54566de28d0fead561c9b4d9e862f1e4.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 43
 “Accelerated Recovery Technique” A unique way to decrease pain and blood loss for Total Joint Replacement H. Morton Bertram III, M. D. Naples, Florida
“Accelerated Recovery Technique” A unique way to decrease pain and blood loss for Total Joint Replacement H. Morton Bertram III, M. D. Naples, Florida
 It all starts with the wound Having the chance to work at the NEBH was one of the best things that ever happened to me n Working with Dr. Scott I was impressed by the extreme importance of the wound closure, and how much attention to detail it received with the “Scott Knot” n
It all starts with the wound Having the chance to work at the NEBH was one of the best things that ever happened to me n Working with Dr. Scott I was impressed by the extreme importance of the wound closure, and how much attention to detail it received with the “Scott Knot” n
 Wound Principles n n n I enjoyed sewing, and still do, using the mattress stitch for closures I confess to backsliding after a few years to using staples, however would still use the stitch for revision knees or at risk wounds I did however start using subcuticular closures for THR in 2002, just not TKRsdon’t ask why
Wound Principles n n n I enjoyed sewing, and still do, using the mattress stitch for closures I confess to backsliding after a few years to using staples, however would still use the stitch for revision knees or at risk wounds I did however start using subcuticular closures for THR in 2002, just not TKRsdon’t ask why
 Platelet gel I started using Platelet gel or “PRP” in or around 1999, with one goal in mindto improve my “Primary Wound Healing”. n My goal was simply to have no drainage once the patient left the operating room, and avoid the use of a drain n
Platelet gel I started using Platelet gel or “PRP” in or around 1999, with one goal in mindto improve my “Primary Wound Healing”. n My goal was simply to have no drainage once the patient left the operating room, and avoid the use of a drain n
 PRP n Platelet gel allowed me to do that, and it had an unanticipated consequencesignificantly decreased rate of transfusions.
PRP n Platelet gel allowed me to do that, and it had an unanticipated consequencesignificantly decreased rate of transfusions.
 7 years go by…… 19992006 n After 7 years, of doing well with my low rate of blood utilization ( lowest of any surgeon of any specialty at our hospital), I was still very unhappy with the pain our patients were having post -operatively
7 years go by…… 19992006 n After 7 years, of doing well with my low rate of blood utilization ( lowest of any surgeon of any specialty at our hospital), I was still very unhappy with the pain our patients were having post -operatively
 Minimally Invasive Craze n n n About this time, the concept of “Minimally Invasive Surgery” came into popularity in my part of the country, and patients would “shop” for our services. I did not buy into that whole concept, and the lectures I attended seemed to gloss over the concept of pain management “ Oh by the way” here is what I am doing for pain management of these patients
Minimally Invasive Craze n n n About this time, the concept of “Minimally Invasive Surgery” came into popularity in my part of the country, and patients would “shop” for our services. I did not buy into that whole concept, and the lectures I attended seemed to gloss over the concept of pain management “ Oh by the way” here is what I am doing for pain management of these patients
 Depressed n n So at this point, I was pretty sure I was never going to learn how to do a THR or TKR through a 5 cm incision, and I was never going to get those patients to walk down the hall the day of surgery like I was seeing on all those videos. So for the first time in my career, I felt pretty inadequate, and quite frankly depressed about it.
Depressed n n So at this point, I was pretty sure I was never going to learn how to do a THR or TKR through a 5 cm incision, and I was never going to get those patients to walk down the hall the day of surgery like I was seeing on all those videos. So for the first time in my career, I felt pretty inadequate, and quite frankly depressed about it.
