661e31163a326f8ac5f1d51f4cf3ba7a.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 34

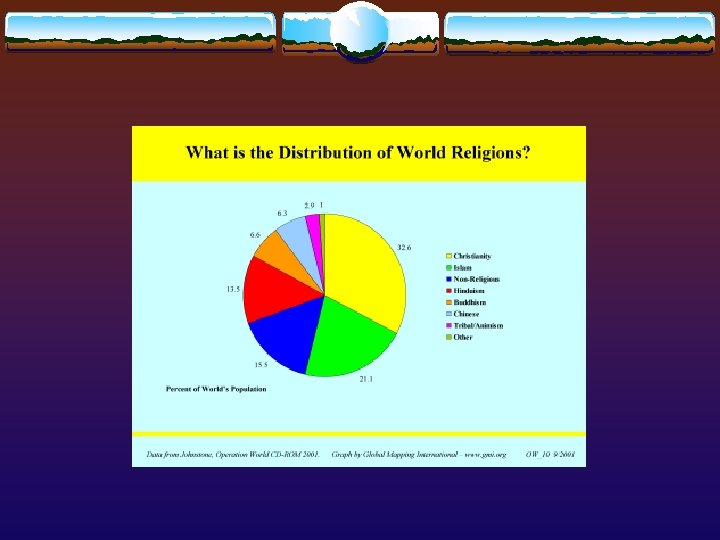
Abrahamic Religions 1
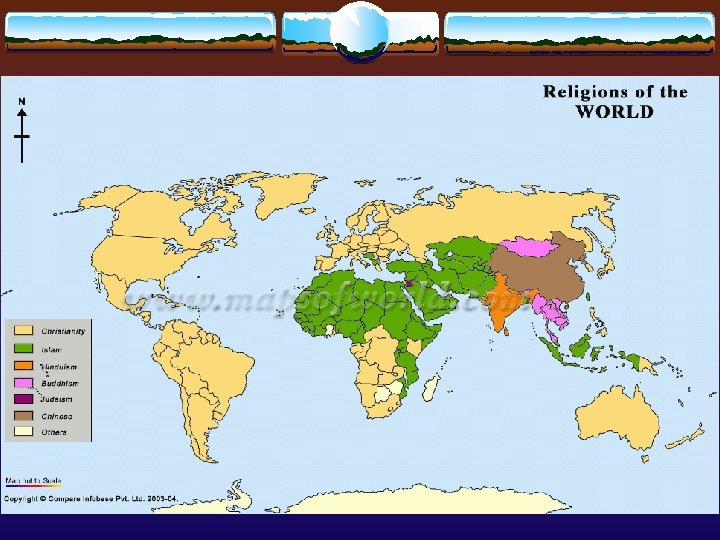

The Middle East

Judaism

In the Ancient World, what did most people believe in ? v Polytheism – Belief in many Gods v Paganism - Religion used as means to explain weather patterns, illness, world events. v Jewish people believe in Monotheism - One God

Judaism - Origins v Hebrew Origins – Fertile Crescent 2000 BC v Abraham - Prophet - Covenant with Yaweh, monotheistic & migrate to Canaan (Palestine) v Due to Famine in Canaan, many Hebrews migrate to Egypt - Pharaoh enslaves Hebrews v Moses leads the Hebrews out of Egypt – Exodus v God revealed his laws and commandments (10 Commandments) to Moses on Mount Sinai in the form of the Torah.

Judaism - Beliefs v God loves and protects his people, but also holds them accountable for their sins and shortcomings. Also, Since God created the world, the world must be good – optimistic message; humanitarianism. v People serve God by studying the Torah and living by its teachings. Torah – the five books of Moses: Genesis, Exodus, Leviticus, Numbers, and Deuteronomy. Oral Torah (Talmud and Mishna) – over the centuries, Rabbis expounded and expanded the Torah. v Ten Commandments – Religious duties towards God & rules of moral conduct; revealed by God to Moses. You. Tube - Ten Commandments - A Parody

Judaism - Holidays v Rosh Hashanah - The Jewish New Year v Yom Kippur - Day of Atonement - is the most solemn day of the Jewish year. It is a day of communal fasting and praying forgiveness for one's sins v Passover (Pesach) - commemorates the Exodus, the liberation of the Israelites from Egyptian slavery. v Hanukkah - Festival of Lights - commemorating the rededication of the Second Temple in Jerusalem. 11

Conclusion v Judaism forever changed the world by believing in one God (monotheism) as opposed to many Gods (polytheism). v Origin story is one of hope- struggling over oppression. v Moral values and laws come from the Torah and the 10 Commandments. v Christianity and Islam are continuations of the Abrahamic Tradition. 10

