a7f8d460fea831542770bdc72389ad10.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 21
 Access Control Lists
Access Control Lists
 Types n n Standard Extended
Types n n Standard Extended
 Standard ACLs n n Use only the packet’s source address for comparison 1 -99
Standard ACLs n n Use only the packet’s source address for comparison 1 -99
 Extended ACLs n Provide more precise (finer tuned) packet selection based on: n n Source and destination addresses Protocols Port numbers 100 -199
Extended ACLs n Provide more precise (finer tuned) packet selection based on: n n Source and destination addresses Protocols Port numbers 100 -199
 Steps to Create an ACL n n n Create ACL in global config Assign to interface Decide the direction n n In Out
Steps to Create an ACL n n n Create ACL in global config Assign to interface Decide the direction n n In Out
 How do ACLs work? n n n Processing occurs line by line from top to bottom. New lines are added at the end of the current list. Last line of an ACL is an implicit “deny any. ”
How do ACLs work? n n n Processing occurs line by line from top to bottom. New lines are added at the end of the current list. Last line of an ACL is an implicit “deny any. ”
 How does a Standard ACL work? n If source IP address is matched: n Permit or deny statement is processed n n n Permit – action in ACL is performed Deny – packet is dropped Implicit Deny – If a packet’s address does not match an earlier statement an implicit deny any occurs at the end of every ACL and the packet is dropped.
How does a Standard ACL work? n If source IP address is matched: n Permit or deny statement is processed n n n Permit – action in ACL is performed Deny – packet is dropped Implicit Deny – If a packet’s address does not match an earlier statement an implicit deny any occurs at the end of every ACL and the packet is dropped.
 Wildcard Masks n n n Are used to specify (by bits) the traffic you are trying to filter by address. Use 1 s to ignore, 0 s to match. In the example below, only the 1 st 2 octets will be examined: n 172. 16. 0. 0. 255
Wildcard Masks n n n Are used to specify (by bits) the traffic you are trying to filter by address. Use 1 s to ignore, 0 s to match. In the example below, only the 1 st 2 octets will be examined: n 172. 16. 0. 0. 255
![Global Standard ACL command n n access-list-number {permit |deny} source-ip-address wildcardmask [log] Log – Global Standard ACL command n n access-list-number {permit |deny} source-ip-address wildcardmask [log] Log –](https://present5.com/presentation/a7f8d460fea831542770bdc72389ad10/image-9.jpg) Global Standard ACL command n n access-list-number {permit |deny} source-ip-address wildcardmask [log] Log – causes each packet that matches this statement to generate a log entry that is recorded by the router.
Global Standard ACL command n n access-list-number {permit |deny} source-ip-address wildcardmask [log] Log – causes each packet that matches this statement to generate a log entry that is recorded by the router.
 Examples of Standard ACLs n To permit all packets for the network number 172. 16. 0. 0 n Access-list 20 permit 172. 16. 0. 0. 255
Examples of Standard ACLs n To permit all packets for the network number 172. 16. 0. 0 n Access-list 20 permit 172. 16. 0. 0. 255
 Examples Cont’d n To permit traffic from the host 172. 16. 1. 1 only n Access-list 20 permit 172. 16. 1. 1 0. 0
Examples Cont’d n To permit traffic from the host 172. 16. 1. 1 only n Access-list 20 permit 172. 16. 1. 1 0. 0