 That is when I got it It was the pain management, not the surgery responsible for these incredible results. n However, I could get no help from my Anesthesia staff, and no one seemed interested in helping me to figure it out. n “It’s supposed to hurt a lot” n
That is when I got it It was the pain management, not the surgery responsible for these incredible results. n However, I could get no help from my Anesthesia staff, and no one seemed interested in helping me to figure it out. n “It’s supposed to hurt a lot” n
 Dr. Carl Highenboten n n About this time, I got a call from this doctor in Dallas, he was doing about 400 TKR/year He wanted to know about our use of PRP, and I told him all I knew about that. I asked him about pain management, and what he was doing He told me about Duramorph spinals in combination with Peri-articular injections, and subcuticular closures, with Dermabond
Dr. Carl Highenboten n n About this time, I got a call from this doctor in Dallas, he was doing about 400 TKR/year He wanted to know about our use of PRP, and I told him all I knew about that. I asked him about pain management, and what he was doing He told me about Duramorph spinals in combination with Peri-articular injections, and subcuticular closures, with Dermabond
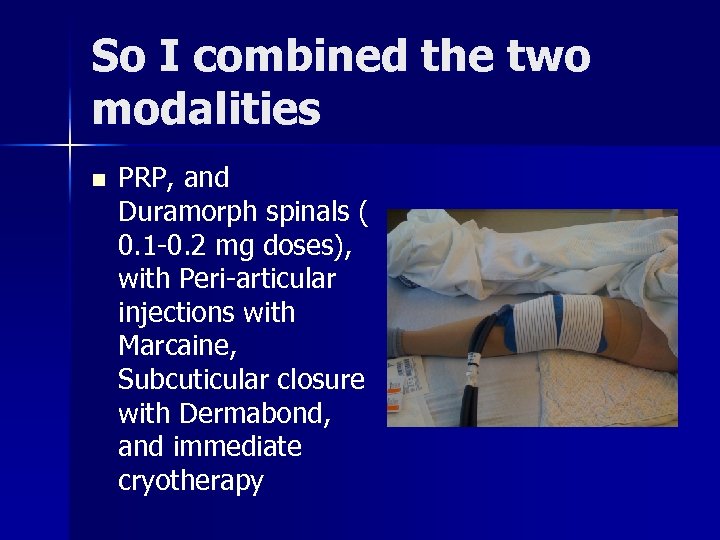 So I combined the two modalities n PRP, and Duramorph spinals ( 0. 1 -0. 2 mg doses), with Peri-articular injections with Marcaine, Subcuticular closure with Dermabond, and immediate cryotherapy
So I combined the two modalities n PRP, and Duramorph spinals ( 0. 1 -0. 2 mg doses), with Peri-articular injections with Marcaine, Subcuticular closure with Dermabond, and immediate cryotherapy
 The Results were shocking!!! We noticed right away a long pain free interval, usually about 24 hours, the Duramorph giving excellent sensory blockade but no motor blockade n Transitioned into p. o. meds for pain n Low transfusion rates n Not much swelling n
The Results were shocking!!! We noticed right away a long pain free interval, usually about 24 hours, the Duramorph giving excellent sensory blockade but no motor blockade n Transitioned into p. o. meds for pain n Low transfusion rates n Not much swelling n
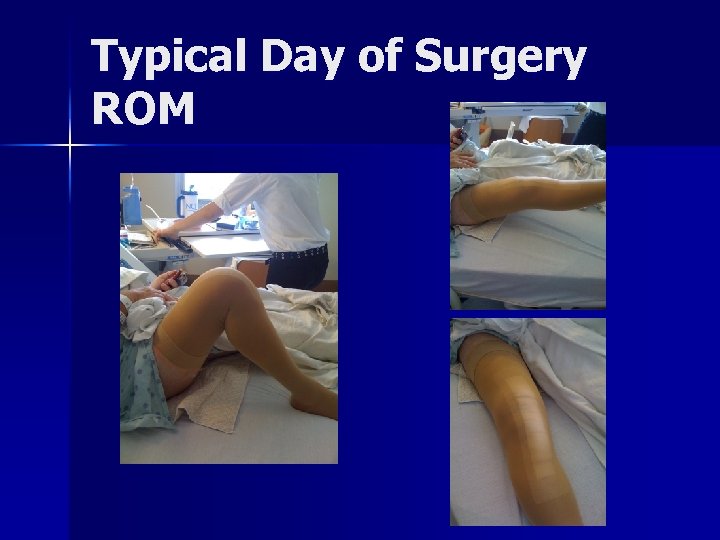 Typical Day of Surgery ROM
Typical Day of Surgery ROM
