c021b4d69307c64783ae1d269696477f.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 38

Accessibility and Drupal: Where do you begin? Communications & Marketing Wright State University (not accessibility experts) Jessi Sparks (jessica. sparks@wright. edu) Mark Anderson (mark. anderson@wright. edu)

Why Drupal?

Choosing Drupal for Wright State CMS Selection Committee • Technology • Accessibility • Branding Committee Recommendations • Drupal • Web Team • Central IT Drupal. Con Chicago • Beta • Usability • Drupal Rebuild

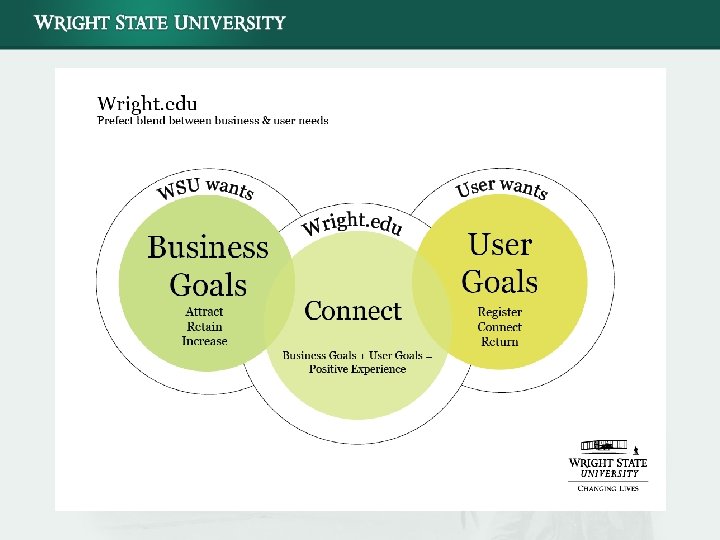
User Experience Considerations Accessibility Web accessibility means that people with disabilities can use the Web. More specifically, Web accessibility means that people with disabilities can perceive, understand, navigate, and interact with the Web, and that they can contribute to the Web. www. w 3. org/WAI/intro/accessibility. php Usability means making products and systems easier to use, and matching them more closely to user needs and requirements. www. usabilitynet. org/management/b_what. htm
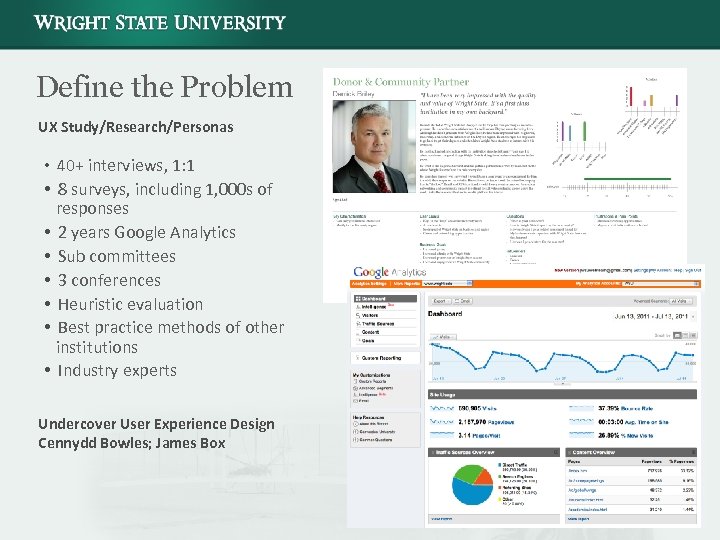
Define the Problem UX Study/Research/Personas • 40+ interviews, 1: 1 • 8 surveys, including 1, 000 s of responses • 2 years Google Analytics • Sub committees • 3 conferences • Heuristic evaluation • Best practice methods of other institutions • Industry experts Undercover User Experience Design Cennydd Bowles; James Box
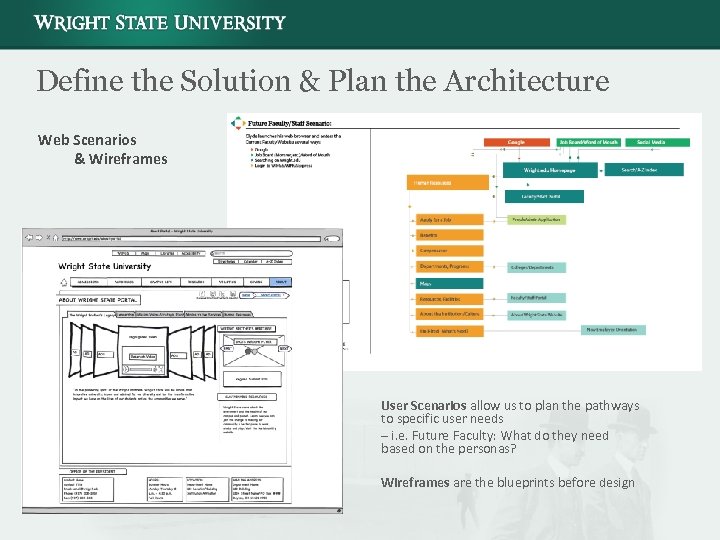
Define the Solution & Plan the Architecture Web Scenarios & Wireframes User Scenarios allow us to plan the pathways to specific user needs – i. e. Future Faculty: What do they need based on the personas? Wireframes are the blueprints before design

