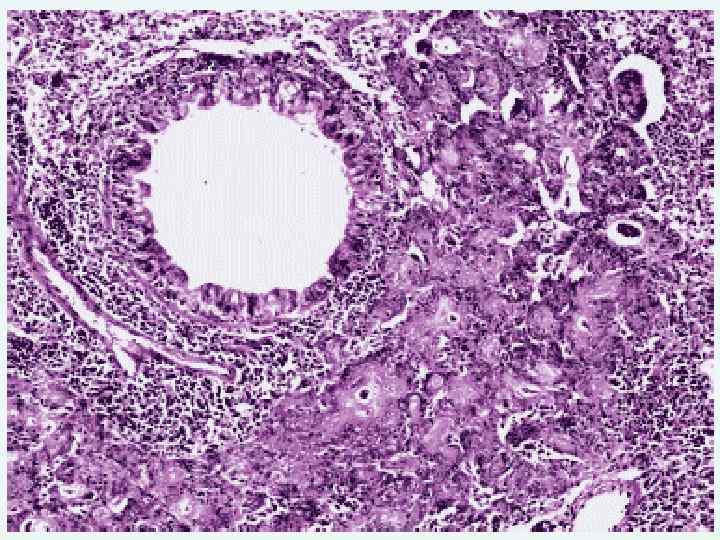
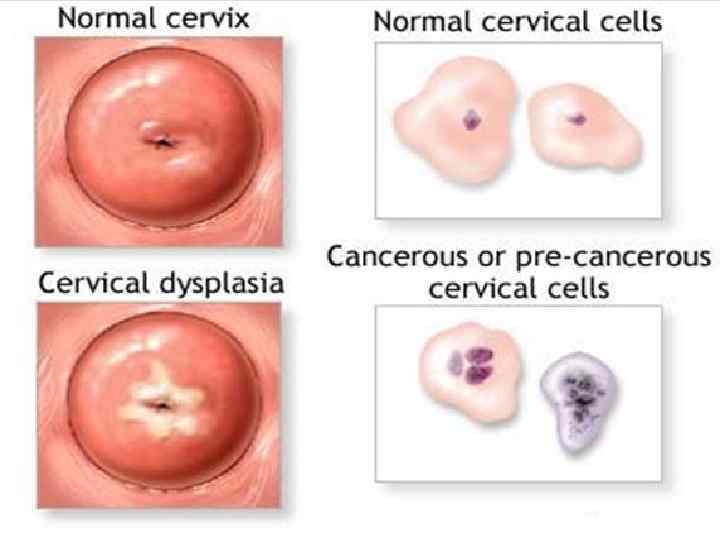
 Dysplasia Derangement of proliferation, epithelium differentiation with development of cellular atypia (precancerous condition)
Dysplasia Derangement of proliferation, epithelium differentiation with development of cellular atypia (precancerous condition)
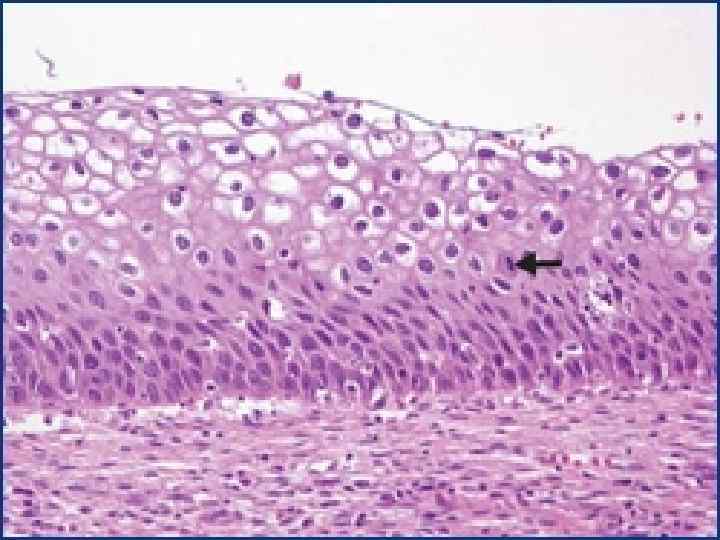
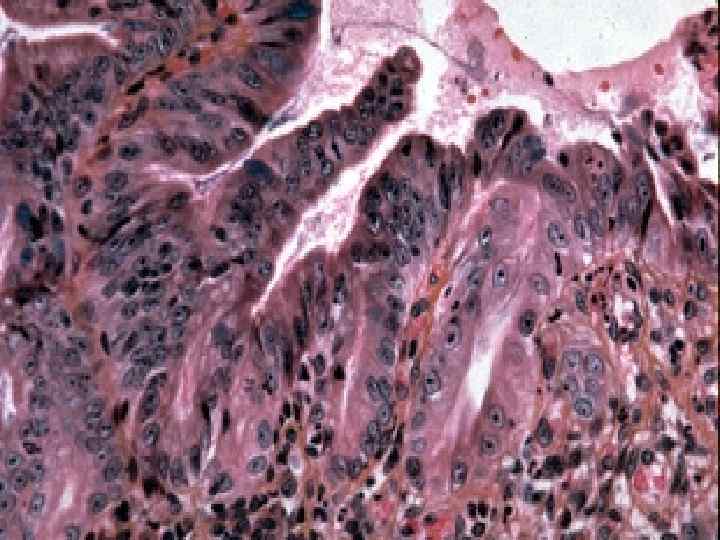

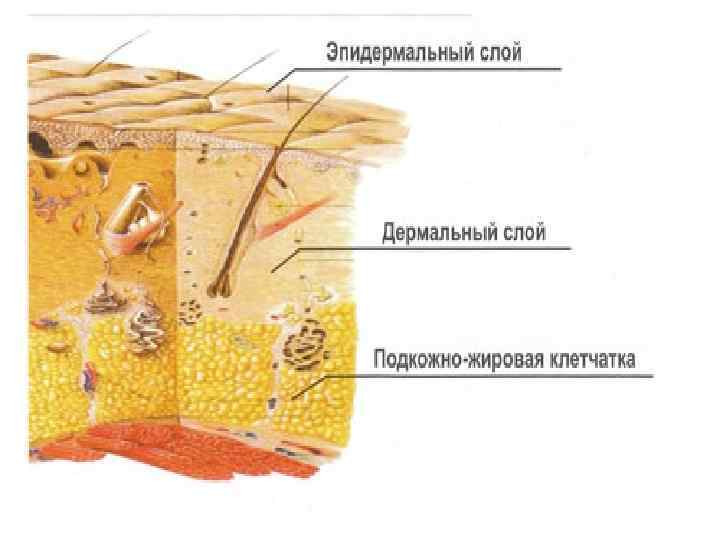
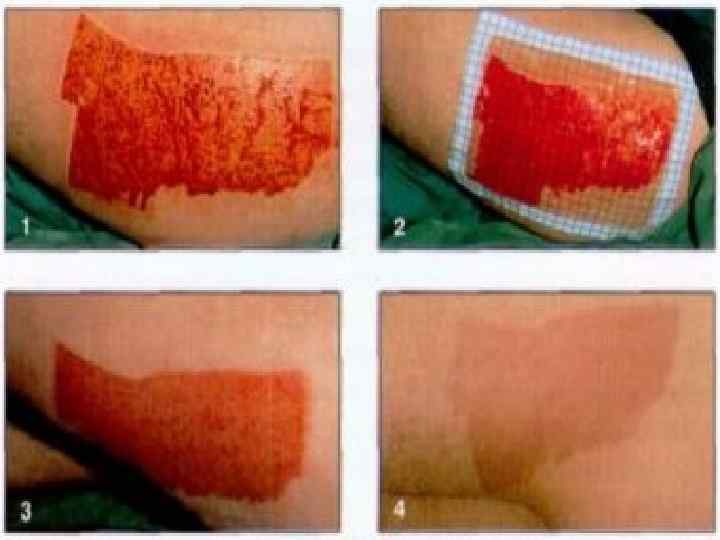
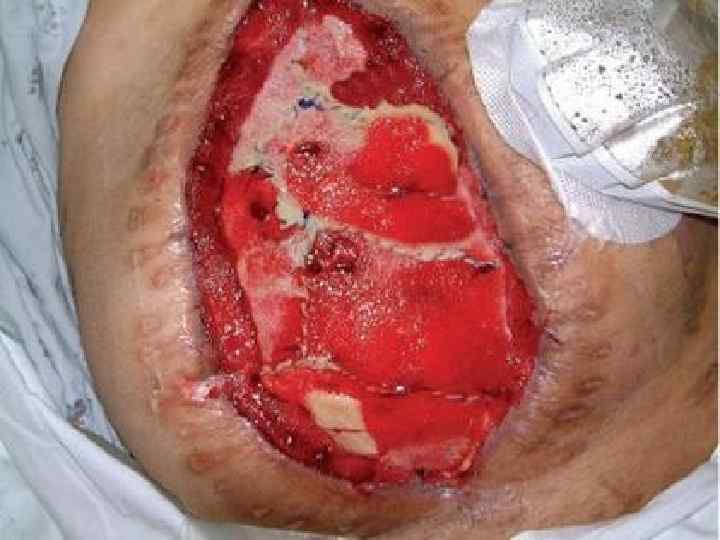
 Connective tissue regeneration o o o It is a granulation tissue Маcrо: juicy, red, fine-grained on the surface Мicro: consists of 3 components – multiple thin-walled neogenic vessels, cells (fibroblasts, fibrocytes etc. ), thin fibers of connective tissue
