3def0c5a96e74e653fbc3642e0f5de7a.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 15
 Achieving Universal Health Coverage Solutions from Home and Abroad www. chanet. org Issue Brief available at: www. chanet. org Many Hospitals. One Voice.
Achieving Universal Health Coverage Solutions from Home and Abroad www. chanet. org Issue Brief available at: www. chanet. org Many Hospitals. One Voice.
 The Statistics percent of Americans have some form of health insurance 45. 7 million Americans lack health insurance www. chanet. org 84 ◦ One in three uninsured has a chronic illness ◦ One in four of this group has not seen a health provider in over a year ◦ The uninsured account for 18, 000 excess deaths each year ◦ The cost to the nation of poorer health status of the uninsured is between $65 billion- $135 billion yearly ◦ The number of uninsured is expected to increase Many Hospitals. One Voice.
The Statistics percent of Americans have some form of health insurance 45. 7 million Americans lack health insurance www. chanet. org 84 ◦ One in three uninsured has a chronic illness ◦ One in four of this group has not seen a health provider in over a year ◦ The uninsured account for 18, 000 excess deaths each year ◦ The cost to the nation of poorer health status of the uninsured is between $65 billion- $135 billion yearly ◦ The number of uninsured is expected to increase Many Hospitals. One Voice.
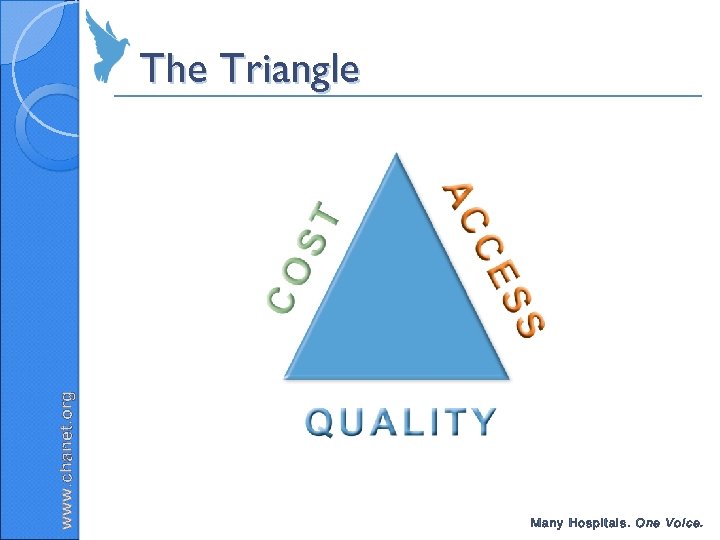 www. chanet. org The Triangle Many Hospitals. One Voice.
www. chanet. org The Triangle Many Hospitals. One Voice.
 The U. S. and Cost $1. 86 trillion or $6401 per capita spent on healthcare in 2005 Cost drivers www. chanet. org ◦ Constant stream of new technologies ◦ Maintaining highly trained workforce ◦ Increased consumption of healthcare services ◦ The health of Americans in general Many Hospitals. One Voice.
The U. S. and Cost $1. 86 trillion or $6401 per capita spent on healthcare in 2005 Cost drivers www. chanet. org ◦ Constant stream of new technologies ◦ Maintaining highly trained workforce ◦ Increased consumption of healthcare services ◦ The health of Americans in general Many Hospitals. One Voice.
 The U. S. and Access Lack of insurance creates barrier to access ◦ 80 percent from working families ◦ The unemployed ◦ Those who don’t think they need it Geography can create a barrier www. chanet. org HPSAs ◦ shortage of primary care physicians ◦ Declines in medical students choosing family practice Many Hospitals. One Voice.
The U. S. and Access Lack of insurance creates barrier to access ◦ 80 percent from working families ◦ The unemployed ◦ Those who don’t think they need it Geography can create a barrier www. chanet. org HPSAs ◦ shortage of primary care physicians ◦ Declines in medical students choosing family practice Many Hospitals. One Voice.
 The U. S. and Quality enjoys excellent medical reputation U. S. fares relatively poorly in the W. H. O. ’s health system performance rankings www. chanet. org U. S. ◦ Nursing shortage ◦ Quality-neutral payment system (until very recently) ◦ Little quality information publicly available Differentiation between quality of healthcare services and general population health Many Hospitals. One Voice.
