9272061f9cfd6cafd4833d151c7030d3.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 61

ABX Pentra DX 120 • Mean features • Leukopoïesis • ABX Erythropoïesis welcomes • Thrombopoïesis the SIMe. L • Expert validation station • ABX SPS evolution April 29 th, 2004 Conclusion

External view Rack loader Reagent compartment Technical software Processed tubes Stat sample Bay Validation station Optional slide maker and stainer

Main features 45 parameters Up to 120 samples / hour Optional and integrated slide maker and stainer Expert Validation Station
Main features 8 types of analyses (with random access) • CBC • DIFF • RET • CBR • DIR • ERB • CBE • SPS(*) (*): With SPS module
Measurement principles overview • IMPEDANCE METHOD: RBC, PLT, WBC, BASO (specific lyse) • PHOTOMETRY: HGB - Cyanmethemoglobin or cyanide free • CYTOCHEMISTRY / IMPEDANCE: 5 DIFF + Immature lines • FLUORESCENCE / IMPEDANCE: NRBC & RET
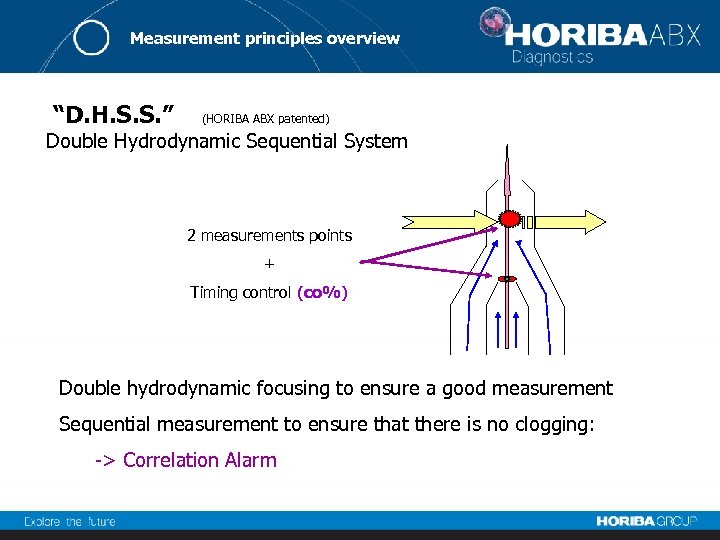
Measurement principles overview “D. H. S. S. ” (HORIBA ABX patented) Double Hydrodynamic Sequential System 2 measurements points + Timing control (co%) Double hydrodynamic focusing to ensure a good measurement Sequential measurement to ensure that there is no clogging: -> Correlation Alarm