 The Evolution n n At this point we are on our 4 th iteration of this technique Have changed the sequence and location of the injections Use the PRP differently for Hips and Knees Added immediate, Pre-emptive Compression Therapy Changed the local to Ropivacaine 0. 2% (safer profile)
The Evolution n n At this point we are on our 4 th iteration of this technique Have changed the sequence and location of the injections Use the PRP differently for Hips and Knees Added immediate, Pre-emptive Compression Therapy Changed the local to Ropivacaine 0. 2% (safer profile)
 Ropivacaine n n n Much safer profile than Marcaine Does not bind to the fat receptors in the heart or the brain Almost can not give a toxic dose of this medication We usually use 100 -120 cc of 0. 2% combined with 5 mg Duramorph and 0. 2 cc Epi @ 1: 1000 concentration Studies have been done using regional anesthesia and with 300 -400 mg doses, no toxicity seen
Ropivacaine n n n Much safer profile than Marcaine Does not bind to the fat receptors in the heart or the brain Almost can not give a toxic dose of this medication We usually use 100 -120 cc of 0. 2% combined with 5 mg Duramorph and 0. 2 cc Epi @ 1: 1000 concentration Studies have been done using regional anesthesia and with 300 -400 mg doses, no toxicity seen
 Sequence of Injection TKR 4 different Aliquots n 1 st- a field block superior to the incision-30 cc n 2 nd- posterior capsule, laterally, LCL, medially, MCL -30 cc n 3 rd – VMO muscle and Quad tendon 30 cc n 4 th- Superior synovium with remainder n
Sequence of Injection TKR 4 different Aliquots n 1 st- a field block superior to the incision-30 cc n 2 nd- posterior capsule, laterally, LCL, medially, MCL -30 cc n 3 rd – VMO muscle and Quad tendon 30 cc n 4 th- Superior synovium with remainder n
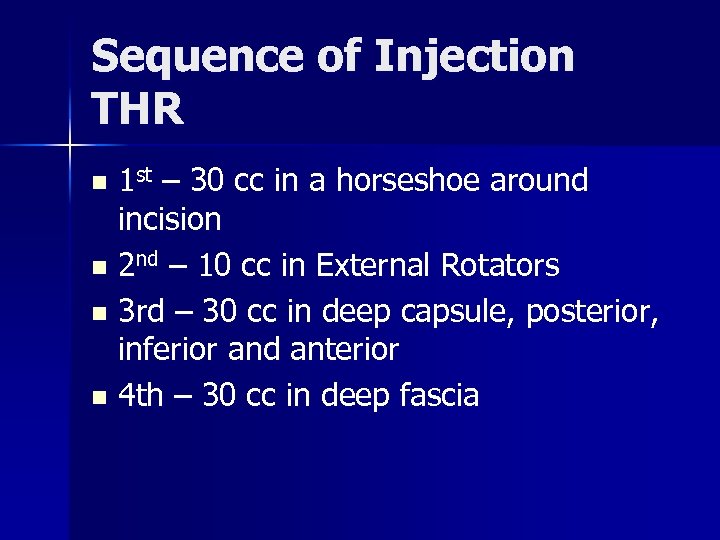 Sequence of Injection THR 1 st – 30 cc in a horseshoe around incision n 2 nd – 10 cc in External Rotators n 3 rd – 30 cc in deep capsule, posterior, inferior and anterior n 4 th – 30 cc in deep fascia n
Sequence of Injection THR 1 st – 30 cc in a horseshoe around incision n 2 nd – 10 cc in External Rotators n 3 rd – 30 cc in deep capsule, posterior, inferior and anterior n 4 th – 30 cc in deep fascia n
 Current Goals n n n “Primary Wound Healing”- no drainage after the first dressing change Avoid Blood Transfusions-Goal is 0%, (currently 35% for TKR and 8 -10% for THR) Avoid intravenous narcotics- our “ART” patients need narcotics 1. 5% of the time Avoid Edema that interferes with recovery of function Greater than 98% patient satisfaction with the process
