ABAP Workbench: ABAP Workbench: Foundations and Concepts BC400


ABAP Workbench: ABAP Workbench: Foundations and Concepts BC400
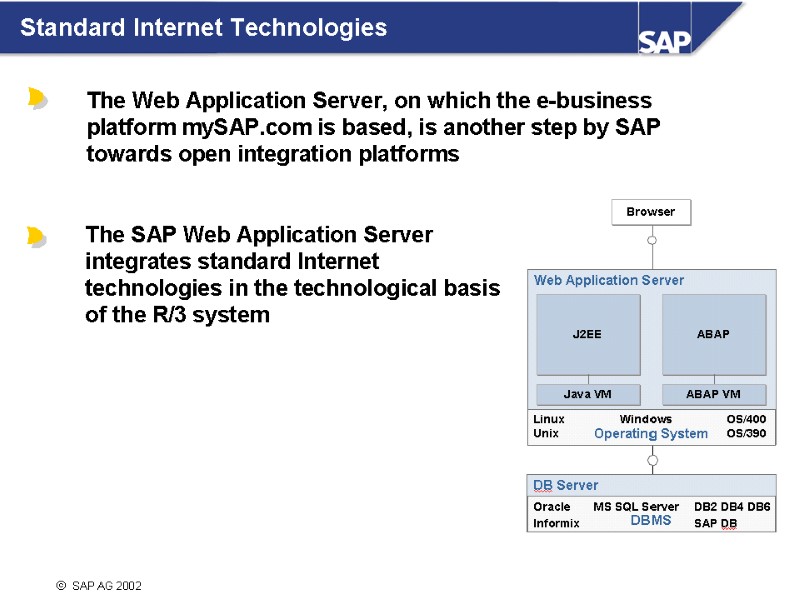
2
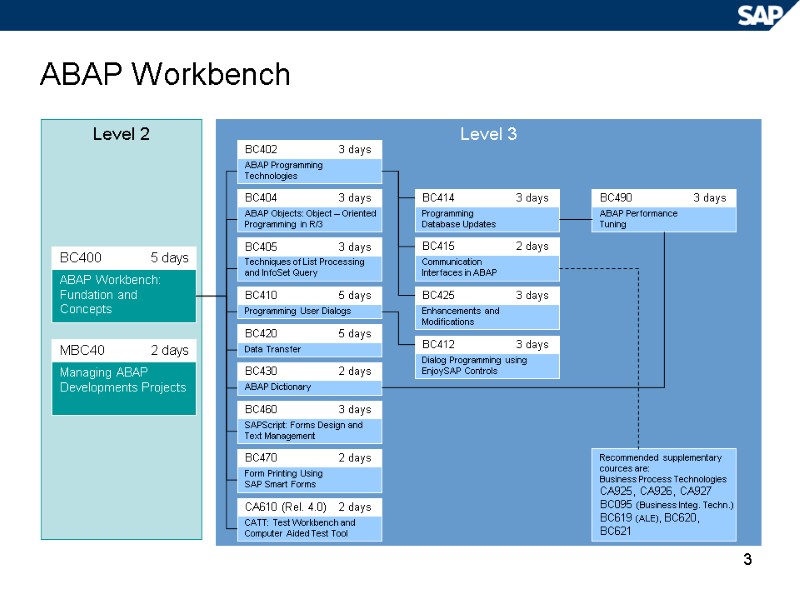
3 ABAP Workbench Level 2 Level 3 ABAP Objects: Object – Oriented Programming in R/3 BC404 3 days Recommended supplementary cources are: Business Process Technologies CA925, CA926, CA927 BC095 (Business Integ. Techn.) BC619 (ALE), BC620, BC621
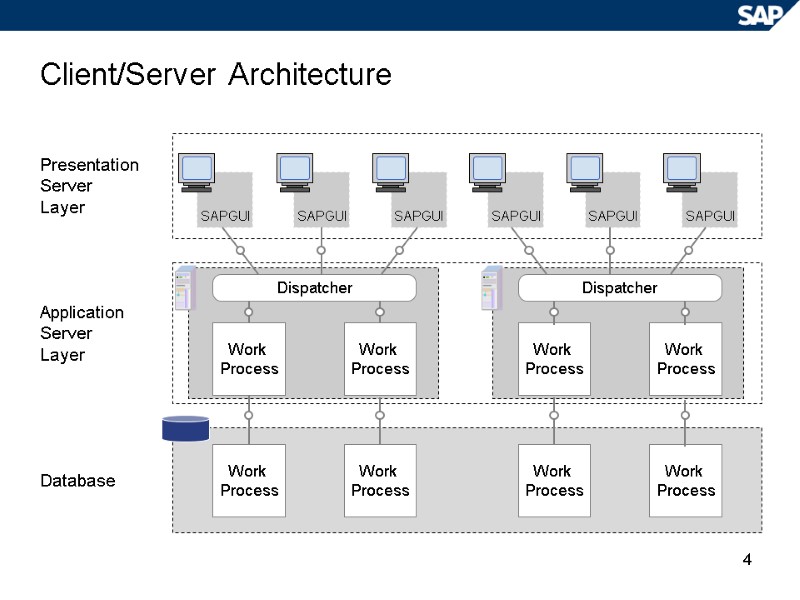
4 SAPGUI SAPGUI SAPGUI SAPGUI SAPGUI SAPGUI Client/Server Architecture Work Process Work Process Work Process Work Process Work Process Work Process Presentation Server Layer Application Server Layer Database Dispatcher Dispatcher Work Process Work Process
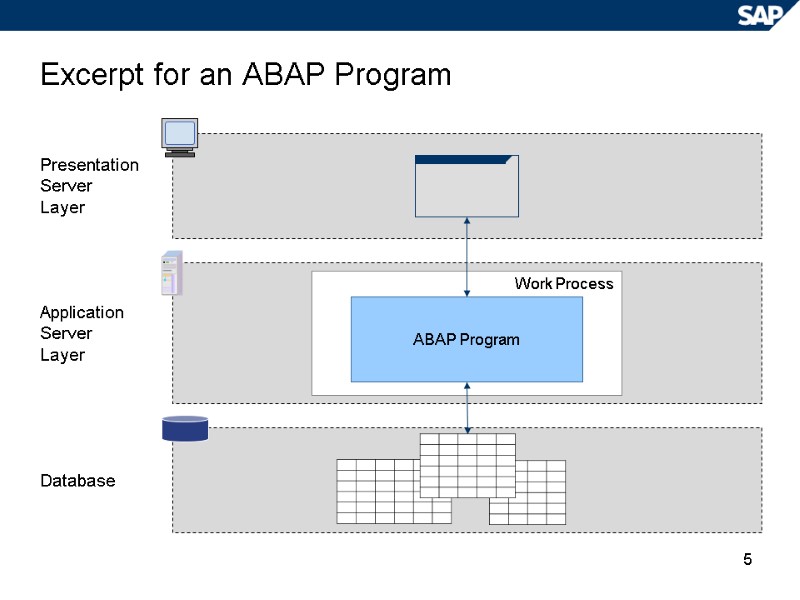
5 Excerpt for an ABAP Program Presentation Server Layer Application Server Layer Database Work Process ABAP Program
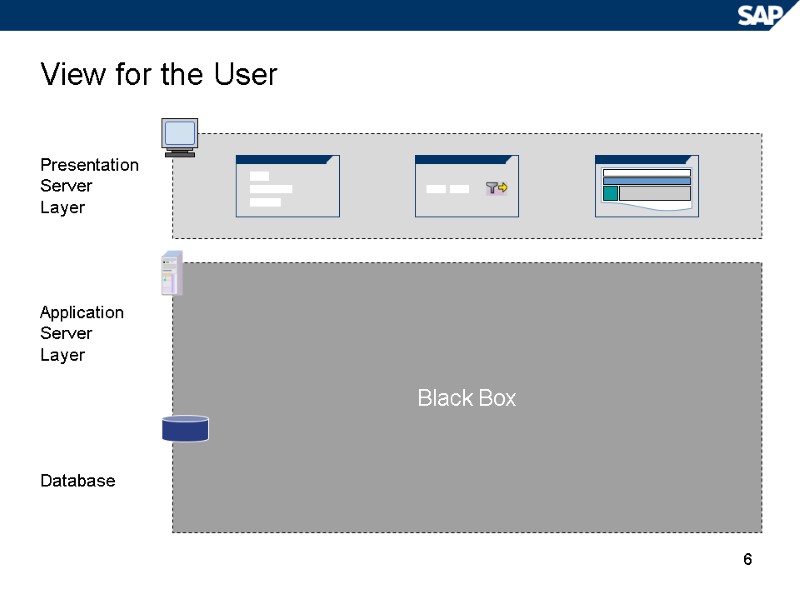
6 Black Box View for the User Presentation Server Layer Application Server Layer Database
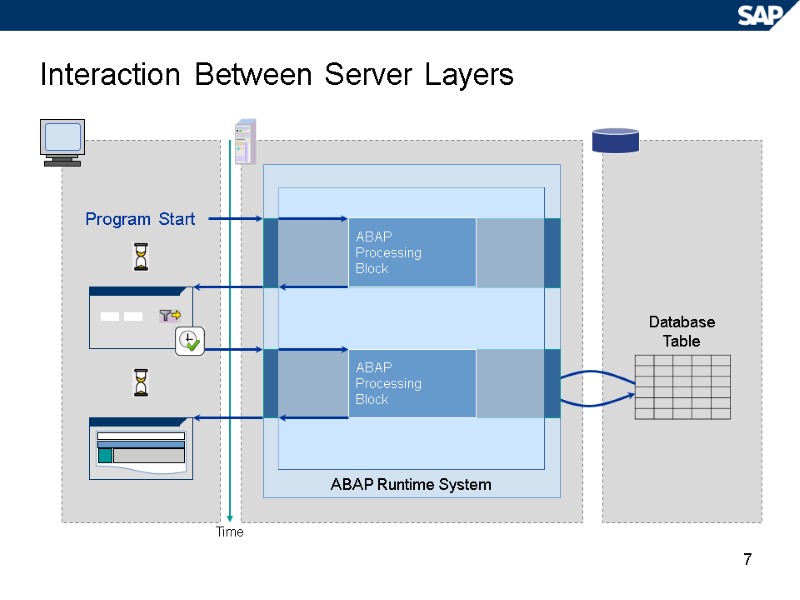
7 Interaction Between Server Layers Time ABAP Runtime System Program Start Database Table ABAP Processing Block ABAP Processing Block
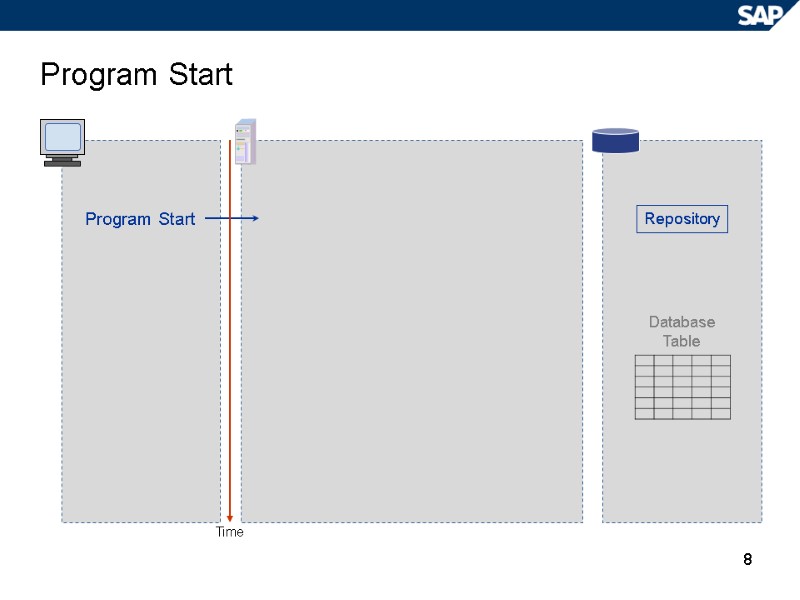
8 Program Start Program Start Database Table Repository Time
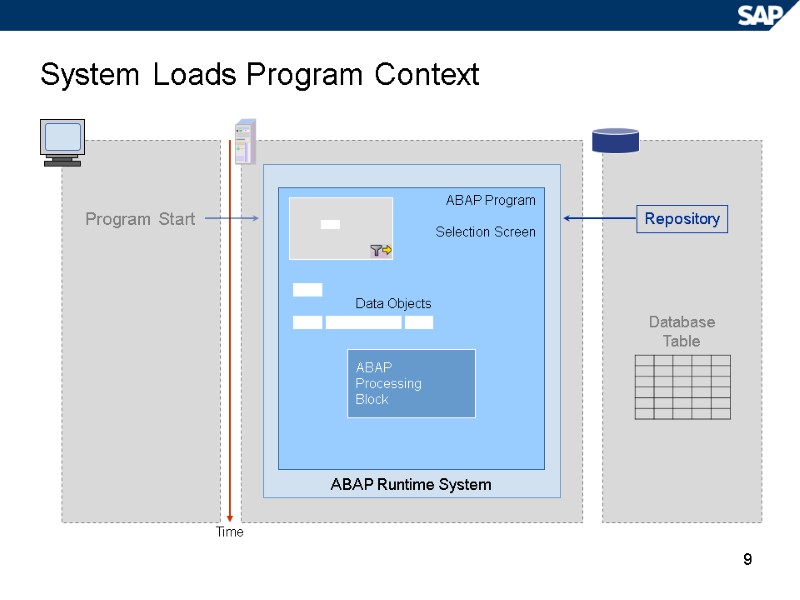
9 System Loads Program Context Program Start Database Table Repository Time ABAP Runtime System ABAP Program Selection Screen ABAP Processing Block Data Objects
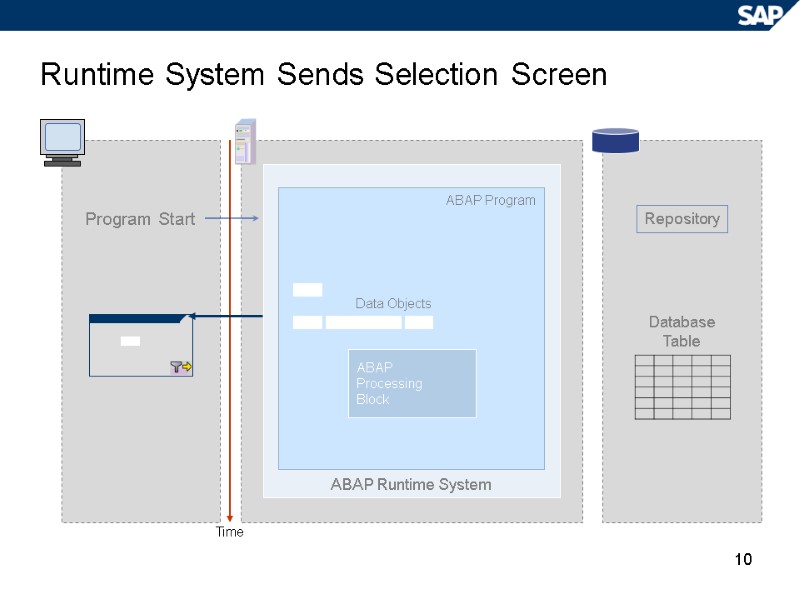
10 Runtime System Sends Selection Screen Program Start Database Table Repository Time ABAP Runtime System ABAP Program ABAP Processing Block Data Objects
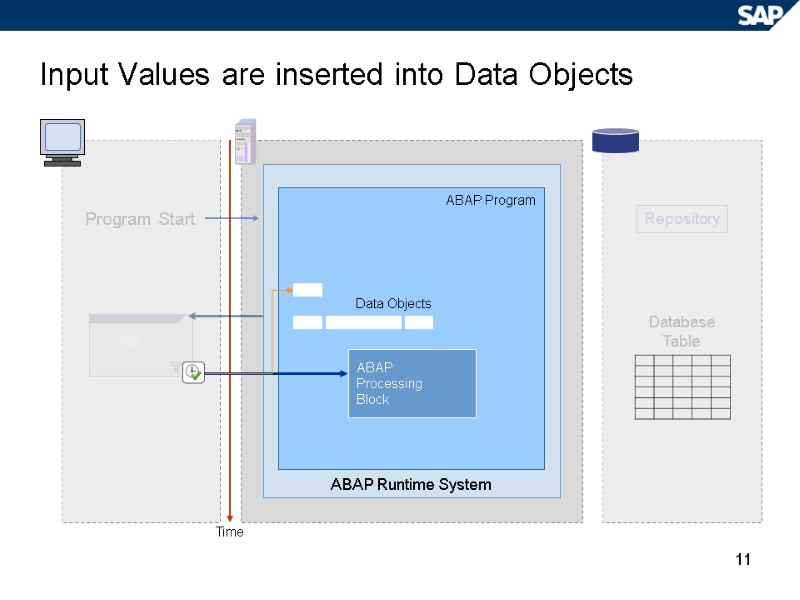
