f768571b04f0187e60f3a8c98e522c08.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 31
 ACCESS CONTROL: THE NEGLECTED FRONTIER Ravi Sandhu George Mason University
ACCESS CONTROL: THE NEGLECTED FRONTIER Ravi Sandhu George Mason University
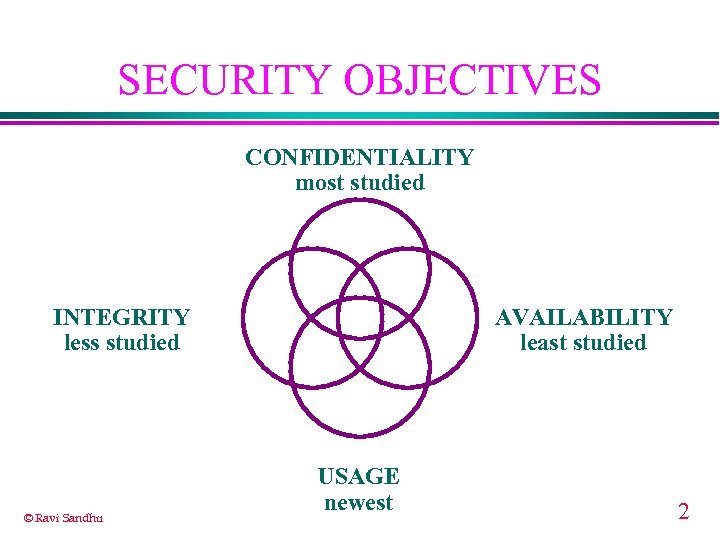 SECURITY OBJECTIVES CONFIDENTIALITY most studied INTEGRITY less studied © Ravi Sandhu AVAILABILITY least studied USAGE newest 2
SECURITY OBJECTIVES CONFIDENTIALITY most studied INTEGRITY less studied © Ravi Sandhu AVAILABILITY least studied USAGE newest 2
 SECURITY TECHNOLOGIES u Access Control u Cryptography u Audit and Intrusion Detection u Authentication u Assurance u Risk Analysis u. . . © Ravi Sandhu 3
SECURITY TECHNOLOGIES u Access Control u Cryptography u Audit and Intrusion Detection u Authentication u Assurance u Risk Analysis u. . . © Ravi Sandhu 3
 CRYPTOGRAPHY LIMITATIONS u Cryptography cannot protect confidentiality and integrity of l data, keys, software in end systems u Prevent or detect use of covert channels © Ravi Sandhu 4
CRYPTOGRAPHY LIMITATIONS u Cryptography cannot protect confidentiality and integrity of l data, keys, software in end systems u Prevent or detect use of covert channels © Ravi Sandhu 4
 AUDIT AND INTRUSION DETECTION LIMITATIONS u Intrusion detection cannot by itself protect audit data and audit collection and analysis software l prevent security breaches l protect against covert channels l © Ravi Sandhu 5
AUDIT AND INTRUSION DETECTION LIMITATIONS u Intrusion detection cannot by itself protect audit data and audit collection and analysis software l prevent security breaches l protect against covert channels l © Ravi Sandhu 5
