656197f8b46dd78460cc7b7515d4526c.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 41

Adapting Behavioural Activation to the Values of Latino Clients Jonathan Kanter, Ph. D.
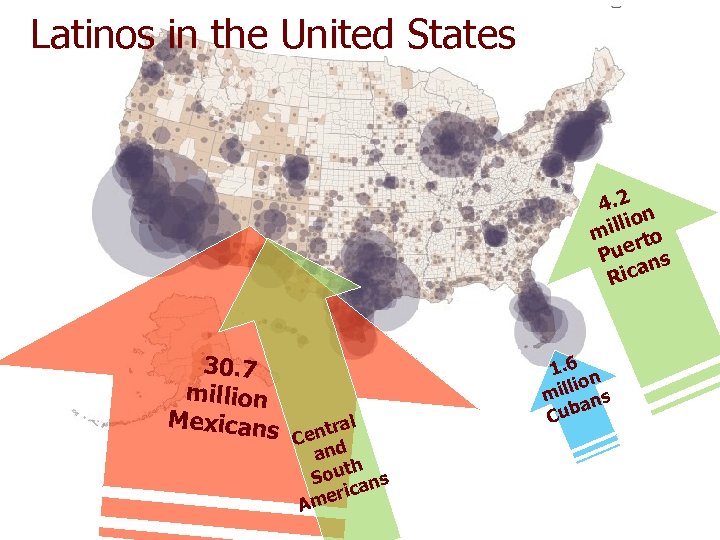
Latinos in the United States 4. 2 n illio m rto Pue ns a Ric 30. 7 million Mexicans l ntra Ce and th Sou ans eric Am 1. 6 n lio mil ns a Cub

My story

Latinos in the United States: • Largest minority group • Currently 14% of population • By 2050, 30% of population By 2050, Caucasians = 47% of population
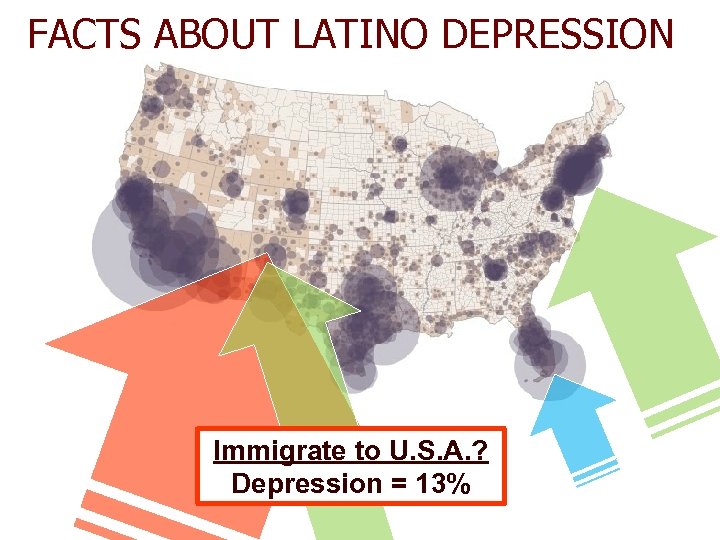
FACTS ABOUT LATINO DEPRESSION Immigrate to U. S. A. ? Depression = 13%
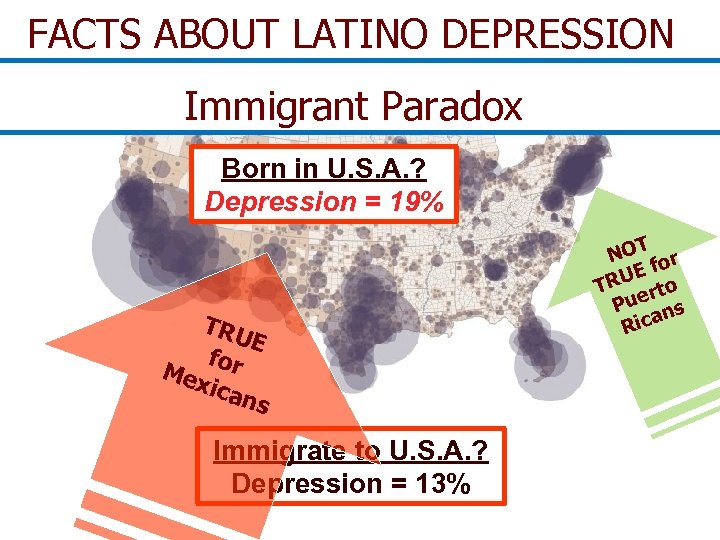
FACTS ABOUT LATINO DEPRESSION Immigrant Paradox Born in U. S. A. ? Depression = 19% TRU E f Mex or ican s Immigrate to U. S. A. ? Depression = 13% T NO for E RU to T uer s P an Ric
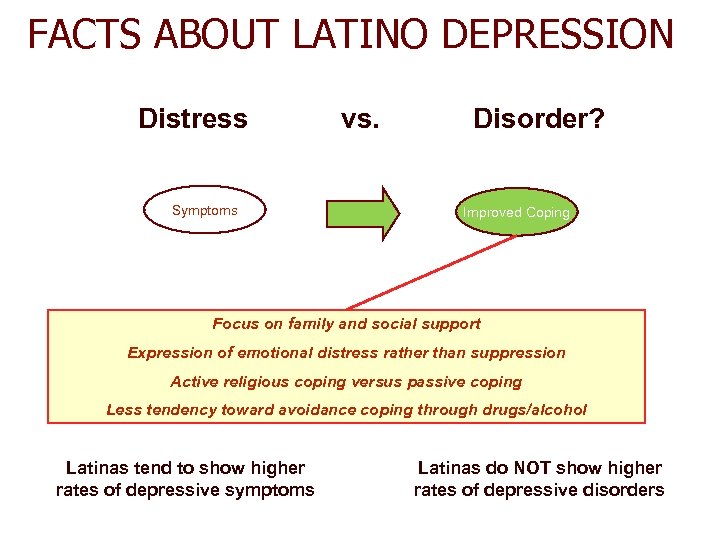
FACTS ABOUT LATINO DEPRESSION Distress Symptoms vs. Disorder? Improved Coping Focus on family and social support Expression of emotional distress rather than suppression Active religious coping versus passive coping Less tendency toward avoidance coping through drugs/alcohol Latinas tend to show higher rates of depressive symptoms Latinas do NOT show higher rates of depressive disorders