Leukopoïesis exploration
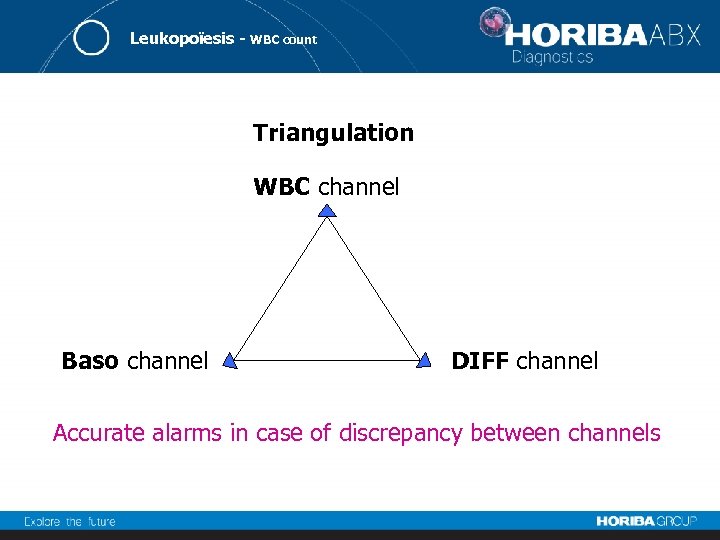
Leukopoïesis - WBC count Triangulation WBC channel Baso channel DIFF channel Accurate alarms in case of discrepancy between channels
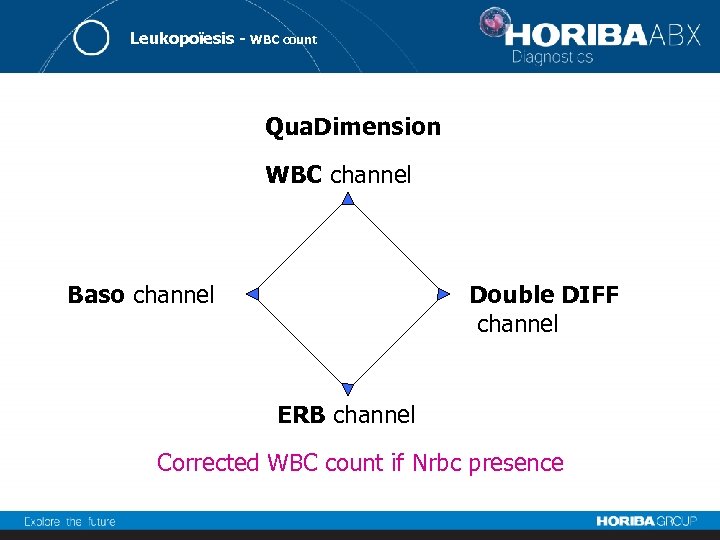
Leukopoïesis - WBC count Qua. Dimension WBC channel Baso channel Double DIFF channel ERB channel Corrected WBC count if Nrbc presence
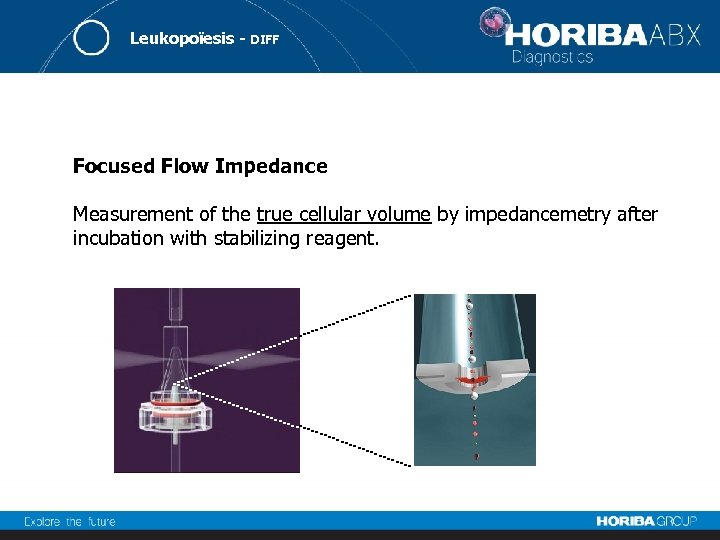
Leukopoïesis - DIFF Focused Flow Impedance Measurement of the true cellular volume by impedancemetry after incubation with stabilizing reagent.
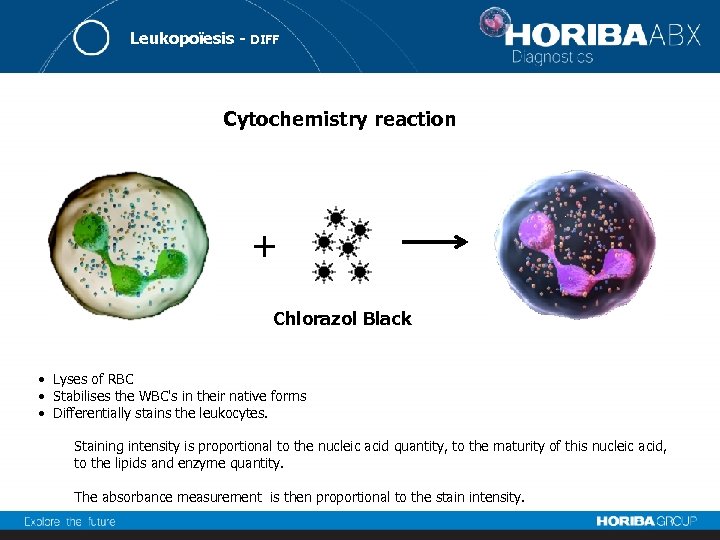
Leukopoïesis - DIFF Cytochemistry reaction + Chlorazol Black • Lyses of RBC • Stabilises the WBC's in their native forms • Differentially stains the leukocytes. Staining intensity is proportional to the nucleic acid quantity, to the maturity of this nucleic acid, to the lipids and enzyme quantity. The absorbance measurement is then proportional to the stain intensity.
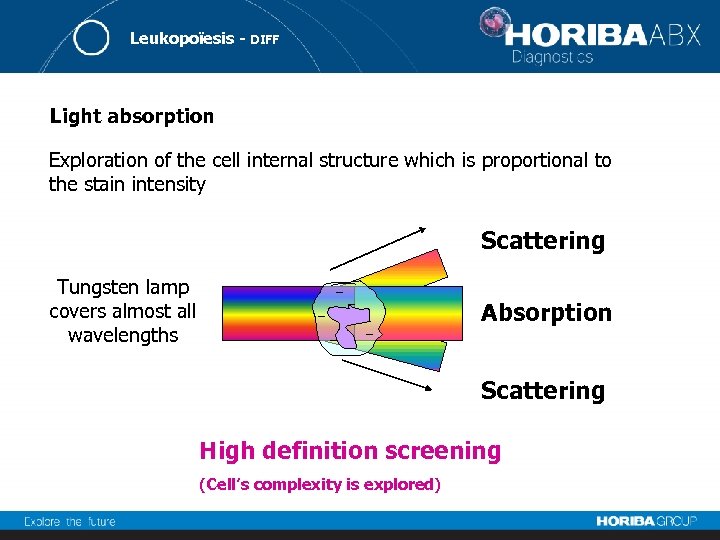
Leukopoïesis - DIFF Light absorption Exploration of the cell internal structure which is proportional to the stain intensity Scattering Tungsten lamp covers almost all wavelengths Absorption Scattering High definition screening (Cell’s complexity is explored)
