c8cbcf30256452f7a59bf4cc91ad703b.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 63

Activity-Based Modeling How does it work?
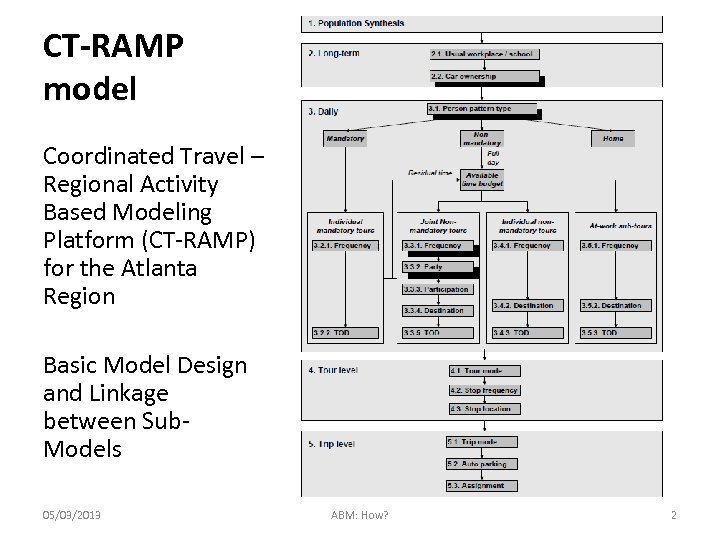
CT-RAMP model Coordinated Travel – Regional Activity Based Modeling Platform (CT-RAMP) for the Atlanta Region Basic Model Design and Linkage between Sub. Models 05/03/2013 ABM: How? 2
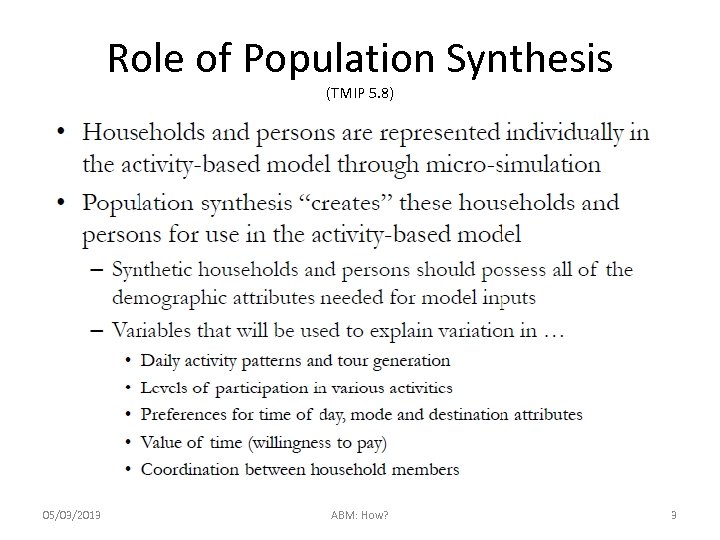
Role of Population Synthesis (TMIP 5. 8) 05/03/2013 ABM: How? 3
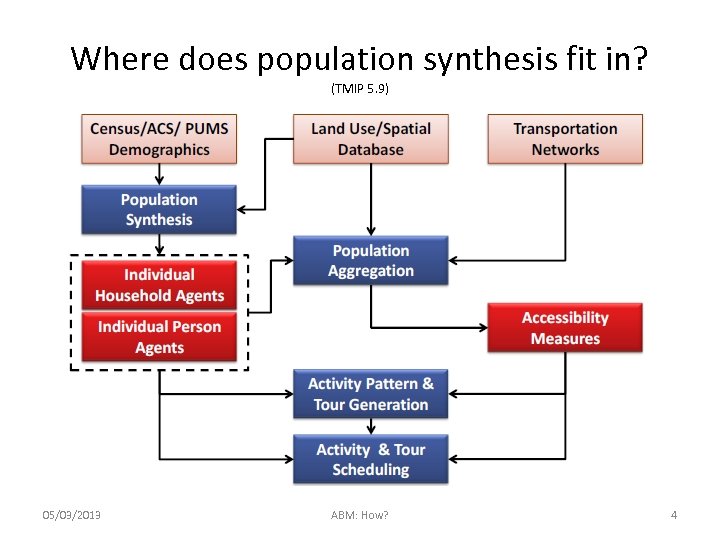
Where does population synthesis fit in? (TMIP 5. 9) 05/03/2013 ABM: How? 4
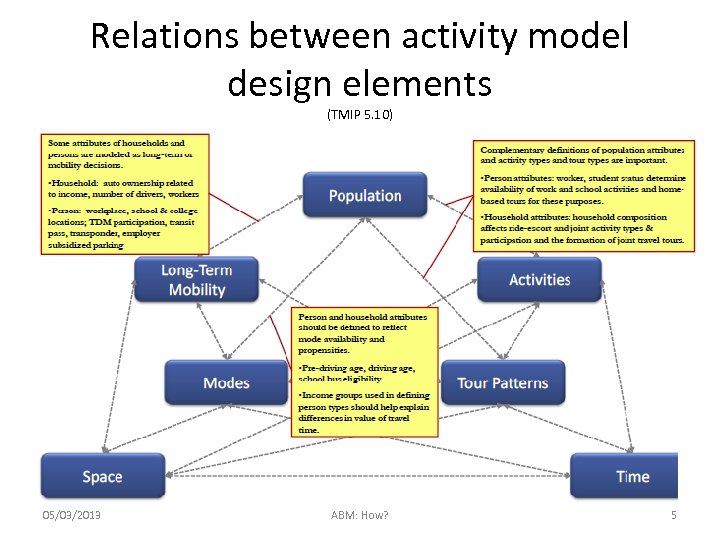
Relations between activity model design elements (TMIP 5. 10) 05/03/2013 ABM: How? 5
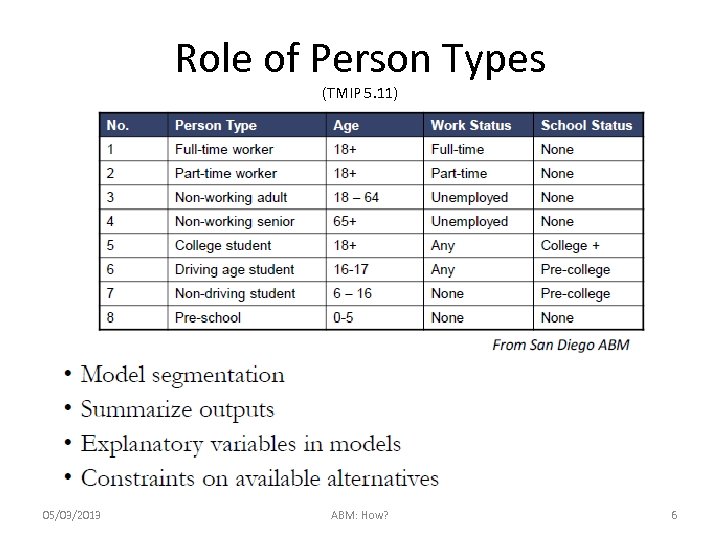
Role of Person Types (TMIP 5. 11) 05/03/2013 ABM: How? 6
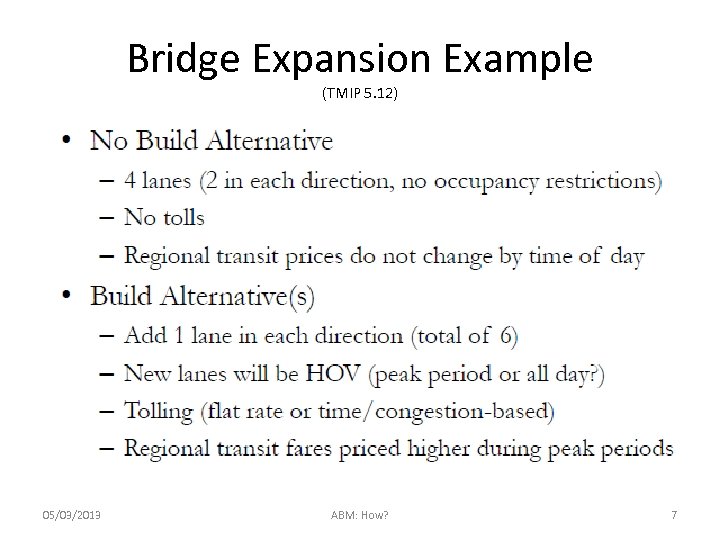
Bridge Expansion Example (TMIP 5. 12) 05/03/2013 ABM: How? 7

