34999999fbf46d765a239f0f24b04ae1.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 64

Abraxane ® (paclitaxel protein-bound particles for injectable suspension). Each 50 m. L vial contains 100 mg of paclitaxel and 900 mg of human albumin as a sterile lyophilized powder. Abraxis Bio. Science, Inc. 1

Approved Indication: “ABRAXANE® is indicated for the treatment of breast cancer after failure of combination chemotherapy for metastatic disease or relapse within 6 months of adjuvant chemotherapy. Prior therapy should have included an anthracycline unless clinically contraindicated. ” The application was approved on January 7, 2005. 2

Sponsor’s Proposed Indication: “ABRAXANE® is indicated for the adjuvant treatment of node-positive breast cancer administered sequentially to standard doxorubicin-containing combination chemotherapy. " 3

Regulatory Pathways to Market a Competitor Drug n NDA n ANDA n 505(b)(2) 4

505(b)(2) n This applies to new formulations of marketed drugs and authorizes the FDA, where appropriate, to base approvals of new drugs entirely or partially on studies not conducted by the applicant and for which the applicant has not obtained a right of use. 5
505(b)(2) Criteria for Abraxane in Metastatic Breast Cancer FDA agreed to use the preclinical genetic toxicology studies from the Taxol application to support Abraxane approval n FDA also agreed to use response rate as a comparative measure of Taxol antitumor activity instead of the more stringent standard time to event endpoint. n 6

Presentation Outline n n n n Abraxis proposal for approval of Abraxane for the new adjuvant indication Pharmacokinetics of Abraxane’s basis of approval for metastatic breast cancer Taxol’s basis of approval for adjuvant breast cancer FDA concerns with Abraxis proposal Statistical plan to approve Abraxane in the adjuvant breast cancer setting Questions to ODAC Committee 7

Abraxis proposal for approval of Abraxane n Results of the randomized Intergroup study that served as the basis for Taxol approval for the adjuvant treatment of node positive early breast cancer. n Preclinical genetic toxicology studies with Taxol. 8

Abraxis proposal for approval of Abraxane (continued) n Comparison of the pharmacokinetics of the Abraxane and Taxol paclitaxel formulations. n Results of the study comparing Abraxane and Taxol that served as the basis for approval of Abraxane for metastatic breast cancer. n Study CA 030, a single arm 30 patient study of dose dense AC q 2 weeks x 4 cycles followed by dose dense Abraxane 260 mg/m 2 q 2 weeks x 4 cycles. 9

Abraxis proposal for approval of Abraxane (continued) n n n March 13, 2006: single arm phase II safety study to support the approval of adjuvant breast cancer July 2006: proposal for a 400 patient randomized safety study comparing Abraxane and Taxol in adjuvant treatment of node positive early breast cancer to be conducted prior to approval. August 9, 2006: changed to a post approval Phase 4 safety study of unspecified size. 10

Is Abraxis proposal acceptable? n n How similar or dissimilar the Abraxane and Taxol formulations are. Risk/benefit ratio of approving Abraxane w/o an efficacy and safety study. Taxol prolongs disease free survival and survival in the adjuvant breast cancer setting. FDA is concerned with the consequences of a potential decrement in DFS and survival in women with node positive early breast cancer. 11

