d4b5207a584539001f83b16f33b4dcc3.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 22
 Access Control CIS 4361 Eng. Hector M Lugo-Cordero, MS April, 2012
Access Control CIS 4361 Eng. Hector M Lugo-Cordero, MS April, 2012
 Most Slides from: Computer Security: Principles and Practice Chapter 4 – Access Control First Edition by William Stallings and Lawrie Brown Lecture slides by Lawrie Brown
Most Slides from: Computer Security: Principles and Practice Chapter 4 – Access Control First Edition by William Stallings and Lawrie Brown Lecture slides by Lawrie Brown
 Access Control Ø “The prevention of unauthorized use of a resource, including the prevention of use of a resource in an unauthorized manner“ Ø central element of computer security Ø assume have users and groups l l authenticate to system assigned access rights to certain resources on system
Access Control Ø “The prevention of unauthorized use of a resource, including the prevention of use of a resource in an unauthorized manner“ Ø central element of computer security Ø assume have users and groups l l authenticate to system assigned access rights to certain resources on system
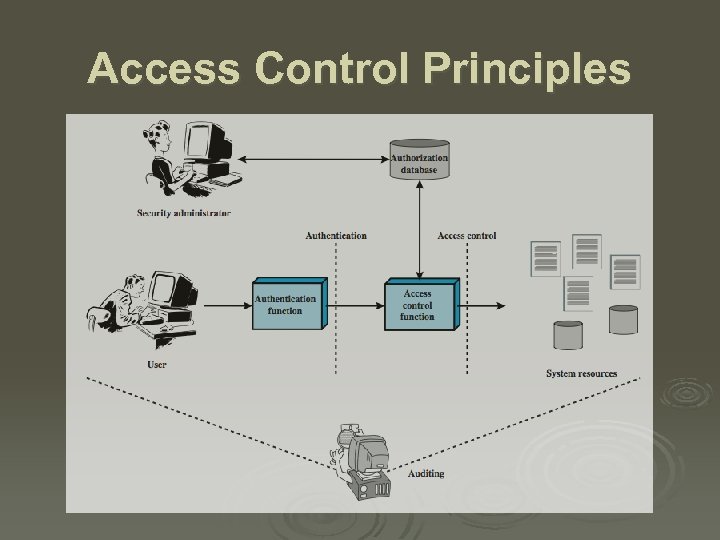 Access Control Principles
Access Control Principles
 Access Control Policies
Access Control Policies
 Access Control Requirements Ø reliable input Ø fine and coarse specifications Ø least privilege Ø separation of duty Ø open and closed policies Ø policy combinations, conflict resolution Ø administrative policies
Access Control Requirements Ø reliable input Ø fine and coarse specifications Ø least privilege Ø separation of duty Ø open and closed policies Ø policy combinations, conflict resolution Ø administrative policies
