острый холицестит.pptx
- Количество слайдов: 10

Acute cholecystitis Student’s name: Aibek Bazilov Faculty : General medicine Course: 2 Group: 206 “A” Teacher: Abdykadyrova G. I.

Plan 1. Acute cholecystitis 2. Classification of acute cholecystitis 3. Etiology and pathogenesis of acute cholecystitis 4. Symptom of acute cholecystitis 5. Diagnosis of acute cholecystitis 6. Question

Acute cholecystitis is an inflammation of the gallbladder, characterized by a sudden disturbance of the bile movement as a result of blockage of its outflow. Possible development of pathological destruction of the gallbladder walls. In the overwhelming majority of cases (85 -95%), the development of acute cholecystitis is combined with concrements (stones), more than half (60%) of patients are determined by bacterial infection of bile (intestinal bacillus, cocci, salmonella, etc. ). In acute cholecystitis, symptomatology occurs once, develops and, with adequate treatment, dies out without leaving any pronounced consequences. With repeated repetition of acute attacks of gallbladder inflammation, they speak of chronic cholecystitis.

Classification of acute cholecystitis Acute cholecystitis is subdivided in form into catarrhal and destructive (purulent). Among destructive forms, in turn, secrete phlegmonous, phlegmonous-ulcerative, gangrenous and perforative, depending on the stage of the inflammatory process.
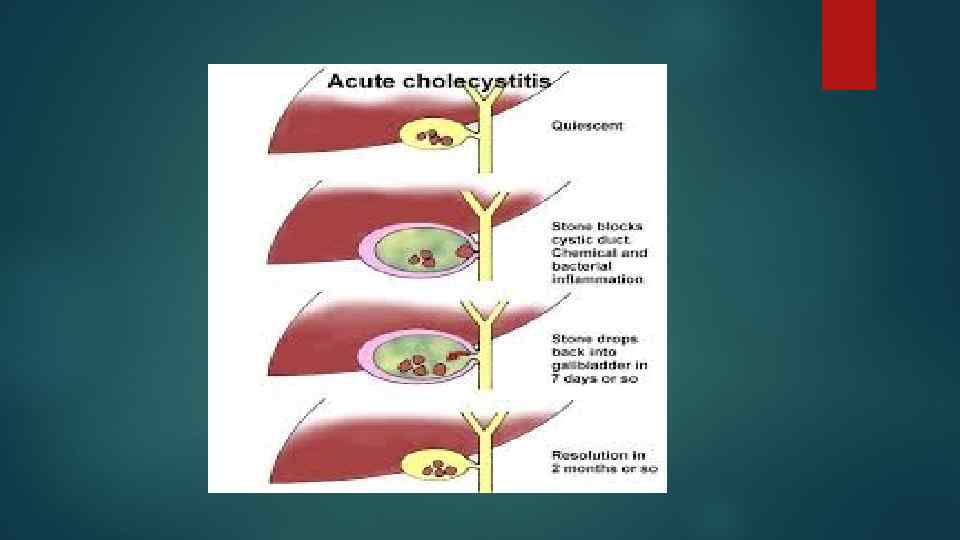

Etiology and pathogenesis of acute cholecystitis Causes of cholecystitis: Damage to the walls of the bladder by solid formations (stones), blockage of the bile duct stones (calculous cholecystitis); Infection of bile with bacterial flora, development of infection (bacterial cholecystitis); Throwing enzymes of the pancreas into the gallbladder (fermentative cholecystitis). In all cases, the development of inflammation in the walls of the gallbladder causes narrowing of the lumen of the bile duct (or its obstruction with calculus) and bile stasis, which gradually thickens.
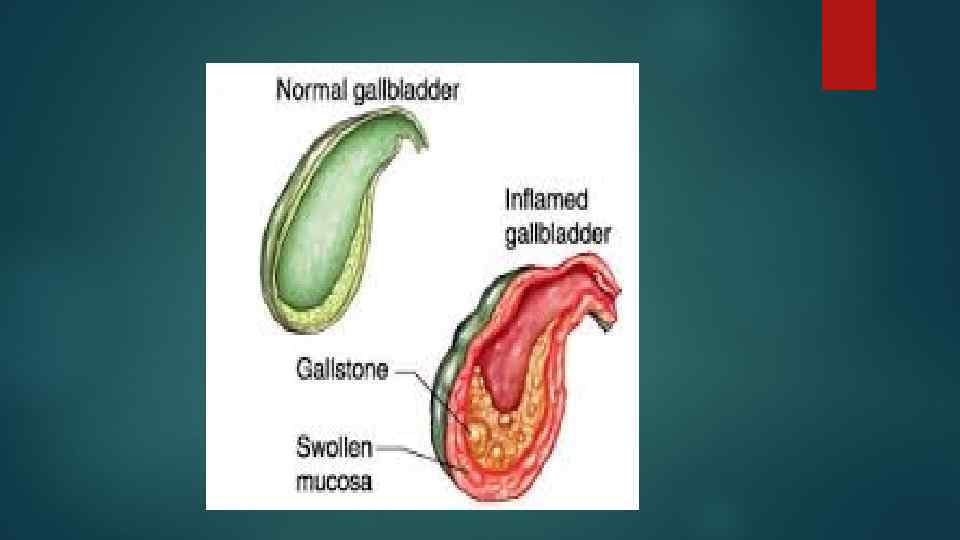

Symptom of acute cholecystitis The main symptom of acute cholecystitis is biliary colic - acute pain in the right upper quadrant, upper abdomen, possibly irradiating in the back (under the right scapula). Less often, irradiation occurs in the left half of the body. Preceding the occurrence of biliary colic can be the intake of alcohol, spicy, fatty foods, severe stress. In addition to the pain syndrome, acute cholecystitis can be accompanied by nausea (up to vomiting with bile), subfebrile temperature. In mild cases (without the presence of gallstones) acute cholecystitis occurs rapidly (5 -10 days) and ends with recovery. When the infection becomes infected purulent cholecystitis develops, in persons with weakened protective forces of the organism it is able to go into gangrene and perforation (breakthrough) of the gallbladder wall. These conditions are fraught with a fatal outcome and require immediate surgical treatment.

Diagnosis of acute cholecystitis Acute cholecystitis (cholangiogram) For the diagnosis of acute cholecystitis, it is important to identify abnormalities in the diet or stress conditions during the survey, the presence of symptoms of biliary colic, palpation of the abdominal wall. If there is a suspicion of acute inflammation of the gallbladder, ultrasound of the abdominal cavity organs must be prescribed. It shows an increase in the organ, presence or absence of stones in the gallbladder and bile duct. In ultrasound examination, the inflamed gallbladder has thickened (more than 4 mm) walls with a double contour, bile duct dilatation may be noted, a positive Murphy symptom (bladder tension under the ultrasound sensor). A detailed picture of the organs of the abdominal cavity is provided by computed tomography. For a detailed study of the bile ducts, the ERCP technique (endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography) is used. The blood test shows signs of inflammation (leukocytosis, high ESR), dysproteinemia and bilirubinemia, increased enzyme activity (amylase, aminotransferase) in biochemical blood and urine tests.

Questions How is acute cholecystitis expressed? What are the forms of acute cholecystitis? Causes of acute cholecystitis? What is the diagnosis of acute cholecystitis?
острый холицестит.pptx