Pharmacokinetics of Abraxane compared to Taxol 12

A Pharmacokinetic Comparison of Abraxane and Taxol Brian Booth Division of Clinical Pharmacology 5 13
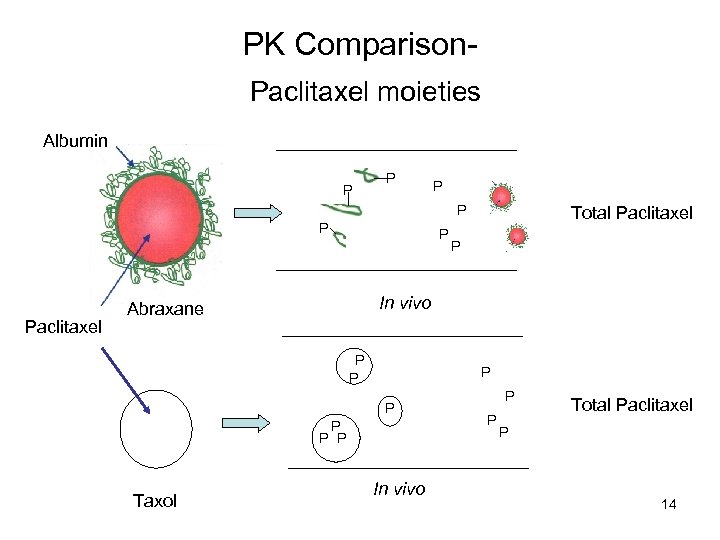
PK Comparison. Paclitaxel moieties Albumin P P Paclitaxel P P In vivo Abraxane P P P P Taxol Total Paclitaxel In vivo P P Total Paclitaxel P 14
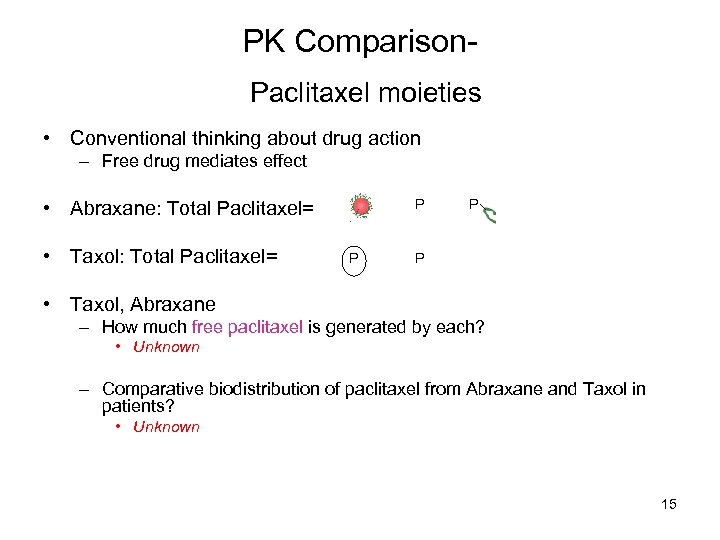
PK Comparison. Paclitaxel moieties • Conventional thinking about drug action – Free drug mediates effect • Abraxane: Total Paclitaxel= • Taxol: Total Paclitaxel= P P • Taxol, Abraxane – How much free paclitaxel is generated by each? • Unknown – Comparative biodistribution of paclitaxel from Abraxane and Taxol in patients? • Unknown 15
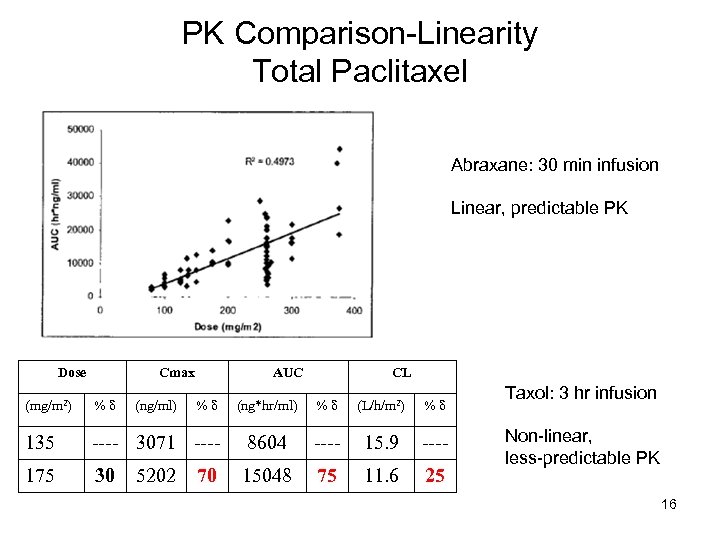
PK Comparison-Linearity Total Paclitaxel Abraxane: 30 min infusion Linear, predictable PK Dose Cmax (mg/m 2) %δ 135 175 (ng/ml) AUC (ng*hr/ml) %δ (L/h/m 2) %δ ---- 3071 ---- 8604 ---- 15. 9 ---- 30 15048 75 11. 6 25 5202 %δ CL 70 Taxol: 3 hr infusion Non-linear, less-predictable PK 16
Clinical PK Comparison of Abraxane and Taxol- Study C 008 -0 Total Paclitaxel • PK study– Abraxane 14 patients – Taxol 12 patients • Comparability issues • Different Doses – Abraxane 260 mg/m 2 – Taxol 175 mg/m 2 • TOTAL Paclitaxel 17
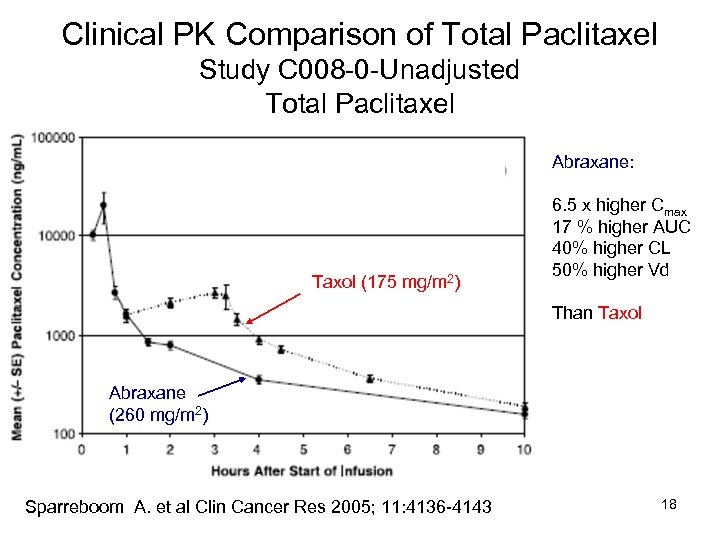
Clinical PK Comparison of Total Paclitaxel Study C 008 -0 -Unadjusted Total Paclitaxel Abraxane: Taxol (175 mg/m 2) 6. 5 x higher Cmax 17 % higher AUC 40% higher CL 50% higher Vd Than Taxol Abraxane (260 mg/m 2) Sparreboom A. et al Clin Cancer Res 2005; 11: 4136 -4143 18
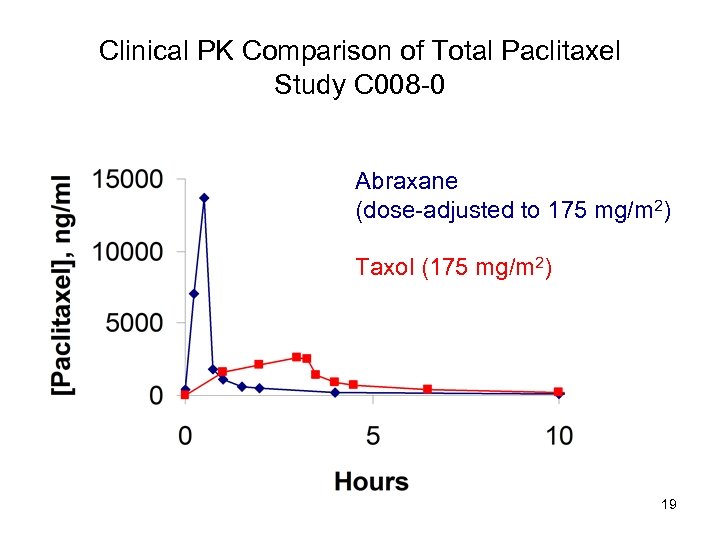
Clinical PK Comparison of Total Paclitaxel Study C 008 -0 Abraxane (dose-adjusted to 175 mg/m 2) Taxol (175 mg/m 2) 19
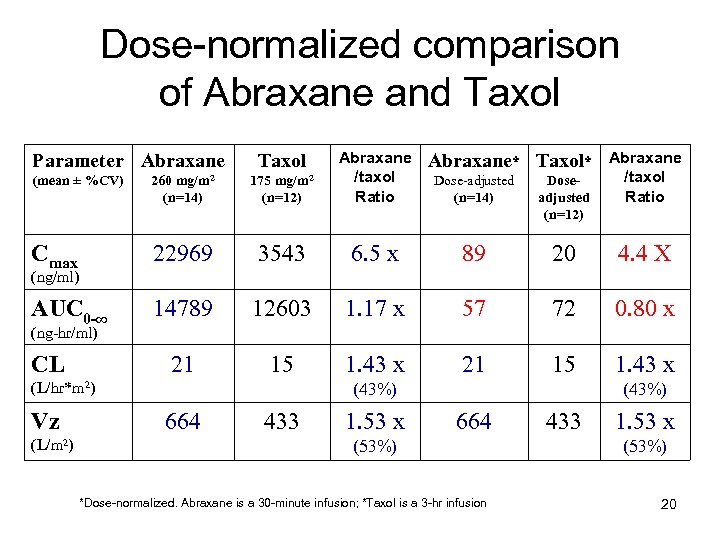
Dose-normalized comparison of Abraxane and Taxol (mean ± %CV) 260 mg/m 2 (n=14) 175 mg/m 2 (n=12) Abraxane /taxol Ratio Cmax 22969 3543 AUC 0 -∞ 14789 21 Parameter Abraxane Taxol Abraxane* Taxol* Abraxane /taxol Ratio Dose-adjusted (n=14) Doseadjusted (n=12) 6. 5 x 89 20 4. 4 X 12603 1. 17 x 57 72 0. 80 x 15 1. 43 x 21 15 1. 43 x (ng/ml) (ng-hr/ml) CL (L/hr*m 2) Vz (L/m 2) (43%) 664 433 1. 53 x (43%) 664 (53%) *Dose-normalized. Abraxane is a 30 -minute infusion; *Taxol is a 3 -hr infusion 433 1. 53 x (53%) 20

