5d54db019303ebb744288dc951a2676b.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 30
 Accessing Grid Resources via Portals and Workflow Tools Sriram Krishnan, Ph. D. sriram@sdsc. edu
Accessing Grid Resources via Portals and Workflow Tools Sriram Krishnan, Ph. D. sriram@sdsc. edu
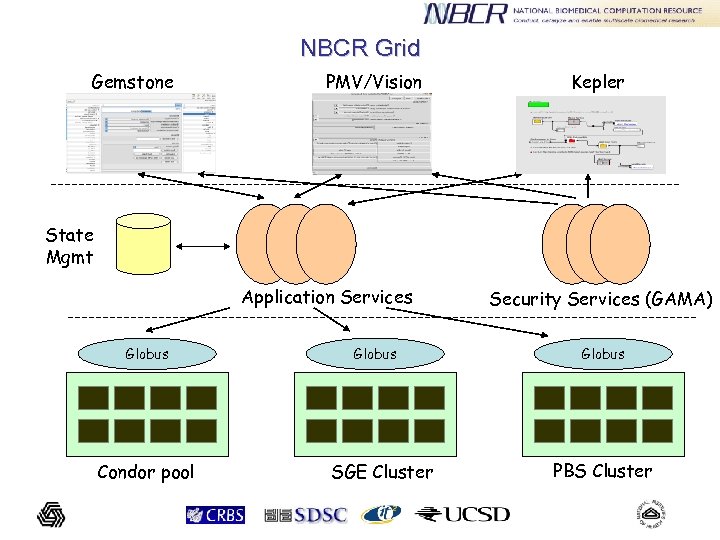 NBCR Grid Gemstone PMV/Vision Kepler State Mgmt Application Services Globus Condor pool Globus SGE Cluster Security Services (GAMA) Globus PBS Cluster
NBCR Grid Gemstone PMV/Vision Kepler State Mgmt Application Services Globus Condor pool Globus SGE Cluster Security Services (GAMA) Globus PBS Cluster
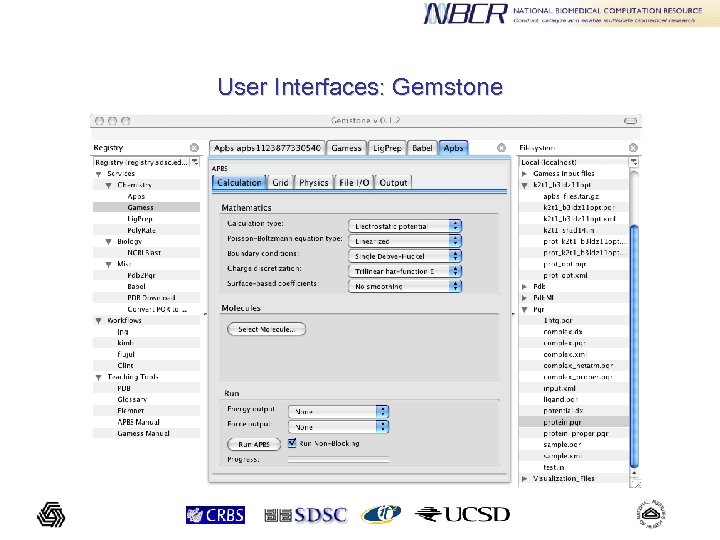 User Interfaces: Gemstone
User Interfaces: Gemstone
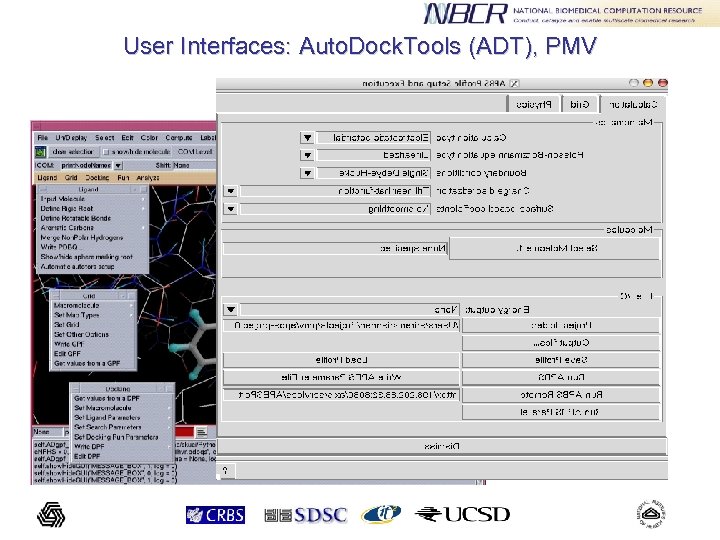 User Interfaces: Auto. Dock. Tools (ADT), PMV
User Interfaces: Auto. Dock. Tools (ADT), PMV
 User Interfaces: What is a Portal? • “A portal is a web based application that commonly provides personalization, single sign on, content aggregation from different sources and hosts the presentation layer of Information Systems”(JSR 168) • Grid/Science Portals build upon the familiar Web portal model, such as Yahoo or Amazon, to deliver the benefits of Grid computing to virtual communities of users, providing a single access point to Grid services and resources.
User Interfaces: What is a Portal? • “A portal is a web based application that commonly provides personalization, single sign on, content aggregation from different sources and hosts the presentation layer of Information Systems”(JSR 168) • Grid/Science Portals build upon the familiar Web portal model, such as Yahoo or Amazon, to deliver the benefits of Grid computing to virtual communities of users, providing a single access point to Grid services and resources.
 User Interfaces: Portals • Pros – Ubiquitous access to applications – No need to install complex software • Cons – Limited interaction with local desktop tools – Interfaces may not be rich enough for complex tasks such as visualization – Not very easy to make highly interactive interfaces
User Interfaces: Portals • Pros – Ubiquitous access to applications – No need to install complex software • Cons – Limited interaction with local desktop tools – Interfaces may not be rich enough for complex tasks such as visualization – Not very easy to make highly interactive interfaces
