8706b4478359af0fb2c1e5233f99923c.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 81

ABOUT THE: IPMC ™ & AAPM ™ International Project Management Commission ™ & The American Academy of Project Management ™

Board Certifications MPM Master Project Manager ™ u CIPM Certified International Project Manager ™ u PME ™ Project Manager EBusiness u u Example: George Mentz, MPM, JD, MBA

Origins of the IPMC u The Graduate Institute of Leadership (1995) and the CEC E-Business Institute (1996) formed an alliance venture to establish the AAPM and the IPMC. The IPMC is the Commission for standards globally u The AAPM is the Official Training Regulator of the Commission that issues u

IPMC & AAPM Now AAPM has liaison offices in: u u u u USA Dubai Hong Kong EU India Singapore Bahamas u u Moscow Istanbul Beijing And more…. .

Global Recognition u u u The AAPM is listed and recognized on the US Dept of Education Brochures. Recognition of 40+ Accredited Graduate Project Management Programs Worldwide. The Graduate Academy of Management IBS Commission Recognition of Military Service The American E-Commerce Association

Global Membership AAPM has members on over 105 countries worldwide including: u Asia u USA u India u EU u Africa u Latin & South America u Russia …… u

AAPM – The Graduate Certification u As there had not been a graduate professional project manager organization specifically for Executives, MBAs, Ph. Ds and accredited degree holders, The AAPM ™ has met this need and become the organization of choice for highly educated individuals or industry experts because AAPM requires an accredited college degree or equivalent for membership and certification. The AAPM receives its

Section 2 Project Management Certification Requirements www. certifiedprojectmanager. org

Certification Requirements u The AAPM ™ Executive Designation Programs provide the assurance that the holder has met the suggested criteria for graduate credentials set out in the Ibanez US Supreme Court Decision. Further, the AAPM board certification requires meeting 6 different levels of global criteria including ethics and our global body of standards which are the 1 st Standards specifically based on the methodology used by government agencies and departments. Acceptance into the AAPM is a high distinction and requires the holder to possess a graduate level portfolio of skills and knowledge. Acceptance statistics are not high, and the designation when achieved is a high honor strictly for accredited degree holders or individuals

Criteria of 6 Levels IPMC Commission Sanctioned Training u College Education or Equiv. u Successful Testing u Ethics Agreement u Experience u Continuing Education u

Best Education Worldwide u AAPM has strategic recognition of over 45 of the top executive trainers and business degree programs globally including schools of the AACSB ™ International and The ACBSP ™ accreditation agencies. Thus, AAPM accredits and recognizes only the best qualified project management

High Standards u A member can be reported by the public for ethics violations which can be judged by the commission for good standing. Also, Anyone who provides false information to the AAPM or provides education and credentials in bad faith can be reported to officials or to their local authorities. We expect all information to be truthful and accurate under the representation laws, digital signature act laws and through treaties and international law. A person can be expelled from the organization and have their name stricken from the record if providing

Section 3 - Alliances Global Alliance with Lignum Technologies Harbor Bay, East Bay Street P. O. Box SS-6295 Nassau, Bahamas Tel. (242) 393 -2164 Fax (242) 394 -4971

Lignum Technologies u Lignum Technologies has been unanimously approved by the board of standards of The IPMC and The AAPM as a sanctioned provider of official Certification Training for the IPMC under the AAPM agreements. All Rights Reserved 1996 -2006

Lignum Certification Training u After completing the approved training with Lignum and successfully completing all membership criteria for AAPM certification, the Lignum Group can then forward the nomination to the Board of Standards for Processing and Registration for MPM, CIPM or PME Certifications

Lignum 4 Day Course u The Lignum 4 day Executive Course is the “Fast Track” management course for certification. u Upon successful completion of this course and meeting good standing requirements, then the candidate can be processed for certification.