Conclusion 1 Traditional Latino cultural values are protective against depression My country’s values are depressing…

FACTS ABOUT LATINO DEPRESSION Preferences: Psychotherapy over medication Engagement: Lower than Caucasians Retention: Lower than Caucasians Quality: Lower than Caucasians Clear health disparity for Latinos with depression Cooper et al. , 2003; Fernandez y Garcia et al. , 2010

Conclusion 2 We need treatments for depression that emphasize traditional Latino cultural values to improve treatment engagement, retention, and outcomes

Behavioural Activation What are your goals and values? I will use my expertise to help you get as active as possible with respect to your goals and values We will be very concrete and come up with specific action plans each time we meet.

Behavioural Activation What are your goals and values? I will use my expertise to help you get as active as possible with respect to your goals and values We will be very concrete and come up with specific action plans each time we meet.

The goal is to help you engage in concrete actions related to your life goals each week, regardless of how you are feeling
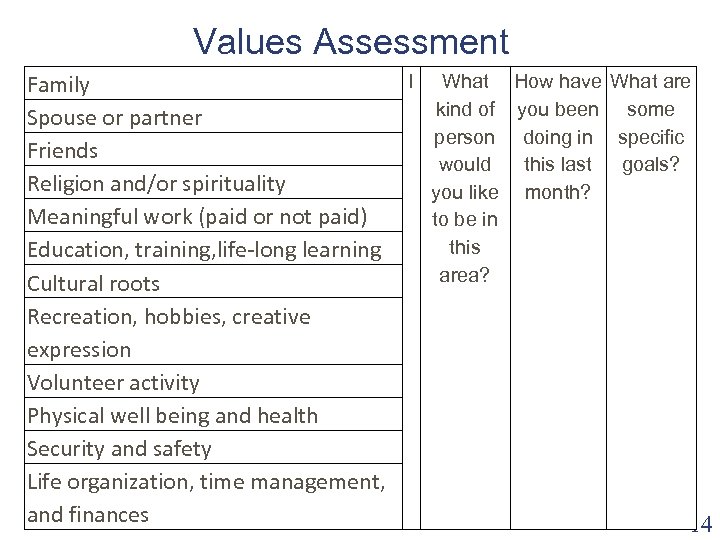
Values Assessment I What How have What are Family kind of you been some Spouse or partner person doing in specific Friends would this last goals? Religion and/or spirituality you like month? Meaningful work (paid or not paid) to be in this Education, training, life-long learning area? Cultural roots Recreation, hobbies, creative expression Volunteer activity Physical well being and health Security and safety Life organization, time management, and finances 14