 Access Control Elements Ø subject - entity that can access objects l l a process representing user/application often have 3 classes: owner, group, world Ø object - access controlled resource l l e. g. files, directories, records, programs etc number/type depend on environment Ø access right - way in which subject accesses an object l e. g. read, write, execute, delete, create, search
Access Control Elements Ø subject - entity that can access objects l l a process representing user/application often have 3 classes: owner, group, world Ø object - access controlled resource l l e. g. files, directories, records, programs etc number/type depend on environment Ø access right - way in which subject accesses an object l e. g. read, write, execute, delete, create, search
 Discretionary Access Control Ø often provided using an access matrix l lists subjects in one dimension (rows) lists objects in the other dimension (columns) each entry specifies access rights of the specified subject to that object Ø access matrix is often sparse Ø can decompose by either row or column
Discretionary Access Control Ø often provided using an access matrix l lists subjects in one dimension (rows) lists objects in the other dimension (columns) each entry specifies access rights of the specified subject to that object Ø access matrix is often sparse Ø can decompose by either row or column
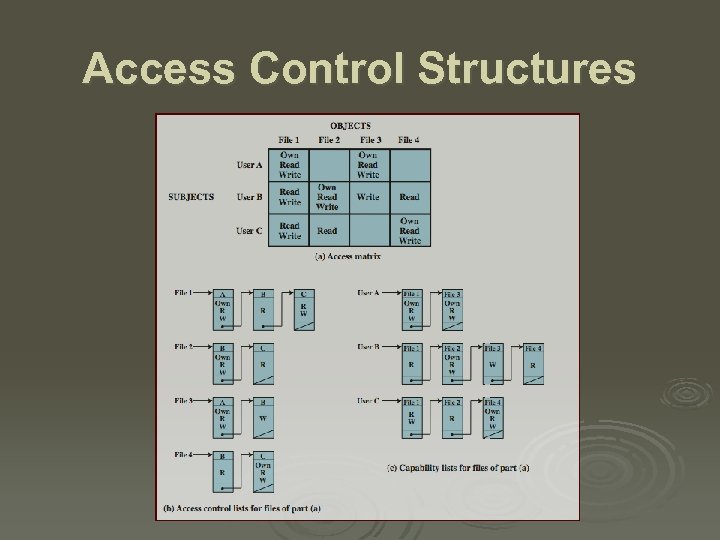 Access Control Structures
Access Control Structures
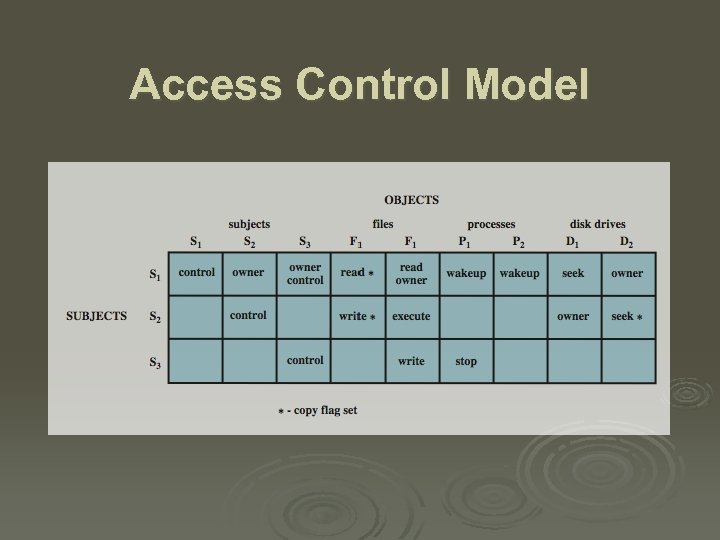 Access Control Model
Access Control Model
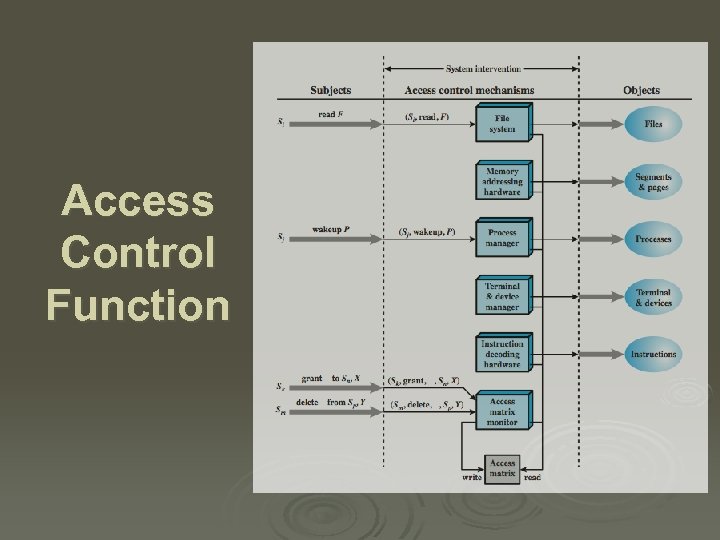 Access Control Function
Access Control Function
 Protection Domains Ø set of objects with associated access rights Ø in access matrix view, each row defines a protection domain l l l but not necessarily just a user may be a limited subset of user’s rights applied to a more restricted process Ø may be static or dynamic