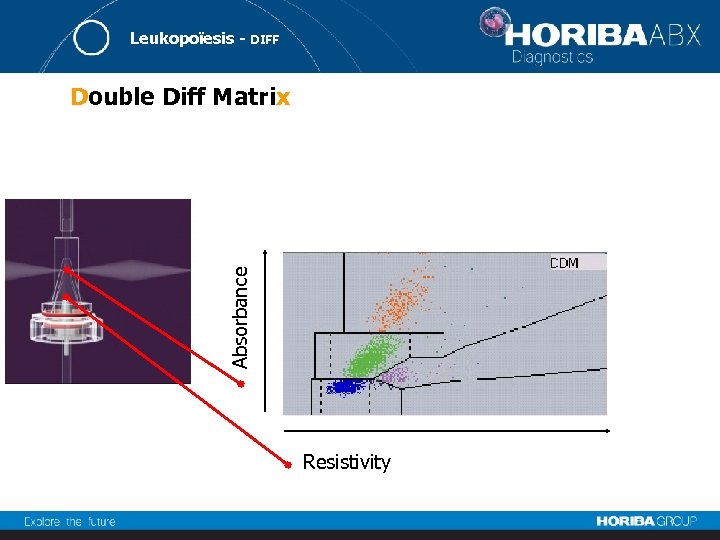
Leukopoïesis - DIFF Absorbance Double Diff Matrix Resistivity
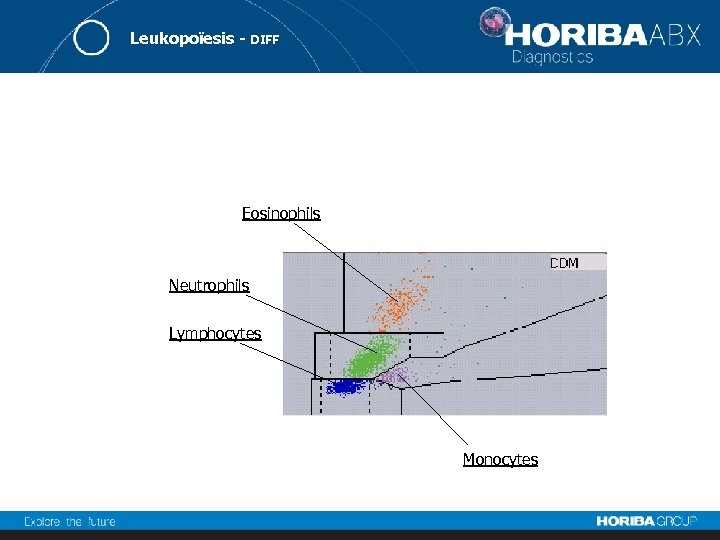
Leukopoïesis - DIFF Eosinophils Neutrophils Lymphocytes Monocytes
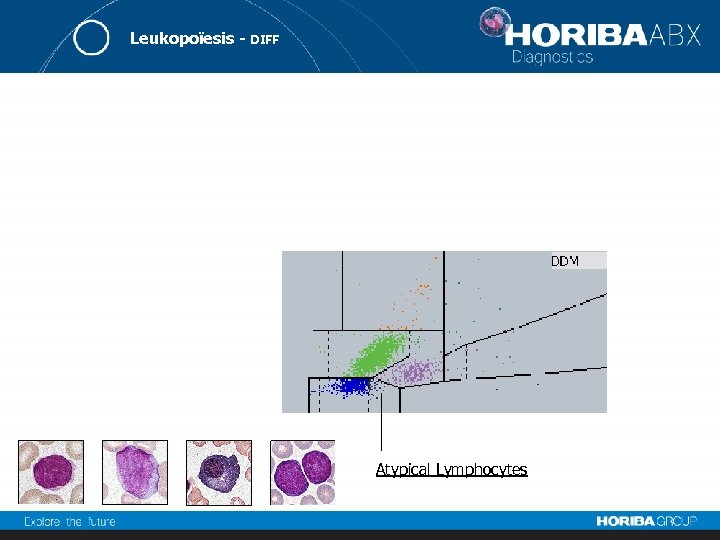
Leukopoïesis - DIFF Atypical Lymphocytes
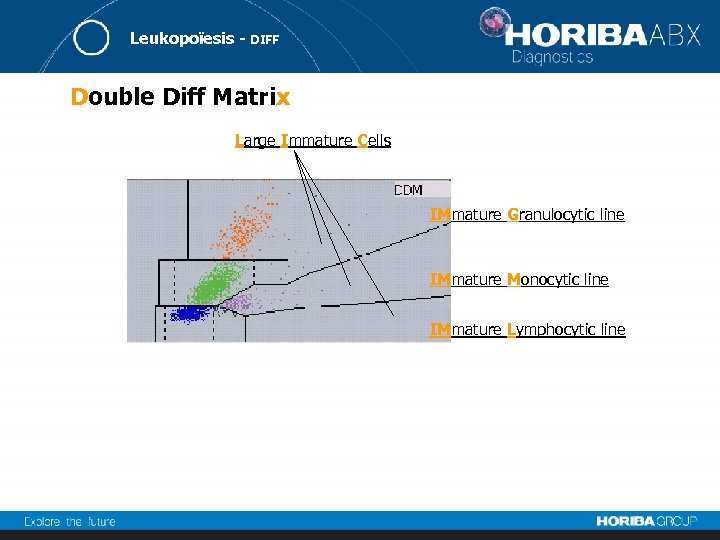
Leukopoïesis - DIFF Double Diff Matrix Large Immature Cells IMmature Granulocytic line IMmature Monocytic line IMmature Lymphocytic line
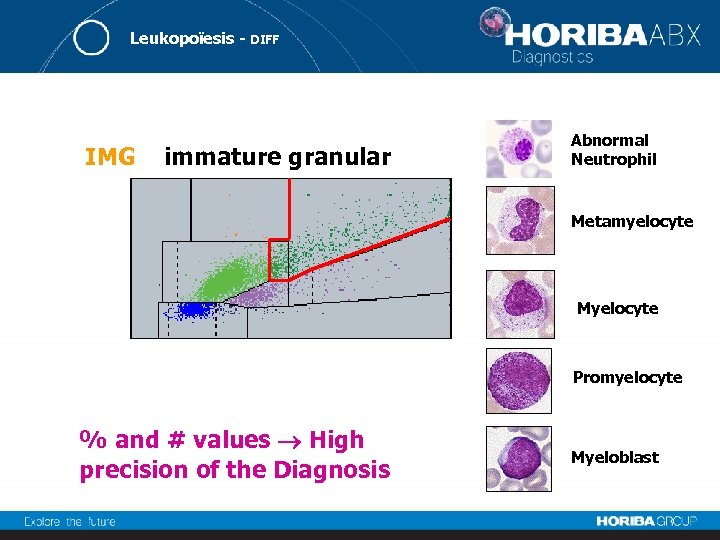
Leukopoïesis - DIFF IMG immature granular Abnormal Neutrophil Metamyelocyte Myelocyte Promyelocyte % and # values High precision of the Diagnosis Myeloblast
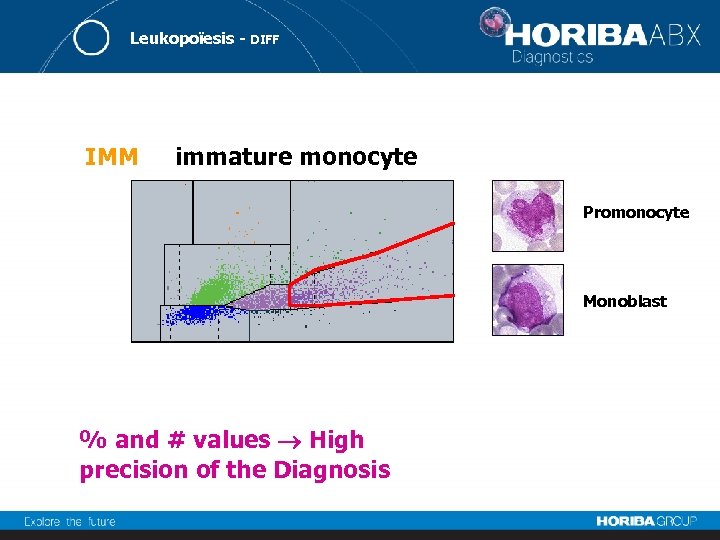
Leukopoïesis - DIFF IMM immature monocyte Promonocyte Monoblast % and # values High precision of the Diagnosis
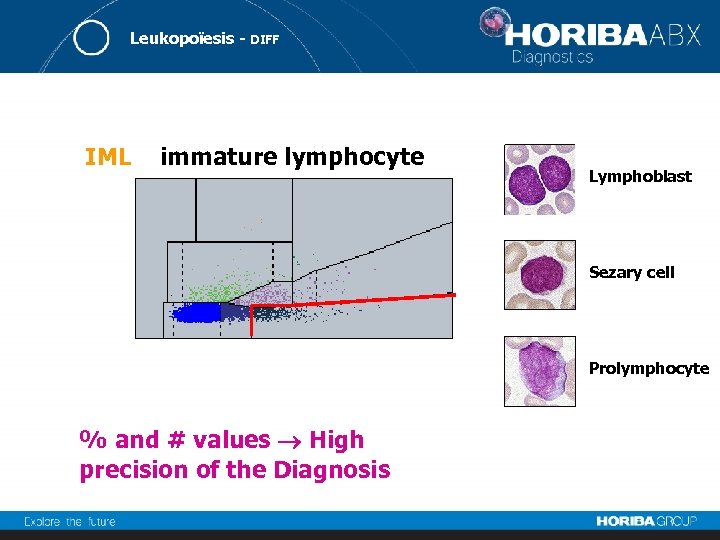
Leukopoïesis - DIFF IML immature lymphocyte Lymphoblast Sezary cell Prolymphocyte % and # values High precision of the Diagnosis
Leukopoïesis - DIFF Additional information provided by Matrix • Detection of platelets aggregates • Detection of Nrbc population • Detection of lyse resistant cells • Detection of band cells