Connective tissue regeneration o o o It is a granulation tissue Маcrо: juicy, red, fine-grained on the surface Мicro: consists of 3 components – multiple thin-walled neogenic vessels, cells (fibroblasts, fibrocytes etc. ), thin fibers of connective tissue
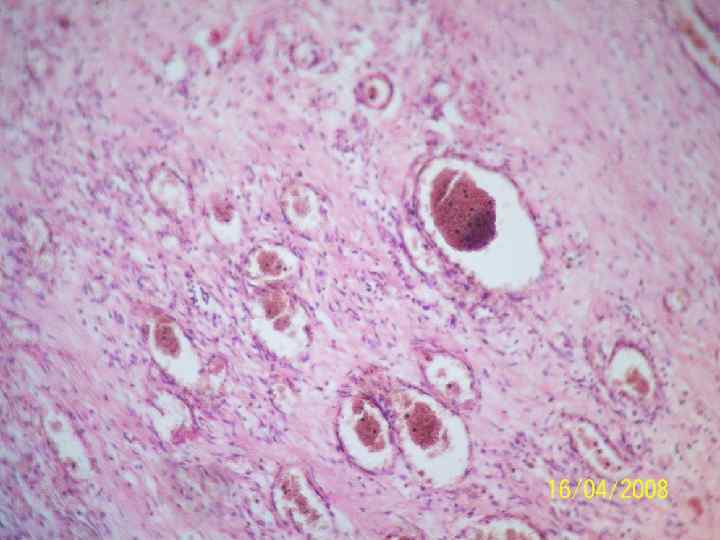
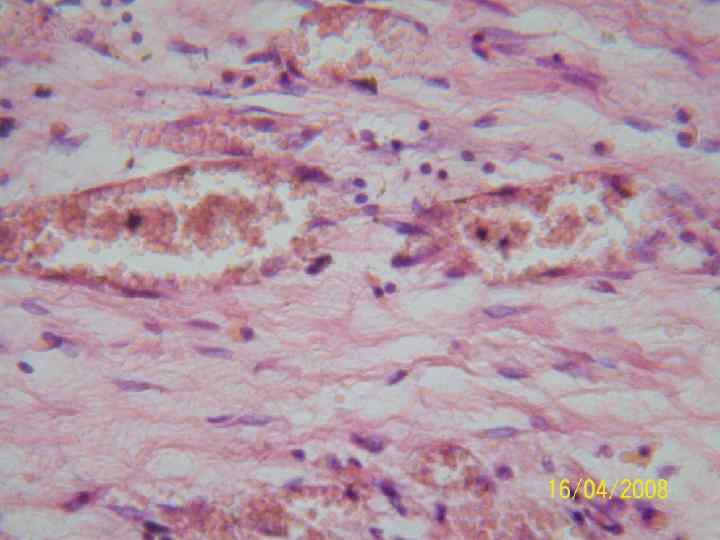
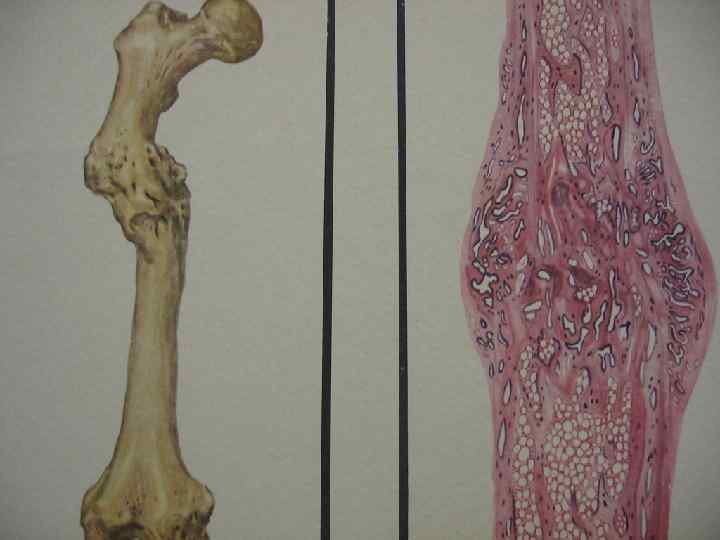
 Regeneration of bone tissue 1. 2. 3. 4. Preliminary connective tissue callosity Preliminary callus Final callus Function restoration and bone restructuring
Regeneration of bone tissue 1. 2. 3. 4. Preliminary connective tissue callosity Preliminary callus Final callus Function restoration and bone restructuring