11 Input Values are inserted into Data Objects Repository Time ABAP Runtime System ABAP Program ABAP Processing Block Data Objects Program Start Database Table
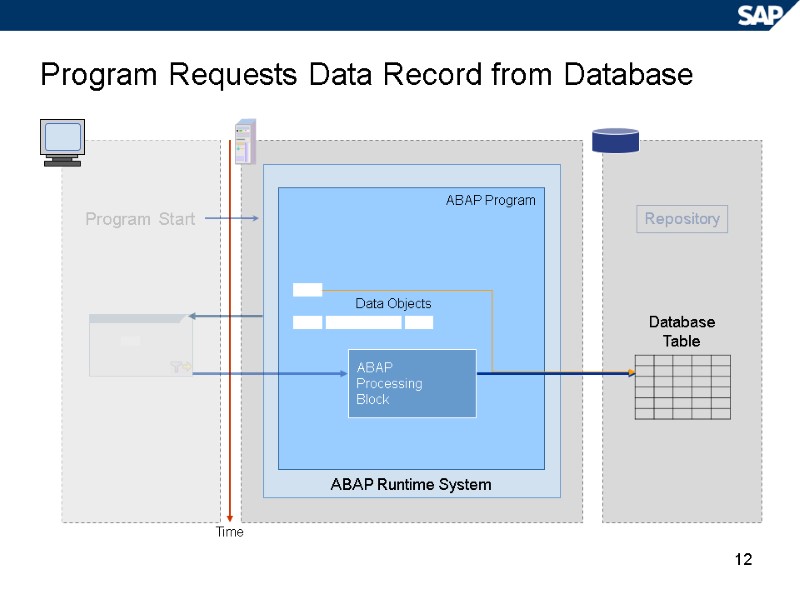
12 Program Requests Data Record from Database Repository Time ABAP Runtime System ABAP Program ABAP Processing Block Data Objects Program Start Database Table
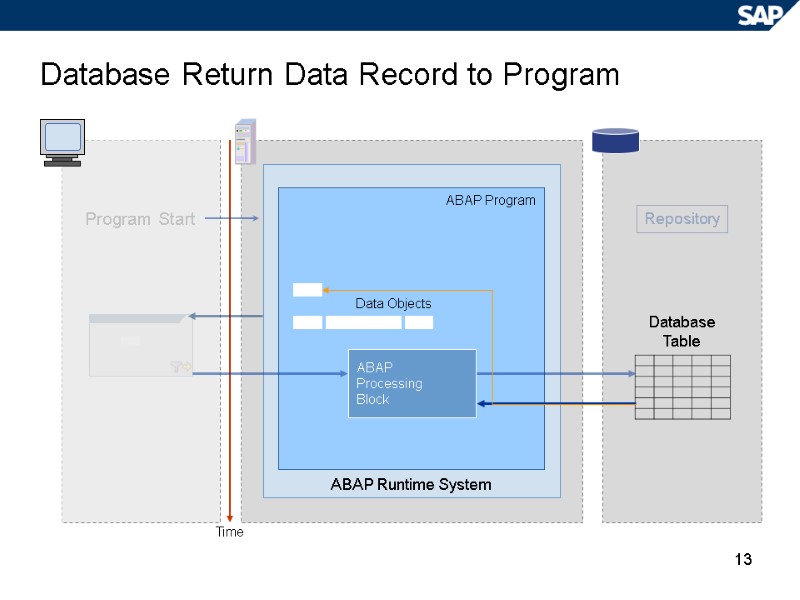
13 Database Return Data Record to Program Repository Time ABAP Runtime System ABAP Program ABAP Processing Block Data Objects Program Start Database Table
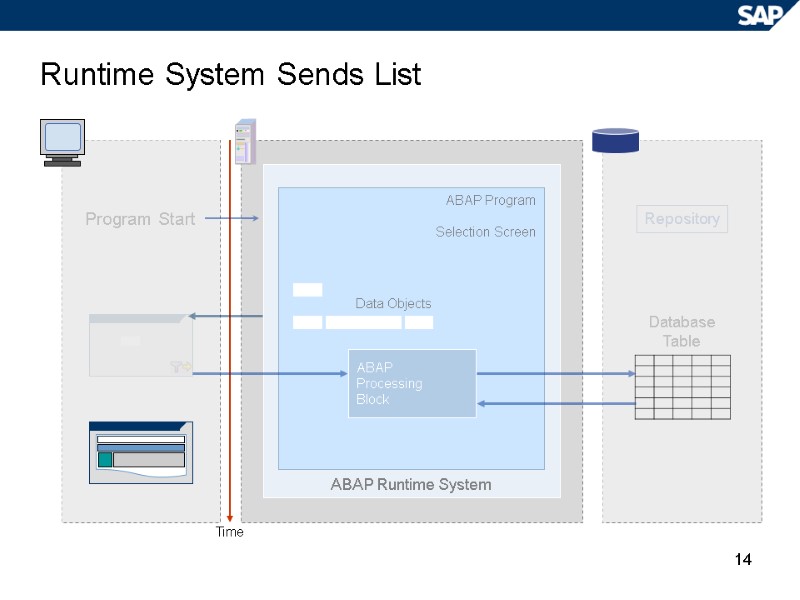
14 Runtime System Sends List Repository Time ABAP Runtime System ABAP Program Selection Screen ABAP Processing Block Data Objects Program Start Database Table
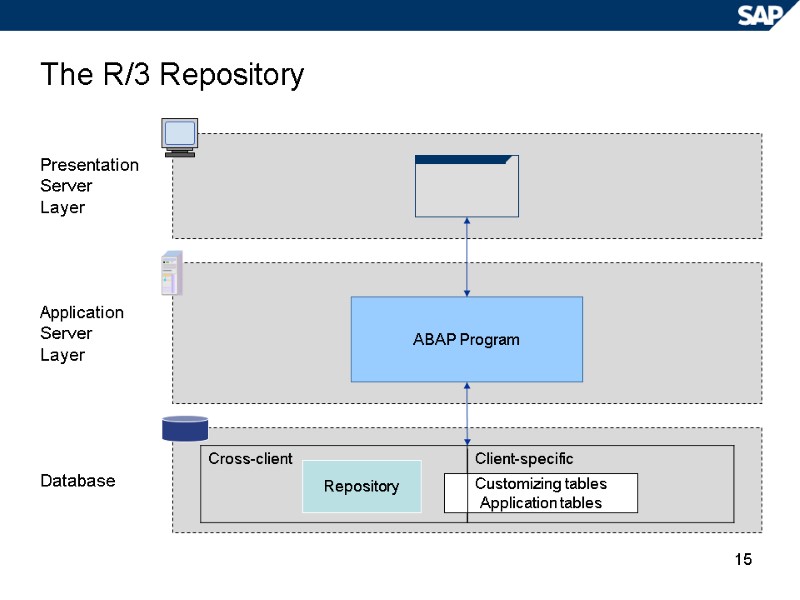
15 The R/3 Repository Presentation Server Layer Application Server Layer Database ABAP Program Repository Customizing tables Application tables
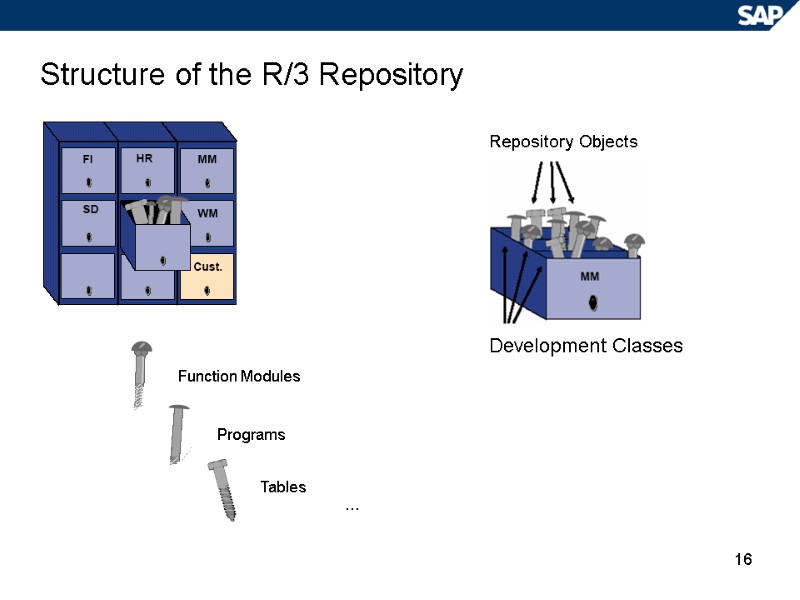
16 Structure of the R/3 Repository Repository Objects Development Classes Function Modules Programs Tables …
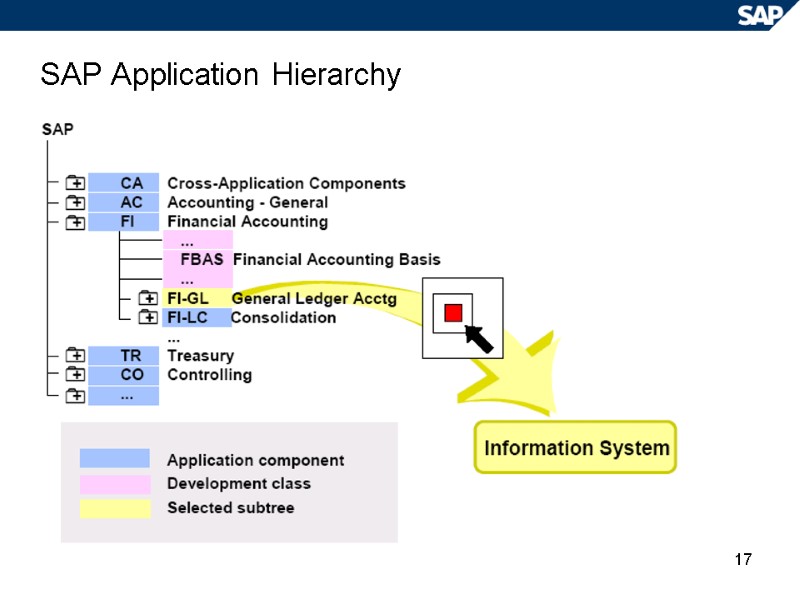
17 SAP Application Hierarchy
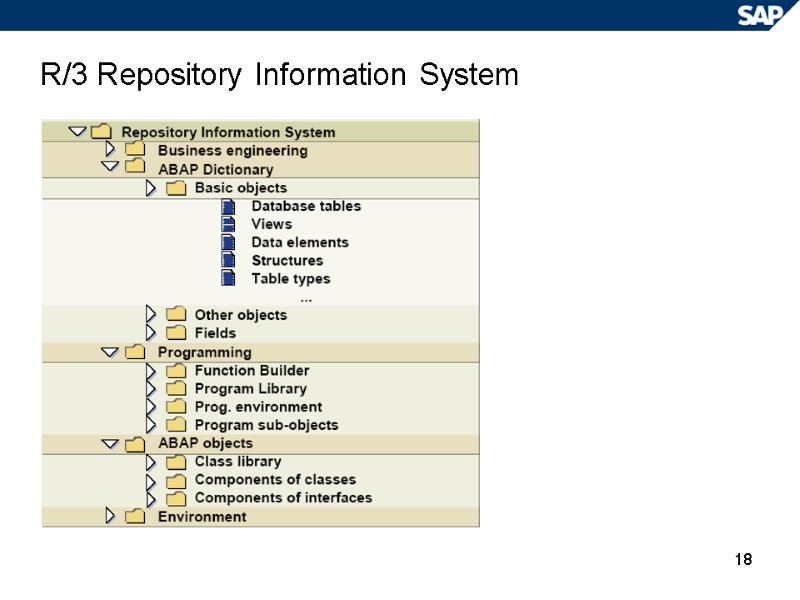
18 R/3 Repository Information System
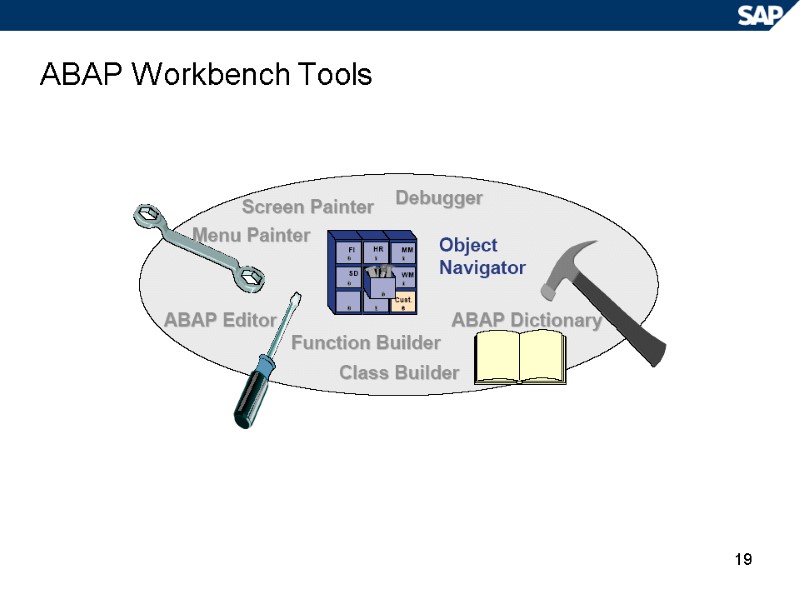
19 ABAP Workbench Tools
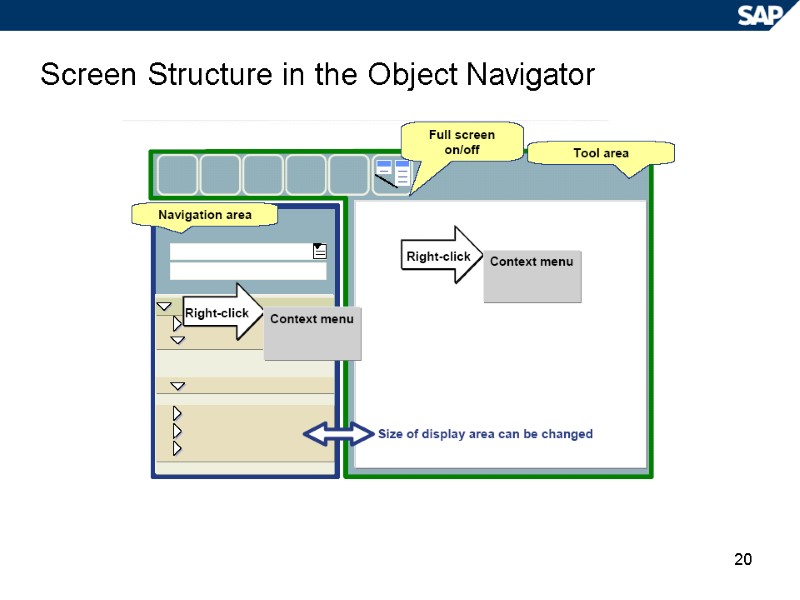
20 Screen Structure in the Object Navigator
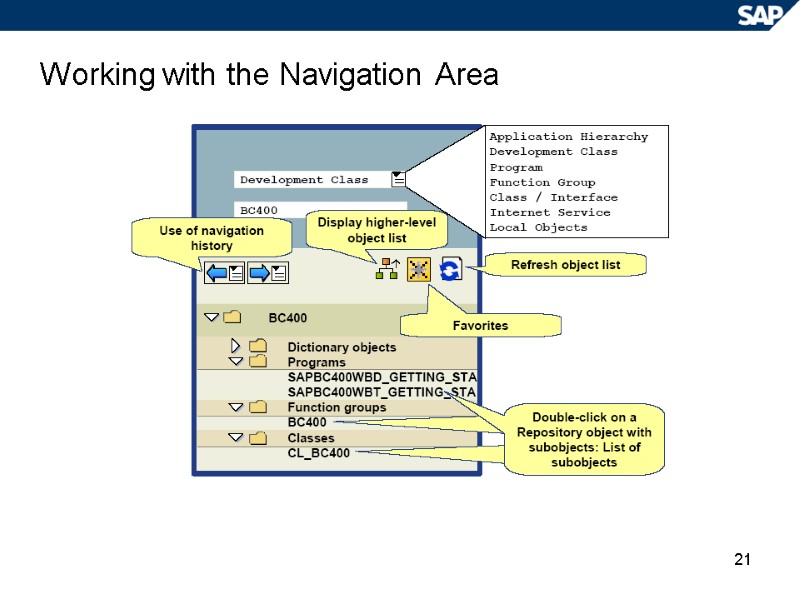
21 Working with the Navigation Area
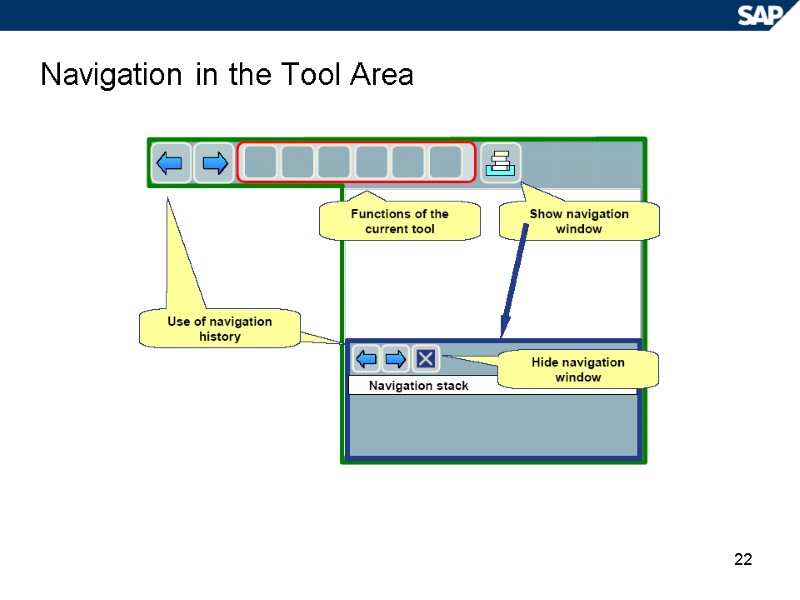
22 Navigation in the Tool Area
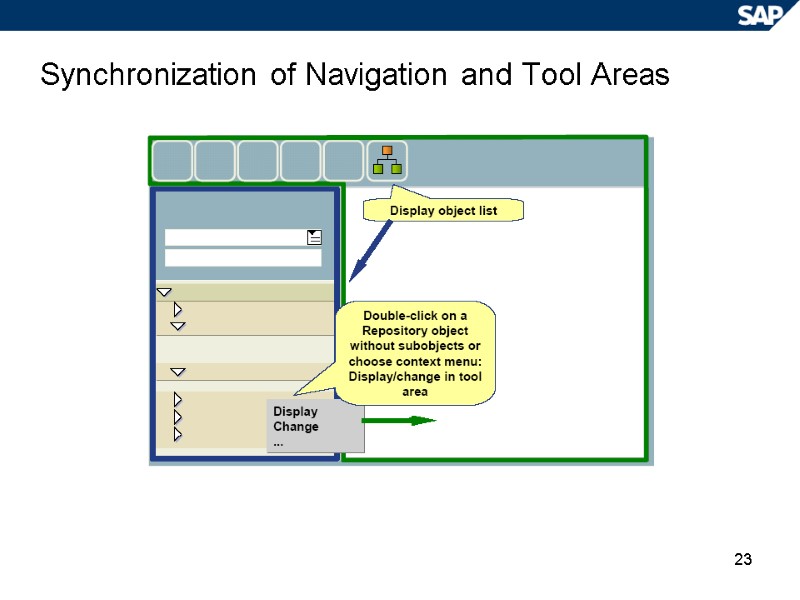
23 Synchronization of Navigation and Tool Areas
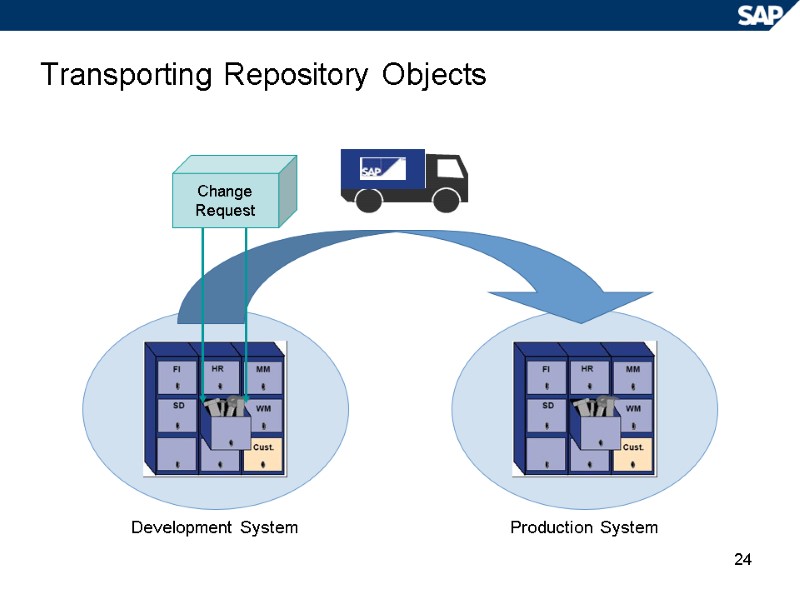
24 Transporting Repository Objects Change Request Development System Production System
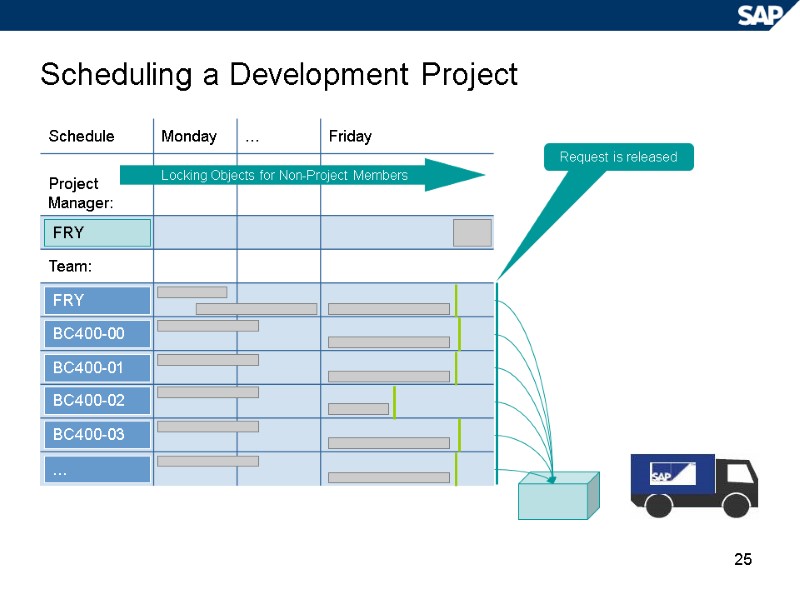
25 Scheduling a Development Project FRY BC400-00 BC400-01 BC400-02 BC400-03 … FRY Request is released Locking Objects for Non-Project Members