COB College of The Bahamas Project Management Certification will be available at the COB beginning 2006 Fall Courses and Examinations are available and proctored through Lignum. Please Contact: A. Dir. Bastian

Section 4 History of Project Management Great Wall of China u Pyramids of Egypt u u Coordination, Labor, Materials, Hours, Teams, Leadership, Design, Masons, Sequencing….

Wars and Planning From World War 1 and 2 and leading up to the Space Race, new ways of planning, creating, and development and implementation have been formed. u Battle Ships, Aircraft and more… u Necessary materials, recycle, configuration, mapping, sequencing, Teams…. u
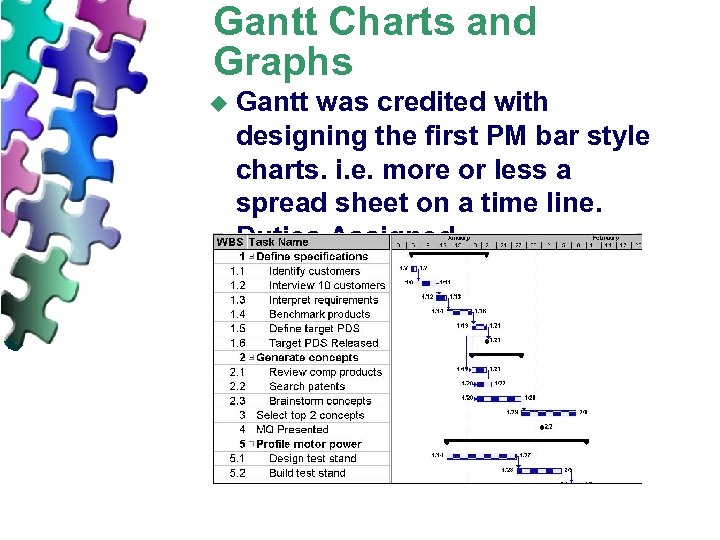
Gantt Charts and Graphs u Gantt was credited with designing the first PM bar style charts. i. e. more or less a spread sheet on a time line. Duties Assigned…

PM History and Military u The United States Department of Defense needed to speed up the military project process. New tools (models) for achieving this goal were invented. In 1958 they invented the Program Evaluation and Review Technique or PERT, as part of the Polaris missile submarine program. At the same time, the Du. Pont corporation invented a similar model called CPM, critical path method. PERT was later extended with a work breakdown structure or WBS. The process flow and structure of the military undertakings quickly spread into many private enterprises.
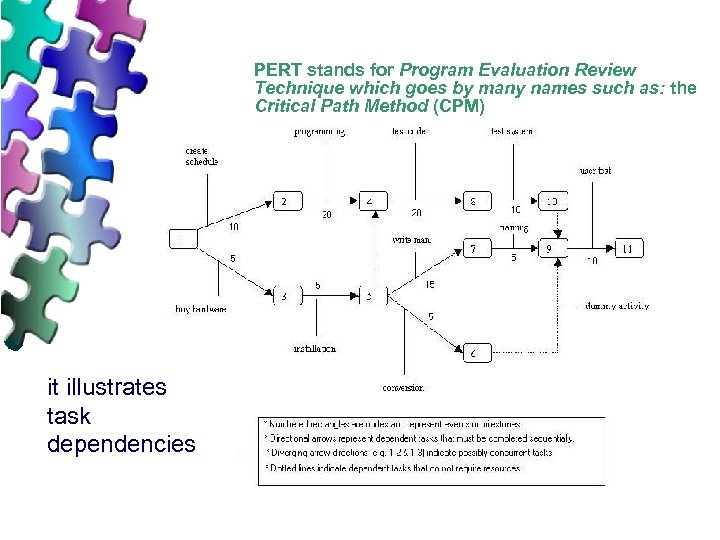
PERT stands for Program Evaluation Review Technique which goes by many names such as: the Critical Path Method (CPM) Chart it illustrates task dependencies

In the traditional approach, we can distinguish 5 components of a project (4 stages plus control) in the development of a project: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. u project initiation (Kick-off) project planning project production or execution project monitoring or controlling project completion Not all projects will visit every stage as projects can be terminated before they reach completion. Some projects probably don't have the planning and/or the monitoring. Some projects will go through steps 2, 3 and 4 multiple times.