Relevance to Population Synthesizer (TMIP 5. 13) 05/03/2013 ABM: How? 8
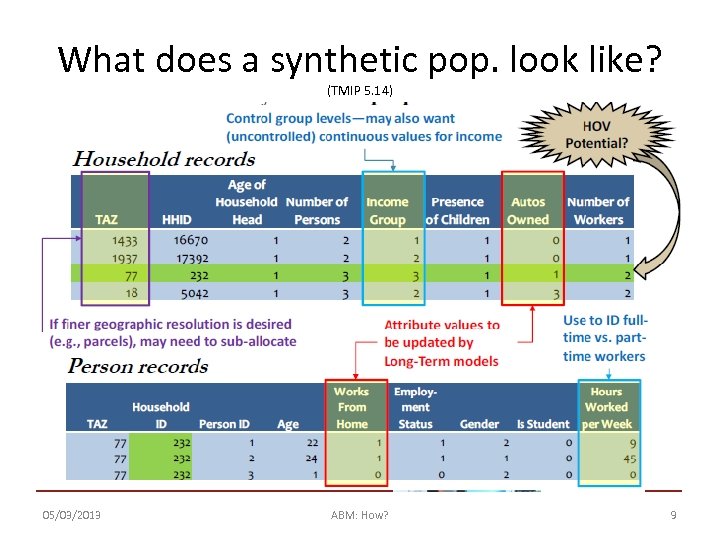
What does a synthetic pop. look like? (TMIP 5. 14) 05/03/2013 ABM: How? 9
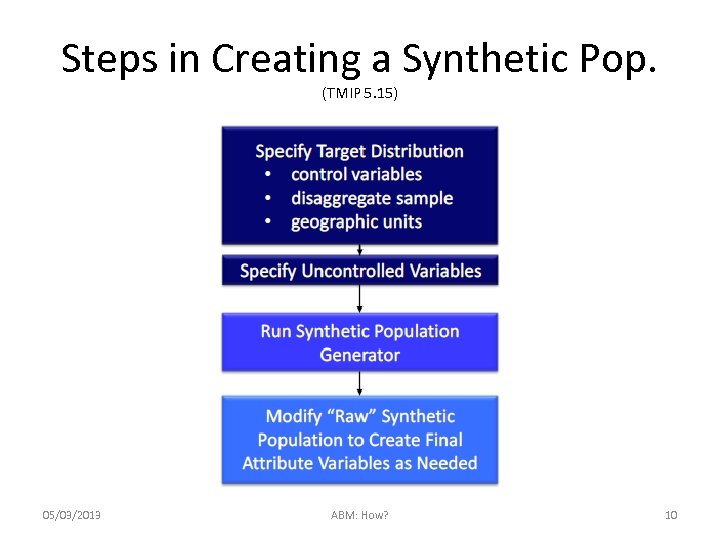
Steps in Creating a Synthetic Pop. (TMIP 5. 15) 05/03/2013 ABM: How? 10
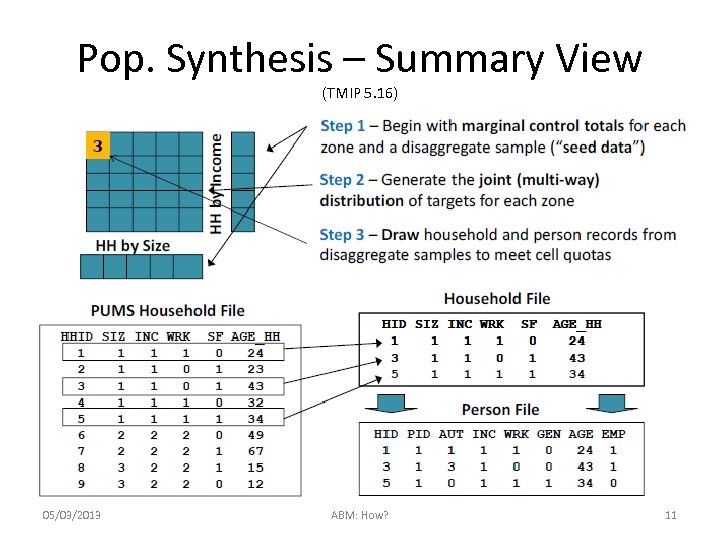
Pop. Synthesis – Summary View (TMIP 5. 16) 05/03/2013 ABM: How? 11
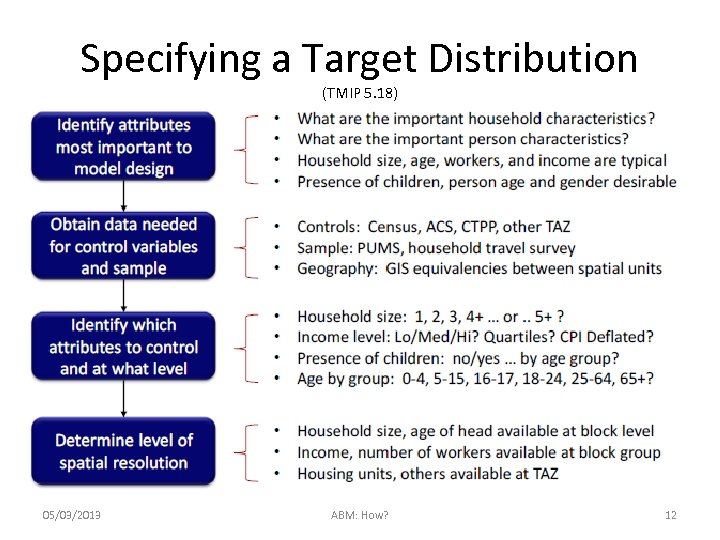
Specifying a Target Distribution (TMIP 5. 18) 05/03/2013 ABM: How? 12
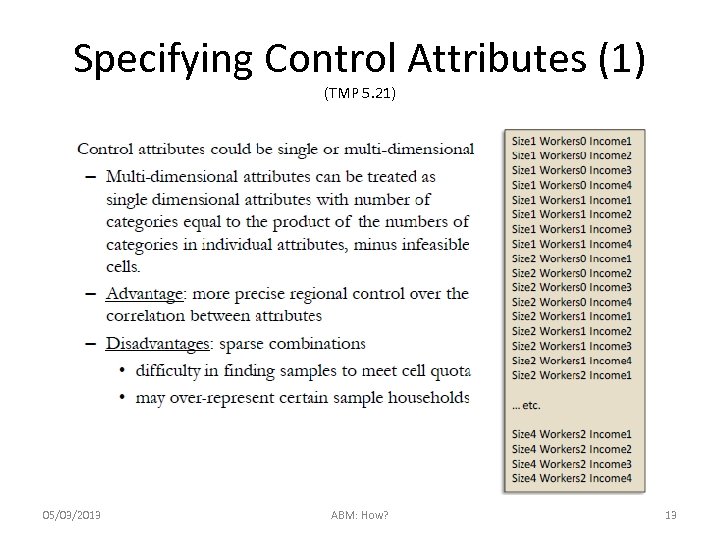
Specifying Control Attributes (1) (TMP 5. 21) 05/03/2013 ABM: How? 13

