da81c4efe695ce85ffebcbfeccc08cd5.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 55

Absolutism in France “L’etat c’est moi” -- Louis XIV

th France in the 17 Century • Population: 19 million – 3 times that of England – 2 times that of Spain • Uneven distribution of wealth – very wealthy, very poor • Large merchant class • Protestantism declining • Self-sufficient economy – Trade with India, settlements in North America and Caribbean (Canada, Mississippi Valley, West Indies)

Absolutism (Absolute Monarch) • Monarch possesses unlimited power – No laws or direct opposition – No constitution or body of law above the king • Monarch is expected to act according to tradition and custom • People must have complete trust in well-bred and well-trained monarchs who were raised for the role from birth • Believe in the Divine Right to Rule • Examples: Russian Tsars, French Kings

Henry IV “Henry the Great” • Ruled 1589 -1610 • Born Protestant (Huguenot) • Converted to Catholicism to become King • 1598: Edict of Nantes – Guaranteed religious liberties to the Protestants – Ended French Wars of Religion • Murdered by a fanatical Catholic

Louis XIII • Ruled 1610 -1643 • Ruled during 30 Years War • Influenced by Cardinal Richelieu • Intrigue: “Three Musketeers” • Married Anne of Austria • Absolute Monarch – French nobility under his control – No more special privileges for the Huguenots – Built powerful navy – No tax reform

Cardinal Richelieu 1585 -1642 Believed in the State above all else Two Goals – Strengthen the power of the king/central government – Make France the dominant power in Europe

Richelieu and Government • Cardinal Richelieu was Louis XIII’s “Chief Minister” • Consolidated royal power • Crushed domestic dissenters • Created stronger economy • Restrained the power of the nobility • Transformed France into a strong, centralized state

Richelieu and France • Main foreign policy objectives: – limit Austrian-Hapsburg Dynasty – Catholic, but made alliances with Protestant rulers • Thirty Years War – France emerges more powerful than other nations – Decline of HRE • Legacy King Louis XIV continued Richelieu's work : – Further suppressed the aristocracy – Edict of Fontainebleau in 1685 • Nullified Edict of Nantes (1598) • Ordered destruction of Huguenot churches • Closed Protestant schools • Result nearly 500, 000 Protestants left France : over the next 20 years – Went to England, Netherlands, Denmark, Germany, North America

Young King Louis XIV • Born 1638 • Ruled 16431715 • Assumed power at age 23

Cardinal Mazarin • Advisor to Louis while he was a child (1643 - 1661) • De facto ruler of France • Italian. Distrusted by the French • Father-figure to Louis XIV • His policies during the Thirty Years War were unpopular • On his death, there was not a successor to “First Minister”

Thirty Years War: Causes • 1618 -1648 • Mostly religious conflict between Catholics and Protestants • Also political conflict between Holy Roman Empire and France

European Results: Thirty Years War • Dutch independence from Spain • France gains Alsace from HRE • Protestant German princes ally themselves with France • Peace of Westphalia : – Everyone must recognize the Peace of Augsburg • Catholics and Protestants are legally equal • Calvinism is permitted – Decline of HRE – Doesn’t end conflict between Spain and France

Thirty Years War: Results for France • Treasury nearly bankrupt • 1659: Spain cedes territory (mostly land in the Spanish Netherlands) to France, ending the conflict • Balance of Power changes Spain begins to. decline, France is rising in power

Just when things are getting better. . Le Fronde • 1648 -- 1653 – Civil War – Began immediately after end of Thirty Years War • Rebellion mostly nobles, and members of : parlements who feared too much royal power – Nobility and Bourgeoisie wanted to defend and protect regional influence, traditions • Long term results : – Louis developed life-long distrust of nobility – Ensured Louis XIV would enforce absolutist rule – Most French realize the benefit of a strong monarch

• Believer in Mercantilism – the prosperity of a nation depends upon its supply of capital. – Economic assets = bullion held by the state – This is best increased through a positive balance of trade with other nations (exports minus imports). – Government must encourage exports and discourage imports, through the use of tariffs. Jean Baptist Colbert Finance Minister