 ACCESS CONTROL LIMITATIONS u Access control cannot by itself protect data in transit or storage on an insecure medium l safeguard against misuse by authorized users l protect against covert channels l © Ravi Sandhu 6
ACCESS CONTROL LIMITATIONS u Access control cannot by itself protect data in transit or storage on an insecure medium l safeguard against misuse by authorized users l protect against covert channels l © Ravi Sandhu 6
 AUTHENTICATION LIMITATIONS u By itself authentication does very little but what it does is critical u pre-requisite for effective cryptography l access control l intrusion detection l © Ravi Sandhu 7
AUTHENTICATION LIMITATIONS u By itself authentication does very little but what it does is critical u pre-requisite for effective cryptography l access control l intrusion detection l © Ravi Sandhu 7
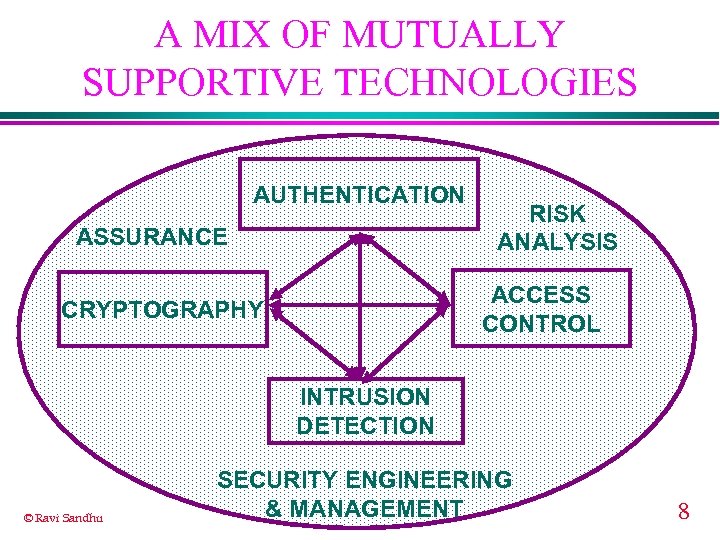 A MIX OF MUTUALLY SUPPORTIVE TECHNOLOGIES AUTHENTICATION ASSURANCE RISK ANALYSIS ACCESS CONTROL CRYPTOGRAPHY INTRUSION DETECTION © Ravi Sandhu SECURITY ENGINEERING & MANAGEMENT 8
A MIX OF MUTUALLY SUPPORTIVE TECHNOLOGIES AUTHENTICATION ASSURANCE RISK ANALYSIS ACCESS CONTROL CRYPTOGRAPHY INTRUSION DETECTION © Ravi Sandhu SECURITY ENGINEERING & MANAGEMENT 8
 CLASSICAL ACCESS CONTROL DOCTRINE u Lattice-based mandatory access control (MAC) strong l too strong l not strong enough l u Owner-based discretionary access control (DAC) too weak l © Ravi Sandhu too confused l 9
