Accounting Introduction to Business BM 004 -4 -0


Accounting Introduction to Business BM004-4-0-ITB

Learning Outcomes Understand the use of accounting information. Identify elements of an income statement. Understand the items in the Balance Sheet. Understand the key items in the Cash Flow Statement.


The recording, measurement, and interpretation of financial information, often used in making business decisions. The Nature of Accounting
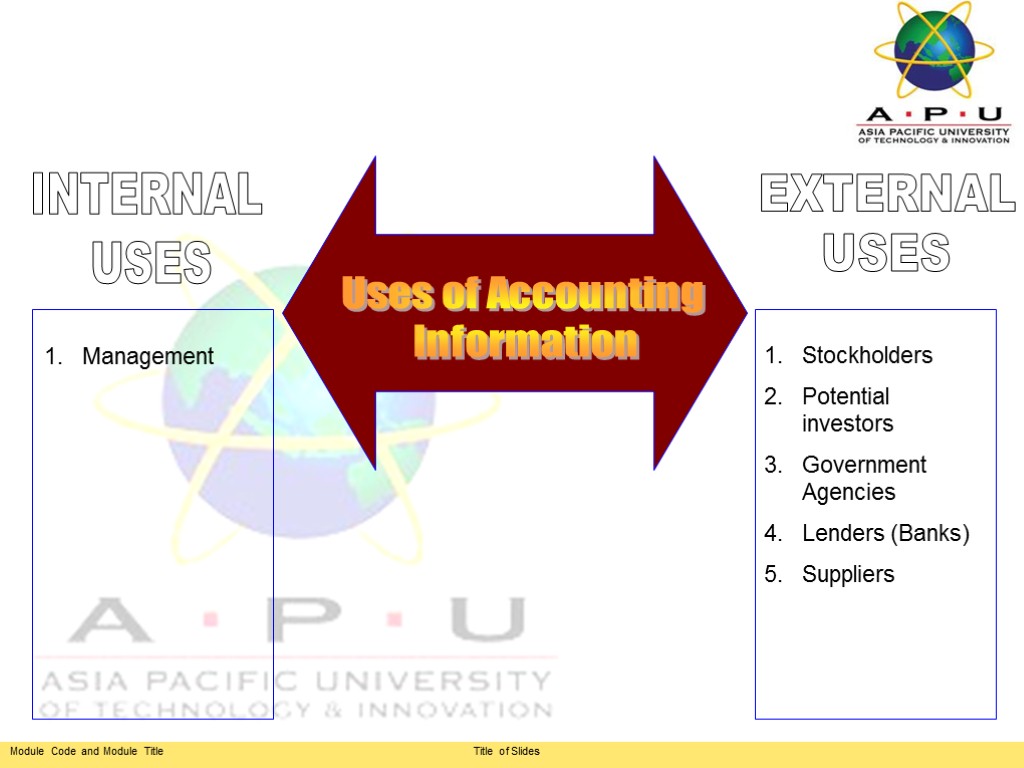
Uses of Accounting Information INTERNAL USES EXTERNAL USES Stockholders Potential investors Government Agencies Lenders (Banks) Suppliers Management
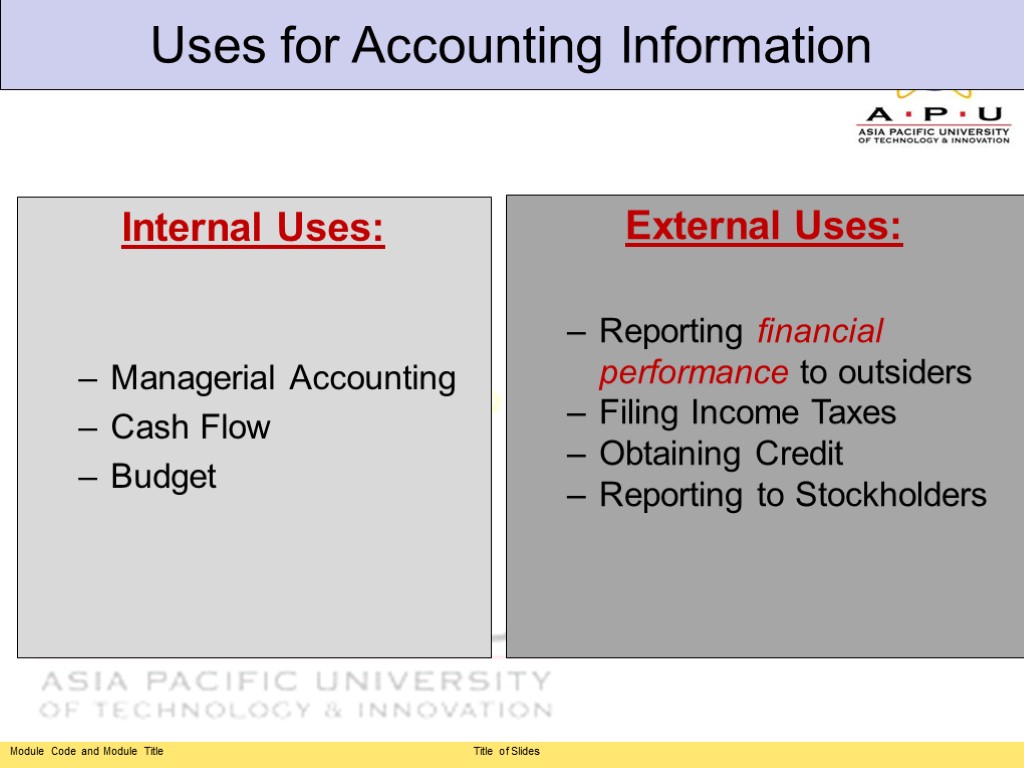
Uses for Accounting Information Internal Uses: Managerial Accounting Cash Flow Budget External Uses: Reporting financial performance to outsiders Filing Income Taxes Obtaining Credit Reporting to Stockholders

