96dfbca4a81c5368cba5220ffa2cd7e7.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 33

Abortion 流产

Ⅰ. Definition Abortion is termination of pregnancy bfore 28 weeks of gestation and the fetal weight is less tan 1000 g. n Abortion : spontaneous: 10%~18% artificial n The early abortion: occurs before 12 w n The late abortion: occurs after 12 w n The miscariage abortion: occurs in 13~28 w n

2. Etiology n (1)Heredity factors Abnormal gene is the commonest cause of Spontaneous abortion. Abnomalities of chromosomes: number: autosomal trisomies polyploidy structural: monosomy X Early abortion 50%~60% is caused by chromosomal abnormalities.

(2)Toxic factors: lead, mercury, DDT, radiation, X-ray n (3)Maternal factors n (4)Immunologic factors Blood type in compatibility between mother and fatus. Imcompatibilily due to ABO, Rh n

①the general diseases Acute infections(systemic or local) n virus infection n hypertension, typhoid, pneumonia, heart disease, nephritis n bacteria, toxin and virus get into fetal blood circulation by placenta. n

②endocrine disorder n Hyper- or hypothyroidism (hyroidism) n hypofunction of corpus luteum

③the genital disease A. uterine deformity double uterus hypoplasia uteri longitadinal uterine septum n B. pelvic tumor(myoma, ovarian tumor) n C. cervical incompetence, laceration n

④abdominal operation during the pregnancy

3. Pathologic change Most commonly, necrotic changes occur in the decidual tissue about the placentation site and result in hemorrhage into this area. As bleeding continues, the sac and the placenta become detached from the uterine wall and are expelled by uterine contractions. n Early pregnancy: abortion is complete n 8~12 w: abortion is incomplete n

4. Clinical classification and feature (1) Threatened abortion n (2)Inevitable abortion n (3)Incomplete abortion n (4)complete abortion n (5)Missed abortion n (6)Habitual abortion n (7)Septic abortion(infect abortion) n

Differential diagnosis of varied abortions

(5)Missed abortion It is that pregnancy has been retained for 2 months or more following death of the fetus. n The abnormally protracted retention of a dead fetus in uterus in over 2 months that don’t expelled. n Missed abortion is manifested by loss of symptoms of pregnancy and decrease in uterine size. n

The embryo or fetus has been dead at least 2 months but no tissue is passed. n Middle pregnancy, no fetal movement and fetus heart tones. n The cervix closed. n

(6)Habitual abortion(recurrent) n Recurrent, or habitual, is the sequential 3 or more spontaneous abortion. n Every abortion times is or not same month of pregnancy.

Early cause ①hypofunction of corpus luteum n ②emotion factor nervous factor n ③hypopituitarism n ④chromosomal abonormalities n

Late abortion (1)incompetence of the cervix n (2)congenital anomalies of the uterus n (3)myomas of the uterus n (4)blood type incompatibility between mother and fetus n

5. Diagnosis

(1)History ①amenorrhea, recurrent abortion symptoms of pregnancy n ②the degree of abdominal pain, vaginal bleeding n ③the products of gestation were expelled or not n

(2)Examination ①general examination: temperature , pulse, respiration, blood pressure. n ②vaginal examination: uterine size: compared to the expected date of pregnancy cervical os: open or close uterine tendeness n

(3)ancillary examination ①pregnancy test: HCG<625 IU/L→abortion n ②measurement of HPL 5~10 w: hpl≤ 0. 01 mg/L n ③ measurement of E 2(estroid) E 2<740 pmol/L n ④measurement of pregnanediol 24 h urinary<15. 6μ/24 h, 95%→abortion n

n ⑤B-ultrasound differential of varieties of abortion gestation sac, embryo status, fetal heart tones, fetus movement Incompetence of the cervix, cervical os>19 mm and have history of abortion
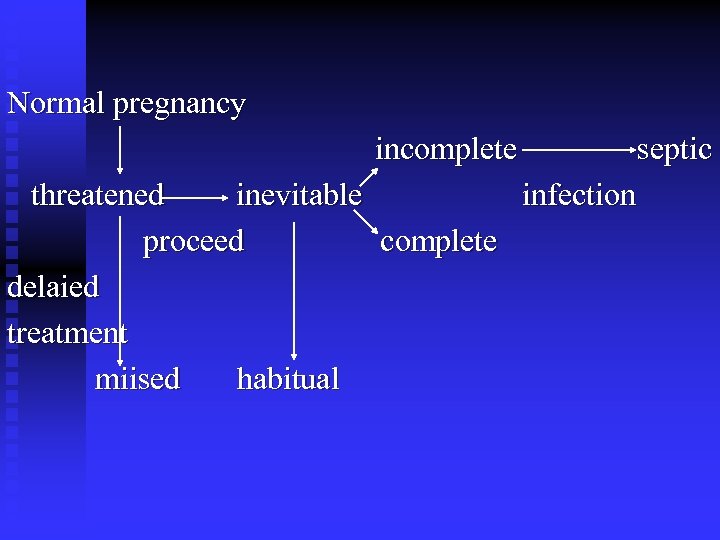
Normal pregnancy incomplete threatened inevitable proceed complete delaied treatment miised habitual septic infection

6. Treatment

(1)Threatened abortion Principle: protect fetus treatment n ①place the patient at bed rest forbid sexual intercourse n ②drug folic acid 5 mg tid. Po. If corpus luteum or low of uterine pregnanediol progesterone 20 mg Qd. Im. VE 30~50 mg Qd po. Seditive: valium 2. 5 mg po. n

(2)Inevitable and incomplete abortion At once D&C(curettage) dilatation n if bleeding is brisk blood transfusion oxytosin 5~10 u iv/im n incomplete abortion antibiotic used for preventive infection tissue examination by a pathologist n

(3)Complete abortion n When the uterus is empty, there are no need for further interference.

(4)Missed abortion After diagnosis of it , as soon as expelled product of conception is necessary. n Because the fetus dead, placenta release thrombocinatse into blood circulation ease occure in coagulability. lead to disseminated intravascular coagulation(DIC) n

n ①examination: bleeding and coagulation time placenta count fibrinogen level thrombinogen

②leveral uterine sentition DES(diethylstibestrol)5~10 mg tid po 5 d n ③before curettage, preparey blood during opreation: oxytocin 10 u im/iv over than 3 month of pregnancy artificial inducte. n

(5)Habitual abortion The first should be examinatin cause of habitual abortion and treatment. n 1)rest, increase nutrition, VB, VC, VE… n 2)medical treatment: hypofunction of corpus luteum--progesterone n 3)surgical treatment: ①correction of congenital anomalies of uterus, removed of myomas ②repair of the incompetent cervix. 12~20 w n

(7)abortion complication infection (septic abortion) Symptoms: temperature ↑, pulse↑, abdominal pain, marked suprapubic tenderness sighs of peritonitis(guarding indentfy)marke tenderness of uterus and uterine adnexa. n Severas: pelvic-peritonitis, septicemia, (endotoxic shock) intoxication shock n

(8)Septic abortion The principle of treatment: bleeding is a few: first treat infection with broad-spectrum antibiotiss second D&C bleeding is sever: we are eryher contract infection or curettage. n

※The producte of conception from the cervix are removed with a sponge holder. n Don’t used curette to curettage uterine wall prevent infection n avoid hematogeous dissemination od the infection. n
96dfbca4a81c5368cba5220ffa2cd7e7.ppt