0c858dd98d9685c7ef84caf1f00e40ca.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 24
 Account Relationship Management Topic 4 Sales Management 1
Account Relationship Management Topic 4 Sales Management 1
 AIM: account relationship management. OBJECTIVES: 4. 1 Identify the steps in the professional purchasing process. 4. 2 Identify the different buying influences in the buying center. 4. 3 Explain how relationships are likely to evolve. 4. 4 Describe factors critical to gaining commitment to a relationship. 2
AIM: account relationship management. OBJECTIVES: 4. 1 Identify the steps in the professional purchasing process. 4. 2 Identify the different buying influences in the buying center. 4. 3 Explain how relationships are likely to evolve. 4. 4 Describe factors critical to gaining commitment to a relationship. 2
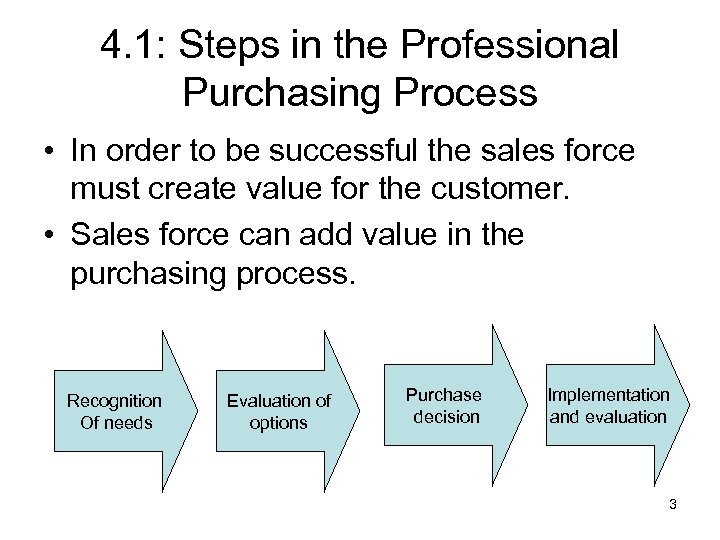 4. 1: Steps in the Professional Purchasing Process • In order to be successful the sales force must create value for the customer. • Sales force can add value in the purchasing process. Recognition Of needs Evaluation of options Purchase decision Implementation and evaluation 3
4. 1: Steps in the Professional Purchasing Process • In order to be successful the sales force must create value for the customer. • Sales force can add value in the purchasing process. Recognition Of needs Evaluation of options Purchase decision Implementation and evaluation 3
 1: Recognition of Needs: • Need may be immediate & focus on resolving a problem. • Help customers recognize a need or problem & to define them in a new or different way. • Derived demand – demand for product is derived from customers demand (in B 2 B, purchasing is for production not personal reasons. 4
1: Recognition of Needs: • Need may be immediate & focus on resolving a problem. • Help customers recognize a need or problem & to define them in a new or different way. • Derived demand – demand for product is derived from customers demand (in B 2 B, purchasing is for production not personal reasons. 4
 2. : Evaluation of Options: • Business may spend a lot of time searching/evaluating suppliers. • Specification- of product which will dictate the cost to produce the product. • In transactional relationship customers mostly develop specs before supplier gets involved. • In consultative relationship customers & suppliers both work jointly to develop product specs. 5
2. : Evaluation of Options: • Business may spend a lot of time searching/evaluating suppliers. • Specification- of product which will dictate the cost to produce the product. • In transactional relationship customers mostly develop specs before supplier gets involved. • In consultative relationship customers & suppliers both work jointly to develop product specs. 5
 • Proposals- a sales proposal is a written offer by a seller to provide a product to a purchasing org. • RFP – (request for proposal) is a notice that a customer sends out to qualified suppliers asking them to bid on a project with a certain spec. • in purchasing for building, contractors may consider service, product quality, supplier support, low price. 6
• Proposals- a sales proposal is a written offer by a seller to provide a product to a purchasing org. • RFP – (request for proposal) is a notice that a customer sends out to qualified suppliers asking them to bid on a project with a certain spec. • in purchasing for building, contractors may consider service, product quality, supplier support, low price. 6
 3. : Purchase Decision: A purchase decision using one of the three: • a straight rebuy (involves replenishing inventories). Seller adds values by making it convenient. • a modified rebuy (some changes in the offering are present) • a new buy (customer has not previously purchased the offering). 7
3. : Purchase Decision: A purchase decision using one of the three: • a straight rebuy (involves replenishing inventories). Seller adds values by making it convenient. • a modified rebuy (some changes in the offering are present) • a new buy (customer has not previously purchased the offering). 7
 4. : Implementation & Evaluation: • Sellers obligation in the purchasing process is to ensure that all promises are fulfilled & customer expectations are met. • Some potential benefits conflict mgt are 1. stimulating interest in exploring new approaches, 2. providing an opportunity to air problems & explore solutions, 3. mobilising the resources of the parties in a relationship. 8