Colbert and the Domestic Economy • Made taxation more efficient to enrich treasury • Pushed Internal commerce – Farmers, small manufacturers penalized – Restricted movement of goods and labor between regions – Unfair tax system was reinforced • Gentry, clergy exempt from taxation • Capitalists have favorable taxes • Land used for export industries (wine, wool)

Louis XIV – Domestic Problems – Inherited weak economy – Civil Unrest – Nobles are still too powerful. Louis must punish them. • Filled high government positions with commoners • Reduced nobles to courtiers • Required nobles to spend the majority of the year with him • “Rewarded” nobles with time spent with him

L’ etat c’est moi! “I am the State” 1643 -1715 France became a world power and a leader in the arts. Fashion: Clothing is large and showy to emphasis the king’s personality

Louis XIV – the “Sun King” • Overall brilliance at court • The nobles stayed within the king’s orbit • Ruled for 72 years • Great influence on French culture – French is language of diplomacy – French style greatly imitated

Life of Opulence and Grandeur • The Daily Routine of the King

Louis as the sun god Apollo

Louis as Apollo by Jean Nocret, 1670

1673 Louis represented as a classical hero

The sun symbol was everywhere at Versailles
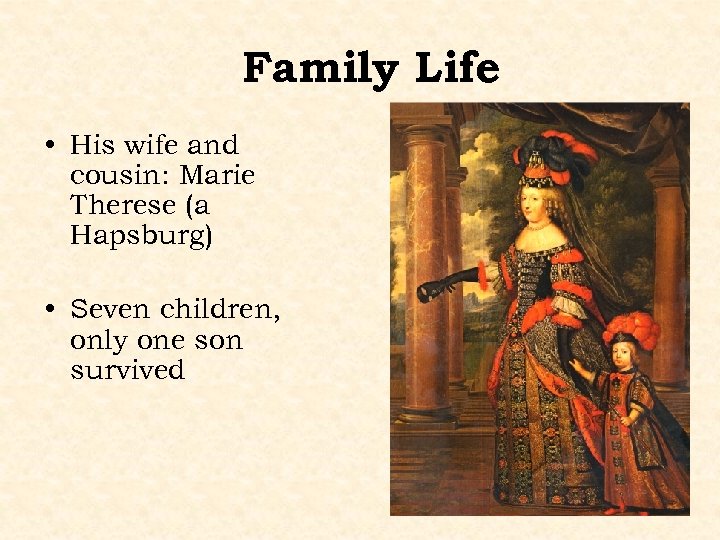
Family Life • His wife and cousin: Marie Therese (a Hapsburg) • Seven children, only one son survived

