9803412b7bd7cfa4e9650c3fb71cf03c.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 37

ADAPTATION OF APPLETS AND LIVE VIDEOS TO MOBILE DEVICES J Manoj Kumar (M. Tech IIT Bombay) Guided by: Prof. Sridhar Iyer
Problem Definition 1. Adapt CDEEP Live Videos to Mobile Devices. Adapt to low bandwidth networks. Ø Problems in video streaming to mobile devices Ø Limited Memory in Mobile devices. Ø Low Bandwidth of Mobile Network like GPRS. 2. Adapt Java Applets to Mobile Devices Java Applets are built with J 2 SE technology that do not work on mobile devices. Limited Memory in Mobile devices work on J 2 ME technology.
Adaptation Of CDEEP Live videos to Mobile Devices
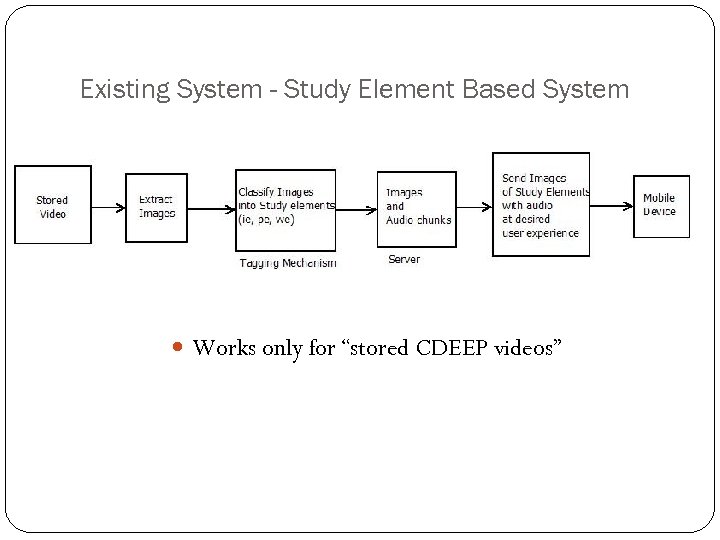
Existing System - Study Element Based System Works only for “stored CDEEP videos”
Study Element Based System Three types of Study Elements are categorized i. Presentation Element -- portion of video that shows one slide of presentation. ii. White paper Element – portion of video that shows white paper. iii. Instructor Element – portion of video that shows instructor.

