becker_fin_1.pptx
- Количество слайдов: 35

Abildayeva Dina Alyokhina Anastasia Borissova Dinara Seilkhanova Diana

Limited Liability Company "Bekker and Co" was created in 1991. Ministry of Finance of the Republic of Kazakhstan issued a registration certificate #6. The company's mission: "to preserve the tradition of consumption of organic food. "

In 1991, LLP "Bekker and Co" was provided by plot of 0. 78 ha in Almaty at the Rozybakiev Satpayev st. for construction of administrative and industrial buildings. In 1992 the construction was started, and in 1994 was commissioned the first phase of the complex. The area of the first stage was 3800 m 2, there were house offices, a brewery, a restaurant "Prussia" and the sausage shop.

The second stage of an area 3800 m 2 began in 2000. Currently, the building has a new meat processing plant, bakery, frozen food shop, cooking, supermarket, cafe "Bistro" and the dining room for the staff.

Purpose of our work is to find out whether the company use it’s resources efficiently. For the analysis we used financial statements & indicators of LLP “Becker & Co” for last 2 years, tools & methods of economics analysis like vertical & horizontal, & different ratios.

Balance Sheet • A summary of a firm’s financial position on a given date that shows total assets = total liabilities + owners’ equity. Income Statement • A summary of a firm’s revenues and expenses over a specified period, ending with net income or loss for the period.