Internal Accounting Information 1) Plan and set goals 2) Organise 3) Lead and motivate 4) Control Management

External Accounting Information 1) Stockholders and Potential Investors - Evaluate soundness of investments 2) Government Agencies - Confirm tax liabilities Confirm payroll Deductions Approve new issues of stocks and bonds 3) Lenders - Capital for new ventures 4) Suppliers - Provide raw materials


Areas of Accounting Managerial Accounting :– Providing information and analysis to managers within the company to assist them in decision making. E.g. cost accounting, controlling. Financial Accounting :- Field of accounting concerned with external users of a company’s financial information. This information usually goes to owners and prospective owners, creditors, employee unions, customers, suppliers and governments agencies.


EXAM
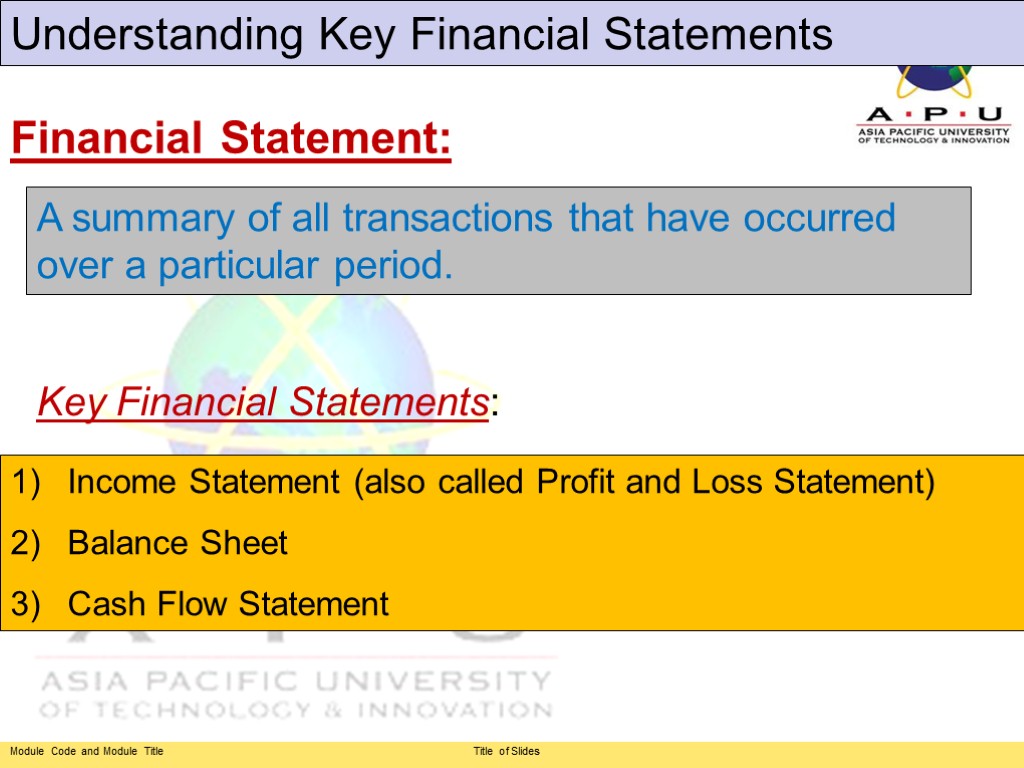
Understanding Key Financial Statements A summary of all transactions that have occurred over a particular period. Income Statement (also called Profit and Loss Statement) Balance Sheet Cash Flow Statement Key Financial Statements: Financial Statement:

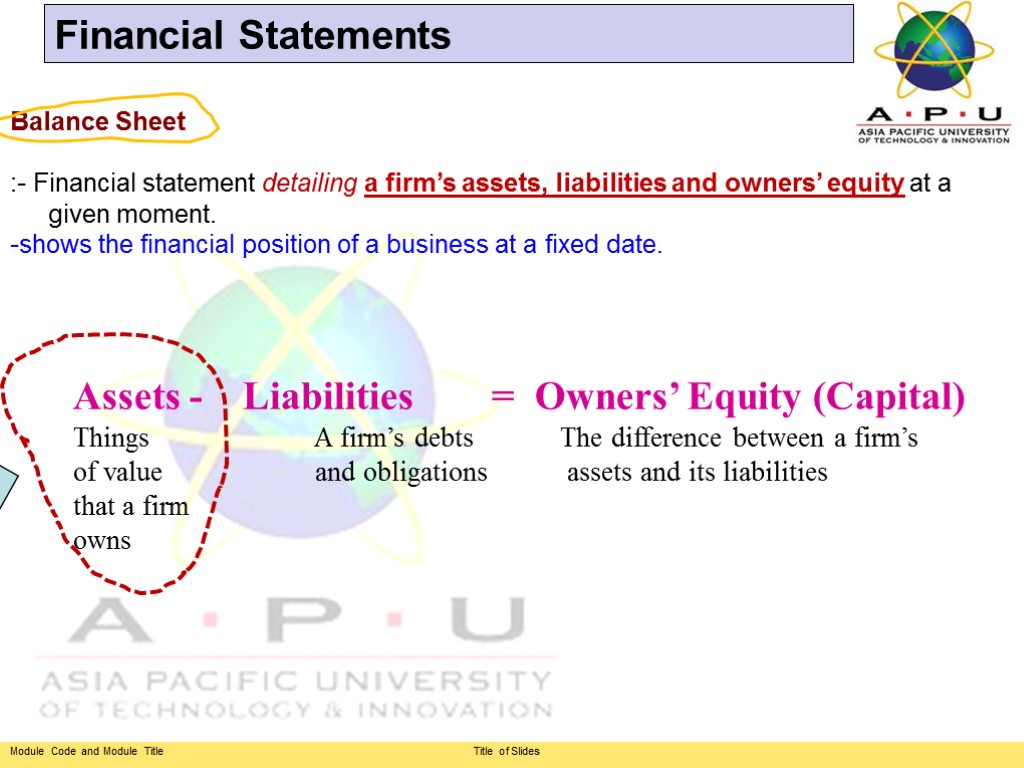
Balance Sheet :- Financial statement detailing a firm’s assets, liabilities and owners’ equity at a given moment. -shows the financial position of a business at a fixed date. Financial Statements Assets - Liabilities = Owners’ Equity (Capital) Things A firm’s debts The difference between a firm’s of value and obligations assets and its liabilities that a firm owns