Evaluations references ABX PENTRA DX 120: EVALUATION OF THE NEW PARAMETERS A side-by-side comparison with manual slide review (Double Matrix / Erythroblasts) and immunophenotyping (Erythroblasts) Dr. Jose Maria JOU Servei d’Hemostàsia i Hemoteràpia Hospital Clínico Universitario de Barcelona, C/ Villarroel nº 170, 08036 Barcelona, SPAIN. Myeloid Immaturity and Instrumental Findings AM. Cenci°, B. Casolari°, M. Maconi* °Laboratory of Clinical Pathology, AUSL Agency S. Agostino Hospital, Modena; *Laboratory of Chemical Analysis Clinics, Santa Maria Nuova General Hospital, Reggio Emilia.

Evaluations references Evaluation of the ABX Pentra DX 120 Dr. Francis Lacombe Laboratoire d’Hématologie, Hôpital Haut-Lévêque, France New technologies and study of blood cells: the performance of HORIBA ABX PENTRA DX 120 B. Casolaria, M. Maconib, A. M. Cencia a. Laboratory of Clinical Pathology, AUSL Agency S. Agostino Hospital, Modena; b. Laboratory of Clinical Pathology, O. I. R. M. Hospital Agency - S. Anna, Turin. Detection of atypical lymphocyte populations and lymphoid pathology diagnosis in adults and children (ALY alarm) P. Lemaire, Laboratoire de Longpont-Sur-Orge (91310) Georges Pompidou European Hospital (75015 Paris), France

Erythropoïesis exploration
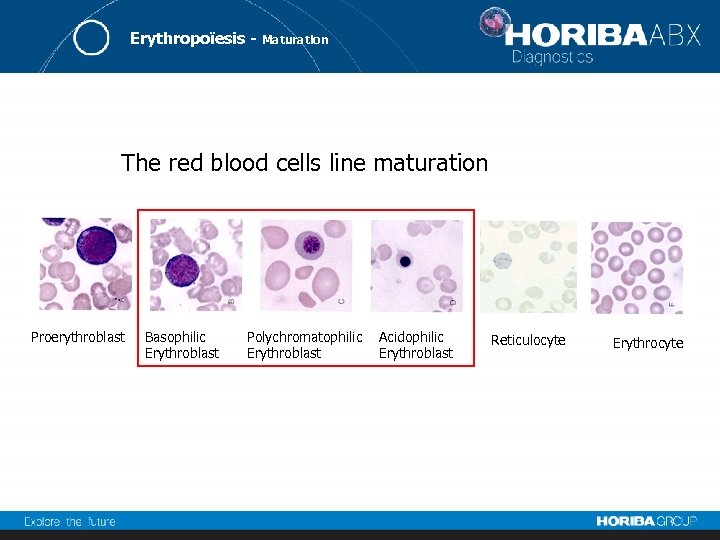
Erythropoïesis - Maturation The red blood cells line maturation Proerythroblast Basophilic Erythroblast Polychromatophilic Erythroblast Acidophilic Erythroblast Reticulocyte Erythrocyte
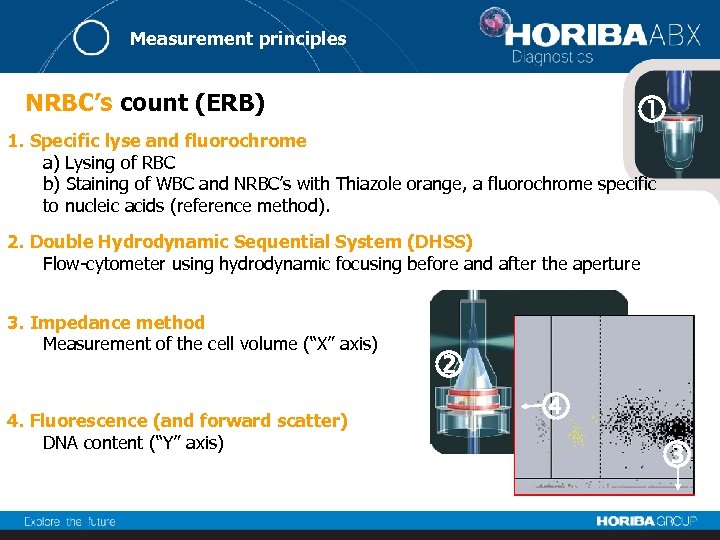
Measurement principles NRBC’s count (ERB) 1. Specific lyse and fluorochrome a) Lysing of RBC b) Staining of WBC and NRBC’s with Thiazole orange, a fluorochrome specific to nucleic acids (reference method). 2. Double Hydrodynamic Sequential System (DHSS) Flow-cytometer using hydrodynamic focusing before and after the aperture 3. Impedance method Measurement of the cell volume (“X” axis) 4. Fluorescence (and forward scatter) DNA content (“Y” axis)
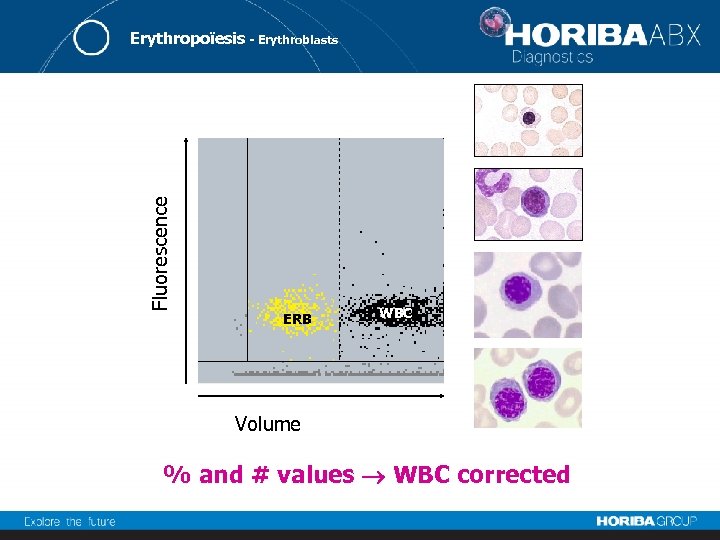
Fluorescence Erythropoïesis - Erythroblasts ERB WBC Volume % and # values WBC corrected