Summary • Abraxane and Taxol are not pharmacokinetically “the same” (Total paclitaxel) – Need to assess free paclitaxel concentrations • • • Different doses Different CL Different Vd Different AUC Different Cmax Abraxane linear PK, Taxol non-linear PK 21

Basis of Approval for Abraxane for Metastatic Breast Cancer 22

Study Design n n n Randomized, Phase 3, open label Sample size: 460 patients 70 sites: Russia (77%), UK (15%), Canada and US (9%) 2 Arm: Abraxane 260 mg/m 2 as a 30 -minute infusion and Taxol 175 mg/m 2 as a 3 -hour infusion 59% second line or greater and 77% previous anthracycline exposure Designed to show non inferiority in RR 23

Study Populations All randomized patients n Subgroups n Receiving drug as 1 st line only n Receiving drug as > 2 nd line n Taxol approved indication: patients who have failed combination chemotherapy for metastatic disease or relapse within 6 months of adjuvant chemotherapy. Prior therapy should have included an anthracycline unless clinically contraindicated n 24

Endpoints n n 1° Endpoint: Response Rate 2° Endpoints: TTP Survival 25

Response Rate (from Abraxane label) Abraxane 260 mg/m 2 All randomized patients Response Rate 95% CI P-value Taxol 175 mg/m 2 50/233 (21. 5%) (16. 19%-26. 73%) 25/227 (11. 1%) (6. 94%-15. 09%) 0. 003 Taxol Indication: Patients who failed combination chemotherapy or relapsed within 6 months of adjuvant chemotherapy Response Rate 20/129 (15. 5%) 12/143 (8. 4%) 95% CI (9. 26%-21. 75%) (3. 85%-12. 94%) 26

TTP At the time of Abraxane approval TTP results were not included in the label because: Evaluation of TTP was not rigorous and data were not sufficiently mature to support a comparative efficacy claim in this single non-blinded study 27

Time to progression (TTP) from July 21, 2006 Submission We have the following concerns: n TTP was not systematically assessed in all patients after cycle 6 n Multiple analyses using different criteria without adjustments n TTP results may not be reliable for a labeling claim 28