Horizontal Analysis • Comparing a company’s financial condition and performance across time. Vertical Analysis • Comparing a company’s financial condition and performance to a base amount.
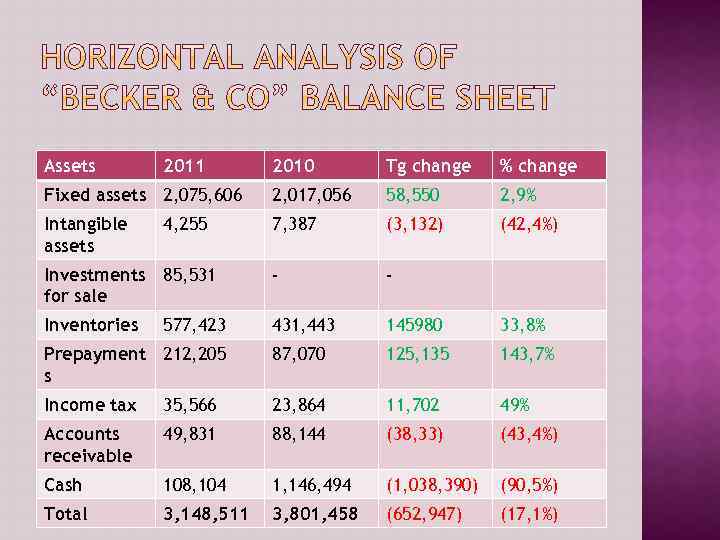
Assets 2011 2010 Tg change % change Fixed assets 2, 075, 606 2, 017, 056 58, 550 2, 9% Intangible assets 7, 387 (3, 132) (42, 4%) Investments 85, 531 for sale - - Inventories 431, 443 145980 33, 8% Prepayment 212, 205 s 87, 070 125, 135 143, 7% Income tax 35, 566 23, 864 11, 702 49% Accounts receivable 49, 831 88, 144 (38, 33) (43, 4%) Cash 108, 104 1, 146, 494 (1, 038, 390) (90, 5%) Total 3, 148, 511 3, 801, 458 (652, 947) (17, 1%) 4, 255 577, 423
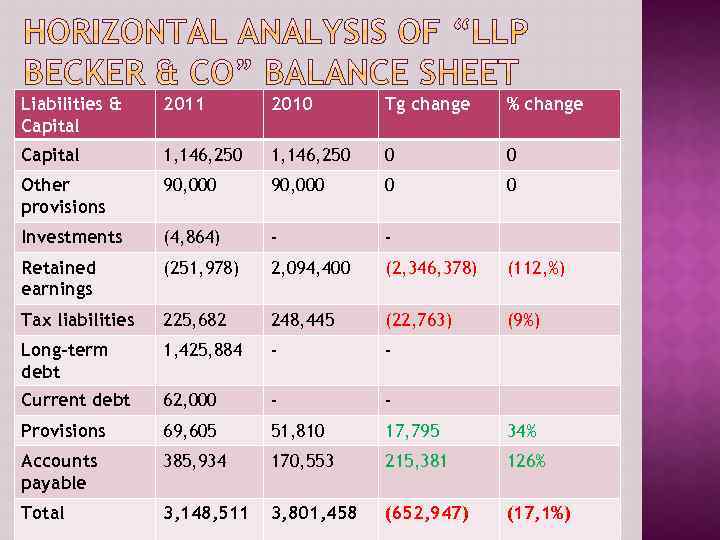
Liabilities & Capital 2011 2010 Tg change % change Capital 1, 146, 250 0 0 Other provisions 90, 000 0 0 Investments (4, 864) - - Retained earnings (251, 978) 2, 094, 400 (2, 346, 378) (112, %) Tax liabilities 225, 682 248, 445 (22, 763) (9%) Long-term debt 1, 425, 884 - - Current debt 62, 000 - - Provisions 69, 605 51, 810 17, 795 34% Accounts payable 385, 934 170, 553 215, 381 126% Total 3, 148, 511 3, 801, 458 (652, 947) (17, 1%)
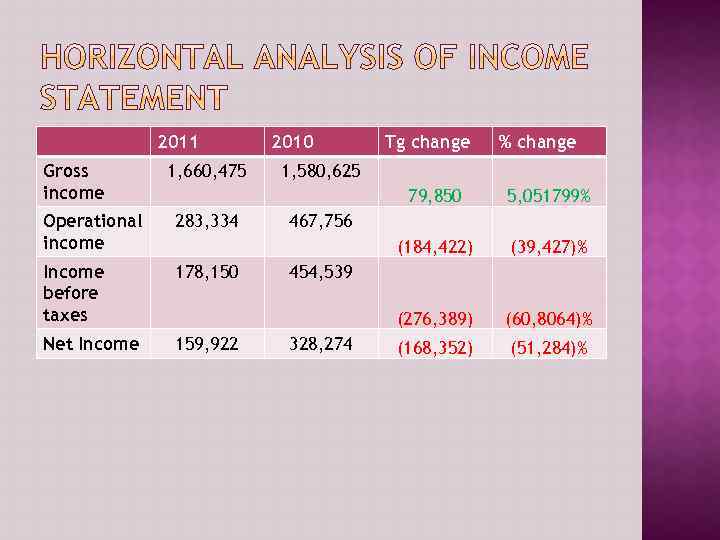
2011 Gross income 1, 660, 475 2010 Tg change % change 1, 580, 625 79, 850 (184, 422) 283, 334 Income before taxes 178, 150 Net Income 159, 922 (39, 427)% (276, 389) Operational income 5, 051799% (60, 8064)% (168, 352) (51, 284)% 467, 756 454, 539 328, 274