4. : Implementation & Evaluation: • Sellers obligation in the purchasing process is to ensure that all promises are fulfilled & customer expectations are met. • Some potential benefits conflict mgt are 1. stimulating interest in exploring new approaches, 2. providing an opportunity to air problems & explore solutions, 3. mobilising the resources of the parties in a relationship. 8
 • Many orgs. Evaluate their suppliers by a formal value analysis (vendor analysis) • VA basis for cost reduction – relative cost of providing a necessary function or service at desired time & place with necessary quality. • VA is similar to value analysis but focuses on the vendor by looking at reliability, product quality, delivery and cost conpetitiveness. 9
• Many orgs. Evaluate their suppliers by a formal value analysis (vendor analysis) • VA basis for cost reduction – relative cost of providing a necessary function or service at desired time & place with necessary quality. • VA is similar to value analysis but focuses on the vendor by looking at reliability, product quality, delivery and cost conpetitiveness. 9
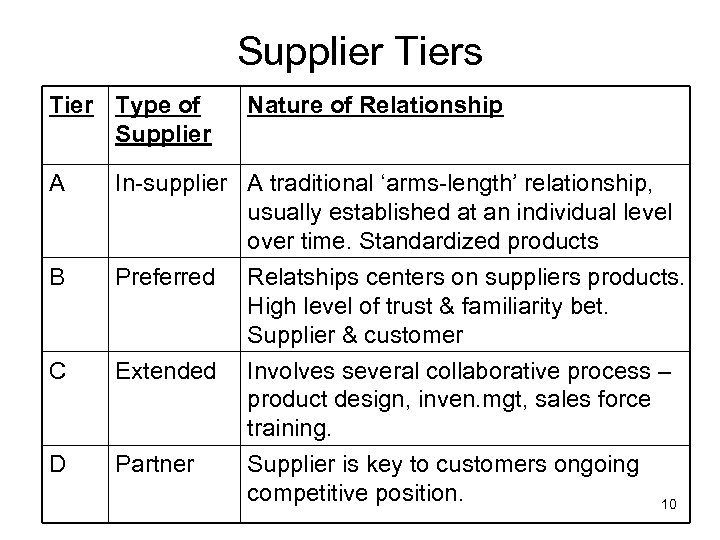 Supplier Tiers Tier Type of Supplier A B Nature of Relationship In-supplier A traditional ‘arms-length’ relationship, usually established at an individual level over time. Standardized products Preferred Relatships centers on suppliers products. High level of trust & familiarity bet. Supplier & customer C Extended Involves several collaborative process – product design, inven. mgt, sales force training. D Partner Supplier is key to customers ongoing competitive position. 10
Supplier Tiers Tier Type of Supplier A B Nature of Relationship In-supplier A traditional ‘arms-length’ relationship, usually established at an individual level over time. Standardized products Preferred Relatships centers on suppliers products. High level of trust & familiarity bet. Supplier & customer C Extended Involves several collaborative process – product design, inven. mgt, sales force training. D Partner Supplier is key to customers ongoing competitive position. 10
 • Companies are segmenting their supplier base according to importance of suppliers product & difficulty of finding alternative sources. • Placing suppliers in tiers. Some suppliers are much more important than others. • Complex sales is when various people in the customers org. must give approval before a sales takes place. 11
• Companies are segmenting their supplier base according to importance of suppliers product & difficulty of finding alternative sources. • Placing suppliers in tiers. Some suppliers are much more important than others. • Complex sales is when various people in the customers org. must give approval before a sales takes place. 11
 4. 2: Different Buying Influences in the Buying Center • Buying centre – all the people formally/informally involved in the purchasing decision. • A purchasing role – the set of issues or concerns that a member of buying center will consider before dis/approving purchase. • An individual may occupy multiple purchasing roles, a 4 th person must be present for sale to be concluded known as an advocate. 12
4. 2: Different Buying Influences in the Buying Center • Buying centre – all the people formally/informally involved in the purchasing decision. • A purchasing role – the set of issues or concerns that a member of buying center will consider before dis/approving purchase. • An individual may occupy multiple purchasing roles, a 4 th person must be present for sale to be concluded known as an advocate. 12
 Purchasing Roles: 1. Economic buyers • person or committee with the power to give final approval to buy a product. • Establishes the priority of projects • Is concerned about the economic health of the business • Focuses on future, asks why and can say ‘yes’ when others say ‘no’ (vice versa) • Seller must identify the EB, by asking who started the project, who will be affected by the outcome of the project, who has highest rank & greatest influence. 13
Purchasing Roles: 1. Economic buyers • person or committee with the power to give final approval to buy a product. • Establishes the priority of projects • Is concerned about the economic health of the business • Focuses on future, asks why and can say ‘yes’ when others say ‘no’ (vice versa) • Seller must identify the EB, by asking who started the project, who will be affected by the outcome of the project, who has highest rank & greatest influence. 13
