b32ef17ea4eee72ce97c25216189c743.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 81
 Across China: China’s Wealth Gap Widens MKT 221 Marketing in the Chinese Mainland Chan Man Lok (1013 638) Cheung Ka Ying (1066 685) Luk Sin Hing (1137 197) Wong Lok Hang (1166 837) Yan Tak Ming (1012 165) Xian Group
Across China: China’s Wealth Gap Widens MKT 221 Marketing in the Chinese Mainland Chan Man Lok (1013 638) Cheung Ka Ying (1066 685) Luk Sin Hing (1137 197) Wong Lok Hang (1166 837) Yan Tak Ming (1012 165) Xian Group
 Agenda Key differences between first-tier, second-tier and third-tier markets in China in terms of their preference foreign vs. domestic brands Variation of Chinese Consumers’ consumption values and marketing responses Influence of regional differences towards marketing strategies in China and Comparison of effectiveness of a standardized approach vs. localized strategies Opportunities foreign brands in rural markets and Suggestions for products and strategies developed in rural markets Conclusion
Agenda Key differences between first-tier, second-tier and third-tier markets in China in terms of their preference foreign vs. domestic brands Variation of Chinese Consumers’ consumption values and marketing responses Influence of regional differences towards marketing strategies in China and Comparison of effectiveness of a standardized approach vs. localized strategies Opportunities foreign brands in rural markets and Suggestions for products and strategies developed in rural markets Conclusion
 1) What are the key differences between first-tier, second tier and third tier (small town) markets in China in terms of their preferences foreign VS domestic brands?
1) What are the key differences between first-tier, second tier and third tier (small town) markets in China in terms of their preferences foreign VS domestic brands?
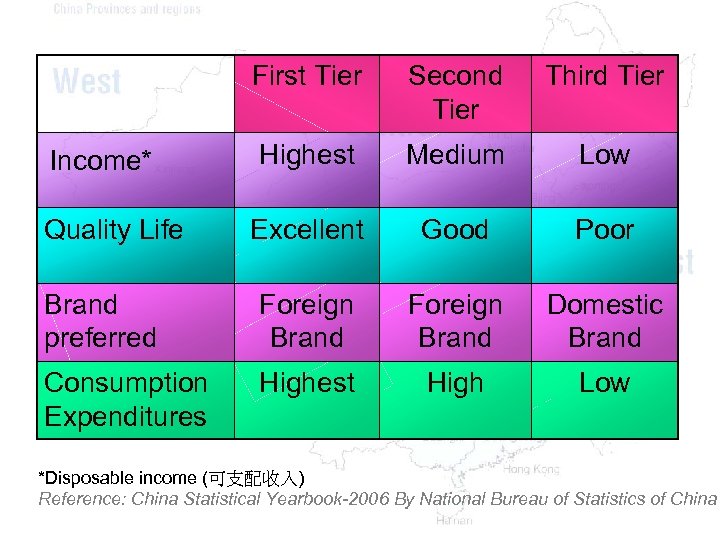 First Tier Second Tier Third Tier Highest Medium Low Excellent Good Poor Brand preferred Foreign Brand Domestic Brand Consumption Expenditures Highest High Low Income* Quality Life *Disposable income (可支配收入) Reference: China Statistical Yearbook-2006 By National Bureau of Statistics of China
First Tier Second Tier Third Tier Highest Medium Low Excellent Good Poor Brand preferred Foreign Brand Domestic Brand Consumption Expenditures Highest High Low Income* Quality Life *Disposable income (可支配收入) Reference: China Statistical Yearbook-2006 By National Bureau of Statistics of China
 Match them up! • • • Beijing Guizhou Guangdong Guangxi Shanghai Zhejiang • First Tier? • Second Tier? • Third Tier?
Match them up! • • • Beijing Guizhou Guangdong Guangxi Shanghai Zhejiang • First Tier? • Second Tier? • Third Tier?
 Suggested Answer Beijing First Tier Shanghai First Tier Guangdong Second Tier Zhejiang Second Tier Guangxi Third Tier Guizhou Third Tier
Suggested Answer Beijing First Tier Shanghai First Tier Guangdong Second Tier Zhejiang Second Tier Guangxi Third Tier Guizhou Third Tier
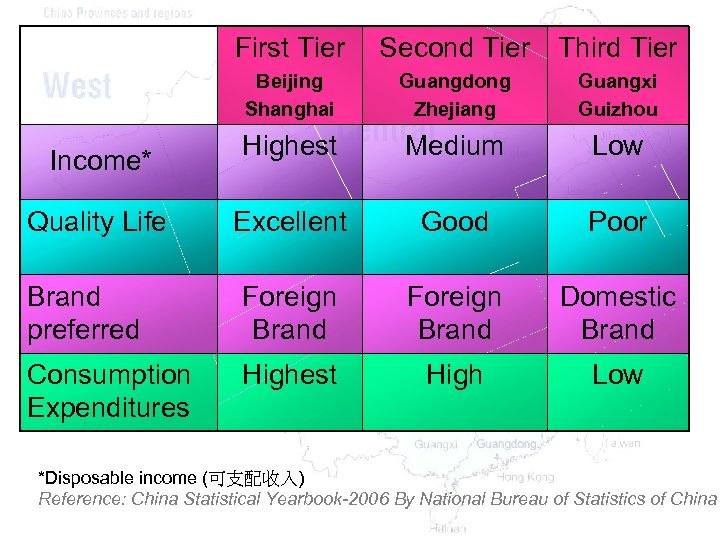 First Tier Second Tier Third Tier Beijing Shanghai Guangdong Zhejiang Guangxi Guizhou Highest Medium Low Excellent Good Poor Brand preferred Foreign Brand Domestic Brand Consumption Expenditures Highest High Low Income* Quality Life *Disposable income (可支配收入) Reference: China Statistical Yearbook-2006 By National Bureau of Statistics of China
First Tier Second Tier Third Tier Beijing Shanghai Guangdong Zhejiang Guangxi Guizhou Highest Medium Low Excellent Good Poor Brand preferred Foreign Brand Domestic Brand Consumption Expenditures Highest High Low Income* Quality Life *Disposable income (可支配收入) Reference: China Statistical Yearbook-2006 By National Bureau of Statistics of China
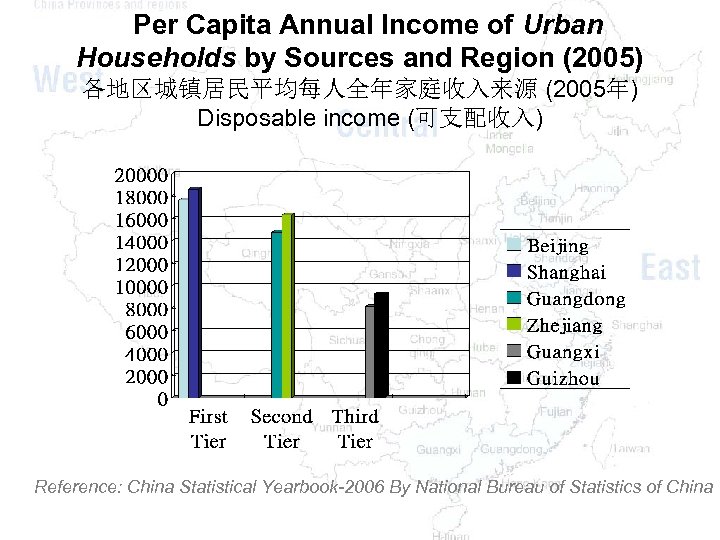 Per Capita Annual Income of Urban Households by Sources and Region (2005) 各地区城镇居民平均每人全年家庭收入来源 (2005年) Disposable income (可支配收入) Reference: China Statistical Yearbook-2006 By National Bureau of Statistics of China
Per Capita Annual Income of Urban Households by Sources and Region (2005) 各地区城镇居民平均每人全年家庭收入来源 (2005年) Disposable income (可支配收入) Reference: China Statistical Yearbook-2006 By National Bureau of Statistics of China
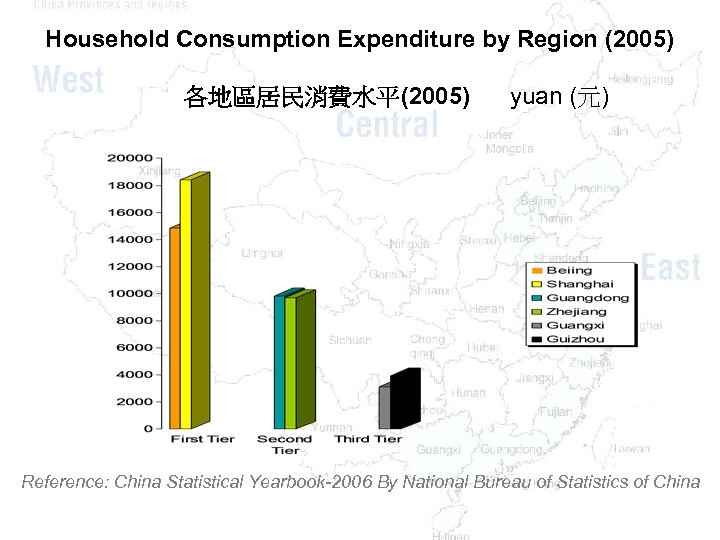 Household Consumption Expenditure by Region (2005) 各地區居民消費水平(2005) yuan (元) Reference: China Statistical Yearbook-2006 By National Bureau of Statistics of China
Household Consumption Expenditure by Region (2005) 各地區居民消費水平(2005) yuan (元) Reference: China Statistical Yearbook-2006 By National Bureau of Statistics of China
 Foreign VS Domestic brands 4 Key Differences • Income • Price • Quality • Reputation
Foreign VS Domestic brands 4 Key Differences • Income • Price • Quality • Reputation
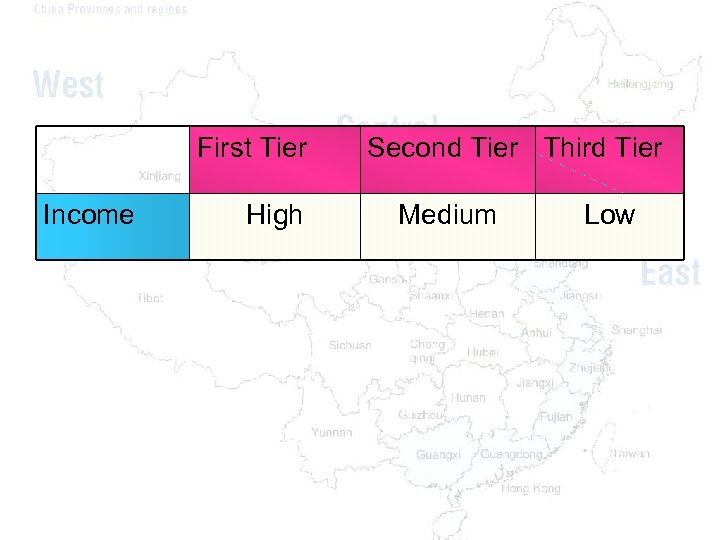 First Tier Income High Second Tier Third Tier Medium Low
First Tier Income High Second Tier Third Tier Medium Low
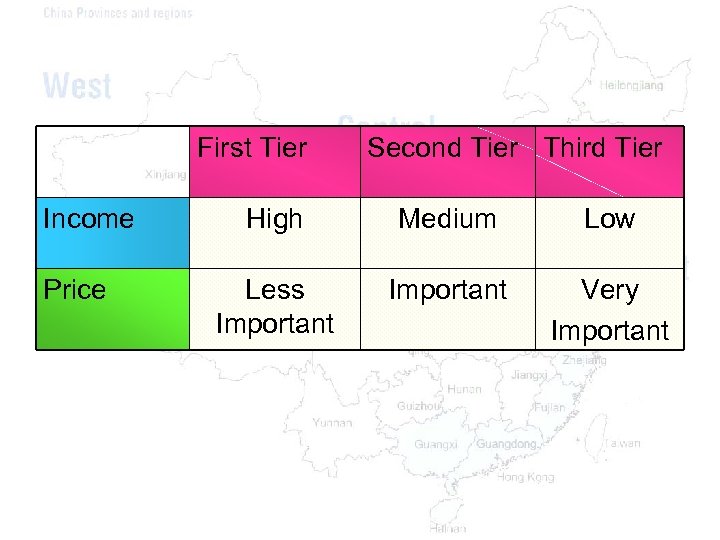 First Tier Income Price Second Tier Third Tier High Medium Low Less Important Very Important
First Tier Income Price Second Tier Third Tier High Medium Low Less Important Very Important
 Adidas VS Doublestar 双星 • Football shoes • Market price: $499 • Football shoes • Market price: $59 Which one would you choose?