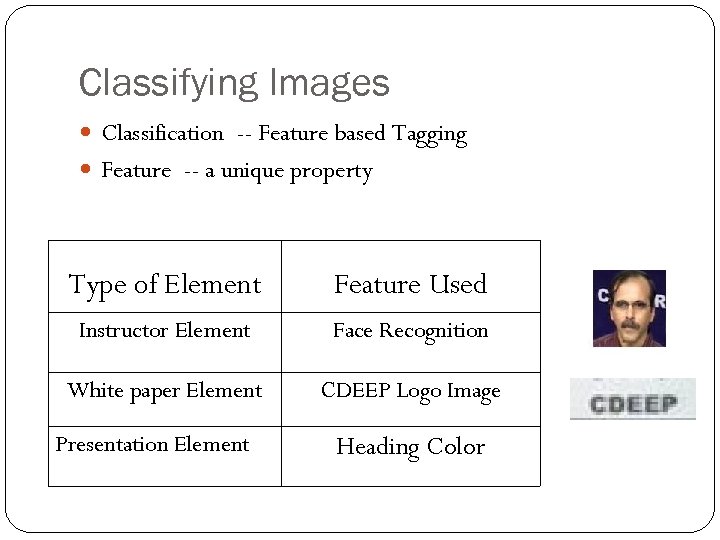
Classifying Images Classification -- Feature based Tagging Feature -- a unique property Type of Element Feature Used Instructor Element Face Recognition White paper Element CDEEP Logo Image Presentation Element Heading Color
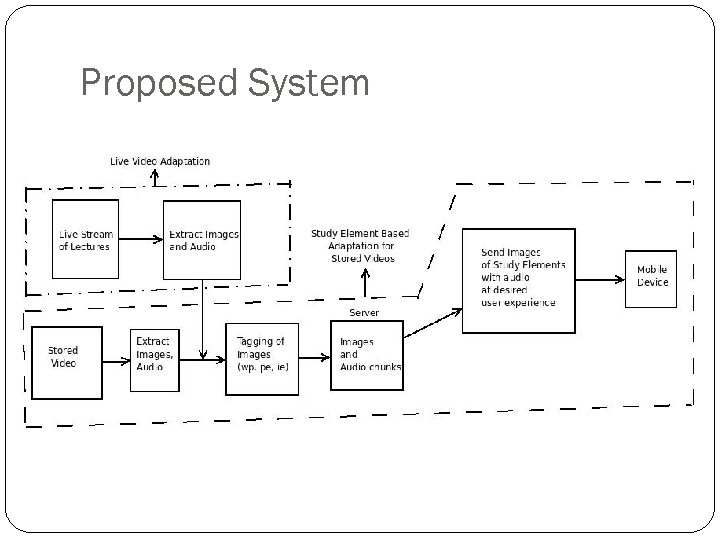
Proposed System
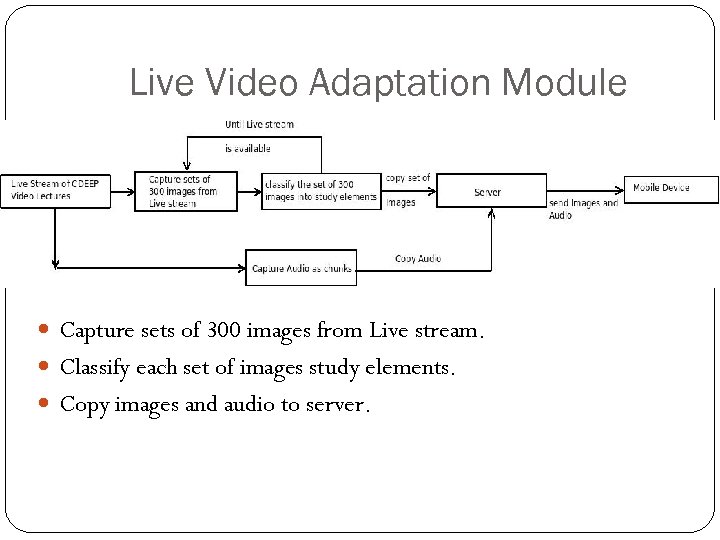
Live Video Adaptation Module Capture sets of 300 images from Live stream. Classify each set of images study elements. Copy images and audio to server.

Image Extraction Methodology Approach 1: Using Video LAN(VLC) Save or Record for five minutes. Extract Images from saved video. Disadvantages High CPU utilization because of Video transcoding. Delay between actual video and seeing video increases for each iteration.

Convert to MJPEG Stream MJPEG - Motion JPEG ( Images are shown one after the other). Ex: surveillance camera. Images are separated by delimiter. Disadvantages High CPU Utilization because of Video Transcoding. Unable to display images.

Approach 2: Using FFmpeg Images extracted directly from live stream. ffmpeg -i url -an -r 1 -f image -s 320 x 240 video%d. jpg Group images to sets of 300. Using Mplayer: Images extracted and grouped directly from live stream. mplayer -nosound -vf framestep=25 -vo jpeg: subdirs=img: maxfiles=300 url
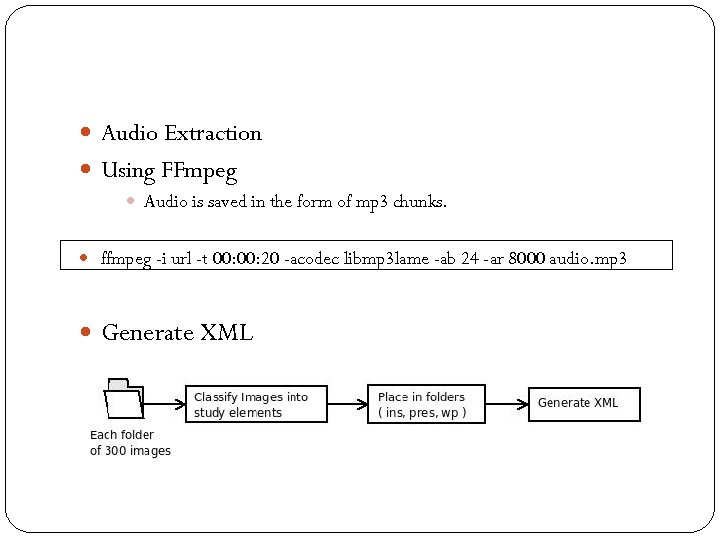
Audio Extraction Using FFmpeg Audio is saved in the form of mp 3 chunks. ffmpeg -i url -t 00: 20 -acodec libmp 3 lame -ab 24 -ar 8000 audio. mp 3 Generate XML

