Asel Diana srs.pptx
- Количество слайдов: 11
 Acylation. The acylating agent.
Acylation. The acylating agent.
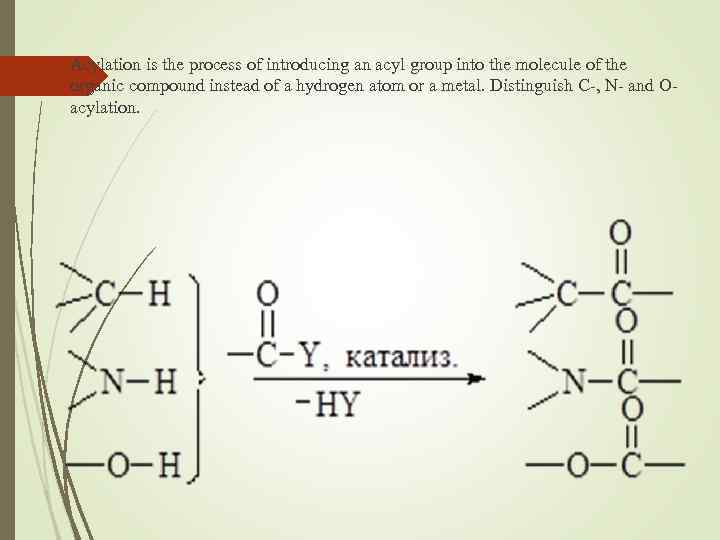 Acylation is the process of introducing an acyl group into the molecule of the organic compound instead of a hydrogen atom or a metal. Distinguish C-, N- and Oacylation.
Acylation is the process of introducing an acyl group into the molecule of the organic compound instead of a hydrogen atom or a metal. Distinguish C-, N- and Oacylation.
 Acylation is one of the most common processes for the synthesis of drugs and vitamins, as well as in the synthesis of prodrugs. Many prodrugs include acyl groups. The body as deacylation form substances with higher biological activity, which can not be introduced into the body directly into the high dose due to toxicity or other reasons.
Acylation is one of the most common processes for the synthesis of drugs and vitamins, as well as in the synthesis of prodrugs. Many prodrugs include acyl groups. The body as deacylation form substances with higher biological activity, which can not be introduced into the body directly into the high dose due to toxicity or other reasons.
 Many substances used during the acylation processes, are toxic, and explosive and flammable. In addition to the mentioned in previous chapters should be noted the danger of the processes carried out in the presence of phosphorus oxychloride, phosphorus and aluminum chloride. These substances are decomposed with water and hydrogen chloride. Entry of water into the machine, where the processes are carried out with the use of these substances may be released into the reaction mass. Due to the ease of decomposition by moisture compounds listed stored and transported in a sealed container.
Many substances used during the acylation processes, are toxic, and explosive and flammable. In addition to the mentioned in previous chapters should be noted the danger of the processes carried out in the presence of phosphorus oxychloride, phosphorus and aluminum chloride. These substances are decomposed with water and hydrogen chloride. Entry of water into the machine, where the processes are carried out with the use of these substances may be released into the reaction mass. Due to the ease of decomposition by moisture compounds listed stored and transported in a sealed container.
 acylating agents Acylating agents include acyl compound of the general formula R -CO-Y, where R = alkyl, aryl, heterocyclyl; Y - leaving group = Hlg, R-COO-, OH, OR, NH 2, NHR, NR 2, and N 3. Additionally as acylating agents used ketene, diketene et al. The acyl group introduced into a molecule of organic matter as the purpose of temporary protection of the labile groups (often NH 2), and to modify the carbon skeleton of the molecule and the substance imparting new properties.
acylating agents Acylating agents include acyl compound of the general formula R -CO-Y, where R = alkyl, aryl, heterocyclyl; Y - leaving group = Hlg, R-COO-, OH, OR, NH 2, NHR, NR 2, and N 3. Additionally as acylating agents used ketene, diketene et al. The acyl group introduced into a molecule of organic matter as the purpose of temporary protection of the labile groups (often NH 2), and to modify the carbon skeleton of the molecule and the substance imparting new properties.