CLASSICAL ACCESS CONTROL DOCTRINE u Lattice-based mandatory access control (MAC) strong l too strong l not strong enough l u Owner-based discretionary access control (DAC) too weak l © Ravi Sandhu too confused l 9
 ISSUES IN LATTICE-BASED MAC u MAC enforces one-directional information flow in a lattice of security labels u can be used for aspects of confidentiality l integrity l aggregation (Chinese Walls) l © Ravi Sandhu 10
ISSUES IN LATTICE-BASED MAC u MAC enforces one-directional information flow in a lattice of security labels u can be used for aspects of confidentiality l integrity l aggregation (Chinese Walls) l © Ravi Sandhu 10
 PROBLEMS WITH LATTICEBASED MAC u does not protect against covert channels and inference l not strong enough u inappropriate l © Ravi Sandhu too strong 11
PROBLEMS WITH LATTICEBASED MAC u does not protect against covert channels and inference l not strong enough u inappropriate l © Ravi Sandhu too strong 11
 ISSUES IN OWNER-BASED DAC u negative “rights” u inheritance of rights l interaction between positive and negative rights u grant flag u delegation of identity u temporal and conditional authorization © Ravi Sandhu 12
ISSUES IN OWNER-BASED DAC u negative “rights” u inheritance of rights l interaction between positive and negative rights u grant flag u delegation of identity u temporal and conditional authorization © Ravi Sandhu 12
 PROBLEMS WITH OWNERBASED DAC u does l not control information flow too weak u inappropriate in many situations too weak l too confused l © Ravi Sandhu 13