System Implementation
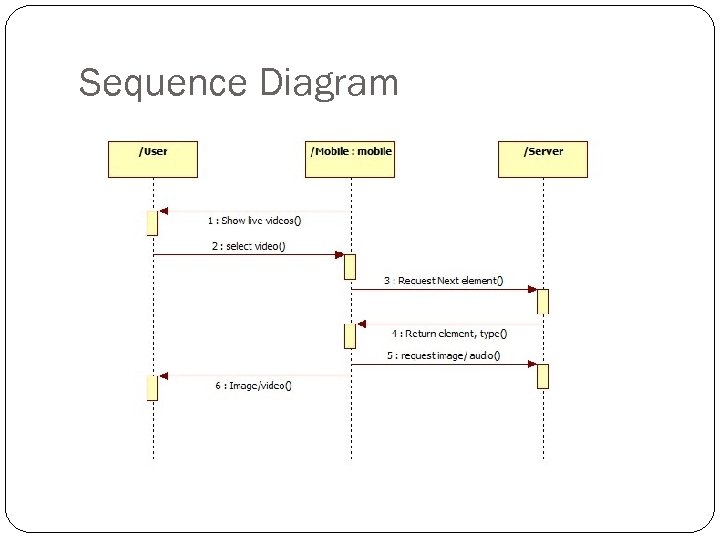
Sequence Diagram
Design Considerations Port blocking in GSM networks Direct TCP connections not possible due to port blocking. Allows only HTTP connection to ports 80 and 8080. Audio Streaming Audio streaming to mobile device is not supported. Hence, need to do progressive download.

Usage 1. Enter URL 2. select video 3. slide show

Comparison to Existing System Supports automatic creation of offline copy of video. Live video can be viewed as soon as it starts. Misclassifications of images cannot be corrected.

