b5db901af8b491317f60fa84c679be89.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 31

Adapted from The UC Berkeley History Social Science Project The Israeli-Palestinian Conflict: A Lesson in Perspective, Abba Eban by Asaf Siniver and Chard CHY 4 UI notes A Historical Perspective on the Arab-Israeli Conflict and Peace Process

Historical Background Israeli-Palestinian Conflict Many Jews began to immigrate to Palestine in the late 1800’s. Pre-WWI: Area of Palestine under Ottoman Empire • 1916 Sykes-Picot Agreement between France and Britain to share Syria, Jordan, Iraq and most of Arabian Peninsula if successful in WW 1 • 1917 Balfour Declaration British Foreign Secretary A. J. Balfour declares Britain’s support for a “national home for the Jewish people in Palestine” (but he never clarified if by “home” he meant an independent country or a country-within-a country) 2

Historical Background Israeli-Palestinian Conflict Israelis Palestinians • Ancestors lived in area • Ancestors have been nearly 2000 years ago • Jerusalem home to most important Jewish site—Western Wall 4/24/2010 living in area nearly 2000 years • Jerusalem home to 3 rd most important Muslim site-Dome of the Rock/Al-Aqsa Mosque 3

1930’s • Zionist groups in Germany and America buy land from Arab landowners in Palestine. Landowners move to neighbouring oil rich Arab countries. Zionists move into Palestine. • Arab Revolt - armed bands attack Jewish settlements. Jewish Defense Force, the Haganah, attacks Arabs. 4/24/2010 4

The Peel Commission 1937 • Lord Peel’s Commission recommends the partition of Palestine into Jewish and Arab (for their help vs the Turks during WWI) states, saying they cannot reconcile their national aspirations (“neither the Arabs nor the Jews will get all they want…they will each get some of what they want. ”) • The Arabs rejected this and wanted one independent state (“Palestine”) that would “protect all legitimate Jewish and other minority rights” and limit future Jewish immigration. The Jews weren’t entirely happy with the exact partition but accepted it because it gave them a state. 4/24/2010 and 5

The White Paper 1939 • concludes that with 450, 000 Jews now in settled in Palestine, the government believes the pledge for “a national home for the Jewish people in Palestine” (Balfour Declaration) has been met and now the aim was to establish an independent Palestinian state within 10 years for both Arabs and Jews • as a response to Arab fears, this paper establishes a ban on the sale of land to Jews by Arabs and restricts future Jewish immigration 4/24/2010 6

Ben Gurion’s Response to the White Paper “We need to fight the war against the Nazi Germany as if there were no White Paper, and fight the White Paper as if there were no war. ” 4/24/2010 7

Holocaust comes to light… 4/24/2010 8

Britain 1945 • New Labour government led by Clement Attlee is elected after WW 2 – hopes are high amongst Zionists that, especially in light of the Holocaust, the White Paper will be reversed • the government is bankrupt and realizes the need for good relations with the Arab countries regarding oil policy, and are also worried about the effects on Muslims in India, so they keep the White Paper in place 4/24/2010 9

UN Plan for Palestine (1947) • • • Partition (separate) the area into 2 countries Israel (Jewish State) and Palestine (Arab State) 55% of land goes to the Jews 45% of land goes to the Arabs Total Population: 1. 8 million • 1. 2 million Arabs living in area • 60, 000 Jews living in area Jerusalem: “international city” controlled by UN Accepted by Jews Rejected by Arabs No Arab on committee 4/24/2010 10

1948 War • May 14, 1948: Israel is officially formed • May 15, 1948: Israel attacked by four Arab nations • Approx. 750, 000 Palestinians fled or were forced to leave • Over approx. 800, 000 Jews in Arab countries also fled or were forced to leave for Israel • Israel After War: Jordan controls West Bank and Egypt controls Gaza Strip • Israel takes much of Palestine and West Jerusalem— East Jerusalem, including many religious sites taken by Jordan, who denied Israelis access 4/24/2010 11

Perspectives on Partition and 1948 War Israelis Creates state of Israel Palestinians • They had no input War of Independence • Nabka: “Catastrophe” Holocaust and other periods • Land set aside for Palestinians of violence against Jews now under control of Arab throughout the past centuries countries or Israel might not have happened if there was a Jewish Homeland 4/24/2010 12

1956 Suez Canal Crisis • Egypt nationalizes the Suez Canal in 1956 and closed the Straits of Tiran to Israel, which blocked Israeli access to the Red Sea. • Israel attacks Egypt with later reinforcements from France and the United Kingdom • Ceasefire agreement and withdrawal of Israeli troops • United Nations Peacekeepers sent to maintain peace in the area 4/24/2010 13