Christianity 11

Christianity v Originally a Sect of Judaism - Follow Jesus v Believe Jesus was the Jewish Messiah v Messiah – savior chosen by God to restore the Kingdom of the Jews v Christians believe that Jesus was the son of God and he died to redeem mankind for their sins. v Jesus used Parables (short stories with simple moral lesson). Gospels: Love Thy Brother; Take Care of the Poor; Compassion for All; Turn the Other Cheek; Peace and Love. v https: //www. youtube. com/watch? v=VA 1 sx-vy. WVk 12

Roman Catholic Church Leadership v Pope – leader of Religion (First Pope: the Apostle Peter) v v Bishop – Church official who is responsible for district area (diocese) Priest work in local parishes History v Constantine - 313 Edict of Milan - Emperor of Rome declared Christianity to be approved by the state. v 380 Theodosius made it the official religion of the state. 13

1054 Great Schism v West v East v Holy v Byzantine Roman Empire v Roman Catholic Church Map: whs 161. swf Empire v Eastern Orthodox Church 14

Protestant Reformation (1517) Protestants reject the Pope’s Leadership v Martin Luther - 95 Theses Against corruption, Indulgences v Protestants have no class of priests with special powers to forgive or anoint the sick v Most have two or three sacraments Baptism, Eucharist, & Matrimony v Do not believe in the miracle of the mass where bread & wine are transformed into the body & blood of Christ v 15

Protestants Protestant Denominations: v Lutherans v Episcopalians v Methodists v Anglicans v Presbyterians v Baptists v Calvinist Adventists v Anabaptist v Congregational v Pentecostal v Quakerism v Reformed v Unitarian v Waldensians v 16

Islam 17

The Rise of Islam v Religion is born in the 600’s in the Arabian Peninsula. v Pre 600’s region is populated with Bedouins (Arab Nomads) live in clans. 18

Mecca Center of polytheistic worship - dotted with temples v People of Mecca provided various services to religious pilgrims that came. v Many come to worship at the Ka’aba, an ancient shrine v 19

The Founder of Islam v Muhammad: born into prominent Meccan family; trader & business manager; great interest in religion v While meditating in cave outside city (Mt. Hira) voice of Angel Gabriel spoke to him v You have been chosen as God’s Prophet. v Muhammed transcribed words of Angel = words of Allah (God). v Words = The Koran (Qur’an) 20

The Teachings of Islam v Islam - “submission to the will of Allah” Muslim: “one who has submitted” v Shari’a – laws based on the Qur’an and Sunna Five Pillars of Islam 1. Shahada: Belief in One God – Allah 2. Sawm: Fast During Holy Month Ramadan 3. Salat: Prayer 5 x’s a day – facing Mecca 4. Zakkat: Give Alms, Charity 5. Hajj: Pilgrimage to Mecca 21
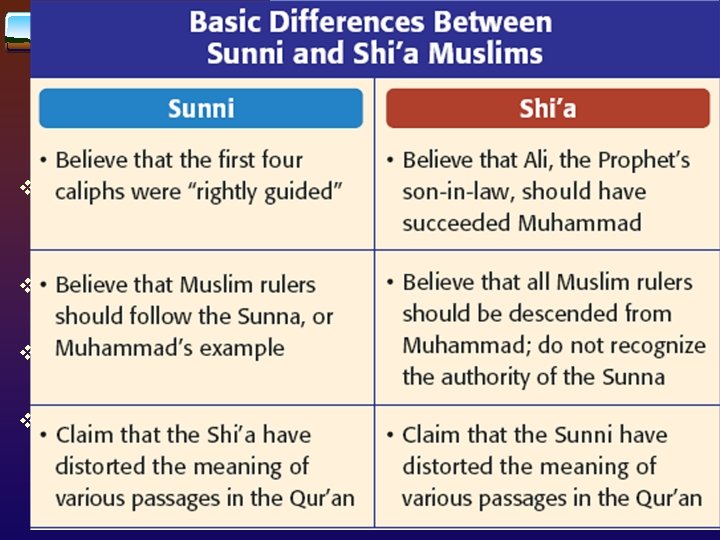
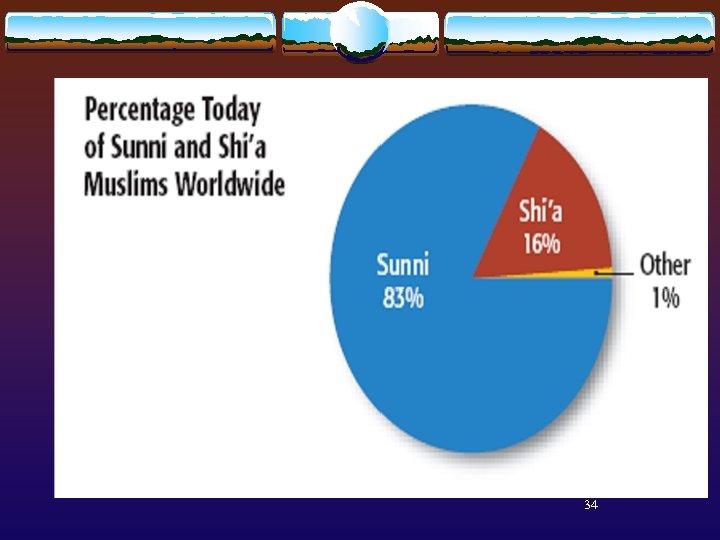
Muhammad spreads Islam 622 Hijra – Muhammad and his followers flee to Medina – In Medina, he becomes a powerful political leader; builds a strong Army v 630 - Conquered enemies in Mecca & destroyed idols in Ka’aba - Dedicates it to Allah. Becomes Holy Site. v Many in Mecca convert to Islam and become part of the Umma (Muslim Community) v Muhammad died 2 years later Who will continue the movement? Sunni – Shia 22 v