Current Goals n n n “Primary Wound Healing”- no drainage after the first dressing change Avoid Blood Transfusions-Goal is 0%, (currently 35% for TKR and 8 -10% for THR) Avoid intravenous narcotics- our “ART” patients need narcotics 1. 5% of the time Avoid Edema that interferes with recovery of function Greater than 98% patient satisfaction with the process
 Results & Observations Hospital Data n A report given to us looked at selected quarter from 2005 & 2007 n ART program started in March of 2006, suspended by Anesthesia, to “study the safety”, then restarted in Late 2006. n
Results & Observations Hospital Data n A report given to us looked at selected quarter from 2005 & 2007 n ART program started in March of 2006, suspended by Anesthesia, to “study the safety”, then restarted in Late 2006. n
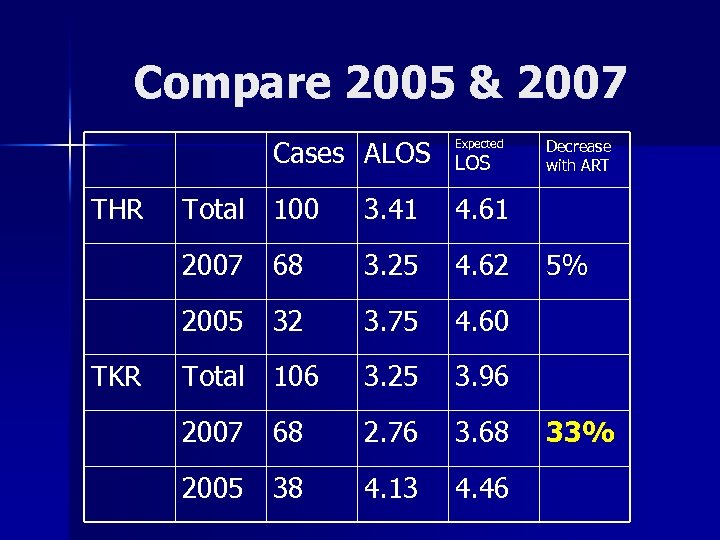 Compare 2005 & 2007 Cases ALOS THR Expected LOS 3. 41 4. 61 2007 68 3. 25 4. 62 2005 TKR Total 100 32 3. 75 4. 60 Total 106 3. 25 3. 96 2007 68 2. 76 3. 68 2005 38 4. 13 4. 46 Decrease with ART 5% 33%
Compare 2005 & 2007 Cases ALOS THR Expected LOS 3. 41 4. 61 2007 68 3. 25 4. 62 2005 TKR Total 100 32 3. 75 4. 60 Total 106 3. 25 3. 96 2007 68 2. 76 3. 68 2005 38 4. 13 4. 46 Decrease with ART 5% 33%
 Complication Rate n n n Q 1, 2 of 2005 and Q 1, 2 of 2007 Total 206 cases- complication rate 0. 97% (Expected was 2. 93%) 2007 136 cases- complication rate 0. 74% (Expected was 3. 34%) 2005 70 cases- complication rate 1. 43% (Expected was 2. 13%) So my profile was better by 50% with a higher expected rate for the 2007 patients
Complication Rate n n n Q 1, 2 of 2005 and Q 1, 2 of 2007 Total 206 cases- complication rate 0. 97% (Expected was 2. 93%) 2007 136 cases- complication rate 0. 74% (Expected was 3. 34%) 2005 70 cases- complication rate 1. 43% (Expected was 2. 13%) So my profile was better by 50% with a higher expected rate for the 2007 patients
 Lowest complication rate n In this review of 1616 cases and 8 surgeons, I had the lowest rate for anyone doing at least 100 cases, using the ART technique
Lowest complication rate n In this review of 1616 cases and 8 surgeons, I had the lowest rate for anyone doing at least 100 cases, using the ART technique