Evaluations references ABX PENTRA DX 120 : EVALUATION OF THE NEW PARAMETERS A side-by-side comparison with manual slide review (Double Matrix / Erythroblasts) and immunophenotyping (Erythroblasts) Dr. Jose Maria JOU Servei d’Hemostàsia i Hemoteràpia Hospital Clínico Universitario de Barcelona, C/ Villarroel nº 170, 08036 Barcelona, SPAIN. Automated Nucleated RBC Counting: Comparison to Flow Cytometry. Bruce H. Davis*, Kathleen T. Davis*, Esther Tournier+, Karen Becker* *Trillium Diagnostics, LLC and Maine Medical Center Research Institute, Scarborough, Maine 04074 USA +Horiba. ABX Diagnostics, Montpellier, France
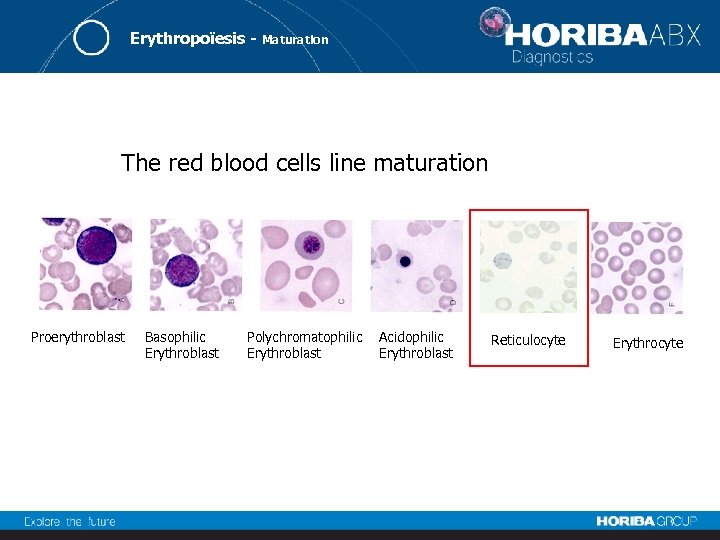
Erythropoïesis - Maturation The red blood cells line maturation Proerythroblast Basophilic Erythroblast Polychromatophilic Erythroblast Acidophilic Erythroblast Reticulocyte Erythrocyte
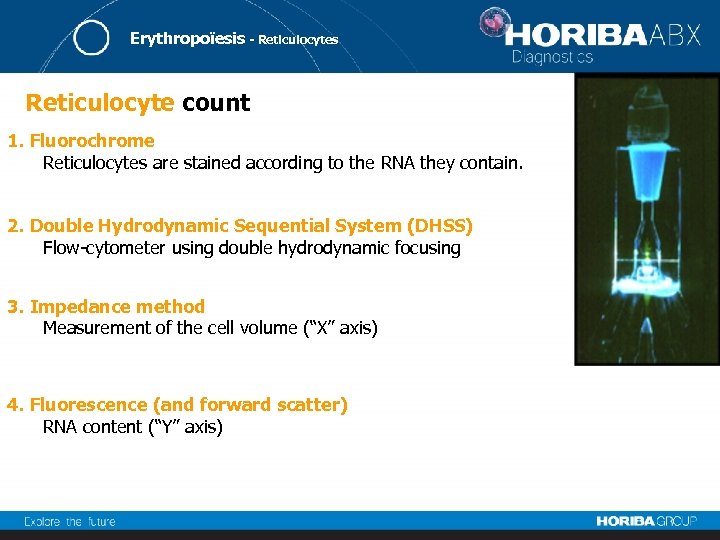
Erythropoïesis - Reticulocytes Reticulocyte count 1. Fluorochrome Reticulocytes are stained according to the RNA they contain. 2. Double Hydrodynamic Sequential System (DHSS) Flow-cytometer using double hydrodynamic focusing 3. Impedance method Measurement of the cell volume (“X” axis) 4. Fluorescence (and forward scatter) RNA content (“Y” axis)
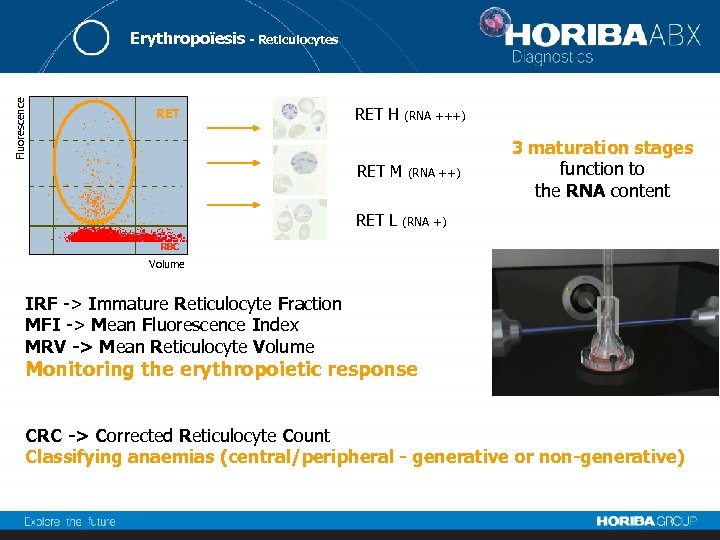
Fluorescence Erythropoïesis - Reticulocytes RET H (RNA +++) RET M RET L (RNA ++) 3 maturation stages function to the RNA content (RNA +) RBC Volume IRF -> Immature Reticulocyte Fraction MFI -> Mean Fluorescence Index MRV -> Mean Reticulocyte Volume Monitoring the erythropoietic response CRC -> Corrected Reticulocyte Count Classifying anaemias (central/peripheral - generative or non-generative)

Evaluations references The Mean Reticulocyte Volume (MRV) on the HORIBA ABX Pentra 120/DX as an alternative measurement to the Reticulocyte Haemoglobin Content (CHr™ ) A. H. Roderick – Department of Haematology, University Hospital of Wales, Cardiff. UK J. M. Jou – Servei d’Hemoterapia, Hospital Clinic, Barcelona. Spain W. G. B. Rees, E. Thomas – Haematology Department, West Wales General Hospital, Carmarthen. UK Early diagnosis of iron deficiency anaemia by Mean Reticulocyte Volume (MRV) screening Dr. Ruud Muusze, clinical chemist, Ziekenhuis Zeeuws Viaanderen, Terneuzen, Holland.
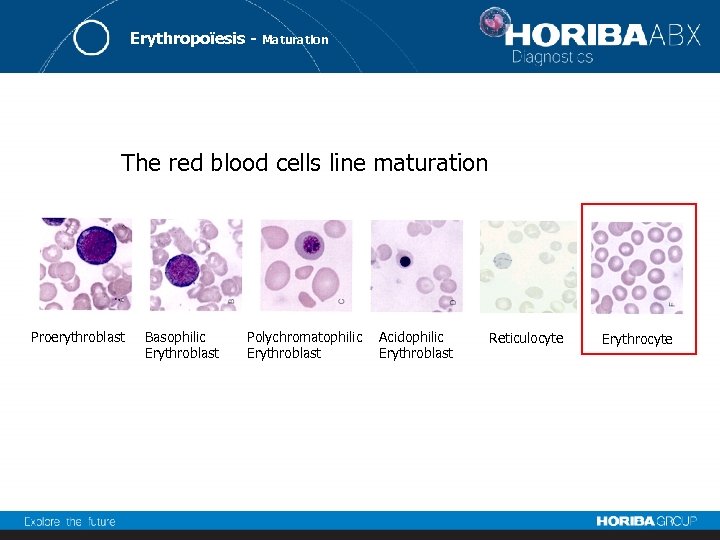
Erythropoïesis - Maturation The red blood cells line maturation Proerythroblast Basophilic Erythroblast Polychromatophilic Erythroblast Acidophilic Erythroblast Reticulocyte Erythrocyte
Erythropoïesis - Red Blood Cells Specific quantitative flags: • Anemia: Hgb • Polyglobulia: RBC • Cold agglutinin: MCHC • Micro/macrocytosis: MCV • Anisocytosis: RDW Reference methods of measurement High precision of the Anemias and RBC pathologies
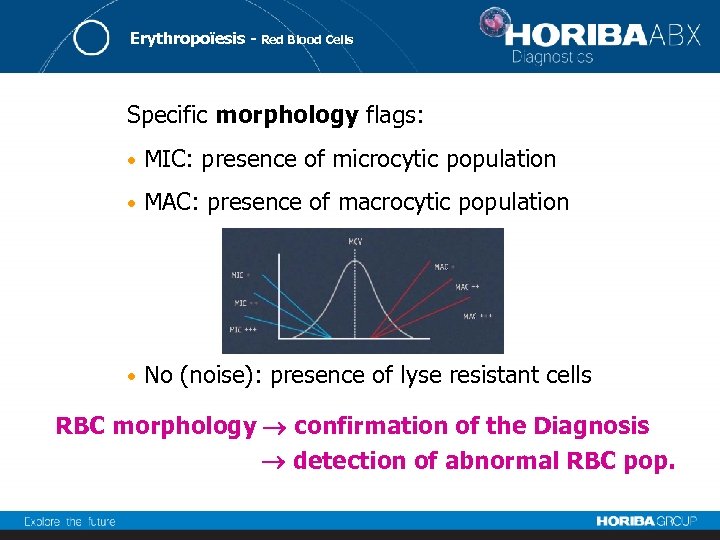
Erythropoïesis - Red Blood Cells Specific morphology flags: • MIC: presence of microcytic population • MAC: presence of macrocytic population • No (noise): presence of lyse resistant cells RBC morphology confirmation of the Diagnosis detection of abnormal RBC pop.
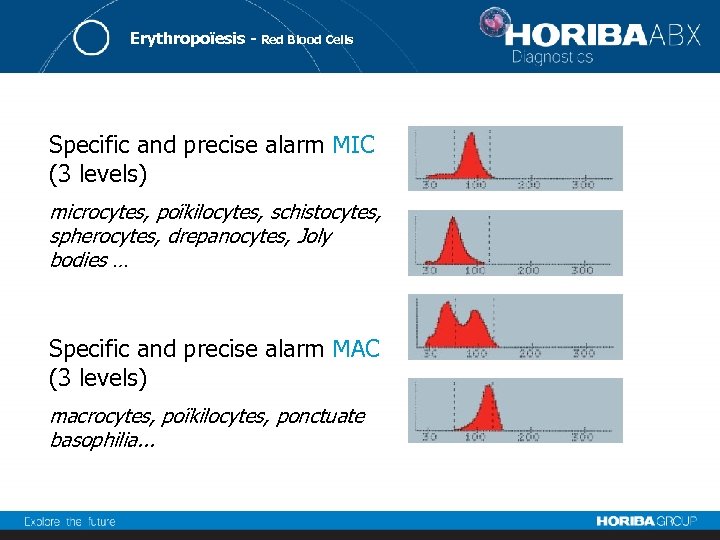
Erythropoïesis - Red Blood Cells Specific and precise alarm MIC (3 levels) microcytes, poïkilocytes, schistocytes, spherocytes, drepanocytes, Joly bodies … Specific and precise alarm MAC (3 levels) macrocytes, poïkilocytes, ponctuate basophilia. . .