21 Century MPM Software u Computers u Spreadsheets u World Wide Web u Tele-Commuting Project Management u 24/7 Communication u Collaboration Worldwide u Shifts and Teams u

Section 5 u Importance and Necessity of Project Management

Understanding MPM and CIPM Training The AAPM combines the philosophy of PM along with other Graduate Studies such as: u Regulatory environment u Legal and Ethics u Marketing u Strategic Costing u Financial Strategy u Using Technologies u Collaboration and Teams. u

Basic Training Goals Understand: what planning is/is not u where and when to start u to adapt or tailor planning u shortening the planning time u what the project plan represents u process and supporting materials u

What it is and is not Initiate Plan Execute Control Close Devising and maintaining a workable scheme to accomplish the business need that the project was undertaken to address. u It is the work plan, not the work. u It is a definition (defining) of needed work and resources
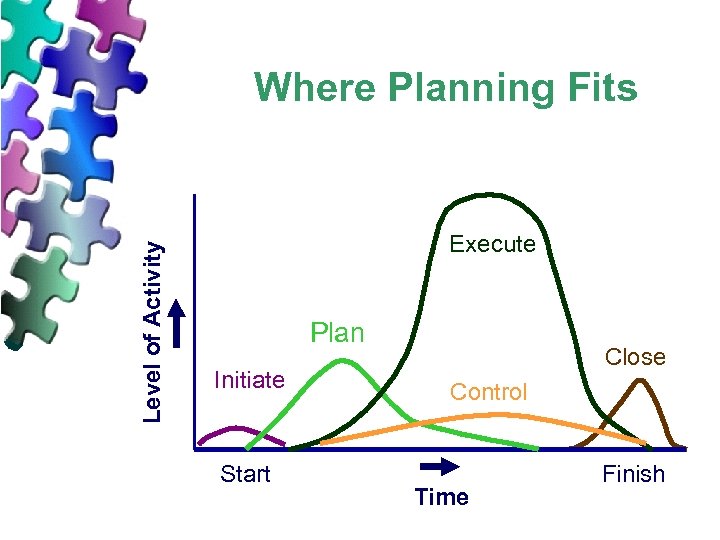
Level of Activity Where Planning Fits Execute Plan Initiate Start Close Control Time Finish

Quote on Planning "Give me six hours to chop down a tree and I will spend the first four sharpening the axe. " (Abraham Lincoln, 1809 -65)
Planning Objectives Define : Scope u Objectives u Work activities u Estimates u Resources required u Roles & responsibilities u How to change & update the plan u

Importance / Lessons u Straying from original goals, u Inadequate resources u Repetitive meetings - on what needs done (prep) u Frustration - poorly defined, communicated, and coordinated work activities u Issues not understood or related u Decisions repetitively re-opened or re-

Project Management is composed of several different types of activities such as: u u u u u Planning the work Assessing risk Estimating resources Organizing the work Acquiring human and material resources Assigning tasks Directing activities Controlling project execution Reporting progress Analyzing the results based on the facts achieved


Develop Scope u All the work, and only the work required u Scope Statement - agreement of what is and is not Includes: · primary objectives (products/deliverables) · major milestones · assumptions · constraints · completion criteria · Agreement design and Contract Specifications