1967 War • Israel believes neighbors are preparing for war – Egypt requests withdrawal of UN in May 1967 and denies Israel access to the Red Sea by closing Straits of Tiran – Jordan and Egypt sign mutual defense agreement – Continued terrorist attacks from Syria’s Golan Heights region • Israeli surprise attack against Egypt on June 5, 1967 – Also attacks Syria, Jordan – Within six days Israel defeats Egypt, Syria, Jordan • Takes control of West Bank and East Jerusalem (from Jordan) • Control of Sinai and the Gaza Strip (from Egypt) • Control of Golan Heights (from Syria) 4/24/2010 14

Perspectives on and Aftermath of 1967 War Israelis • Land gained is a buffer zone to deter future attacks • Begin to build settlements in West Bank, Gaza Strip and Golan Heights • Unified Jerusalem under Israeli control 4/24/2010 Palestinians • West Bank and Gaza Strip become known as “Occupied Territories” • Some will accept Israel at pre 1967 War borders • Palestinian Liberation Organization (PLO) later begins to use terrorism to attract attention to its cause of an independent state. 15

Thomas Friedman (New York Times) Quote “After the Six Day War, Israel could be two out of three of the following, but not three out of three – a Jewishmajority state, a democratic state, a state that keeps the West Bank and Gaza Strip. ” 4/24/2010 16

Munich 1972 • Arab Black September group massacres 11 Israeli athletes at Munich Olympics - PM Golda Meir authorizes secret assassination operation • Watch the film – optional ASSIGNMENT in place of one article review. Length – 1 page Briefly describe what happened at the Munich Olympics, and the Israeli response. Do you think this is the right way to deal with “terrorism ? ” Why or why not ? Explain. 4/24/2010 17

The Yom Kippur War, 1973 • On Yom Kippur in 1973, Egypt and Syria attacked Israel, but Israel pushed back the attack • For many Israelis, the war reinforced the need for buffer zones gained in 1967 • After the war, Israel retained the territories captured in 1967 (West Bank, Gaza, Golan Heights) but gave back land gained in the 1973 war • Eventually, in 1979, Egypt became the first Arab country to recognize Israel and entered into a peace treaty 4/24/2010 18

The Camp David Accords • 1977: Egypt (led by Anwar Sadat, assassinated in 1982 by Muslim Brotherhood group) engages Israel in peace efforts • 1978: Camp David Accords – U. S. President Carter invites Sadat and Israeli Prime Minister Begin to Camp David – Egypt recognizes Israel as a country – Israel gives Sinai peninsula back to Egypt – First agreement between Israel and an Arab nation 4/24/2010 19

The Intifada • Palestinian uprising or Intifada against Israeli occupation, living conditions, and to demand independence that begins in 1987. – Includes Palestinian demonstrations, strikes, boycotts, rock throwing and gasoline bombs. • Israeli military response • Over approx. 400 Israelis killed • Over approx. 1500 Palestinians killed 4/24/2010 20

Oslo Accords, 1993 • In the 1990’s several advances towards peace were made with several meetings taking place in places such as Egypt, Spain, the United States, and Norway. – 1993 Oslo Accords: Palestinian Leader Yasser Arafat and Israel’s Prime Minister Yitzhak Rabin met to begin to work out a peace deal that included each side recognizing the right of the other to exist. – Arafat and Rabin received the Nobel Peace Prize for their efforts • In 1994, Israel and Jordan signed a peace agreement • Rabin assassinated by Jewish extremist in November of 1995 4/24/2010 21

The Camp David Summit • In 2000, President Clinton, Israeli Prime Minister Ehud Barak, and Palestinian President Yasser Arafat met at Camp David to negotiate a final peace agreement • Prime Minister Barak agreed to pull out from the majority of the West Bank but President Arafat refused • The two sides were not able to bridge their differences to reach an agreement • Though the negotiations were conducted secretly, some say that President Arafat refused to compromise and made no proposals 4/24/2010 22

Second Intifada • By 2000, peace process has faded. • In 2000, Israeli political figure Ariel Sharon visits Temple Mount (Western Wall area and Al Aqsa Mosque area) in Jerusalem • Palestinian violence erupts beginning the Second Intifada • Buses, discos, hotels, fast food restaurants, etc in Israel blown up by Palestinian suicide bombers • Israel responds militarily • From 2000 -June 2008 • Over 4500 Palestinians killed • Over 1000 Israelis killed • In 2002, Israel begins building a security barrier in the West Bank, to protect Israelis from “terrorists” 4/24/2010 23