Let’s pick five goals for But I feel so I understand – if we could you But this week. Wethe depressed. I just for how you feel you get change I want to helpon will active without waiting for inside then changing andwant schedule each oneyour to feel better. I feelings the outside would behavior on tohowbetter. Havefeel like such a talk about get to make youso much easier. to act able be ever beenthem. failure. Help me with sure you do even if you haven’t felt like it? that, then I could do what you’re asking. Act from “outside-in” rather than “inside-out”
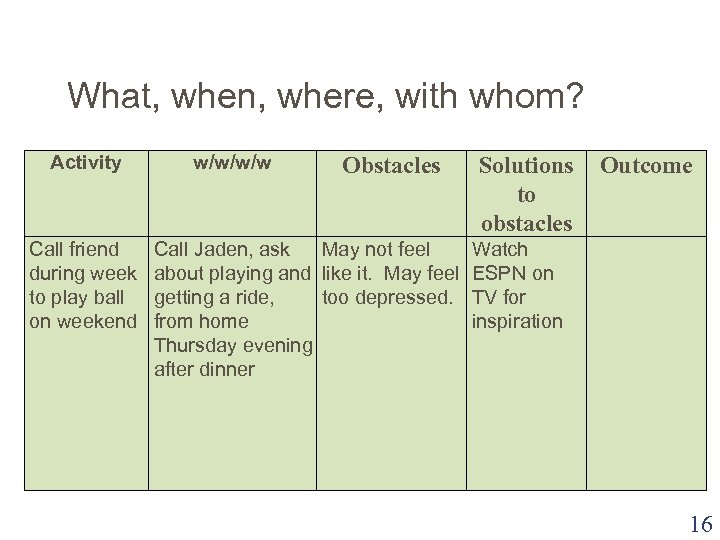
What, when, where, with whom? Activity Call friend during week to play ball on weekend w/w/w/w Obstacles Call Jaden, ask May not feel about playing and like it. May feel getting a ride, too depressed. from home Thursday evening after dinner Solutions to obstacles Outcome Watch ESPN on TV for inspiration 16