The U. S. and Quality enjoys excellent medical reputation U. S. fares relatively poorly in the W. H. O. ’s health system performance rankings www. chanet. org U. S. ◦ Nursing shortage ◦ Quality-neutral payment system (until very recently) ◦ Little quality information publicly available Differentiation between quality of healthcare services and general population health Many Hospitals. One Voice.
 Recent U. S. Quality Initiatives www. chanet. org 2002: Nurse Reinvestment Act 2003: CMS Quality Reporting Program 2005: Hospital Compare Web site 2008: CMS and many private insurers refuse to pay for care resulting from medical errors Now: Pilot projects that tie reimbursement to quality outcomes Many Hospitals. One Voice.
Recent U. S. Quality Initiatives www. chanet. org 2002: Nurse Reinvestment Act 2003: CMS Quality Reporting Program 2005: Hospital Compare Web site 2008: CMS and many private insurers refuse to pay for care resulting from medical errors Now: Pilot projects that tie reimbursement to quality outcomes Many Hospitals. One Voice.
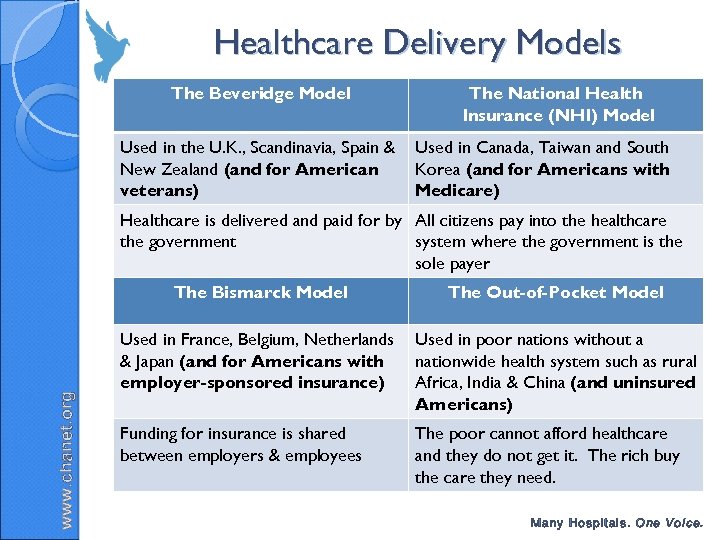 Healthcare Delivery Models The Beveridge Model Used in the U. K. , Scandinavia, Spain & New Zealand (and for American veterans) The National Health Insurance (NHI) Model Used in Canada, Taiwan and South Korea (and for Americans with Medicare) Healthcare is delivered and paid for by All citizens pay into the healthcare the government system where the government is the sole payer www. chanet. org The Bismarck Model The Out-of-Pocket Model Used in France, Belgium, Netherlands & Japan (and for Americans with employer-sponsored insurance) Used in poor nations without a nationwide health system such as rural Africa, India & China (and uninsured Americans) Funding for insurance is shared between employers & employees The poor cannot afford healthcare and they do not get it. The rich buy the care they need. Many Hospitals. One Voice.
Healthcare Delivery Models The Beveridge Model Used in the U. K. , Scandinavia, Spain & New Zealand (and for American veterans) The National Health Insurance (NHI) Model Used in Canada, Taiwan and South Korea (and for Americans with Medicare) Healthcare is delivered and paid for by All citizens pay into the healthcare the government system where the government is the sole payer www. chanet. org The Bismarck Model The Out-of-Pocket Model Used in France, Belgium, Netherlands & Japan (and for Americans with employer-sponsored insurance) Used in poor nations without a nationwide health system such as rural Africa, India & China (and uninsured Americans) Funding for insurance is shared between employers & employees The poor cannot afford healthcare and they do not get it. The rich buy the care they need. Many Hospitals. One Voice.
 The United Kingdom www. chanet. org Beveridge model- the government pays for the healthcare services of all of its citizens through taxes, including doctor care and hospital visits. Care coordinated through GP Low per-capita cost compared to U. S. Equal access to healthcare (though not perfect) ◦ Wait time ◦ Limiting types of services Many Hospitals. One Voice.