Why the Urgency on Accessibility?
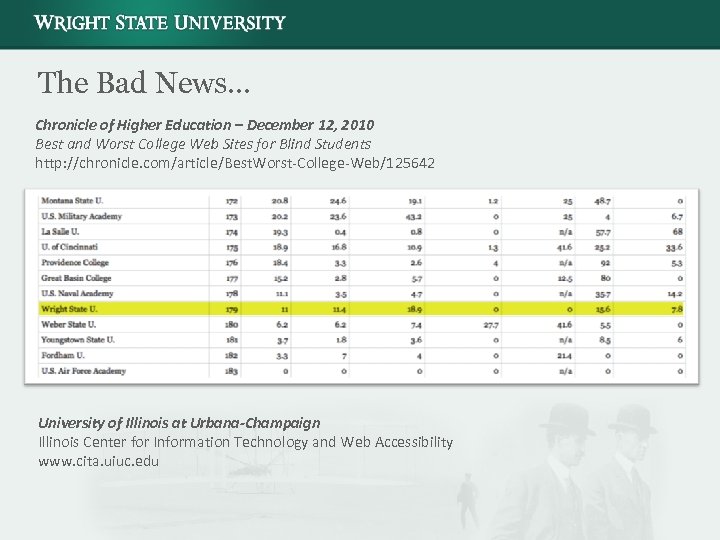
The Bad News… Chronicle of Higher Education – December 12, 2010 Best and Worst College Web Sites for Blind Students http: //chronicle. com/article/Best. Worst-College-Web/125642 University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign Illinois Center for Information Technology and Web Accessibility www. cita. uiuc. edu

Why Is Accessibility Important? It’s the law Currently there are only federal and state requirements for government websites from the Americans with Disabilities Act of 1973, however it’s clear this will be an ongoing issue, and legal precedents set recently in the commercial and public sectors will only increase It hurts your bottom line to ignore • Stress the importance to upper and middle management, buy-in is key • Remember 25% of internet users are disabled—do the math! That’s 1 in 4 opportunities to miss out in e-commerce, advertising, and promotions. * • Lawsuits are expensive • Target Corporation: $6 Million in Damages + Court-ordered $145, 000 in Certification Fees** • Florida State University, Arizona State University, and Penn State University It’s the right thing to do *An Idiot’s Guide To Accessible Website Design “According to a report by the Danish Center for Accessibility, as many as 25% of the world’s Internet users have some sort of visual, auditory or mobility disability. “ http: //webdesignledger. com/tips/an-idiot%E 2%80%99 s-guide-to-accessible-website-design Accessed on 11/22 ** Target lawsuit settled http: //webaim. org/blog/target-lawsuit-settled/ accessed 11 -29 -11