Thrombopoïesis exploration
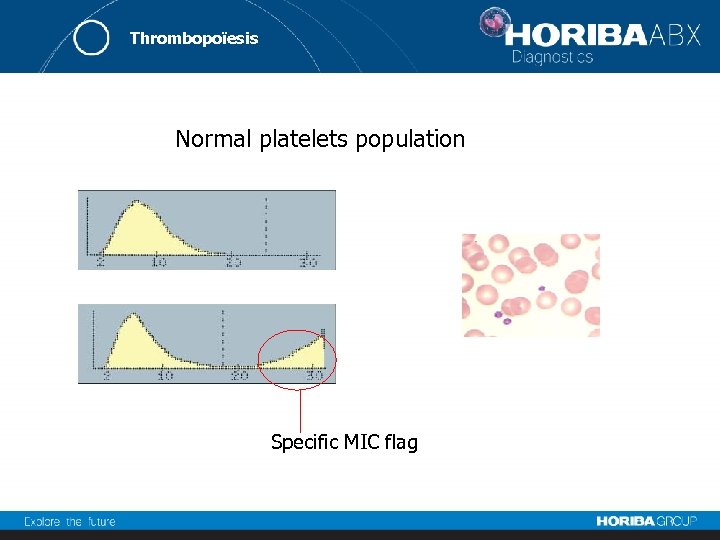
Thrombopoïesis Normal platelets population Specific MIC flag
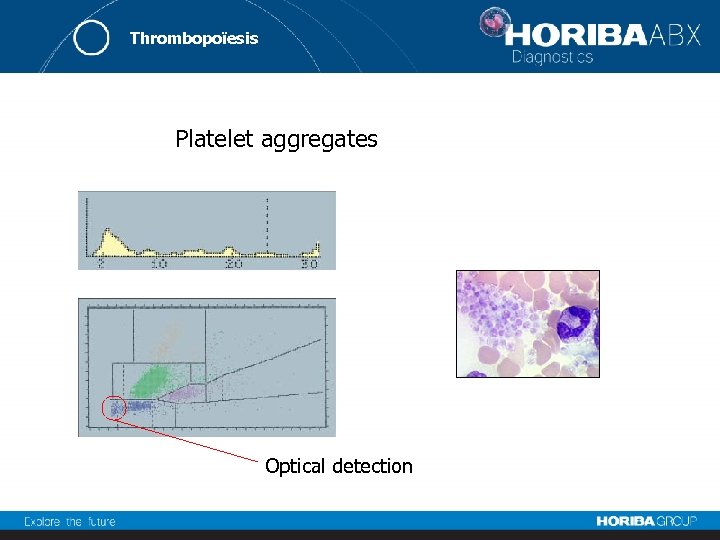
Thrombopoïesis Platelet aggregates Optical detection
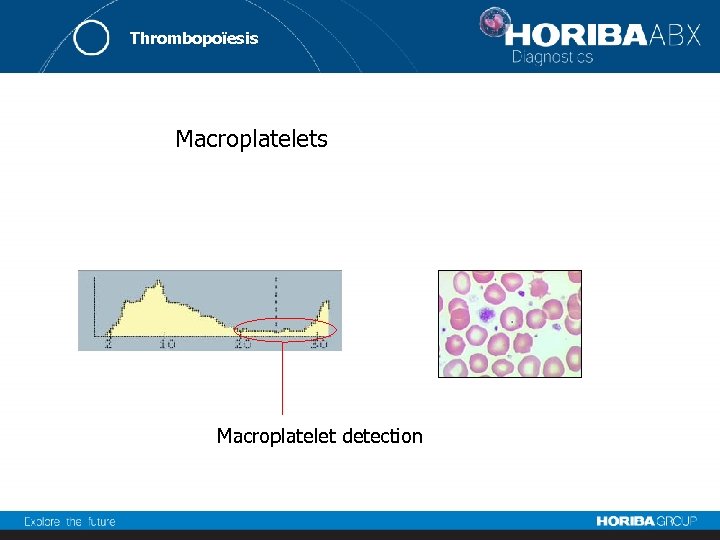
Thrombopoïesis Macroplatelet detection
Evaluation references Evaluation of Platelets count below 40. 109/L: Hematologic Analyzers ABX Pentra DX 120 versus platelet reference method Dr. Jose Maria JOU Servei d’Hemostàsia i Hemoteràpia Hospital Clínico Universitario de Barcelona, C/ Villarroel nº 170, 08036 Barcelona, SPAIN.