Protection Domains Ø set of objects with associated access rights Ø in access matrix view, each row defines a protection domain l l l but not necessarily just a user may be a limited subset of user’s rights applied to a more restricted process Ø may be static or dynamic
 UNIX File Concepts Ø UNIX files administered using l inodes control structure with key info on file • attributes, permissions of a single file l l may have several names for same inode have inode table / list for all files on a disk • copied to memory when disk mounted Ø directories form a hierarchical tree l l may contain files or other directories are a file of names and inode numbers
UNIX File Concepts Ø UNIX files administered using l inodes control structure with key info on file • attributes, permissions of a single file l l may have several names for same inode have inode table / list for all files on a disk • copied to memory when disk mounted Ø directories form a hierarchical tree l l may contain files or other directories are a file of names and inode numbers
 UNIX File Access Control
UNIX File Access Control
 UNIX File Access Control Ø “set user ID”(Set. UID) or “set group ID”(Set. GID) l l Ø sticky bit l Ø system temporarily uses rights of the file owner / group in addition to the real user’s rights when making access control decisions enables privileged programs to access files / resources not generally accessible on directory limits rename/move/delete to owner superuser l is exempt from usual access control restrictions
UNIX File Access Control Ø “set user ID”(Set. UID) or “set group ID”(Set. GID) l l Ø sticky bit l Ø system temporarily uses rights of the file owner / group in addition to the real user’s rights when making access control decisions enables privileged programs to access files / resources not generally accessible on directory limits rename/move/delete to owner superuser l is exempt from usual access control restrictions