Accessibility Basics

Examples of Accessibility User by Profiles Visual Impairments Blind users Low vision Motor Impairments Device independent (cannot use input device) Learning Disability Impairments Dyslexia (reading impairment) Dyscalculia (math impairment) Audial Impairments Hearing Loss

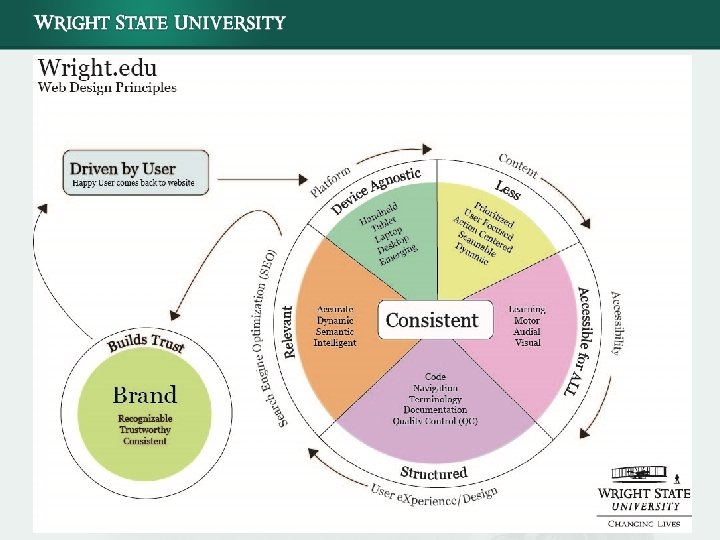
Basic Accessibility Considerations for Content Copy & Layout • • • Check color contrast: Not about “red and green, ” but about contrast ratios Avoid PDF-only delivery: Include html option for each PDF, if you can Do not use color as a directional tool (i. e. “Click the blue link”) Avoid tables for layout: Tables should only be used for tabular data; use CSS for layout Text size should be able to be increased or decreased Institute Aria tagging if you can Avoid animations on your website or implement a way to disable animations Allow users to tab from section to section, instead of being reliant on a mouse Provide text-only option if all else fails that syncs to real-time content Avoid embedding math equations by image; use Math. ML if need be

Basic Accessibility Considerations for Content Linking Remember the word “Link” is being inserted right before or after your text by the screen reader • • Avoid link references embedded in the paragraphs, try to place at the end of copy Use directional statements, “Visit the Bursar Website now” not “Click Here” Always label the file in parentheses, so users and screen readers are aware of a download, “Common Text (PDF)” not “Common Text” Provide skip navigation feature

Basic Accessibility Considerations for Content Media • Videos and/or audio should not be Flash, move to H 264 (HTML 5) • • Remove Flash from your website as its inaccessible (and will be depreciated soon) Have synchronized transcript for videos if possible; or at least have HTML-based text under the video • Good news! You. Tube already does this. Use the You. Tube transcription service Images • • • Use Alt Tags for ALL images Avoid embedding text into graphics that cannot be replaced by straight HTML Images should always be used as supplemental content. Avoid data delivery in images only (i. e. graphs and charts only in an image) Have an HTML version with data only if need be (i. e. Say “ 67% of college students”) Files • Avoid PDF-only delivery; have an HTML option for each PDF option if you can

Basic Accessibility Considerations for Content Training End Users Education of users is really key; teaching users the basics will help improve overall accessibility Mobile is Key Consider “mobile-friendliness, ” “accessible-friendliness” because many of the same considerations for mobile apply for accessibility