Specifying Control Attributes (2) (TMP 5. 23) 05/03/2013 ABM: How? 14
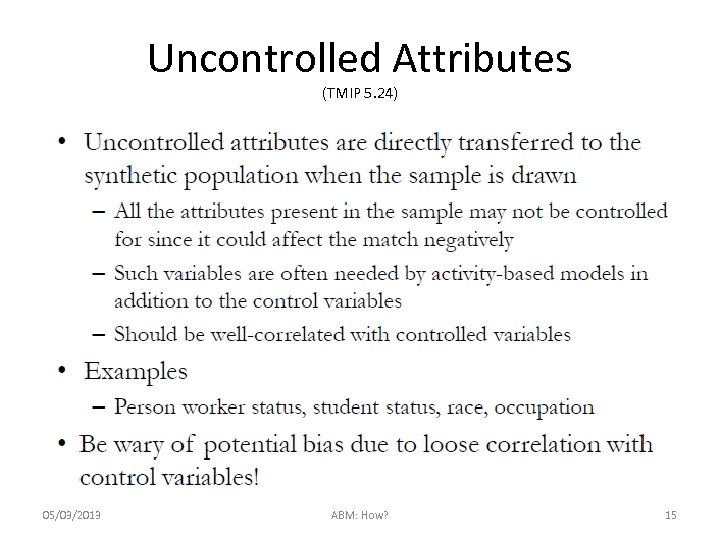
Uncontrolled Attributes (TMIP 5. 24) 05/03/2013 ABM: How? 15
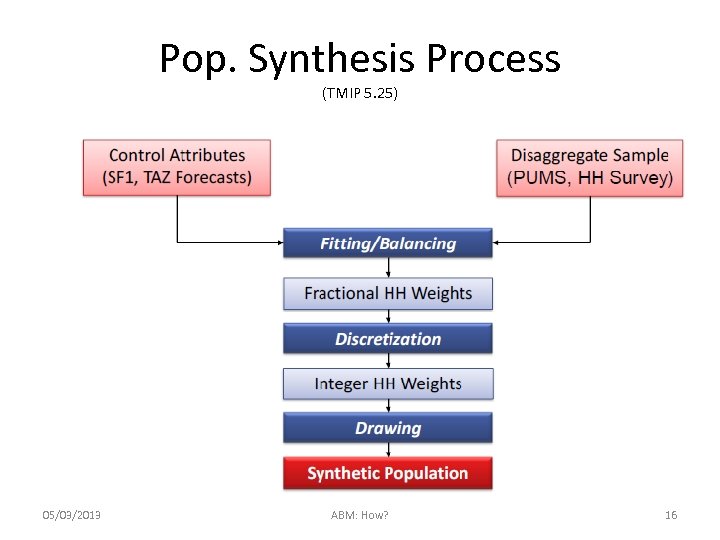
Pop. Synthesis Process (TMIP 5. 25) 05/03/2013 ABM: How? 16
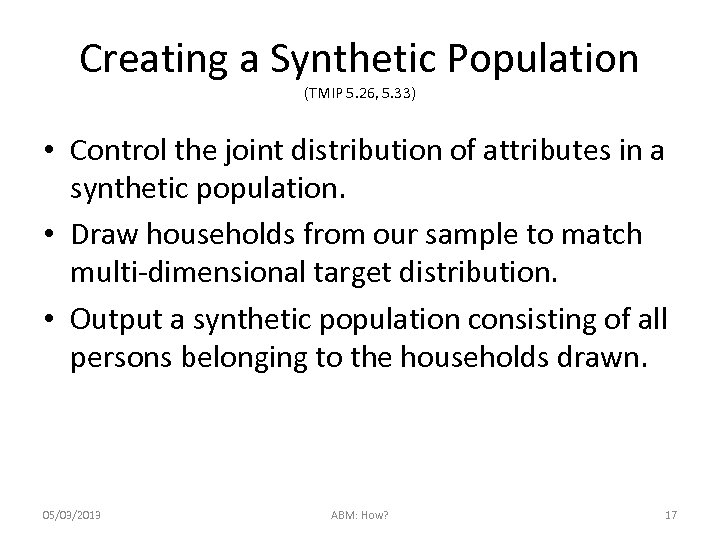
Creating a Synthetic Population (TMIP 5. 26, 5. 33) • Control the joint distribution of attributes in a synthetic population. • Draw households from our sample to match multi-dimensional target distribution. • Output a synthetic population consisting of all persons belonging to the households drawn. 05/03/2013 ABM: How? 17
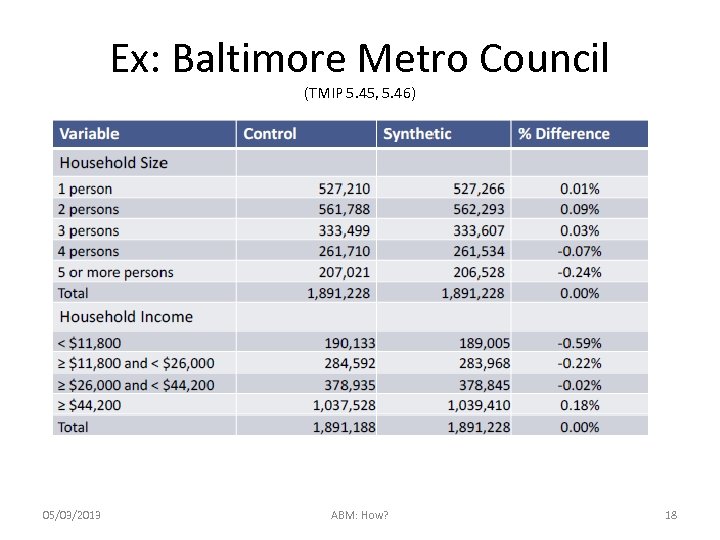
Ex: Baltimore Metro Council (TMIP 5. 45, 5. 46) 05/03/2013 ABM: How? 18

Forecasting Future Synthetic Pops. (TMIP 5. 57) 05/03/2013 ABM: How? 19
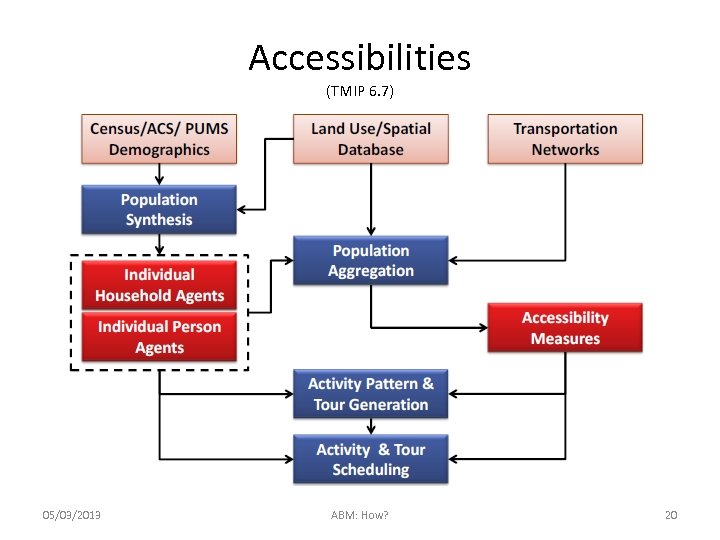
Accessibilities (TMIP 6. 7) 05/03/2013 ABM: How? 20