Adidas VS Doublestar 双星 • Football shoes • Market price: $499 • Football shoes • Market price: $59 Which one would you choose?
 First Tier and Second Tier would choose… Doublestar, We are so Sorry! even though the price is much higher!!!!!!
First Tier and Second Tier would choose… Doublestar, We are so Sorry! even though the price is much higher!!!!!!
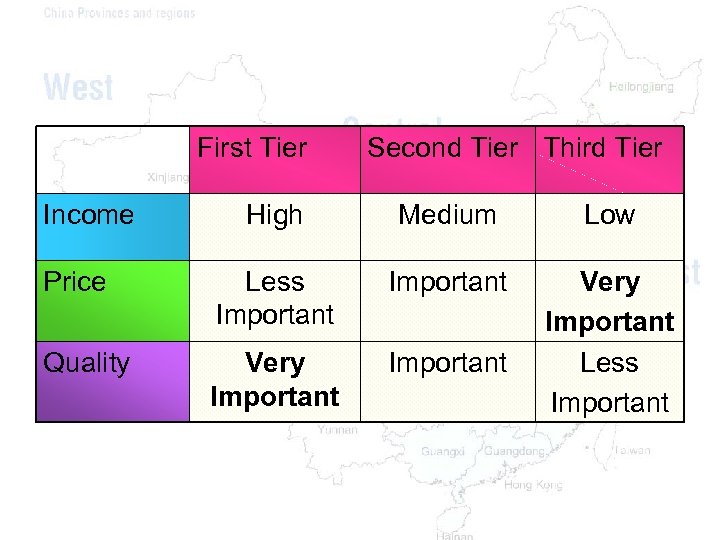 First Tier Income Second Tier Third Tier High Medium Low Price Less Important Quality Very Important Less Important
First Tier Income Second Tier Third Tier High Medium Low Price Less Important Quality Very Important Less Important
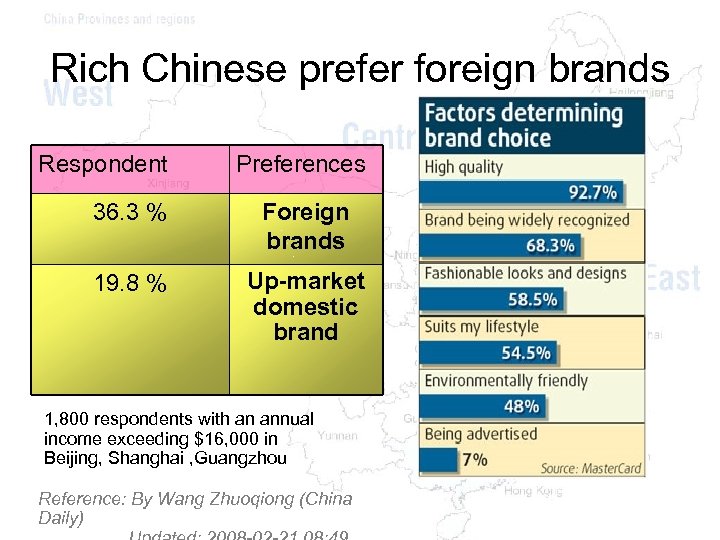 Rich Chinese prefer foreign brands Respondent Preferences 36. 3 % Foreign brands 19. 8 % Up-market domestic brand 1, 800 respondents with an annual income exceeding $16, 000 in Beijing, Shanghai , Guangzhou Reference: By Wang Zhuoqiong (China Daily)
Rich Chinese prefer foreign brands Respondent Preferences 36. 3 % Foreign brands 19. 8 % Up-market domestic brand 1, 800 respondents with an annual income exceeding $16, 000 in Beijing, Shanghai , Guangzhou Reference: By Wang Zhuoqiong (China Daily)
 Chinese parents favor foreign-brand toys For wealthiest, foreign-made brands are seen as safer for kids A mother and son shop for toys in a store in Shanghai, China. Chinese families who can afford it are opting foreign-brand toys. Reference: MSNBC NEWS updated 1: 56 p. m. ET Dec. 16, 2007 http: //www. msnbc. msn. com/id/22262800/
Chinese parents favor foreign-brand toys For wealthiest, foreign-made brands are seen as safer for kids A mother and son shop for toys in a store in Shanghai, China. Chinese families who can afford it are opting foreign-brand toys. Reference: MSNBC NEWS updated 1: 56 p. m. ET Dec. 16, 2007 http: //www. msnbc. msn. com/id/22262800/
 • Quality and safety issues are drawing more attention as incomes rise and upwardly mobile Chinese grow more health conscious. • Chinese families who can afford it opt foreign-brand toys — even if they are made in China. Reference: MSNBC NEWS updated 1: 56 p. m. ET Dec. 16, 2007 http: //www. msnbc. msn. com/id/22262800/
• Quality and safety issues are drawing more attention as incomes rise and upwardly mobile Chinese grow more health conscious. • Chinese families who can afford it opt foreign-brand toys — even if they are made in China. Reference: MSNBC NEWS updated 1: 56 p. m. ET Dec. 16, 2007 http: //www. msnbc. msn. com/id/22262800/
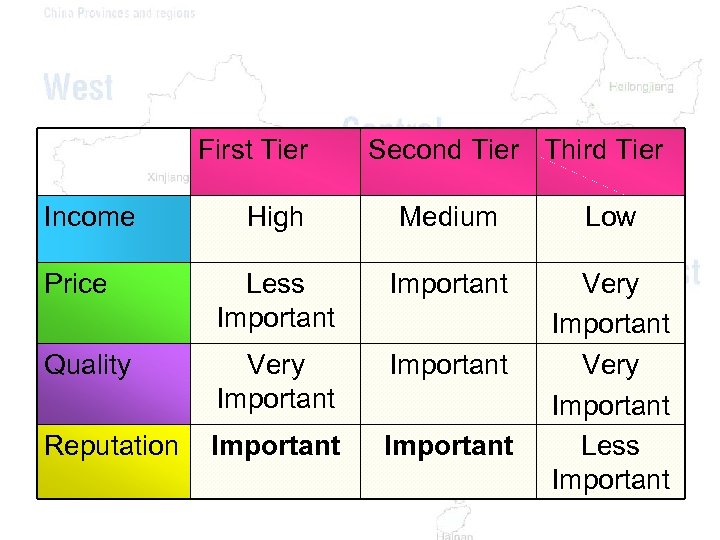 First Tier Income Second Tier Third Tier High Medium Low Price Less Important Quality Very Important Reputation Important Very Important Less Important
First Tier Income Second Tier Third Tier High Medium Low Price Less Important Quality Very Important Reputation Important Very Important Less Important
 • 3 shops in Beijing (First Tier) • 1 shop in Shanghai (First Tier) • 1 shop in Guangdong( Second Tier) Third Tier cities? SORRY, NO SHOP!
• 3 shops in Beijing (First Tier) • 1 shop in Shanghai (First Tier) • 1 shop in Guangdong( Second Tier) Third Tier cities? SORRY, NO SHOP!
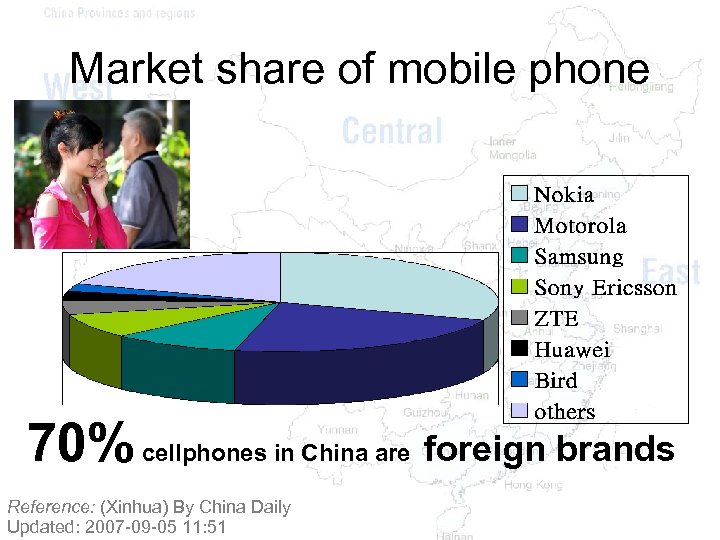 Market share of mobile phone 70% cellphones in China are foreign brands Reference: (Xinhua) By China Daily Updated: 2007 -09 -05 11: 51
Market share of mobile phone 70% cellphones in China are foreign brands Reference: (Xinhua) By China Daily Updated: 2007 -09 -05 11: 51
 2) Do Chinese consumers from different regions vary in their consumption values and marketing responses, such as quality- price tradeoff, husband-wife dyad, decision making style, reactions to promotion and sales, service expectations, and perhaps even their complaint behavior?
2) Do Chinese consumers from different regions vary in their consumption values and marketing responses, such as quality- price tradeoff, husband-wife dyad, decision making style, reactions to promotion and sales, service expectations, and perhaps even their complaint behavior?