 2. User Buyer • Role is to determine the impact of purchase on the job that they/workers perform. • Their focus is more narrow than economic buyer. • Users are mostly personnel whose daily work will be affected by the product. • Focus on past & present rather than future (except to ask how will this affect me). 14
2. User Buyer • Role is to determine the impact of purchase on the job that they/workers perform. • Their focus is more narrow than economic buyer. • Users are mostly personnel whose daily work will be affected by the product. • Focus on past & present rather than future (except to ask how will this affect me). 14
 3. Technical Buyers • Act as gatekeepers by screening out products & suppliers that do not meet the needs of the buying org. • Can have powerful influence on final decision but by themselves cant say ‘yes’ or ‘no’. • Focus on specifications of the product e. g. engineers, legal counsel & purchasing agents. • May be able to say ‘no’ but needs approval to say ‘yes’, can recommend, influencer to decision maker, focused on present, asks ‘what’ but does not ask ‘why not’. 15
3. Technical Buyers • Act as gatekeepers by screening out products & suppliers that do not meet the needs of the buying org. • Can have powerful influence on final decision but by themselves cant say ‘yes’ or ‘no’. • Focus on specifications of the product e. g. engineers, legal counsel & purchasing agents. • May be able to say ‘no’ but needs approval to say ‘yes’, can recommend, influencer to decision maker, focused on present, asks ‘what’ but does not ask ‘why not’. 15
 • Advocate – used in a complex selling involving multiple buying influences. • Role of advocate is to help guide you in the sale by providing critical infor. about the org. & people involved in buying. • Advocate may be internal or external to org. they are able to sell for you in your absence. • Advocates may win due to personal (want u to win bec they like you), professional (are better), recognition (from their own org), negative (wants someone else to lose) reasons. 16
• Advocate – used in a complex selling involving multiple buying influences. • Role of advocate is to help guide you in the sale by providing critical infor. about the org. & people involved in buying. • Advocate may be internal or external to org. they are able to sell for you in your absence. • Advocates may win due to personal (want u to win bec they like you), professional (are better), recognition (from their own org), negative (wants someone else to lose) reasons. 16
 Advocate may help the sales person: • Recommending selling strategies • Build a groundswell of interest (encourage discussion among decision makers) • Refer you to other advocates • Review your presentation • Gain access to decision makers. An advocate is critical & must be selected & developed with care. 17
Advocate may help the sales person: • Recommending selling strategies • Build a groundswell of interest (encourage discussion among decision makers) • Refer you to other advocates • Review your presentation • Gain access to decision makers. An advocate is critical & must be selected & developed with care. 17
 Challenges • Salespeople must be diverse in their knowledge & flexible in behavior. • Technical buyers may be the most frustrating & professionally challenging people in the buying center. • It is important to understand why a gatekeeper would want to block you from completing a sale. 18
Challenges • Salespeople must be diverse in their knowledge & flexible in behavior. • Technical buyers may be the most frustrating & professionally challenging people in the buying center. • It is important to understand why a gatekeeper would want to block you from completing a sale. 18
 4. 3: How Relationships Evolve. Growing relationships evolve through 5 stages: • Awareness • Exploration • Expansion • Commitment • Dissolution May be difficult to determine exactly when a relationship moves to next stage. Salespeople should be aware of these chagnes & proceed accordingly. 19
4. 3: How Relationships Evolve. Growing relationships evolve through 5 stages: • Awareness • Exploration • Expansion • Commitment • Dissolution May be difficult to determine exactly when a relationship moves to next stage. Salespeople should be aware of these chagnes & proceed accordingly. 19