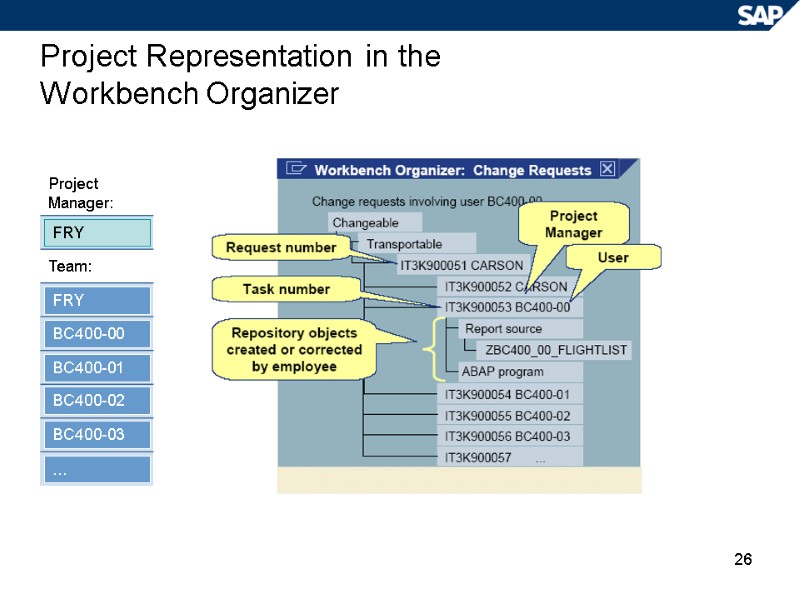
26 Project Representation in the Workbench Organizer FRY BC400-00 BC400-01 BC400-02 BC400-03 … FRY
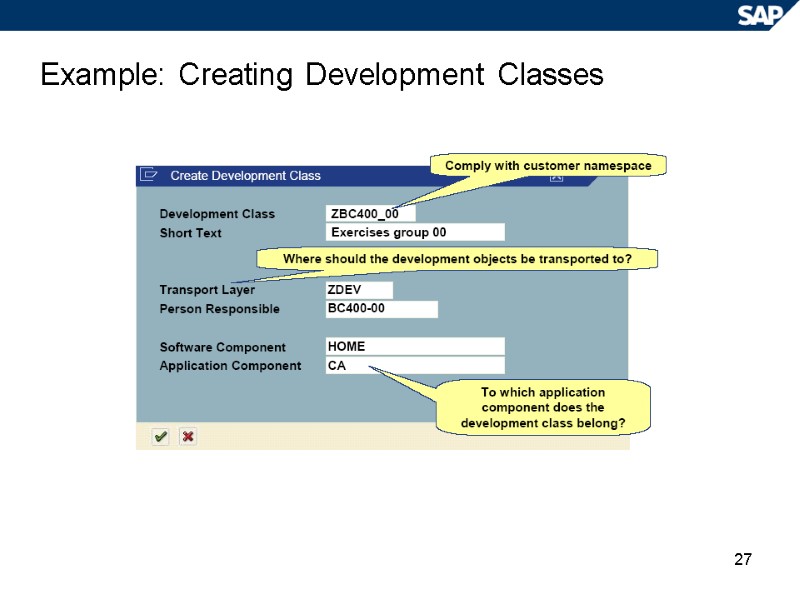
27 Example: Creating Development Classes
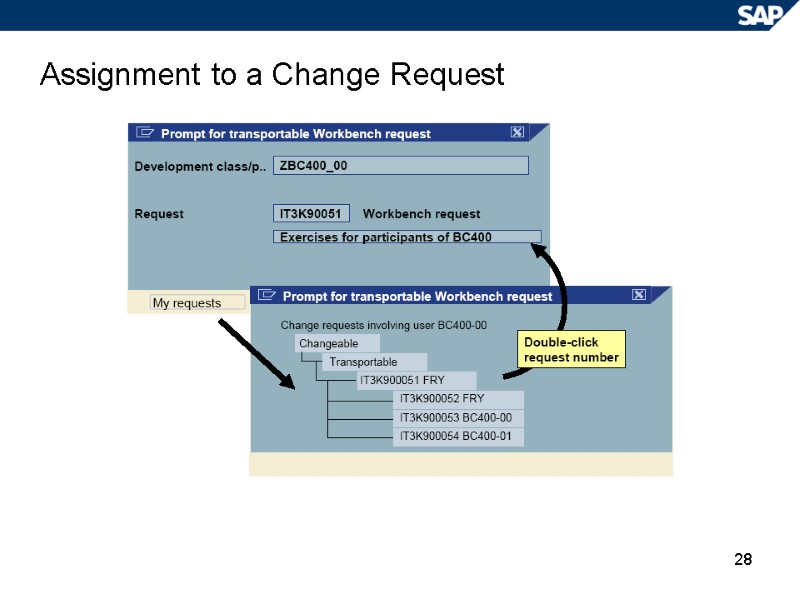
28 Assignment to a Change Request
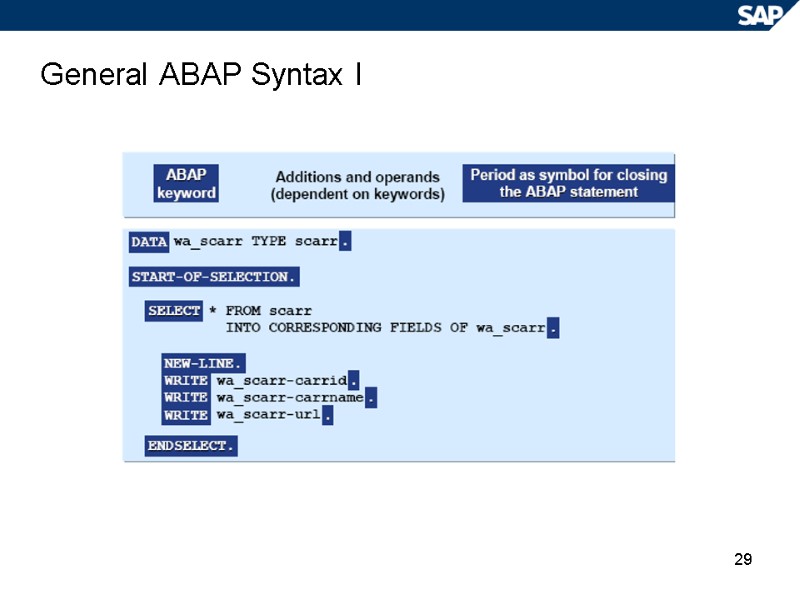
29 General ABAP Syntax I
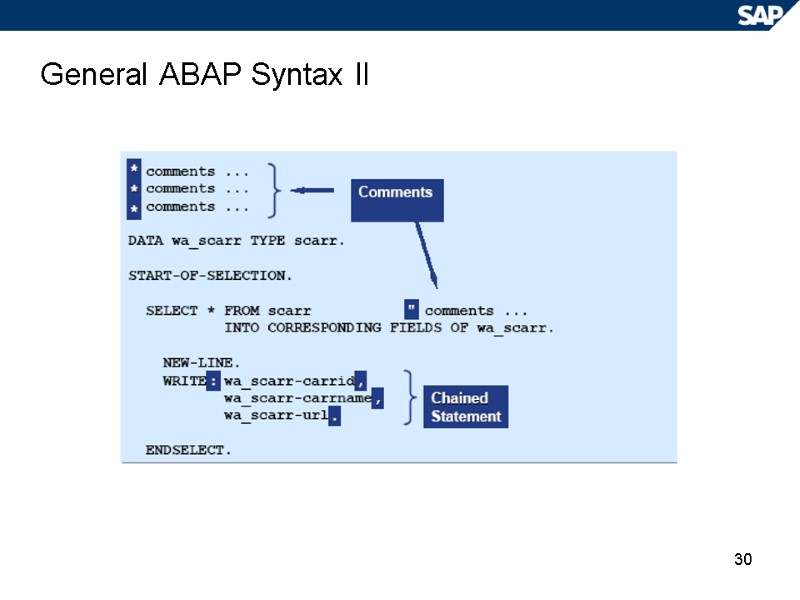
30 General ABAP Syntax II

31 Return Value After ABAP Statements

32 Creating in ABAP Program
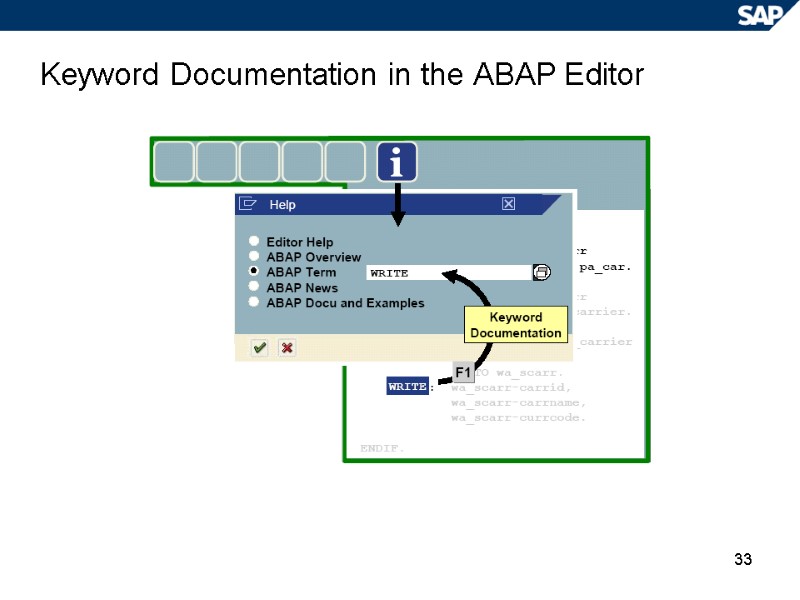
33 Keyword Documentation in the ABAP Editor
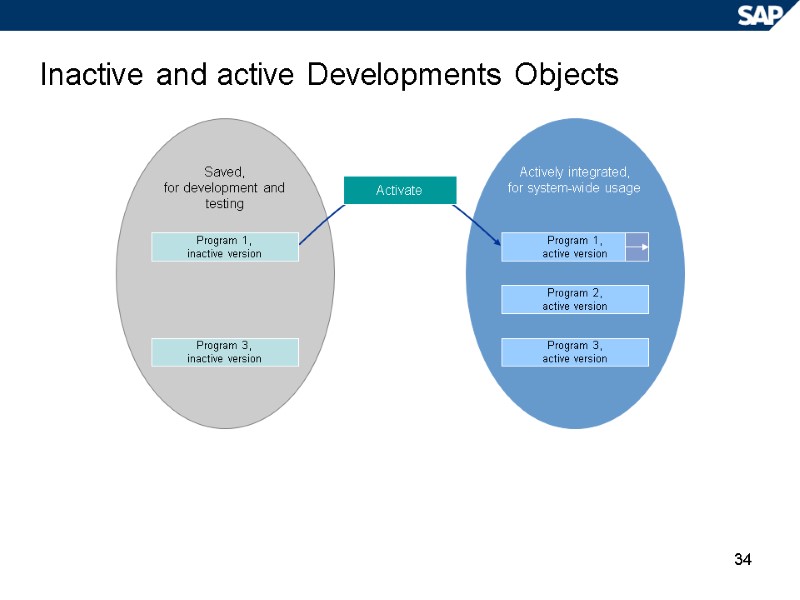
34 Saved, for development and testing Actively integrated, for system-wide usage Inactive and active Developments Objects Program 1, inactive version Program 1, active version Program 3, inactive version Program 2, active version Program 3, active version Activate
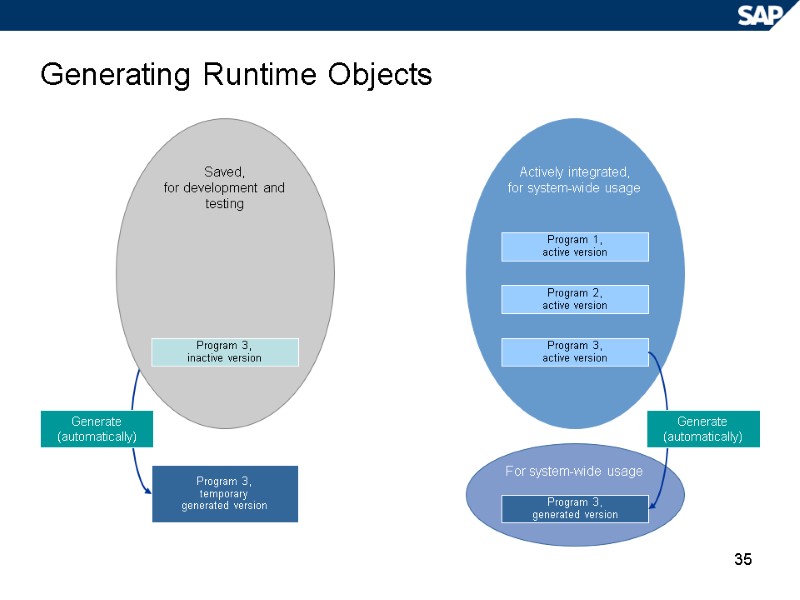
35 Generating Runtime Objects For system-wide usage Saved, for development and testing Actively integrated, for system-wide usage Program 1, active version Program 3, inactive version Program 2, active version Program 3, active version Program 3, generated version Program 3, temporary generated version Generate (automatically) Generate (automatically)

36 Creating Transaction Codes
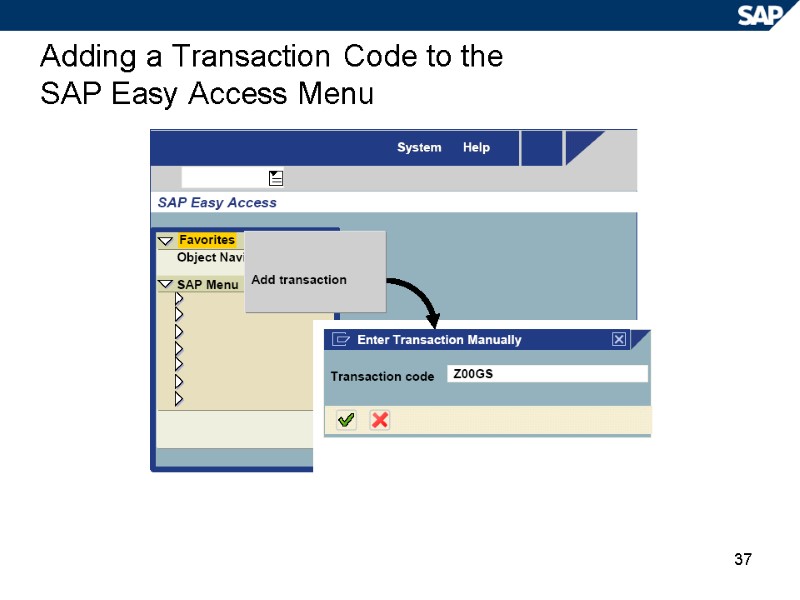
37 Adding a Transaction Code to the SAP Easy Access Menu
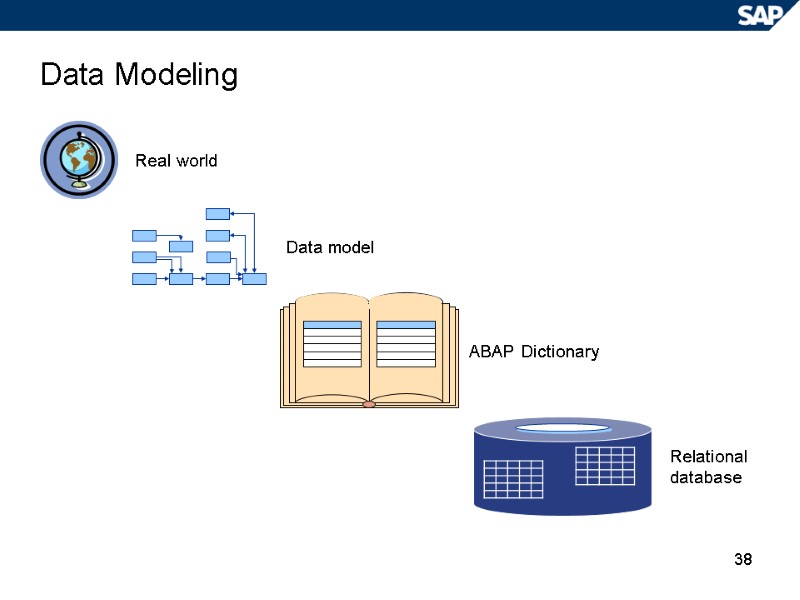
38 Data Modeling Real world Data model ABAP Dictionary Relational database
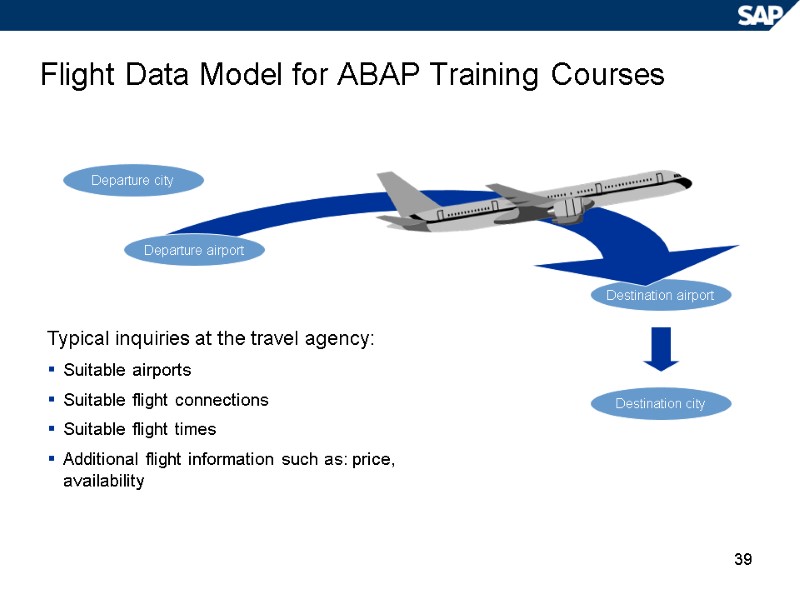
39 Flight Data Model for ABAP Training Courses Destination airport Typical inquiries at the travel agency: Suitable airports Suitable flight connections Suitable flight times Additional flight information such as: price, availability Destination city Departure city Departure airport
