b5918dadecdeb7c0834d50d0fb4c75b2.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 18
 Access control for IP multicast T-110. 557 Petri Jokela petri. jokela@nomadiclab. com
Access control for IP multicast T-110. 557 Petri Jokela petri. jokela@nomadiclab. com
 Contents ● ● Unicasting / multicasting HIP – ● Certificates – ● ● ● User authentication User authorization Certificate based Multicast Access Control C-MAC Future work Summary
Contents ● ● Unicasting / multicasting HIP – ● Certificates – ● ● ● User authentication User authorization Certificate based Multicast Access Control C-MAC Future work Summary
 Multicasting ● Unicasting – – ● Point-to-point connection Multiple receivers -> resources wasted Multicasting – – One outgoing stream, multiplied near recipients How to control stream receiving?
Multicasting ● Unicasting – – ● Point-to-point connection Multiple receivers -> resources wasted Multicasting – – One outgoing stream, multiplied near recipients How to control stream receiving?
 3 I based multicast ● Traffic is sent with a stream identifier – ● Chord routing protocol used for data routing End-user sets a trigger at an I 3 server – Receive a stream ● – stream identifier in the trigger Traffic unicasted from the server to the end-user
3 I based multicast ● Traffic is sent with a stream identifier – ● Chord routing protocol used for data routing End-user sets a trigger at an I 3 server – Receive a stream ● – stream identifier in the trigger Traffic unicasted from the server to the end-user
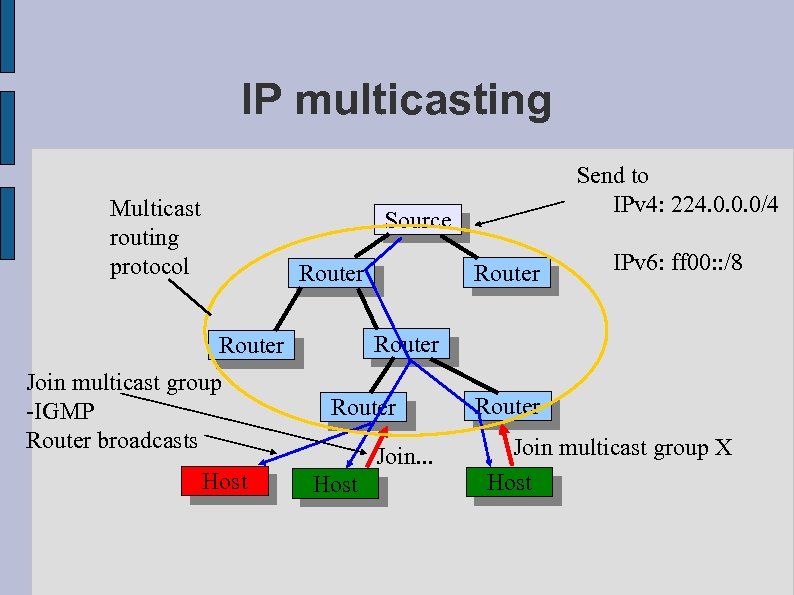 IP multicasting Multicast routing protocol Send to IPv 4: 224. 0. 0. 0/4 Source Router Join multicast group -IGMP Router broadcasts Host IPv 6: ff 00: : /8 Router Join. . . Host Router Join multicast group X Host
IP multicasting Multicast routing protocol Send to IPv 4: 224. 0. 0. 0/4 Source Router Join multicast group -IGMP Router broadcasts Host IPv 6: ff 00: : /8 Router Join. . . Host Router Join multicast group X Host
 HIP usage ● The end-user authentication – – – ● During HIP 4 -way handshake End-user sends HI (public key) Use private key to prove HI ownership IPsec usage – Data decryption key information sent over IPsec ESP
HIP usage ● The end-user authentication – – – ● During HIP 4 -way handshake End-user sends HI (public key) Use private key to prove HI ownership IPsec usage – Data decryption key information sent over IPsec ESP
 Certificates ● SPKI certificates – ● RFC 2693 Certificate – 5 -tuple, containing: – – – Issuer: Who gives the rights Subject: To who this certificate gives rights Authorization: What this certificate authorizes the subject to do Validity: How long this cert is valid Delegation: Can the subject delegate this further? Certificate signed with issuer’s private key