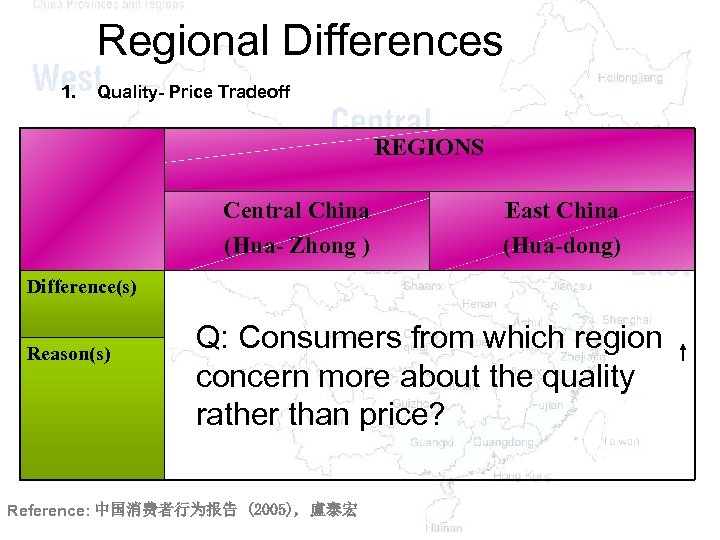 Regional Differences 1. Quality- Price Tradeoff REGIONS Central China (Hua- Zhong ) East China (Hua-dong) Difference(s) Reason(s) Q: Consumers from which region concern more about the quality rather than price? Reference: 中国消费者行为报告 (2005), 盧泰宏
Regional Differences 1. Quality- Price Tradeoff REGIONS Central China (Hua- Zhong ) East China (Hua-dong) Difference(s) Reason(s) Q: Consumers from which region concern more about the quality rather than price? Reference: 中国消费者行为报告 (2005), 盧泰宏
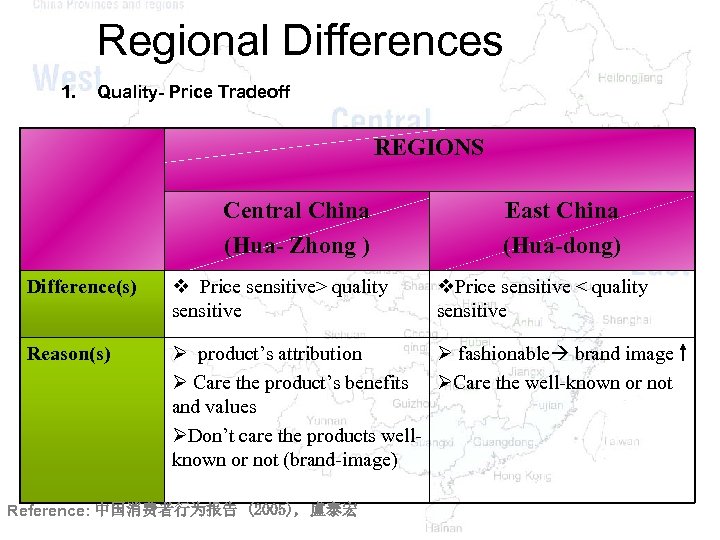 Regional Differences 1. Quality- Price Tradeoff REGIONS Central China (Hua- Zhong ) East China (Hua-dong) Difference(s) v Price sensitive> quality sensitive Reason(s) Ø product’s attribution Ø fashionable brand image Ø Care the product’s benefits ØCare the well-known or not and values ØDon’t care the products wellknown or not (brand-image) Reference: 中国消费者行为报告 (2005), 盧泰宏 v. Price sensitive < quality sensitive
Regional Differences 1. Quality- Price Tradeoff REGIONS Central China (Hua- Zhong ) East China (Hua-dong) Difference(s) v Price sensitive> quality sensitive Reason(s) Ø product’s attribution Ø fashionable brand image Ø Care the product’s benefits ØCare the well-known or not and values ØDon’t care the products wellknown or not (brand-image) Reference: 中国消费者行为报告 (2005), 盧泰宏 v. Price sensitive < quality sensitive
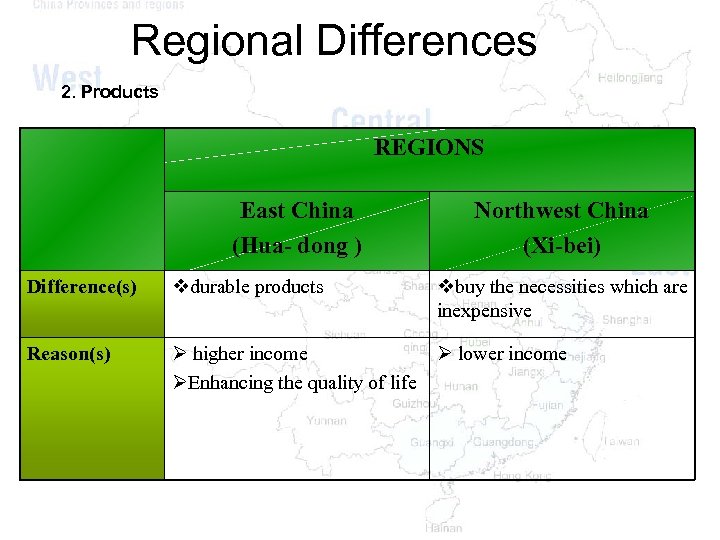 Regional Differences 2. Products REGIONS East China (Hua- dong ) Northwest China (Xi-bei) Difference(s) vdurable products vbuy the necessities which are inexpensive Reason(s) Ø higher income Ø lower income ØEnhancing the quality of life
Regional Differences 2. Products REGIONS East China (Hua- dong ) Northwest China (Xi-bei) Difference(s) vdurable products vbuy the necessities which are inexpensive Reason(s) Ø higher income Ø lower income ØEnhancing the quality of life
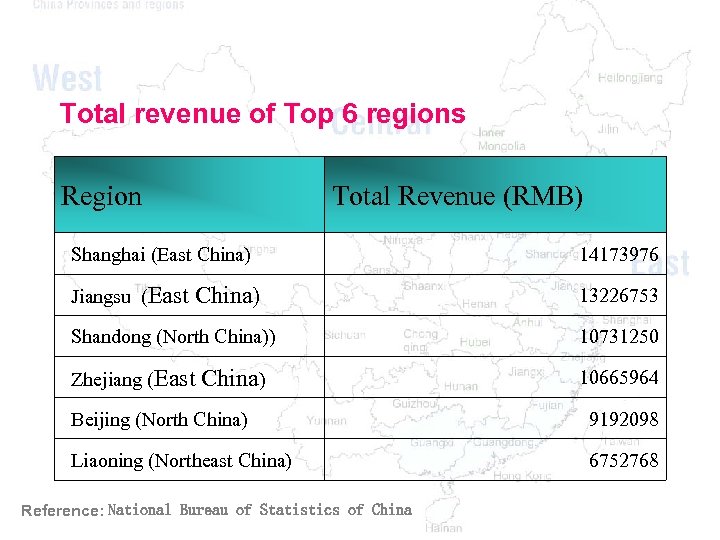 Total revenue of Top 6 regions Region Total Revenue (RMB) Shanghai (East China) 14173976 Jiangsu (East 13226753 China) Shandong (North China)) 10731250 Zhejiang (East 10665964 China) Beijing (North China) 9192098 Liaoning (Northeast China) 6752768 Reference: National Bureau of Statistics of China
Total revenue of Top 6 regions Region Total Revenue (RMB) Shanghai (East China) 14173976 Jiangsu (East 13226753 China) Shandong (North China)) 10731250 Zhejiang (East 10665964 China) Beijing (North China) 9192098 Liaoning (Northeast China) 6752768 Reference: National Bureau of Statistics of China
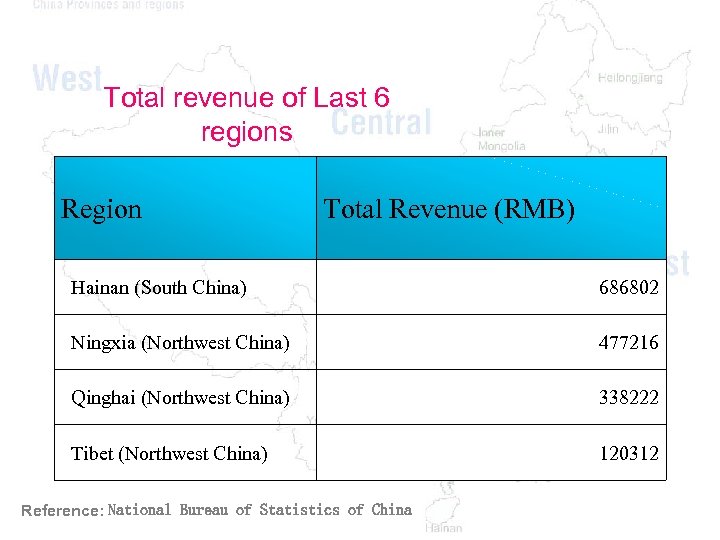 Total revenue of Last 6 regions Region Total Revenue (RMB) Hainan (South China) 686802 Ningxia (Northwest China) 477216 Qinghai (Northwest China) 338222 Tibet (Northwest China) 120312 Reference: National Bureau of Statistics of China
Total revenue of Last 6 regions Region Total Revenue (RMB) Hainan (South China) 686802 Ningxia (Northwest China) 477216 Qinghai (Northwest China) 338222 Tibet (Northwest China) 120312 Reference: National Bureau of Statistics of China
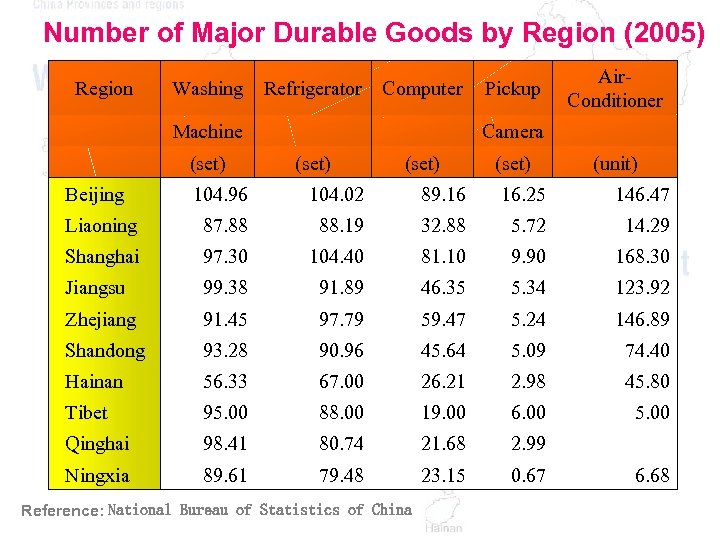 Number of Major Durable Goods by Region (2005) Region Washing Refrigerator Computer Pickup Machine (set) Camera Beijing (set) Air. Conditioner (unit) 104. 96 104. 02 89. 16 16. 25 146. 47 Liaoning 87. 88 88. 19 32. 88 5. 72 14. 29 Shanghai 97. 30 104. 40 81. 10 9. 90 168. 30 Jiangsu 99. 38 91. 89 46. 35 5. 34 123. 92 Zhejiang 91. 45 97. 79 59. 47 5. 24 146. 89 Shandong 93. 28 90. 96 45. 64 5. 09 74. 40 Hainan 56. 33 67. 00 26. 21 2. 98 45. 80 Tibet 95. 00 88. 00 19. 00 6. 00 5. 00 Qinghai 98. 41 80. 74 21. 68 2. 99 Ningxia 89. 61 79. 48 23. 15 0. 67 6. 68 Reference: National Bureau of Statistics of China
Number of Major Durable Goods by Region (2005) Region Washing Refrigerator Computer Pickup Machine (set) Camera Beijing (set) Air. Conditioner (unit) 104. 96 104. 02 89. 16 16. 25 146. 47 Liaoning 87. 88 88. 19 32. 88 5. 72 14. 29 Shanghai 97. 30 104. 40 81. 10 9. 90 168. 30 Jiangsu 99. 38 91. 89 46. 35 5. 34 123. 92 Zhejiang 91. 45 97. 79 59. 47 5. 24 146. 89 Shandong 93. 28 90. 96 45. 64 5. 09 74. 40 Hainan 56. 33 67. 00 26. 21 2. 98 45. 80 Tibet 95. 00 88. 00 19. 00 6. 00 5. 00 Qinghai 98. 41 80. 74 21. 68 2. 99 Ningxia 89. 61 79. 48 23. 15 0. 67 6. 68 Reference: National Bureau of Statistics of China
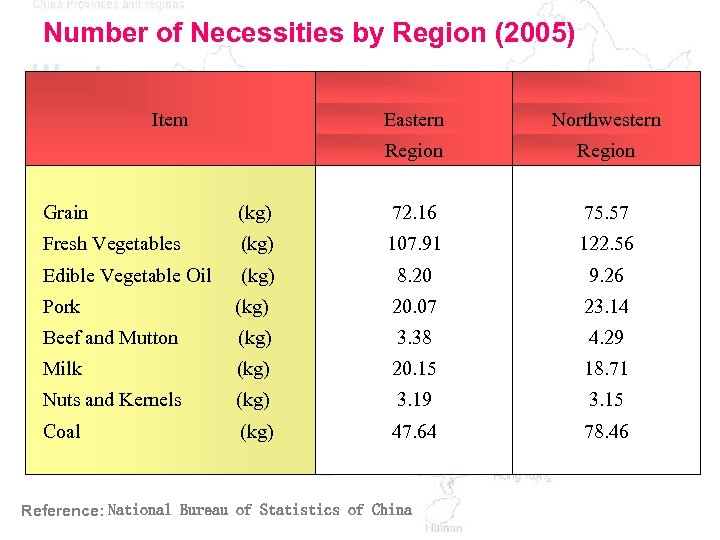 Number of Necessities by Region (2005) Eastern Northwestern Region (kg) 72. 16 75. 57 Fresh Vegetables (kg) 107. 91 122. 56 Edible Vegetable Oil (kg) 8. 20 9. 26 Pork (kg) 20. 07 23. 14 Beef and Mutton (kg) 3. 38 4. 29 Milk (kg) 20. 15 18. 71 Nuts and Kernels (kg) 3. 19 3. 15 Coal (kg) 47. 64 78. 46 Item Grain Reference: National Bureau of Statistics of China
Number of Necessities by Region (2005) Eastern Northwestern Region (kg) 72. 16 75. 57 Fresh Vegetables (kg) 107. 91 122. 56 Edible Vegetable Oil (kg) 8. 20 9. 26 Pork (kg) 20. 07 23. 14 Beef and Mutton (kg) 3. 38 4. 29 Milk (kg) 20. 15 18. 71 Nuts and Kernels (kg) 3. 19 3. 15 Coal (kg) 47. 64 78. 46 Item Grain Reference: National Bureau of Statistics of China
 Regional Differences 3. Husband-wife dyad REGIONS East China , Southeast Northwest China (Xi-bei) (Hau- dong, Hau-nan) Difference(s) Reason(s) Q: Does “husband” dominate the whole China as the decision maker? *Reference: Husband-Wife Decision Making in Purchasing and Renewing Auto Insurance
Regional Differences 3. Husband-wife dyad REGIONS East China , Southeast Northwest China (Xi-bei) (Hau- dong, Hau-nan) Difference(s) Reason(s) Q: Does “husband” dominate the whole China as the decision maker? *Reference: Husband-Wife Decision Making in Purchasing and Renewing Auto Insurance