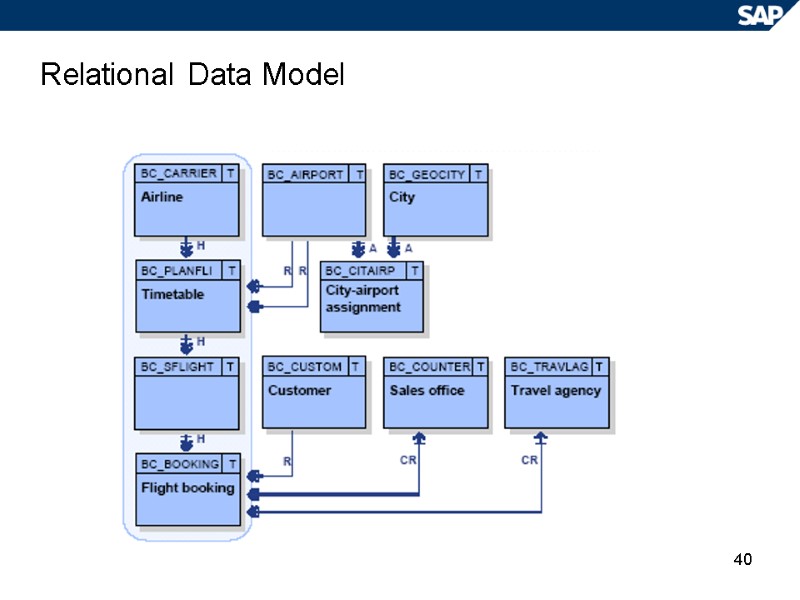
40 Relational Data Model
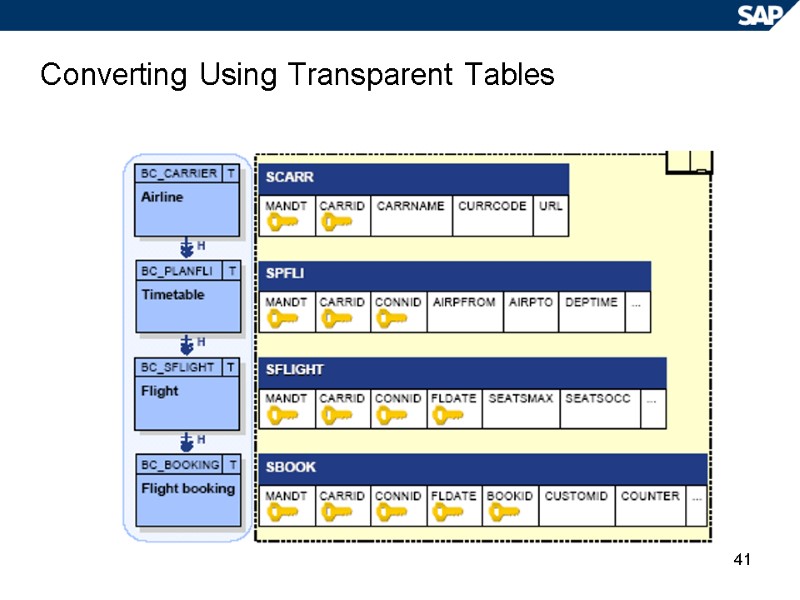
41 Converting Using Transparent Tables
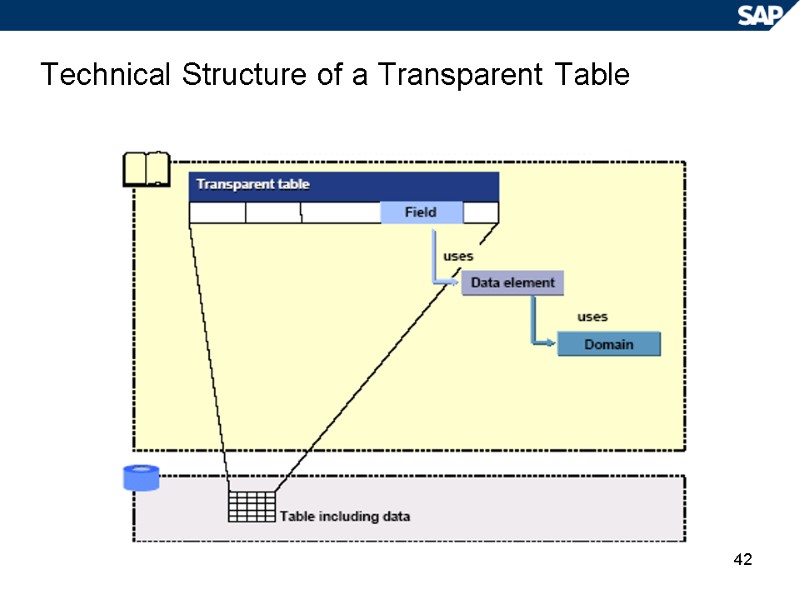
42 Technical Structure of a Transparent Table
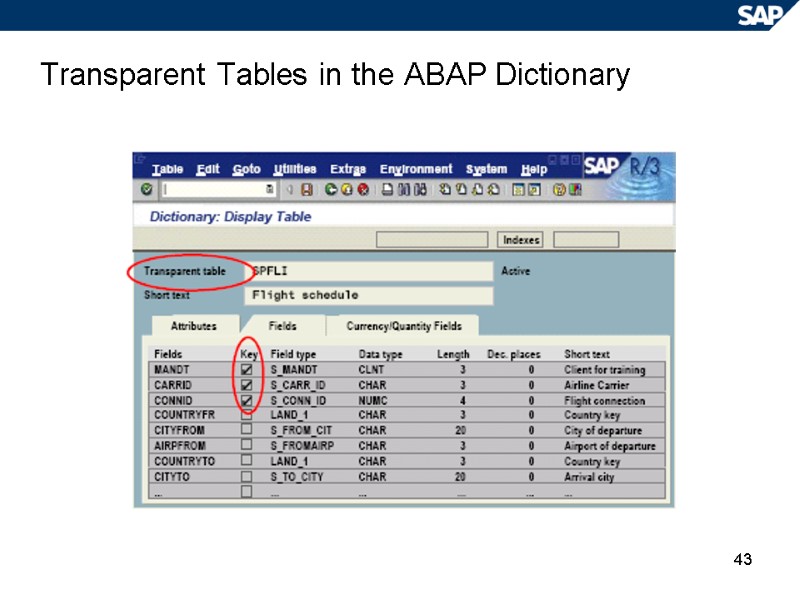
43 Transparent Tables in the ABAP Dictionary
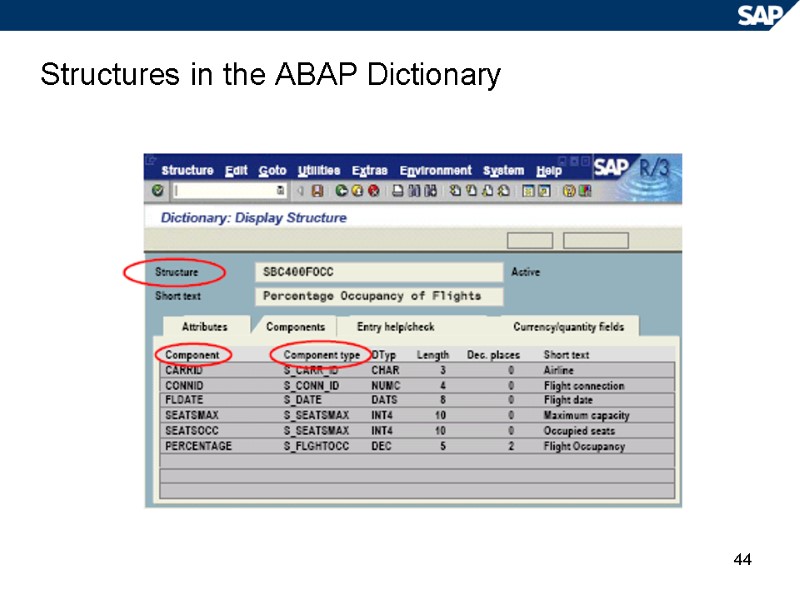
44 Structures in the ABAP Dictionary
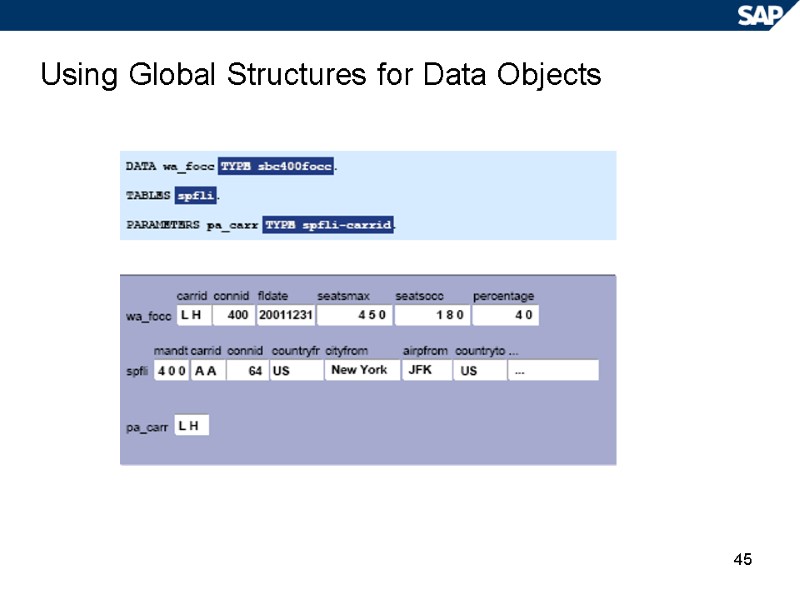
45 Using Global Structures for Data Objects
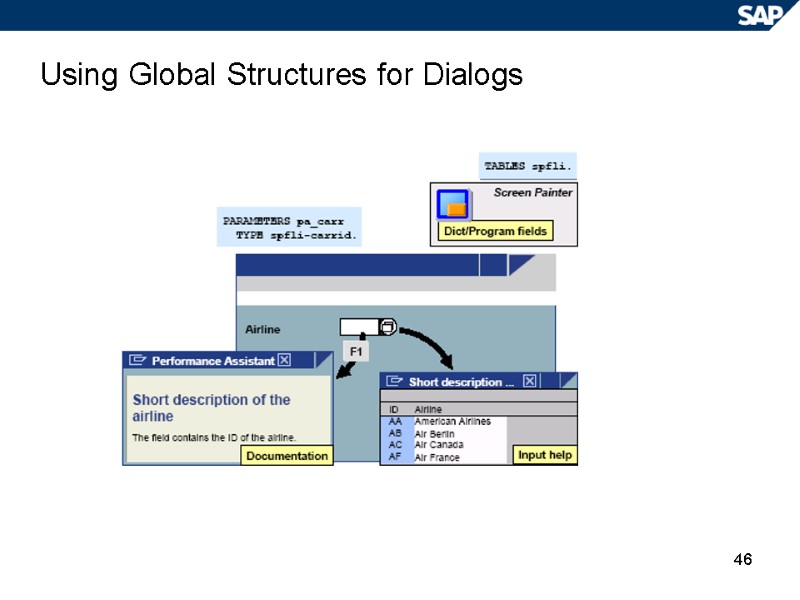
46 Using Global Structures for Dialogs
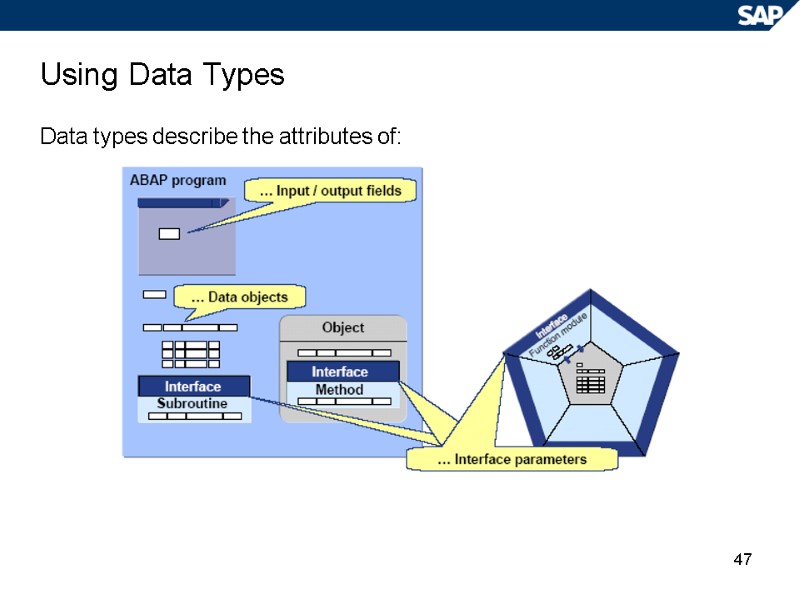
47 Using Data Types Data types describe the attributes of:
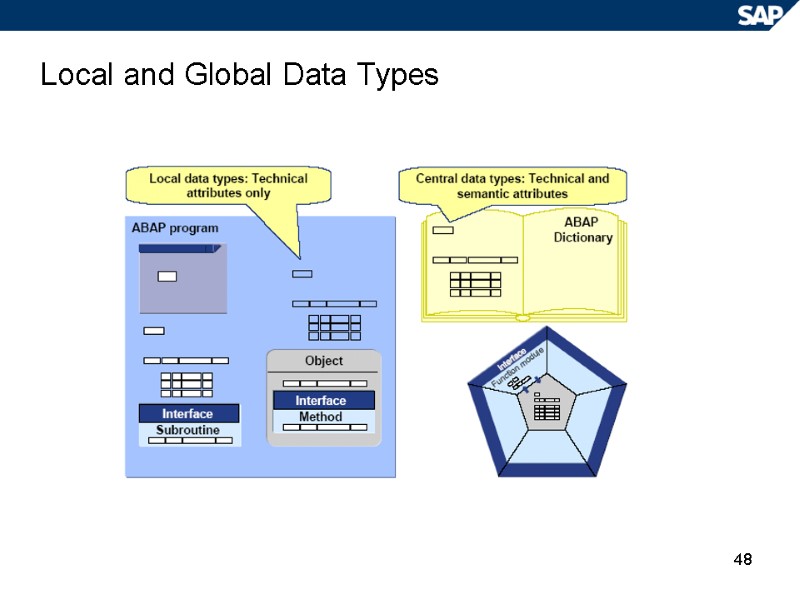
48 Local and Global Data Types
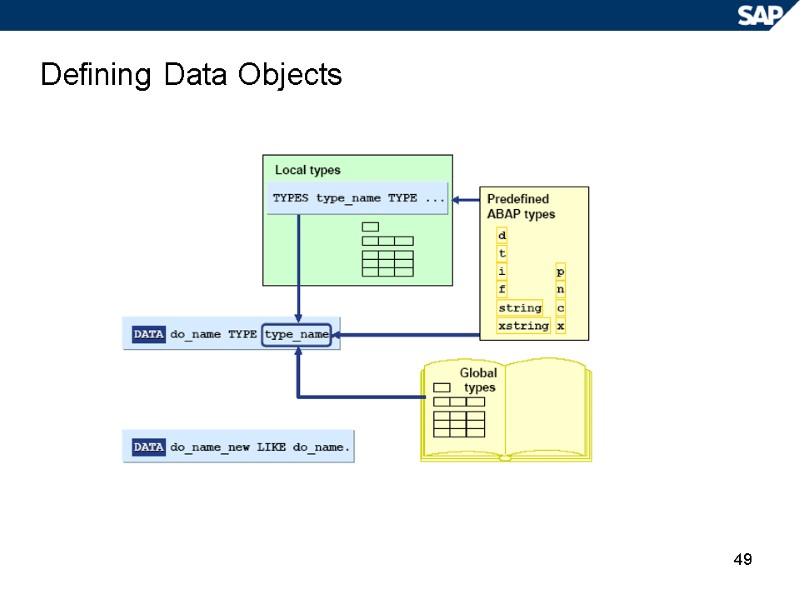
49 Defining Data Objects
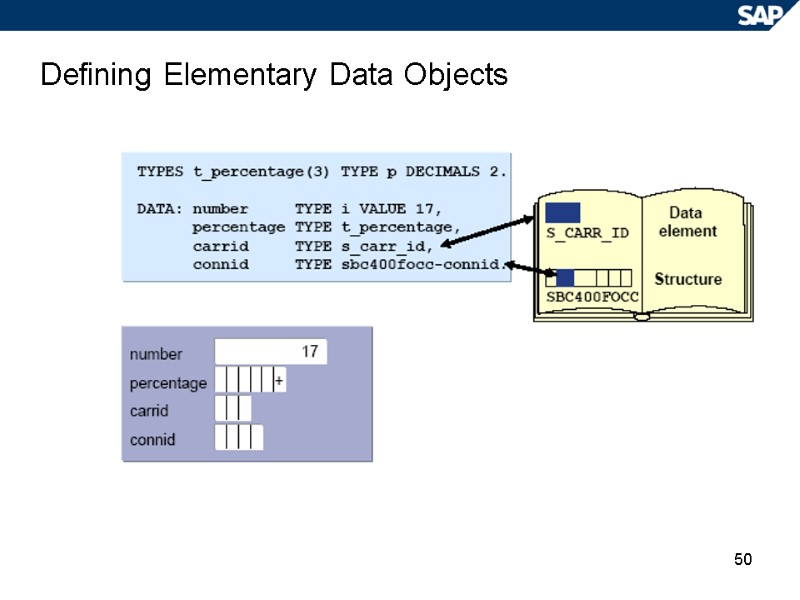
50 Defining Elementary Data Objects
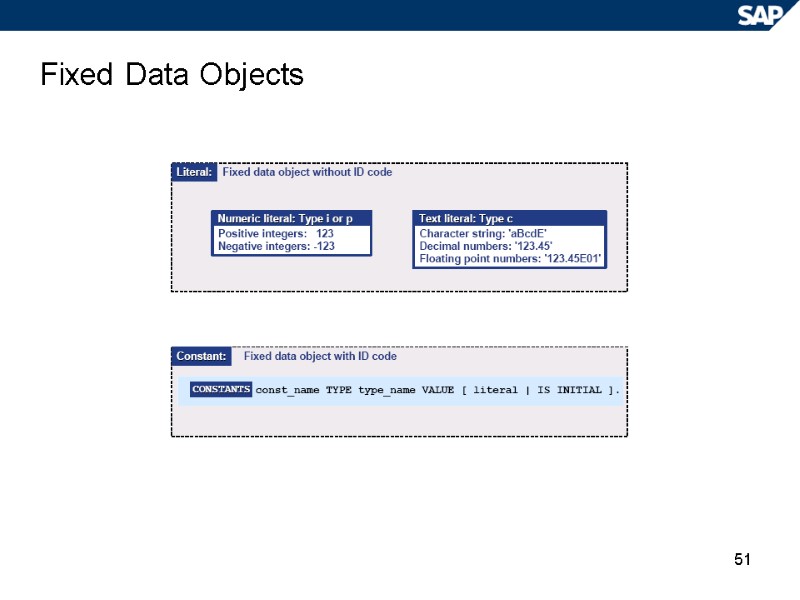
51 Fixed Data Objects
52 Basic ABAP Statements Data Types and Data Objects Basic ABAP Statements Using the ABAP Debugger Working with Structures Working with Internal Tables
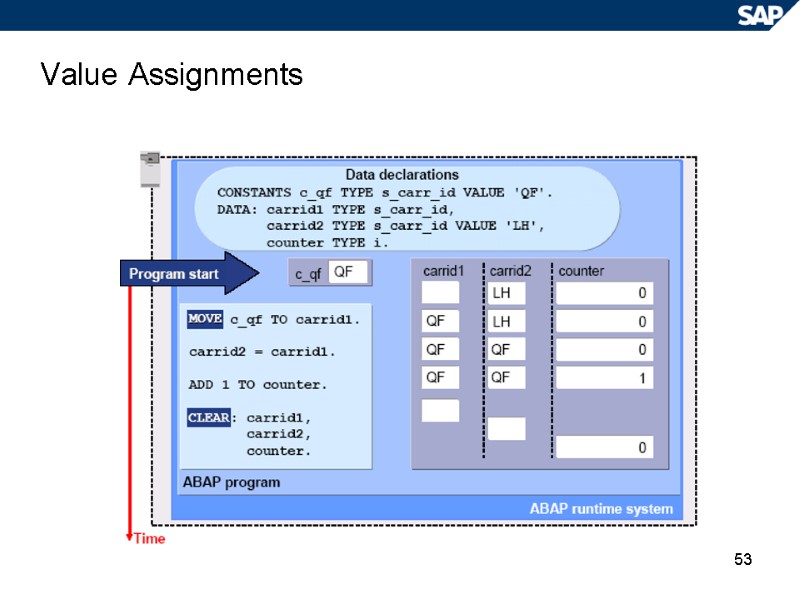
53 Value Assignments
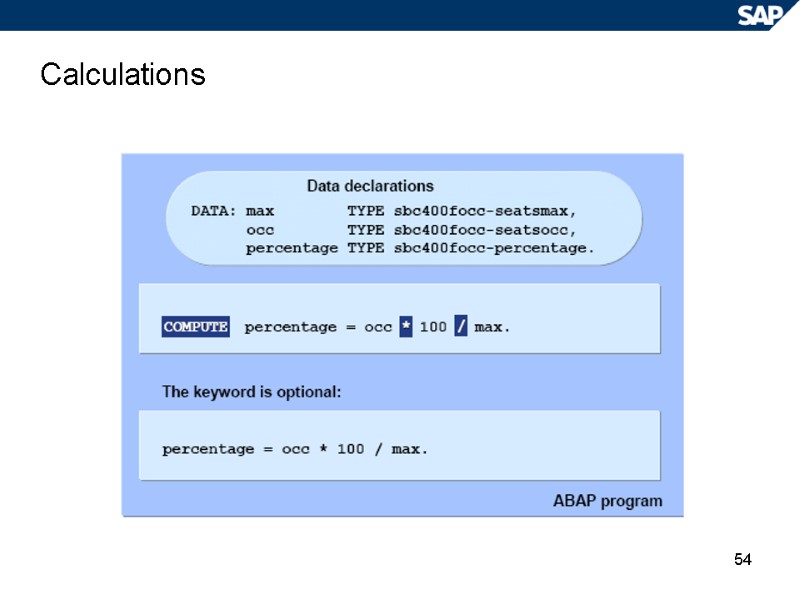
54 Calculations
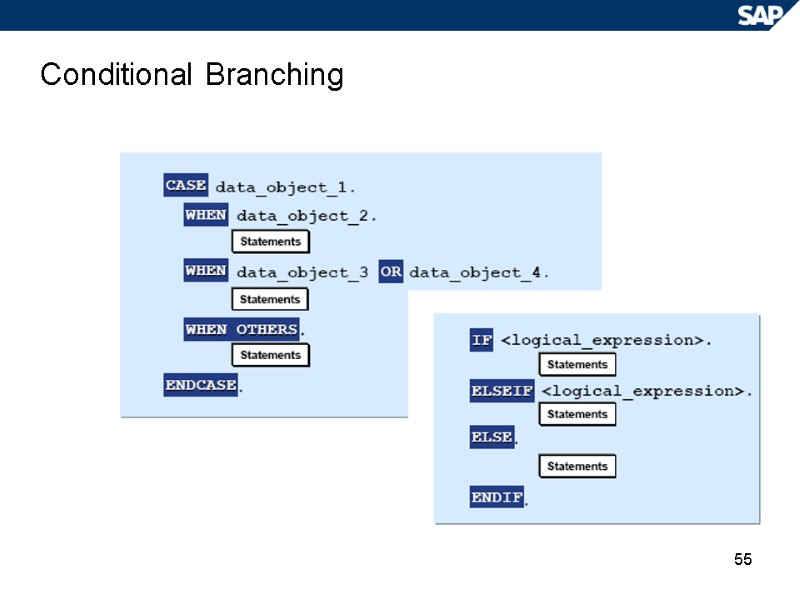
55 Conditional Branching
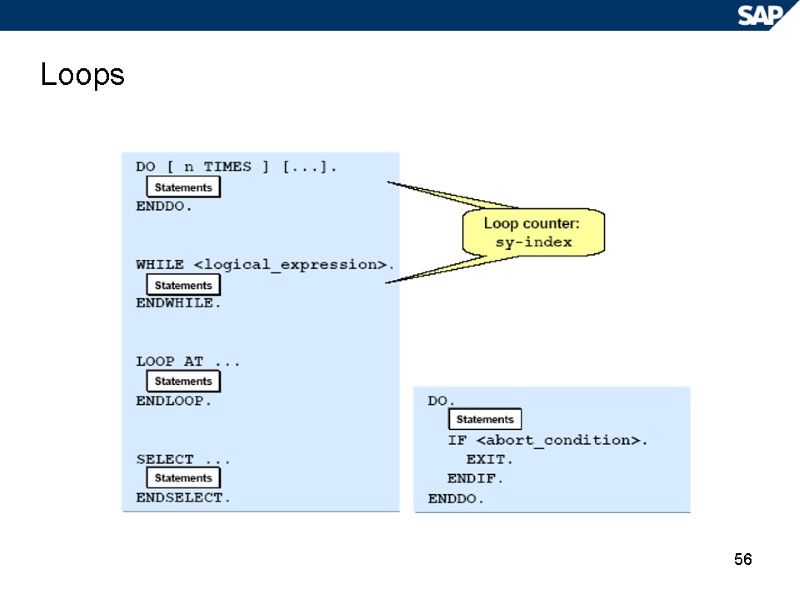
56 Loops
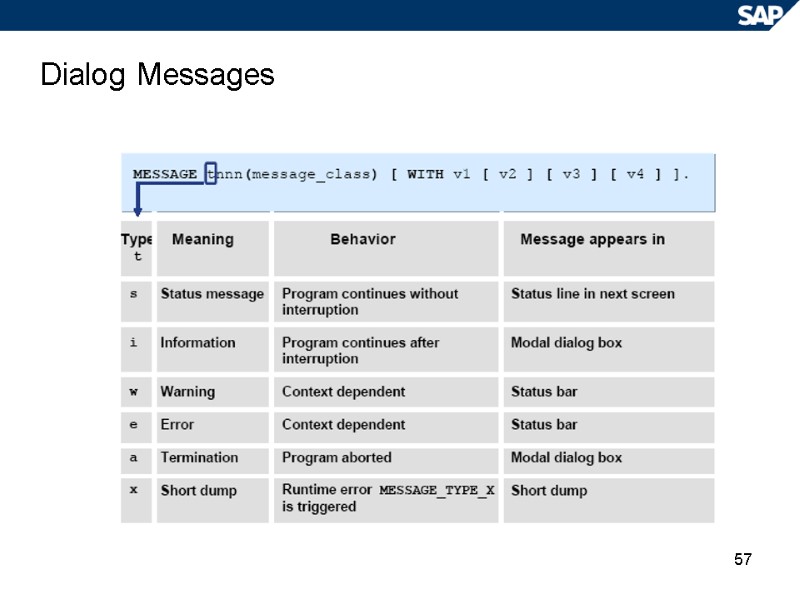
57 Dialog Messages

58 Runtime Behavior of Dialog Messages
59 Using the ABAP Debugger Data Types and Data Objects Basic ABAP Statements Using the ABAP Debugger Working with Structures Working with Internal Tables
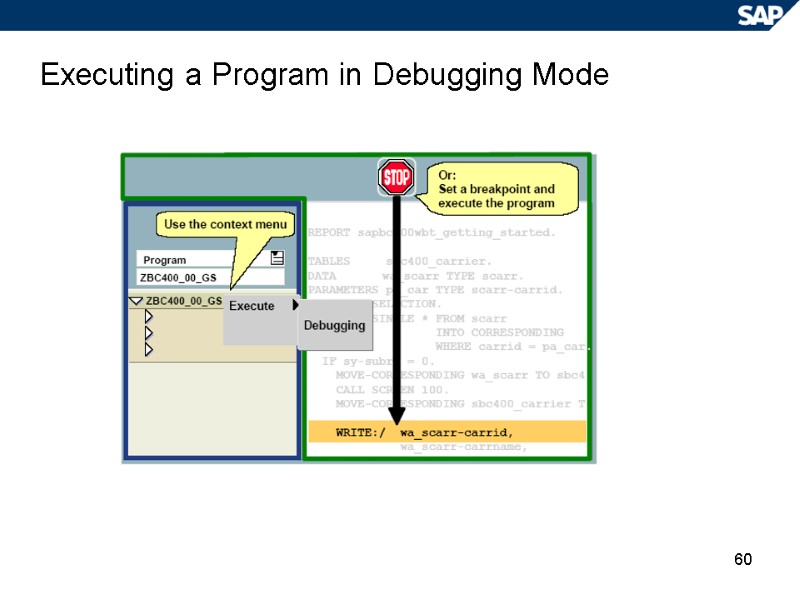
60 Executing a Program in Debugging Mode
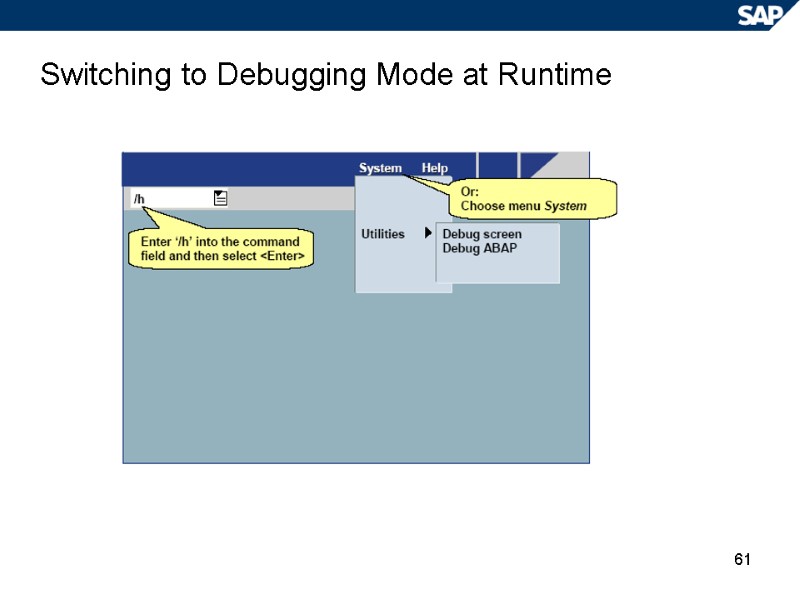
61 Switching to Debugging Mode at Runtime