Overall Survival from July 21, 2006 Submission We have the following concerns: n There was no difference in overall survival between the Abraxane and Taxol treatment groups. HR (Abraxane/Taxol) was 0. 90, p=0. 348 (log rank). n No conclusions can be drawn from a subgroup analysis when the main analysis was not statistically significant. n Multiple subgroup analyses using different criteria without p value adjustments n P-values are not interpretable 29
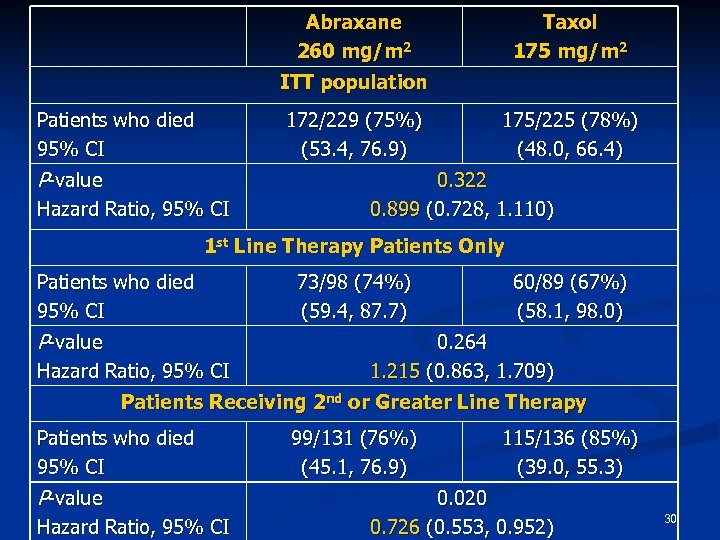
Abraxane 260 mg/m 2 Taxol 175 mg/m 2 ITT population Patients who died 95% CI 172/229 (75%) (53. 4, 76. 9) P-value Hazard Ratio, 95% CI 175/225 (78%) (48. 0, 66. 4) 0. 322 0. 899 (0. 728, 1. 110) 1 st Line Therapy Patients Only Patients who died 95% CI P-value Hazard Ratio, 95% CI 73/98 (74%) (59. 4, 87. 7) 60/89 (67%) (58. 1, 98. 0) 0. 264 1. 215 (0. 863, 1. 709) Patients Receiving 2 nd or Greater Line Therapy Patients who died 95% CI P-value Hazard Ratio, 95% CI 99/131 (76%) (45. 1, 76. 9) 115/136 (85%) (39. 0, 55. 3) 0. 020 0. 726 (0. 553, 0. 952) 30
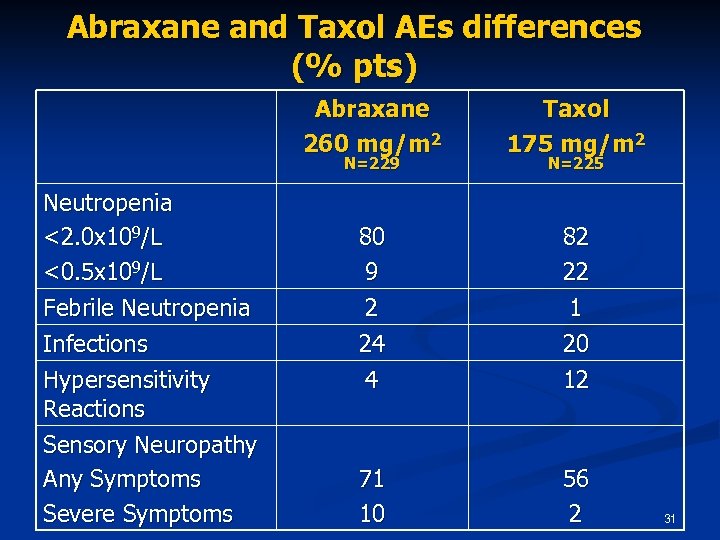
Abraxane and Taxol AEs differences (% pts) Abraxane 260 mg/m 2 Taxol 175 mg/m 2 80 9 2 24 4 82 22 1 20 12 71 10 56 2 N=229 Neutropenia <2. 0 x 109/L <0. 5 x 109/L Febrile Neutropenia Infections Hypersensitivity Reactions Sensory Neuropathy Any Symptoms Severe Symptoms N=225 31
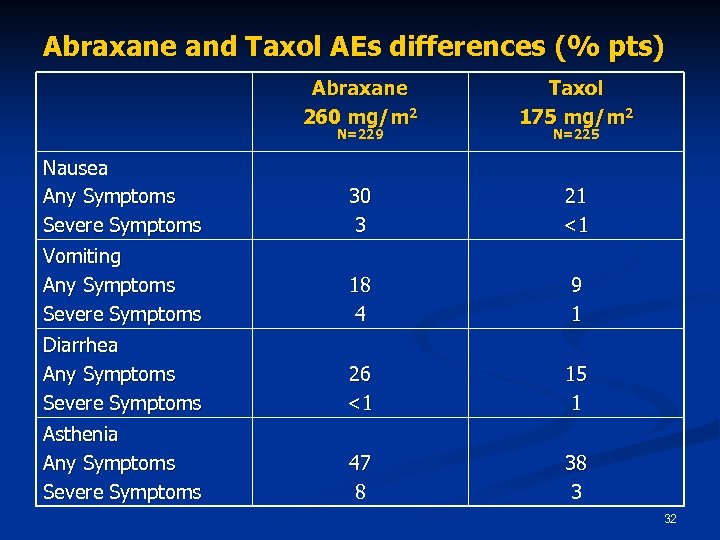
Abraxane and Taxol AEs differences (% pts) Abraxane 260 mg/m 2 Taxol 175 mg/m 2 Nausea Any Symptoms Severe Symptoms 30 3 21 <1 Vomiting Any Symptoms Severe Symptoms 18 4 9 1 Diarrhea Any Symptoms Severe Symptoms 26 <1 15 1 Asthenia Any Symptoms Severe Symptoms 47 8 38 3 N=229 N=225 32