Tips to Implement an Accessibility Plan

Houston…We Have a Problem • Admit your site has a problem • Write up a list of accessibility issues you know of first-hand, then compare this to your checklist of bugs to fix after you write and develop your plan • You may instinctively know more than you realize about your website’s user interface, or lack thereof
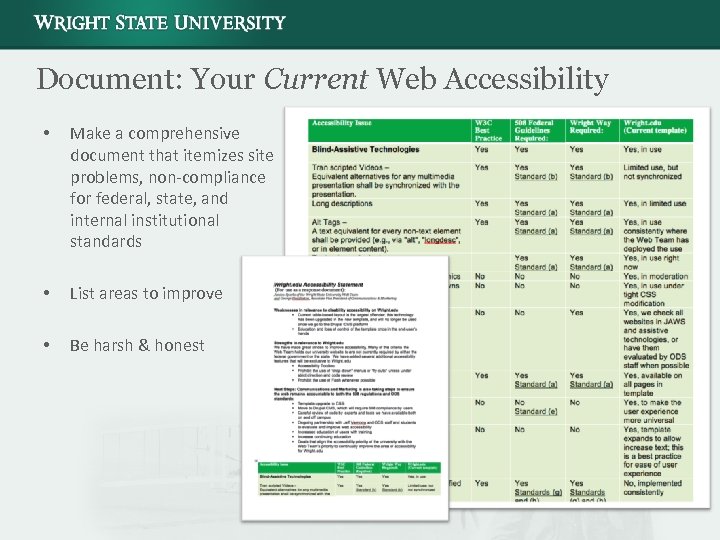
Document: Your Current Web Accessibility • Make a comprehensive document that itemizes site problems, non-compliance for federal, state, and internal institutional standards • List areas to improve • Be harsh & honest

Get Compassionate • Understand the user problems • Experience first-hand the stumbling blocks http: //dotsub. com/view/121318 e 1 -4 f 35 -459 b-a 91 c-d 07 bb 275310 e • Don’t assume anything; throw out your misconceptions • Watch impairment personas provided by the W 3 C http: //www. w 3. org/WAI/intro/people-use-web/

Get Passionate! • Know the difference between 508 Compliance and WCAG A-AAA Priorities • Read the entire specification • Read any institutional regulations required by your client and/or office • Familiarity is key as you will have to draft the guidelines, check your team’s work, and/or work through problems with developers

Grab the Ball Take Ownership • Appoint an “Accessibility Czar” This should be a primary task assigned for one member of your team • It’s not the responsibility of your “____” (fill in the blank) team. • It’s your whole team’s responsibility Each member above and below should have buy in

Join the Pack Attend conferences on accessibility • Focus on technology, but be open to the whole experience • Attend non-technology related sessions • Some of the most riveting experiences at conferences don’t have anything to do with technology (This session at Ohio. Drupal. Camp counts)

Location, Location • Find users and experts in your office or institution Talk with HR and/or your ODS office • Don’t have any? Network with organizations that support these users for options • Illicit their help to solve this problem together – Honesty – Communication