Defining Accessibility (TMIP 6. 9, 6. 10) 05/03/2013 ABM: How? 21
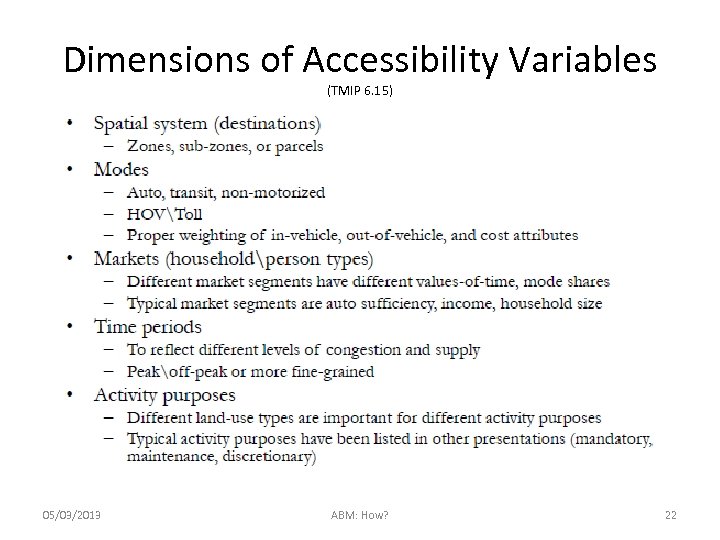
Dimensions of Accessibility Variables (TMIP 6. 15) 05/03/2013 ABM: How? 22
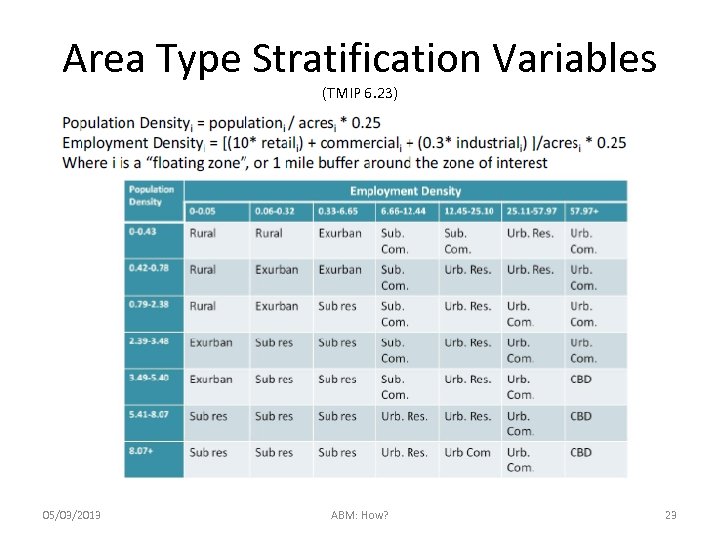
Area Type Stratification Variables (TMIP 6. 23) 05/03/2013 ABM: How? 23
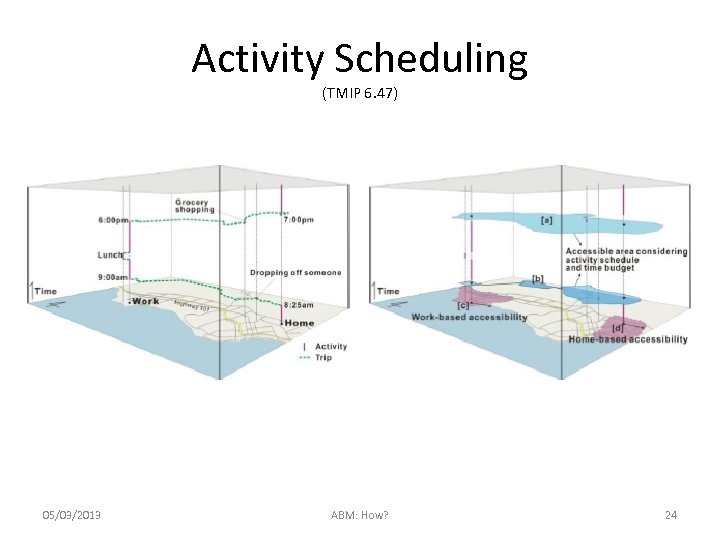
Activity Scheduling (TMIP 6. 47) 05/03/2013 ABM: How? 24
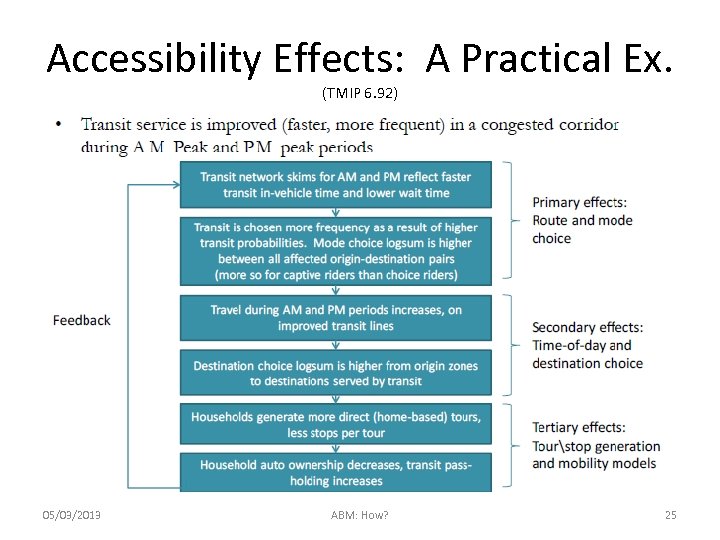
Accessibility Effects: A Practical Ex. (TMIP 6. 92) 05/03/2013 ABM: How? 25
Long-Term and Mobility Choice Models (TMIP 7. 7) • Longer-term decisions such as buying a car and medium-term decisions such as whether to buy a transit pass or a toll transponder. • They affect travel choices over the course of the year, as well as influencing travel choices on a day-to-day basis. 05/03/2013 ABM: How? 26
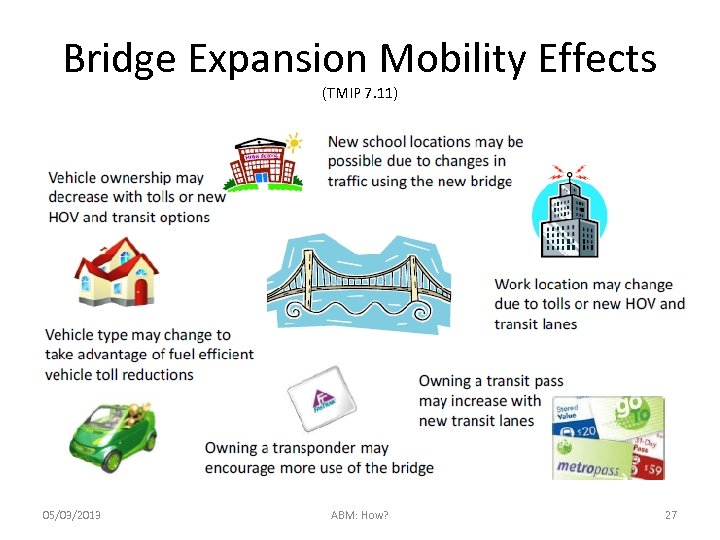
Bridge Expansion Mobility Effects (TMIP 7. 11) 05/03/2013 ABM: How? 27
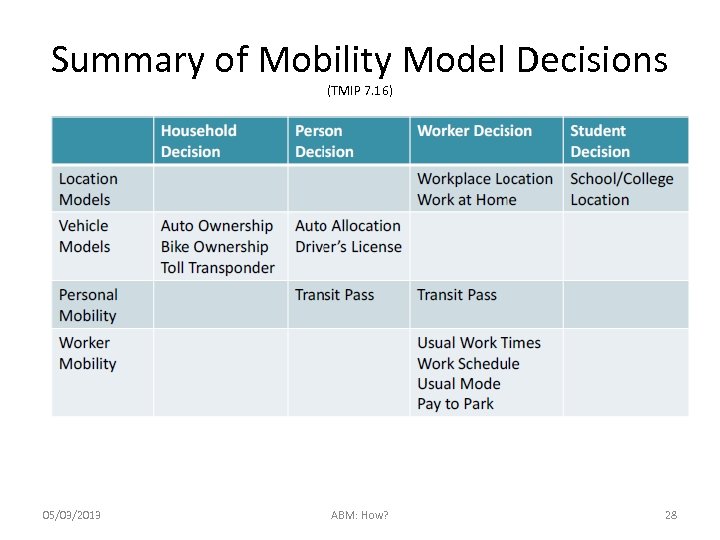
Summary of Mobility Model Decisions (TMIP 7. 16) 05/03/2013 ABM: How? 28
Mobility Decisions w/in ____ Model (TMIP 7. 18, 7. 19, 7. 20) • Within day pattern models and as long-term choices, or represented in one or the other. • Within the land-use model instead of the travel model. • Within the population synthesizer. These might include auto ownership, driver’s licenses, or people who work at home. Most likely as uncontrolled population attributes. 05/03/2013 ABM: How? 29
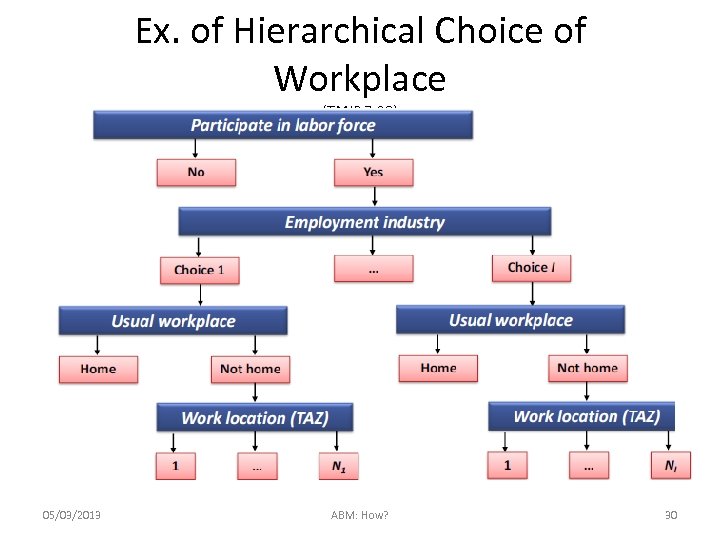
Ex. of Hierarchical Choice of Workplace (TMIP 7. 38) 05/03/2013 ABM: How? 30
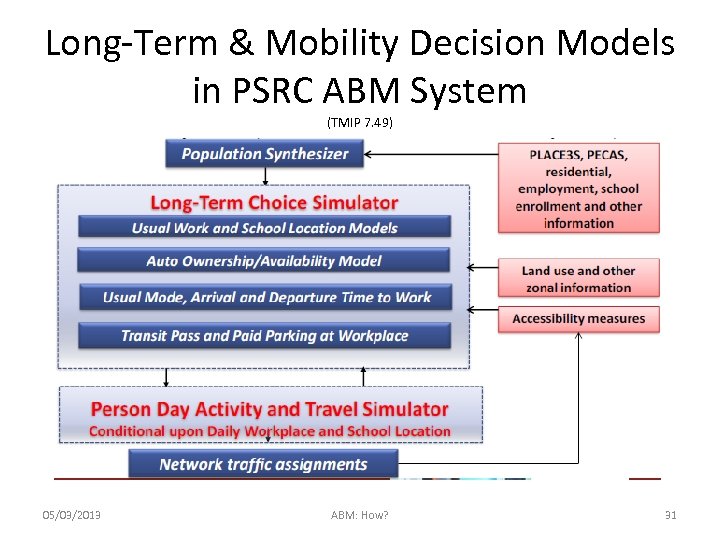
Long-Term & Mobility Decision Models in PSRC ABM System (TMIP 7. 49) 05/03/2013 ABM: How? 31