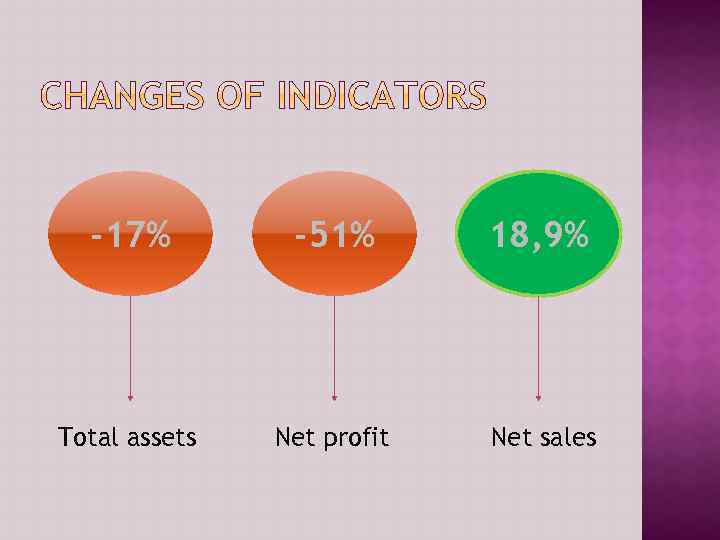
-17% -51% 18, 9% Total assets Net profit Net sales
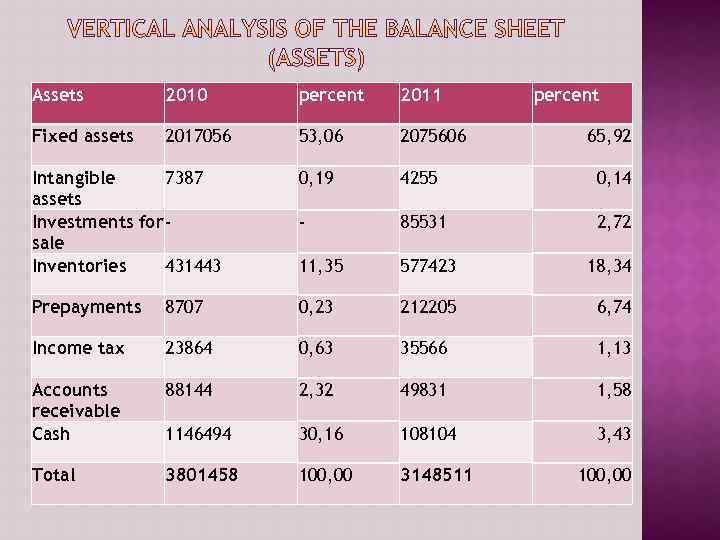
Assets 2010 percent 2011 percent Fixed assets 2017056 53, 06 2075606 Intangible 7387 assets Investments for sale Inventories 431443 0, 19 4255 0, 14 - 85531 2, 72 11, 35 577423 18, 34 Prepayments 8707 0, 23 212205 6, 74 Income tax 23864 0, 63 35566 1, 13 Accounts receivable Cash 88144 2, 32 49831 1, 58 1146494 30, 16 108104 3, 43 Total 3801458 100, 00 3148511 65, 92 100, 00
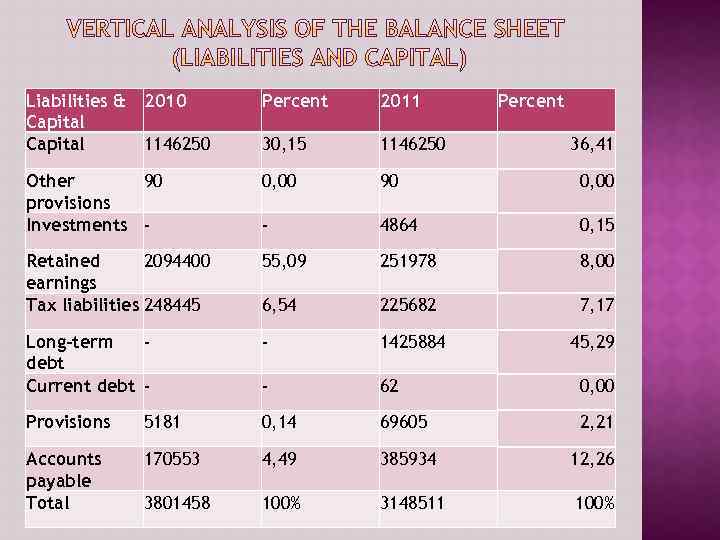
Liabilities & 2010 Capital 1146250 Percent 2011 Percent 30, 15 1146250 Other 90 provisions Investments - 0, 00 90 0, 00 - 4864 0, 15 Retained 2094400 earnings Tax liabilities 248445 55, 09 251978 8, 00 6, 54 225682 7, 17 Long-term debt Current debt - - 1425884 45, 29 - 62 0, 00 Provisions 5181 0, 14 69605 2, 21 Accounts payable Total 170553 4, 49 385934 12, 26 3801458 100% 3148511 100% 36, 41
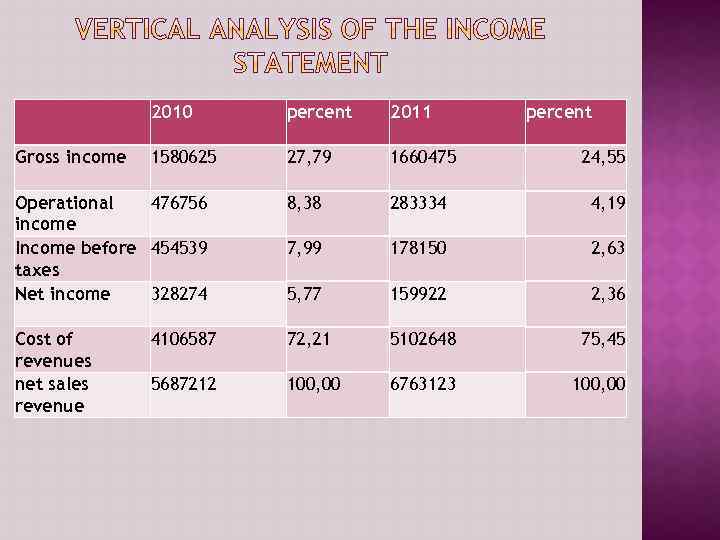
2010 percent 2011 percent Gross income 1580625 27, 79 1660475 24, 55 Operational 476756 income Income before 454539 taxes Net income 328274 8, 38 283334 4, 19 7, 99 178150 2, 63 5, 77 159922 2, 36 Cost of revenues net sales revenue 4106587 72, 21 5102648 75, 45 5687212 100, 00 6763123 100, 00