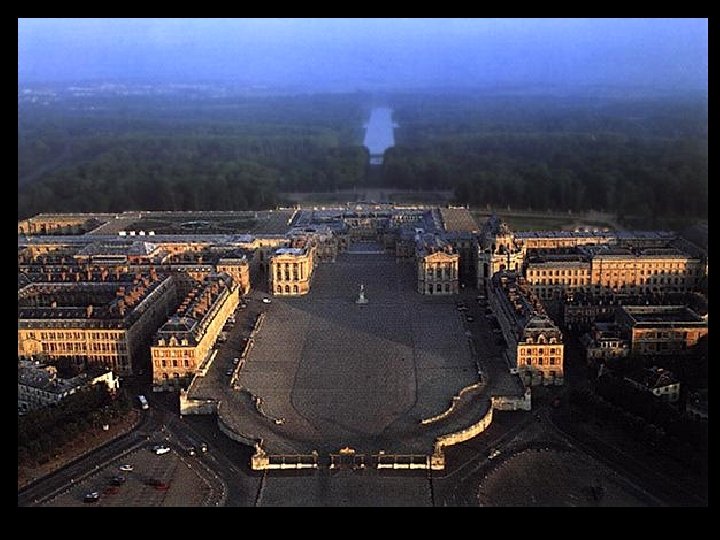
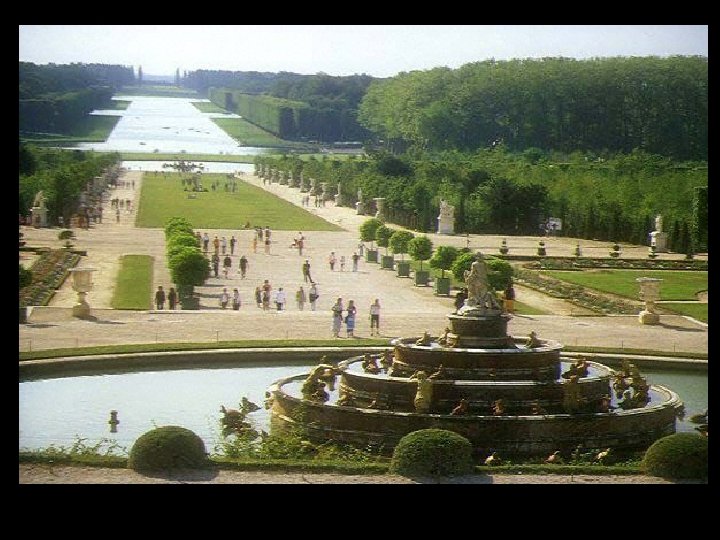
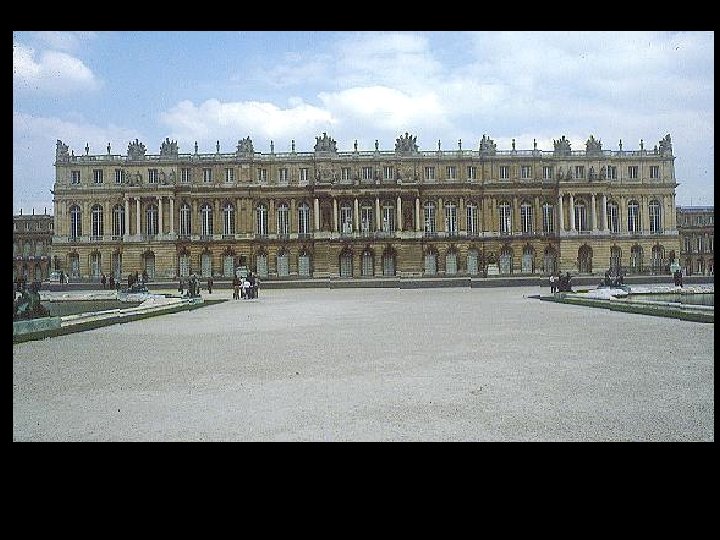
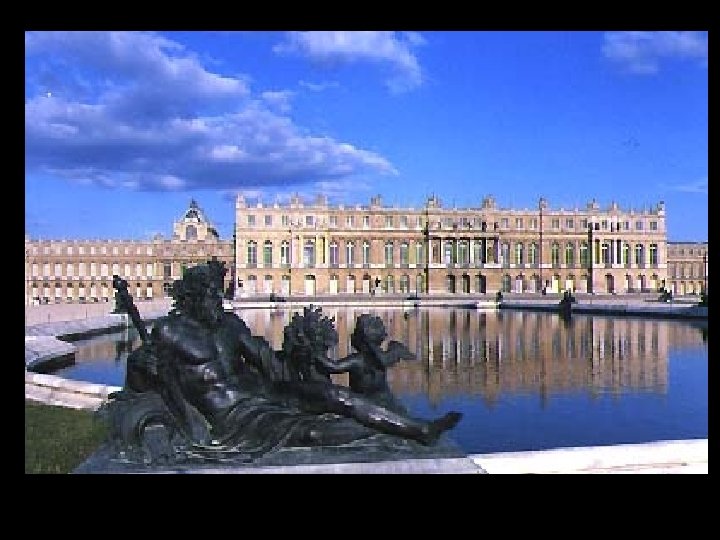
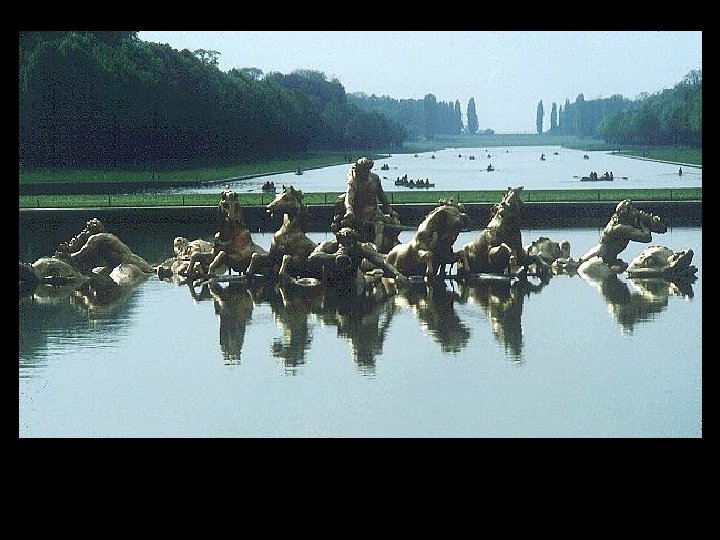
Versailles Glory of the monarch glory of the state =