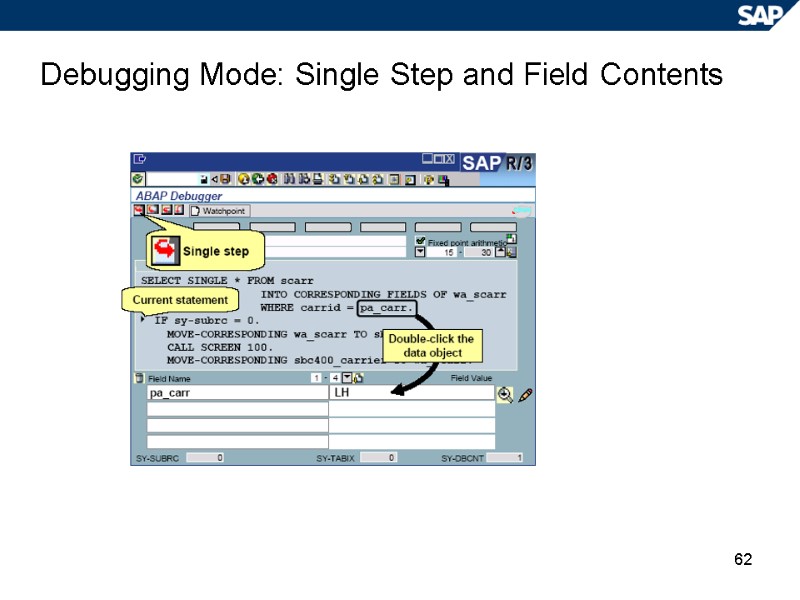
62 Debugging Mode: Single Step and Field Contents
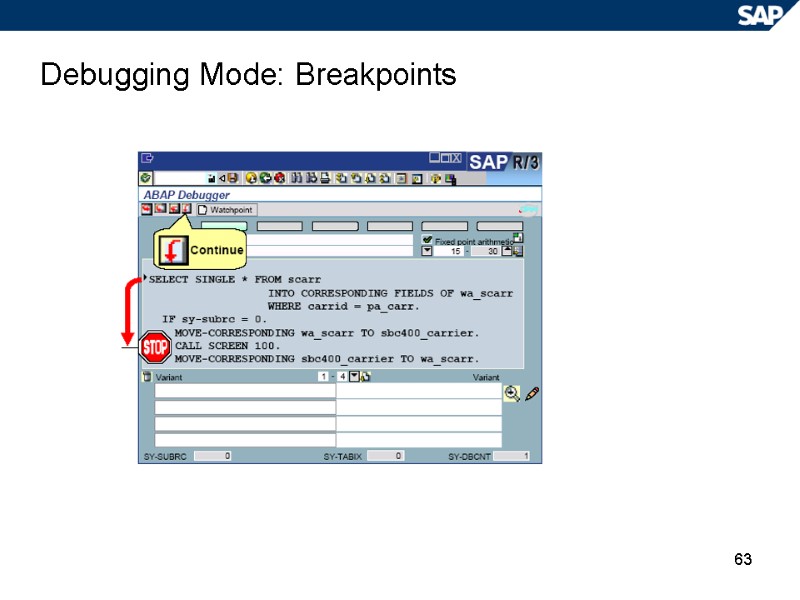
63 Debugging Mode: Breakpoints
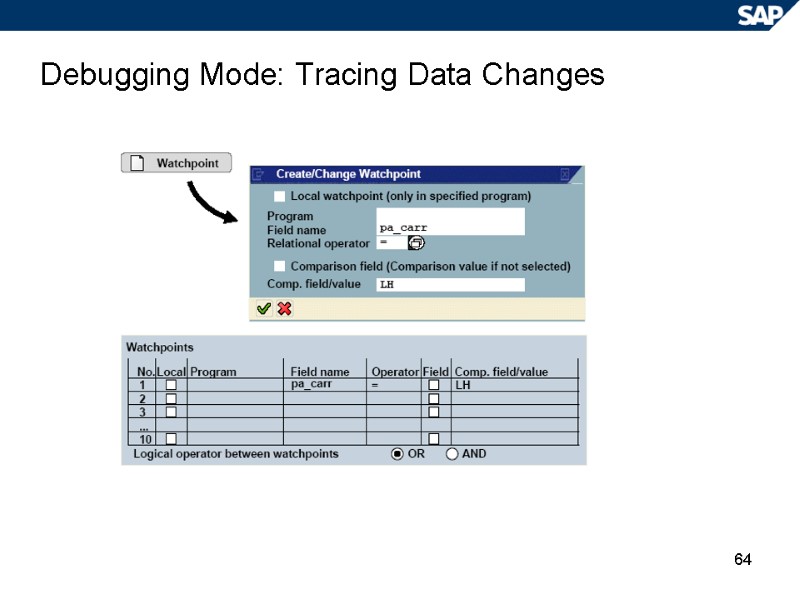
64 Debugging Mode: Tracing Data Changes
65 Working with Structures Data Types and Data Objects Basic ABAP Statements Using the ABAP Debugger Working with Structures Working with Internal Tables
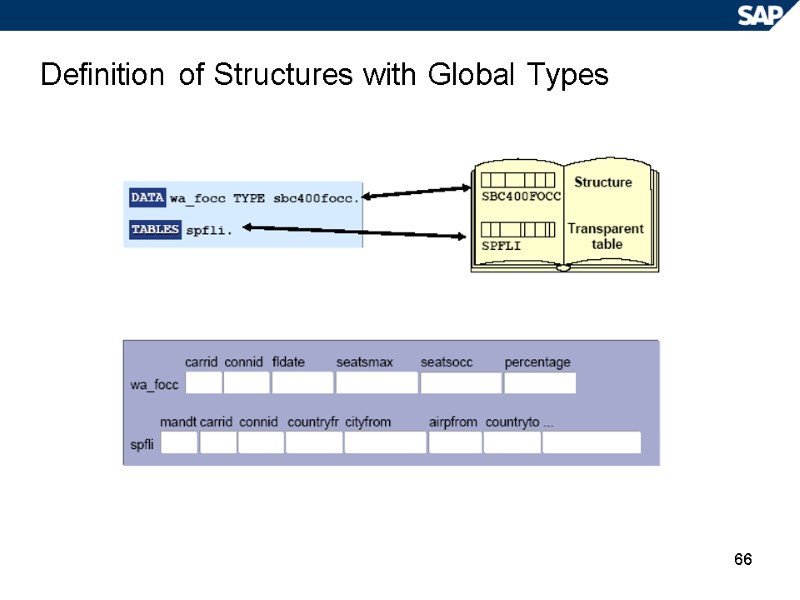
66 Definition of Structures with Global Types
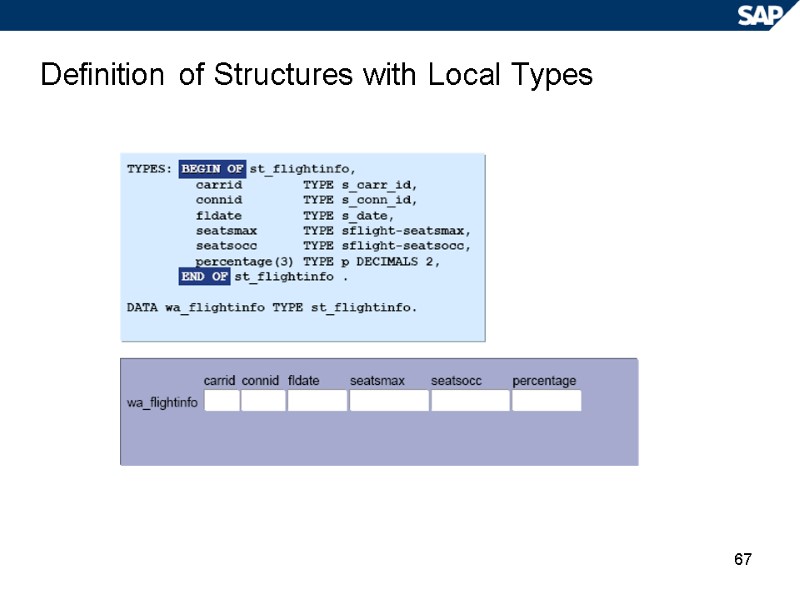
67 Definition of Structures with Local Types
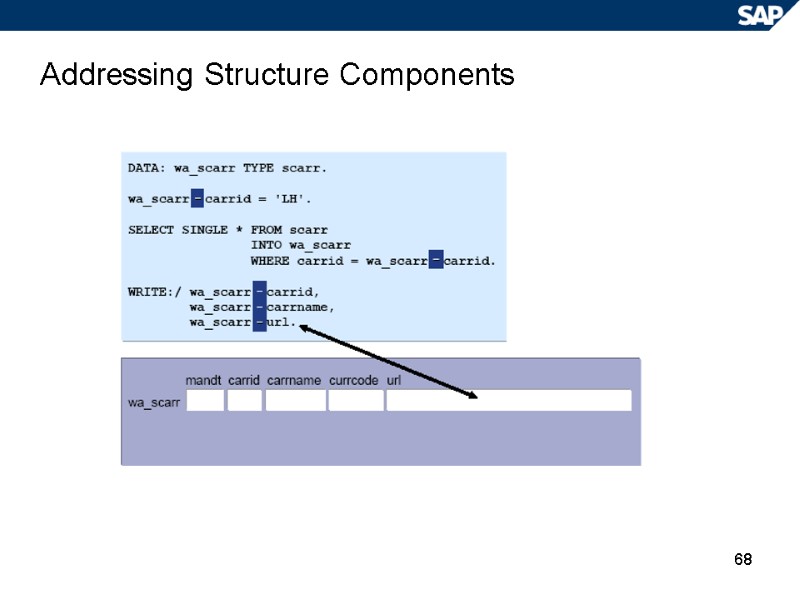
68 Addressing Structure Components
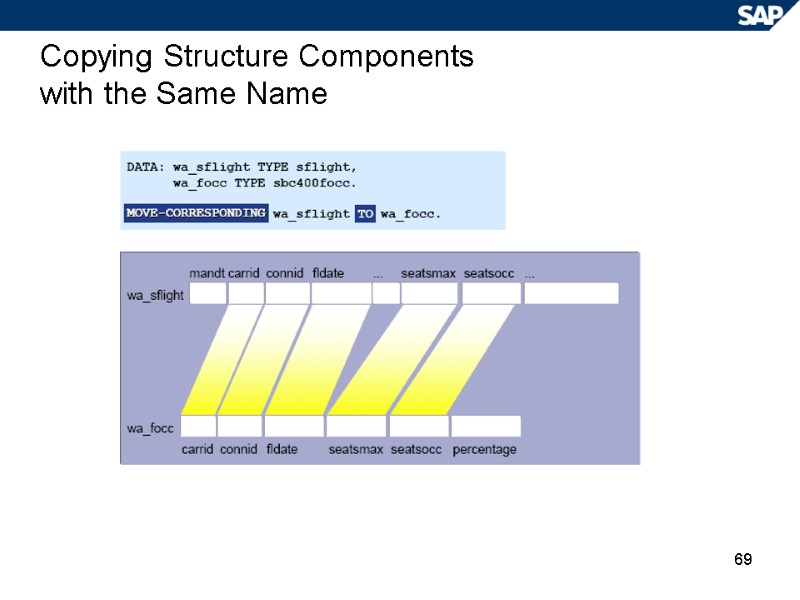
69 Copying Structure Components with the Same Name
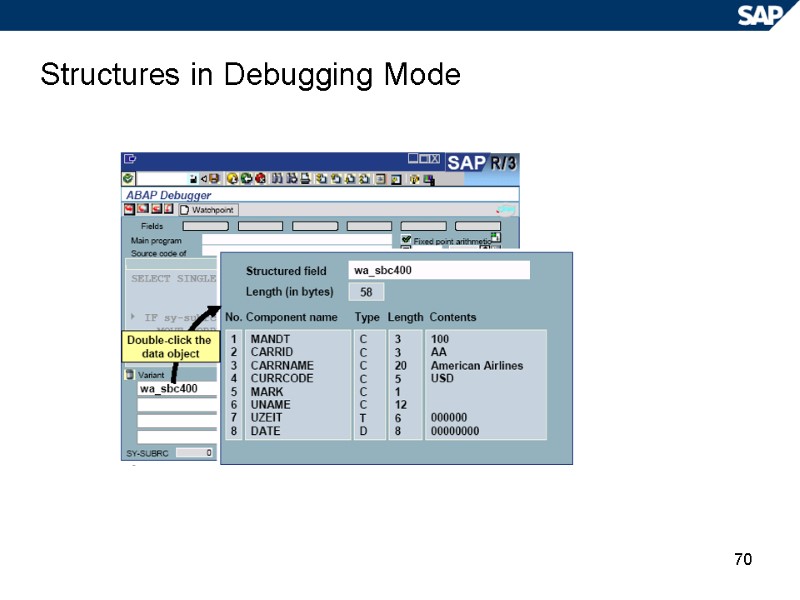
70 Structures in Debugging Mode
71 Working with Internal Tables Data Types and Data Objects Basic ABAP Statements Using the ABAP Debugger Working with Structures Working with Internal Tables
72 Internal Tables
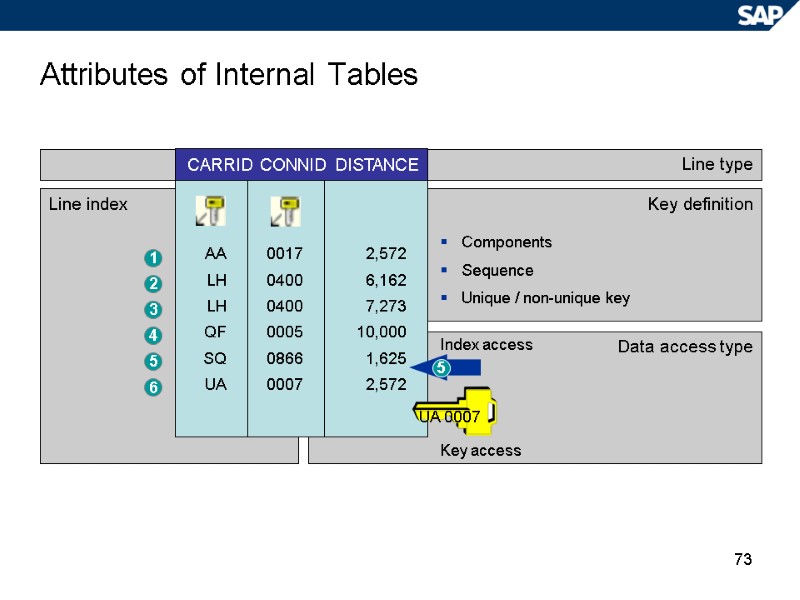
73 Attributes of Internal Tables Line type Line index Key definition Data access type Components Sequence Unique / non-unique key Index access Key access AA LH LH QF SQ UA 0017 0400 0400 0005 0866 0007 2,572 6,162 7,273 10,000 1,625 2,572 CARRID CONNID DISTANCE 1 2 3 4 5 6 5 UA 0007
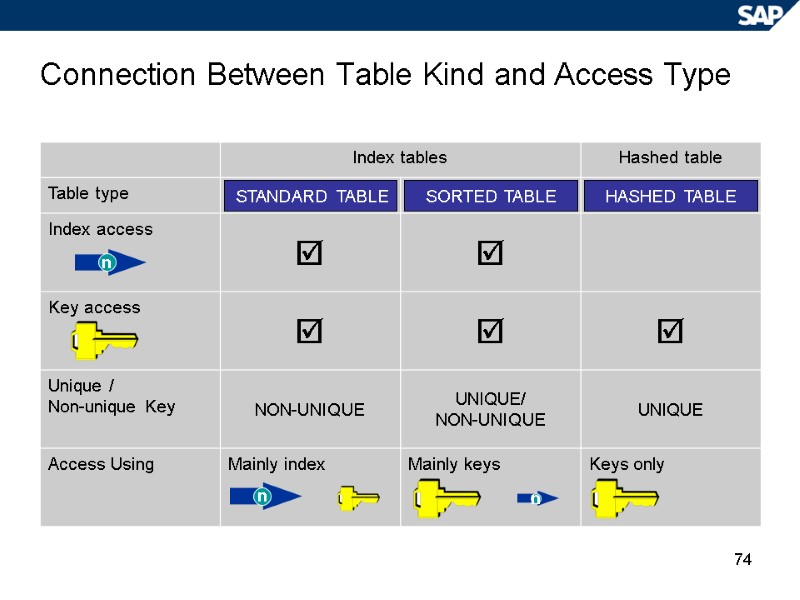
74 Connection Between Table Kind and Access Type STANDARD TABLE SORTED TABLE HASHED TABLE n
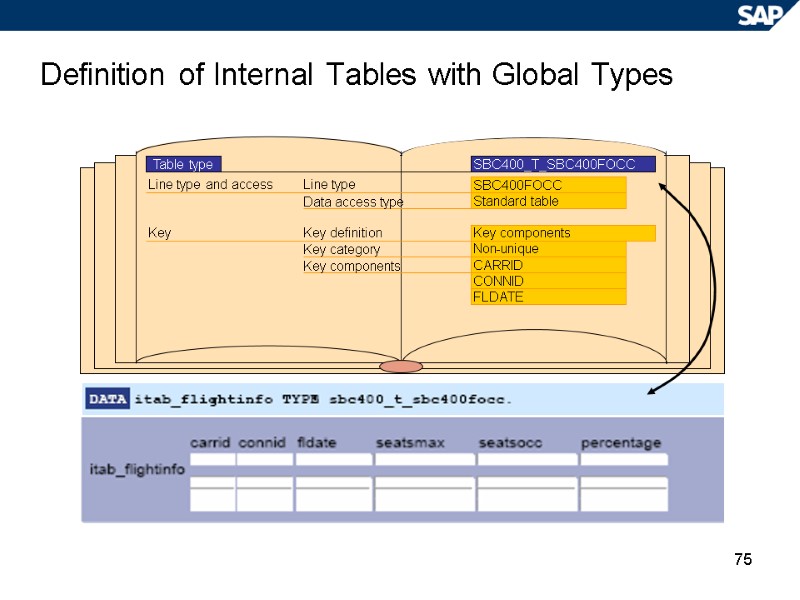
75 Definition of Internal Tables with Global Types Table type SBC400_T_SBC400FOCC SBC400FOCC Standard table Key components Non-unique CARRID CONNID FLDATE Line type and access Line type Data access type Key Key definition Key category Key components
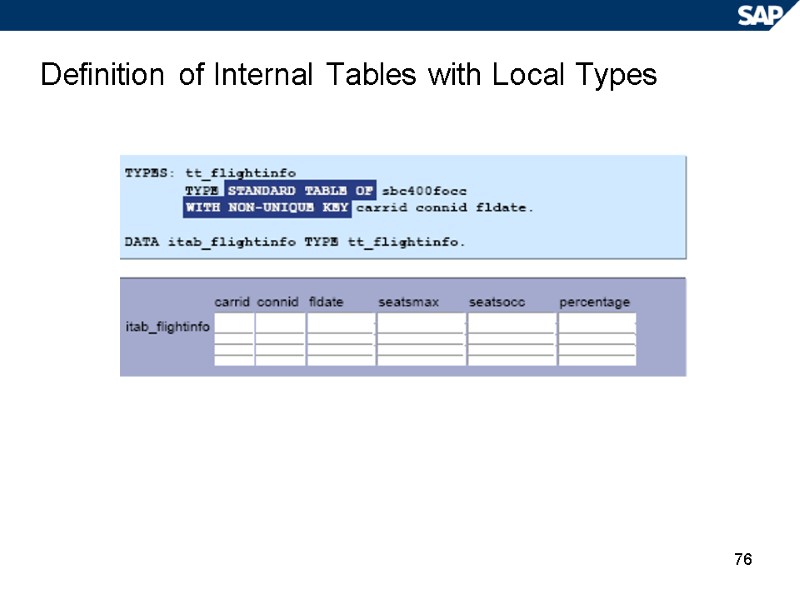
76 Definition of Internal Tables with Local Types