What is Depression? Negative Life Events: Will vary depending on cultural background Daily stress/hassles Unemployment and poverty Homelessness Trauma, violence Physical/medical conditions Harassment, racism, discrimination Losses, separation from loved ones and family Intergenerational acculturation conflicts “Presencios, ” “curses” and similar events Eventos Negativos 17
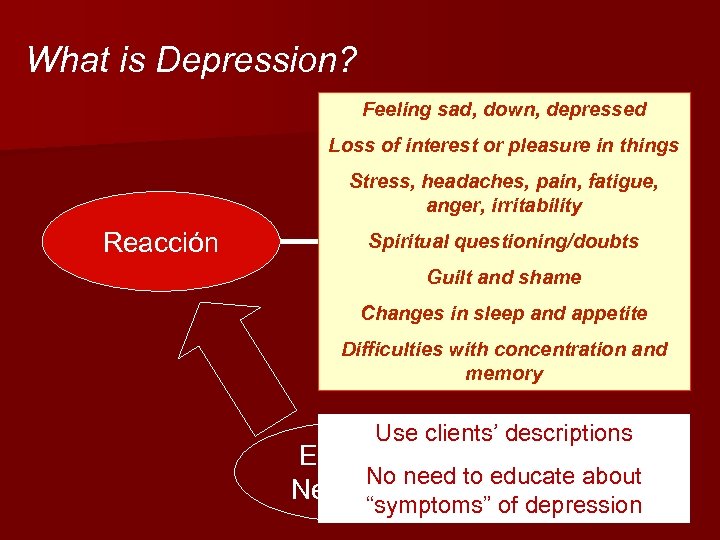
What is Depression? Feeling sad, down, depressed Loss of interest or pleasure in things Stress, headaches, pain, fatigue, anger, irritability Reacción Spiritual questioning/doubts Guilt and shame Changes in sleep and appetite Difficulties with concentration and memory Use clients’ descriptions Eventos No need to educate about Negativos “symptoms” of depression 18
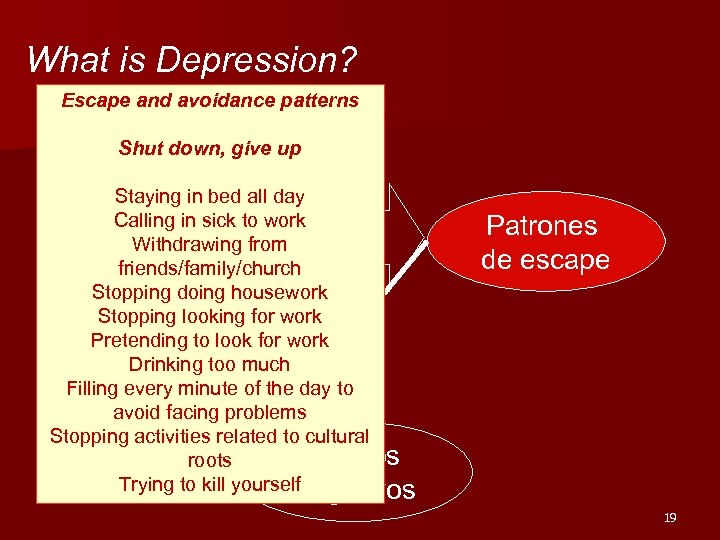
What is Depression? Escape and avoidance patterns Shut down, give up Staying in bed all day Calling in sick to work Withdrawing Reacción from friends/family/church Stopping doing housework Stopping looking for work Pretending to look for work Drinking too much Filling every minute of the day to avoid facing problems Stopping activities related to cultural Eventos roots Trying to kill yourself Negativos Patrones de escape 19
What is Depression? Patrones de escape Reacción Eventos Negativos 20
What is Depression? Patrones de escape Reacción Eventos Negativos 21
What is Depression? Patrones de escape Reacción Eventos Negativos 22
What is Depression? Patrones de escape Reacción Eventos Negativos 23
What is Depression? Patrones de escape Reacción Eventos Negativos 24
Patrones de escape Reacción Instead of reacting to your problems with poor coping and avoidance… Eventos Negativos 25
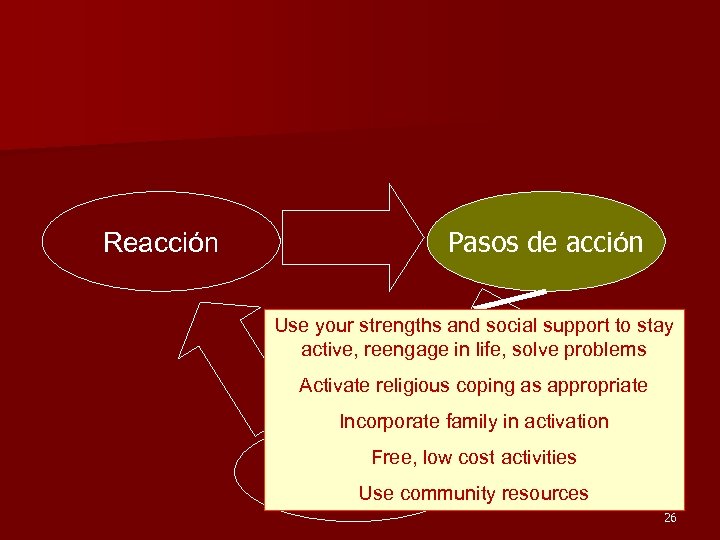
Reacción Pasos de acción Use your strengths and social support to stay active, reengage in life, solve problems Activate religious coping as appropriate Incorporate family in activation Free, Eventos low cost activities Negativos Use community resources 26