Peace Proposals • In 2002, the prince of Saudi Arabia proposed the Arab Pease Initiative, endorsed by all members of the Arab league - it calls for Israel to return to its pre-1967 territories, recognition of Palestine with East Jerusalem as its capital, and a solution for Palestinian refugees • Road Map for Peace is proposed in 2003 by the U. S. , Russia, EU, and UN - three phases to attain an independent Palestinian state and secure Israel - has never progressed due to the 2006 Hamas election 4/24/2010 24

The Gaza Strip • In 2005, Israel removed its settlements from the Gaza Strip and gave much control of the area to the Palestinian government (with exceptions such as the border, airspace, coastline) • Gaza later comes under the control of Hamas, a group considered by Israel and other countries to be a terrorist organization. 4/24/2010 25

Current State of Affairs • With the election of a majority of Hamas to the Palestinian Authority (PA) legislature in 2006, and their platform calling for the destruction of Israel, violence and tension erupted once again. Hamas is internationally recognized as a terrorist organization; thus many countries have imposed sanctions and suspended aid to the PA. • The rise of the radical organization Hezbollah has further increased violence and instigated the 2006 Lebanon War. • After Hamas attacked PLO Fatah members, the PA president dissolved Hamas. Now, Hamas controls Gaza and the PA controls the West Bank. Suicide bombings through the use of human shields (including women and children) continues to kill Israelis. • President Obama continues to try to facilitate negotiations between Israel and the Palestinian Authority. 4/24/2010 26

Current Issue : Is Resolution Possible? Palestinian and Israeli leaders backed by US and other countries are working towards the existence of Israel and of Palestine. But the following issues remain: • Jerusalem • Settlements • Security (including barriers, terrorism, checkpoints) • Refugees and Right of Return • Two States or One/Borders 4/24/2010 27

