Absolute vs. Relative Quantities 2 Methods Particularly if


Absolute vs. Relative Quantities

2 Methods Particularly if goal is to measure the least and greatest occurrence of some quantifiable variable Absolute Quantities Relative Quantities Measuring Numerical Data

Measure of the absolute occurrence of the variable A “sheer” number Tells how many or how much Examples Number of students enrolled at DePaul Number of people in this class Number of babies born this year Absolute Quantities

An absolute quantity divided by some other quantity Calculated value Tells percent, rate, fraction or ratio Examples: Ticket sales per person Percentage of population infected with HIV by country Percent increase in population by state Relative Quantity

Fraction or Percent Used when comparing part to total of the same type of variable Percent of people infected with HIV Infected population/Total population Also used to show relative change More to come… Types of Relative Quantities

Ratio Used to compare the same type of variable from two sources Example: California’s population is 33,872,000 Oregon’s population is 3,421,000 How many times larger is CA than OR? Divide CA/OR = 9.90 CA is almost 10 times larger Types of Relative Quantities

Rates Used to compare different types of variables Examples Miles per hour Tickets per person Crimes per 1000 people Types of Relative Quantities

Let’s work with some absolute and relative quantities HIV_Adults_By_Country_2001.xls StateLotteries.xls How it works…

Describes the actual increase or decrease from a reference (or old/earlier) value to a new (or later) value Formula Absolute Change = new value – reference value Absolute Change
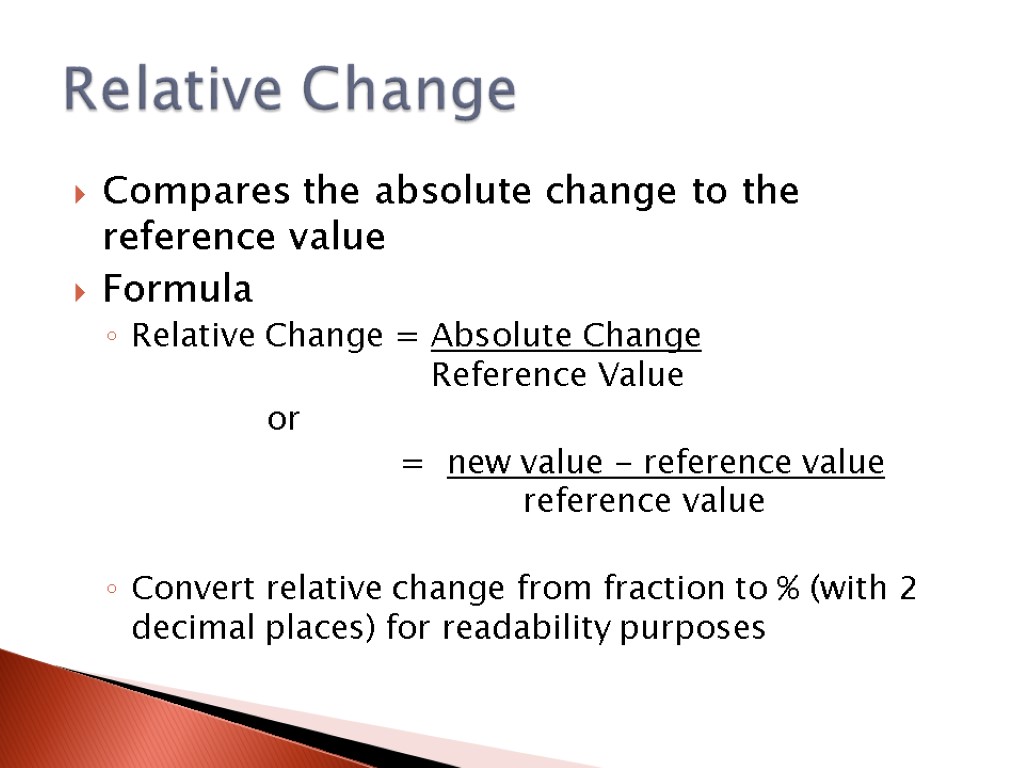
Compares the absolute change to the reference value Formula Relative Change = Absolute Change Reference Value or = new value - reference value reference value Convert relative change from fraction to % (with 2 decimal places) for readability purposes Relative Change