Basis of Approval for Taxol for Adjuvant Breast Cancer 33
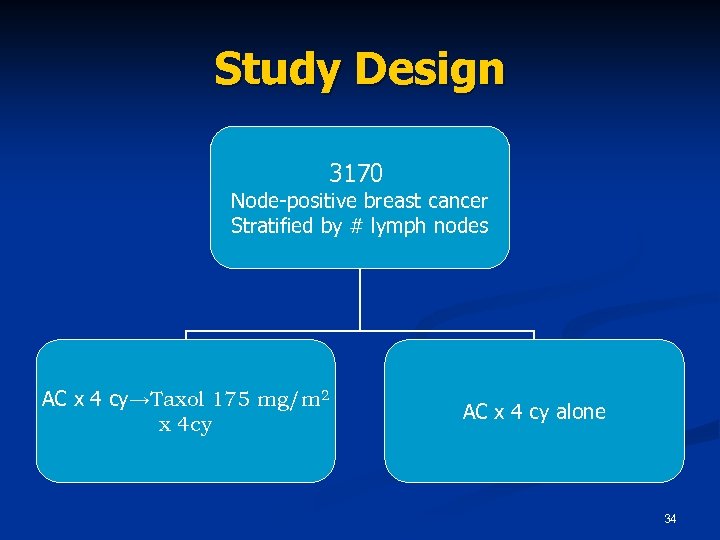
Study Design 3170 Node-positive breast cancer Stratified by # lymph nodes AC x 4 cy→Taxol 175 mg/m 2 x 4 cy AC x 4 cy alone 34
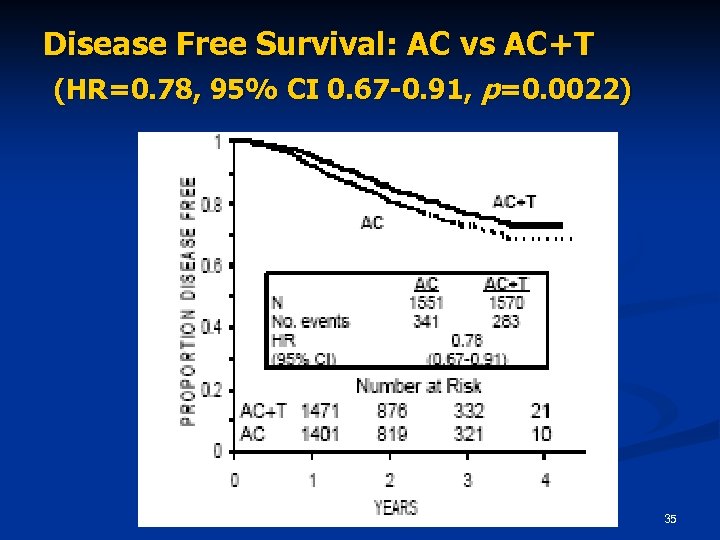
Disease Free Survival: AC vs AC+T (HR=0. 78, 95% CI 0. 67 -0. 91, p=0. 0022) 35
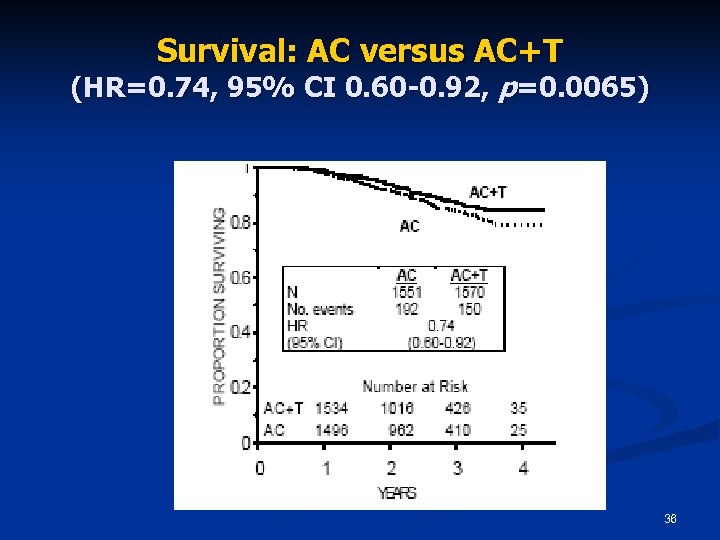
Survival: AC versus AC+T (HR=0. 74, 95% CI 0. 60 -0. 92, p=0. 0065) 36
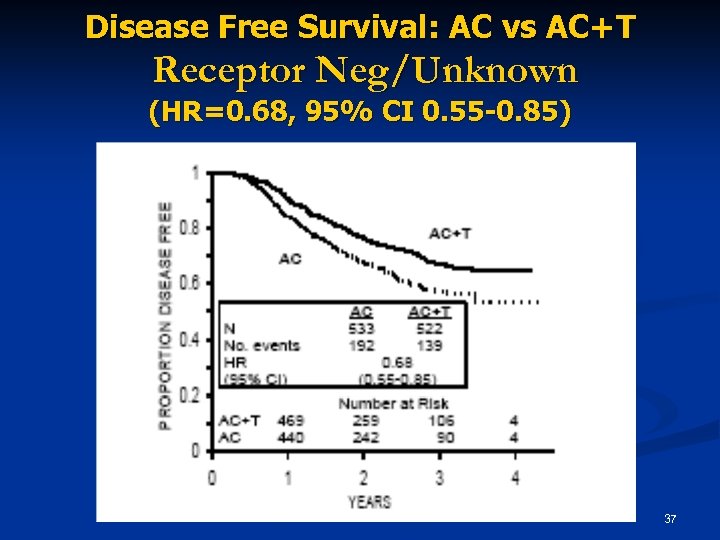
Disease Free Survival: AC vs AC+T Receptor Neg/Unknown (HR=0. 68, 95% CI 0. 55 -0. 85) 37

Should Abraxane be approved for the adjuvant treatment of node positive early breast cancer without an adequate RCT powered for DFS, OS and safety? 38

Abraxane and Taxol are different Formulations are different n Pharmacokinetics are different n Not bioequivalent n Free paclitaxel not measured n Abraxane does not contain cremophor, given by 30 minute infusion w/o premedication n Taxol is given by 3 hour infusion and requires premedication n 39

Abraxane and Taxol toxicity profiles are different Taxol has a higher incidence of neutropenia and hypersensitivity reactions n Abraxane has a higher incidence of peripheral neuropathy, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea and asthenia n 40

FDA Agrees that in the metastatic breast cancer study Abraxane had a higher tumor response rate than Taxol 41

FDA believes that in the MBC study TTP improvement has not been adequately demonstrated n n n There was no type 1 error allocated for TTP analysis. TTP claims could not be confirmed since no IRL review was conducted beyond cycle 6. Patients were not systematically evaluated after cycle 6. In an open label study, there is a potential for bias in progression assessments. P-values for TTP analyses are not interpretable. 42