Challenges to Resolution Issue Israelis Palestinians Jerusalem See united Jerusalem as its capital See East Jerusalem as its capitoal Settlements For religious, political, and security reasons a large number of Israeli settlements exist in the West Bank and East Jerusalem. 270, 000 Israeli settlers in the West Bank Israeli settlements go against the idea of a future Palestinian state. Security Barriers, Movement, and Terrorism Israel is building a barrier between it and the West Bank. Israel sees this as a way to prevent further suicide bombings. The barrier goes beyond the border between the West Bank and Israel: the barrier route is 449 miles, while the “Green Line”—the “border” between the West Bank and Israel is 199 miles Palestinians need permission to leave West Bank. Israelis see this as needed security to prevent terrorism. The restriction on movement limits jobs, health care, education, etc. contributing to standard of living in West Bank being significantly less than that of Israel. Terrorist organizations like Hamas (which controls the Gaza Strip) and Hezbollah (based in Lebanon and who was at war with Israel in the summer of 2006) continue to fire rockets into Israel. Individuals also continue to commit other acts of terror. Can’t stereotype all Palestinians as terrorists as the majority are not terrorists. Palestinian government denounced terrorism. Refugees & the Right of Return If Palestinians living in Arab nations or in the Occupied Territories return to Israel to reclaim land, it can mean the end of Israel as a Jewish state. As refugees, Palestinians believe they should be able to return to their or their families land in Israel and receive reimbursement for expenses incurred as refugees. Two States or One/borders Israelis do not want to give up Jerusalem to Palestinian Authority. Many Israelis do not recognize Palestinians as a people separate from Arabs, therefore, they are not entitled to their own state. Palestinians should be granted all of the West Bank and Gaza independently and as a separate state, and that Israelis settled there should leave. 4/24/2010 28
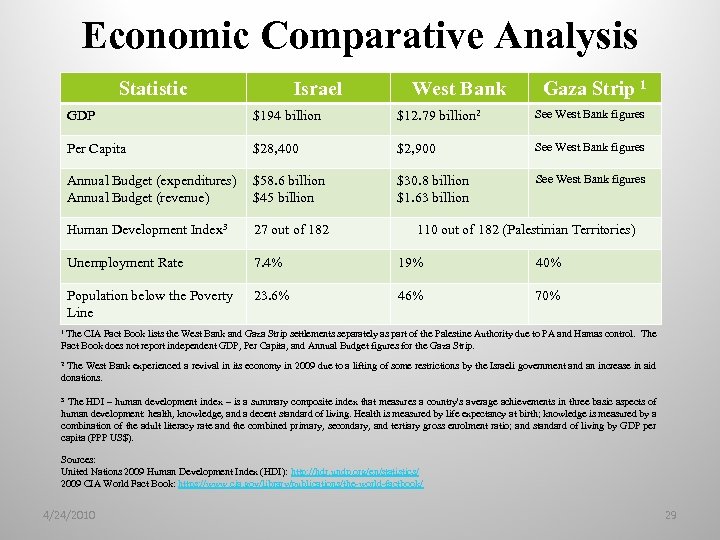
Economic Comparative Analysis Statistic Israel West Bank Gaza Strip 1 GDP $194 billion $12. 79 billion 2 See West Bank figures Per Capita $28, 400 $2, 900 See West Bank figures Annual Budget (expenditures) Annual Budget (revenue) $58. 6 billion $45 billion $30. 8 billion $1. 63 billion See West Bank figures Human Development Index 3 27 out of 182 Unemployment Rate 7. 4% 19% 40% Population below the Poverty Line 23. 6% 46% 70% 110 out of 182 (Palestinian Territories) 1 The CIA Fact Book lists the West Bank and Gaza Strip settlements separately as part of the Palestine Authority due to PA and Hamas control. The Fact Book does not report independent GDP, Per Capita, and Annual Budget figures for the Gaza Strip. The West Bank experienced a revival in its economy in 2009 due to a lifting of some restrictions by the Israeli government and an increase in aid donations. 2 The HDI – human development index – is a summary composite index that measures a country's average achievements in three basic aspects of human development: health, knowledge, and a decent standard of living. Health is measured by life expectancy at birth; knowledge is measured by a combination of the adult literacy rate and the combined primary, secondary, and tertiary gross enrolment ratio; and standard of living by GDP per capita (PPP US$). 3 Sources: United Nations 2009 Human Development Index (HDI): http: //hdr. undp. org/en/statistics/ 2009 CIA World Fact Book: https: //www. cia. gov/library/publications/the-world-factbook/ 4/24/2010 29
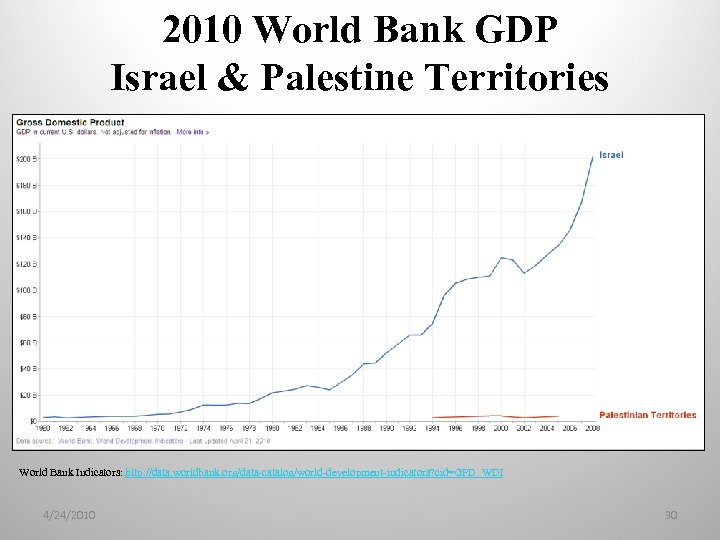
2010 World Bank GDP Israel & Palestine Territories World Bank Indicators: http: //data. worldbank. org/data-catalog/world-development-indicators? cid=GPD_WDI 4/24/2010 30

Works Cited Mary. Lynne Fillmon, The Israeli-Palestinian Conflict: A Lesson in Perspective: 2008. http: //www. cmes. arizona. edu/outreach/files/Sec. %20 Lesson%20 -%20%20 Israeli-Palestinian%20 Conflict%20%20 Perspective/The%20 Israeli-Palestinian%20 Conflict%20 A%20 Lesson%20 in%20 Perspective. ppt United Nations 2009 Human Development Index (HDI): http: //hdr. undp. org/en/statistics/ 2009 CIA World Fact Book: https: //www. cia. gov/library/publications/the-world-factbook/ World Bank Indicators: http: //data. worldbank. org/data-catalog/world-development-indicators? cid=GPD_WDI A Historical Perspective on the Arab-Israeli Conflict and Peace Process: A Curriculum for Modern World History Teachers. Institute for Curriculum Services, www. icsresources. org. 4/24/2010 31
b5db901af8b491317f60fa84c679be89.ppt