Change Management of changes to the primary objectives and major deliverables milestones. The plan should include agreements of: 1. Change acceptance/expectations 2. How changes will be evaluated 3. How change will be e. g. Steel Prices for government contract
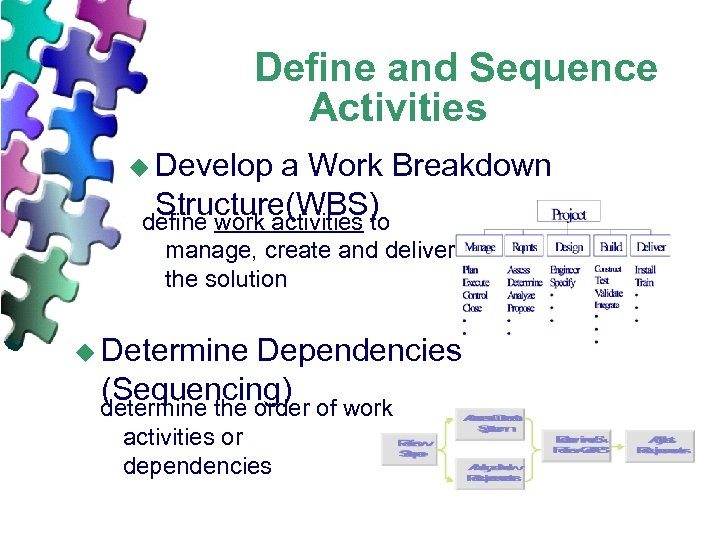
Define and Sequence Activities u Develop a Work Breakdown Structure(WBS) define work activities to manage, create and deliver the solution u Determine Dependencies (Sequencing) determine the order of work activities or dependencies
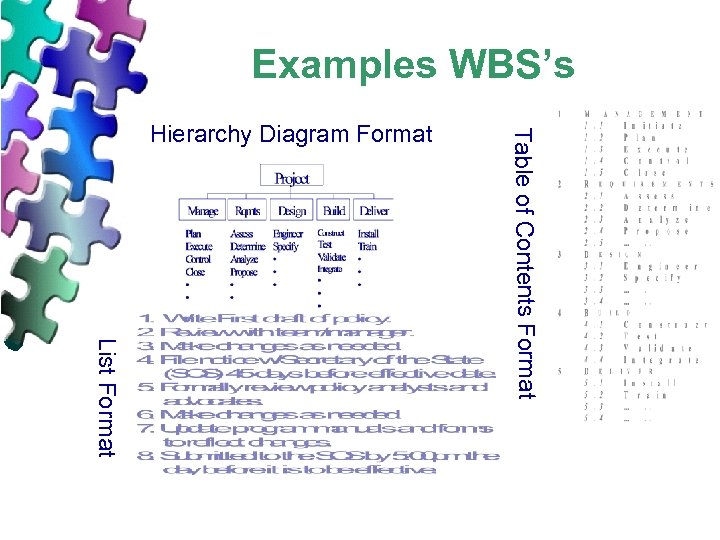
Examples WBS’s List Format Table of Contents Format Hierarchy Diagram Format
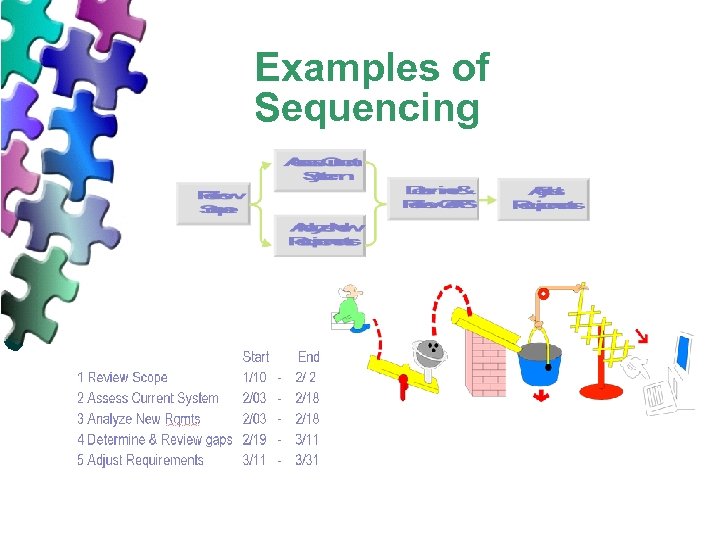
Examples of Sequencing
Estimate Duration Determine Resource Needs u Obtain initial estimate of likely duration for tasks does not take into account the number of people expected to perform the task. u For each task - determine skills, worker allocation and resources