FDA believes that in the MBC study survival improvement has not been adequately demonstrated n n n There was no type 1 error allocated for OS analysis. There is no significant OS effect in the all randomized population Subgroup analysis is not appropriate when the study failed to demonstrate an effect in the overall population. Multiple analyses in multiple subgroups with no adjustment P-values for OS analyses is not interpretable. 43

n 1 st line patients, survival trended against Abraxane HR (A/T)= 1. 215 44

There is a need for a RCT in the adjuvant population to properly estimate the risk: benefit ratio of Abraxane 45

Data on toxicity comparisons from the metastatic study may not be appropriate to the adjuvant setting were Abraxane would be given following AC. 46

Taxol increases DFS and OS in the adjuvant treatment of women with node positive early breast cancer. 22% reduction in the risk of disease recurrence n 26% reduction in the risk of death n 47

FDA is concerned with the consequences of a potential decrement in DFS and survival in women with node positive early breast cancer 48

Trial Design Considerations 49

Trial Design Considerations R. Sridhara, Ph. D. 50

Randomized Clinical Trial to Demonstrate DFS Efficacy of Abraxane Is it required? Is it feasible? 51
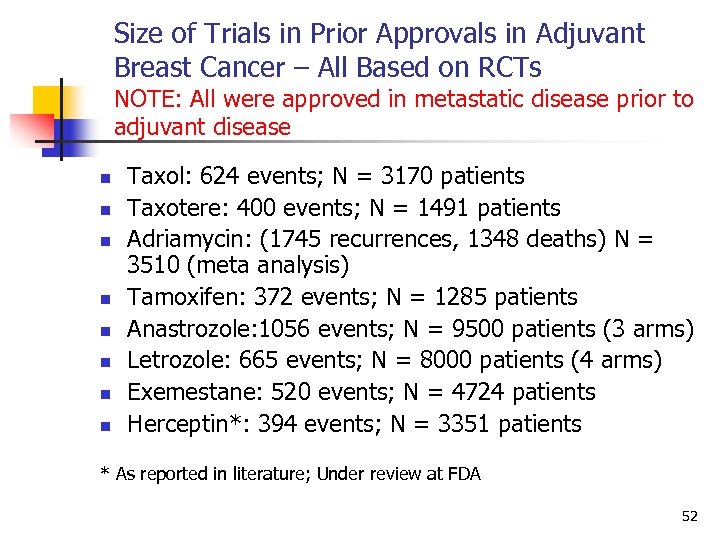
Size of Trials in Prior Approvals in Adjuvant Breast Cancer – All Based on RCTs NOTE: All were approved in metastatic disease prior to adjuvant disease n n n n Taxol: 624 events; N = 3170 patients Taxotere: 400 events; N = 1491 patients Adriamycin: (1745 recurrences, 1348 deaths) N = 3510 (meta analysis) Tamoxifen: 372 events; N = 1285 patients Anastrozole: 1056 events; N = 9500 patients (3 arms) Letrozole: 665 events; N = 8000 patients (4 arms) Exemestane: 520 events; N = 4724 patients Herceptin*: 394 events; N = 3351 patients * As reported in literature; Under review at FDA 52
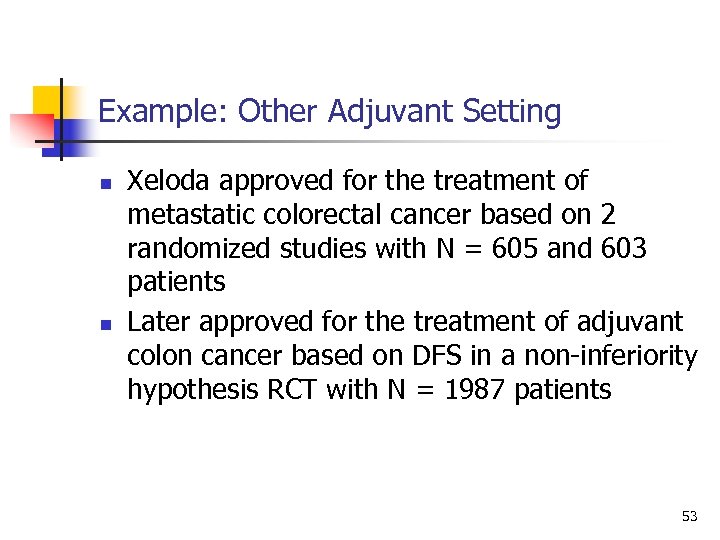
Example: Other Adjuvant Setting n n Xeloda approved for the treatment of metastatic colorectal cancer based on 2 randomized studies with N = 605 and 603 patients Later approved for the treatment of adjuvant colon cancer based on DFS in a non-inferiority hypothesis RCT with N = 1987 patients 53
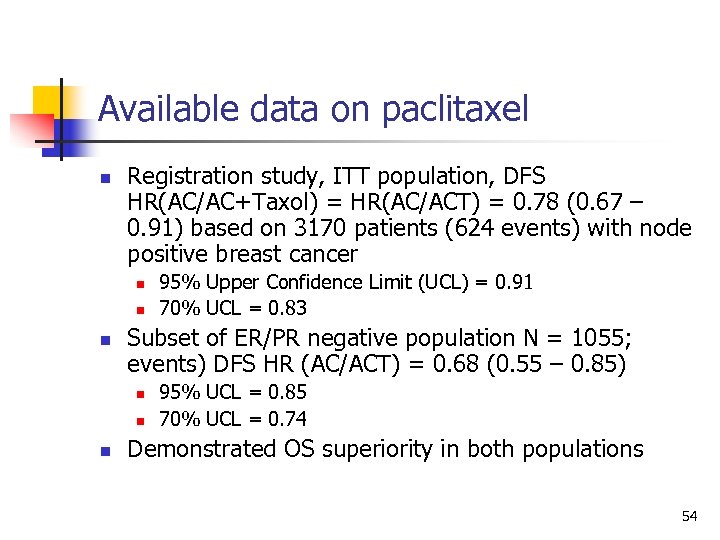
Available data on paclitaxel n Registration study, ITT population, DFS HR(AC/AC+Taxol) = HR(AC/ACT) = 0. 78 (0. 67 – 0. 91) based on 3170 patients (624 events) with node positive breast cancer n n n Subset of ER/PR negative population N = 1055; events) DFS HR (AC/ACT) = 0. 68 (0. 55 – 0. 85) n n n 95% Upper Confidence Limit (UCL) = 0. 91 70% UCL = 0. 83 95% UCL = 0. 85 70% UCL = 0. 74 Demonstrated OS superiority in both populations 54