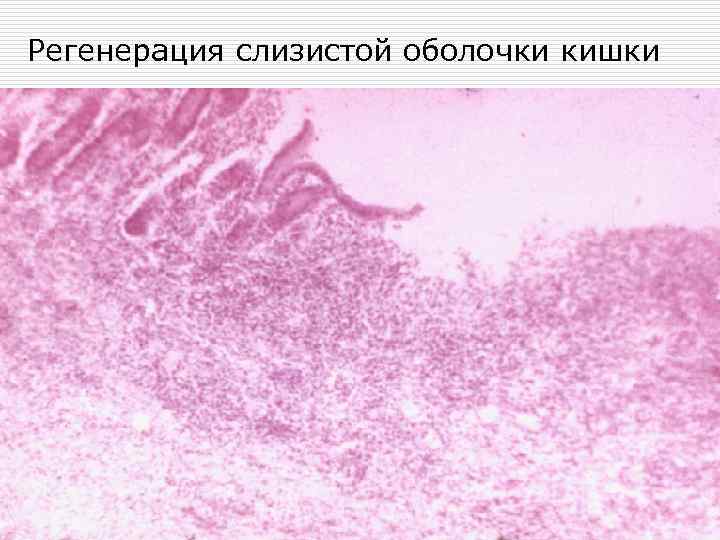 Регенерация слизистой оболочки кишки
Регенерация слизистой оболочки кишки
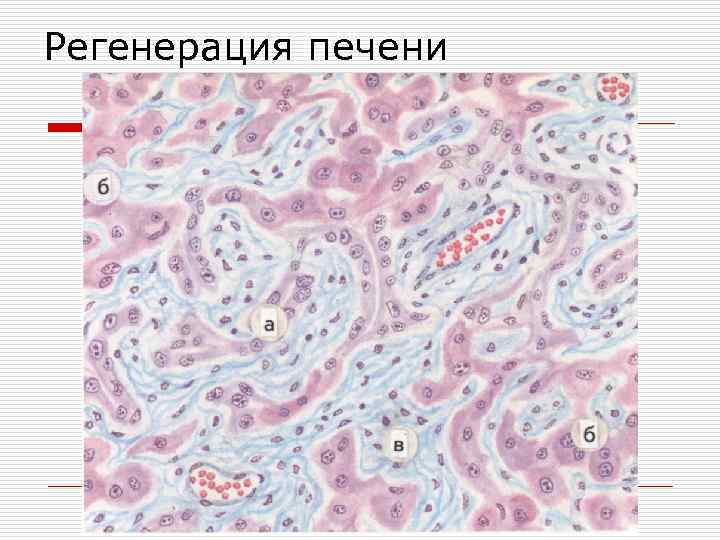 Регенерация печени
Регенерация печени
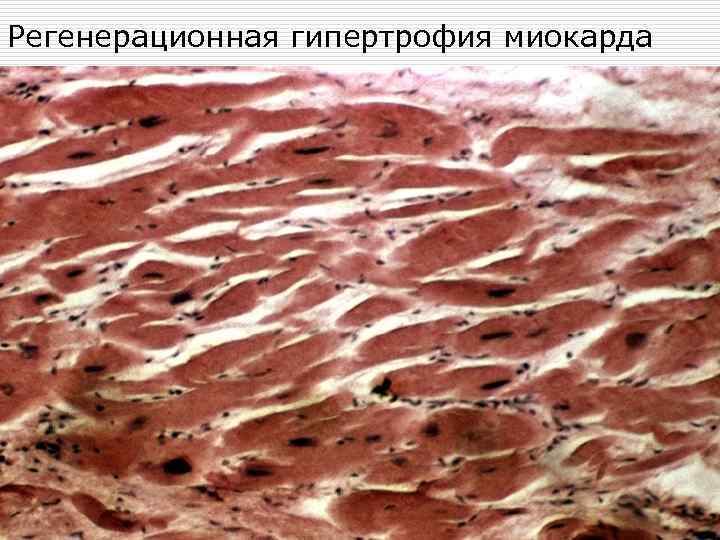 Регенерационная гипертрофия миокарда
Регенерационная гипертрофия миокарда
 Regulation of regeneration o Humoral mechanisms o Immunological o Neural o Functional
Regulation of regeneration o Humoral mechanisms o Immunological o Neural o Functional
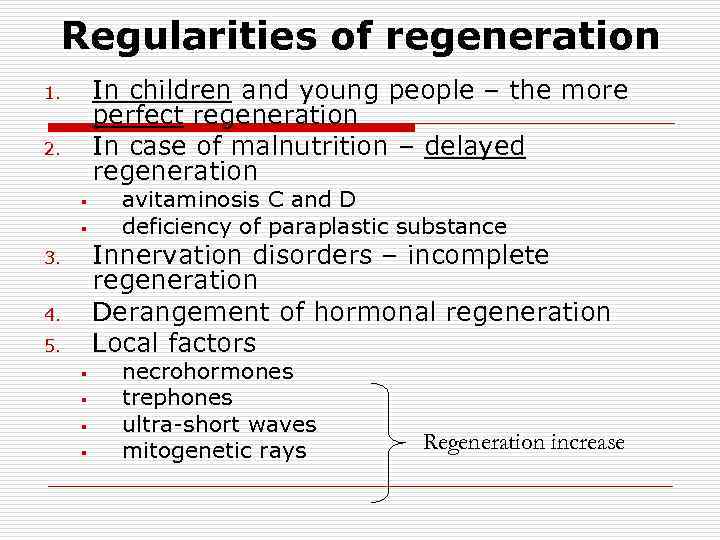 Regularities of regeneration In children and young people – the more perfect regeneration In case of malnutrition – delayed regeneration 1. 