Determine How Quality will be Managed How will quality assurance and control be conducted? Wha t? • Identify Quality Standards How ? • Quality Assurance Chec k • Quality Control Quality Plan Sometimes performed by a 3 rd Party
Determine How to Meet Communications, Data and Collaboration Needs The plan should determine: • who needs what information • when will they need it • how will it be given to them • by whom And determine how to: See IPMC Standards • store, update, and disseminate information • close, file and archive information • update the comm. plan

Develop Schedule determining start and finish dates for tasks and assigning resources May Jun Jul Aug Sep Oct Nov
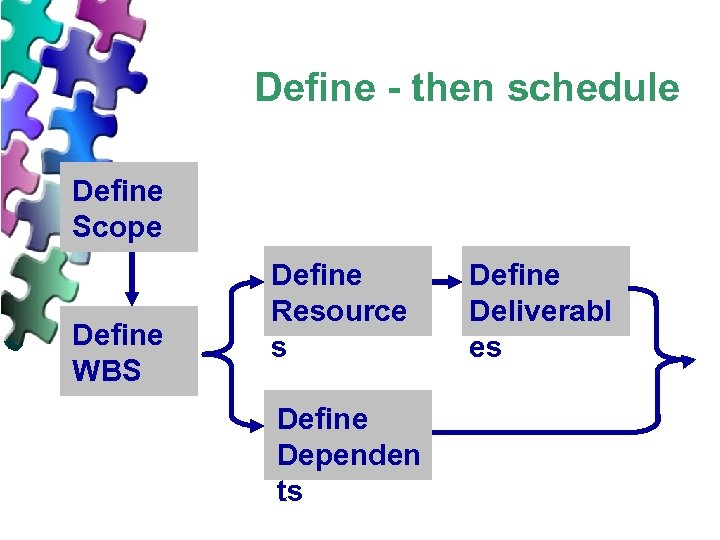
Define - then schedule Define Scope Define WBS Define Resource s Define Dependen ts Define Deliverabl es
Terminology This is a schedule or Gantt chart, not a WBS, not the project plan

Estimate Resource Costs Develop cost estimates for: ·internal & external labor (hrs, rates) refined during the ·materials course of the project , ·supplies definitive just prior ·contracts and legal costs to construction ·special costs Estimate
Organize and Acquire Staff
Determine What to Procure and When Procurement planning determines: ·whether, what, and how much, Actual solicitation ·how and when, is part of execution ·how to manage solicitations, selection, contract administration, and closeout Procurement documents: ·SOW - Statement of Work ·RFP - Request for Proposal ·Evaluation Criteria

Build Budget and Spending Plan Budgeting involves assigning the cost estimates to all the tasks creating a cost baseline.

Project Management tries to gain control over five variables: u u u TIME - The amount of time required to complete the project. Typically broken down for analytical purposes into the time required to complete the components of the project, which is then further broken down into the time required to complete each task contributing to the completion of each component. COST - Calculated from the time variable. Cost to develop an internal project is time multiplied by the cost of the team members involved. When hiring an independent consultant for a project, cost will typically be determined by the consultant or firm's hourly rate multiplied by an estimated time to complete. QUALITY - The amount of time put into individual tasks determines the overall quality of the project. Some tasks may require a given amount of time to complete adequately, but given more time could be completed exceptionally. Over the course of a large project, quality can have a significant impact on time and cost (or vice versa). SCOPE - Requirements specified for the end result. The overall definition of what the project is supposed to accomplish, and a specific description of what the end result should be or accomplish. RISK - Potential points of failure. Most risks or potential

Identify Risk & Create Risk Response Plan Risk planning involves: ·identifying risks w/high effect and impact ·planning for risk mitigation or contingency Common sources of risk: ·Changes in requirements ·Design errors and omissions ·Roles and responsibilities misunderstood ·Poor estimates or unsupported estimates ·Insufficiently skilled staff
Integrate the Plans Previous steps are reiterated and reevaluated to create a coherent plan. for example: • initial draft - reflects generic skills and duration • final plan - reflects specific resources and dates