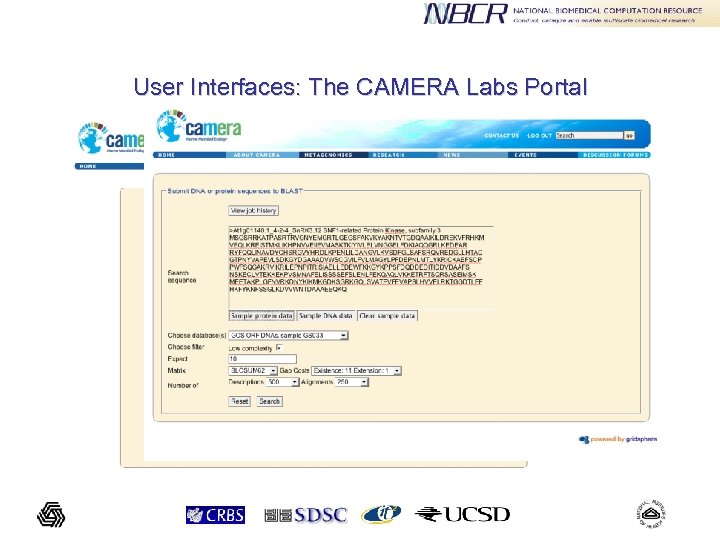 User Interfaces: The CAMERA Labs Portal
User Interfaces: The CAMERA Labs Portal
 CAMERA Labs Demo
CAMERA Labs Demo
 Portal Technology • Built on top of the Grid. Sphere Portal Framework – http: //www. gridsphere. org • JSR 168 Portlet API compliant – Similar to Servlet API in providing reusable Web applications – Ratified in August 2003 by vendors including BEA, Sun, IBM, Oracle, Plumtree, etc
Portal Technology • Built on top of the Grid. Sphere Portal Framework – http: //www. gridsphere. org • JSR 168 Portlet API compliant – Similar to Servlet API in providing reusable Web applications – Ratified in August 2003 by vendors including BEA, Sun, IBM, Oracle, Plumtree, etc
 What is a Portlet? • • Standardized packaging model to share portlet applications among portal vendors Builds off Servlet API and spec. so no major surprises for existing Java portal developers Supports window states and mode settings like desktop environment API provides useful methods for storing per user data and configuration settings
What is a Portlet? • • Standardized packaging model to share portlet applications among portal vendors Builds off Servlet API and spec. so no major surprises for existing Java portal developers Supports window states and mode settings like desktop environment API provides useful methods for storing per user data and configuration settings
 What makes Grid. Sphere different? • Already many other OS portals out there: – • A handy template build system using Apache Ant: – • • ant new-project Lightweight: no EJB, based on popular, robust libraries – • Jetspeed 2, u. Portal, String. Beans, Exo, Liferay, JBoss e. g. Hibernate for persistence Visual UI tags and beans makes presentation development much easier Support for the Grid!! – – Grid. Portlets offered as add-on webapp Provides Library and collection of portlets for: • Credential support, job launch (GRAM), data transfer (Grid. FTP) • Used by several Cyber. Infrastructure projects like BIRN, NBCR, GEON, CAMERA – Lots of reusable software!