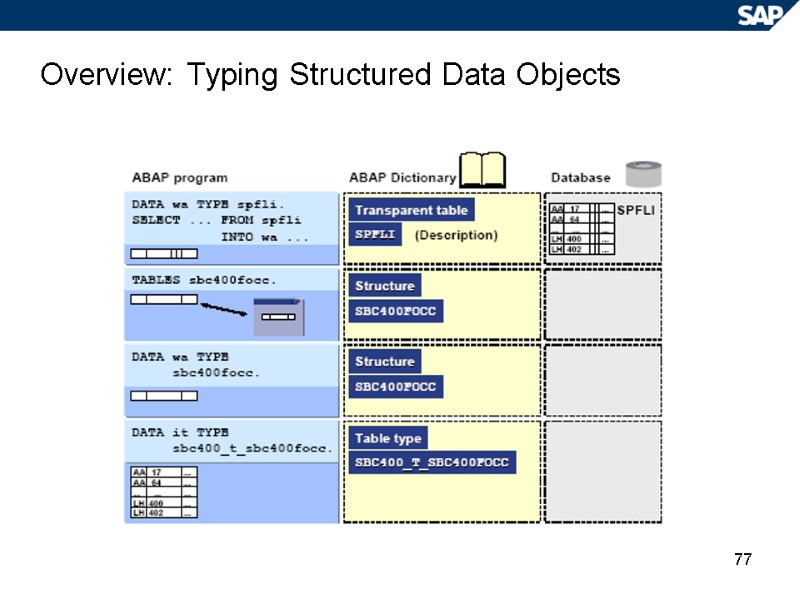
77 Overview: Typing Structured Data Objects
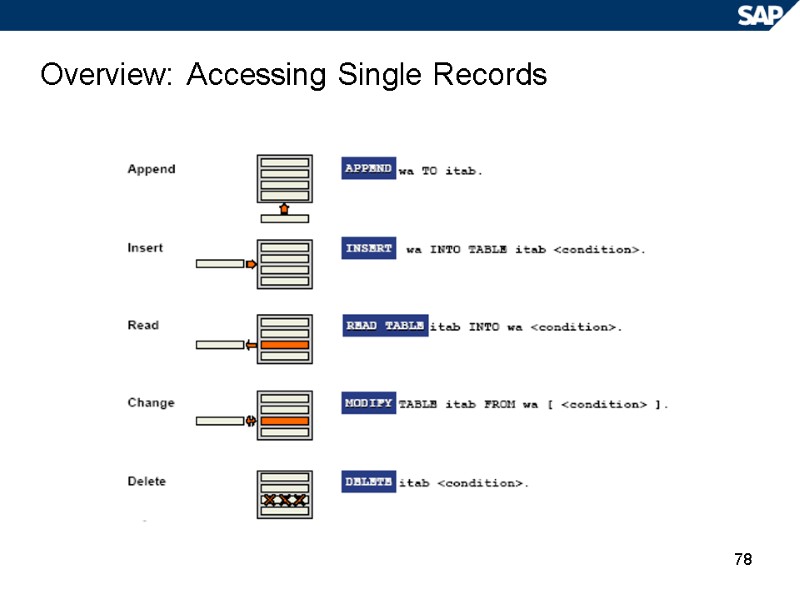
78 Overview: Accessing Single Records
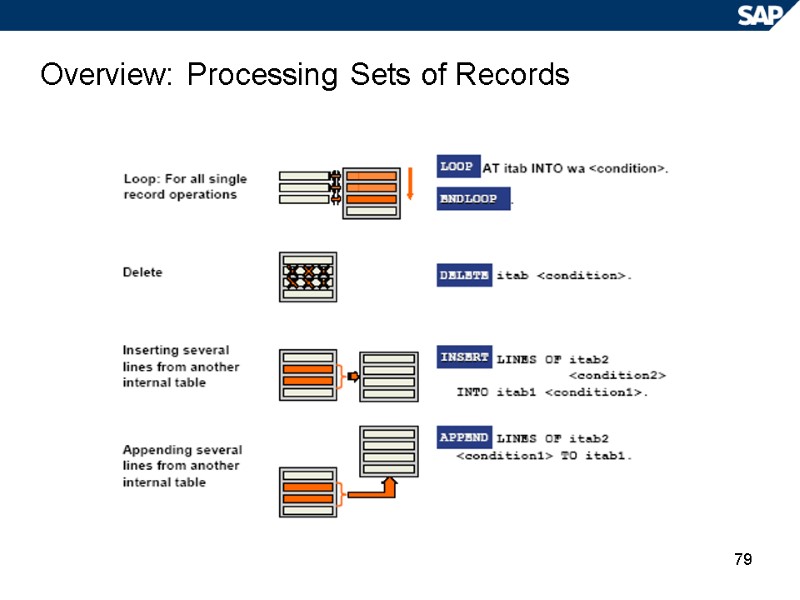
79 Overview: Processing Sets of Records

80 Syntax Example: Filling Line by Line
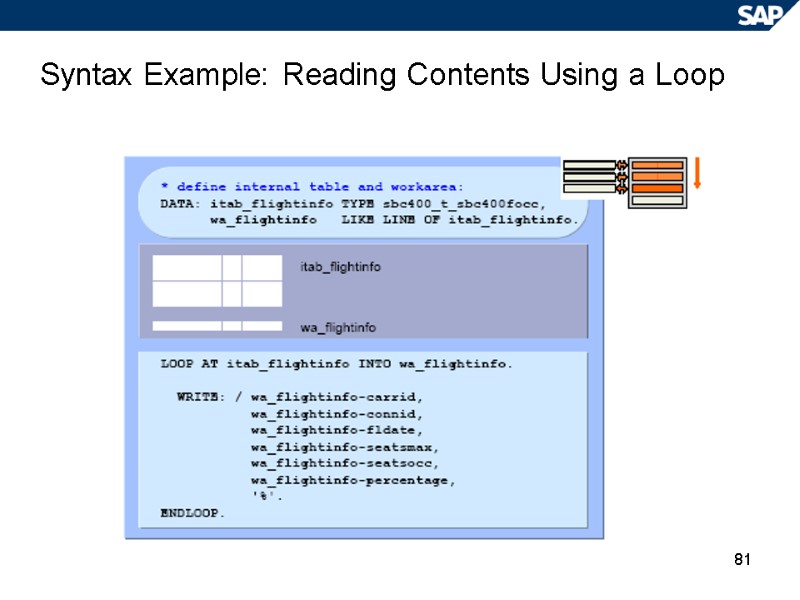
81 Syntax Example: Reading Contents Using a Loop
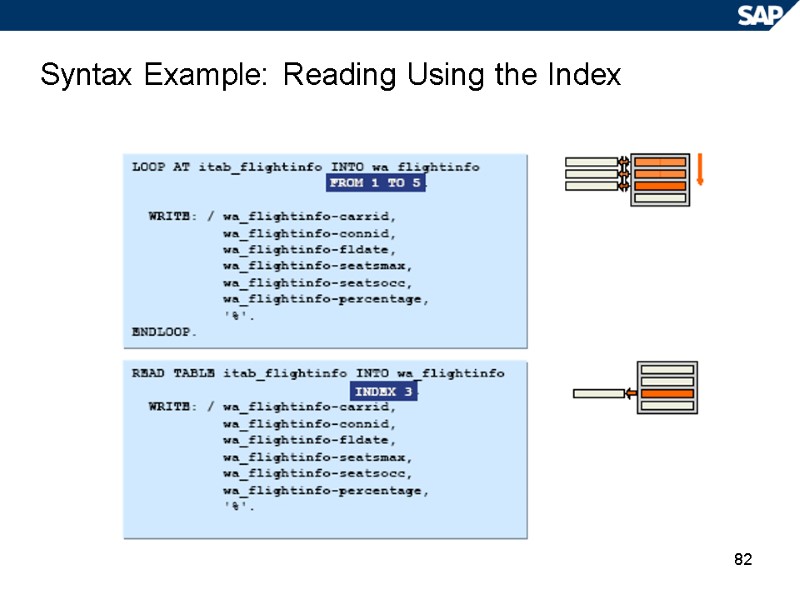
82 Syntax Example: Reading Using the Index
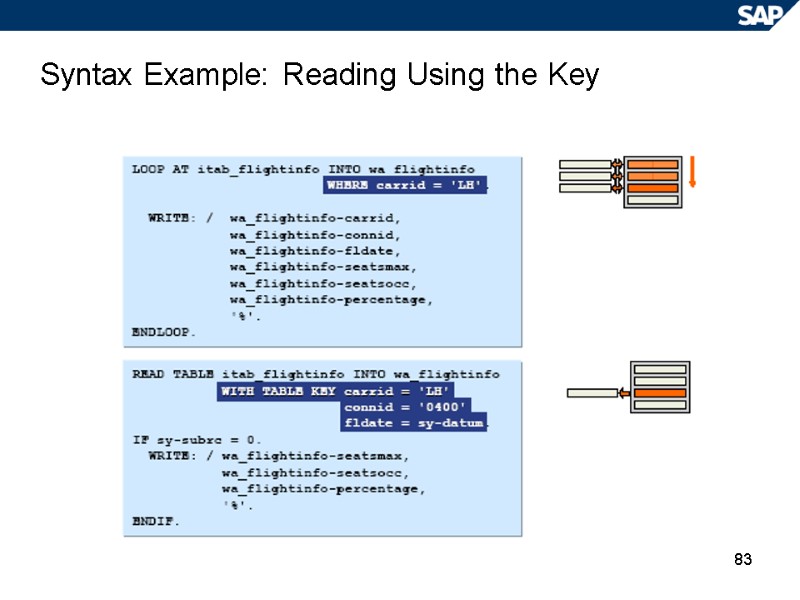
83 Syntax Example: Reading Using the Key
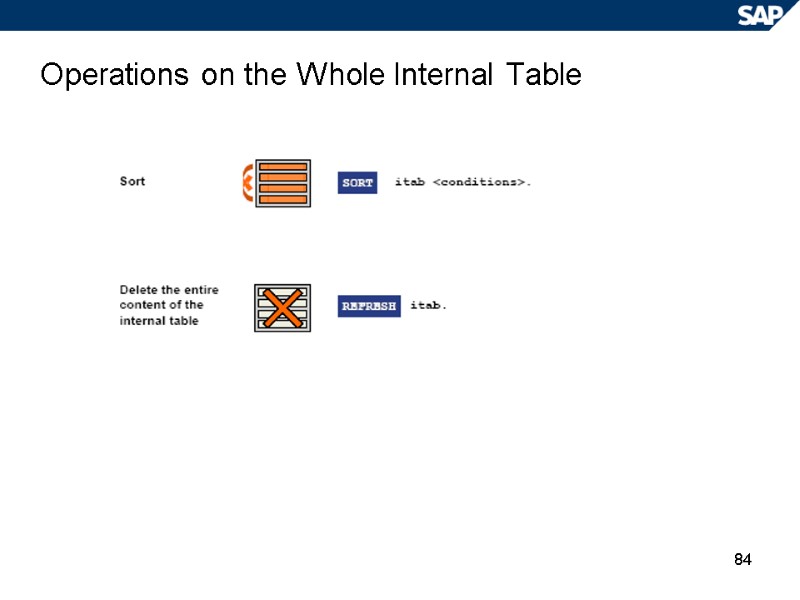
84 Operations on the Whole Internal Table
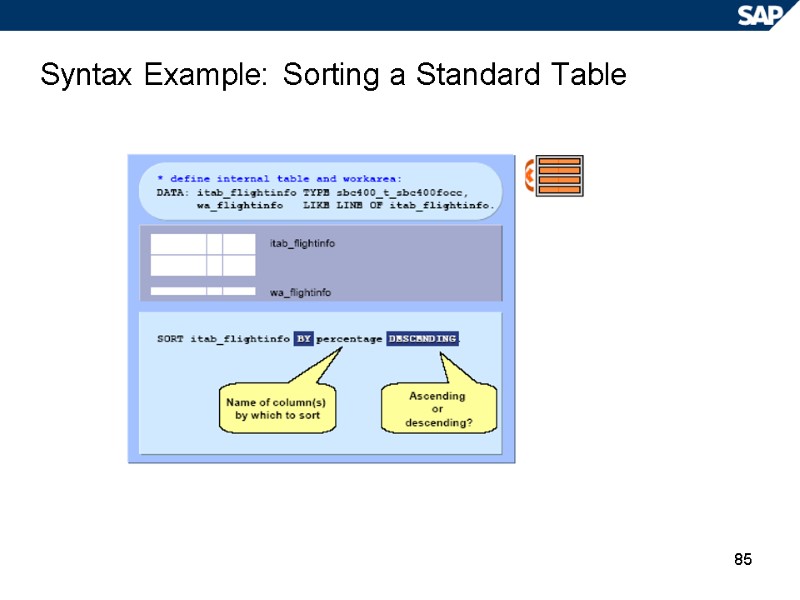
85 Syntax Example: Sorting a Standard Table
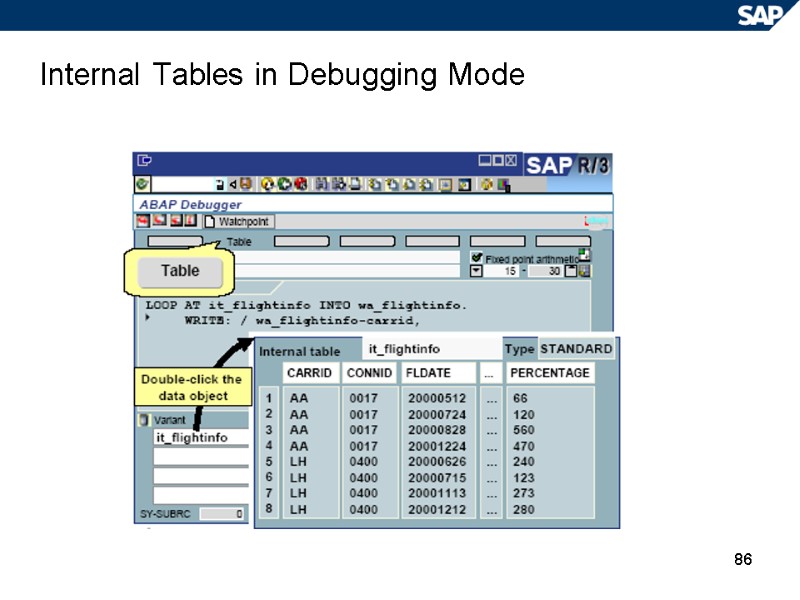
86 Internal Tables in Debugging Mode
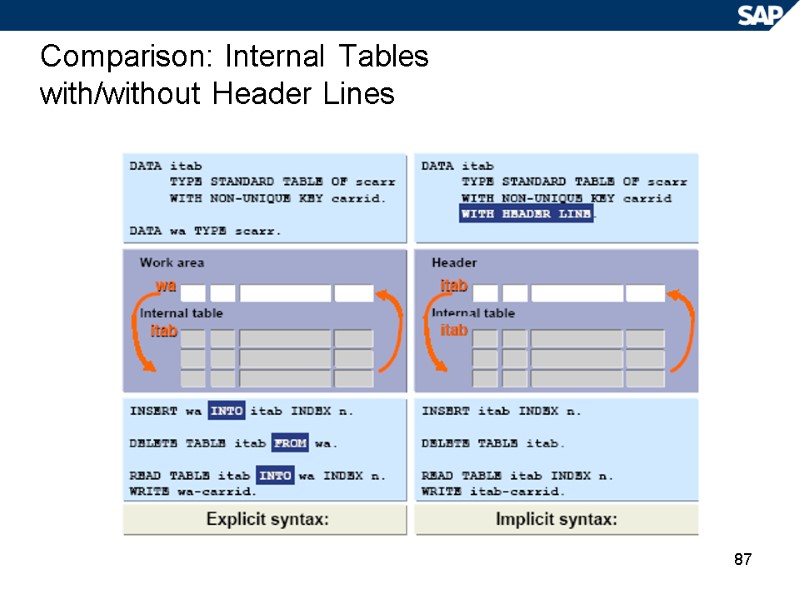
87 Comparison: Internal Tables with/without Header Lines

88 Basic ABAP Language Elements: Unit Summary You are now able to: Define elementary and structured data objects Use basic ABAP statements Execute and analyze programs in debugging mode

89 EXERCISES!

90 Data Retrieval Contents: Data Retrieval for Database Tables Querying the Database Reading Database Tables Authorization Checks Preview

91 Data Retrieval: Unit Objectives At the conclusion of this unit, you will be able to: List various ways of finding database tables Program read access to specific columns and lines within a particular database table Implement authorization checks List the read access options for multiple database tables
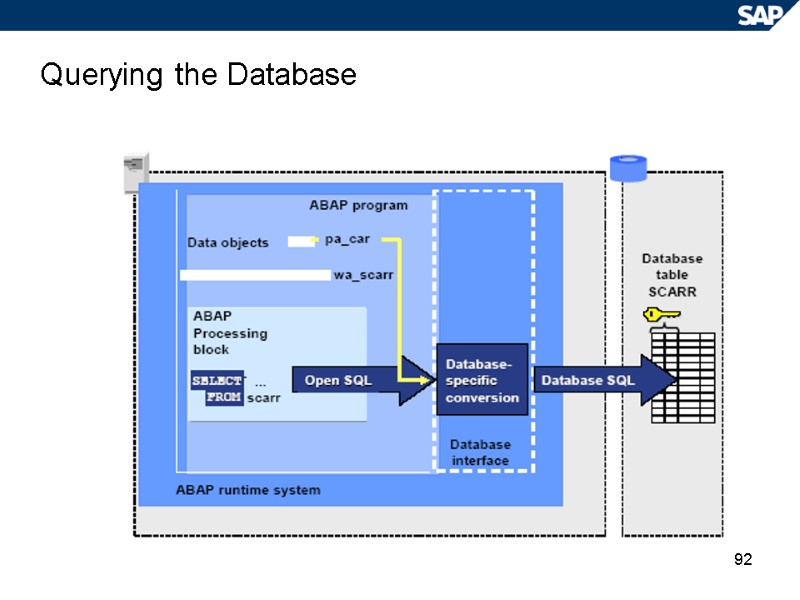
92 Querying the Database
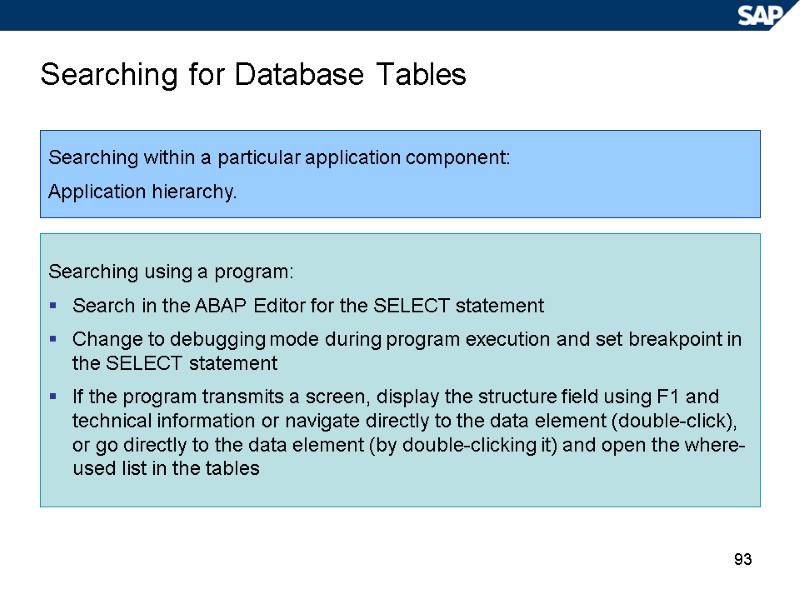