Challenges with New Policies and Technologies (TMIP 7. 56) 05/03/2013 ABM: How? 32
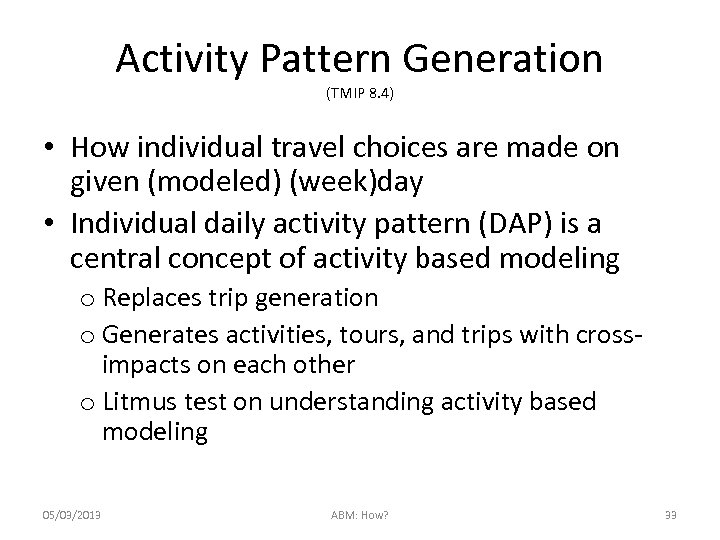
Activity Pattern Generation (TMIP 8. 4) • How individual travel choices are made on given (modeled) (week)day • Individual daily activity pattern (DAP) is a central concept of activity based modeling o Replaces trip generation o Generates activities, tours, and trips with crossimpacts on each other o Litmus test on understanding activity based modeling 05/03/2013 ABM: How? 33
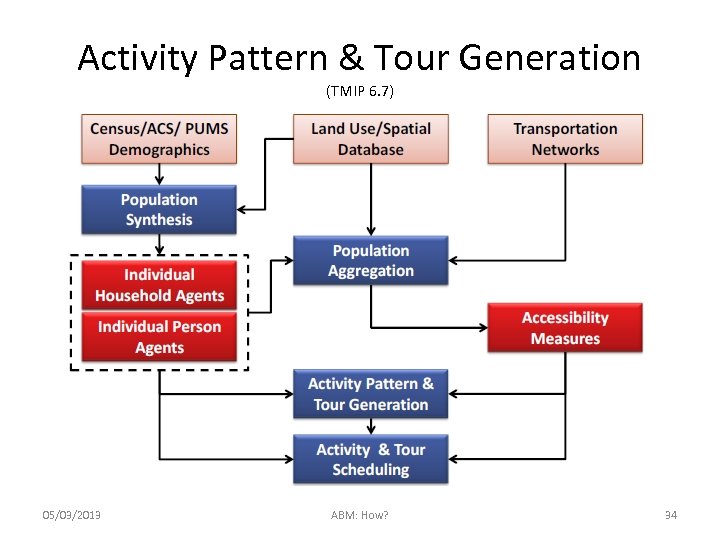
Activity Pattern & Tour Generation (TMIP 6. 7) 05/03/2013 ABM: How? 34

Daily Activity Pattern (TMIP 8. 7) • A typology describing a combination of tours made by persons over the course of a day. • Simple form: the number of tours of a particular purpose, such as “ 1 home-based work tour + 1 home-based social/recreational tour”. • Or, use an over-arching description such as “mandatory” or “discretionary” or “stay home all day. ” 05/03/2013 ABM: How? 35