Align the Project Mission with the Agency’s Mission What is your agency’s mission? What is the relationship of your project to your agency’s mission? u Project activities need to support this mission. u

Know the Project Stakeholders Who are the people with an interest in the outcome of the project? A strong project mission can not be created in a vacuum. u What are their common expectations? Stakeholders’ expectations are rarely spelled out in legislation, executive orders, or formal memoranda. u

Amplify the Voices of Your Customers Who will be paying for this project? Who will actually be using the structures, systems and processes being designed? u Clarify the business priorities of these customers and their criteria for success. Actively and emphatically communicate this information. Do this for customers inside the organization as well as those outside the organization. u

Maintain High-Level Communication About the Project Mission Communicate steadily with stakeholders and customers throughout the project. This will help to manage their expectations and requirements over time. u Design project development so that requirements and expectations can be reconfirmed at regular junctures. Periodically check to see that stakeholders and customers understand support changes, delays, and u

Strategies What do you want to accomplish? Set Realistic Business Objectives What are the common business needs of the organizations that will depend on the system? What accomplishments will be critical for the project to be considered successful? Define project boundaries at the outset, and use this definition to manage requirements throughout the project. A clear definition of business success will also help ensure that project efforts support the agency’s strategic plan.

Gain Agreement on the Project Plan The project plan formally captures and documents agreements among customers, stakeholders and project participants. Secure an informed agreement up front, and maintain this agreement throughout the project life. This will ensure that the project meets expected results. This will also help align the project with the organization’s business plans and supporting plans. Over time, manage the project scope carefully, since there will be a tendency for different areas of the project to acquire their own divergent momentum.

People and Leadership u Understand the project participants Listen to the Customer and Create a Vision u The project sponsor manages high-level customer relationships, translating key customer expectations into a practical vision for the project. To be effective, this vision must be u

Commit to the Project u The most frequent cause of project failure is the lack of involvement of the organizational leaders. Ongoing involvement is crucial. It is critical to structure the project in such a way that go/nogo decisions may be made at highly visible milestones. Leadership commitment stabilizes the project so that it can accommodate changes over time.

Leverage the Existing Organizational Structure u The roles and responsibilities of the project and its partners are most effective when they correspond with the way in which the overall agency is managed. For example, in an organization in which field offices have a great deal of autonomy, a centralized approach to project management could bring about unnecessary conflict.

Project Leadership Select a Strong Project Manager u Empower a central point of responsibility for project decisions, and clearly distinguish this role from functional program management roles. Clarify the risks which the project manager is expected to manage strategically. "Leadership ability" is difficult to articulate, and even more difficult to find.

MPM Leadership Qualities u u u u Drive. Does the project manager have a strong desire to succeed? Ability to Build Consensus. Can the project manager get key individuals to work together towards common ends? Ability to Take Risks. Can the project manager recognize opportunities and find ways to seize them? Ability to Communicate. Is the project manager able to communicate clearly and convincingly to all parties? Experience. Does the project manager have a track record of success? Look for characteristics and experiences that relate directly to the project at hand. Technical Knowledge. Does the project manager possess demonstrated knowledge in the appropriate technical fields? Sense of the Big Picture. Does the project manager understand the project from a broad business perspective?