Adaptation of Applets to Mobile Devices

Project OSCAR – Open Source Courseware Animations Repository for web-based, interactive animations for various teaching concepts. Animation is typically an Java Applet with brief description of concept.
Overview of J 2 ME Java Micro Edition J 2 ME – small devices like mobiles, PDA’s with low RAM and speed. J 2 ME has 3 principles Configuration – JVM + set of API’s Profile – set of API’s designed for specific configuration Optional package –technology specific API’s to extend the capabilities of JVM
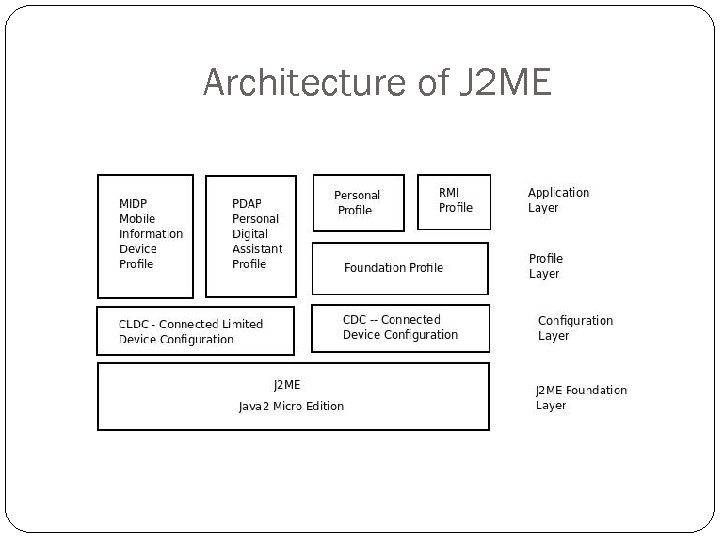
Architecture of J 2 ME
J 2 ME Configuration: specifies JVM and core set of API’s for a specific family of devices. Two types of configuration Connected Device Configuration CDC – minimum of 512 KB ROM, 256 KB of RAM, full JVM must be supported. High end PDA’s, TV setup boxes, car navigation systems. Connected Limited Device Configuration CLDC – minimum of 160 KB of ROM, 32 KB RAM, KVM Mobiles, pagers, PDA’s. Cannot add native methods.
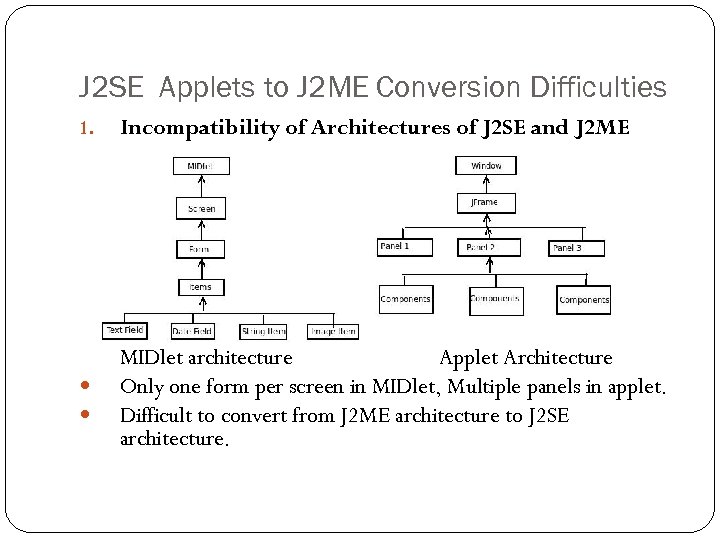
J 2 SE Applets to J 2 ME Conversion Difficulties 1. Incompatibility of Architectures of J 2 SE and J 2 ME MIDlet architecture Applet Architecture Only one form per screen in MIDlet, Multiple panels in applet. Difficult to convert from J 2 ME architecture to J 2 SE architecture.
1. . 2. Canvas size and Co-ordinates of Image Object Designed for Desktop systems Co-ordinates have to be set manually – cannot be automated Sample OSCAR paint code public void paint(Graphics G){ g. draw. Image(Image img 1, 480, 600, this); g. draw. Image(Image img 2, 530, 400, this); g, draw. Image(Image img 3, 60, 370, this); }

Amount of Text on Screen 1. Designed for Desktop Resolutions – cannot be fit mobile screen, preplanning cannot be automated. Sample OSCAR animation with text field. public void init(){ ta = new Text. Area("", 31, 47); ta. set. Text("nt Energy Transaction in Biological Systemsn"+ "n In this animation you will learn the concepts of ATP Metabolism………. ……………… 10 lines };

Other General Differences No floating point support in J 2 ME. No Java Native Interface (JNI) in J 2 ME. No finalize method in J 2 ME. No Thread Groups.
J 2 SE to J 2 ME – Conversion Possibilities 1. Copy of Paint Method J 2 ME uses J 2 SE’s Graphics class with minor changes -- enables copy paint method as it is during conversion Sample applet with paint method public void paint( Graphics g){ g. draw. String("Sending", 150, 75); g. draw. Rect("40, 50, 10, 20); g. draw. Img(Image img, 20, 30, center); g. draw. Arc(30, 40, 10, 30, 60, 120); } g. draw. String, g. draw. Rect, g. draw. Img, g. draw. Arc are common in both j 2 se and j 2 me
Buttons to Key mapping J 2 ME doesn’t display buttons, it uses mobile device keys take input OSCAR animations -- buttons like start, stop. Buttons to key mapping is possible. LWUIT Light Weight User Interface Toolkit is a UI library developed by Sun. Offers advanced UI capabilities and API inspired by Swing. LWUIT allows multiple panels on screen.
Overview of Flash and Action Script Flash – multimedia platform language for creating animations Action Script can be embedded. – ECMA script. AS is Object Oriented similar to Java Script. AS + Flash – more interactive animations. Used to build Rich Internet Applications. Flash Lite – highly optimized flash runtime for mobiles. Provides same functionality similar to desktop.