What makes Grid. Sphere different? • Already many other OS portals out there: – • A handy template build system using Apache Ant: – • • ant new-project Lightweight: no EJB, based on popular, robust libraries – • Jetspeed 2, u. Portal, String. Beans, Exo, Liferay, JBoss e. g. Hibernate for persistence Visual UI tags and beans makes presentation development much easier Support for the Grid!! – – Grid. Portlets offered as add-on webapp Provides Library and collection of portlets for: • Credential support, job launch (GRAM), data transfer (Grid. FTP) • Used by several Cyber. Infrastructure projects like BIRN, NBCR, GEON, CAMERA – Lots of reusable software!
 Advanced Usage: Workflows • Need for automation of processes (scientific or otherwise) – An end-to-end application is typically more than a single application run – Must be reproducible and maintainable – Should be easy to compose from individual components
Advanced Usage: Workflows • Need for automation of processes (scientific or otherwise) – An end-to-end application is typically more than a single application run – Must be reproducible and maintainable – Should be easy to compose from individual components
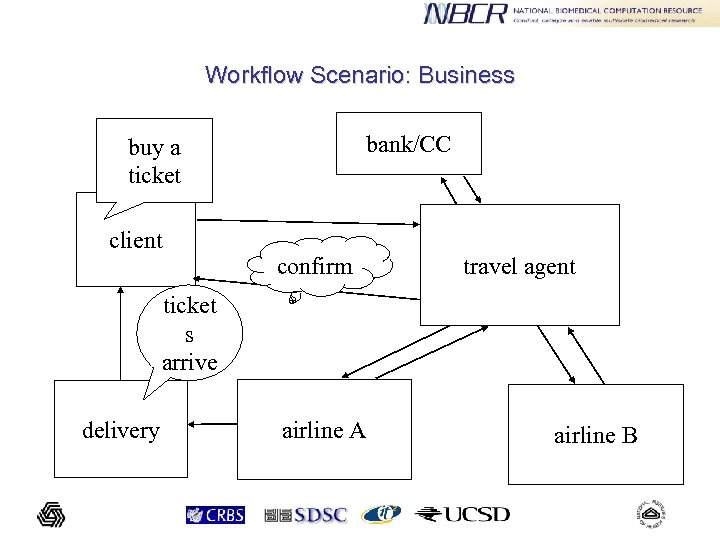 Workflow Scenario: Business bank/CC buy a ticket client confirm travel agent ticket s arrive delivery airline A airline B
Workflow Scenario: Business bank/CC buy a ticket client confirm travel agent ticket s arrive delivery airline A airline B
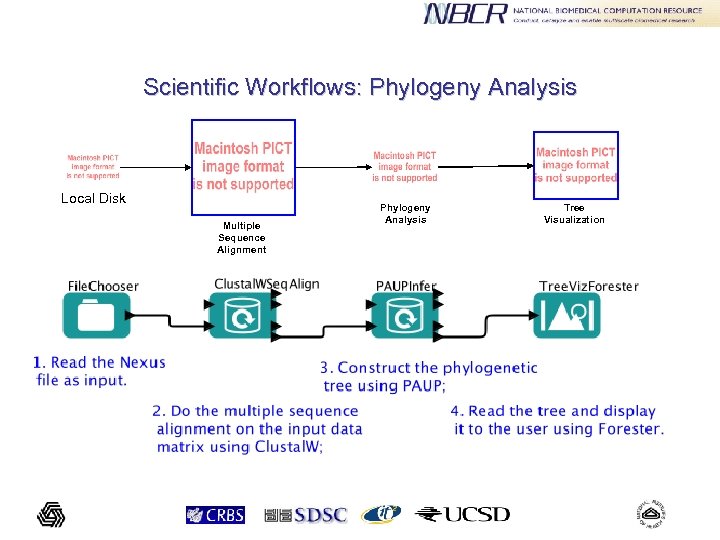 Scientific Workflows: Phylogeny Analysis Local Disk Multiple Sequence Alignment Phylogeny Analysis Tree Visualization
Scientific Workflows: Phylogeny Analysis Local Disk Multiple Sequence Alignment Phylogeny Analysis Tree Visualization
 Scientific Workflow Systems • Combination of – data integration, analysis, and visualization steps – larger, automated "scientific process" • Mission of scientific workflow systems – Promote “scientific discovery” by providing tools and methods to generate scientific workflows – Create an extensible and customizable graphical user interface for scientists from different scientific domains – Support computational experiment creation, execution, sharing, reuse and provenance – Design frameworks which define efficient ways to connect to the existing data and integrate heterogeneous data from multiple resources