Pilot Study Intake Evaluation BA (N=10) Week 20 Evaluation 12 sessions max. TAU (N=10) 12 sessions max. – – – 2 BA therapists 2 Treatment as Usual (TAU) therapists Brief BA training provided Weekly consultation meetings for BA No restrictions on medication referrals 28

Treatment of Latino Depression Total Sample (N=20) Gender 100% Female Age 39. 60 (SD = 13. 44) Income $4, 221 (SD = $6, 357) Country of Origin 40% Mexico 35% Puerto Rico 10% U. S. 5% El Salvador 5% Nicaragua 5% Peru Years in U. S. 9. 75 (SD = 11. 18) Kanter, J. W. , Santiago-Rivera, A. , Rusch, L. C. , Busch, A. M. , & West, P. (2010). Initial outcomes of a culturally adapted behavioral activation for Latinas diagnosed with depression at a community clinic. Behavior Modification, 34, 120 -144.
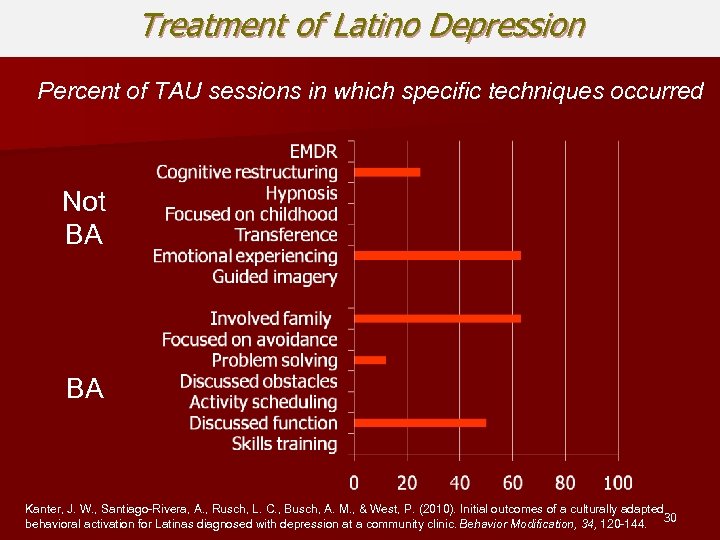
Treatment of Latino Depression Percent of TAU sessions in which specific techniques occurred Not BA BA Kanter, J. W. , Santiago-Rivera, A. , Rusch, L. C. , Busch, A. M. , & West, P. (2010). Initial outcomes of a culturally adapted behavioral activation for Latinas diagnosed with depression at a community clinic. Behavior Modification, 34, 120 -144. 30
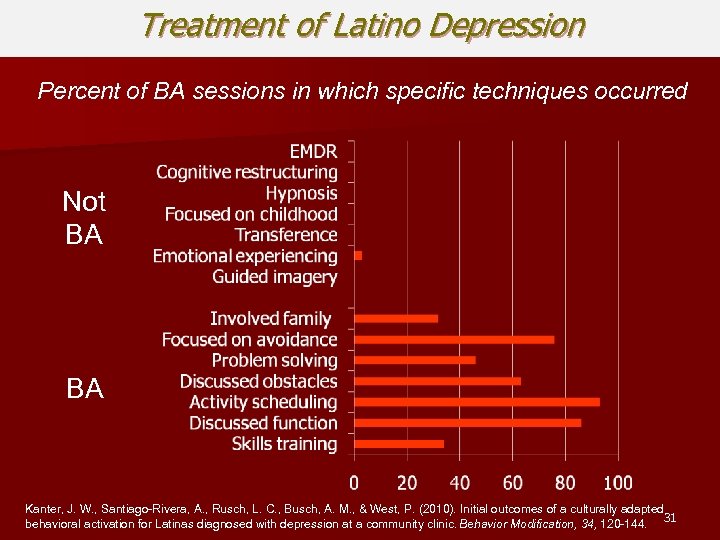
Treatment of Latino Depression Percent of BA sessions in which specific techniques occurred Not BA BA Kanter, J. W. , Santiago-Rivera, A. , Rusch, L. C. , Busch, A. M. , & West, P. (2010). Initial outcomes of a culturally adapted behavioral activation for Latinas diagnosed with depression at a community clinic. Behavior Modification, 34, 120 -144. 31