As we can see from the results of analysis, total assets and liabilities of the company have been reduced by 17%, net profit also shows negative indicator of more than 50%, but sales revenue increased up to 19%. This is because of rapid change of cash, most of which was invested for sale issues, and there were also made prepayments that can turn into benefit for the company in near future. But still it’s required to have more cash, as it’s liquid enough.
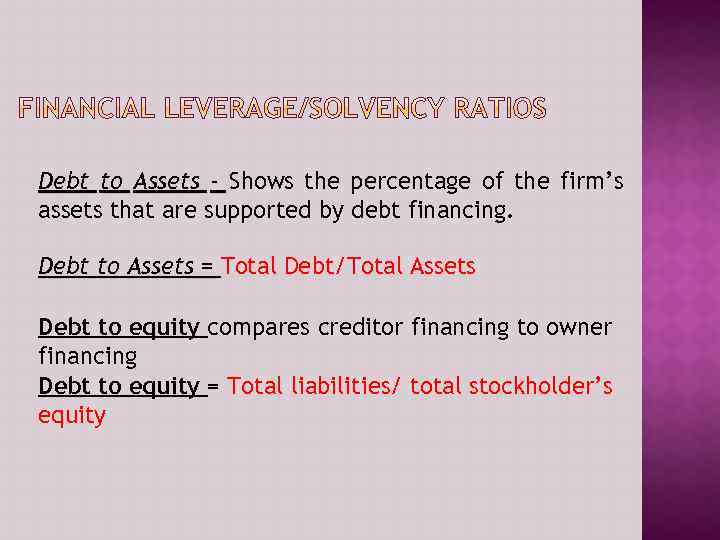
Debt to Assets - Shows the percentage of the firm’s assets that are supported by debt financing. Debt to Assets = Total Debt/Total Assets Debt to equity compares creditor financing to owner financing Debt to equity = Total liabilities/ total stockholder’s equity
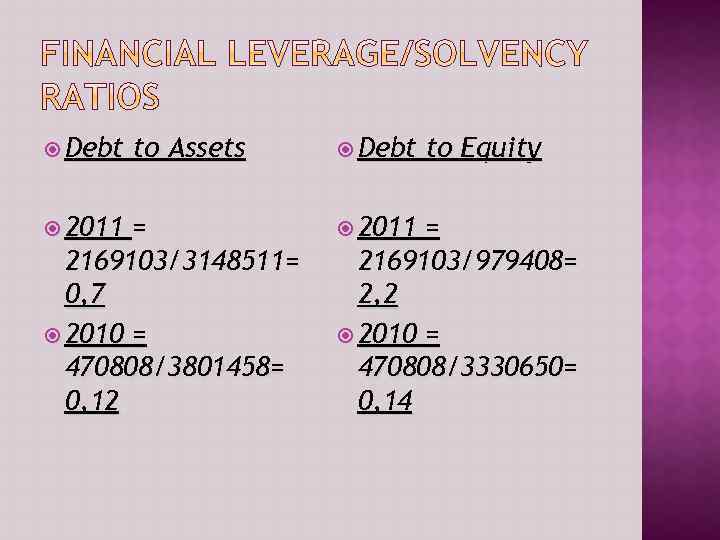
Debt 2011 to Assets = 2169103/3148511= 0, 7 2010 = 470808/3801458= 0, 12 Debt 2011 to Equity = 2169103/979408= 2, 2 2010 = 470808/3330650= 0, 14