Scientific Workflow Systems • Combination of – data integration, analysis, and visualization steps – larger, automated "scientific process" • Mission of scientific workflow systems – Promote “scientific discovery” by providing tools and methods to generate scientific workflows – Create an extensible and customizable graphical user interface for scientists from different scientific domains – Support computational experiment creation, execution, sharing, reuse and provenance – Design frameworks which define efficient ways to connect to the existing data and integrate heterogeneous data from multiple resources
 Why not just a Python script? • End-users who define, reuse, modify, and specialize workflows would find visual interfaces much easier than scripts – Typically also possible to compile scripts from designed workflows • Other advantages: – – Modular reuse, application interoperability Debugging and monitoring Automated data management (e. g. provenance) Validation (e. g. data, structural, semantic typing) • From integrated modeling to execution, optimization, and archival
Why not just a Python script? • End-users who define, reuse, modify, and specialize workflows would find visual interfaces much easier than scripts – Typically also possible to compile scripts from designed workflows • Other advantages: – – Modular reuse, application interoperability Debugging and monitoring Automated data management (e. g. provenance) Validation (e. g. data, structural, semantic typing) • From integrated modeling to execution, optimization, and archival
 Kepler: A Scientific Workflow System www. kepler-project. org • 1 st Beta release (June 2, 2006) • Builds upon the open-source Ptolemy II framework Ptolemy II: A laboratory for investigating design KEPLER: A problem-solving environment for Scientific Workflow KEPLER = “Ptolemy II + X” for Scientific Workflows
Kepler: A Scientific Workflow System www. kepler-project. org • 1 st Beta release (June 2, 2006) • Builds upon the open-source Ptolemy II framework Ptolemy II: A laboratory for investigating design KEPLER: A problem-solving environment for Scientific Workflow KEPLER = “Ptolemy II + X” for Scientific Workflows