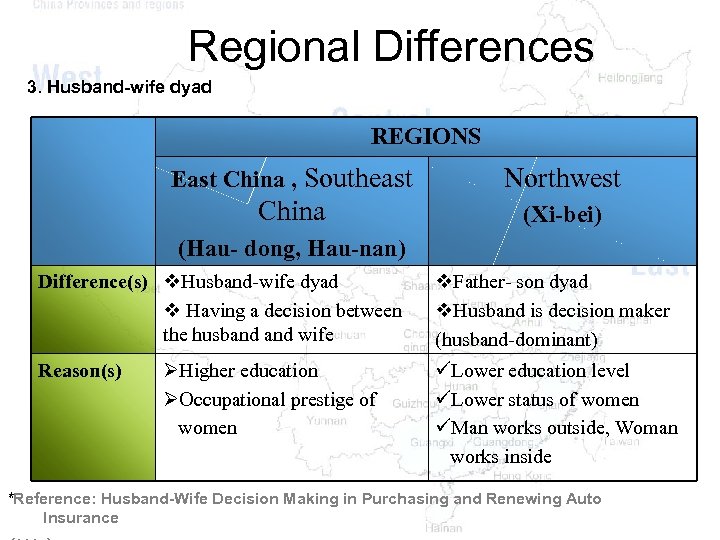 Regional Differences 3. Husband-wife dyad REGIONS East China , Southeast Northwest China (Xi-bei) (Hau- dong, Hau-nan) Difference(s) v. Husband-wife dyad v Having a decision between the husband wife Reason(s) ØHigher education ØOccupational prestige of women v. Father- son dyad v. Husband is decision maker (husband-dominant) üLower education level üLower status of women üMan works outside, Woman works inside *Reference: Husband-Wife Decision Making in Purchasing and Renewing Auto Insurance
Regional Differences 3. Husband-wife dyad REGIONS East China , Southeast Northwest China (Xi-bei) (Hau- dong, Hau-nan) Difference(s) v. Husband-wife dyad v Having a decision between the husband wife Reason(s) ØHigher education ØOccupational prestige of women v. Father- son dyad v. Husband is decision maker (husband-dominant) üLower education level üLower status of women üMan works outside, Woman works inside *Reference: Husband-Wife Decision Making in Purchasing and Renewing Auto Insurance
 q. Example: ¡ East China ü Husband wife may share responsibility for paying the bills (about 50% half of each) and also make a payment decision together ¡ Northwest ü Husband is decision maker of buying house and washing machines. Reference: Modeling Affective Processes in Dyadic Relations via Dynamic Factor Analysis (2003), Emilio Ferrer and John R. Nesselroade
q. Example: ¡ East China ü Husband wife may share responsibility for paying the bills (about 50% half of each) and also make a payment decision together ¡ Northwest ü Husband is decision maker of buying house and washing machines. Reference: Modeling Affective Processes in Dyadic Relations via Dynamic Factor Analysis (2003), Emilio Ferrer and John R. Nesselroade
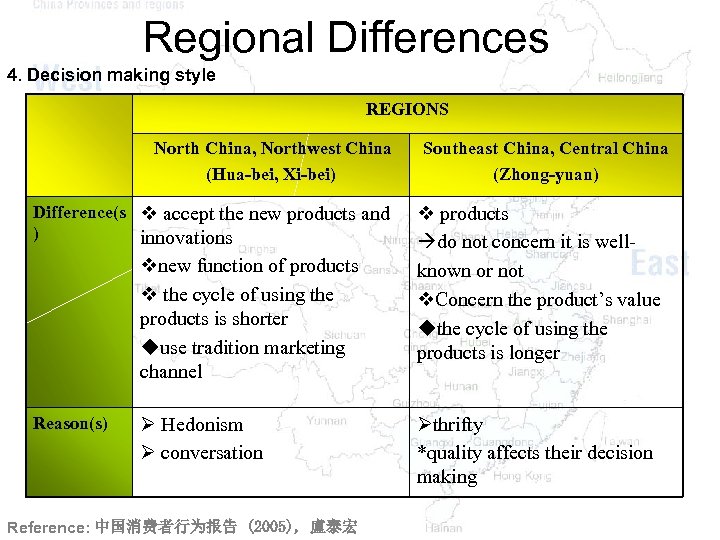 Regional Differences 4. Decision making style REGIONS North China, Northwest China (Hua-bei, Xi-bei) Difference(s v accept the new products and ) innovations vnew function of products v the cycle of using the products is shorter uuse tradition marketing channel Reason(s) Ø Hedonism Ø conversation Reference: 中国消费者行为报告 (2005), 盧泰宏 Southeast China, Central China (Zhong-yuan) v products do not concern it is wellknown or not v. Concern the product’s value uthe cycle of using the products is longer Øthrifty *quality affects their decision making
Regional Differences 4. Decision making style REGIONS North China, Northwest China (Hua-bei, Xi-bei) Difference(s v accept the new products and ) innovations vnew function of products v the cycle of using the products is shorter uuse tradition marketing channel Reason(s) Ø Hedonism Ø conversation Reference: 中国消费者行为报告 (2005), 盧泰宏 Southeast China, Central China (Zhong-yuan) v products do not concern it is wellknown or not v. Concern the product’s value uthe cycle of using the products is longer Øthrifty *quality affects their decision making
 q. Example § Northwest China ü likes face to the teller of the bank and don’t like e-commerce and e-shopping
q. Example § Northwest China ü likes face to the teller of the bank and don’t like e-commerce and e-shopping
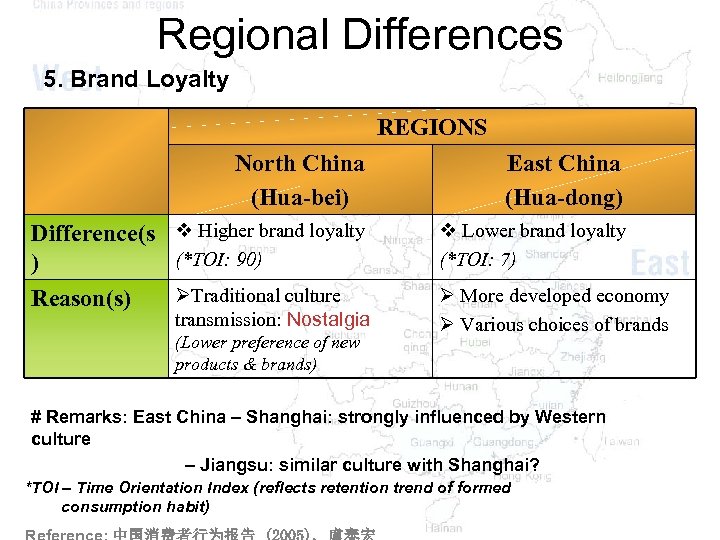
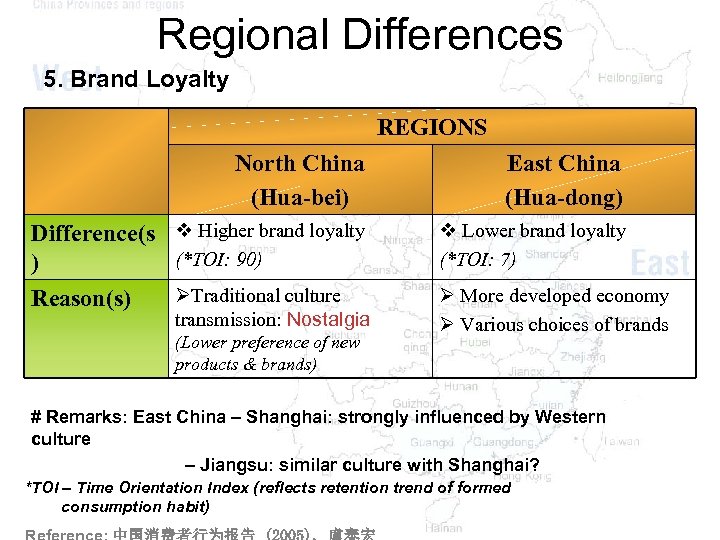 Regional Differences 5. Brand Loyalty REGIONS North China (Hua-bei) East China (Hua-dong) Difference(s v Higher brand loyalty (*TOI: 90) ) ØTraditional culture Reason(s) v Lower brand loyalty (*TOI: 7) transmission: Nostalgia (Lower preference of new products & brands) Ø More developed economy Ø Various choices of brands # Remarks: East China – Shanghai: strongly influenced by Western culture – Jiangsu: similar culture with Shanghai? *TOI – Time Orientation Index (reflects retention trend of formed consumption habit)
Regional Differences 5. Brand Loyalty REGIONS North China (Hua-bei) East China (Hua-dong) Difference(s v Higher brand loyalty (*TOI: 90) ) ØTraditional culture Reason(s) v Lower brand loyalty (*TOI: 7) transmission: Nostalgia (Lower preference of new products & brands) Ø More developed economy Ø Various choices of brands # Remarks: East China – Shanghai: strongly influenced by Western culture – Jiangsu: similar culture with Shanghai? *TOI – Time Orientation Index (reflects retention trend of formed consumption habit)
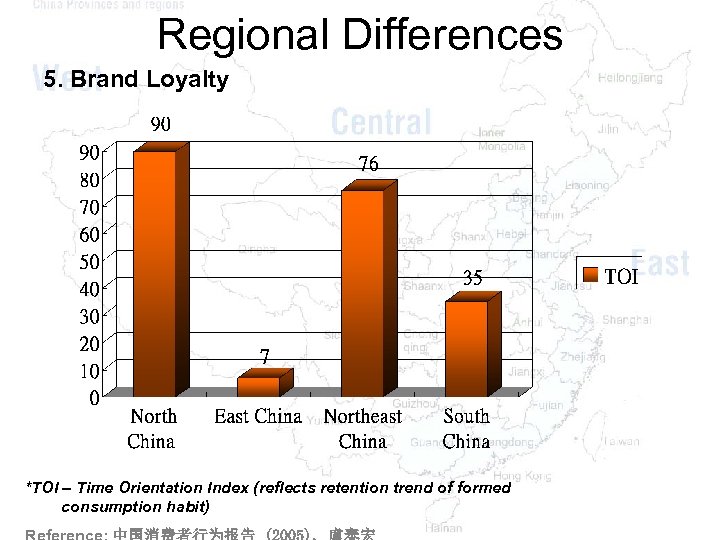 Regional Differences 5. Brand Loyalty *TOI – Time Orientation Index (reflects retention trend of formed consumption habit)
Regional Differences 5. Brand Loyalty *TOI – Time Orientation Index (reflects retention trend of formed consumption habit)
 Regional Differences 5. Brand Loyalty REGIONS North China (Hua-bei) East China (Hua-dong) Difference(s v Higher brand loyalty (*TOI: 90) ) ØTraditional culture Reason(s) v Lower brand loyalty (*TOI: 7) transmission: Nostalgia (Lower preference of new products & brands) Ø More developed economy Ø Various choices of brands # Remarks: East China – Shanghai: strongly influenced by Western culture – Jiangsu: similar culture with Shanghai? *TOI – Time Orientation Index (reflects retention trend of formed consumption habit)
Regional Differences 5. Brand Loyalty REGIONS North China (Hua-bei) East China (Hua-dong) Difference(s v Higher brand loyalty (*TOI: 90) ) ØTraditional culture Reason(s) v Lower brand loyalty (*TOI: 7) transmission: Nostalgia (Lower preference of new products & brands) Ø More developed economy Ø Various choices of brands # Remarks: East China – Shanghai: strongly influenced by Western culture – Jiangsu: similar culture with Shanghai? *TOI – Time Orientation Index (reflects retention trend of formed consumption habit)
 Regional Differences 6. Social Group Influence REGIONS Southwest China (Xi-nan) East China (Hua-dong) Difference(s ) Reason(s) Q: Consumers from which region has a stronger social group influence? *CII – Collectivism & Individualism Index (reflects collectivity of consumption behavior)