Planning Making it Happen ·Define Success Up Front - Define project success in terms of specific business objectives. From the customer’s point of view, how should different business objectives be prioritized? ·Use Metrics to Focus On Outcomes - Focus on outcomes rather than outputs. Prioritize the metrics for which project participants will be held responsible. Gain agreement on critical metrics and use them to drive planning and delivery. ·Integrate Planning Activities Across the Project - Formalize planning processes. Assign roles and responsibilities specifically for planning-related activities. The CEO or other executives can help anchor project plans in the organization’s business and planning. ·Realign Plans Over Time - How will plans need to be modified along the way? Make sure project plans continue to support intended business priorities. If the project encounters significant changes, then the original plans will have to be realigned to ensure desired results.
Section 6: Morning Break

Section 7 Questions Answers u Best Practices u More on: Legal Contracting u Cost Fluctuations u Capacity to Handle u Coordinating Marketing and Legal with your teams? u

Section 8 – Case Studies The Cross Sell - Project Management Plan for Financial Services or IT Services…. u Existing Client u Client Needs or RFP implied or given. u Objectives u Products and Services – IT or Banking u Develop Plan and Proposal u Make Presentation u Offer services and prices u Implement Requests u Monitor and Evaluate u Redesign over Time.

Case Study: The Project of a Lifetime Huge Money u Huge Job u Long-Term u Resources u Commitments u Demands/Timeline u And more u What do we do? ? ?

Section 9 u Workshop and Lecture

Workshop and Breakout Session You have just been given the following offer: u u Your company has just received the contract to maintain the hotel grounds. Your contract provides for 35, 000 dollars per month Your services are to be provided 7 Days per week. You have 30 employees that are paid 40 dollars per day and work 5 days

Issues u u u u You have trouble meeting Deadlines of care. Gas Prices go up Cost of labor goes up Some good employees are offered more money elsewhere The hotel demands that you provide more care in common areas. Much of your equipment needs to be replaced Teens in the neighborhood want to work for you? Issues?

Recent Activity Bahamas – Amazing Business Progress and Opportunities for MPMs & CIPMs. u Phase 3 of Kerzner International or more reknown as ATLANTIS, phase three involves a marina, aqua park (dolphins, sting rays, etc. ) facilities, hotel facility of additional 2800 rooms.

Resorts, Casinos and Hotels u Bah-Mar Resort, at Cable Beach a $2 billion project with a complete overall of Cable Beach Area. A new 36 hole golf course, world’s largest casino, new conference buildings, and renovated hotels, and new hotel buildings.

Other Developments including Golf and Family Resorts South Ocean Development project – new hotel, renovated golf course, new housing development. u New Tiger Woods Development at South Ocean with new housing development, new golf course u Family Island projects in Exuma, Abaco, etc. u

Bahamas Government Work – Ever Growing Opportunities Government projects such as: housing, GIS, works and sewerage projects, airport construction projects, communications (BTC – Bahamas Telecommunications Co. ), BEC – Bahamas Electricity Corp. projects, etc. u We all know that IT and Financial Services are Giant Business in this region. u

Construction PM u In project architecture and civil engineering, construction is the building or assembly of any infrastructure. Although this may be thought of as a single activity, in fact construction is a feat of multitasking. Normally the job is managed by the construction manager, supervised by the project manager, design engineer or project architect. While these people work in offices and make the most money, every construction project requires a large number of laborers to complete the physical task of construction.

Construction Execution u u For the successful execution of a project effective planning is often essential. Those involved with the design and execution of the infrastructure in question must consider the environmental impact of the job, the successful scheduling, budgeting, site safety, inconvenience to the public caused by construction delays, preparing tender documents, etc. Communications, Billing, Receivables

Company Stakeholders Shareholders u Employees u Suppliers u Customers u Community u

Construction Teams u u u Building construction- Building construction is the process of adding structure to real property. Tender requirements - & a public bid process Design team including architects, interior designers, civil engineers, cost engineers (or quantity surveyors), mechanical engineers, electrical engineers, and structural engineers. Mortgage bankers, accountants, and cost engineers are likely participants in creating an overall plan for the financial management of the building construction project. Legal considerations – Use and Regulations and Code

How to deal with all… u Putting it all together and working with all stakeholders is important. PR & Marketing, CRM, Government, satisfying the contract, Managing Existing Jobs, Marketing for new jobs, and closing and collecting on jobs will all be important facets of projects.

Thank you for your time! IPMC International Project Management Commission ™ and The AAPM ™
8706b4478359af0fb2c1e5233f99923c.ppt