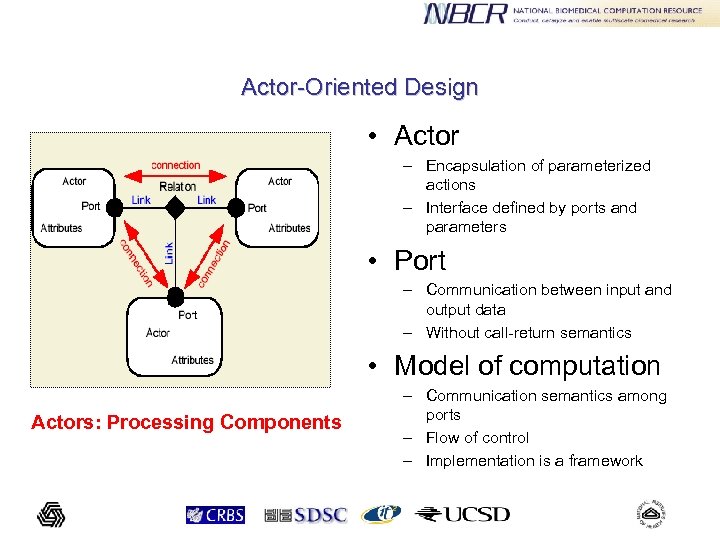 Actor-Oriented Design • Actor – Encapsulation of parameterized actions – Interface defined by ports and parameters • Port – Communication between input and output data – Without call-return semantics • Model of computation Actors: Processing Components – Communication semantics among ports – Flow of control – Implementation is a framework
Actor-Oriented Design • Actor – Encapsulation of parameterized actions – Interface defined by ports and parameters • Port – Communication between input and output data – Without call-return semantics • Model of computation Actors: Processing Components – Communication semantics among ports – Flow of control – Implementation is a framework
 Available Actors • • Generic Web Service Client and Web Service Harvester Customizable RDBMS query and update Command-line wrapper tools (local, ssh, scp, ftp, etc. ) Some Grid actors – • • Globus Job runner, Grid. FTP-based file access, Proxy Certificate Generator SRB support Imaging, Visualization Support Textual and Graphical Output Some domain-specific actors for Geosciences and Bioinformatics
Available Actors • • Generic Web Service Client and Web Service Harvester Customizable RDBMS query and update Command-line wrapper tools (local, ssh, scp, ftp, etc. ) Some Grid actors – • • Globus Job runner, Grid. FTP-based file access, Proxy Certificate Generator SRB support Imaging, Visualization Support Textual and Graphical Output Some domain-specific actors for Geosciences and Bioinformatics
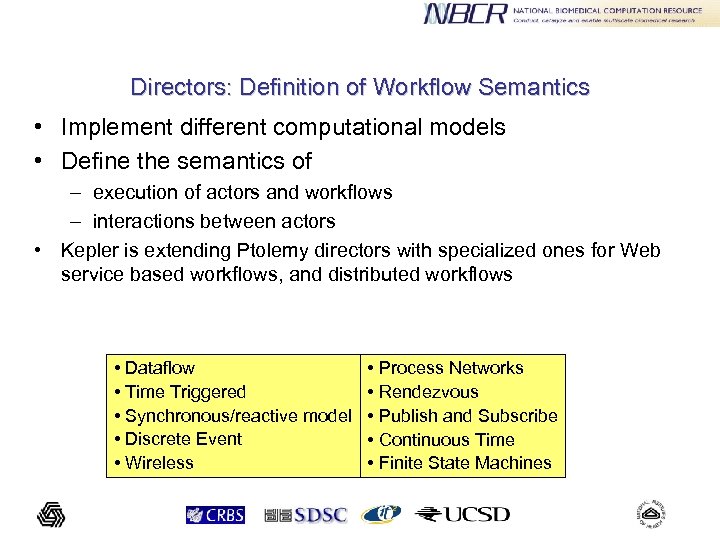 Directors: Definition of Workflow Semantics • Implement different computational models • Define the semantics of – execution of actors and workflows – interactions between actors • Kepler is extending Ptolemy directors with specialized ones for Web service based workflows, and distributed workflows • Dataflow • Time Triggered • Synchronous/reactive model • Discrete Event • Wireless • Process Networks • Rendezvous • Publish and Subscribe • Continuous Time • Finite State Machines
Directors: Definition of Workflow Semantics • Implement different computational models • Define the semantics of – execution of actors and workflows – interactions between actors • Kepler is extending Ptolemy directors with specialized ones for Web service based workflows, and distributed workflows • Dataflow • Time Triggered • Synchronous/reactive model • Discrete Event • Wireless • Process Networks • Rendezvous • Publish and Subscribe • Continuous Time • Finite State Machines