 Suitable acylating agents are used, some acids having different acylating ability depending on the degree of dissociation, and substituted acid anhydrides, acid chlorides, amides and esters of the acids which are good acylating agents in connection with the inability of their acid dissociation. Acylation of amines can be taken free acids, but for the acylation of phenols are mainly anhydrides
Suitable acylating agents are used, some acids having different acylating ability depending on the degree of dissociation, and substituted acid anhydrides, acid chlorides, amides and esters of the acids which are good acylating agents in connection with the inability of their acid dissociation. Acylation of amines can be taken free acids, but for the acylation of phenols are mainly anhydrides
 There was widespread in the chemicalpharmaceutical industry as acylating agents following phosgene chlorides, acetyl chloride, benzoyl chloride, methyl and ethyl esters of chlorocarbonic acid, benzenesulfonyl, feniluretansulfoсhlorid
There was widespread in the chemicalpharmaceutical industry as acylating agents following phosgene chlorides, acetyl chloride, benzoyl chloride, methyl and ethyl esters of chlorocarbonic acid, benzenesulfonyl, feniluretansulfoсhlorid
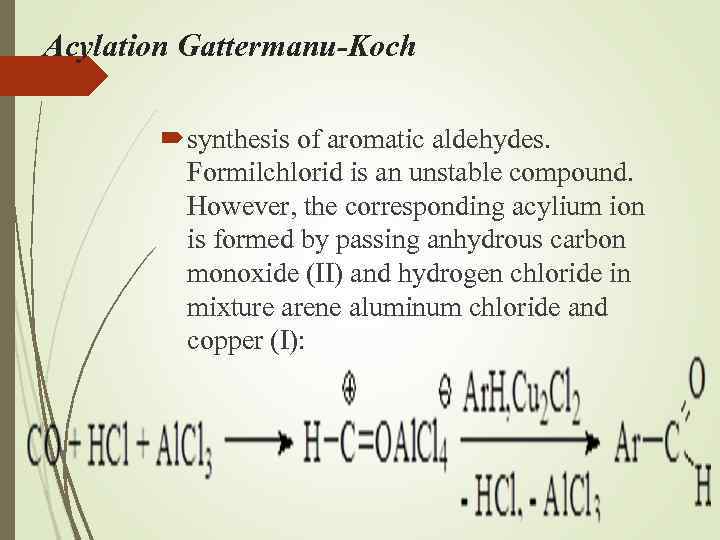 Acylation Gattermanu-Koch synthesis of aromatic aldehydes. Formilсhlorid is an unstable compound. However, the corresponding acylium ion is formed by passing anhydrous carbon monoxide (II) and hydrogen chloride in mixture arene aluminum chloride and copper (I):
Acylation Gattermanu-Koch synthesis of aromatic aldehydes. Formilсhlorid is an unstable compound. However, the corresponding acylium ion is formed by passing anhydrous carbon monoxide (II) and hydrogen chloride in mixture arene aluminum chloride and copper (I):
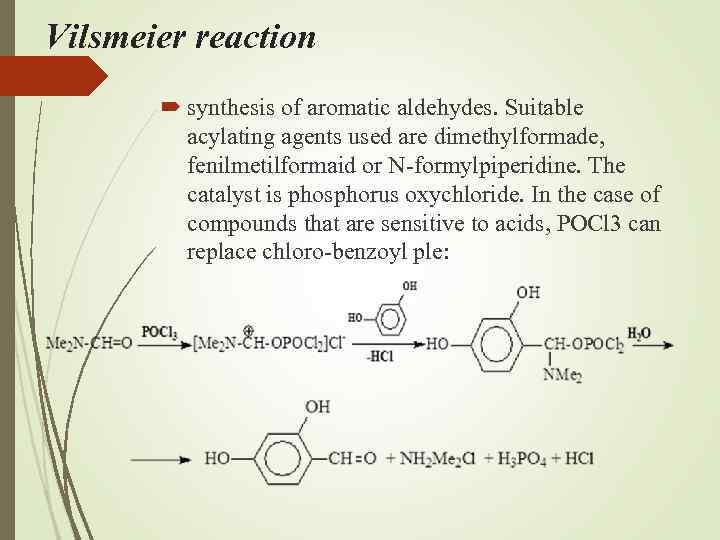 Vilsmeier reaction synthesis of aromatic aldehydes. Suitable acylating agents used are dimethylformade, fenilmetilformaid or N-formylpiperidine. The catalyst is phosphorus oxychloride. In the case of compounds that are sensitive to acids, POCl 3 can replace chloro-benzoyl ple:
Vilsmeier reaction synthesis of aromatic aldehydes. Suitable acylating agents used are dimethylformade, fenilmetilformaid or N-formylpiperidine. The catalyst is phosphorus oxychloride. In the case of compounds that are sensitive to acids, POCl 3 can replace chloro-benzoyl ple:
 For the introduction of an acetyl group to amines and phenols recently proposed ketone CH 2 O C, the internal anhydride of acetic acid
For the introduction of an acetyl group to amines and phenols recently proposed ketone CH 2 O C, the internal anhydride of acetic acid
 N-Acylation of carbonic acid chlorides and arensulfon acids is of great importance in the synthesis of medicines.
N-Acylation of carbonic acid chlorides and arensulfon acids is of great importance in the synthesis of medicines.