Absolute and Relative Change Try this…
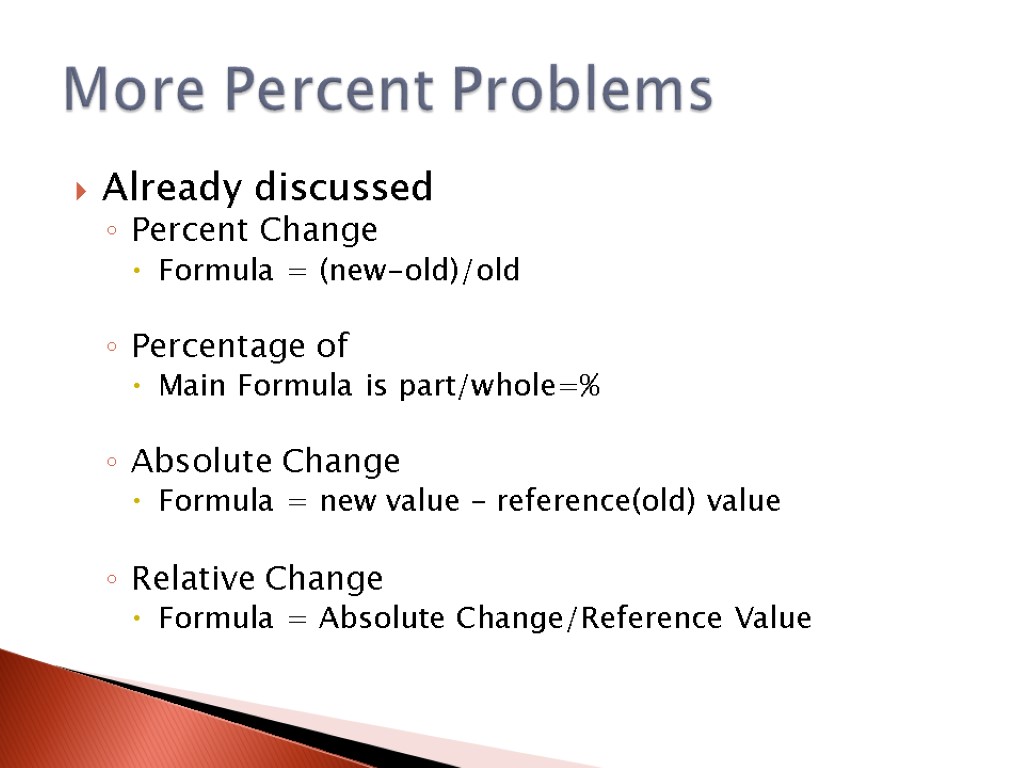
Already discussed Percent Change Formula = (new-old)/old Percentage of Main Formula is part/whole=% Absolute Change Formula = new value – reference(old) value Relative Change Formula = Absolute Change/Reference Value More Percent Problems
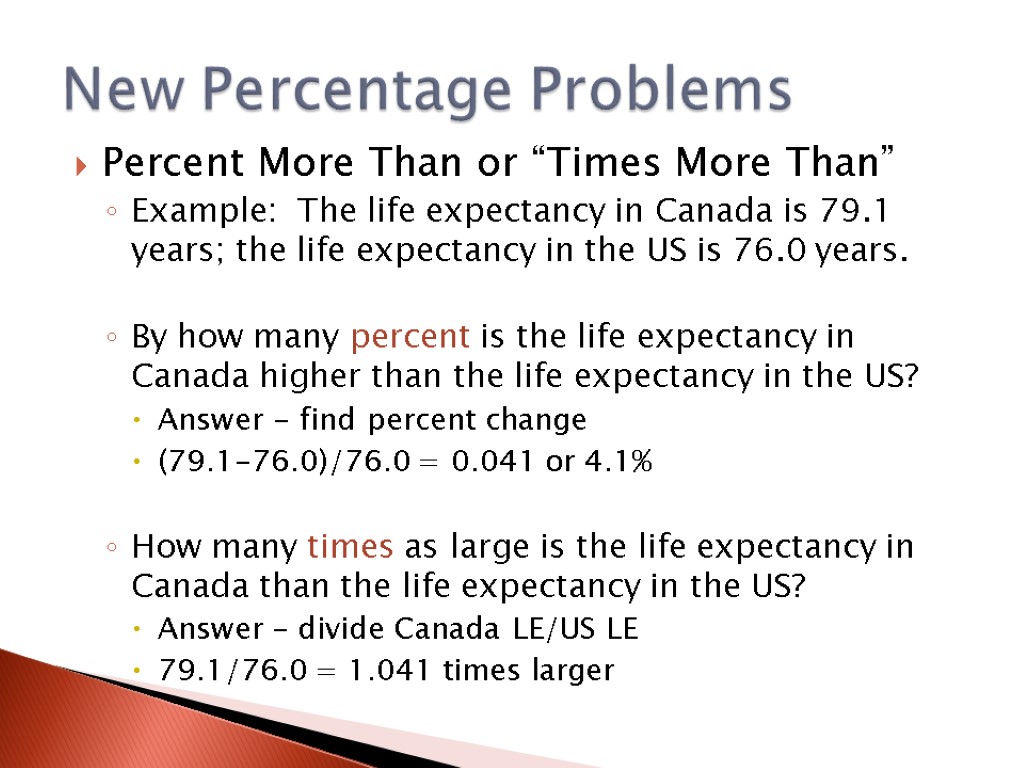
Percent More Than or “Times More Than” Example: The life expectancy in Canada is 79.1 years; the life expectancy in the US is 76.0 years. By how many percent is the life expectancy in Canada higher than the life expectancy in the US? Answer - find percent change (79.1-76.0)/76.0 = 0.041 or 4.1% How many times as large is the life expectancy in Canada than the life expectancy in the US? Answer – divide Canada LE/US LE 79.1/76.0 = 1.041 times larger New Percentage Problems

Percent Less Than Same Example: The life expectancy in Canada is 79.1 years; the life expectancy in the US is 76.0 years. By how many percent is the life expectancy of people in the US lower than the life expectancy in Canada? Answer – find percent change but divide by Canadian LE (76.0-79.1)/79.1 = -0.039 or -3.9% One More…
absolute-relative.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 14

