d231639f89cd6b43fc0feba92fd728a0.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 22

Accelerating e-Learning Interoperability Introducing the CLEO Lab Tyde Richards IBM Mindspan Solutions Daniel R. Rehak Carnegie Mellon University

Overview e-Learning interoperability ADL and the Sharable Content Object Reference Model (SCORM) Introducing the CLEO Lab discussion
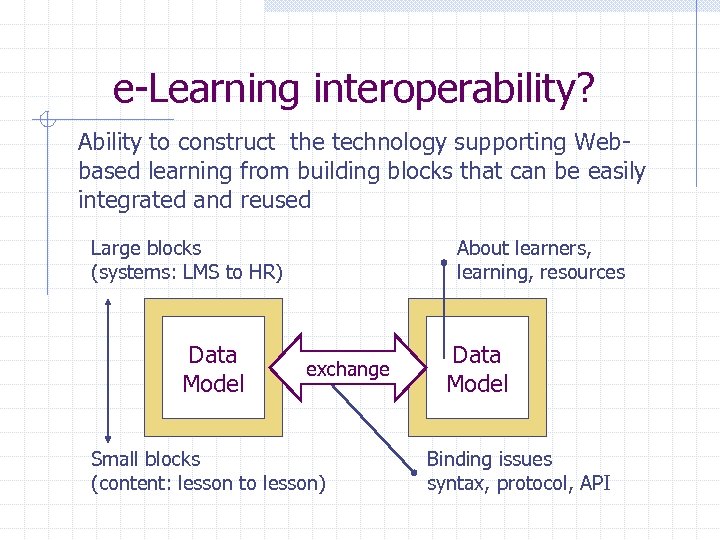
e-Learning interoperability? Ability to construct the technology supporting Webbased learning from building blocks that can be easily integrated and reused Large blocks (systems: LMS to HR) Data Model About learners, learning, resources exchange Small blocks (content: lesson to lesson) Data Model Binding issues syntax, protocol, API

Growth of interest in the problem 1988 - early interest in aviation industry due to special circumstances (AICC) 1996/97 - Web sparks general interest, many new players n ARIADNE, IMS, ADL, IEEE LTSC 1998/present – collaboration, division of labor, and still more players n Prometeus, ALIC, SC 36, CLEO Lab