Certificates ● SPKI certificates – ● RFC 2693 Certificate – 5 -tuple, containing: – – – Issuer: Who gives the rights Subject: To who this certificate gives rights Authorization: What this certificate authorizes the subject to do Validity: How long this cert is valid Delegation: Can the subject delegate this further? Certificate signed with issuer’s private key
 Certificate delegation ● Certificate delegated: new and old cert concatenated – – – ● Issuer: itself Subject: next retailer or end-user Authorization: subset of original Validity: subset of original Delegation: depends on subject Signature over the whole certificate chain The receiver can validate – – Knows the first public key Goes through the certificate chain
Certificate delegation ● Certificate delegated: new and old cert concatenated – – – ● Issuer: itself Subject: next retailer or end-user Authorization: subset of original Validity: subset of original Delegation: depends on subject Signature over the whole certificate chain The receiver can validate – – Knows the first public key Goes through the certificate chain
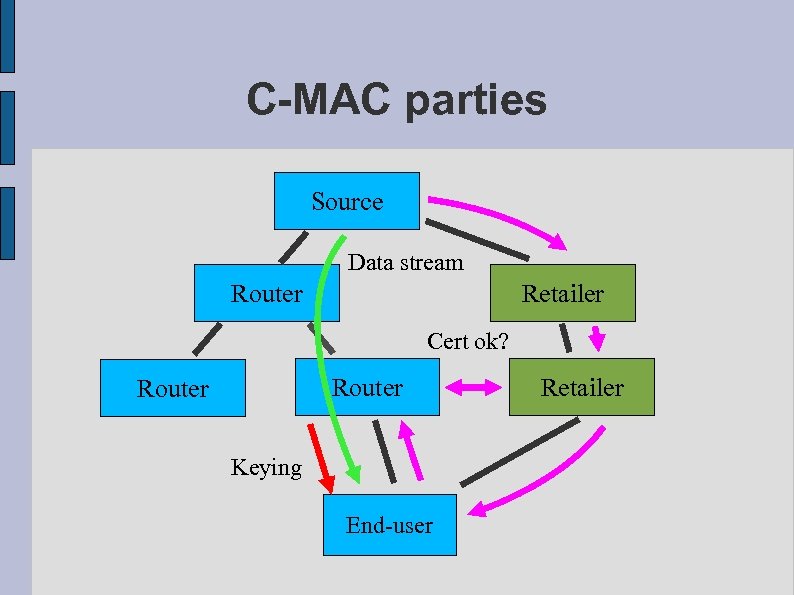 C-MAC parties Source Data stream Router Retailer Cert ok? Router Keying End-user Retailer
C-MAC parties Source Data stream Router Retailer Cert ok? Router Keying End-user Retailer
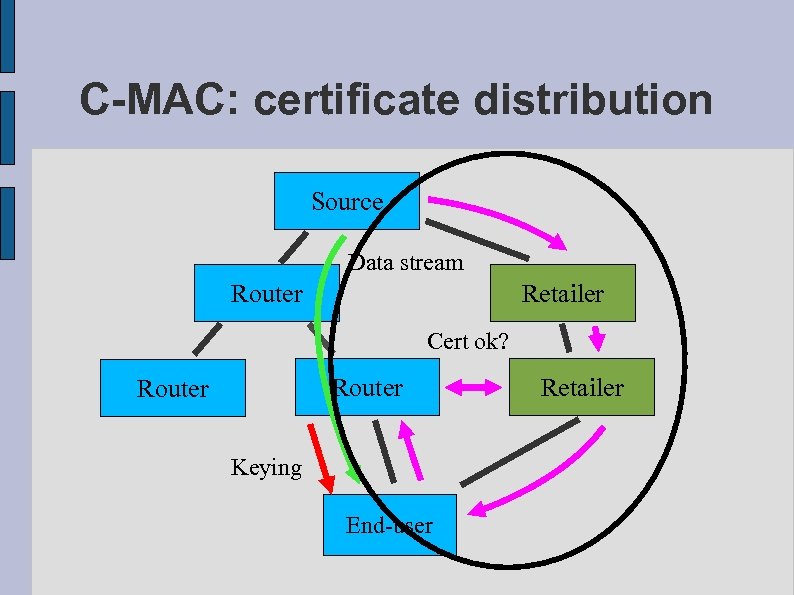 C-MAC: certificate distribution Source Data stream Router Retailer Cert ok? Router Keying End-user Retailer
C-MAC: certificate distribution Source Data stream Router Retailer Cert ok? Router Keying End-user Retailer
 C-MAC operation: cert distribution ● The data source issues a certificate – – – ● ● ● Issuer: data source public key Subject: retailer’s public key Authorization: receive data multicasting X Validity: how long valid Delegation: yes – Payment: VISA, other. . . – not specified here Certificate given to a retailer Retailer can further delegate to another retailer Finally, certificate is sold to the end-user
C-MAC operation: cert distribution ● The data source issues a certificate – – – ● ● ● Issuer: data source public key Subject: retailer’s public key Authorization: receive data multicasting X Validity: how long valid Delegation: yes – Payment: VISA, other. . . – not specified here Certificate given to a retailer Retailer can further delegate to another retailer Finally, certificate is sold to the end-user
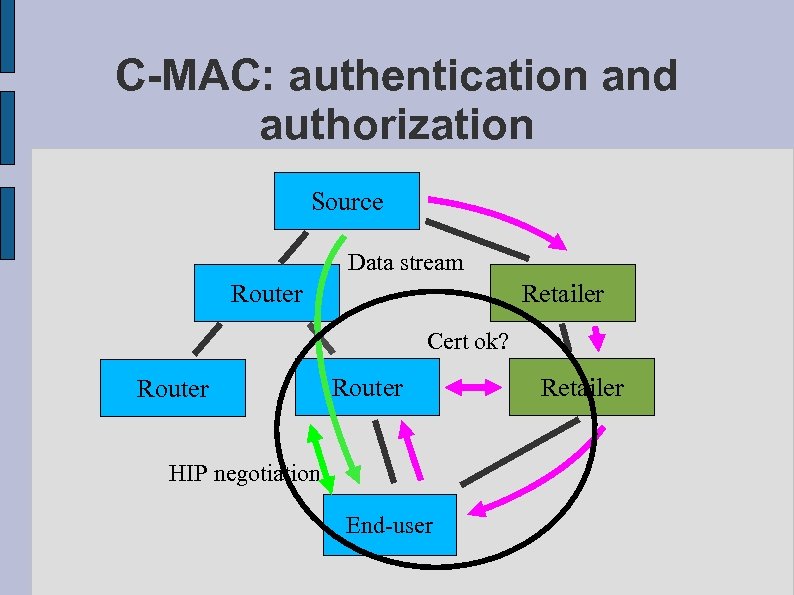 C-MAC: authentication and authorization Source Data stream Router Retailer Cert ok? Router HIP negotiation End-user Retailer
C-MAC: authentication and authorization Source Data stream Router Retailer Cert ok? Router HIP negotiation End-user Retailer