PROBLEMS WITH OWNERBASED DAC u does l not control information flow too weak u inappropriate in many situations too weak l too confused l © Ravi Sandhu 13
 BEYOND OWNER-BASED DAC u separation between ability to use a right l to grant a right l u non-discretionary l © Ravi Sandhu elements user who can use a right should not be able to grant it and vice versa 14
BEYOND OWNER-BASED DAC u separation between ability to use a right l to grant a right l u non-discretionary l © Ravi Sandhu elements user who can use a right should not be able to grant it and vice versa 14
 NON-DISCRETIONARY (BEYOND LATTICE-BASED MAC) u control of administrative scope rights that can be granted l to whom rights can be granted l u rights that cannot be simultaneously granted to same user u rights that cannot be granted to too many users © Ravi Sandhu 15
NON-DISCRETIONARY (BEYOND LATTICE-BASED MAC) u control of administrative scope rights that can be granted l to whom rights can be granted l u rights that cannot be simultaneously granted to same user u rights that cannot be granted to too many users © Ravi Sandhu 15
 WHAT IS THE POLICY IN NONDISCRETIONARY ACCESS CONTROL? u Non-discretionary access control is a means to articulate policy u does not incorporate policy but does support security principles least privilege l abstract operations l separation of duties l © Ravi Sandhu 16
WHAT IS THE POLICY IN NONDISCRETIONARY ACCESS CONTROL? u Non-discretionary access control is a means to articulate policy u does not incorporate policy but does support security principles least privilege l abstract operations l separation of duties l © Ravi Sandhu 16