The United Kingdom www. chanet. org Beveridge model- the government pays for the healthcare services of all of its citizens through taxes, including doctor care and hospital visits. Care coordinated through GP Low per-capita cost compared to U. S. Equal access to healthcare (though not perfect) ◦ Wait time ◦ Limiting types of services Many Hospitals. One Voice.
 Taiwan model- One national, government run insurer that covers all citizens, all of whom are mandated to participate. Implemented in 1995 Low costs and high access achieved www. chanet. org NHI ◦ Single-payer model ◦ Smart Card ◦ Quality a lower priority Many Hospitals. One Voice.
Taiwan model- One national, government run insurer that covers all citizens, all of whom are mandated to participate. Implemented in 1995 Low costs and high access achieved www. chanet. org NHI ◦ Single-payer model ◦ Smart Card ◦ Quality a lower priority Many Hospitals. One Voice.
 Germany model- insurance is mandatory and is paid for by employers and employees Insurance companies nonprofit and administered by the state Quality a high priority High costs www. chanet. org Bismarck ◦ Abundant self-referral to specialists Many Hospitals. One Voice.
Germany model- insurance is mandatory and is paid for by employers and employees Insurance companies nonprofit and administered by the state Quality a high priority High costs www. chanet. org Bismarck ◦ Abundant self-referral to specialists Many Hospitals. One Voice.
 Massachusetts health reform legislation passed known as Chapter 58 www. chanet. org 2006 - ◦ Individual Mandate for insurance coverage ◦ Expanded Medicaid to include children with families between 200 -300% FPL ◦ Provided subsidies ◦ Imposed penalties on companies not offering insurance to their employees ◦ Created an insurance connector ◦ Included pay-for-performance measures Many Hospitals. One Voice.
Massachusetts health reform legislation passed known as Chapter 58 www. chanet. org 2006 - ◦ Individual Mandate for insurance coverage ◦ Expanded Medicaid to include children with families between 200 -300% FPL ◦ Provided subsidies ◦ Imposed penalties on companies not offering insurance to their employees ◦ Created an insurance connector ◦ Included pay-for-performance measures Many Hospitals. One Voice.
 Vermont www. chanet. org Health Care Affordability Act, 2006 ◦ Catamount Health Plan- affordable insurance plan open to all uninsured residents ◦ State offers subsidies to those 300% FPL for employer plan or Catamount plan ◦ Businesses assessed $365/employee not offered insurance ◦ Focus on chronic disease management with comprehensive Blueprint for Health initiative Many Hospitals. One Voice.
Vermont www. chanet. org Health Care Affordability Act, 2006 ◦ Catamount Health Plan- affordable insurance plan open to all uninsured residents ◦ State offers subsidies to those 300% FPL for employer plan or Catamount plan ◦ Businesses assessed $365/employee not offered insurance ◦ Focus on chronic disease management with comprehensive Blueprint for Health initiative Many Hospitals. One Voice.
 Lessons Learned U. K. → Stress importance of primary care ◦ Pay general practitioners more generously ◦ Financial incentives for GPs to keep patients healthy Vermont→ Chronic disease management www. chanet. org Massachusetts→ Payment incentives to eliminate ethnic/racial disparities Taiwan→ Health information technology Germany→ Excessive use of specialists Many Hospitals. One Voice.
Lessons Learned U. K. → Stress importance of primary care ◦ Pay general practitioners more generously ◦ Financial incentives for GPs to keep patients healthy Vermont→ Chronic disease management www. chanet. org Massachusetts→ Payment incentives to eliminate ethnic/racial disparities Taiwan→ Health information technology Germany→ Excessive use of specialists Many Hospitals. One Voice.
 Conclusion www. chanet. org Let’s first take a lesson from Taiwan, which may be the most important one of all. In response to its very poor healthcare system, Taiwan radically and fundamentally changed healthcare delivery. The lesson is, healthcare reform can occur. Many Hospitals. One Voice.
Conclusion www. chanet. org Let’s first take a lesson from Taiwan, which may be the most important one of all. In response to its very poor healthcare system, Taiwan radically and fundamentally changed healthcare delivery. The lesson is, healthcare reform can occur. Many Hospitals. One Voice.