Follow the Little Birdie Follow some accessibility experts on Twitter • Standards. Sherpa • webaxe • Stcaccess Get connected, ask questions, join groups. Drupal Accessibility Groups: groups. drupal. org Accessibility
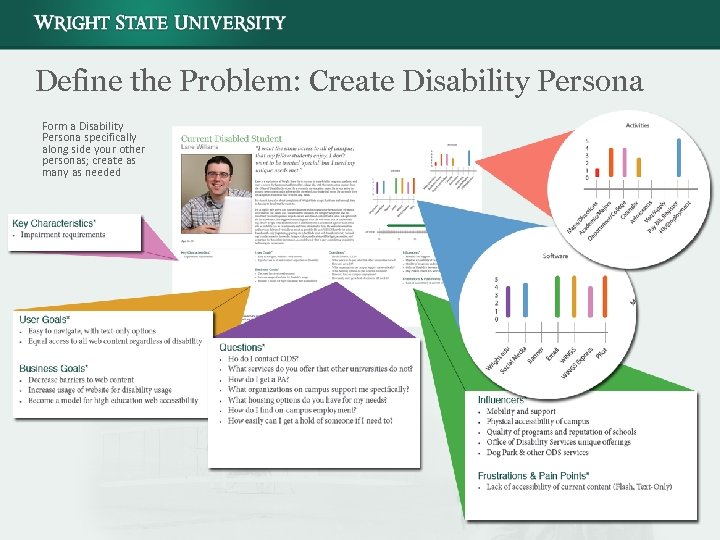
Define the Problem: Create Disability Persona Form a Disability Persona specifically along side your other personas; create as many as needed
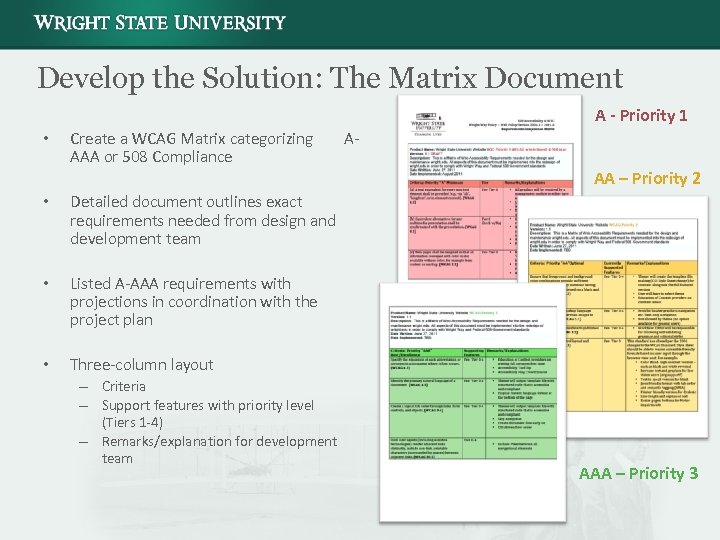
Develop the Solution: The Matrix Document A - Priority 1 • Create a WCAG Matrix categorizing AAA or 508 Compliance • Listed A-AAA requirements with projections in coordination with the project plan • AA – Priority 2 Detailed document outlines exact requirements needed from design and development team • A- Three-column layout – Criteria – Support features with priority level (Tiers 1 -4) – Remarks/explanation for development team AAA – Priority 3

Organize Efforts, Keep Moving Forward • Make deadlines and stick to them • Have disabled user group; solicit feedback • Test and re-test • Good accessibility user experience doesn’t stop—keep building on the foundation you have set

The Demo wright. edu Accessibility and Usability Features

www. wright. edu Ticket System • Content type • Views • Custom code • Email notifications • Change log Tooltips Menu Structure • Mega menus • Flat structure

Drupal’s Accessibility D 7 core – WCAG 2. 0 and ATAG 2. 0 Some WAI-ARIA support Other improvements: • • Search engine form and presentation Drag-and-drop functionality Color contrast and intensity Adding skip navigation to core themes Image handling Form labeling Removing duplicate or null tags http: //drupal. org/about/accessibility

Drupal’s Accessibility Resources Modules that Improve Accessibility http: //groups. drupal. org/node/85199 Theme switching Theme changes Text resizing HTML clean up/modification

Drupal’s Accessibility Resources Drupal Groups http: //groups. drupal. org/accessibility Monthly Skype Calls, Dec. 13 th Roadmap Discussions Technical Help Wiki Drupal Documentation http: //drupal. org/node/394094

Theming for Accessibility Tool for testing—Voice over on OSX Zen • Well documented • Does not really have accessibility features built in off the top HTML Changes • ARIA, defining CSS Classes Jquery • Be careful (hiding things) CSS • Readable by screen readers but hidden from view • Place items off screen

Theming for Accessibility Text-only and high-contrast theme changes Not using sub themes Get Variables • Did not want to rely on cookies due to embedding of pages on other systems • Google ranks Get Variables as separate pages • Poor for SEO • Robots meta tag to ignore Get Variable pages of same content • Server side, which allows us to kill Javascript Once Get Variable is set • Reset CSS • Reset Javascript • Set new CSS

Theming for Accessibility Disabling animations • Setting a hash tag • Set a cookie Use hash tags as they do not compromise SEO • Not embedding pages with this feature • Client side

Questions? Communications & Marketing Wright State University Jessi Sparks (jessica. sparks@wright. edu) Mark Anderson (mark. anderson@wright. edu)
c021b4d69307c64783ae1d269696477f.ppt