 ISSUES IN NON-DISCRETIONARY ACCESS CONTROL u models for non-discretionary propagation of access rights u role-based access control (RBAC) u task-based authorization (TBA) © Ravi Sandhu 17
ISSUES IN NON-DISCRETIONARY ACCESS CONTROL u models for non-discretionary propagation of access rights u role-based access control (RBAC) u task-based authorization (TBA) © Ravi Sandhu 17
 NON-DISCRETIONARY PROPAGATION MODELS u HRU, 1976 u TAKE-GRANT, 1976 -82 u SPM/ESPM, 1985 -92 u TAM/ATAM, 1992 onwards © Ravi Sandhu 18
NON-DISCRETIONARY PROPAGATION MODELS u HRU, 1976 u TAKE-GRANT, 1976 -82 u SPM/ESPM, 1985 -92 u TAM/ATAM, 1992 onwards © Ravi Sandhu 18
 NON-DISCRETIONARY PROPAGATION MODELS u type-based non-discretionary controls u rights that authorize propagation can be separate or closely related to right being propagated u testing for absence of rights is essential for dynamic separation policies © Ravi Sandhu 19
NON-DISCRETIONARY PROPAGATION MODELS u type-based non-discretionary controls u rights that authorize propagation can be separate or closely related to right being propagated u testing for absence of rights is essential for dynamic separation policies © Ravi Sandhu 19
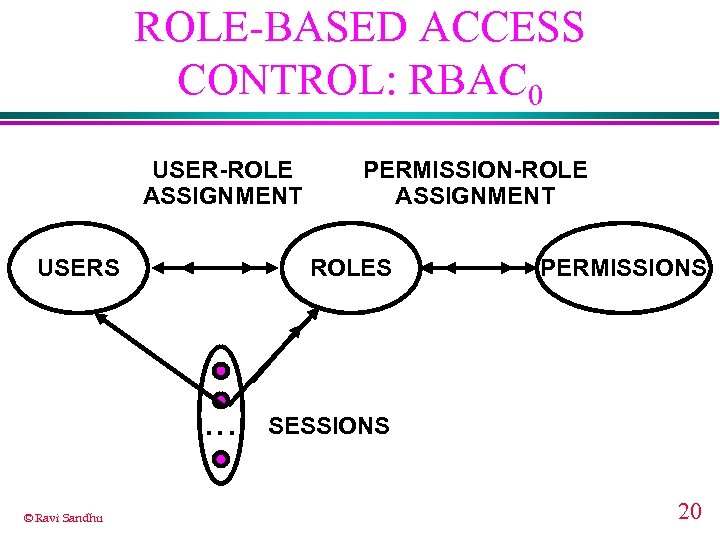 ROLE-BASED ACCESS CONTROL: RBAC 0 USER-ROLE ASSIGNMENT USERS ROLES . . . © Ravi Sandhu PERMISSION-ROLE ASSIGNMENT PERMISSIONS SESSIONS 20
ROLE-BASED ACCESS CONTROL: RBAC 0 USER-ROLE ASSIGNMENT USERS ROLES . . . © Ravi Sandhu PERMISSION-ROLE ASSIGNMENT PERMISSIONS SESSIONS 20