 UNIX Access Control Lists Ø modern UNIX systems support ACLs Ø can specify any number of additional users / groups and associated rwx permissions Ø ACLs are optional extensions to std perms Ø group perms also set max ACL perms Ø when access is required l select most appropriate ACL • owner, named users, owning / named groups, others l check if have sufficient permissions for access
UNIX Access Control Lists Ø modern UNIX systems support ACLs Ø can specify any number of additional users / groups and associated rwx permissions Ø ACLs are optional extensions to std perms Ø group perms also set max ACL perms Ø when access is required l select most appropriate ACL • owner, named users, owning / named groups, others l check if have sufficient permissions for access
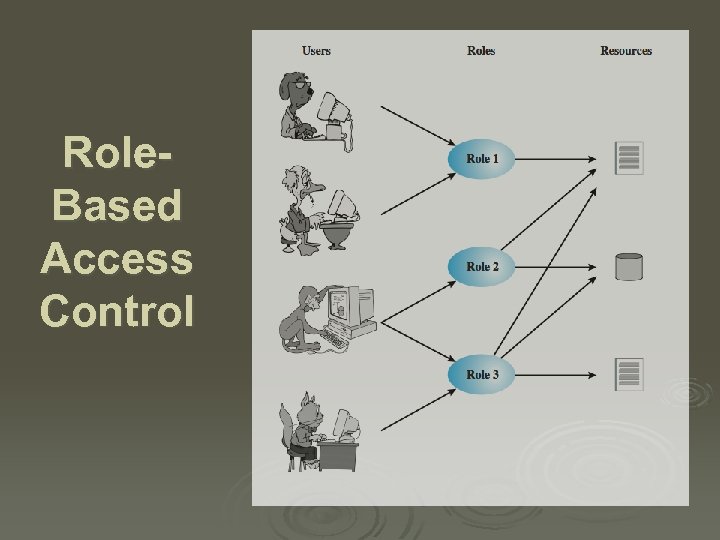 Role. Based Access Control
Role. Based Access Control
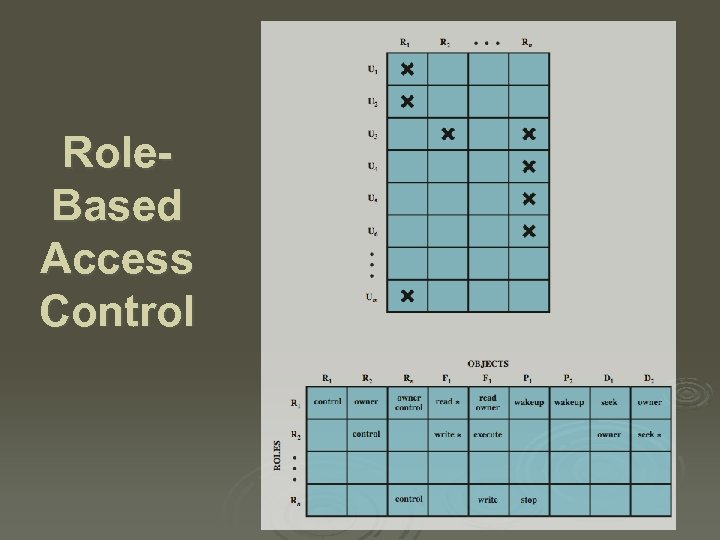 Role. Based Access Control
Role. Based Access Control
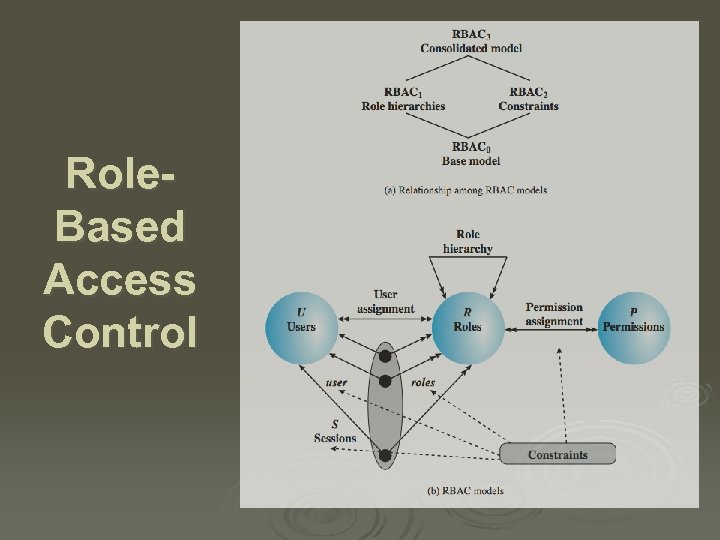 Role. Based Access Control
Role. Based Access Control
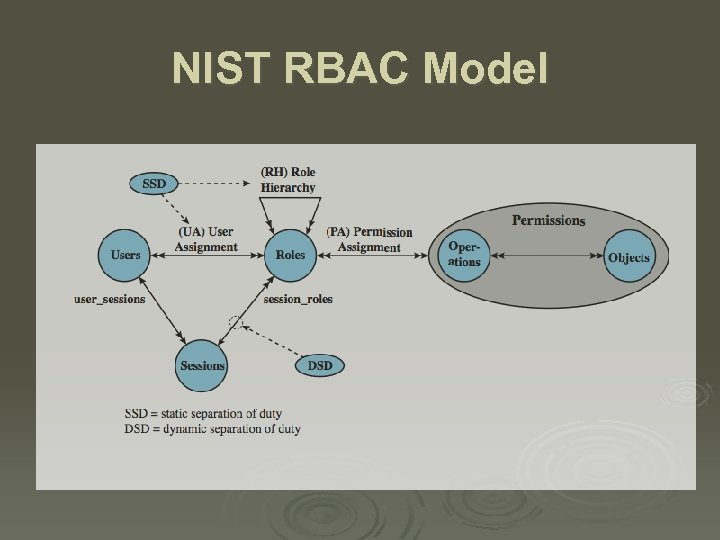 NIST RBAC Model
NIST RBAC Model
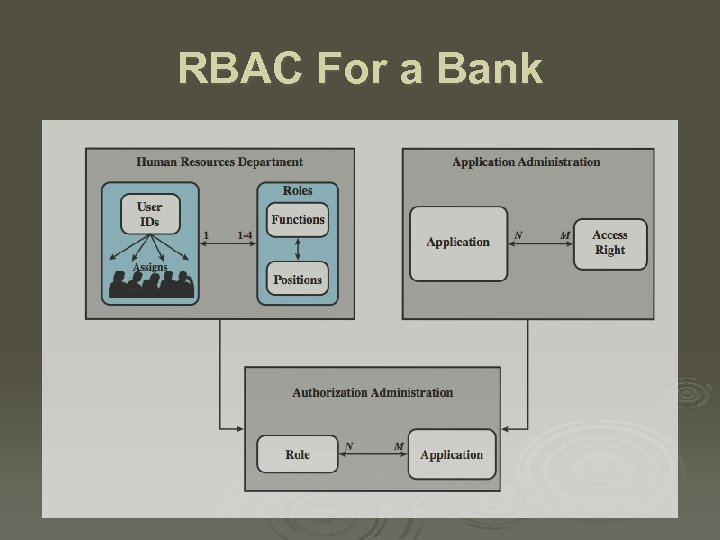 RBAC For a Bank
RBAC For a Bank
 Summary Ø introduced access control principles l subjects, objects, access rights Ø discretionary access controls l l access matrix, access control lists (ACLs), capability tickets UNIX traditional and ACL mechanisms Ø role-based access control Ø case study
Summary Ø introduced access control principles l subjects, objects, access rights Ø discretionary access controls l l access matrix, access control lists (ACLs), capability tickets UNIX traditional and ACL mechanisms Ø role-based access control Ø case study