Current ratio - Shows a firm’s ability to cover its current liabilities with its current assets. Working capital - This ratio indicates whether a company has enough short term assets to cover its short term debt. Acid-Test (Quick)- Shows a firm’s ability to meet current liabilities with its most liquid assets.
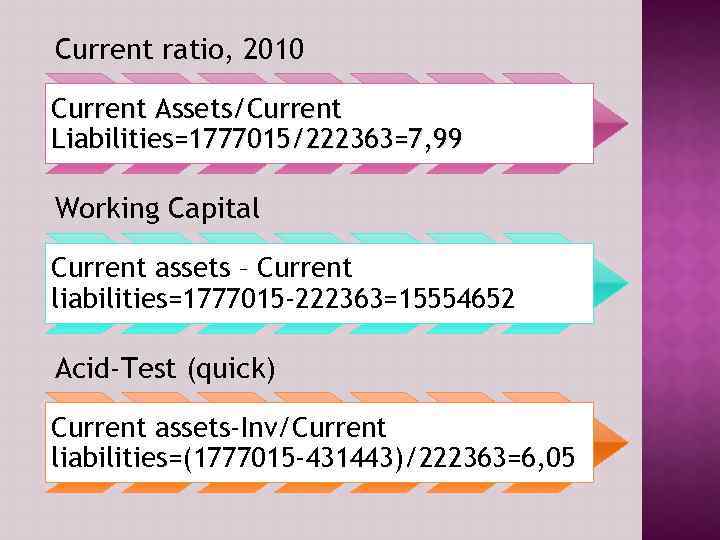
Current ratio, 2010 Current Assets/Current Liabilities=1777015/222363=7, 99 Working Capital Current assets – Current liabilities=1777015 -222363=15554652 Acid-Test (quick) Current assets-Inv/Current liabilities=(1777015 -431443)/222363=6, 05
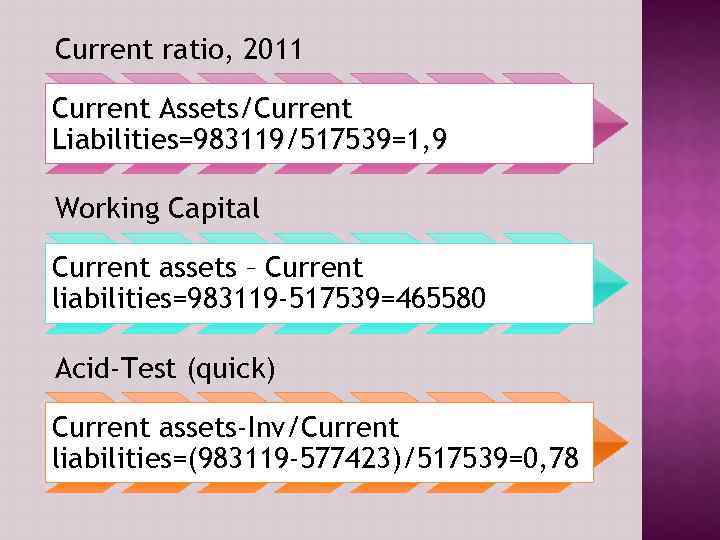
Current ratio, 2011 Current Assets/Current Liabilities=983119/517539=1, 9 Working Capital Current assets – Current liabilities=983119 -517539=465580 Acid-Test (quick) Current assets-Inv/Current liabilities=(983119 -577423)/517539=0, 78