 Dataflow as a Computation Model • Dataflow: Abstract representation of how data flows in the system • A dataflow program: a graph – Nodes represent operations, edges represent data paths • Sound, simple, powerful model of parallel computation – NOT having a locus of control makes it simple! – Naturally distributed model of computation: – Asynchronous: Many actors can be ready to fire simultaneously – Execution ("firing") of a node starts when (matching) data is available at a node's input ports. – Locally controlled events – Events correspond to the “firing” of an actor – Actor: – A single instruction – A sequence of instructions – Actors fire when all the inputs are available
Dataflow as a Computation Model • Dataflow: Abstract representation of how data flows in the system • A dataflow program: a graph – Nodes represent operations, edges represent data paths • Sound, simple, powerful model of parallel computation – NOT having a locus of control makes it simple! – Naturally distributed model of computation: – Asynchronous: Many actors can be ready to fire simultaneously – Execution ("firing") of a node starts when (matching) data is available at a node's input ports. – Locally controlled events – Events correspond to the “firing” of an actor – Actor: – A single instruction – A sequence of instructions – Actors fire when all the inputs are available
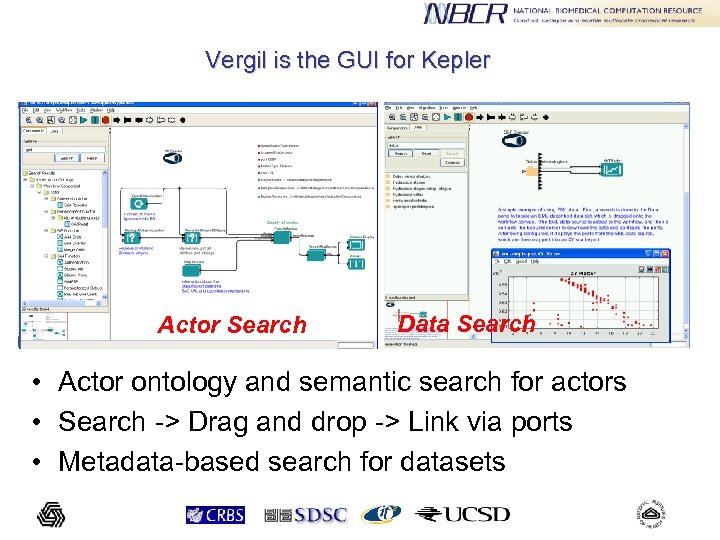 Vergil is the GUI for Kepler Actor Search Data Search • Actor ontology and semantic search for actors • Search -> Drag and drop -> Link via ports • Metadata-based search for datasets
Vergil is the GUI for Kepler Actor Search Data Search • Actor ontology and semantic search for actors • Search -> Drag and drop -> Link via ports • Metadata-based search for datasets
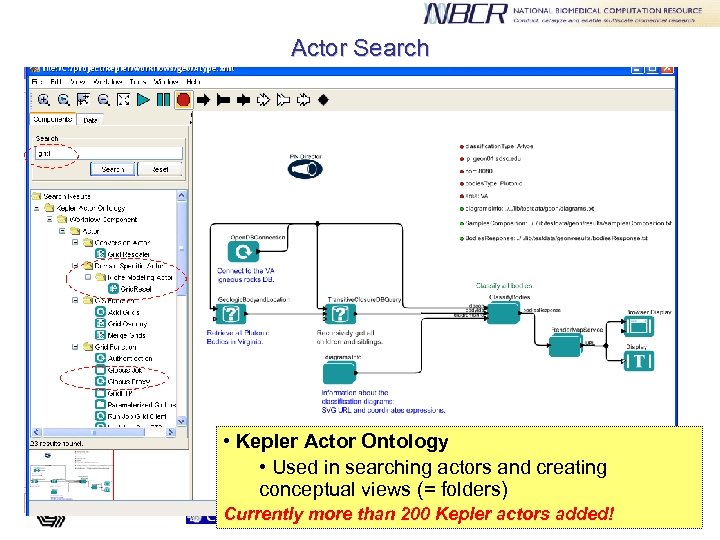 Actor Search • Kepler Actor Ontology • Used in searching actors and creating conceptual views (= folders) Currently more than 200 Kepler actors added!
Actor Search • Kepler Actor Ontology • Used in searching actors and creating conceptual views (= folders) Currently more than 200 Kepler actors added!