 C-MAC: end-user authentication and authorization ● End user joins a multicast group – – ● HIP association with the router Router learns end-hosts public key (HI) End user sends the certificate to the router – – Router verifies the certificate chain Verify the subject, must match the end-user HI Make a verification to the last retailer Retailer marks the certificate used
C-MAC: end-user authentication and authorization ● End user joins a multicast group – – ● HIP association with the router Router learns end-hosts public key (HI) End user sends the certificate to the router – – Router verifies the certificate chain Verify the subject, must match the end-user HI Make a verification to the last retailer Retailer marks the certificate used
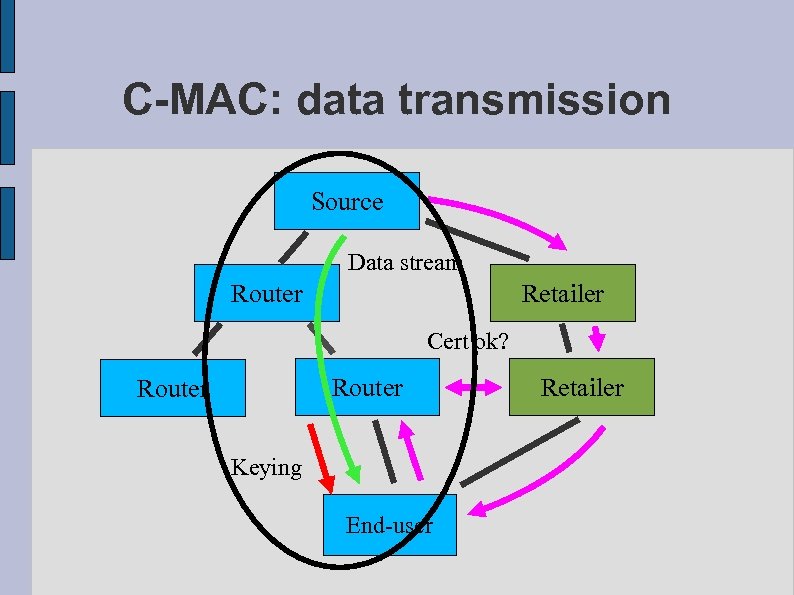 C-MAC: data transmission Source Data stream Router Retailer Cert ok? Router Keying End-user Retailer
C-MAC: data transmission Source Data stream Router Retailer Cert ok? Router Keying End-user Retailer
 C-MAC: Data transmission ● Data must be encrypted – – ● ● The decryption key is sent to valid receivers Key sent over the IPsec ESP – – ● IP multicast: sent to everyone on the link Where? At the last router How validity times are defined? Minutes, hours, days, . . . ? – – How to prevent end-user to redistribute the key? And if prevented, how to prevent resending decrypted data? Valid receiver needs a key Rekeying needed Problems
C-MAC: Data transmission ● Data must be encrypted – – ● ● The decryption key is sent to valid receivers Key sent over the IPsec ESP – – ● IP multicast: sent to everyone on the link Where? At the last router How validity times are defined? Minutes, hours, days, . . . ? – – How to prevent end-user to redistribute the key? And if prevented, how to prevent resending decrypted data? Valid receiver needs a key Rekeying needed Problems
 Future work ● Trust relations between entities – ● Security – ● How this system could be adopted in real business No security analysis made on this (complex) system Performance optimization – – – ● ● Encoding of data Key distribution Not studied in this paper Payment system Prototyping
Future work ● Trust relations between entities – ● Security – ● How this system could be adopted in real business No security analysis made on this (complex) system Performance optimization – – – ● ● Encoding of data Key distribution Not studied in this paper Payment system Prototyping
 Summary ● Access Control system for IP multicast – – IP multicasting Certificates for access control ● – User authentication ● – ● certificate chain HIP Data encryption A lot of work to do
Summary ● Access Control system for IP multicast – – IP multicasting Certificates for access control ● – User authentication ● – ● certificate chain HIP Data encryption A lot of work to do
 Thank you!
Thank you!