93 Searching for Database Tables Searching within a particular application component: Application hierarchy. Searching using a program: Search in the ABAP Editor for the SELECT statement Change to debugging mode during program execution and set breakpoint in the SELECT statement If the program transmits a screen, display the structure field using F1 and technical information or navigate directly to the data element (double-click), or go directly to the data element (by double-clicking it) and open the where-used list in the tables
94 Reading Database Tables Reading Database Tables Authorization Checks Preview
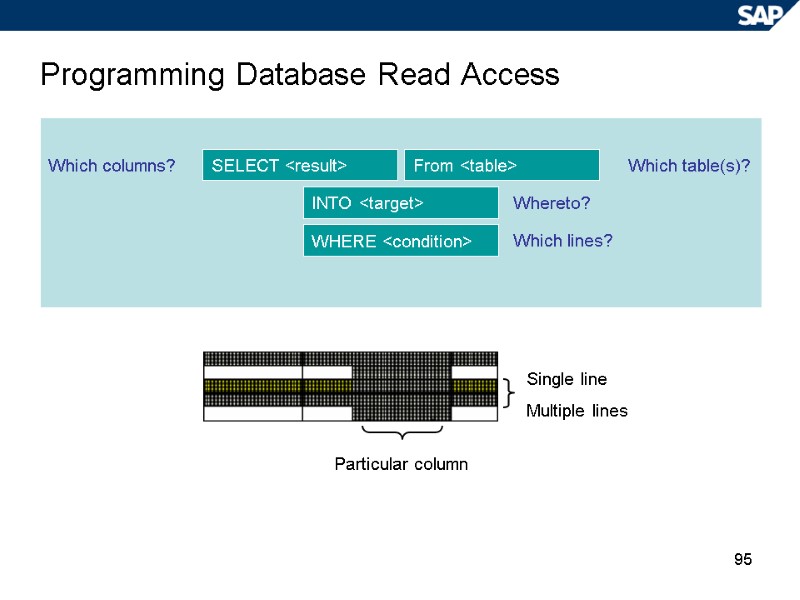
95 Programming Database Read Access Which columns? Which table(s)? Whereto? Which lines? Particular column Single line Multiple lines
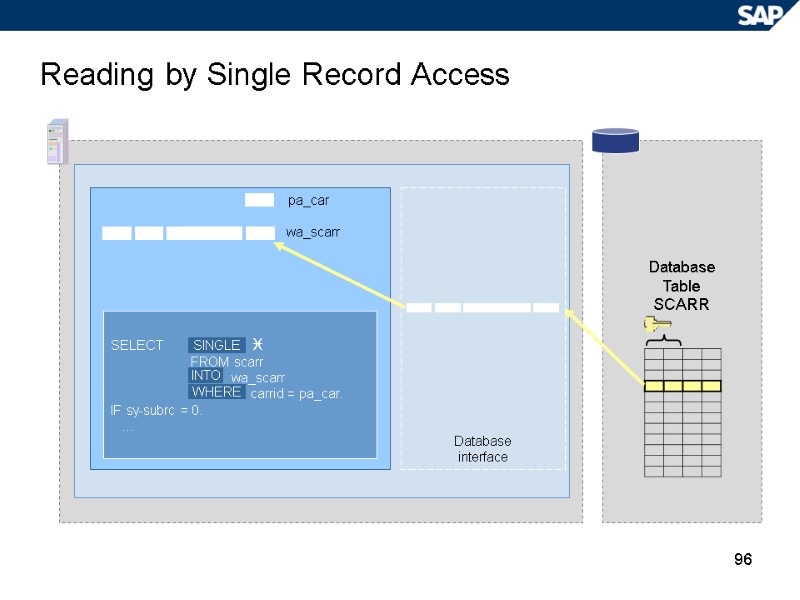
96 Reading by Single Record Access Database Table SCARR pa_car wa_scarr SELECT FROM scarr wa_scarr carrid = pa_car. IF sy-subrc = 0. … Database interface SINGLE INTO WHERE
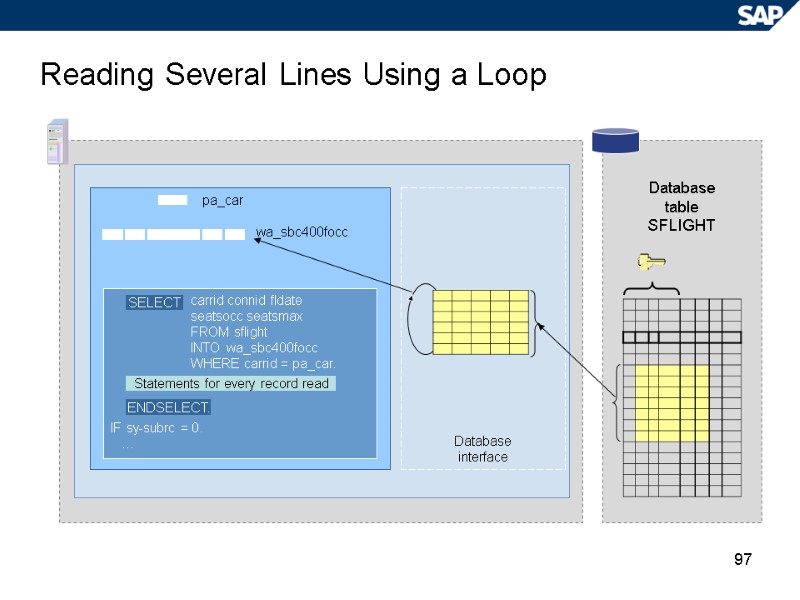
97 Reading Several Lines Using a Loop Database table SFLIGHT pa_car wa_sbc400focc carrid connid fldate seatsocc seatsmax FROM sflight INTO wa_sbc400focc WHERE carrid = pa_car. IF sy-subrc = 0. … Database interface SELECT ENDSELECT. Statements for every record read
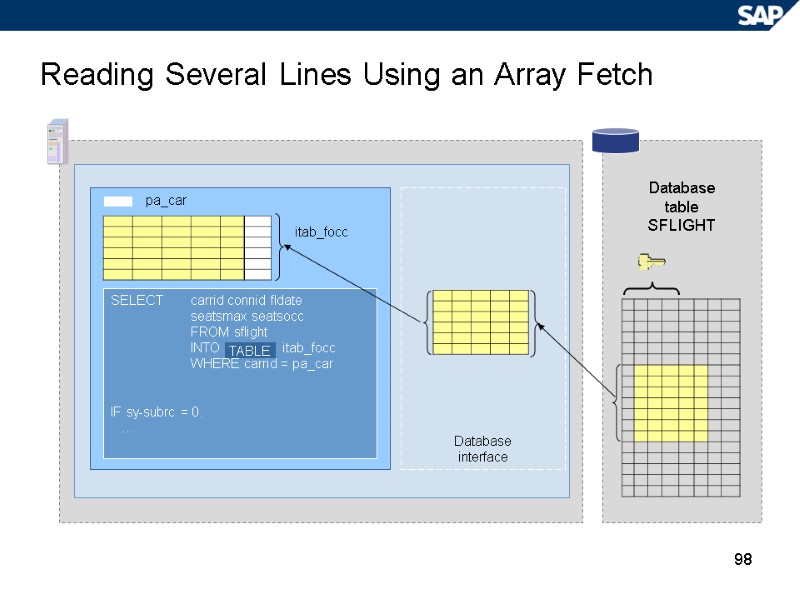
98 Reading Several Lines Using an Array Fetch Database table SFLIGHT pa_car itab_focc SELECT carrid connid fldate seatsmax seatsocc FROM sflight INTO itab_focc WHERE carrid = pa_car IF sy-subrc = 0. … Database interface TABLE
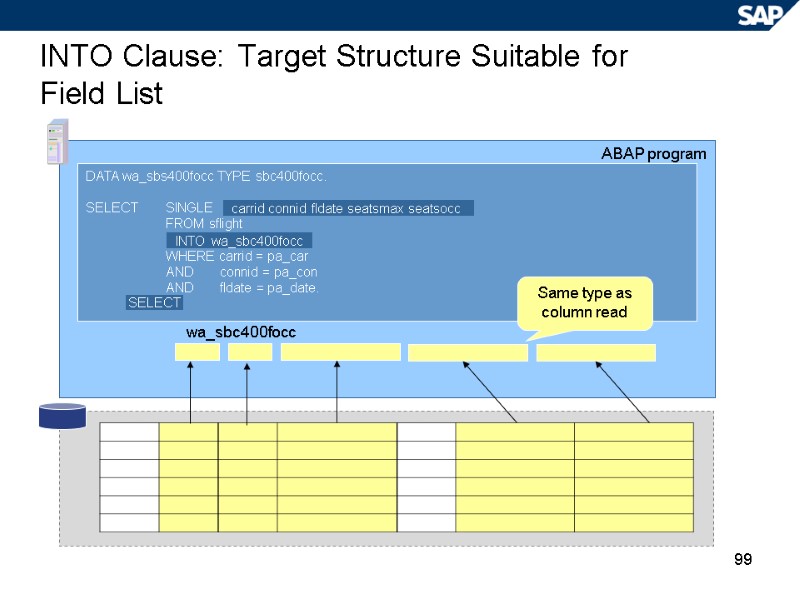
99 INTO Clause: Target Structure Suitable for Field List ABAP program DATA wa_sbs400focc TYPE sbc400focc. SELECT SINGLE FROM sflight WHERE carrid = pa_car AND connid = pa_con AND fldate = pa_date. SELECT INTO wa_sbc400focc carrid connid fldate seatsmax seatsocc Same type as column read wa_sbc400focc
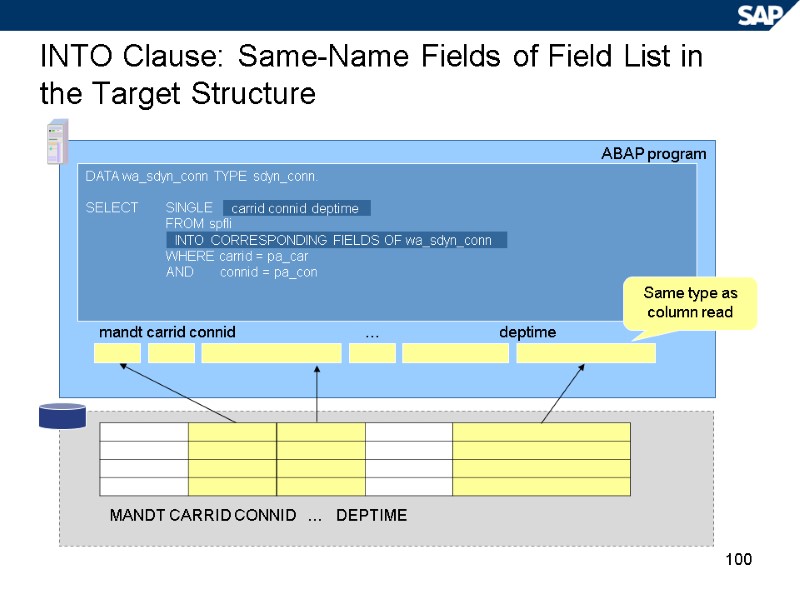