Many Initiatives, Many Differences Geography n U. S. , Europe, Asia Intended Learner n Corporate, Military, Higher Ed, K 12 Technical focus n Meta-data, learning management, simulation Work products n Research, specifications, profiles & conformance, formal standards
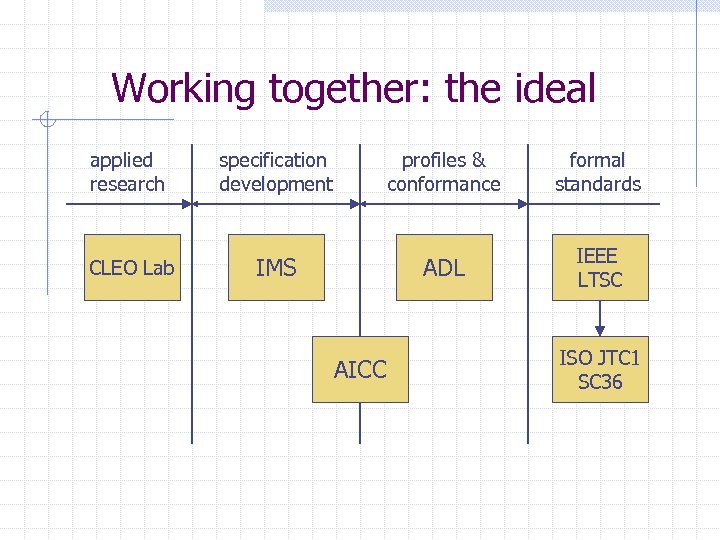
Working together: the ideal applied research CLEO Lab specification development profiles & conformance ADL IMS AICC formal standards IEEE LTSC ISO JTC 1 SC 36
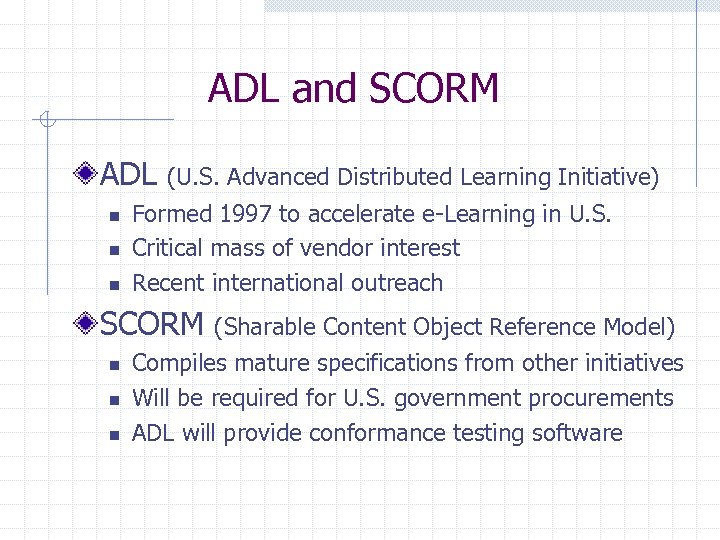
ADL and SCORM ADL n n n (U. S. Advanced Distributed Learning Initiative) Formed 1997 to accelerate e-Learning in U. S. Critical mass of vendor interest Recent international outreach SCORM n n n (Sharable Content Object Reference Model) Compiles mature specifications from other initiatives Will be required for U. S. government procurements ADL will provide conformance testing software
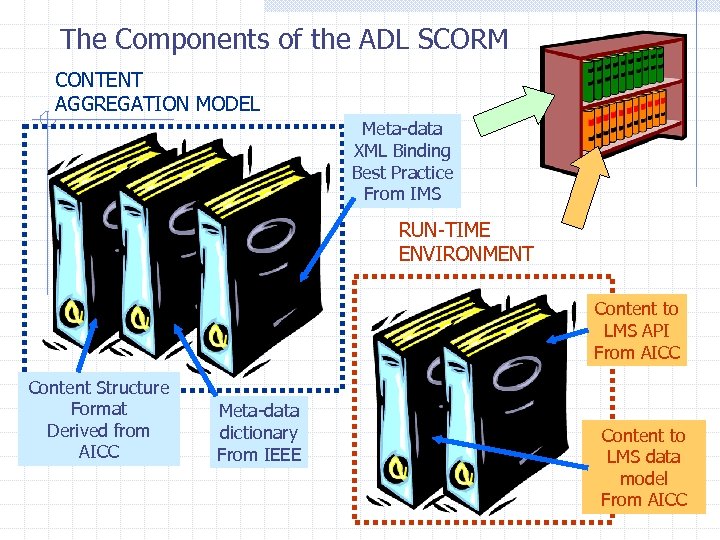
The Components of the ADL SCORM CONTENT AGGREGATION MODEL Meta-data XML Binding Best Practice From IMS RUN-TIME ENVIRONMENT Content to LMS API From AICC Content Structure Format Derived from AICC Meta-data dictionary From IEEE Content to LMS data model From AICC
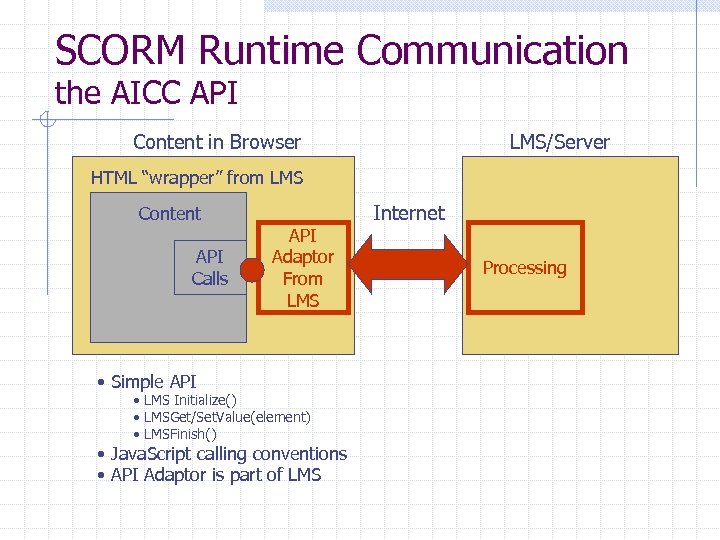
SCORM Runtime Communication the AICC API Content in Browser LMS/Server HTML “wrapper” from LMS Content API Calls API Adaptor From LMS • Simple API • LMS Initialize() • LMSGet/Set. Value(element) • LMSFinish() • Java. Script calling conventions • API Adaptor is part of LMS Internet Processing
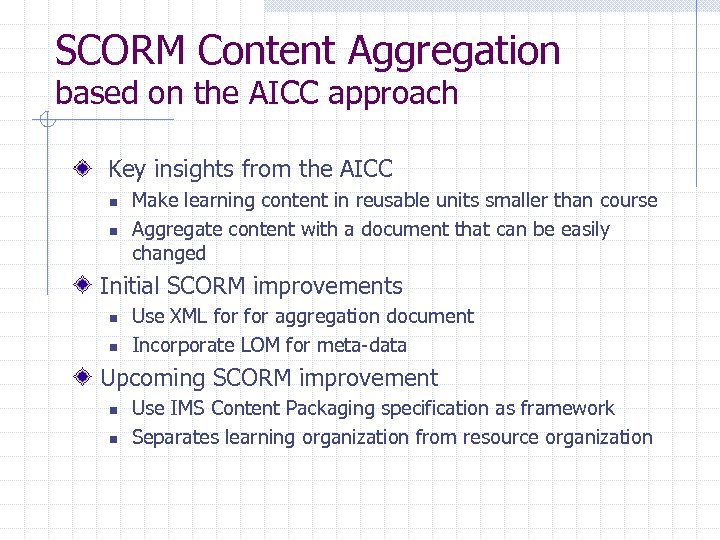
SCORM Content Aggregation based on the AICC approach Key insights from the AICC n n Make learning content in reusable units smaller than course Aggregate content with a document that can be easily changed Initial SCORM improvements n n Use XML for aggregation document Incorporate LOM for meta-data Upcoming SCORM improvement n n Use IMS Content Packaging specification as framework Separates learning organization from resource organization