 Kepler Provenance Framework • OPTIONAL! – Modeled as a separate concern in the system – Listens to the execution and saves information customized by a set of parameters • • Context: who, what, where, when, and why that is associated with the run Input data and its associated metadata Workflow outputs and intermediate data products Workflow definition (entities, parameters, connections): a specification of what exists in the workflow and can have a context of its own • Information about the workflow evolution -- workflow trail • Types of Provenance Information: – Data provenance • Intermediate and end results including files and db references – Process provenance • Keep the workflow definition with data and parameters used in the run – Error and execution logs – Workflow design provenance
Kepler Provenance Framework • OPTIONAL! – Modeled as a separate concern in the system – Listens to the execution and saves information customized by a set of parameters • • Context: who, what, where, when, and why that is associated with the run Input data and its associated metadata Workflow outputs and intermediate data products Workflow definition (entities, parameters, connections): a specification of what exists in the workflow and can have a context of its own • Information about the workflow evolution -- workflow trail • Types of Provenance Information: – Data provenance • Intermediate and end results including files and db references – Process provenance • Keep the workflow definition with data and parameters used in the run – Error and execution logs – Workflow design provenance
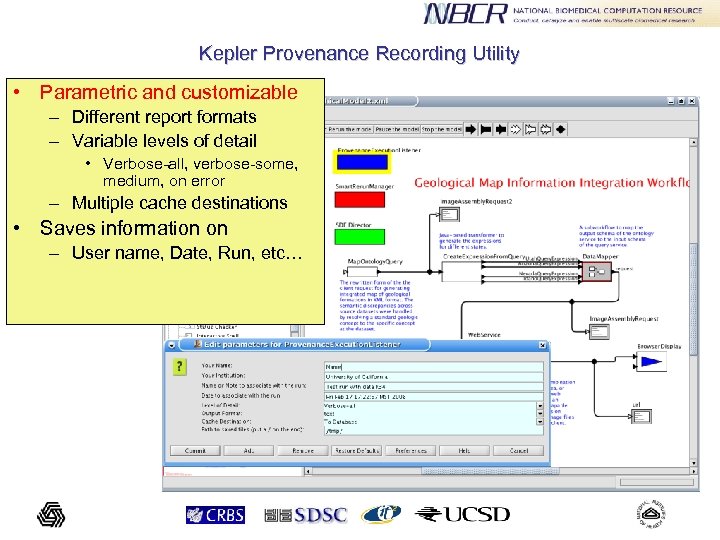 Kepler Provenance Recording Utility • Parametric and customizable – Different report formats – Variable levels of detail • Verbose-all, verbose-some, medium, on error – Multiple cache destinations • Saves information on – User name, Date, Run, etc…
Kepler Provenance Recording Utility • Parametric and customizable – Different report formats – Variable levels of detail • Verbose-all, verbose-some, medium, on error – Multiple cache destinations • Saves information on – User name, Date, Run, etc…
 Kepler Basics: Hello World Demo
Kepler Basics: Hello World Demo
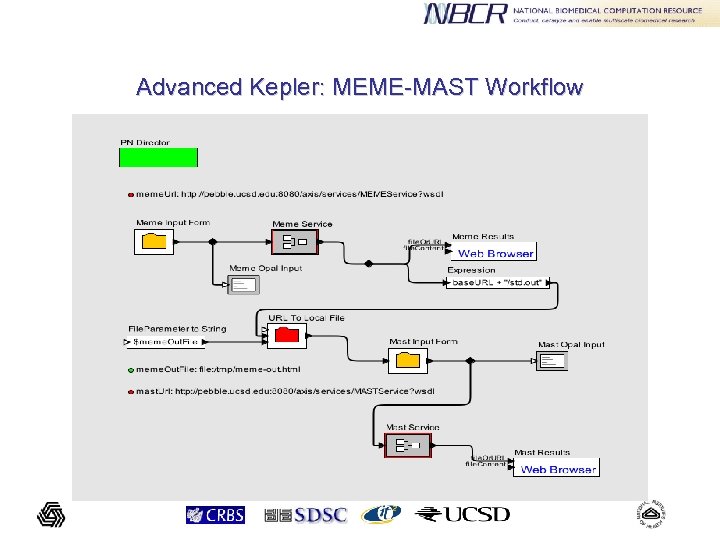 Advanced Kepler: MEME-MAST Workflow