Regional Differences 6. Social Group Influence REGIONS Southwest China (Xi-nan) East China (Hua-dong) Difference(s ) Reason(s) Q: Consumers from which region has a stronger social group influence? *CII – Collectivism & Individualism Index (reflects collectivity of consumption behavior)
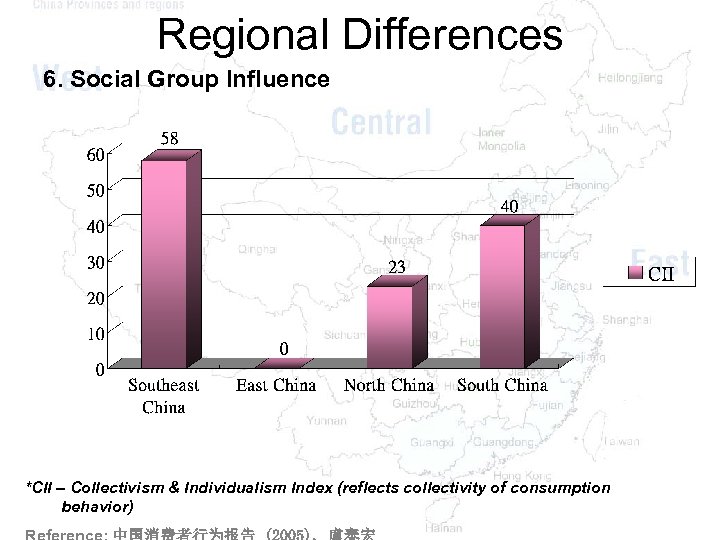
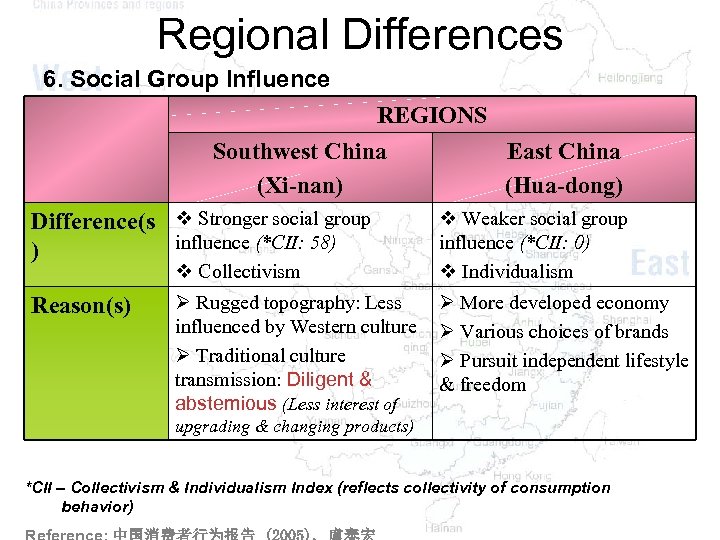
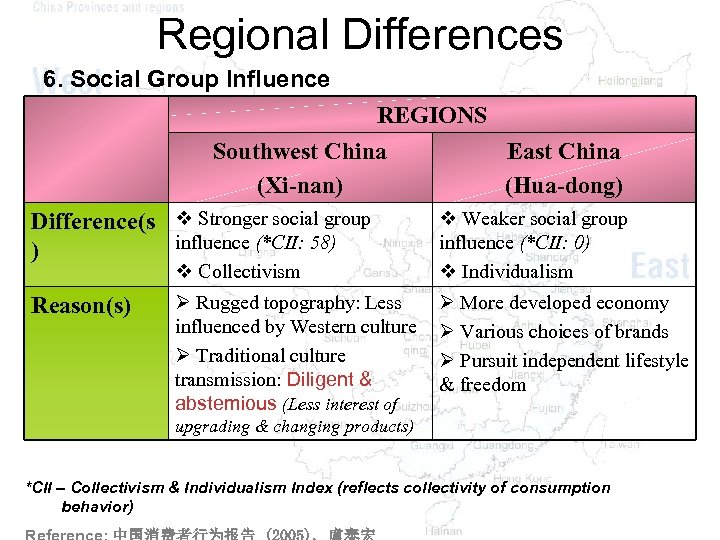 Regional Differences 6. Social Group Influence REGIONS Southwest China East China (Xi-nan) (Hua-dong) Difference(s v Stronger social group influence (*CII: 58) ) v Collectivism Reason(s) Ø Rugged topography: Less influenced by Western culture Ø Traditional culture transmission: Diligent & abstemious (Less interest of v Weaker social group influence (*CII: 0) v Individualism Ø More developed economy Ø Various choices of brands Ø Pursuit independent lifestyle & freedom upgrading & changing products) *CII – Collectivism & Individualism Index (reflects collectivity of consumption behavior)
Regional Differences 6. Social Group Influence REGIONS Southwest China East China (Xi-nan) (Hua-dong) Difference(s v Stronger social group influence (*CII: 58) ) v Collectivism Reason(s) Ø Rugged topography: Less influenced by Western culture Ø Traditional culture transmission: Diligent & abstemious (Less interest of v Weaker social group influence (*CII: 0) v Individualism Ø More developed economy Ø Various choices of brands Ø Pursuit independent lifestyle & freedom upgrading & changing products) *CII – Collectivism & Individualism Index (reflects collectivity of consumption behavior)
 Regional Differences 6. Social Group Influence *CII – Collectivism & Individualism Index (reflects collectivity of consumption behavior)
Regional Differences 6. Social Group Influence *CII – Collectivism & Individualism Index (reflects collectivity of consumption behavior)
 Regional Differences 6. Social Group Influence REGIONS Southwest China East China (Xi-nan) (Hua-dong) Difference(s v Stronger social group influence (*CII: 58) ) v Collectivism Reason(s) Ø Rugged topography: Less influenced by Western culture Ø Traditional culture transmission: Diligent & abstemious (Less interest of v Weaker social group influence (*CII: 0) v Individualism Ø More developed economy Ø Various choices of brands Ø Pursuit independent lifestyle & freedom upgrading & changing products) *CII – Collectivism & Individualism Index (reflects collectivity of consumption behavior)
Regional Differences 6. Social Group Influence REGIONS Southwest China East China (Xi-nan) (Hua-dong) Difference(s v Stronger social group influence (*CII: 58) ) v Collectivism Reason(s) Ø Rugged topography: Less influenced by Western culture Ø Traditional culture transmission: Diligent & abstemious (Less interest of v Weaker social group influence (*CII: 0) v Individualism Ø More developed economy Ø Various choices of brands Ø Pursuit independent lifestyle & freedom upgrading & changing products) *CII – Collectivism & Individualism Index (reflects collectivity of consumption behavior)
 Regional Differences 5. Social Group Influence q Examples § Southwest China (Xi-nan): ü Not like outstanding apparel ü Prefer to buy products that relatives & friends recognized good enough § East China (Hua-dong): ü Increase in demand of small but spacious studios/ apartments with well transportation & property management in Shanghai
Regional Differences 5. Social Group Influence q Examples § Southwest China (Xi-nan): ü Not like outstanding apparel ü Prefer to buy products that relatives & friends recognized good enough § East China (Hua-dong): ü Increase in demand of small but spacious studios/ apartments with well transportation & property management in Shanghai
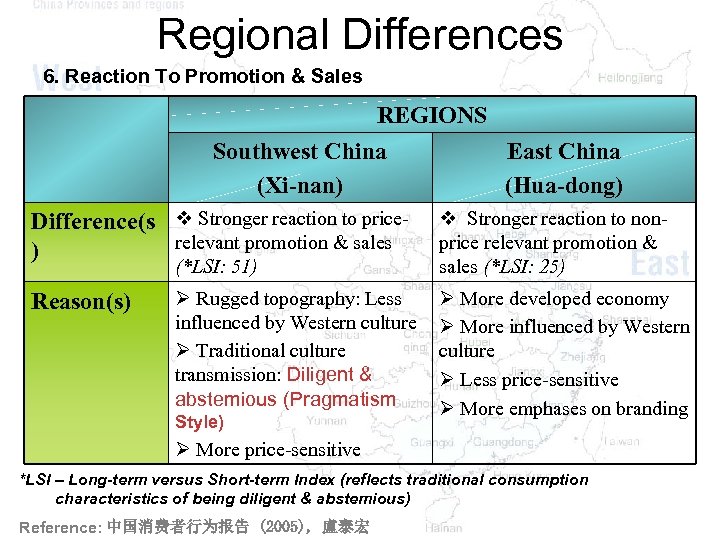 Regional Differences 6. Reaction To Promotion & Sales REGIONS Southwest China East China (Xi-nan) (Hua-dong) Difference(s v Stronger reaction to pricerelevant promotion & sales ) (*LSI: 51) Reason(s) v Stronger reaction to nonprice relevant promotion & sales (*LSI: 25) Ø Rugged topography: Less influenced by Western culture Ø Traditional culture transmission: Diligent & abstemious (Pragmatism Ø More developed economy Ø More influenced by Western culture Ø Less price-sensitive Ø More emphases on branding Style) Ø More price-sensitive *LSI – Long-term versus Short-term Index (reflects traditional consumption characteristics of being diligent & abstemious) Reference: 中国消费者行为报告 (2005), 盧泰宏
Regional Differences 6. Reaction To Promotion & Sales REGIONS Southwest China East China (Xi-nan) (Hua-dong) Difference(s v Stronger reaction to pricerelevant promotion & sales ) (*LSI: 51) Reason(s) v Stronger reaction to nonprice relevant promotion & sales (*LSI: 25) Ø Rugged topography: Less influenced by Western culture Ø Traditional culture transmission: Diligent & abstemious (Pragmatism Ø More developed economy Ø More influenced by Western culture Ø Less price-sensitive Ø More emphases on branding Style) Ø More price-sensitive *LSI – Long-term versus Short-term Index (reflects traditional consumption characteristics of being diligent & abstemious) Reference: 中国消费者行为报告 (2005), 盧泰宏
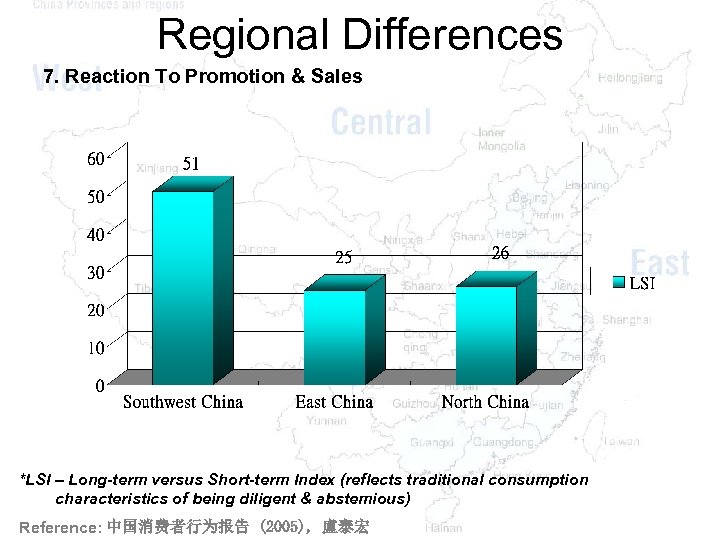 Regional Differences 7. Reaction To Promotion & Sales *LSI – Long-term versus Short-term Index (reflects traditional consumption characteristics of being diligent & abstemious) Reference: 中国消费者行为报告 (2005), 盧泰宏
Regional Differences 7. Reaction To Promotion & Sales *LSI – Long-term versus Short-term Index (reflects traditional consumption characteristics of being diligent & abstemious) Reference: 中国消费者行为报告 (2005), 盧泰宏