550, 000 square feet Versailles Statistics 2, 153 windows 700 rooms 67 staircases 6, 000 paintings 2, 100 sculptures 5, 000 pieces of furniture 6, 500 Acres







Temple of Love

Mistresses of the King • Mistress of the king is a very public role – sits next to the queen at court. • Mademoiselle de la Vallière 3 – children, later fled to a convent • Madame de Montespan 7 – children, also “retired” to a convent • Madame de Maintenon no – children, but married Louis in secret.

Hall of Mirrors

The King’s Chapel

Opera Stage at Versailles

Furniture: “Louis XIV Style”

Imitators Winter Palace in St. Petersburg and Peterhof summer palace near St. Petersburg

Blenheim Palace: England

Schonbrunn: Austria
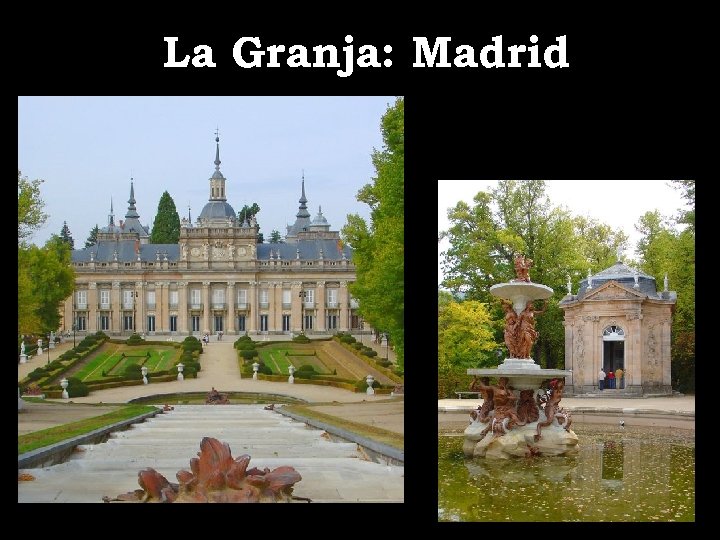

La Granja: Madrid

Marie Antoinette’s “Peasant” House • Looks rustic, but opulent on the inside • Many aristocrats mimicked this style – Revolution wiped out that idea
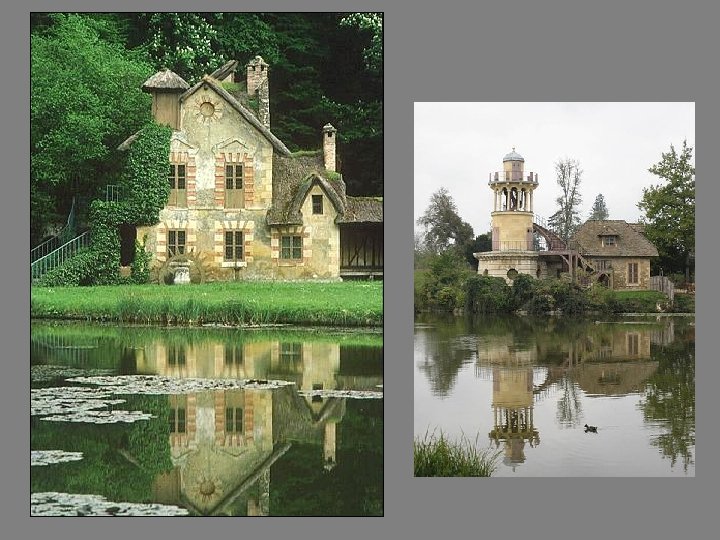


Marie Antoinette’s “Peasant’s Hut”

War of Spanish Succession • Carlos II (16691700) • Descended from Joanna the Mad 14 times -- twice as a great, great grandson
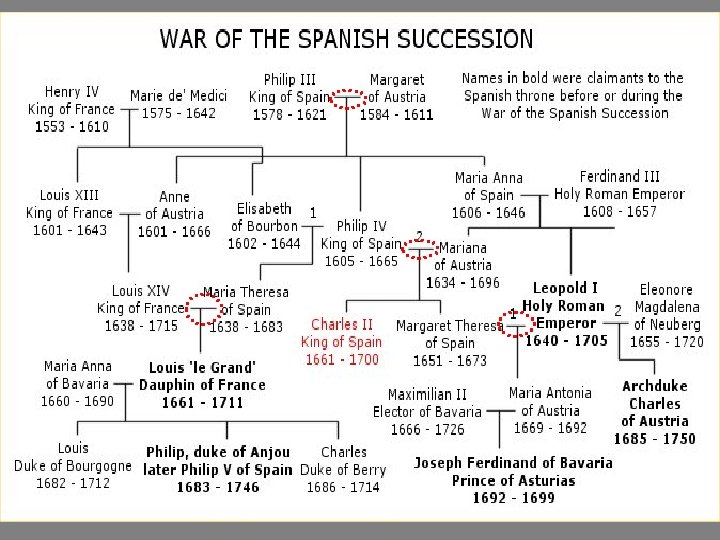

War of Spanish Succession 1702 -1713 – France and HRE want to share Spanish territory – Spanish king’s will favors France – This would make France too powerful, disrupt balance of power – War • Two sides: Grand Alliance(led by England, Holland, HRE) vs. France • France loses war but gains Spanish , throne