Applet to Flash – Conversion Difficulties No Multi-Threading in Flash Multi-Threading – two or more parts in a program to run concurrently ( Multitasking ). Essential ability to have code do something while UI is doing something else. Single Thread – Having heavy computation, cannot update UI. Program becomes un-responsive and crashes after 60 seconds. Sample OSCAR program with thread class Timer extends Thread { //code// void Settime(); void sleep(); }
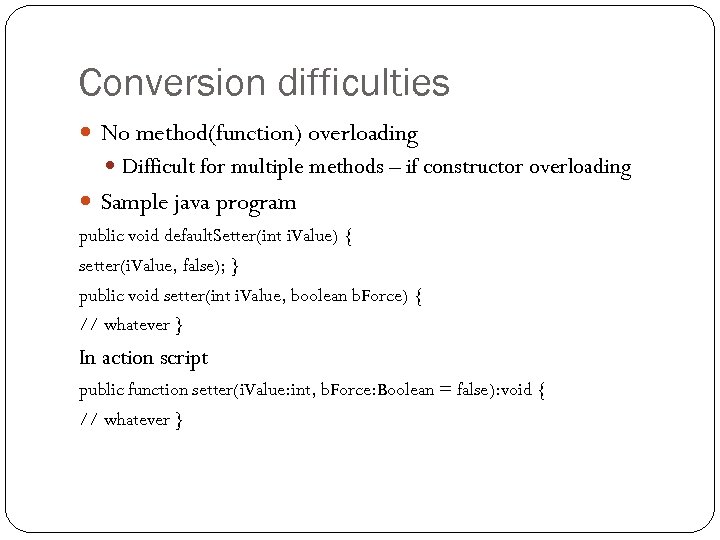
Conversion difficulties No method(function) overloading Difficult for multiple methods – if constructor overloading Sample java program public void default. Setter(int i. Value) { setter(i. Value, false); } public void setter(int i. Value, boolean b. Force) { // whatever } In action script public function setter(i. Value: int, b. Force: Boolean = false): void { // whatever }
Other General Difficulties and Possibilities 1. Limited Data Structures Action script supports only Arrays and Dictionary. No queues, no linked List, no stack compared to Java. Need to re-implement data structures which are wrapped. No Blocking 2. Next code of line is supposed to run, user cannot prevent it from run – Alert. show(); does not stop exexctuing next line. q Possibilities • • Java and Action Script have same syntax with a little change. Syntax change automated by Java to Action script converter (J 2 AS 3)
Conclusion Successfully integrated to existing Study element based adaptation. Live video transmission of CDEEP videos can be adapted to networks with low bandwidth. Automated porting Java applets to mobile devices as J 2 ME MIDlets and flash files is difficult and infeasible.
Future Work 1. Decrease Misclassifications of images 2. Synchronization between audio and images 3. Study element based system is prone to errors. Better feature based classification. Synchronizing audio with the image slideshow. Text Improvement Identify text in study elements and improve text quality.

References 1. Fabrice Bellard. Ffmpeg codec manual. http: //www. ffmpeg. org/ffmpegdoc. html. 2. Free Software Foundation. Mplayer manual. http: //www. mplayerhq. hu/DOCS/HTML/en/index. html. 3. G. N. Murthy and S. Iyer. Study element based adaptation of lecture videos to mobile devices. In Communications (NCC), 2010 National Conférence on, pages 1 - 5, 29 -31 2010. 4. Herbert Schildt. Java 2 ME the complete reference. Osborne/Mc. Graw-Hill, fourth edition, 2001.

Questions?
9803412b7bd7cfa4e9650c3fb71cf03c.ppt