Judaism, Christianity, and Islam A number of commonalities exist: Ø Ø Ø Ø Monotheism. All three religions are monotheistic. A prophetic tradition. All three religions recognize figures called "prophets, " though their lists differ. Semitic origins. Judaism and Islam originated among Semitic peoples – namely the Jews and Arabs, respectively – while Christianity arose out of Judaism. A basis in divine revelation rather than, for example, philosophical speculation or custom. An ethical orientation. All three religions speak of a choice between good and evil, which is conflated with obedience or disobedience to God. A linear concept of history, beginning with the Creation and the concept that God works through history. Devotion to the traditions found in the Bible and the Qur'an, such as the stories of Adam, Noah, Abraham, and Moses. 23

Additional Information Click on to enhance your knowledge of the Three Abrahamic Religions. 24

Differences Catholics & Eastern Orthodox Catholic Priests Can not Marry v Services Conducted in Latin v Pope claims authority over all kings & emperors v Divorce is not allowed v Eastern orthodox Priests can Marry v Services Conducted in Greek or local languages v Emperor claims authority over Patriarch & Bishops, P &B head Church as a Group v Divorce is allowed under certain circumstances 25 v

Kingdom of Israel 1020 -922 BC v 1 st loosely organized into 12 tribes/independent states, largest Judah “Jews”, Judaism v Rulers – Saul – drove Philistines out v David united tribes, est. Jerusalem as Capital v Solomon – son of David v Built temple for the Ark of Covenant in Jerusalem & Royal Palace v Costly – High Taxes & Forced Labor

Collapse of the Kingdom v 922 BC revolts & foreign invasions – Kingdom splits into two Israel in North, Judah in South v 722 Israel falls to Assyrians v 586 Babylonians captured Judah v King Nebuchadnezzar destroyed temple in Jerusalem v Babylonian Empire conquered by Persians – 40, 000 Jewish Refugees to return to the region

Blue Mosque, inspired by Muslim tradition. Istanbul, Turkey. 29

Following Muhammad v Muhammad is God’s Final Messenger v Sunna: Muhammad’s example. Best to follow v Shar’ia: Guidance of Qur’an & Sunna assembled into body of law. v Regulates family life, moral conduct, Business, & community life. 30

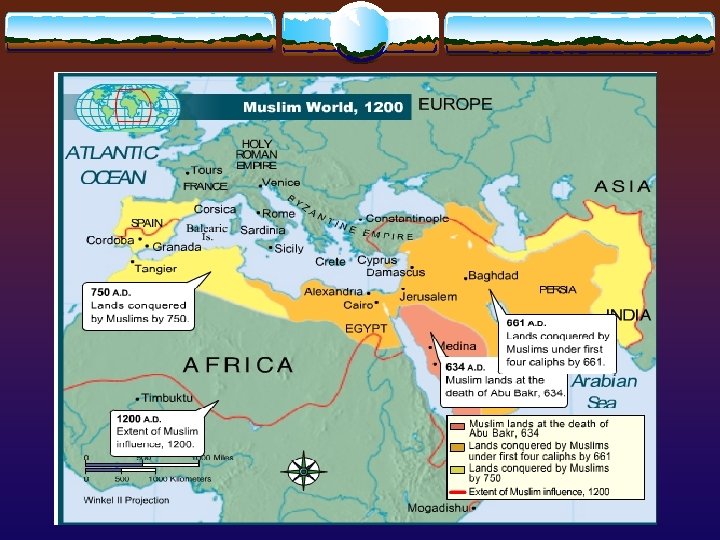
Moving Across Continents v Abu Bakr: loyal friend of Muhammad elected Caliph “leader” v First Four Caliphs expanded Islam 6, 000 miles Atlantic Ocean to Indus River – Wars of Expansion v Jihad: “striving”; inner struggle against evil; armed struggle against nonbelievers/Holy War guarantee entrance into paradise 31

732 - Battle of Tours v Islamic Army stopped by Charles Martel (French) in Tours, France v Protected Christianity in Europe 32
33
34
661e31163a326f8ac5f1d51f4cf3ba7a.ppt