Advanced Kepler: MEME-MAST Workflow
 Advantages of Scientific Workflow Systems • Formalization of the scientific process • Easy to share, adapt and reuse – Deployable, customizable, extensible • Management of complexity and usability – Support for hierarchical composition – Interfaces to different technologies from a unified interface – Can be annotated with domain-knowledge • Tracking provenance of the data and processes – Keep the association of results to processes – Make it easier to validate/regenerate results and processes – Enable comparison between different workflow versions • Execution monitoring and fault tolerance • Interaction with multiple tools and resources at once
Advantages of Scientific Workflow Systems • Formalization of the scientific process • Easy to share, adapt and reuse – Deployable, customizable, extensible • Management of complexity and usability – Support for hierarchical composition – Interfaces to different technologies from a unified interface – Can be annotated with domain-knowledge • Tracking provenance of the data and processes – Keep the association of results to processes – Make it easier to validate/regenerate results and processes – Enable comparison between different workflow versions • Execution monitoring and fault tolerance • Interaction with multiple tools and resources at once
 Summary • Presented access to Grid applications via Portals and Workflow tools • References – PMV, ADT: http: //mgltools. scripps. edu/ – CAMERA: http: //camera. calit 2. net – Grid. Sphere: http: //www. gridsphere. org – Kepler: http: //www. kepler-project. org
Summary • Presented access to Grid applications via Portals and Workflow tools • References – PMV, ADT: http: //mgltools. scripps. edu/ – CAMERA: http: //camera. calit 2. net – Grid. Sphere: http: //www. gridsphere. org – Kepler: http: //www. kepler-project. org
 Acknowledgements • CAMERA labs portal built in conjunction with the rest of the CAMERA team • Several slides borrowed from Kepler tutorials presented by Ilkay Altintas [altintas@sdsc. edu]
Acknowledgements • CAMERA labs portal built in conjunction with the rest of the CAMERA team • Several slides borrowed from Kepler tutorials presented by Ilkay Altintas [altintas@sdsc. edu]