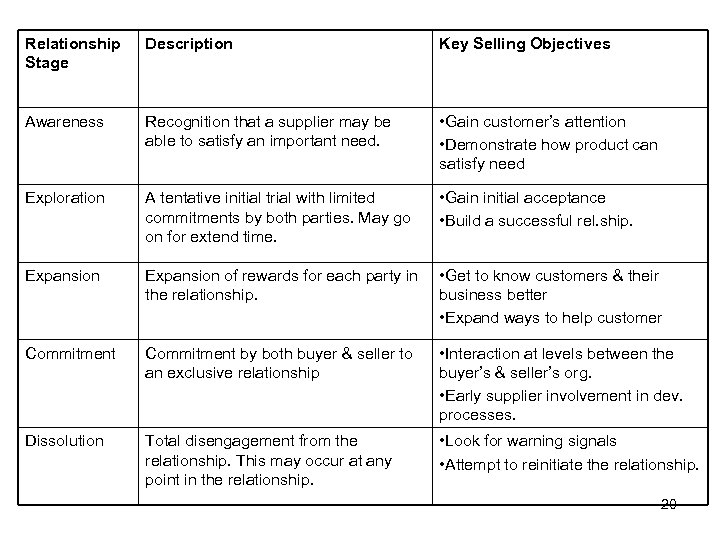 Relationship Stage Description Key Selling Objectives Awareness Recognition that a supplier may be able to satisfy an important need. • Gain customer’s attention • Demonstrate how product can satisfy need Exploration A tentative initial trial with limited commitments by both parties. May go on for extend time. • Gain initial acceptance • Build a successful rel. ship. Expansion of rewards for each party in the relationship. • Get to know customers & their business better • Expand ways to help customer Commitment by both buyer & seller to an exclusive relationship • Interaction at levels between the buyer’s & seller’s org. • Early supplier involvement in dev. processes. Dissolution Total disengagement from the relationship. This may occur at any point in the relationship. • Look for warning signals • Attempt to reinitiate the relationship. 20
Relationship Stage Description Key Selling Objectives Awareness Recognition that a supplier may be able to satisfy an important need. • Gain customer’s attention • Demonstrate how product can satisfy need Exploration A tentative initial trial with limited commitments by both parties. May go on for extend time. • Gain initial acceptance • Build a successful rel. ship. Expansion of rewards for each party in the relationship. • Get to know customers & their business better • Expand ways to help customer Commitment by both buyer & seller to an exclusive relationship • Interaction at levels between the buyer’s & seller’s org. • Early supplier involvement in dev. processes. Dissolution Total disengagement from the relationship. This may occur at any point in the relationship. • Look for warning signals • Attempt to reinitiate the relationship. 20
 4. 4: Factors Critical to Gaining Commitment to a Relationship Salespeople should be aware of factors that lead to committed relationships – • creating value, • meeting expectations & • building trust. 21
4. 4: Factors Critical to Gaining Commitment to a Relationship Salespeople should be aware of factors that lead to committed relationships – • creating value, • meeting expectations & • building trust. 21
 Creating Value • Value refers to the perception that the rewards exceed the costs associated with establishing and/or expanding a relationship. • Value may be low price, save time & labour. • Transactional relationship makes purchasing hassle free & easy, in the last 2 stages of purchasing. • Consultative customer relationships create value by helping customers solve problems & identify opportunities for growth in the 1 st 2 stages of purchasing. • Enterprice relationship is to create exceptional customer value in all 4 phases of the purchasing process. 22
Creating Value • Value refers to the perception that the rewards exceed the costs associated with establishing and/or expanding a relationship. • Value may be low price, save time & labour. • Transactional relationship makes purchasing hassle free & easy, in the last 2 stages of purchasing. • Consultative customer relationships create value by helping customers solve problems & identify opportunities for growth in the 1 st 2 stages of purchasing. • Enterprice relationship is to create exceptional customer value in all 4 phases of the purchasing process. 22
 Meeting Expectations • Involved parties develop expectations (referred to as rules/norms) with respect to acceptable conduct & performance. • This depends on company policies, individual preferences, national cultures. • Salesperson must be careful not to encourage unfavorable buyer expectations as a result of present behaviors. • At times cross functional teams are assigned to meet customer expectations. 23
Meeting Expectations • Involved parties develop expectations (referred to as rules/norms) with respect to acceptable conduct & performance. • This depends on company policies, individual preferences, national cultures. • Salesperson must be careful not to encourage unfavorable buyer expectations as a result of present behaviors. • At times cross functional teams are assigned to meet customer expectations. 23
 Building Trust • That an individual's word/promise can be believed. • Very important to buyers and sellers. 5 most important trust earning attributes of salespeople are: - dependability (complete promises) - competence (know what they are talking) - customer orientation (put buyers interest) - honesty (tell truth) - likeability (buyer enjoys knowing) 24
Building Trust • That an individual's word/promise can be believed. • Very important to buyers and sellers. 5 most important trust earning attributes of salespeople are: - dependability (complete promises) - competence (know what they are talking) - customer orientation (put buyers interest) - honesty (tell truth) - likeability (buyer enjoys knowing) 24