Non-inferiority or Superiority n Risks with Non-inferiority Trial n n How well we know the effect of the control How much of the control effect can we afford to give up At least 50% - 75% retention of the control effect necessary to rule out that the new treatment is significantly better than placebo Sponsor claims Abraxane could be superior to Paclitaxel 55
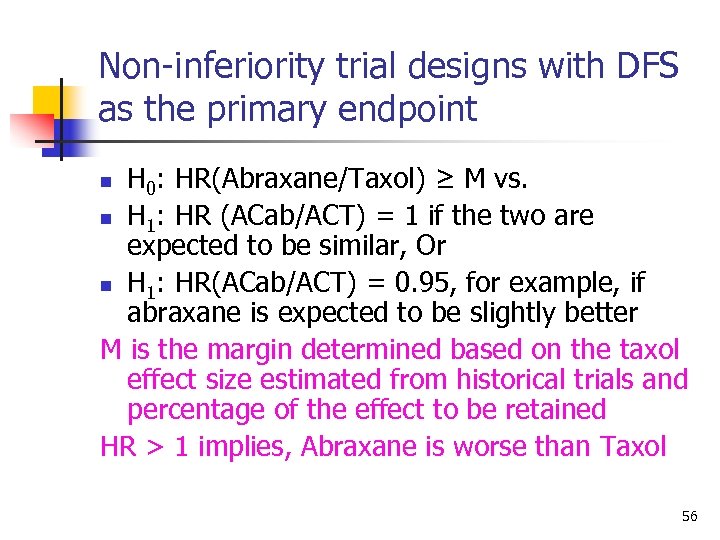
Non-inferiority trial designs with DFS as the primary endpoint H 0: HR(Abraxane/Taxol) ≥ M vs. n H 1: HR (ACab/ACT) = 1 if the two are expected to be similar, Or n H 1: HR(ACab/ACT) = 0. 95, for example, if abraxane is expected to be slightly better M is the margin determined based on the taxol effect size estimated from historical trials and percentage of the effect to be retained HR > 1 implies, Abraxane is worse than Taxol n 56

Percent Retention and Estimated Active Control Effect Size n n n Non-inferiority ≈ “not much less effective” ‘X’ is the effect size of the active control; example: Point estimate of HR (AC+Taxol/AC) = 0. 78 implies an estimate of taxol effect size (over the control) was a 22% reduction in the risk of DFS event Percent retention is a percentage of ‘X’ that is retained; example: a 50% retention of the 22% effect size is 11% effect size, i. e. , the putative HR(AC+Abraxane/AC) = 0. 89; similarly a 25% retention implies putative HR(ACab/AC) = 0. 945; a 75% retention implies putative HR(ACab/AC) = 0. 835 57