Any economic resource expected to benefit a firm or individual who owns it. Financial Statements Current Assets Fixed Assets Intangible Assets ASSETS

Current assets: - Items that can be converted into cash within one year. E.g. inventory, cash, debtors Fixed assets : - Assets with a long-term use or value, such as land, buildings and equipment. (not intended for re-sale) Intangible assets :- Items of value such as patents and copyrights that have no real physical form.

LIABILITY :- Debt owed by a firm to an outside organisation or individual. 1) Current Liability :- Debt that must be paid within a year. E.g. Accounts payable. 2) Long-term Liability :- Debt due after a year. OWNERS EQUITY(Capital) :- Is the net worth of an individual or business - asset minus liabilities. Understanding Key Financial Statements
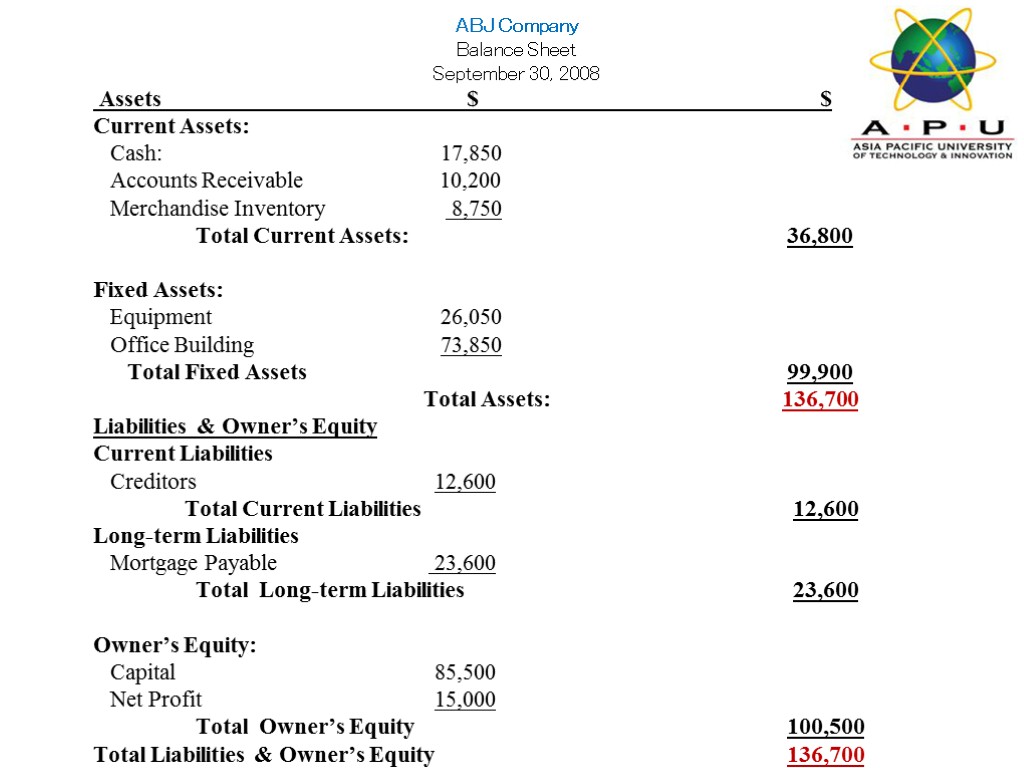
Assets $ $ Current Assets: Cash: 17,850 Accounts Receivable 10,200 Merchandise Inventory 8,750 Total Current Assets: 36,800 Fixed Assets: Equipment 26,050 Office Building 73,850 Total Fixed Assets 99,900 Total Assets: 136,700 Liabilities & Owner’s Equity Current Liabilities Creditors 12,600 Total Current Liabilities 12,600 Long-term Liabilities Mortgage Payable 23,600 Total Long-term Liabilities 23,600 Owner’s Equity: Capital 85,500 Net Profit 15,000 Total Owner’s Equity 100,500 Total Liabilities & Owner’s Equity 136,700 ABJ Company Balance Sheet September 30, 2008


