bce1057d08a3ac0eccdd6c6311d5389e.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 95




 “Actions are right in proportion as they tend to promote happiness; wrong as they tend to produce the reverse of happiness. By happiness is intended pleasure and the absence of pain. ” ~ John Stuart Mill
“Actions are right in proportion as they tend to promote happiness; wrong as they tend to produce the reverse of happiness. By happiness is intended pleasure and the absence of pain. ” ~ John Stuart Mill
 Major Ideas:
Major Ideas:
 Major Ideas:
Major Ideas:
 Major Ideas:
Major Ideas:
 Major Ideas:
Major Ideas:
 What is Pluralism?
What is Pluralism?
 What is Relativism?
What is Relativism?

 Relativism assumes the following:
Relativism assumes the following:
 3 a. Cultural Relativism:
3 a. Cultural Relativism:
 3 b. Individual Relativism:
3 b. Individual Relativism:
 In contrast, what is Absolutism?
In contrast, what is Absolutism?




 Consequential Ethics:
Consequential Ethics:
 A. Consequential Ethics:
A. Consequential Ethics:
 A closer look at Utilitarianism:
A closer look at Utilitarianism:


 A closer look at Utilitarianism:
A closer look at Utilitarianism:
 A closer look at Utilitarianism:
A closer look at Utilitarianism:
 A closer look at Utilitarianism:
A closer look at Utilitarianism:
 A closer look at Utilitarianism:
A closer look at Utilitarianism:
 A closer look at Utilitarianism:
A closer look at Utilitarianism:
 A closer look at Utilitarianism:
A closer look at Utilitarianism:







 Conclusion to Consequentialism:
Conclusion to Consequentialism:



 Deontological Ethics
Deontological Ethics
 Deontological Framework:
Deontological Framework:
 Deontological Framework:
Deontological Framework:
 Deontological Framework:
Deontological Framework:
 Deontological Ethics
Deontological Ethics
 Deontological Ethics
Deontological Ethics
 Deontological Ethics
Deontological Ethics
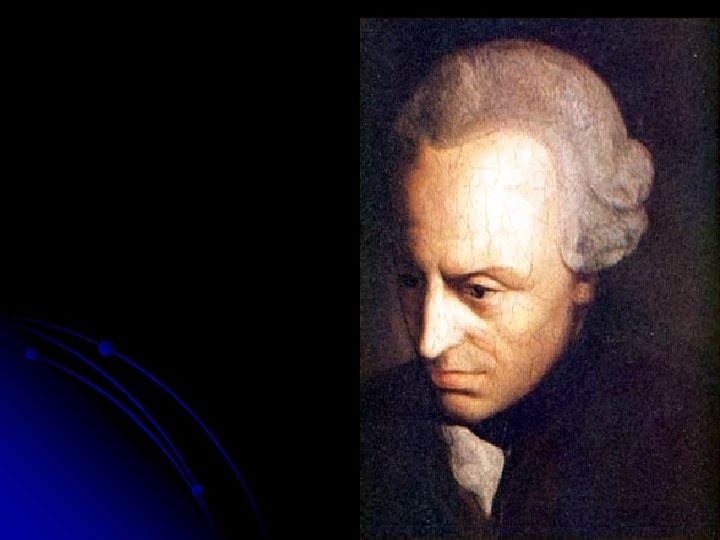
 . To act morally you must be motivated exclusively by rational commitment to the universal moral law or the categorical Imperative: “Act in conformity with that maxim, and that maxim only, that you can will at the same time be a universal law. ” Right actions flow out of right principles Do the act that is motivated by the sincere belief that what you are doing is the right thing not merely for you, but for anybody seeking to act properly in any situation. To act morally requires the rational power to recognize absolute moral laws that transcend our natural world. To act morally requires the power of the will to rise above all natural feelings and inclinations. This raises us above our natural world. Second form of categorical imperative: “Act in such a way that you always treat humans not merely as a means to an end but also as an end. ”
. To act morally you must be motivated exclusively by rational commitment to the universal moral law or the categorical Imperative: “Act in conformity with that maxim, and that maxim only, that you can will at the same time be a universal law. ” Right actions flow out of right principles Do the act that is motivated by the sincere belief that what you are doing is the right thing not merely for you, but for anybody seeking to act properly in any situation. To act morally requires the rational power to recognize absolute moral laws that transcend our natural world. To act morally requires the power of the will to rise above all natural feelings and inclinations. This raises us above our natural world. Second form of categorical imperative: “Act in such a way that you always treat humans not merely as a means to an end but also as an end. ”
 Basic Terms to Know:
Basic Terms to Know:
 Summary:
Summary:
 Categorical Imperative:
Categorical Imperative:

 Major Points to Consider:
Major Points to Consider:
 Major Points to Consider:
Major Points to Consider:
 Major Points to Consider:
Major Points to Consider:
 According the first formula:
According the first formula:









 1 st example: Suicide
1 st example: Suicide





 4 th example: Helping Others:
4 th example: Helping Others:




 Kant’s View of Virtue/Vice
Kant’s View of Virtue/Vice
 Kant’s View of Virtue/Vice
Kant’s View of Virtue/Vice
 Kant’s View of Virtue/Vice
Kant’s View of Virtue/Vice
 Kant’s View of Virtue/Vice
Kant’s View of Virtue/Vice
 Kant’s View of Virtue/Vice
Kant’s View of Virtue/Vice
 Kant’s View of Virtue/Vice
Kant’s View of Virtue/Vice
 Kant’s View of Virtue/Vice
Kant’s View of Virtue/Vice