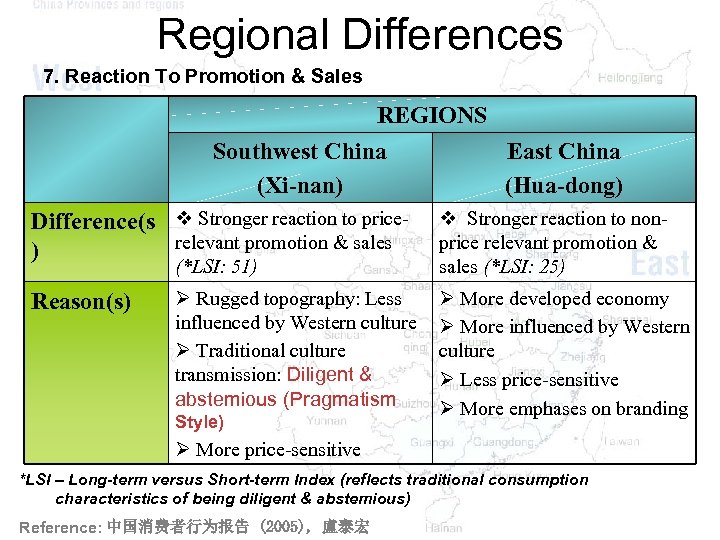 Regional Differences 7. Reaction To Promotion & Sales REGIONS Southwest China East China (Xi-nan) (Hua-dong) Difference(s v Stronger reaction to pricerelevant promotion & sales ) (*LSI: 51) Reason(s) v Stronger reaction to nonprice relevant promotion & sales (*LSI: 25) Ø Rugged topography: Less influenced by Western culture Ø Traditional culture transmission: Diligent & abstemious (Pragmatism Ø More developed economy Ø More influenced by Western culture Ø Less price-sensitive Ø More emphases on branding Style) Ø More price-sensitive *LSI – Long-term versus Short-term Index (reflects traditional consumption characteristics of being diligent & abstemious) Reference: 中国消费者行为报告 (2005), 盧泰宏
Regional Differences 7. Reaction To Promotion & Sales REGIONS Southwest China East China (Xi-nan) (Hua-dong) Difference(s v Stronger reaction to pricerelevant promotion & sales ) (*LSI: 51) Reason(s) v Stronger reaction to nonprice relevant promotion & sales (*LSI: 25) Ø Rugged topography: Less influenced by Western culture Ø Traditional culture transmission: Diligent & abstemious (Pragmatism Ø More developed economy Ø More influenced by Western culture Ø Less price-sensitive Ø More emphases on branding Style) Ø More price-sensitive *LSI – Long-term versus Short-term Index (reflects traditional consumption characteristics of being diligent & abstemious) Reference: 中国消费者行为报告 (2005), 盧泰宏
 Regional Differences 6. Reaction To Promotion & Sales q Examples § Southwest China (Xinan): ü More prefer sales promotion: incentives like discounts & free gifts § East China (Hua-dong): ü More prefer advertising, public relations, personal selling & direct marketing: brand building like product exhibition & singing concerts
Regional Differences 6. Reaction To Promotion & Sales q Examples § Southwest China (Xinan): ü More prefer sales promotion: incentives like discounts & free gifts § East China (Hua-dong): ü More prefer advertising, public relations, personal selling & direct marketing: brand building like product exhibition & singing concerts
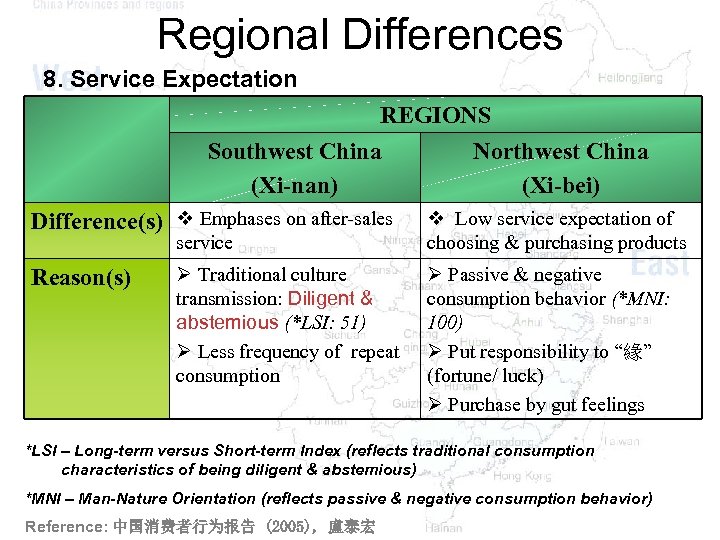 Regional Differences 8. Service Expectation REGIONS Southwest China Northwest China (Xi-nan) (Xi-bei) Difference(s) v Emphases on after-sales service Reason(s) Ø Traditional culture transmission: Diligent & abstemious (*LSI: 51) Ø Less frequency of repeat consumption v Low service expectation of choosing & purchasing products Ø Passive & negative consumption behavior (*MNI: 100) Ø Put responsibility to “緣” (fortune/ luck) Ø Purchase by gut feelings *LSI – Long-term versus Short-term Index (reflects traditional consumption characteristics of being diligent & abstemious) *MNI – Man-Nature Orientation (reflects passive & negative consumption behavior) Reference: 中国消费者行为报告 (2005), 盧泰宏
Regional Differences 8. Service Expectation REGIONS Southwest China Northwest China (Xi-nan) (Xi-bei) Difference(s) v Emphases on after-sales service Reason(s) Ø Traditional culture transmission: Diligent & abstemious (*LSI: 51) Ø Less frequency of repeat consumption v Low service expectation of choosing & purchasing products Ø Passive & negative consumption behavior (*MNI: 100) Ø Put responsibility to “緣” (fortune/ luck) Ø Purchase by gut feelings *LSI – Long-term versus Short-term Index (reflects traditional consumption characteristics of being diligent & abstemious) *MNI – Man-Nature Orientation (reflects passive & negative consumption behavior) Reference: 中国消费者行为报告 (2005), 盧泰宏
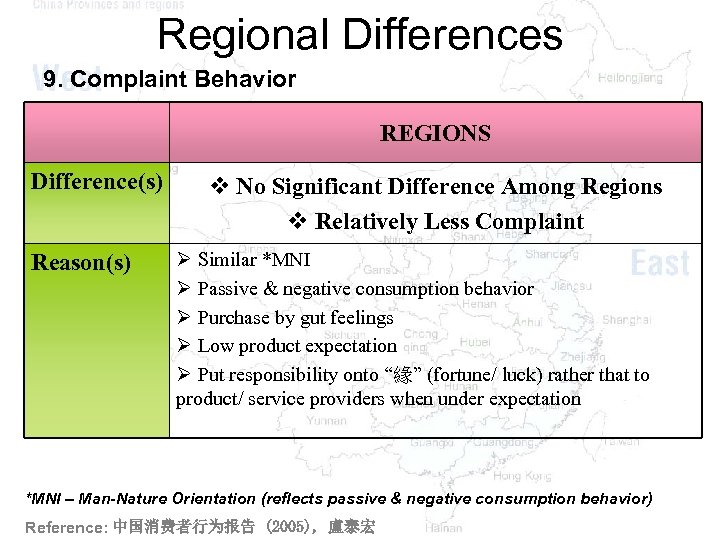 Regional Differences 9. Complaint Behavior REGIONS Difference(s) Reason(s) v No Significant Difference Among Regions v Relatively Less Complaint Ø Similar *MNI Ø Passive & negative consumption behavior Ø Purchase by gut feelings Ø Low product expectation Ø Put responsibility onto “緣” (fortune/ luck) rather that to product/ service providers when under expectation *MNI – Man-Nature Orientation (reflects passive & negative consumption behavior) Reference: 中国消费者行为报告 (2005), 盧泰宏
Regional Differences 9. Complaint Behavior REGIONS Difference(s) Reason(s) v No Significant Difference Among Regions v Relatively Less Complaint Ø Similar *MNI Ø Passive & negative consumption behavior Ø Purchase by gut feelings Ø Low product expectation Ø Put responsibility onto “緣” (fortune/ luck) rather that to product/ service providers when under expectation *MNI – Man-Nature Orientation (reflects passive & negative consumption behavior) Reference: 中国消费者行为报告 (2005), 盧泰宏
 Regional Differences 9. Complaint Behavior
Regional Differences 9. Complaint Behavior
 Question 3 How regional differences affect marketing strategies in China?
Question 3 How regional differences affect marketing strategies in China?
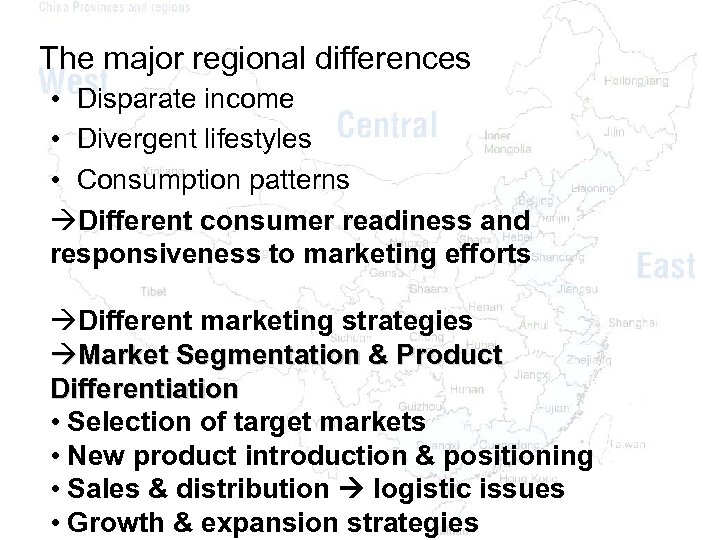 The major regional differences • Disparate income • Divergent lifestyles • Consumption patterns Different consumer readiness and responsiveness to marketing efforts Different marketing strategies Market Segmentation & Product Differentiation • Selection of target markets • New product introduction & positioning • Sales & distribution logistic issues • Growth & expansion strategies
The major regional differences • Disparate income • Divergent lifestyles • Consumption patterns Different consumer readiness and responsiveness to marketing efforts Different marketing strategies Market Segmentation & Product Differentiation • Selection of target markets • New product introduction & positioning • Sales & distribution logistic issues • Growth & expansion strategies
 For Foreign companies, • Higher income and education level result in greater readiness and frequency of purchase of foreign goods and luxury products. • Yuppies: better educated, wealthier , more receptive, early adopters & trend setters • High end products, fashion, lifestyle-related goods, etc.
For Foreign companies, • Higher income and education level result in greater readiness and frequency of purchase of foreign goods and luxury products. • Yuppies: better educated, wealthier , more receptive, early adopters & trend setters • High end products, fashion, lifestyle-related goods, etc.