2. § § avitaminosis C and D deficiency of paraplastic substance Innervation disorders – incomplete regeneration Derangement of hormonal regeneration Local factors 3. 4. 5. § § necrohormones trephones ultra-short waves mitogenetic rays Regeneration increase
Regularities of regeneration In children and young people – the more perfect regeneration In case of malnutrition – delayed regeneration 1. 2. § § avitaminosis C and D deficiency of paraplastic substance Innervation disorders – incomplete regeneration Derangement of hormonal regeneration Local factors 3. 4. 5. § § necrohormones trephones ultra-short waves mitogenetic rays Regeneration increase
 Оrganization Substitution of necrosis area, tissue defect (wounds), thrombus by the connective tissue Encapsulation – a sort of organization
Оrganization Substitution of necrosis area, tissue defect (wounds), thrombus by the connective tissue Encapsulation – a sort of organization
 Character of the organizing substrates: o o o Encapsulation and organization of necrosis foci. Organization of thrombi, exudate, blood clots. Encapsulation of the foreign bodies and parasites.
Character of the organizing substrates: o o o Encapsulation and organization of necrosis foci. Organization of thrombi, exudate, blood clots. Encapsulation of the foreign bodies and parasites.
 Biological meaning: o o To localize the pathologic process, isolate it from surrounding tissue. Organization and encapsulation are developing through formation of granulation tissue.