Income Statement A financial report that shows an organisation’s profitability over a period of time. E.g. a month, quarter or year.

Income Statement (cont) Revenue: Funds that flow into a business from the sales of goods or services. 2) Cost of goods sold: Total cost of obtaining materials for making the products sold by a firm during a year. 3) Gross Profit: How much the firm earned by buying or selling merchandise. 5) Operating Expenses: Cost incurred in operating a business such as rent, utilities and salaries. 6) Net income: Profit or loss over a specific period after subtracting all costs and expenses including taxes.

Income Statement (cont) Revenue Cost of goods sold Gross Profit Operating expenses Net income before taxes Taxes Net income or loss *Gross profit or sales profit or gross operating profit is the difference between revenue and the cost of making a product or providing a service, before deducting overheads, payroll, taxation, and interest payments
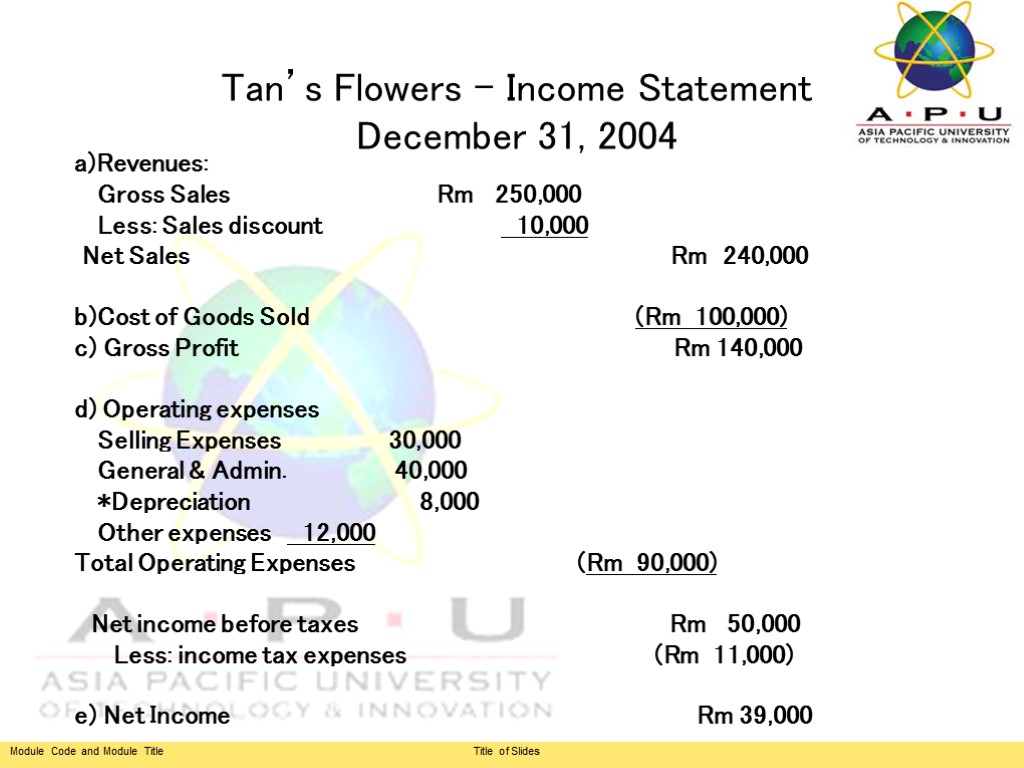
Tan’s Flowers - Income Statement December 31, 2004 a)Revenues: Gross Sales Rm 250,000 Less: Sales discount 10,000 Net Sales Rm 240,000 b)Cost of Goods Sold (Rm 100,000) c) Gross Profit Rm 140,000 d) Operating expenses Selling Expenses 30,000 General & Admin. 40,000 *Depreciation 8,000 Other expenses 12,000 Total Operating Expenses (Rm 90,000) Net income before taxes Rm 50,000 Less: income tax expenses (Rm 11,000) e) Net Income Rm 39,000