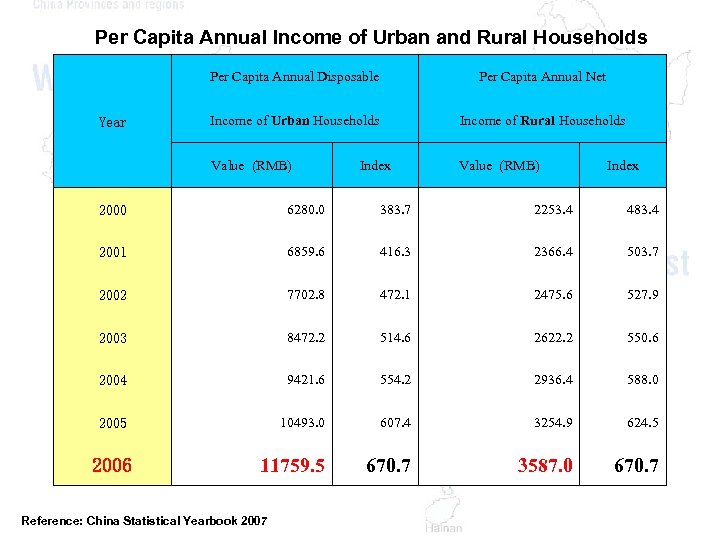 Per Capita Annual Income of Urban and Rural Households Per Capita Annual Disposable Income of Urban Households Income of Rural Households Value (RMB) Year Per Capita Annual Net Value (RMB) Index 2000 6280. 0 383. 7 2253. 4 483. 4 2001 6859. 6 416. 3 2366. 4 503. 7 2002 7702. 8 472. 1 2475. 6 527. 9 2003 8472. 2 514. 6 2622. 2 550. 6 2004 9421. 6 554. 2 2936. 4 588. 0 2005 10493. 0 607. 4 3254. 9 624. 5 11759. 5 670. 7 3587. 0 670. 7 2006 Reference: China Statistical Yearbook 2007
Per Capita Annual Income of Urban and Rural Households Per Capita Annual Disposable Income of Urban Households Income of Rural Households Value (RMB) Year Per Capita Annual Net Value (RMB) Index 2000 6280. 0 383. 7 2253. 4 483. 4 2001 6859. 6 416. 3 2366. 4 503. 7 2002 7702. 8 472. 1 2475. 6 527. 9 2003 8472. 2 514. 6 2622. 2 550. 6 2004 9421. 6 554. 2 2936. 4 588. 0 2005 10493. 0 607. 4 3254. 9 624. 5 11759. 5 670. 7 3587. 0 670. 7 2006 Reference: China Statistical Yearbook 2007
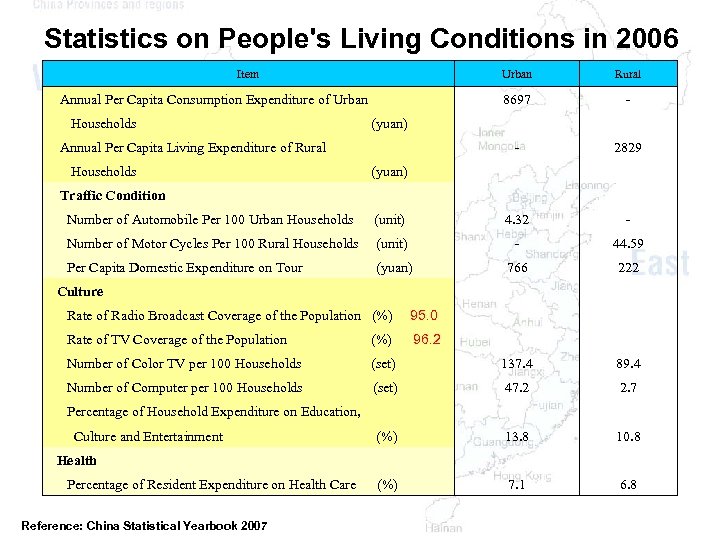 Statistics on People's Living Conditions in 2006 Item Urban 8697 Annual Per Capita Consumption Expenditure of Urban Households - (yuan) - Annual Per Capita Living Expenditure of Rural Households Rural (yuan) 2829 Traffic Condition Number of Automobile Per 100 Urban Households (unit) 4. 32 - Number of Motor Cycles Per 100 Rural Households (unit) - 44. 59 Per Capita Domestic Expenditure on Tour (yuan) 766 222 Culture Rate of Radio Broadcast Coverage of the Population (%) 95. 0 Rate of TV Coverage of the Population (%) 96. 2 Number of Color TV per 100 Households (set) 137. 4 89. 4 Number of Computer per 100 Households (set) 47. 2 2. 7 Percentage of Household Expenditure on Education, Culture and Entertainment (%) 13. 8 Health Percentage of Resident Expenditure on Health Care Reference: China Statistical Yearbook 2007 10. 8 (%) 7. 1 6. 8
Statistics on People's Living Conditions in 2006 Item Urban 8697 Annual Per Capita Consumption Expenditure of Urban Households - (yuan) - Annual Per Capita Living Expenditure of Rural Households Rural (yuan) 2829 Traffic Condition Number of Automobile Per 100 Urban Households (unit) 4. 32 - Number of Motor Cycles Per 100 Rural Households (unit) - 44. 59 Per Capita Domestic Expenditure on Tour (yuan) 766 222 Culture Rate of Radio Broadcast Coverage of the Population (%) 95. 0 Rate of TV Coverage of the Population (%) 96. 2 Number of Color TV per 100 Households (set) 137. 4 89. 4 Number of Computer per 100 Households (set) 47. 2 2. 7 Percentage of Household Expenditure on Education, Culture and Entertainment (%) 13. 8 Health Percentage of Resident Expenditure on Health Care Reference: China Statistical Yearbook 2007 10. 8 (%) 7. 1 6. 8
 Marketing Techniques • • • Advertising (TV Broadcast) Sales promotion Personal Selling & Public Relations Large TV networks & quality programming Sweepstakes and contests with weighty prizes, e. g. cars and overseas trips
Marketing Techniques • • • Advertising (TV Broadcast) Sales promotion Personal Selling & Public Relations Large TV networks & quality programming Sweepstakes and contests with weighty prizes, e. g. cars and overseas trips
 Standardized Approach vs. Localized Strategies in China
Standardized Approach vs. Localized Strategies in China
 Standardized approach • Globalization & Westernization • Human Universals with similar attitudes, lifestyles & aspirations • Global brands, Standardized products • Superior Quality + Social Status
Standardized approach • Globalization & Westernization • Human Universals with similar attitudes, lifestyles & aspirations • Global brands, Standardized products • Superior Quality + Social Status
 Localized Strategies • Adopt local market conditions & consumer preference • Deployment of local talent • Use local celebrities to endorse their e. g. Nike ads (Liu Xiang) products
Localized Strategies • Adopt local market conditions & consumer preference • Deployment of local talent • Use local celebrities to endorse their e. g. Nike ads (Liu Xiang) products
 strategy of “Glocalization" • Globalization + Localization • localize global brands to Chinese context, even regional extent • Idea of a single China market is inadequate & some how misleading • Lead to misconceptions about the opportunities and risks in China • In stead of mass marketing approach, more MNCs today focus on a specific target market and to position the products accordingly.
strategy of “Glocalization" • Globalization + Localization • localize global brands to Chinese context, even regional extent • Idea of a single China market is inadequate & some how misleading • Lead to misconceptions about the opportunities and risks in China • In stead of mass marketing approach, more MNCs today focus on a specific target market and to position the products accordingly.
 Example: Mc. Donald • Global image • Universal slogan: I’m lovin’ it • Local taste & dialects • Campaign : Spice up 2008 http: //www. mcdonalds. com. cn/minisite/spicy_up_2008/? sec=show
Example: Mc. Donald • Global image • Universal slogan: I’m lovin’ it • Local taste & dialects • Campaign : Spice up 2008 http: //www. mcdonalds. com. cn/minisite/spicy_up_2008/? sec=show
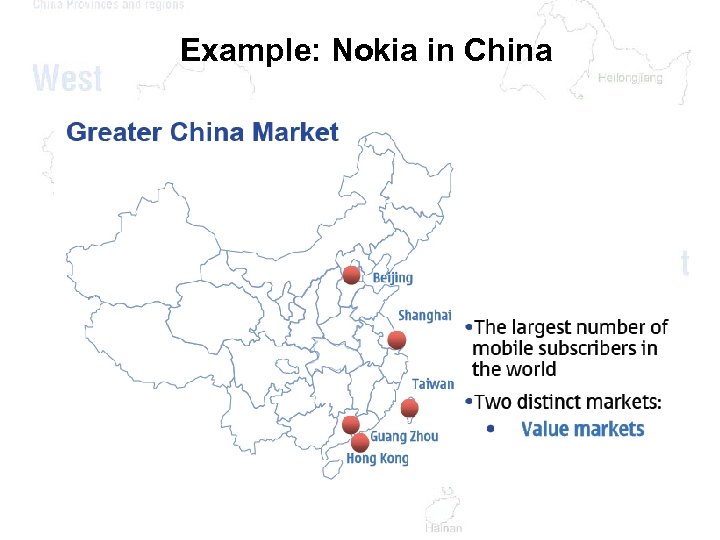 Example: Nokia in China
Example: Nokia in China
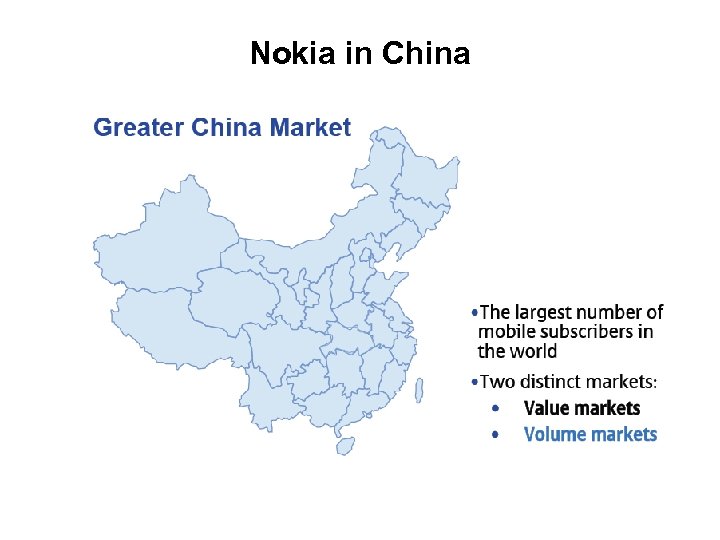 Nokia in China
Nokia in China
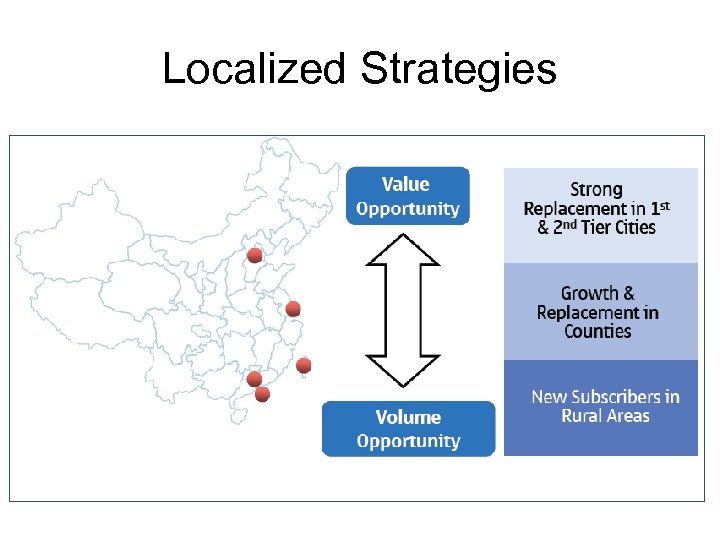 Localized Strategies
Localized Strategies
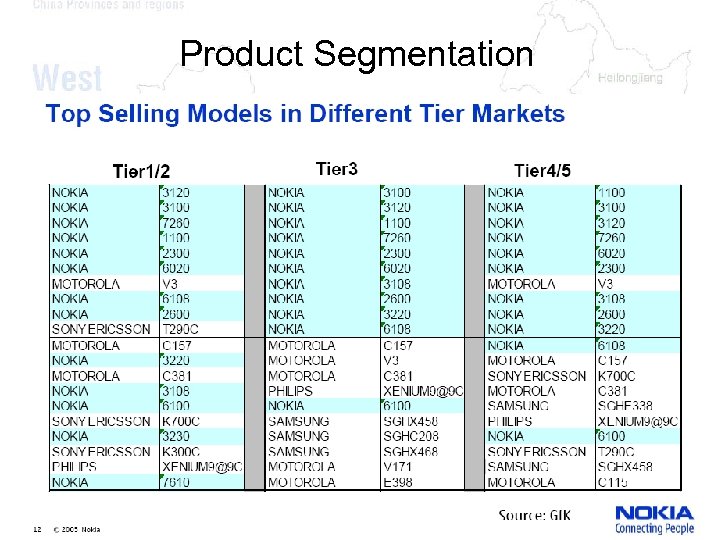 Product Segmentation
Product Segmentation
 • Tailoring Products for China
• Tailoring Products for China
 • 4) Major urban markets are saturated and very competitive. How do you assess the opportunities foreign brands in rural markets? What kind of products and strategies will do well there?