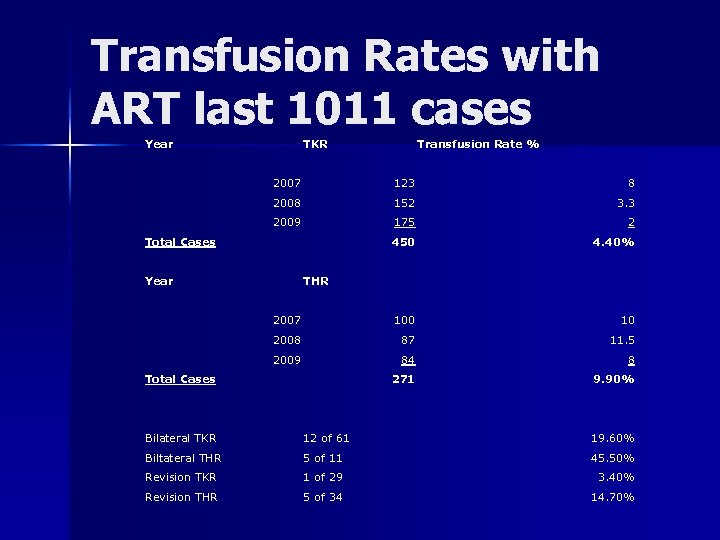 Transfusion Rates with ART last 1011 cases Year TKR Transfusion Rate % 2007 123 8 2008 152 3. 3 2009 175 2 450 4. 40% 2007 100 10 2008 87 11. 5 2009 84 8 271 9. 90% Total Cases Year THR Total Cases Bilateral TKR 12 of 61 19. 60% Biltateral THR 5 of 11 45. 50% Revision TKR 1 of 29 3. 40% Revision THR 5 of 34 14. 70%
Transfusion Rates with ART last 1011 cases Year TKR Transfusion Rate % 2007 123 8 2008 152 3. 3 2009 175 2 450 4. 40% 2007 100 10 2008 87 11. 5 2009 84 8 271 9. 90% Total Cases Year THR Total Cases Bilateral TKR 12 of 61 19. 60% Biltateral THR 5 of 11 45. 50% Revision TKR 1 of 29 3. 40% Revision THR 5 of 34 14. 70%
 Pierson-JBJS 2004 Algorithm using Procrit for high risk of transfusion ( predicted Hgb < 7. 0 ) assuming Hgb drop of 4 + or – 1 for THR and 3 + or – 1 for TKR n Transfusion trigger of 7. 0 n We used no Procrit and trigger of 8. 0 n
Pierson-JBJS 2004 Algorithm using Procrit for high risk of transfusion ( predicted Hgb < 7. 0 ) assuming Hgb drop of 4 + or – 1 for THR and 3 + or – 1 for TKR n Transfusion trigger of 7. 0 n We used no Procrit and trigger of 8. 0 n
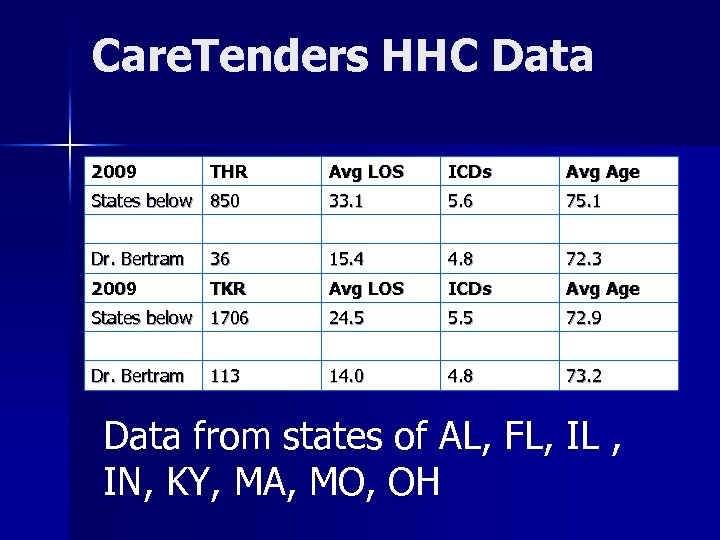 Care. Tenders HHC Data 2009 THR Avg LOS ICDs Avg Age States below 850 33. 1 5. 6 75. 1 Dr. Bertram 36 15. 4 4. 8 72. 3 2009 TKR Avg LOS ICDs Avg Age States below 1706 24. 5 5. 5 72. 9 Dr. Bertram 14. 0 4. 8 73. 2 113 Data from states of AL, FL, IL , IN, KY, MA, MO, OH
Care. Tenders HHC Data 2009 THR Avg LOS ICDs Avg Age States below 850 33. 1 5. 6 75. 1 Dr. Bertram 36 15. 4 4. 8 72. 3 2009 TKR Avg LOS ICDs Avg Age States below 1706 24. 5 5. 5 72. 9 Dr. Bertram 14. 0 4. 8 73. 2 113 Data from states of AL, FL, IL , IN, KY, MA, MO, OH
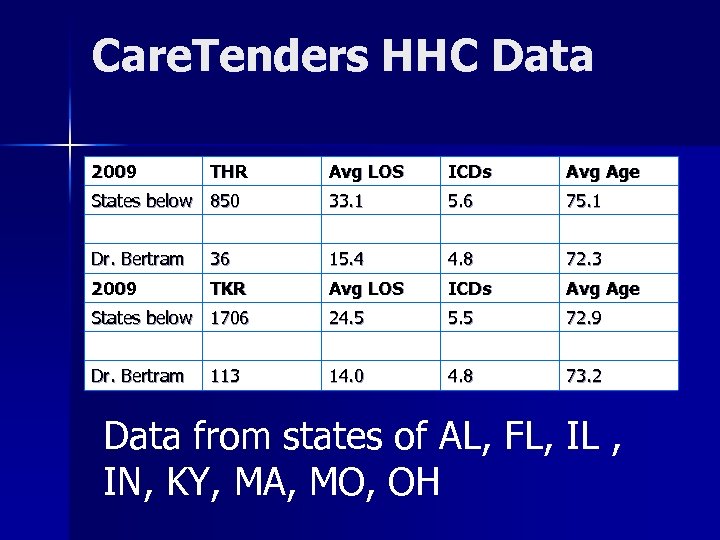 Care. Tenders HHC Data 2009 THR Avg LOS ICDs Avg Age States below 850 33. 1 5. 6 75. 1 Dr. Bertram 36 15. 4 4. 8 72. 3 2009 TKR Avg LOS ICDs Avg Age States below 1706 24. 5 5. 5 72. 9 Dr. Bertram 14. 0 4. 8 73. 2 113 Data from states of AL, FL, IL , IN, KY, MA, MO, OH
Care. Tenders HHC Data 2009 THR Avg LOS ICDs Avg Age States below 850 33. 1 5. 6 75. 1 Dr. Bertram 36 15. 4 4. 8 72. 3 2009 TKR Avg LOS ICDs Avg Age States below 1706 24. 5 5. 5 72. 9 Dr. Bertram 14. 0 4. 8 73. 2 113 Data from states of AL, FL, IL , IN, KY, MA, MO, OH
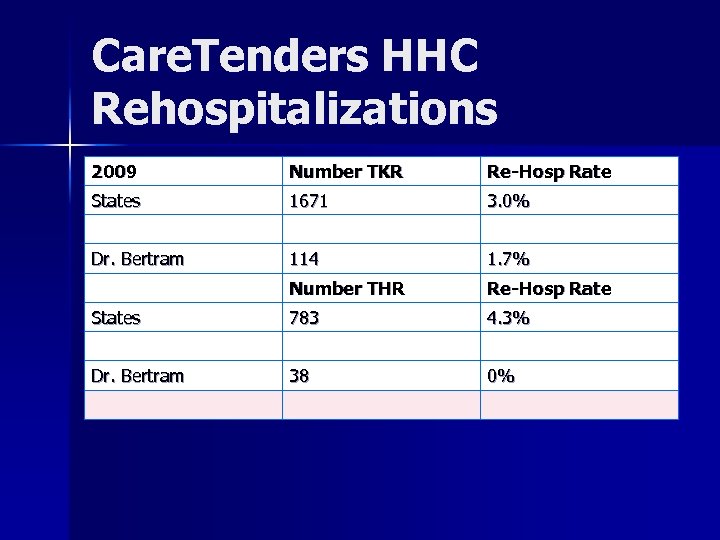 Care. Tenders HHC Rehospitalizations 2009 Number TKR Re-Hosp Rate States 1671 3. 0% Dr. Bertram 114 1. 7% Number THR Re-Hosp Rate States 783 4. 3% Dr. Bertram 38 0%
Care. Tenders HHC Rehospitalizations 2009 Number TKR Re-Hosp Rate States 1671 3. 0% Dr. Bertram 114 1. 7% Number THR Re-Hosp Rate States 783 4. 3% Dr. Bertram 38 0%