Classification of Activities (TMIP 8. 8) 05/03/2013 ABM: How? 36

Out-of-Home Activities / Travel Purposes (TMIP 8. 10) 05/03/2013 ABM: How? 37
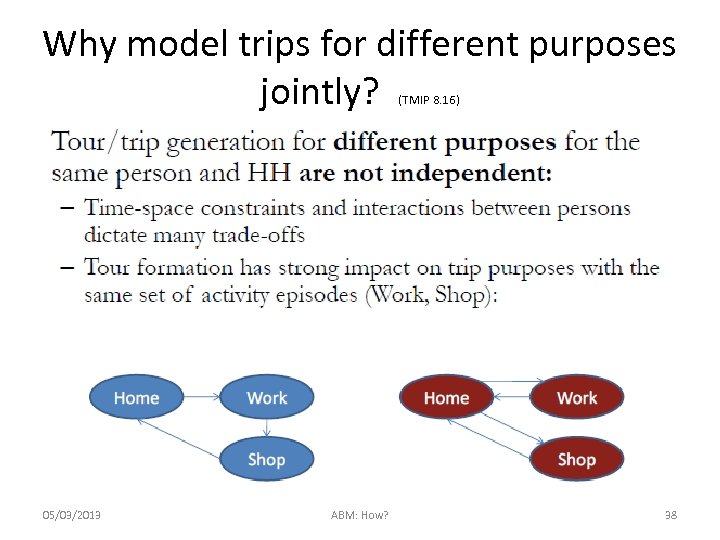
Why model trips for different purposes jointly? (TMIP 8. 16) 05/03/2013 ABM: How? 38
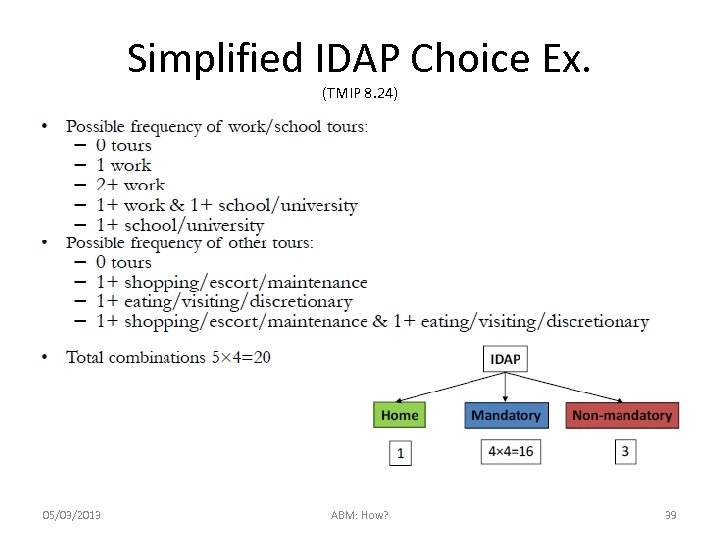
Simplified IDAP Choice Ex. (TMIP 8. 24) 05/03/2013 ABM: How? 39
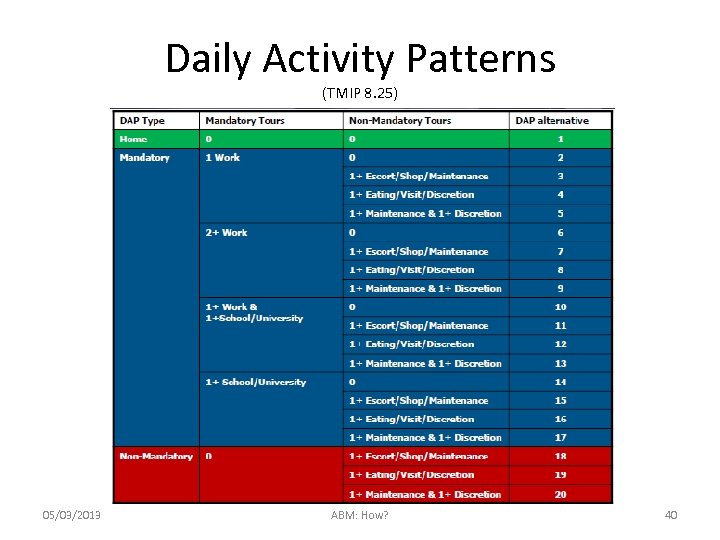
Daily Activity Patterns (TMIP 8. 25) 05/03/2013 ABM: How? 40
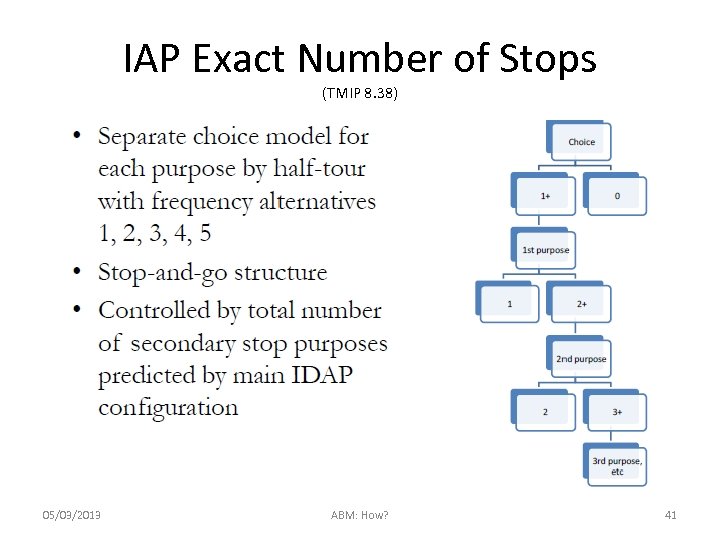
IAP Exact Number of Stops (TMIP 8. 38) 05/03/2013 ABM: How? 41
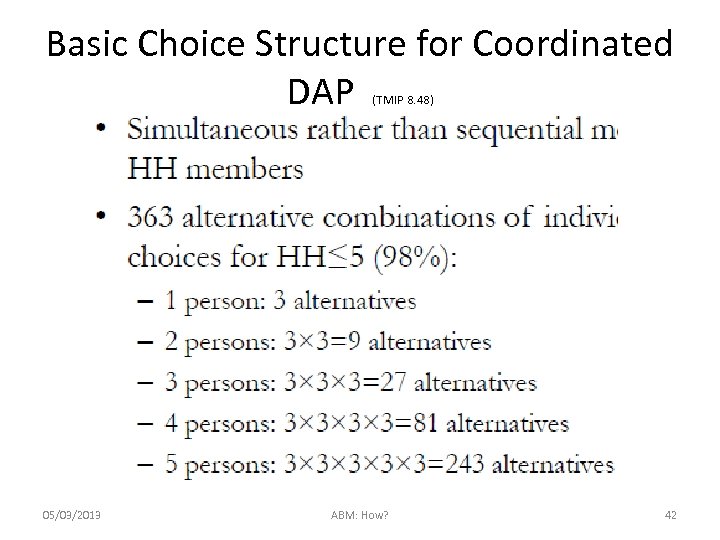
Basic Choice Structure for Coordinated DAP (TMIP 8. 48) 05/03/2013 ABM: How? 42
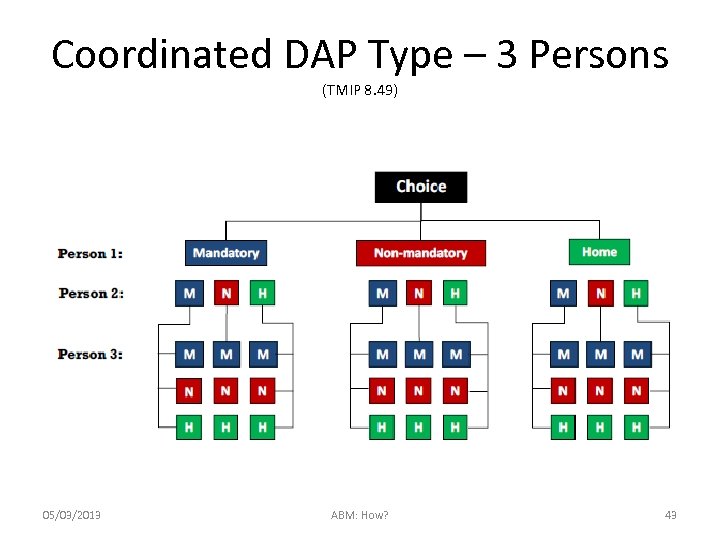
Coordinated DAP Type – 3 Persons (TMIP 8. 49) 05/03/2013 ABM: How? 43
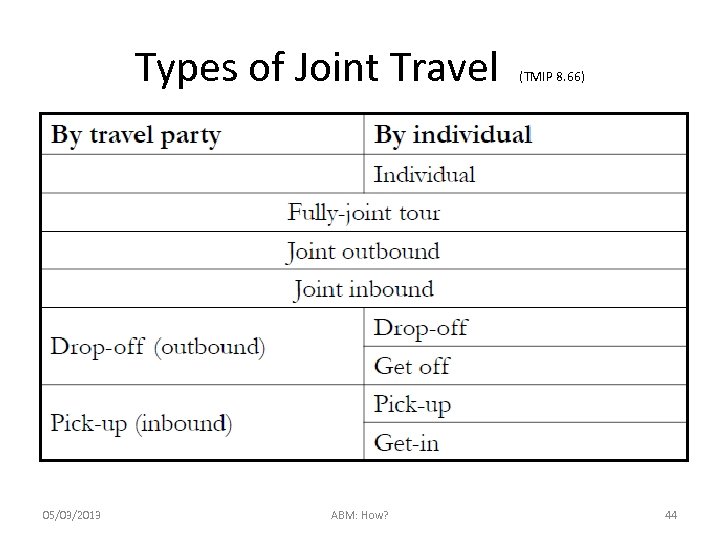
Types of Joint Travel 05/03/2013 ABM: How? (TMIP 8. 66) 44
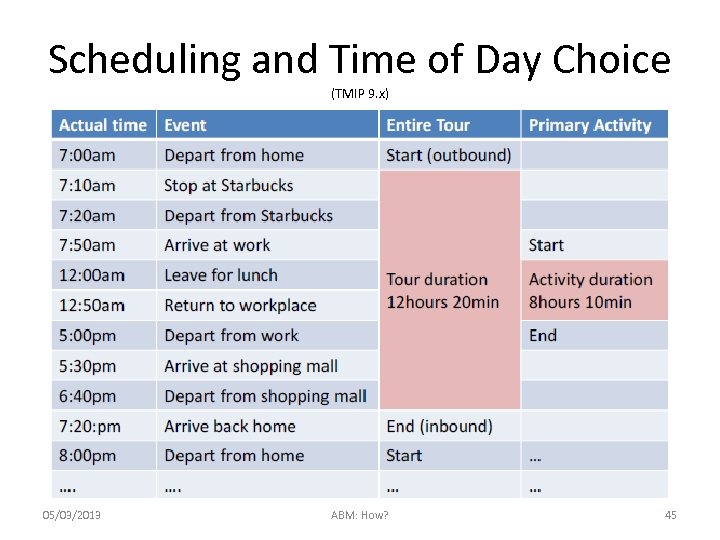
Scheduling and Time of Day Choice (TMIP 9. x) 05/03/2013 ABM: How? 45
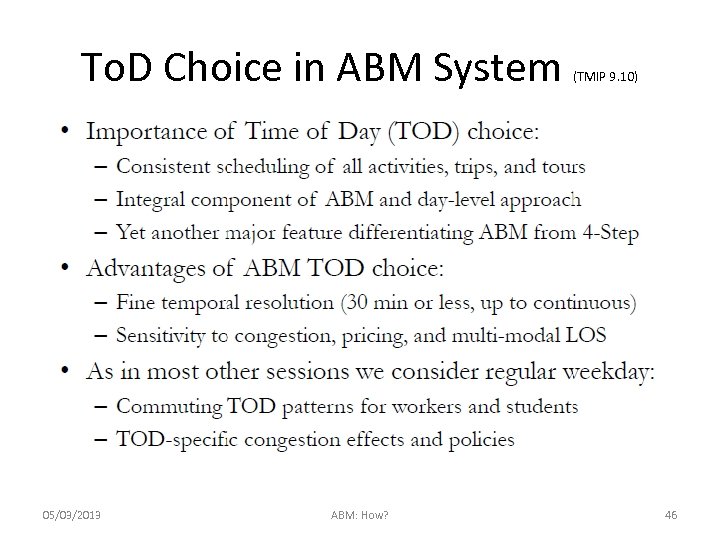
To. D Choice in ABM System 05/03/2013 ABM: How? (TMIP 9. 10) 46
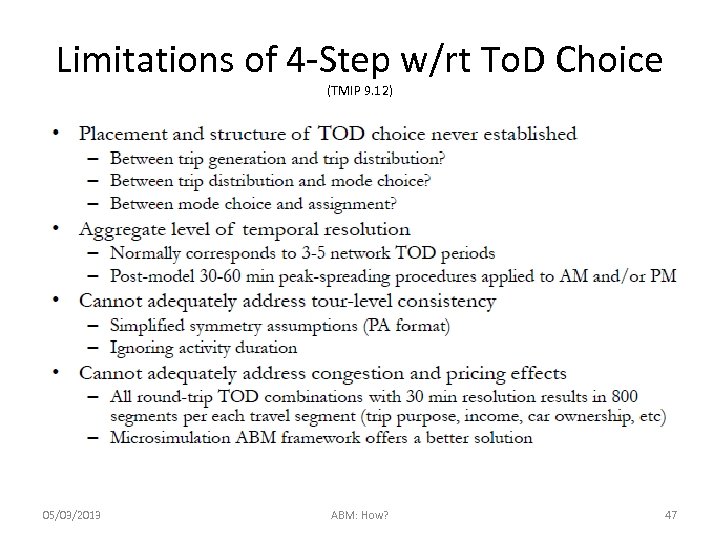
Limitations of 4 -Step w/rt To. D Choice (TMIP 9. 12) 05/03/2013 ABM: How? 47
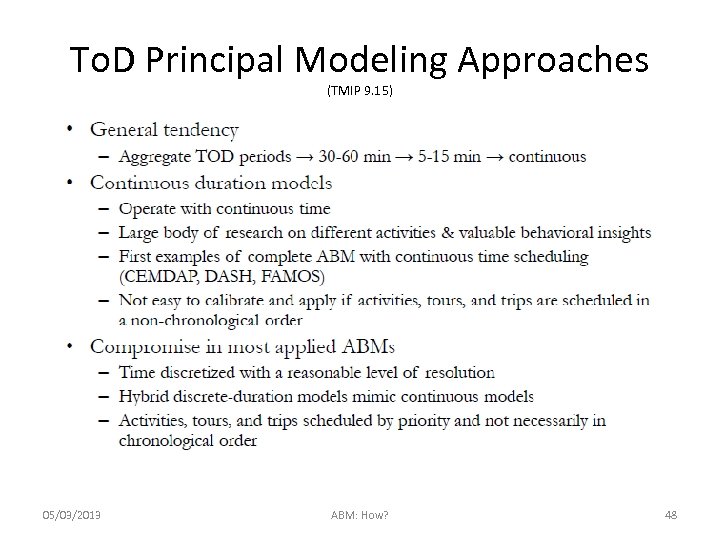
To. D Principal Modeling Approaches (TMIP 9. 15) 05/03/2013 ABM: How? 48
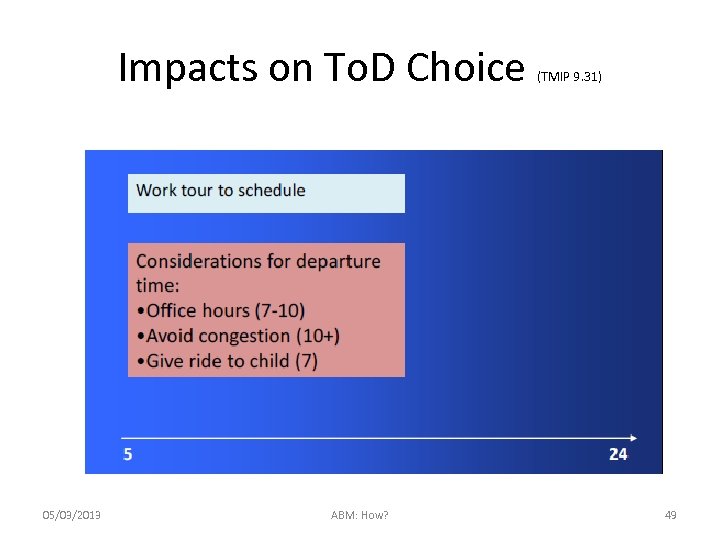
Impacts on To. D Choice 05/03/2013 ABM: How? (TMIP 9. 31) 49

