 Accumulation & Crisis Capital, Chapters 23 -25
Accumulation & Crisis Capital, Chapters 23 -25
 Definition? • • Accumulation = expanded reproduction Accumulation = growth Accumulation = development Accumulation means accumulation of all the elements of capital, but especially accumulation of class relations, more “capital”, more “labor”.
Definition? • • Accumulation = expanded reproduction Accumulation = growth Accumulation = development Accumulation means accumulation of all the elements of capital, but especially accumulation of class relations, more “capital”, more “labor”.
 Simple Reproduction • Reproducing what already is • Marx conceived “reproduction schemes” – Department I = production of MP – Department II = production of MS • DI must produce MP for DI and DII • DII must produce MS for DI and DII • There must be balance
Simple Reproduction • Reproducing what already is • Marx conceived “reproduction schemes” – Department I = production of MP – Department II = production of MS • DI must produce MP for DI and DII • DII must produce MS for DI and DII • There must be balance
 Simple Reproduction • In simple reproduction surplus value spent on capitalist consumption • DII produces MS for WC and for Kclass • No investment (beyond depreciation, ie. , replacing what is worn out) • No growth
Simple Reproduction • In simple reproduction surplus value spent on capitalist consumption • DII produces MS for WC and for Kclass • No investment (beyond depreciation, ie. , replacing what is worn out) • No growth
 Expanded Reproduction • • • Expanded Reproduction = growth Investment, I. e. , S is spent on more C + V So Investment in DI must buy MP + MS So investment in DII must by MP + MS There must be balance between the two departments, proportionality
Expanded Reproduction • • • Expanded Reproduction = growth Investment, I. e. , S is spent on more C + V So Investment in DI must buy MP + MS So investment in DII must by MP + MS There must be balance between the two departments, proportionality
 Reserve Army • But accumulation always includes not only the waged working in DI and DII • But also unwaged who have no “jobs” • This is usually conceived as unemployed • But for Marx, the reserve army = – latent reserve – floating reserve (frictional unemployed) – stagnant reserve (structural unemployed)
Reserve Army • But accumulation always includes not only the waged working in DI and DII • But also unwaged who have no “jobs” • This is usually conceived as unemployed • But for Marx, the reserve army = – latent reserve – floating reserve (frictional unemployed) – stagnant reserve (structural unemployed)
 Accumulation and Crisis • Along with laws and force, business could go on strike, i. e. , refuse to invest • For example in period of rapid growth, high profits and high investment, labor markets get tight, workers get higher wages, rate of profit fills and business cuts back on investment, reducing aggregate demand • Thus a downturn as economic activity diminishes, unemployment rises
Accumulation and Crisis • Along with laws and force, business could go on strike, i. e. , refuse to invest • For example in period of rapid growth, high profits and high investment, labor markets get tight, workers get higher wages, rate of profit fills and business cuts back on investment, reducing aggregate demand • Thus a downturn as economic activity diminishes, unemployment rises
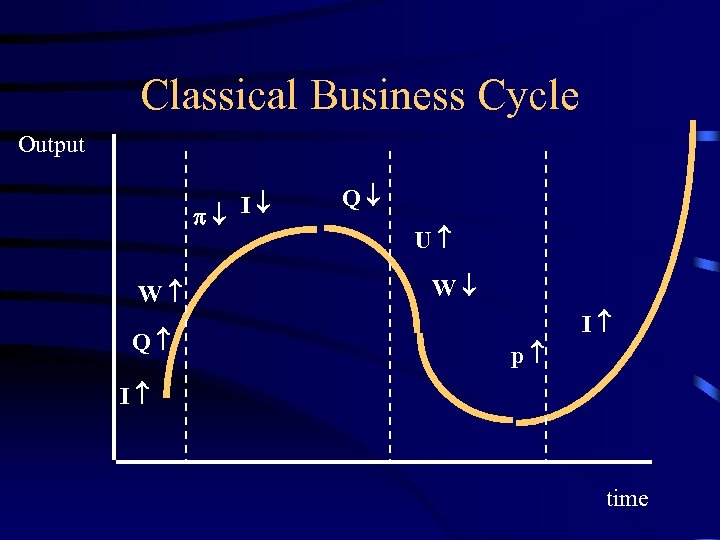 Classical Business Cycle Output I W Q Q U W I p I time
Classical Business Cycle Output I W Q Q U W I p I time
 Reserve Army • • Expands during downturn Contracts during upturn Undermines struggle for higher wages Undermines struggle against falling wages
Reserve Army • • Expands during downturn Contracts during upturn Undermines struggle for higher wages Undermines struggle against falling wages
 Crisis as Regulator • • • Crisis for business Is turned into crisis for labor Crisis becomes a “solution” for business To restore balance of class power But…. Always open ended
Crisis as Regulator • • • Crisis for business Is turned into crisis for labor Crisis becomes a “solution” for business To restore balance of class power But…. Always open ended
 Crisis to Revolution • Crisis for capital may be over come and expanded reproduction renewed • Or. . . • Crisis may explode into uncontainable revolution that ruptures all of capitalist circuits and liberates emerging alternatives from capitalist constraints.
Crisis to Revolution • Crisis for capital may be over come and expanded reproduction renewed • Or. . . • Crisis may explode into uncontainable revolution that ruptures all of capitalist circuits and liberates emerging alternatives from capitalist constraints.
 --END--
--END--