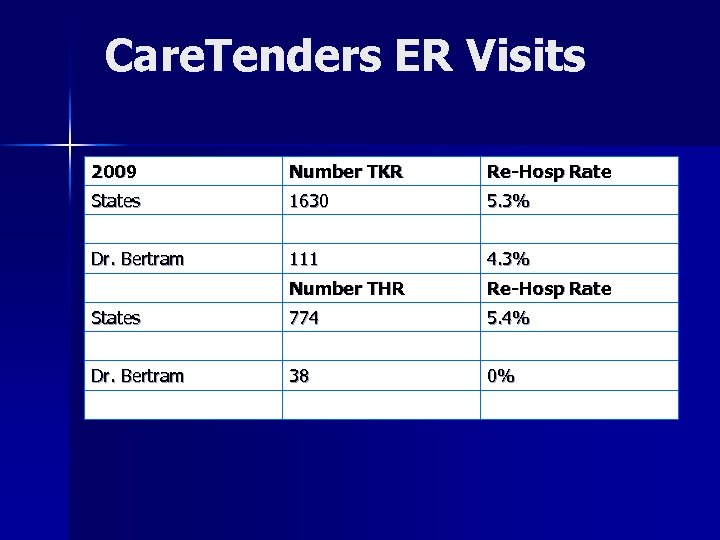 Care. Tenders ER Visits 2009 Number TKR Re-Hosp Rate States 1630 5. 3% Dr. Bertram 111 4. 3% Number THR Re-Hosp Rate States 774 5. 4% Dr. Bertram 38 0%
Care. Tenders ER Visits 2009 Number TKR Re-Hosp Rate States 1630 5. 3% Dr. Bertram 111 4. 3% Number THR Re-Hosp Rate States 774 5. 4% Dr. Bertram 38 0%
 NCH ADE data ( Adverse Drug Events) n n Last 3 years, post-op oversedation events have decreased by 63% This includes all general surgery patients as well For the TJR receiving a Duramorph spinal, NO oversedation events in the last 12 months For this review of 2007 -2009 for my patients, NO oversedation events in over 1000 cases
NCH ADE data ( Adverse Drug Events) n n Last 3 years, post-op oversedation events have decreased by 63% This includes all general surgery patients as well For the TJR receiving a Duramorph spinal, NO oversedation events in the last 12 months For this review of 2007 -2009 for my patients, NO oversedation events in over 1000 cases
 Spinal Anesthesia Review of 2007 -2009 n Spinal Anesthesia 90% of patients overall for my TJR n 98. 5% of those patients with Duramorph Spinal received only p. o. meds post operatively ( this includes Bilateral TKR patients !!!!) n This is reason for low incidence of ADE n
Spinal Anesthesia Review of 2007 -2009 n Spinal Anesthesia 90% of patients overall for my TJR n 98. 5% of those patients with Duramorph Spinal received only p. o. meds post operatively ( this includes Bilateral TKR patients !!!!) n This is reason for low incidence of ADE n
 Concluding Statements n n n Imperative we provide “Primary Wound Healing” Stitches versus Staples BMJ 2010 “Sutures versus Staples for skin closure in orthopaedic surgery: meta-analysis. Smith et. al. Risk of superficial wound infection was over 3 times greater after staple closure, and with hip surgery over 4 times greater Each day of wound drainage increases our infection rate by 40% per day.
Concluding Statements n n n Imperative we provide “Primary Wound Healing” Stitches versus Staples BMJ 2010 “Sutures versus Staples for skin closure in orthopaedic surgery: meta-analysis. Smith et. al. Risk of superficial wound infection was over 3 times greater after staple closure, and with hip surgery over 4 times greater Each day of wound drainage increases our infection rate by 40% per day.