Biological meaning: o o To localize the pathologic process, isolate it from surrounding tissue. Organization and encapsulation are developing through formation of granulation tissue.
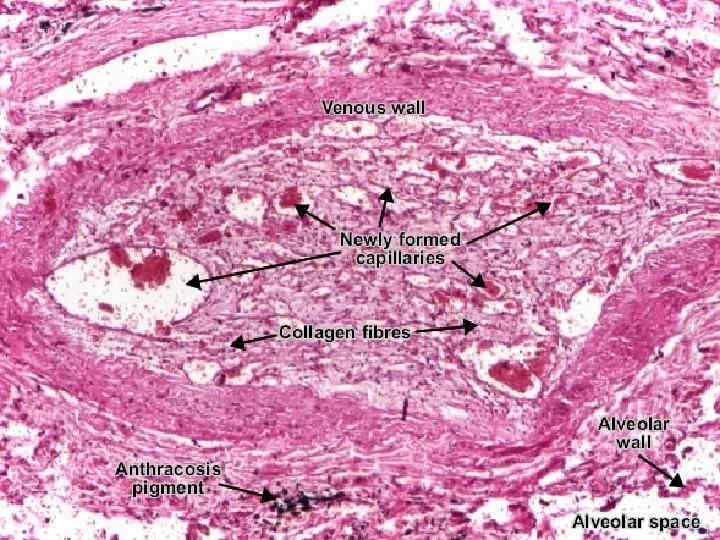 Организация тромба
Организация тромба
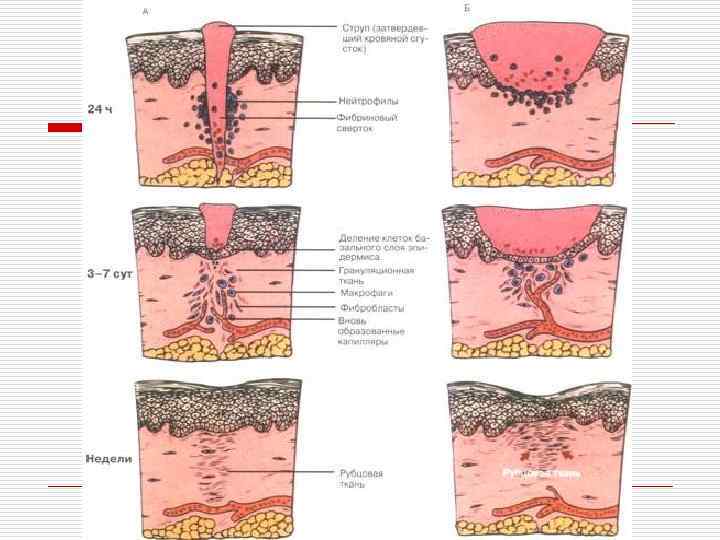
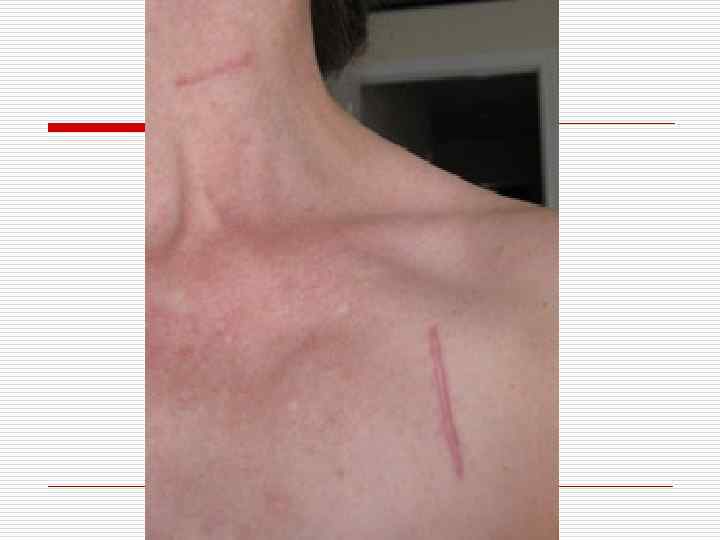
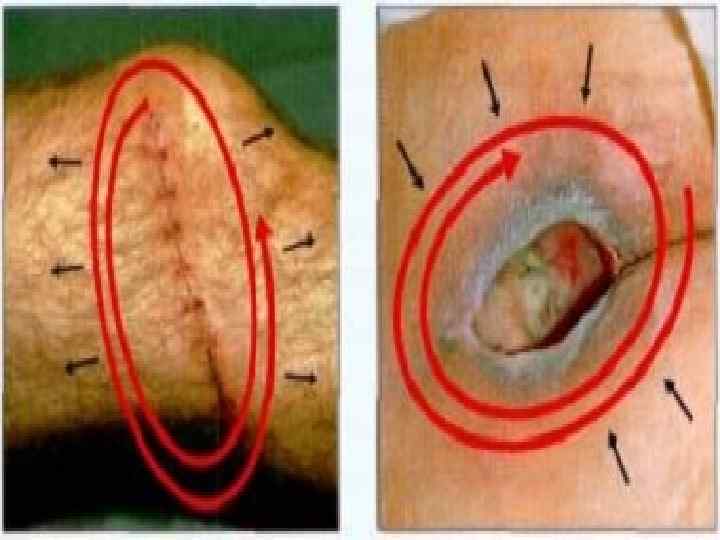
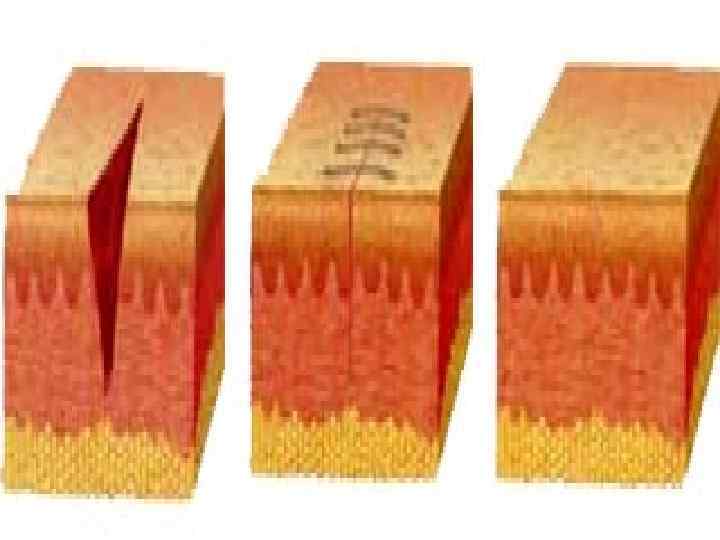
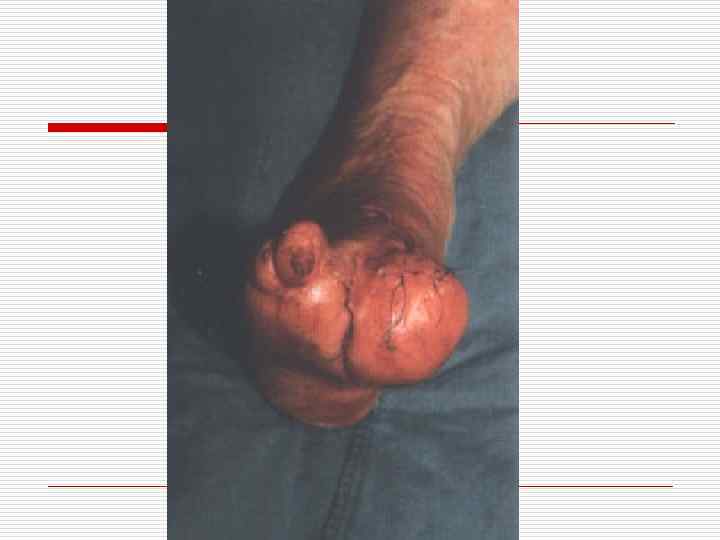
 Forms of wound healing o o Immediate closing of epithelial effect Healing under scab – scratch (3 -7 days) First intention (10 -15 days) Second intention (traumatic inflammation → granulation tissue → epithelium regeneration → scarring)
Forms of wound healing o o Immediate closing of epithelial effect Healing under scab – scratch (3 -7 days) First intention (10 -15 days) Second intention (traumatic inflammation → granulation tissue → epithelium regeneration → scarring)