Looking forward Aggregation using IMS Content Packaging Example simplified <manifest identifier="Course 01" xmlns: adl=”http: //www. adlnet. org”> <organization identifier="sample course"> learning <item identifier="sco 1" resourceref="sco 1 Res">> activities <adl: SCORMdata>some data</adl: SCORMdata> <item identifier="sco 1" resourceref="sco 2 Res"> <adl: SCORMdata>some data</adl: SCORMdata> data to support </item> a learning style </item> activities mapped to resources </organization> <resources> resources <resource identifier="sco 1 Res" type="webcontent"> for activities <metadata> sco 1 metadata record </metadata> <file href="Course 01Lesson 01sco 01. htm"/> </resource> <resource identifier="sco 2 Res" type="webcontent"> <metadata> sco 2 metadata record </metadata> LOM record <file href="Course 01Lesson 02sco 02. htm"/> for resource </resource> </resources> </manifest>
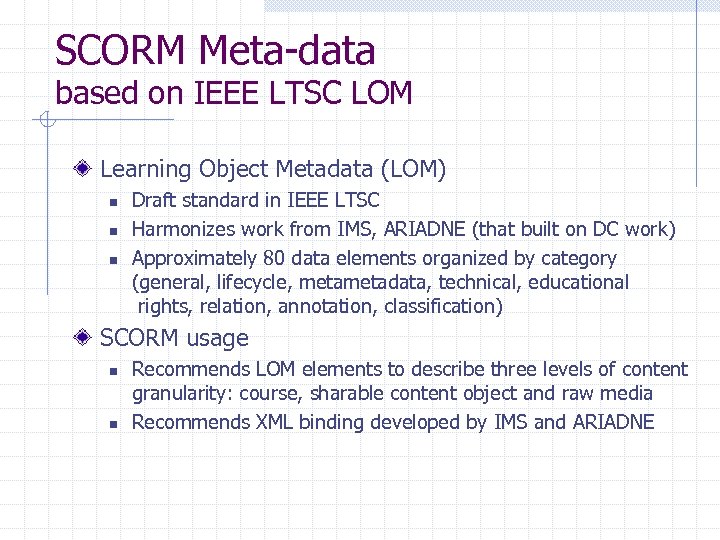
SCORM Meta-data based on IEEE LTSC LOM Learning Object Metadata (LOM) n n n Draft standard in IEEE LTSC Harmonizes work from IMS, ARIADNE (that built on DC work) Approximately 80 data elements organized by category (general, lifecycle, metadata, technical, educational rights, relation, annotation, classification) SCORM usage n n Recommends LOM elements to describe three levels of content granularity: course, sharable content object and raw media Recommends XML binding developed by IMS and ARIADNE

Experience with SCORM to date Positives n n Technical approach appears viable Significant endorsement from content and LMS vendors Challenges n SCORM design center the conventional self-paced course w What about other approaches to learning? n With interoperability loose important capabilities found in proprietary approaches w User interface consistency across reusable components w Rule-based control of learning activities