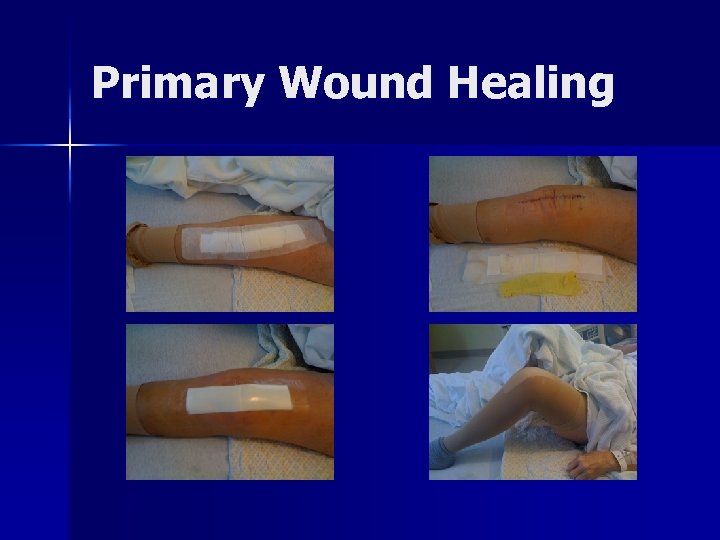 Primary Wound Healing
Primary Wound Healing
 Blood Transfusions n n n We must avoid blood transfusions at all costs. Blood transfusions associate with higher risk of infection, overall mortality & increased length of stay Med Par Data 2008: Average per surgery costs were $3, 000 higher in TKR, and $2, 000 higher in THR when a blood transfusion was given
Blood Transfusions n n n We must avoid blood transfusions at all costs. Blood transfusions associate with higher risk of infection, overall mortality & increased length of stay Med Par Data 2008: Average per surgery costs were $3, 000 higher in TKR, and $2, 000 higher in THR when a blood transfusion was given
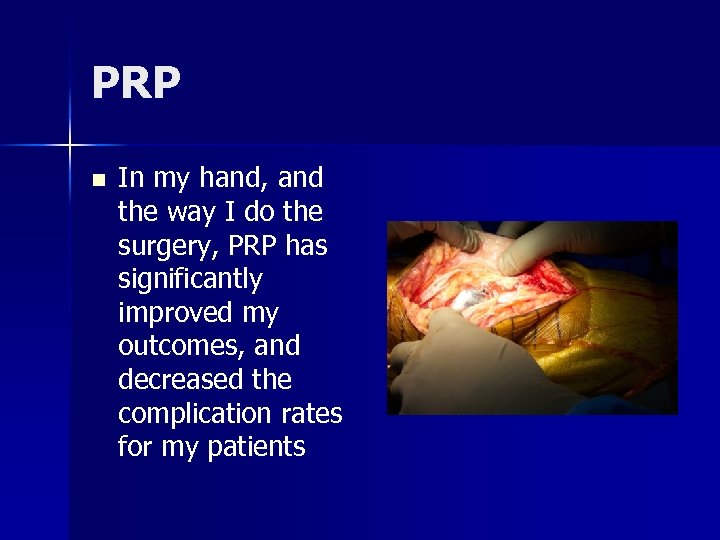 PRP n In my hand, and the way I do the surgery, PRP has significantly improved my outcomes, and decreased the complication rates for my patients
PRP n In my hand, and the way I do the surgery, PRP has significantly improved my outcomes, and decreased the complication rates for my patients
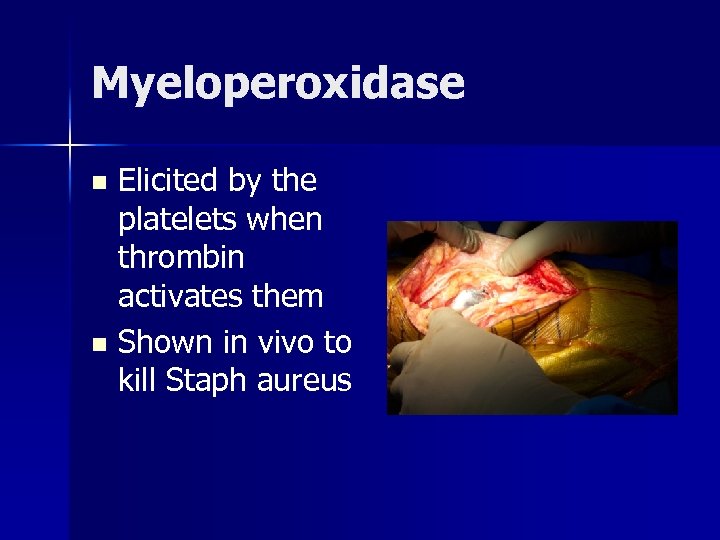 Myeloperoxidase Elicited by the platelets when thrombin activates them n Shown in vivo to kill Staph aureus n
Myeloperoxidase Elicited by the platelets when thrombin activates them n Shown in vivo to kill Staph aureus n
 Spinal Anesthesia n n Spinal Anesthesia should be done for TJR whenever possible. Neuraxial Anesthesia and Surgical Site Infection, Anesthesiology 2010; 113: 265– 7 All wounds become contaminated, and the development of infection is in large degree determined by the host defense mechanisms. Oxidative killing by neutrophils is the most important defense mechanism Oxidative killing is a function of local tissue oxygenation, which is improved by spinal anesthesia
Spinal Anesthesia n n Spinal Anesthesia should be done for TJR whenever possible. Neuraxial Anesthesia and Surgical Site Infection, Anesthesiology 2010; 113: 265– 7 All wounds become contaminated, and the development of infection is in large degree determined by the host defense mechanisms. Oxidative killing by neutrophils is the most important defense mechanism Oxidative killing is a function of local tissue oxygenation, which is improved by spinal anesthesia
 Chang Article n Anesthesiology: August 2010 - Volume 113 -Issue 2 -pp 279 -284 “Anesthetic Management and Surgical Site Infections in Total Hip or Knee Replacement: A Population based Study” n Risk for infection was 2. 21 times higher for patients receiving general anesthesia compared with regional anesthesia
Chang Article n Anesthesiology: August 2010 - Volume 113 -Issue 2 -pp 279 -284 “Anesthetic Management and Surgical Site Infections in Total Hip or Knee Replacement: A Population based Study” n Risk for infection was 2. 21 times higher for patients receiving general anesthesia compared with regional anesthesia
 Afferent inputs General anesthesia does not block the affferent input to the brain, and results in a higher stress response, releasing catecholamines, impairing tissue perfusion, decreasing oxygen tension n Volatile anesthetics impair neutrophil, macrophage, T-cell and natural killer cell functions, diminishing host defense. n