 Examples Cont’d n To permit traffic from any source address. n Access-list 20 permit 0. 0 255 OR n Access-list 20 permit any
Examples Cont’d n To permit traffic from any source address. n Access-list 20 permit 0. 0 255 OR n Access-list 20 permit any
 Examples Cont’d n To permit traffic from the subnet 12. 16. 0. 0 through 12. 31. 0. 0 n Access-list 20 permit 12. 16. 0. 0 0. 15. 255
Examples Cont’d n To permit traffic from the subnet 12. 16. 0. 0 through 12. 31. 0. 0 n Access-list 20 permit 12. 16. 0. 0 0. 15. 255
 Identical Statements n n Access-list 22 permit 0. 0 255 Access-list 22 permit any
Identical Statements n n Access-list 22 permit 0. 0 255 Access-list 22 permit any
 Identical Statements n n Access-list 23 permit 172. 16. 1. 1 0. 0 Access-list 23 permit host 172. 16. 1. 1
Identical Statements n n Access-list 23 permit 172. 16. 1. 1 0. 0 Access-list 23 permit host 172. 16. 1. 1
 How does an Extended ACL work? n n All conditions must match Test sequence in this order n n n Source Address Destination Address Protocol Port No. or Protocol Options Permit or Deny decision
How does an Extended ACL work? n n All conditions must match Test sequence in this order n n n Source Address Destination Address Protocol Port No. or Protocol Options Permit or Deny decision
 Extended ACL command n access-list number {permit|deny} protocol source-ip-address sourcewildcard-mask destination-ip-address destination-wildcard-mask eq portnumber [log]
Extended ACL command n access-list number {permit|deny} protocol source-ip-address sourcewildcard-mask destination-ip-address destination-wildcard-mask eq portnumber [log]
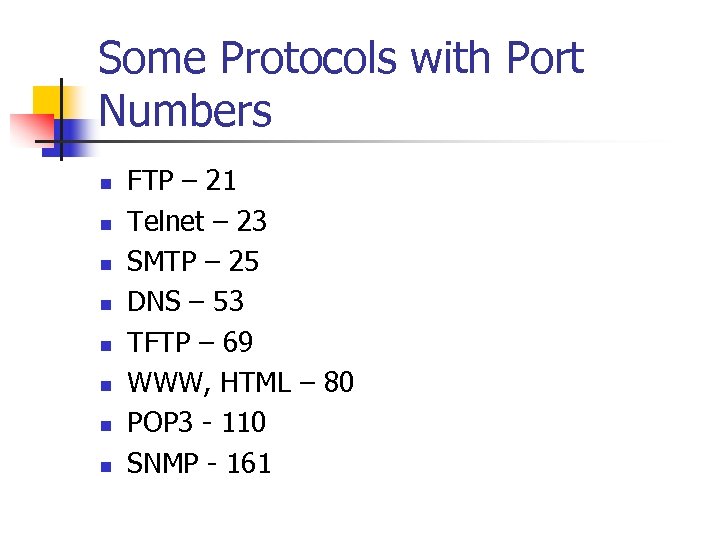 Some Protocols with Port Numbers n n n n FTP – 21 Telnet – 23 SMTP – 25 DNS – 53 TFTP – 69 WWW, HTML – 80 POP 3 - 110 SNMP - 161
Some Protocols with Port Numbers n n n n FTP – 21 Telnet – 23 SMTP – 25 DNS – 53 TFTP – 69 WWW, HTML – 80 POP 3 - 110 SNMP - 161
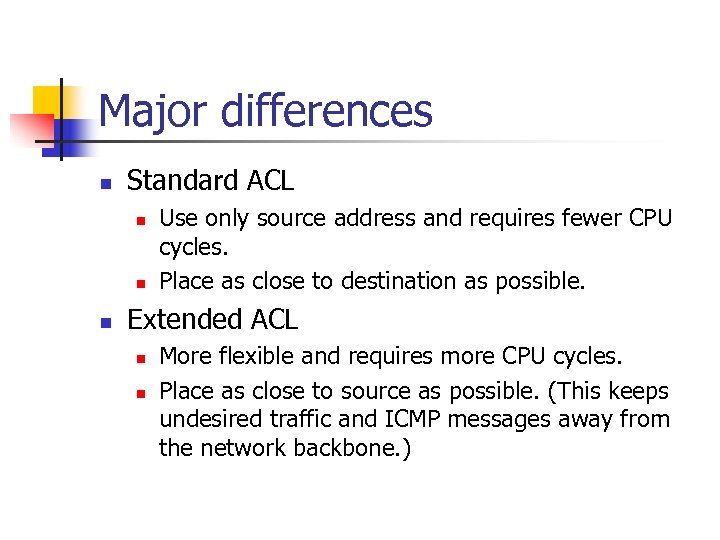 Major differences n Standard ACL n n n Use only source address and requires fewer CPU cycles. Place as close to destination as possible. Extended ACL n n More flexible and requires more CPU cycles. Place as close to source as possible. (This keeps undesired traffic and ICMP messages away from the network backbone. )
Major differences n Standard ACL n n n Use only source address and requires fewer CPU cycles. Place as close to destination as possible. Extended ACL n n More flexible and requires more CPU cycles. Place as close to source as possible. (This keeps undesired traffic and ICMP messages away from the network backbone. )
 Do I place an ACL in? n In n n Requires less CPU processing because every packet bypasses processing before it is routed. Filtering decision is made prior to the routing table.
Do I place an ACL in? n In n n Requires less CPU processing because every packet bypasses processing before it is routed. Filtering decision is made prior to the routing table.
 Do I place an ACL out? n Out n n Routing decision has been made and the packet is switched to the proper outbound interface before it is tested against the access list. ACLs are outbound unless otherwise specified.
Do I place an ACL out? n Out n n Routing decision has been made and the packet is switched to the proper outbound interface before it is tested against the access list. ACLs are outbound unless otherwise specified.