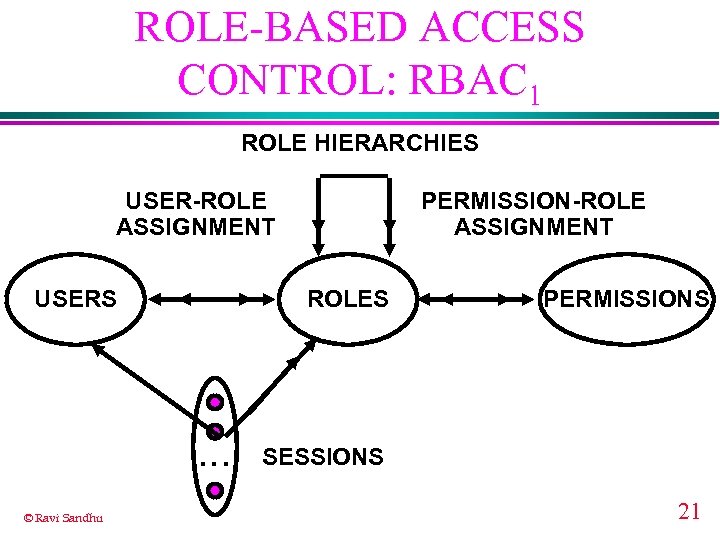 ROLE-BASED ACCESS CONTROL: RBAC 1 ROLE HIERARCHIES USER-ROLE ASSIGNMENT USERS ROLES . . . © Ravi Sandhu PERMISSION-ROLE ASSIGNMENT PERMISSIONS SESSIONS 21
ROLE-BASED ACCESS CONTROL: RBAC 1 ROLE HIERARCHIES USER-ROLE ASSIGNMENT USERS ROLES . . . © Ravi Sandhu PERMISSION-ROLE ASSIGNMENT PERMISSIONS SESSIONS 21
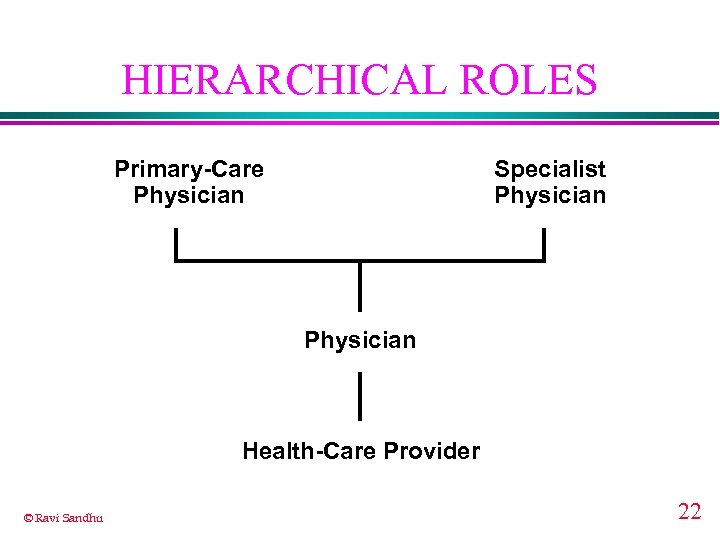 HIERARCHICAL ROLES Primary-Care Physician Specialist Physician Health-Care Provider © Ravi Sandhu 22
HIERARCHICAL ROLES Primary-Care Physician Specialist Physician Health-Care Provider © Ravi Sandhu 22
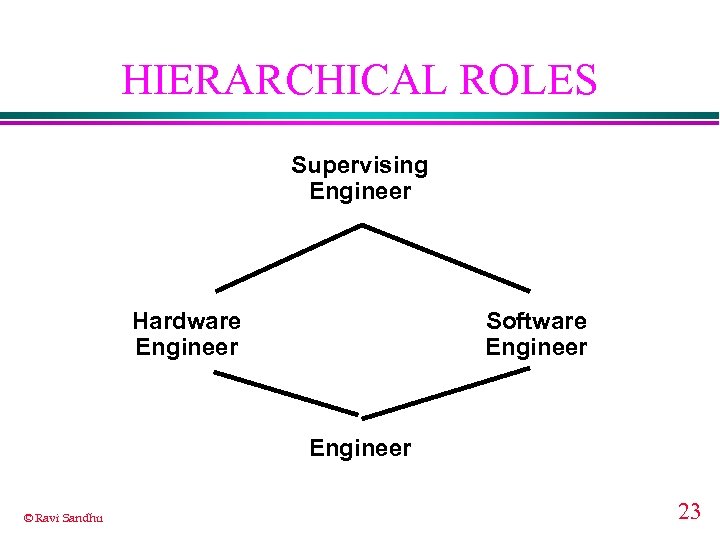 HIERARCHICAL ROLES Supervising Engineer Hardware Engineer Software Engineer © Ravi Sandhu 23
HIERARCHICAL ROLES Supervising Engineer Hardware Engineer Software Engineer © Ravi Sandhu 23
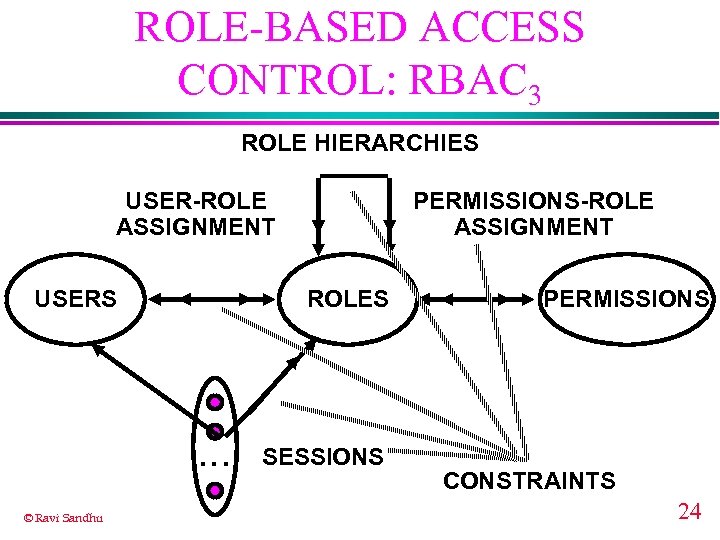 ROLE-BASED ACCESS CONTROL: RBAC 3 ROLE HIERARCHIES USER-ROLE ASSIGNMENT USERS ROLES . . . © Ravi Sandhu PERMISSIONS-ROLE ASSIGNMENT SESSIONS PERMISSIONS CONSTRAINTS 24
ROLE-BASED ACCESS CONTROL: RBAC 3 ROLE HIERARCHIES USER-ROLE ASSIGNMENT USERS ROLES . . . © Ravi Sandhu PERMISSIONS-ROLE ASSIGNMENT SESSIONS PERMISSIONS CONSTRAINTS 24
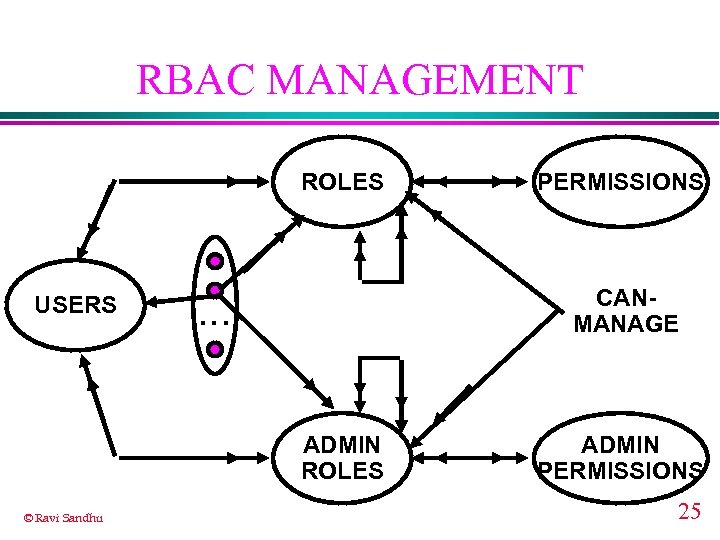 RBAC MANAGEMENT ROLES USERS CANMANAGE . . . ADMIN ROLES © Ravi Sandhu PERMISSIONS ADMIN PERMISSIONS 25
RBAC MANAGEMENT ROLES USERS CANMANAGE . . . ADMIN ROLES © Ravi Sandhu PERMISSIONS ADMIN PERMISSIONS 25
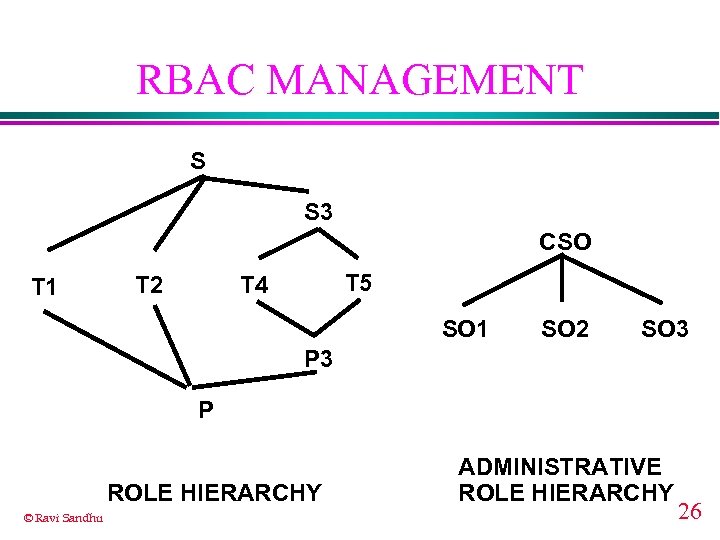 RBAC MANAGEMENT S S 3 CSO T 1 T 2 T 5 T 4 SO 1 SO 2 SO 3 P ROLE HIERARCHY © Ravi Sandhu ADMINISTRATIVE ROLE HIERARCHY 26