Treatment of Latino Depression Activities scheduled in BA sessions • • • • • Dancing, walking, exercising, playing sports Listening to favorite Latin music Community center activities, relaxation group, stress management group Attending a community fiesta Go to museum, seasonal free concerts, library Church activities and events Visit friends, play with children/grandchildren Reading Spanish language magazines Preparing a traditional family meal Cleaning house, knitting Employment seeking Medical appointments and care, diabetes care Call family and friends in country of origin Social service agency problems Asking others for help, saying no to requests Spend time with family English-language, computer classes Asking others for help Maintaining personal hygiene Talking with husband about parenting issues 32
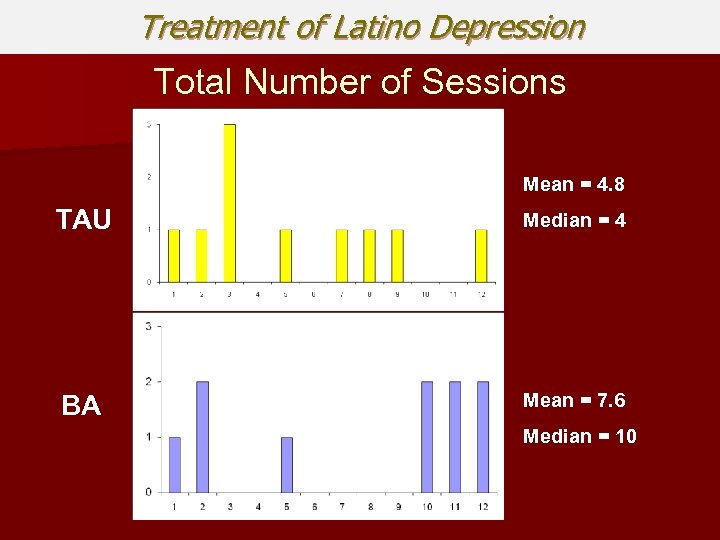
Treatment of Latino Depression Total Number of Sessions Mean = 4. 8 TAU Median = 4 BA Mean = 7. 6 Median = 10
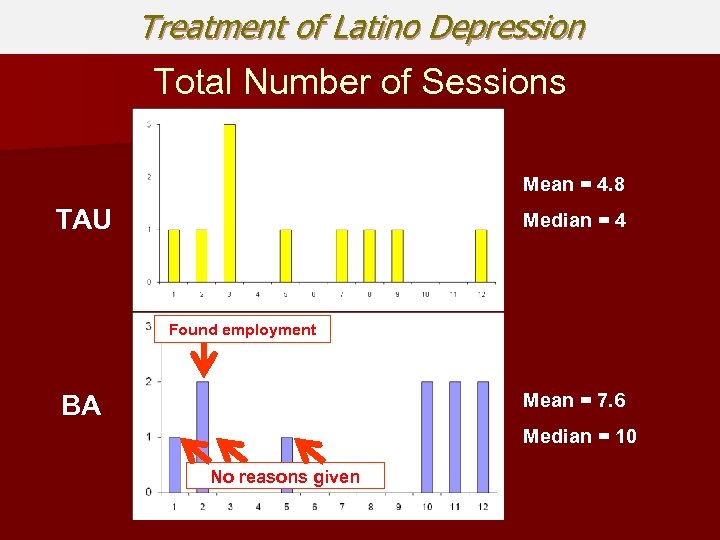
Treatment of Latino Depression Total Number of Sessions Mean = 4. 8 TAU Median = 4 Found employment Mean = 7. 6 BA Median = 10 No reasons given
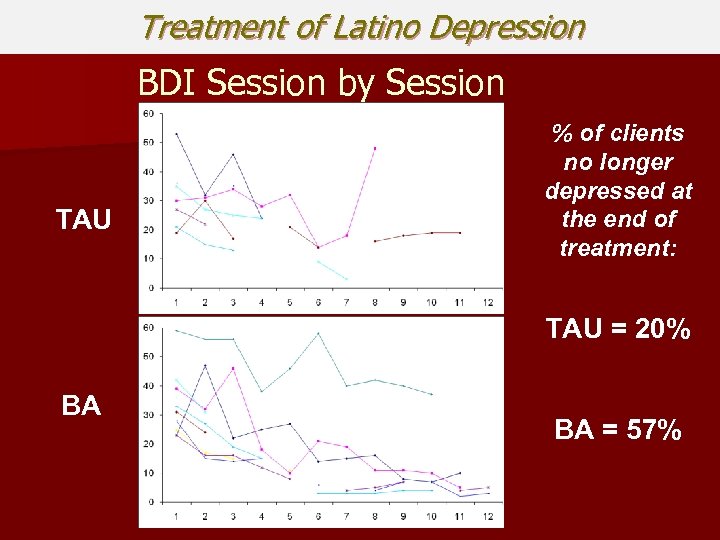
Treatment of Latino Depression BDI Session by Session TAU % of clients no longer depressed at the end of treatment: TAU = 20% BA BA = 57%
Future 1 Many BA studies currently ongoing Directions
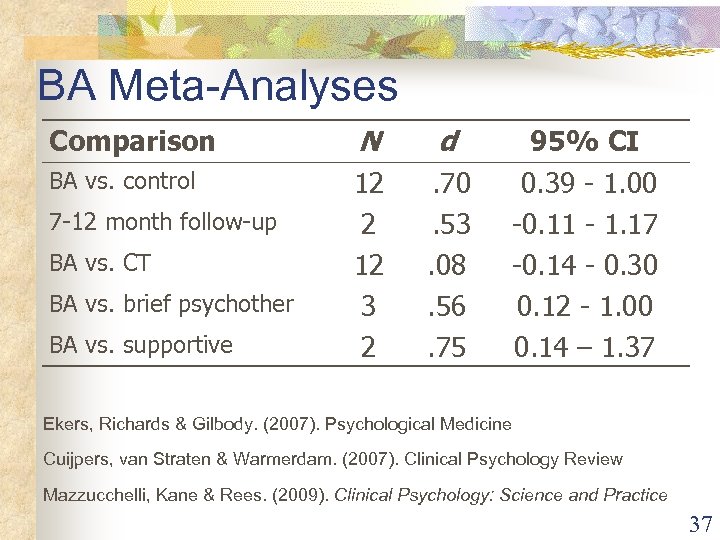