Location & Accessibility Effects (TMIP 9. 49) 05/03/2013 ABM: How? 50
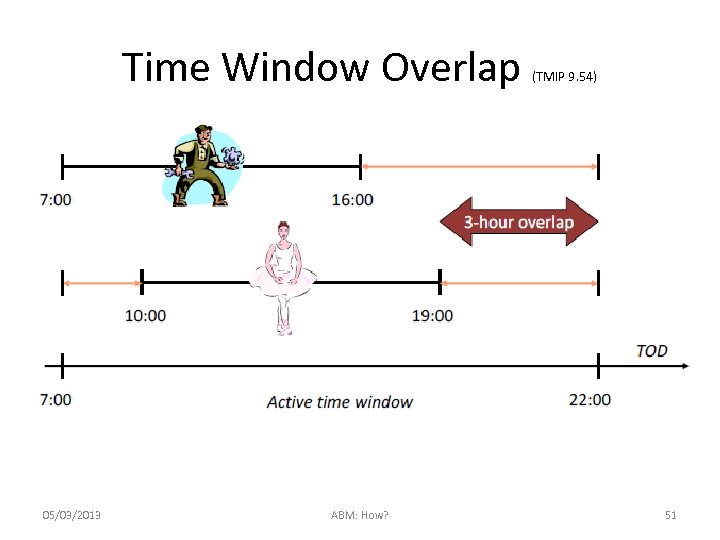
Time Window Overlap 05/03/2013 ABM: How? (TMIP 9. 54) 51
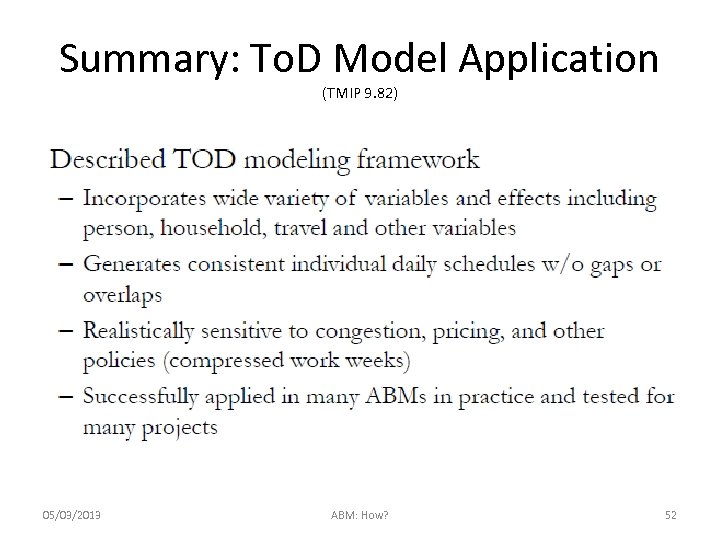
Summary: To. D Model Application (TMIP 9. 82) 05/03/2013 ABM: How? 52
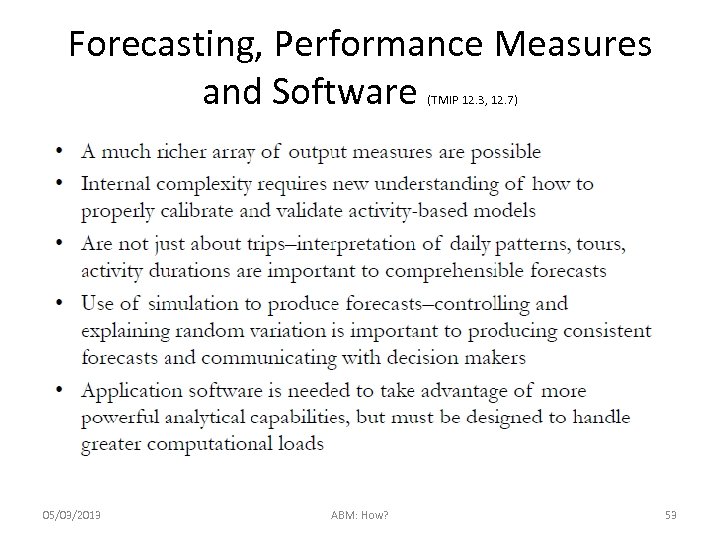
Forecasting, Performance Measures and Software (TMIP 12. 3, 12. 7) 05/03/2013 ABM: How? 53
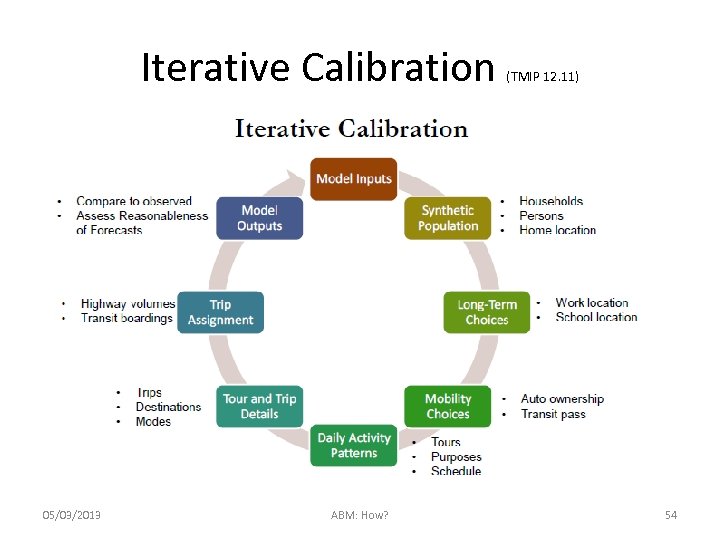
Iterative Calibration 05/03/2013 ABM: How? (TMIP 12. 11) 54
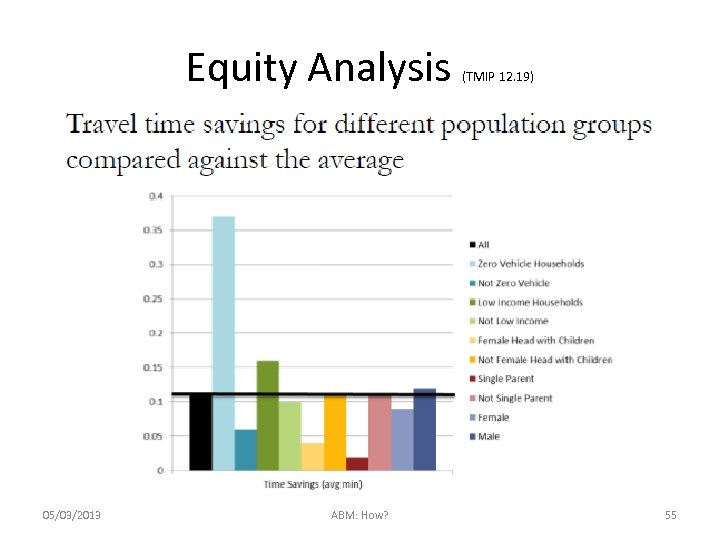
Equity Analysis 05/03/2013 ABM: How? (TMIP 12. 19) 55