Methods for estimating active control effect size: No method is ideal and no particular method is endorsed by the Agency n n n All methods assume that the control effect has not changed over time Some methods do not consider the variation between and within studies Other methods incorporate variation between and within studies 58
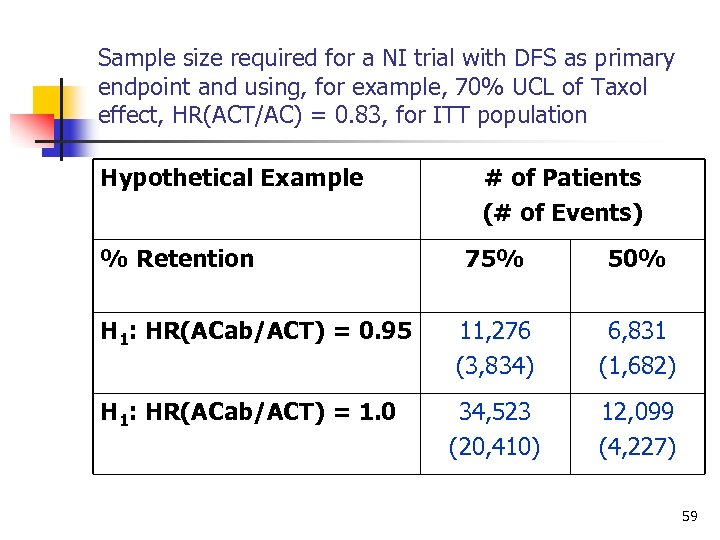
Sample size required for a NI trial with DFS as primary endpoint and using, for example, 70% UCL of Taxol effect, HR(ACT/AC) = 0. 83, for ITT population Hypothetical Example % Retention # of Patients (# of Events) 75% 50% H 1: HR(ACab/ACT) = 0. 95 11, 276 (3, 834) 6, 831 (1, 682) H 1: HR(ACab/ACT) = 1. 0 34, 523 (20, 410) 12, 099 (4, 227) 59
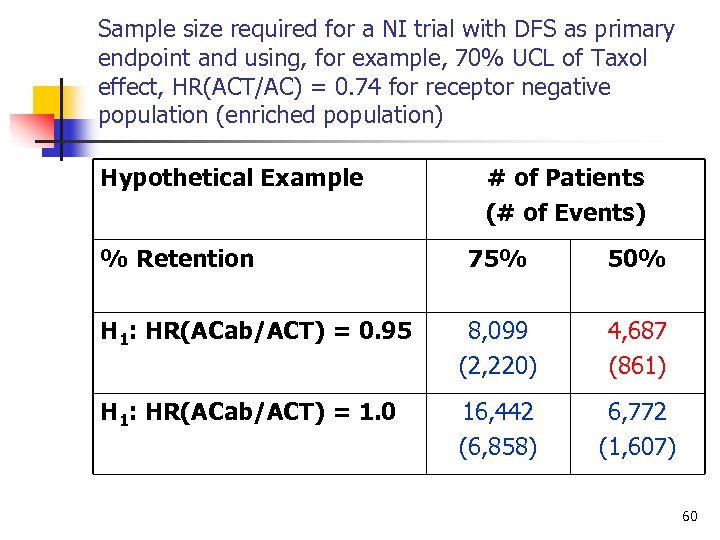
Sample size required for a NI trial with DFS as primary endpoint and using, for example, 70% UCL of Taxol effect, HR(ACT/AC) = 0. 74 for receptor negative population (enriched population) Hypothetical Example % Retention # of Patients (# of Events) 75% 50% H 1: HR(ACab/ACT) = 0. 95 8, 099 (2, 220) 4, 687 (861) H 1: HR(ACab/ACT) = 1. 0 16, 442 (6, 858) 6, 772 (1, 607) 60
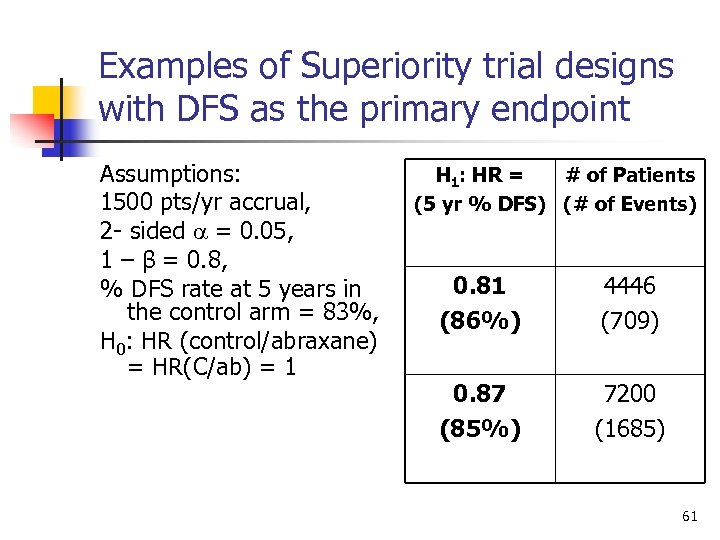
Examples of Superiority trial designs with DFS as the primary endpoint Assumptions: 1500 pts/yr accrual, 2 - sided = 0. 05, 1 – β = 0. 8, % DFS rate at 5 years in the control arm = 83%, H 0: HR (control/abraxane) = HR(C/ab) = 1 H 1: HR = # of Patients (5 yr % DFS) (# of Events) 0. 81 (86%) 4446 (709) 0. 87 (85%) 7200 (1685) 61
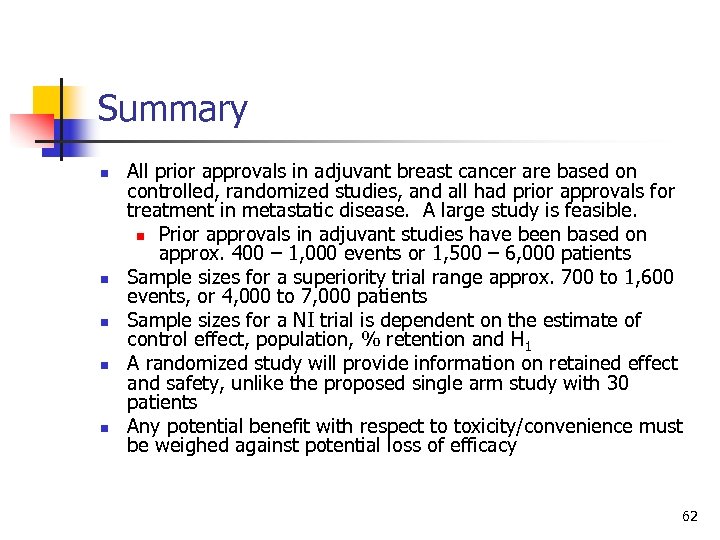
Summary n n n All prior approvals in adjuvant breast cancer are based on controlled, randomized studies, and all had prior approvals for treatment in metastatic disease. A large study is feasible. n Prior approvals in adjuvant studies have been based on approx. 400 – 1, 000 events or 1, 500 – 6, 000 patients Sample sizes for a superiority trial range approx. 700 to 1, 600 events, or 4, 000 to 7, 000 patients Sample sizes for a NI trial is dependent on the estimate of control effect, population, % retention and H 1 A randomized study will provide information on retained effect and safety, unlike the proposed single arm study with 30 patients Any potential benefit with respect to toxicity/convenience must be weighed against potential loss of efficacy 62

Important Issues to Consider Pharmacokinetics of Abraxane and Taxol are different n Free paclitaxel was not measured n Differences in Abraxane and Taxol tumor response rate and toxicity profiles in the MBC study indicates they are different drugs n 63

Important Issues to Consider Treatment of MBC has different risk: benefit n Treatment of adjuvant breast cancer is given with curative intent therefore risk: benefit should be well established in a RCT adequately powered for efficacy and safety n FDA is concerned that the gains with Taxol therapy may not be maintained with Abraxane n 64
34999999fbf46d765a239f0f24b04ae1.ppt