BA Meta-Analyses Comparison N d BA vs. control 12 2 12 3 2 . 70. 53. 08. 56. 75 7 -12 month follow-up BA vs. CT BA vs. brief psychother BA vs. supportive 95% CI 0. 39 - 1. 00 -0. 11 - 1. 17 -0. 14 - 0. 30 0. 12 - 1. 00 0. 14 – 1. 37 Ekers, Richards & Gilbody. (2007). Psychological Medicine Cuijpers, van Straten & Warmerdam. (2007). Clinical Psychology Review Mazzucchelli, Kane & Rees. (2009). Clinical Psychology: Science and Practice 37
Current BA investigations Medical issues Depressed cancer patients, cancer survivors, post-cardiac Vets with PTSD in primary care, general primary care tx Obese women, diabetes, HIV+, chronic pain, CVD Primary care treatment Other populations Depressed smokers, mobility impaired smokers, rural, youth Meth users, minority drug users, depressed SA Elderly caregivers, Spouses of Alzheimer patients Depressed with epilepsy
Current BA investigations Age ranges Depressed adolescents College students Perinatal depression Elderly Depressed nursing home residents Diversity Muslims in UK African Americans Latino Americans at a community clinic Nurse led tx in Zimbabwe Indonesians
Future Directions 1 Many BA studies currently ongoing 2 Developing model of BA to maximize efficient crosscultural adaptation Developing technology for rapid and effective training in BA skills, including multi-cultural competency

Thank You
656197f8b46dd78460cc7b7515d4526c.ppt