• 4) Major urban markets are saturated and very competitive. How do you assess the opportunities foreign brands in rural markets? What kind of products and strategies will do well there?
 Opportunities foreign brands Ø purchasing power of the rural community After cancelation of agriculture taxes in 2006, Zhuang Jian(a senior economist with the Asian Development Bank. ) said, "These measures will help improve the rural areas' consumption environment and increase rural farmers' consumption power. “ Ø competitive marketers are looking for extending their product categories to an unexplored market Ø educational level no. of available intellectual labors Ø Governmental supports construction of infrastructures e. g. electronics, highways and mass train railway system Ø Lots of lands + lower rent lower the TC
Opportunities foreign brands Ø purchasing power of the rural community After cancelation of agriculture taxes in 2006, Zhuang Jian(a senior economist with the Asian Development Bank. ) said, "These measures will help improve the rural areas' consumption environment and increase rural farmers' consumption power. “ Ø competitive marketers are looking for extending their product categories to an unexplored market Ø educational level no. of available intellectual labors Ø Governmental supports construction of infrastructures e. g. electronics, highways and mass train railway system Ø Lots of lands + lower rent lower the TC
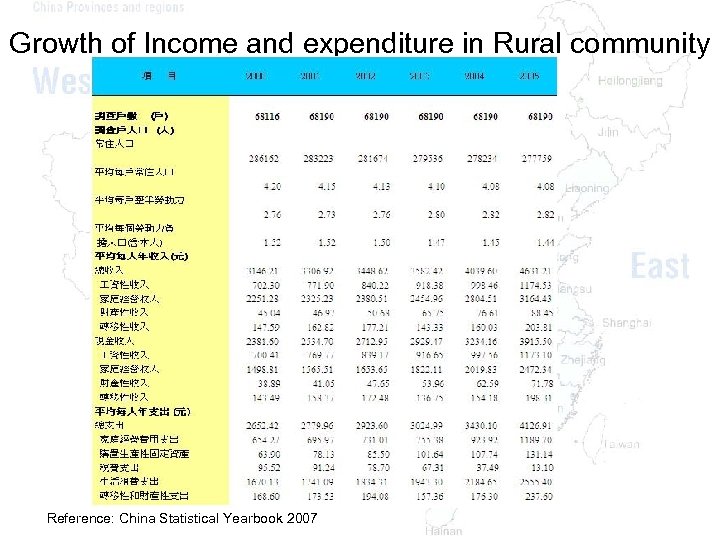 Growth of Income and expenditure in Rural community Reference: China Statistical Yearbook 2007
Growth of Income and expenditure in Rural community Reference: China Statistical Yearbook 2007
 Opportunities foreign brands Ø purchasing power of the rural community After cancelation of agriculture taxes in 2006, Zhuang Jian(a senior economist with the Asian Development Bank. ) said, "These measures will help improve the rural areas' consumption environment and increase rural farmers' consumption power. “ Ø competitive marketers are looking for extending their product categories to an unexplored market Ø educational level no. of available intellectual labors Ø Governmental supports construction of infrastructures e. g. electronics, highways and mass train railway system Ø Lots of lands + lower rent lower the TC
Opportunities foreign brands Ø purchasing power of the rural community After cancelation of agriculture taxes in 2006, Zhuang Jian(a senior economist with the Asian Development Bank. ) said, "These measures will help improve the rural areas' consumption environment and increase rural farmers' consumption power. “ Ø competitive marketers are looking for extending their product categories to an unexplored market Ø educational level no. of available intellectual labors Ø Governmental supports construction of infrastructures e. g. electronics, highways and mass train railway system Ø Lots of lands + lower rent lower the TC
 Opportunities foreign brands Ø • Ø purchasing power of the rural community After cancelation of agriculture taxes in 2006, Zhuang Jian(a senior economist with the Asian Development Bank. ) said, "These measures will help improve the rural areas' consumption environment and increase rural farmers' consumption power. “ Competitive marketers are looking for extending their product categories to an unexplored market educational level no. of available intellectual labors Ø Governmental supports construction of infrastructures e. g. electronics, highways and mass train railway system Ø Lots of lands + lower rent lower the TC
Opportunities foreign brands Ø • Ø purchasing power of the rural community After cancelation of agriculture taxes in 2006, Zhuang Jian(a senior economist with the Asian Development Bank. ) said, "These measures will help improve the rural areas' consumption environment and increase rural farmers' consumption power. “ Competitive marketers are looking for extending their product categories to an unexplored market educational level no. of available intellectual labors Ø Governmental supports construction of infrastructures e. g. electronics, highways and mass train railway system Ø Lots of lands + lower rent lower the TC
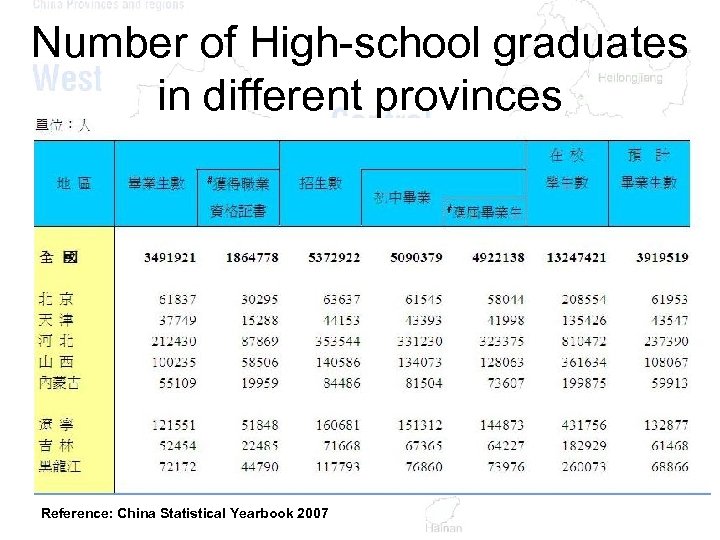 Number of High-school graduates in different provinces Reference: China Statistical Yearbook 2007
Number of High-school graduates in different provinces Reference: China Statistical Yearbook 2007
 Opportunities foreign brands Ø purchasing power of the rural community After cancelation of agriculture taxes in 2006, Zhuang Jian(a senior economist with the Asian Development Bank. ) said, "These measures will help improve the rural areas' consumption environment and increase rural farmers' consumption power. “ Ø competitive marketers are looking for extending their product categories to an unexplored market Ø Ø educational level no. of available intellectual labors Governmental supports construction of infrastructures e. g. electronics, highways and mass train railway system Ø Lots of lands + lower rent lower the TC
Opportunities foreign brands Ø purchasing power of the rural community After cancelation of agriculture taxes in 2006, Zhuang Jian(a senior economist with the Asian Development Bank. ) said, "These measures will help improve the rural areas' consumption environment and increase rural farmers' consumption power. “ Ø competitive marketers are looking for extending their product categories to an unexplored market Ø Ø educational level no. of available intellectual labors Governmental supports construction of infrastructures e. g. electronics, highways and mass train railway system Ø Lots of lands + lower rent lower the TC
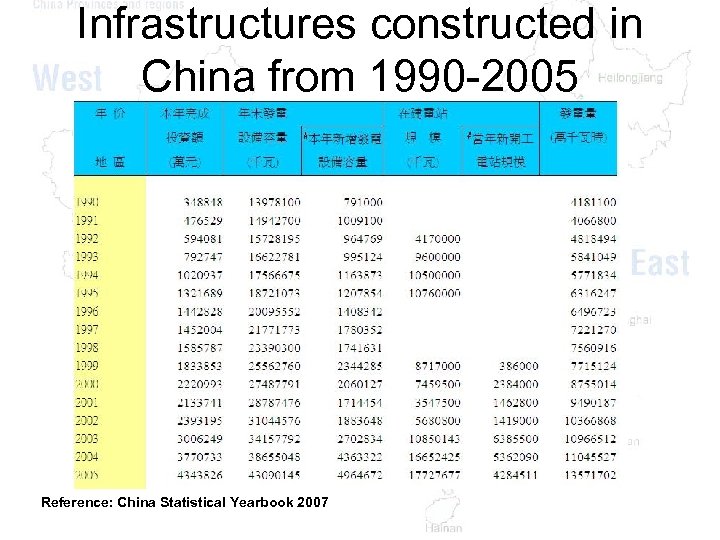 Infrastructures constructed in China from 1990 -2005 Reference: China Statistical Yearbook 2007
Infrastructures constructed in China from 1990 -2005 Reference: China Statistical Yearbook 2007
 Kinds of products corresponding strategies Current Market Current Product New Market Penetration Product Development Market Development Diversification
Kinds of products corresponding strategies Current Market Current Product New Market Penetration Product Development Market Development Diversification
 ~Strategies~ Product Development Ø For existing goods to seek new markets • review new demographic + geographic mkt • MR whether the market is profitable e. g. Lhasa (拉薩) ü not exploit yet ü Good infrastructure supports e. g. Tibet Sky Railway (青藏鐵路) ü Rapid economic growth ( increase 20% )
~Strategies~ Product Development Ø For existing goods to seek new markets • review new demographic + geographic mkt • MR whether the market is profitable e. g. Lhasa (拉薩) ü not exploit yet ü Good infrastructure supports e. g. Tibet Sky Railway (青藏鐵路) ü Rapid economic growth ( increase 20% )
 Case Studies • Starbucks 1996 150 Coffee Shops in China + mainly in coastal cities Current over 2000 Coffee shops in China Occupy most of the cities and rural areas
Case Studies • Starbucks 1996 150 Coffee Shops in China + mainly in coastal cities Current over 2000 Coffee shops in China Occupy most of the cities and rural areas
 ~Strategies~ Diversification Ø For new products to seek new markets • category of products • Diverse locations • Cooperation with other related firms • Highly practical
~Strategies~ Diversification Ø For new products to seek new markets • category of products • Diverse locations • Cooperation with other related firms • Highly practical
 Case Study Ø Lacoste • diversity of products e. g. Shoes, clothes • Station in most of the cities and rural areas Over 400, 000 items of Lacoste products were sold at its 200 sales points in China in 2003 e. g. Shanghai, Xian, Jilin, Hubei, with total sales of about US$70 million • Cooperation with other firms exposure to all Chinese Chance of e. g. International Tennis Federation, French Golf Federation
Case Study Ø Lacoste • diversity of products e. g. Shoes, clothes • Station in most of the cities and rural areas Over 400, 000 items of Lacoste products were sold at its 200 sales points in China in 2003 e. g. Shanghai, Xian, Jilin, Hubei, with total sales of about US$70 million • Cooperation with other firms exposure to all Chinese Chance of e. g. International Tennis Federation, French Golf Federation
 Ø Product Strategies • Practical, Necessities, quality-guaranteed Ø Price Strategies • Affordable, maintenance needed Ø Promotion Strategies • TV ad, Newspapers ad, Bus Stop ad, vehicles ad Ø Place Strategies • Downtowns, town centers, even stores in villages
Ø Product Strategies • Practical, Necessities, quality-guaranteed Ø Price Strategies • Affordable, maintenance needed Ø Promotion Strategies • TV ad, Newspapers ad, Bus Stop ad, vehicles ad Ø Place Strategies • Downtowns, town centers, even stores in villages
 Conclusion Wealth gap between urban And rural area is still big Government puts efforts on Self - Advance FOREIGN BRANDS IS ABLE TO INVEST IN ALL PROVINCES IN CHINA
Conclusion Wealth gap between urban And rural area is still big Government puts efforts on Self - Advance FOREIGN BRANDS IS ABLE TO INVEST IN ALL PROVINCES IN CHINA