Afferent inputs General anesthesia does not block the affferent input to the brain, and results in a higher stress response, releasing catecholamines, impairing tissue perfusion, decreasing oxygen tension n Volatile anesthetics impair neutrophil, macrophage, T-cell and natural killer cell functions, diminishing host defense. n
 Spinal Anesthesia n n The mechanism is that spinal anesthesia is associated with less release of vasoconstrictors and norepinephrine, which cause decrease in tissue oxygen levels. The pain relief that patients receive after spinal helps by blocking the autonomic response Severe surgical pain decreases tissue oxygenation by 15 mm Hg. “Postoperative pain and subcutaneous oxygen tension” THE LANCET • Vol 354 • July 3, 1999 Hopf in Arch Surg 1997 “Wound tissue oxygenation tension predicts the risk of wound infection in surgical patients”
Spinal Anesthesia n n The mechanism is that spinal anesthesia is associated with less release of vasoconstrictors and norepinephrine, which cause decrease in tissue oxygen levels. The pain relief that patients receive after spinal helps by blocking the autonomic response Severe surgical pain decreases tissue oxygenation by 15 mm Hg. “Postoperative pain and subcutaneous oxygen tension” THE LANCET • Vol 354 • July 3, 1999 Hopf in Arch Surg 1997 “Wound tissue oxygenation tension predicts the risk of wound infection in surgical patients”
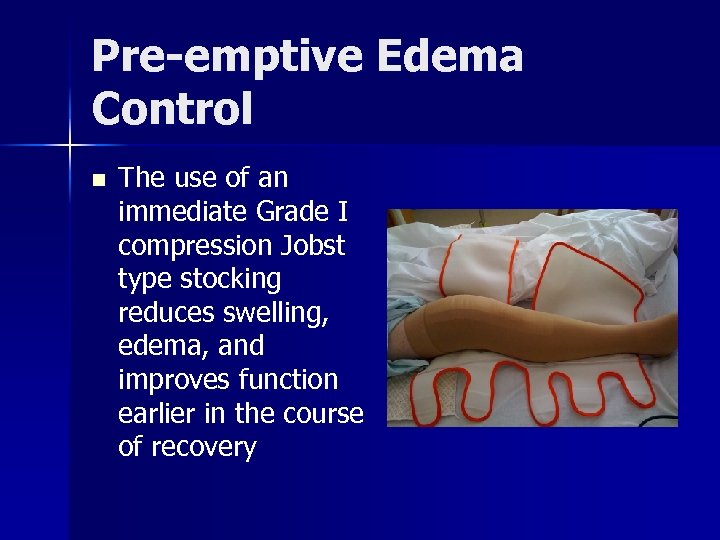 Pre-emptive Edema Control n The use of an immediate Grade I compression Jobst type stocking reduces swelling, edema, and improves function earlier in the course of recovery
Pre-emptive Edema Control n The use of an immediate Grade I compression Jobst type stocking reduces swelling, edema, and improves function earlier in the course of recovery
 Case example-Videos Revision TKR one day post op n Primary TKR compares ART technique to “MIS” TKR done 6 months earlier by different surgeon n
Case example-Videos Revision TKR one day post op n Primary TKR compares ART technique to “MIS” TKR done 6 months earlier by different surgeon n
 I would like to close by saying that I believe the next advances in Total Joint Replacement Surgery will come in the areas of Pain Management, and Blood conservation. This will result in the best outcomes we have ever enjoyed in our surgical lifetimes. Our goal is no intravenous narcotics, and no need for blood transfusions, with absolute “Primary Wound Healing”.
I would like to close by saying that I believe the next advances in Total Joint Replacement Surgery will come in the areas of Pain Management, and Blood conservation. This will result in the best outcomes we have ever enjoyed in our surgical lifetimes. Our goal is no intravenous narcotics, and no need for blood transfusions, with absolute “Primary Wound Healing”.
 Thanks for having me, I enjoyed my whirlwind here in Boston and would like to challenge these minds here today, to take this concept and make it better.
Thanks for having me, I enjoyed my whirlwind here in Boston and would like to challenge these minds here today, to take this concept and make it better.