Bicycle and Walk Considerations (TMIP 12. 25) 05/03/2013 ABM: How? 56

Scenario Testing 05/03/2013 ABM: How? (TMIP 12. 26) 57
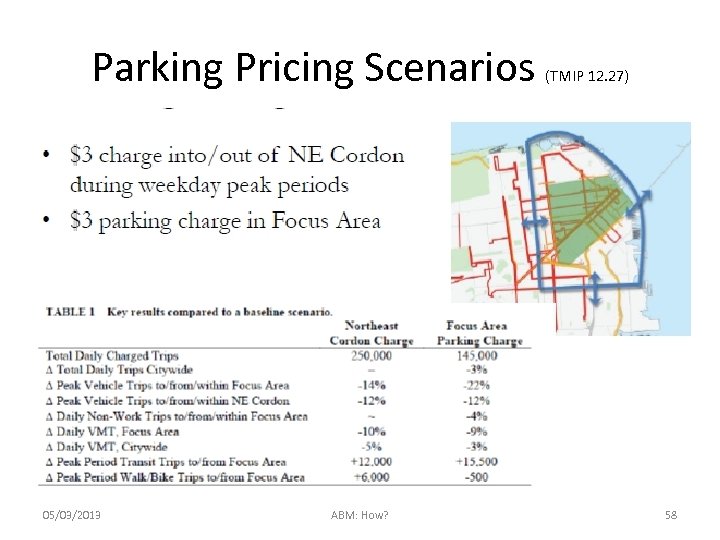
Parking Pricing Scenarios 05/03/2013 ABM: How? (TMIP 12. 27) 58

Alternatives Analysis with ABMs (TMIP 12. 33) 05/03/2013 ABM: How? 59

Stochastic Variation 05/03/2013 ABM: How? (TMIP 12. 34) 60
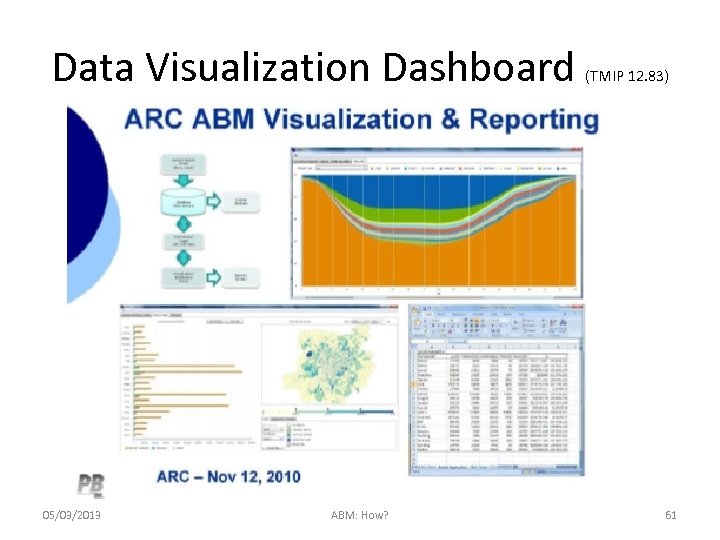
Data Visualization Dashboard 05/03/2013 ABM: How? (TMIP 12. 83) 61

Summary (TMIP 12. 90) • Requires new approaches to data collection, new skill sets, new hardware and software? • Disaggregate representation of individuals provides summarization by any available attributes, enabling more sophisticated, higher-resolution analyses of transportation policy and investment alternatives. 05/03/2013 ABM: How? 62

-end. Activity-Based Modeling How does it work?
c8cbcf30256452f7a59bf4cc91ad703b.ppt