Accounting ratios that measure a firm's ability to convert different accounts within its balance sheets into cash or sales. Activity ratios are used to measure the relative efficiency of a firm based on its use of its assets, leverage or other such balance sheet items. These ratios are important in determining whether a company's management is doing a good enough job of generating revenues, cash, etc. from its resources. v. Receivable Turnover v. Average Collection Period v. Inventory Turnover

RECEIVABLE TURNOVER Is used to quantify a firm's effectiveness in extending credit as well as collecting debts, measuring how efficiently a firm uses its assets. Annual Net Credit Sales Receivables 2011 6763123/49831=135, 7 2010 5687212/88144=64, 52

AVERAGE COLLECTION PERIOD The average collection period ratio represents the average number of days for which a firm has to wait before its debtors are converted into cash. Days in the Year Receivable Turnover 2011 365/135, 7=2, 7 2010 365/64, 52=5, 65

INVENTORY TURNOVER A ratio showing how many times a company's inventory is sold and replaced over a period. Cost of Goods Sold Inventory 2011 5102648/577423=8, 83 2010 4106587/431443=9, 51

COVERAGE RATIOS INTEREST COVERAGE A ratio used to determine how easily a company can pay interest on outstanding debt. The interest coverage ratio is calculated by dividing a company's earnings before interest and taxes (EBIT) of one period by the company's interest expenses of the same period EBIT Interest Charges 2011: 178150/18228=9, 8 2010: 454539/126265=3, 6

A class of financial metrics that are used to assess a business's ability to generate earnings as compared to its expenses and other relevant costs incurred during a specific period of time. For most of these ratios, having a higher value relative to a competitor's ratio or the same ratio from a previous period is indicative that the company is doing well. üGross profit margin üNet profit margin üReturn on investment üReturn on equity üAsset turnover

A financial metric used to assess a firm's financial health by revealing the proportion of money left over from revenues after accounting for the cost of goods sold. Gross profit margin serves as the source for paying additional expenses and future savings. Gross Profit Net Sales 2011=1660475/288334=5, 76 2012=1580625/467756=3, 38

A ratio of profitability calculated as net income divided by revenues, or net profits divided by sales. It measures how much out of every dollar of sales a company actually keeps in earnings. Net Profit after Taxes Net Sales 2011= 159922/283334=0, 56 2010=328274/467756=0, 7

A performance measure used to evaluate the efficiency of an investment or to compare the efficiency of a number of different investments. To calculate ROI, the benefit (return) of an investment is divided by the cost of the investment. Net Profit after Taxes Total Assets 2011: 159922/3148511=0, 05 2010: 328274/3801458=0, 086

The amount of net income returned as a percentage of shareholders equity. Return on equity measures a corporation's profitability by revealing how much profit a company generates with the money shareholders have invested. Net Profit after Taxes Shareholders’ Equity 2011: 159922/979408=0, 163 2010: 328274/3330650=0, 098

Indicates the overall effectiveness of the firm in utilizing its assets to generate sales. Net Sales / (AVERAGE) Total Assets 2011=283334/3148511=0, 09 2010=467756/3801458=0, 12

As we could see from the data above, the overall assets amount have been reduced since the previous period of time and net income have also reduced mostly because of some investments company did. In order to avoid those negative tendencies in future, company should increase amount of liquid assets and reduce its expenses.

Kase. kz – financial statements Becker. kz Principles of Financial Accounting, 11 th Edition, Belverd Needles and Marian Powers Экономика предприятия. Учебное пособие. Баженов Г. Е. , Гнездилова Л. И. , Стародубцева О. А. Яцко В. А, Новосибирск 2000 Экономика предприятия: Учебник. Практикум. - 3 -е изд. , В. Д. Грибов, В. П. Грузинов, Москва – 2005


becker_fin_1.pptx