Evaluation references Am J Clin Pathol 115(3): 460 -464, 2001. © 2001 American Society of Clinical Pathologists, Inc
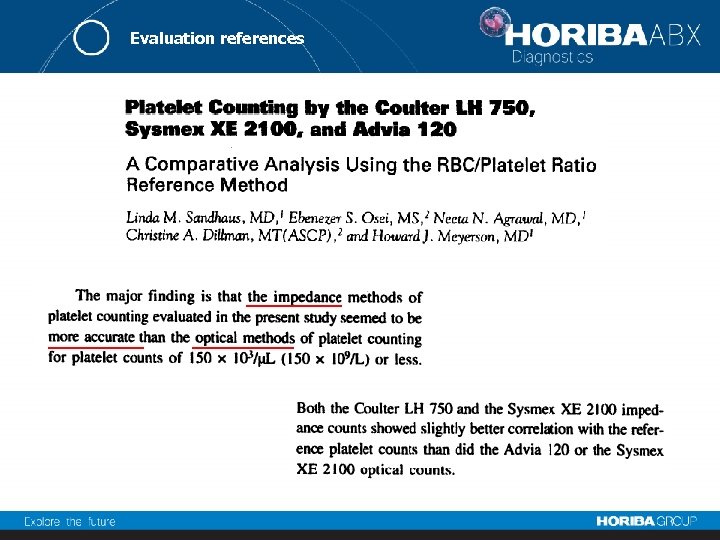
Evaluation references

Expert validation station
Specs & functionality Dedicated PC Windows XP, CD-ROM burner Onboard user manual Mono or bi-directional host connection Connection of 3 ABX analyzers Query mode Download capability
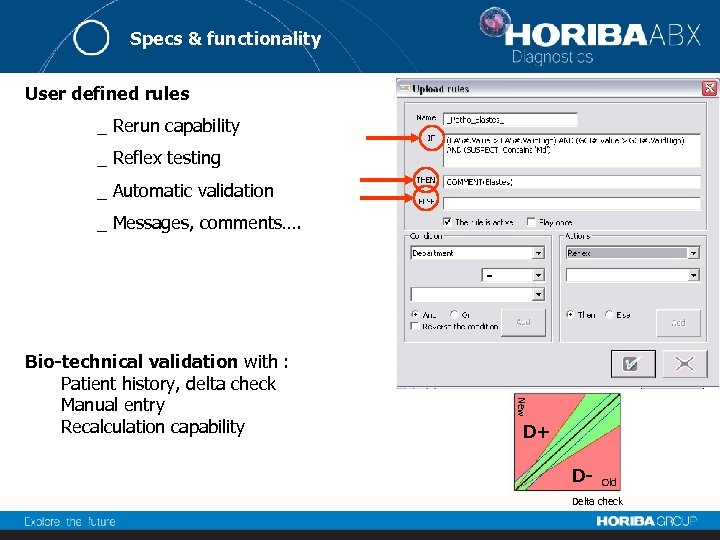
Specs & functionality User defined rules _ Rerun capability _ Reflex testing _ Automatic validation _ Messages, comments…. New Bio-technical validation with : Patient history, delta check Manual entry Recalculation capability D+ D- Old Delta check
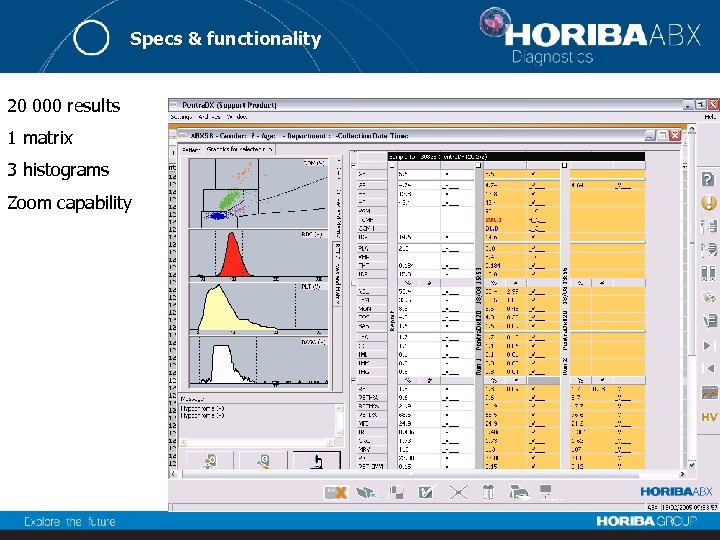
Specs & functionality 20 000 results 1 matrix 3 histograms Zoom capability
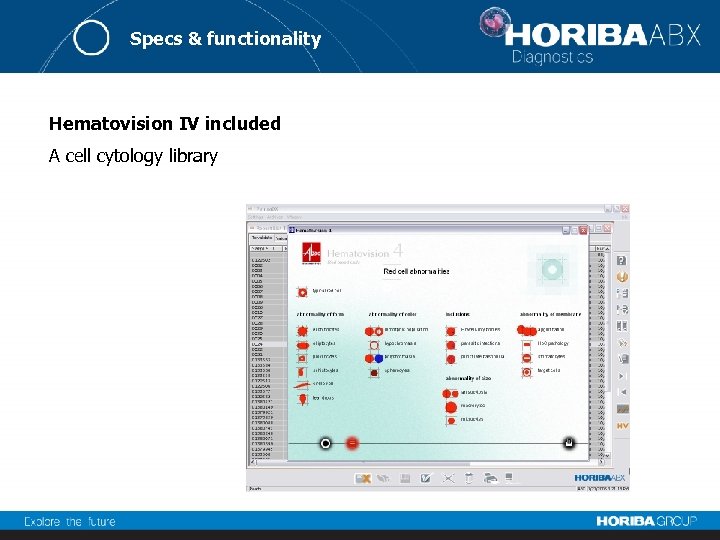
Specs & functionality Hematovision IV included A cell cytology library
SPS EVOLUTION

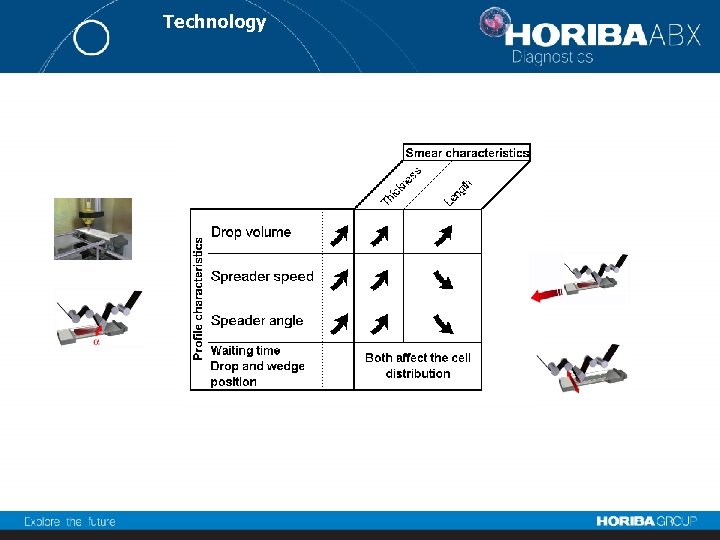
Specification Throughput : 120 stained slides per hour Sample volume: 50µl Stain : MGG, Wright-Giemsa User defined smear criteria Smearing profile function to each individual sample and to each hematology parameter Automatic maintenance