RBAC MANAGEMENT S S 3 CSO T 1 T 2 T 5 T 4 SO 1 SO 2 SO 3 P ROLE HIERARCHY © Ravi Sandhu ADMINISTRATIVE ROLE HIERARCHY 26
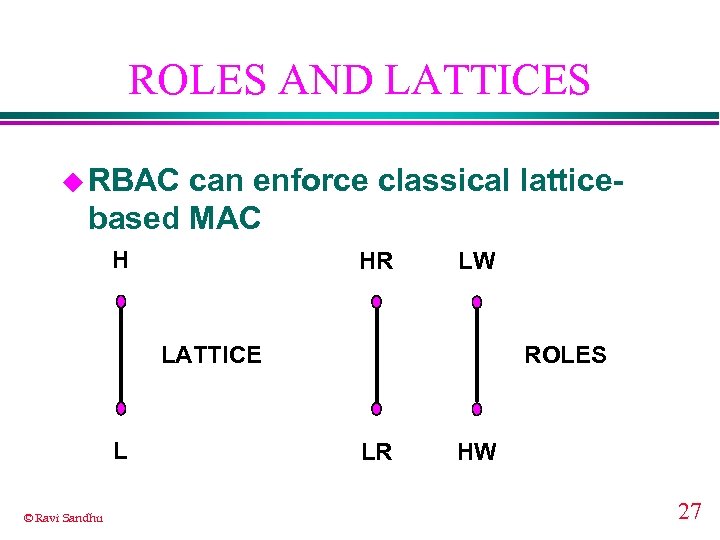 ROLES AND LATTICES u RBAC can enforce classical latticebased MAC H HR LW LATTICE L © Ravi Sandhu ROLES LR HW 27
ROLES AND LATTICES u RBAC can enforce classical latticebased MAC H HR LW LATTICE L © Ravi Sandhu ROLES LR HW 27
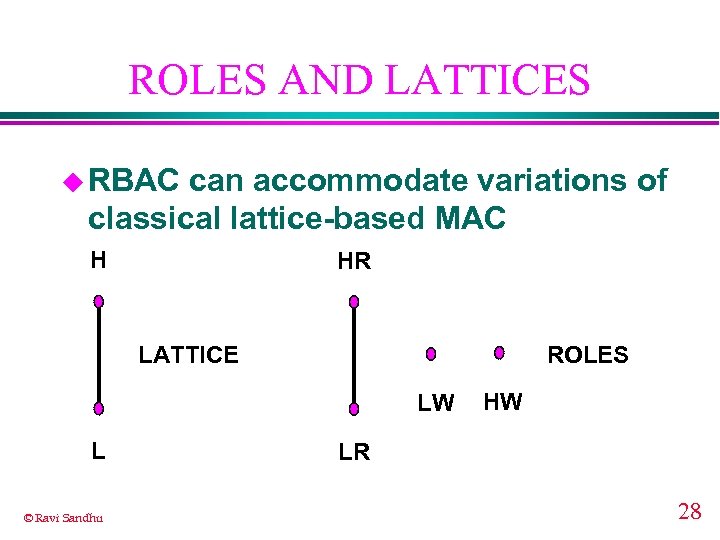 ROLES AND LATTICES u RBAC can accommodate variations of classical lattice-based MAC H HR LATTICE ROLES LW L © Ravi Sandhu HW LR 28
ROLES AND LATTICES u RBAC can accommodate variations of classical lattice-based MAC H HR LATTICE ROLES LW L © Ravi Sandhu HW LR 28
 TASK-BASED AUTHORIZATION (TBA) u beyond subjects and objects u authorization is in context of some task u transient use-once permissions instead of long-lived use-many-times permissions © Ravi Sandhu 29
TASK-BASED AUTHORIZATION (TBA) u beyond subjects and objects u authorization is in context of some task u transient use-once permissions instead of long-lived use-many-times permissions © Ravi Sandhu 29
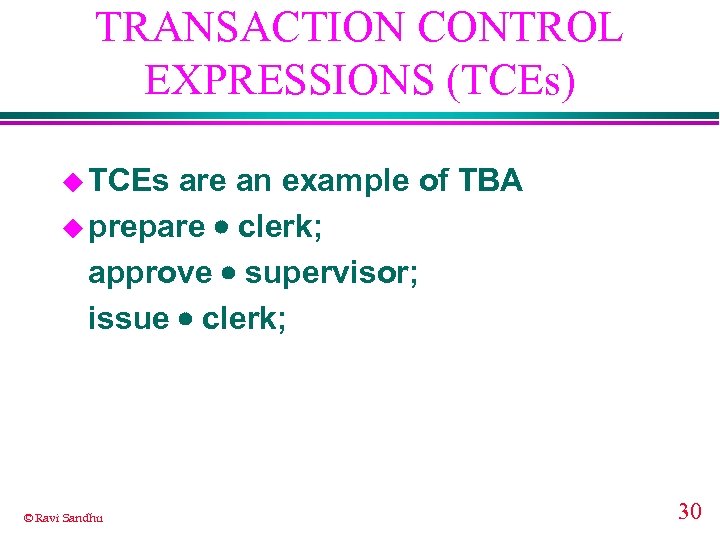 TRANSACTION CONTROL EXPRESSIONS (TCEs) u TCEs are an example of TBA u prepare clerk; approve supervisor; issue clerk; © Ravi Sandhu 30
TRANSACTION CONTROL EXPRESSIONS (TCEs) u TCEs are an example of TBA u prepare clerk; approve supervisor; issue clerk; © Ravi Sandhu 30
 CONCLUSION u access control is important u there are many open issues © Ravi Sandhu 31
CONCLUSION u access control is important u there are many open issues © Ravi Sandhu 31