Statement of Cash Flow : :- Financial statement that describes a firm’s yearly cash receipts and cash payment related to a firm’s major activities; (records the inflow and outflow of cash over a period of time) Purpose: provide information on a firm's liquidity -does not include the amount of future incoming and outgoing cash Statement of Cash Flow
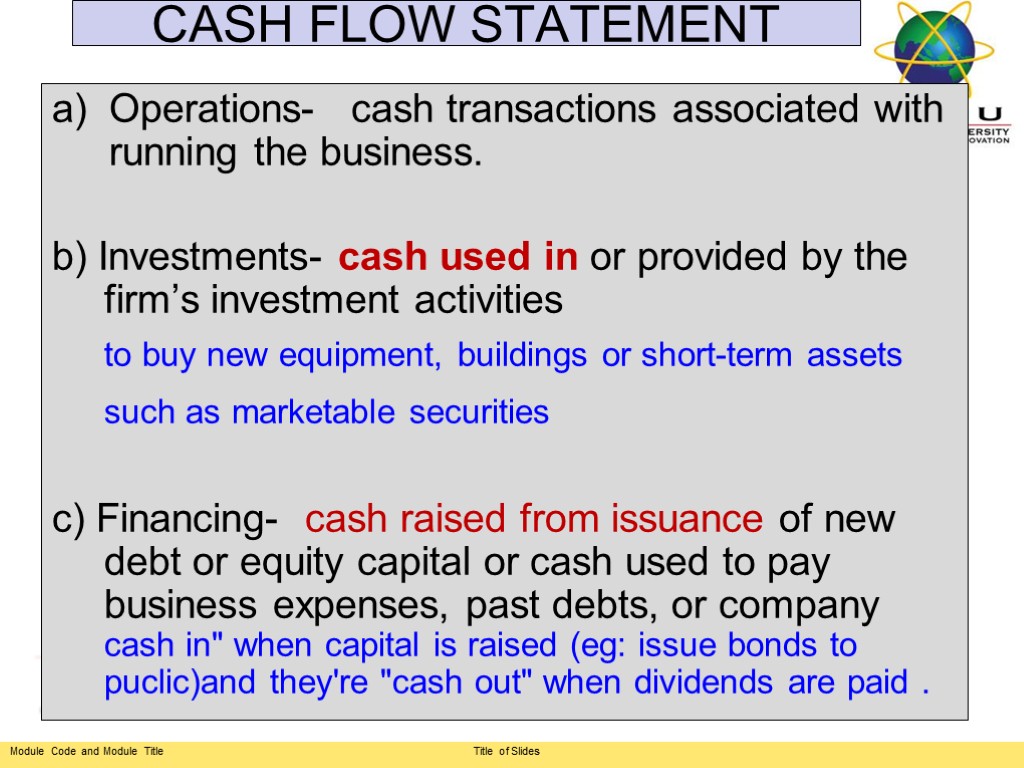
CASH FLOW STATEMENT Operations- cash transactions associated with running the business. b) Investments- cash used in or provided by the firm’s investment activities to buy new equipment, buildings or short-term assets such as marketable securities c) Financing- cash raised from issuance of new debt or equity capital or cash used to pay business expenses, past debts, or company cash in" when capital is raised (eg: issue bonds to puclic)and they're "cash out" when dividends are paid .


Budget – A financial plan that sets forth for the future in which it describes how it will use its resources to meet its goals. Budgeting

Question and Answer Session Q & A
itb_chp_7_accounting.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 30