Technology Slide stacker capacity of 160 slides When dispensed, slides are twisted to avoid blockages Rack stacker capacity of 8 racks Located outside, slides and racks are easily reloaded at any time

Technology Titanium coated wedge : No change, no adjustment Smearing tape : Moves forward between each sample to avoid contamination and to avoid a complex mechanism to clean and dry the wedge

Technology User’s defined smearing profile : - Blood drop volume adjustable by increment of 0, 1 µl - 2 smearing angles (40° or 45°) - Waiting time adjustable by increment of 1 ms - Smearing speed adjustable by increment of 1 step/ms
Technology
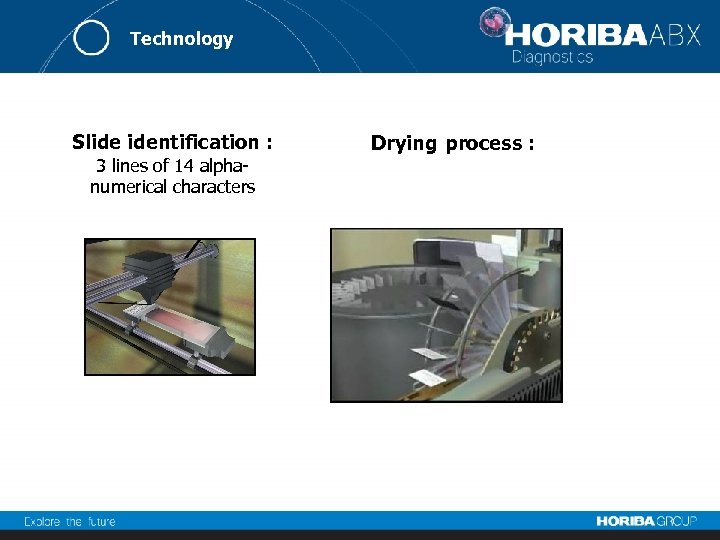
Technology Slide identification : 3 lines of 14 alphanumerical characters Drying process :

Technology Individual staining wells : Use of fresh stains ensures a good staining stability User defined stain volume Automatic stain dilution Staining steps adjustable by increment of 30 s Maximum staining duration of 16 mn

Technology Manual mode : Pre-smeared slide: Bone marrow Biologic fluid Cyto-centrifuging Leuko-concentration Slide outlet : 20 slides can collected in one rack
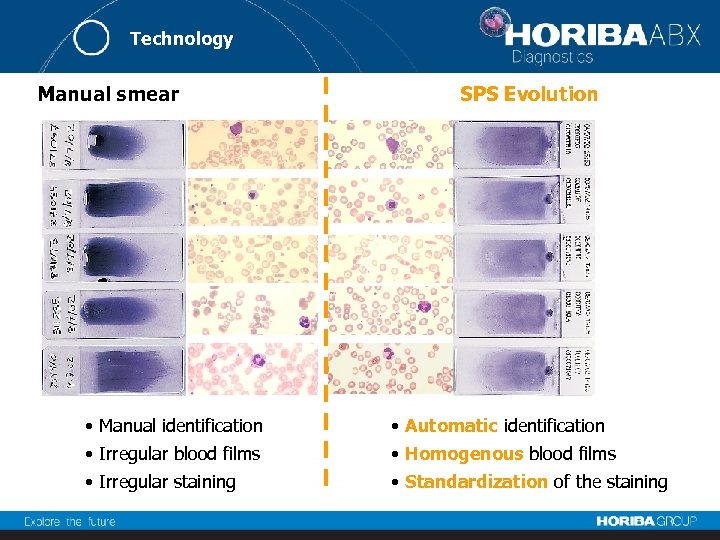
Technology Manual smear SPS Evolution • Manual identification • Automatic identification • Irregular blood films • Homogenous blood films • Irregular staining • Standardization of the staining
ABX Pentra DX 120 Conclusion Dr. Echevarne laboratory
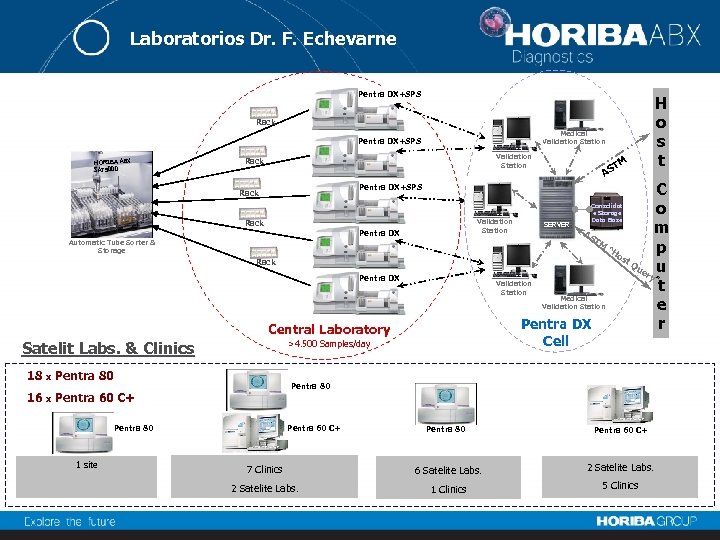
Laboratorios Dr. F. Echevarne Pentra DX+SPS Rack Medical Validation Station Pentra DX+SPS HORIBA ABX SAT 5000 Validation Station Rack C o Validation SERVER Station m AS TM “H p os t. Q ue u ry ” Validation t Station Medical Validation Station e Pentra DX r Pentra DX+SPS Rack Consolidat e Storage Data Base Rack Pentra DX Automatic Tube Sorter & Storage Rack Pentra DX Central Laboratory Cell >4. 500 Samples/day Satelit Labs. & Clinics 18 x Pentra 80 16 x Pentra 60 C+ Pentra 80 1 site TM AS H o s t Pentra 80 Pentra 60 C+ 7 Clinics 6 Satelite Labs. 2 Satelite Labs. 1 Clinics 5 Clinics

Conclusion HORIBA ABX is differentiating itself from the other “suppliers of systems” in being a “partner providing solutions” for the laboratory. HORIBA ABX ambitious goals will be reached by becoming the “preferred partner” of its customers worldwide.

Thank you ABX welcomes the SIMe. L April 29 th, 2004
9272061f9cfd6cafd4833d151c7030d3.ppt