Introducing the CLEO Lab Customized Learning Experiences Online Research collaboration on future SCORM capabilities with focus on learning experience customization Organized under aegis of IEEE ISTO Participants - CISCO Systems, Click 2 Learn, IBM Mindspan Solutions, Microsoft Corporation, NETg, U. S. ADL Initiative Funded research at Carnegie Mellon University and the Open University, U. K. Duration one year, may be extended Findings to be contributed to initiatives developing open specifications in support of the ADL SCORM
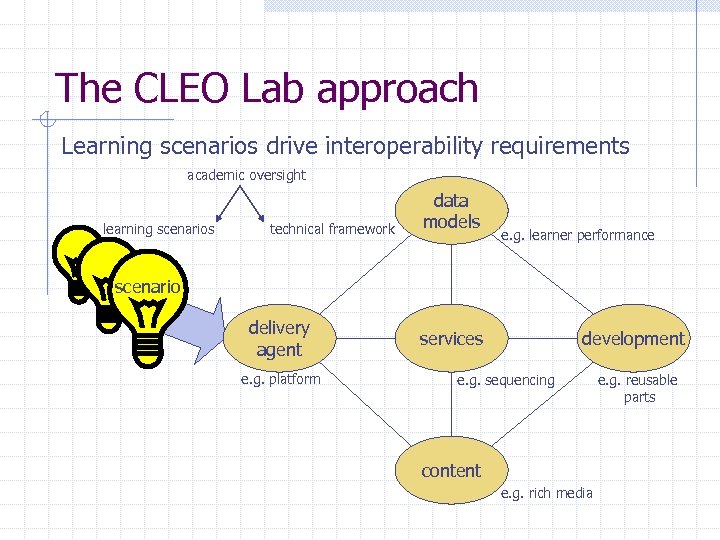
The CLEO Lab approach Learning scenarios drive interoperability requirements academic oversight learning scenarios technical framework data models e. g. learner performance scenario delivery agent e. g. platform services development e. g. sequencing content e. g. rich media e. g. reusable parts

CLEO Lab Deliverables Framework and data models for learning content structure, sequencing, rendering and control used to create customized learning experiences Learning model descriptions Technical findings from test bed activities

CLEO Lab Scenario Requirements Define taxonomy of learning models Assume content samples from participants Use conventional CBT as baseline n “do it right” Demonstrate generality with two additional models n Under discussion: collaboration, performance support, intelligent tutoring Address additional models if collaboration continues past initial year

CLEO Lab Framework Requirements For runtime, authoring, interoperability Support different “Learning Models” A content structure representation Models for behavior and sequencing Models for rendering look and feel Content repositories with metadata Content to System communications

CLEO Lab “Speculations” Models and frameworks for specifications Intended to aide organizations developing open specifications to advance the ADL SCORM Identified candidates n n Content Structure Sequencing Presentation Variants
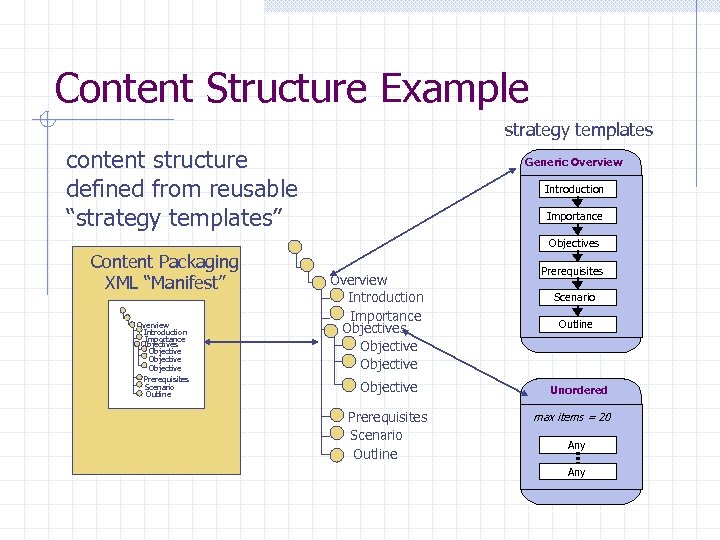
Content Structure Example strategy templates content structure defined from reusable “strategy templates” Generic Overview Introduction Importance Objectives Content Packaging XML “Manifest” Overview Introduction Importance Objectives Objective Objective Prerequisites Scenario Outline Unordered max items = 20 Any

Relation to W 3 C technologies Appropriate forum to explore relevance of emerging W 3 C technologies to e-Learning Content formats and processing n XHTML, SMIL, SVG, Math. ML, XSLT Meta-data n Relation of LOM to RDF, Semantic Web Data Models n XML bindings assumed, evaluate supporting technologies Communication n Current Java. Script API, exploring SOAP, XMLP

Summary and Discussion The CLEO Lab www. cleolab. org contact Greg Kohn g. kohn@ieee. org
d231639f89cd6b43fc0feba92fd728a0.ppt