1713: Treaty of Utrecht • The Grand Alliance – England finally becomes one of the “great powers” of Europe • Made Louis XIV unpopular at home, but his grandson is now king of Spain • Spain loses Italian possessions • France gives England Hudson’s Bay territory • Balance of Power is preserved

Death of Louis XIV • "Je m'en vais, mais l'État demeurera toujours. ("I am going away, but the State " will always remain") • Advice to Louis XV"Do not follow the bad : example which I have set you; I have often undertaken war too lightly and have sustained it for vanity. Do not imitate me. . may you apply yourself to the alleviation of the burdens of your subjects".

1715: Death of Louis XIV • War left France in need of revenue • Despite losing the war, Louis’ reign saw the spread of French culture and style throughout Europe – Other monarchs mimicked his lifestyle – French is the lingua franca of Europe, the language of diplomacy

• Great-grandson of Louis XIV • Mismanagement of finances • Loss of colonial possession during the 7 Years War with England • Scandalous private life • Where did all this lead? To questions about Absolutism. Louis XV Reigned 1715 -1774

Limits to Royal Absolutism • King’s power is really NOT absolute – His rule must be reasonable, conform to the will of God • Power is still limited by traditions, customs • King must still operate under a recognized body of law
da81c4efe695ce85ffebcbfeccc08cd5.ppt