100 INTO Clause: Same-Name Fields of Field List in the Target Structure ABAP program DATA wa_sdyn_conn TYPE sdyn_conn. SELECT SINGLE FROM spfli WHERE carrid = pa_car AND connid = pa_con INTO CORRESPONDING FIELDS OF wa_sdyn_conn carrid connid deptime Same type as column read mandt carrid connid … deptime MANDT CARRID CONNID … DEPTIME
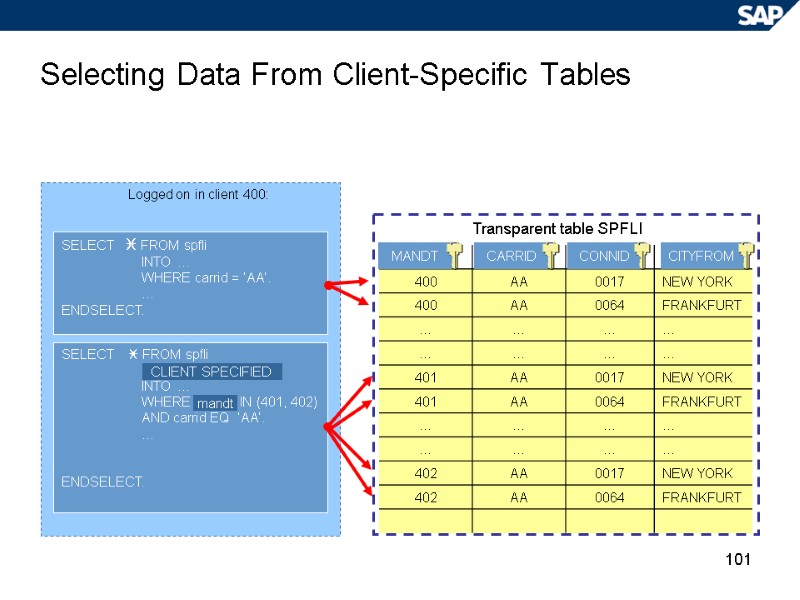
101 Selecting Data From Client-Specific Tables Logged on in client 400: SELECT FROM spfli INTO … WHERE IN (401, 402) AND carrid EQ ‘AA’. … ENDSELECT. SELECT FROM spfli INTO … WHERE carrid = ‘AA’. … ENDSELECT. mandt CLIENT SPECIFIED MANDT CITYFROM CONNID CARRID Transparent table SPFLI
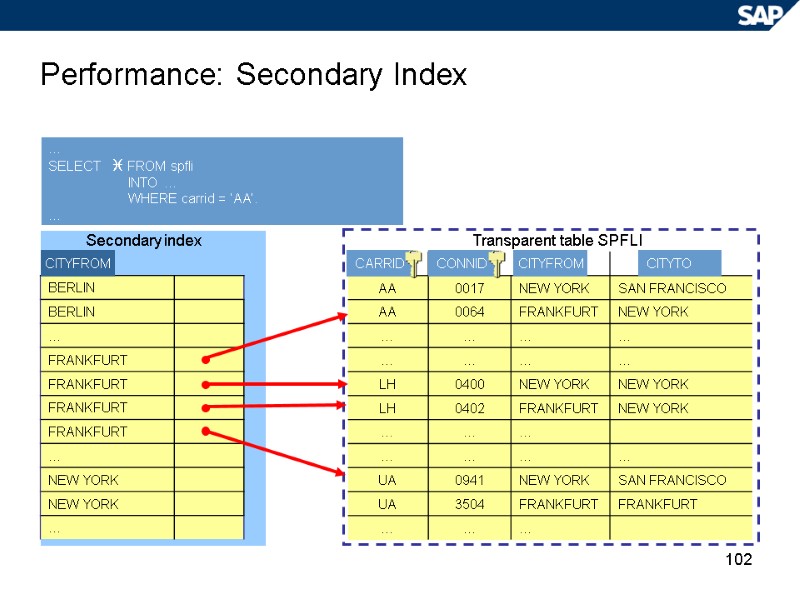
102 Performance: Secondary Index … SELECT FROM spfli INTO … WHERE carrid = ‘AA’. … CARRID CITYTO CITYFROM CONNID Transparent table SPFLI CITYFROM Secondary index
103 Authorization Checks Reading Database Tables Authorization Checks Preview
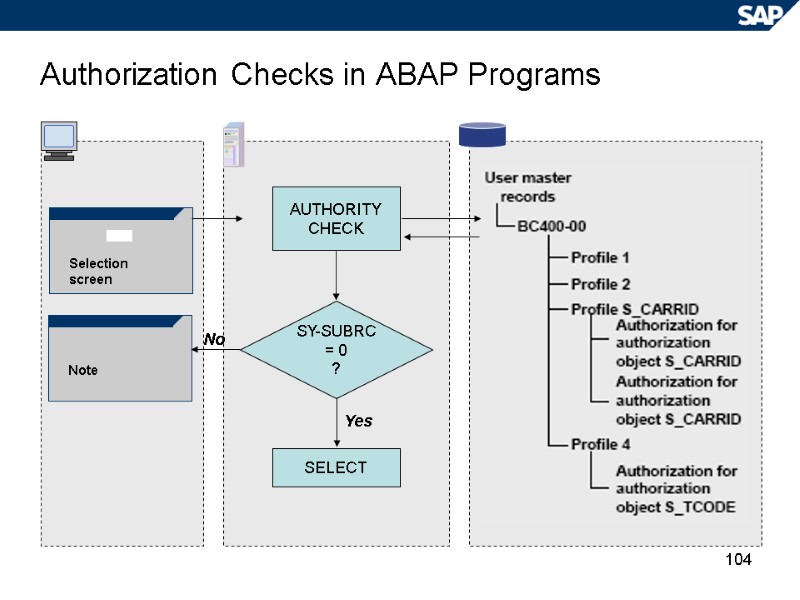
104 Authorization Checks in ABAP Programs Selection screen Note AUTHORITY CHECK SELECT SY-SUBRC = 0 ? Yes No
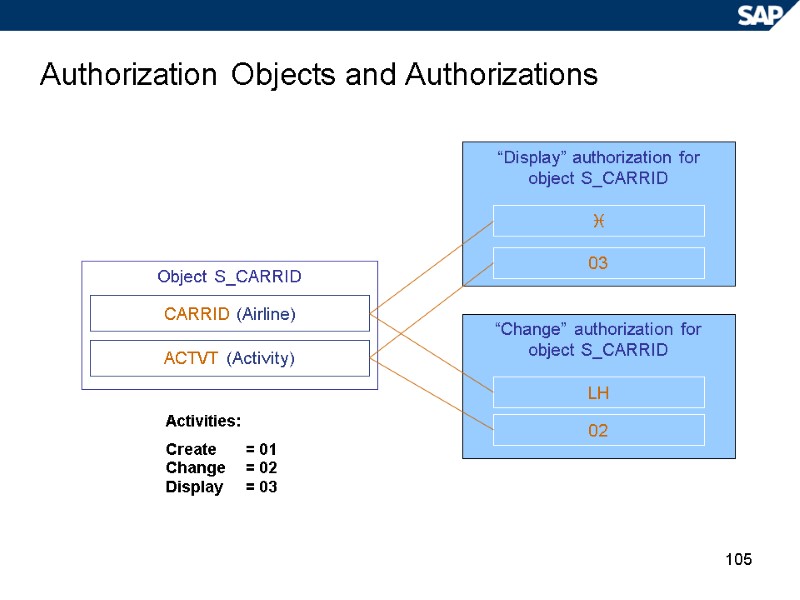
105 Authorization Objects and Authorizations “Display” authorization for object S_CARRID “Change” authorization for object S_CARRID LH 02 03 Object S_CARRID CARRID (Airline) ACTVT (Activity) Activities: Create = 01 Change = 02 Display = 03
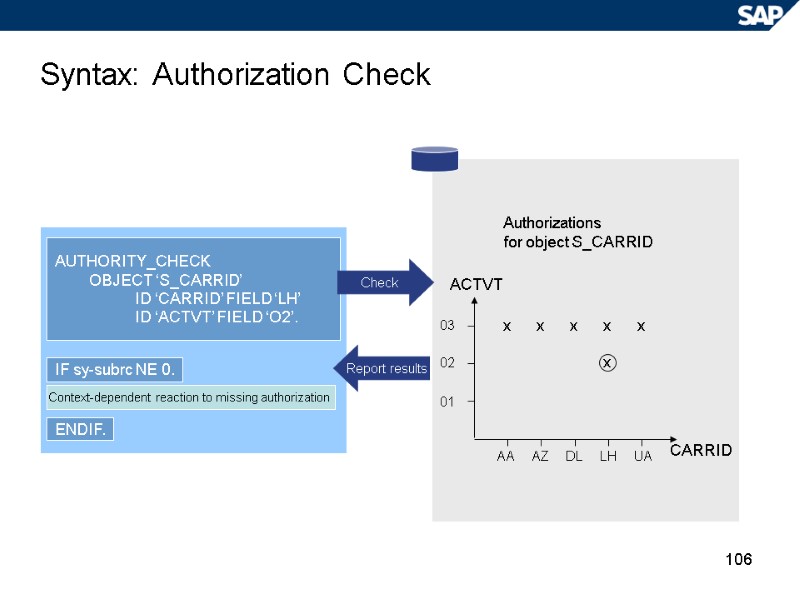
106 Syntax: Authorization Check Authorizations for object S_CARRID CARRID ACTVT AA AZ DL LH UA 01 03 02 x x x x x x AUTHORITY_CHECK OBJECT ‘S_CARRID’ ID ‘CARRID’ FIELD ‘LH’ ID ‘ACTVT’ FIELD ‘O2’. Context-dependent reaction to missing authorization IF sy-subrc NE 0. ENDIF. Check Report results
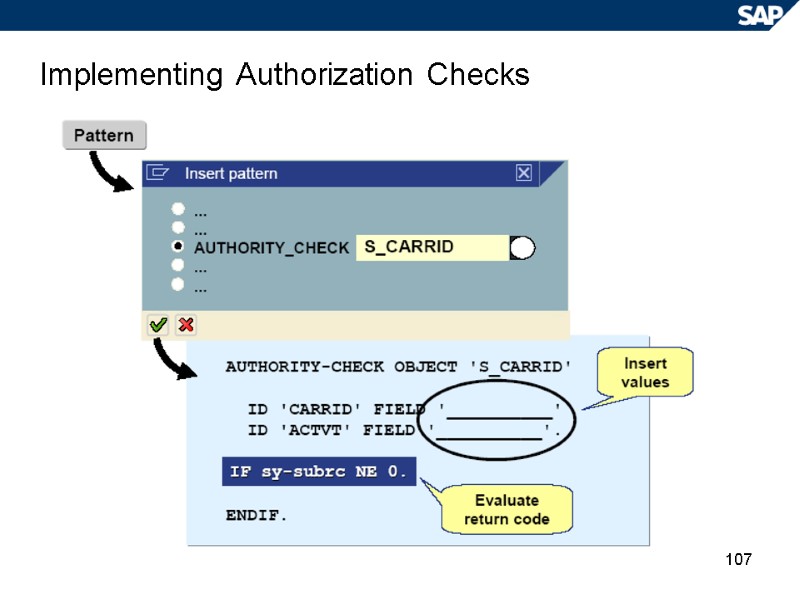
107 Implementing Authorization Checks

108 Preview Reading Database Tables Authorization Checks Preview
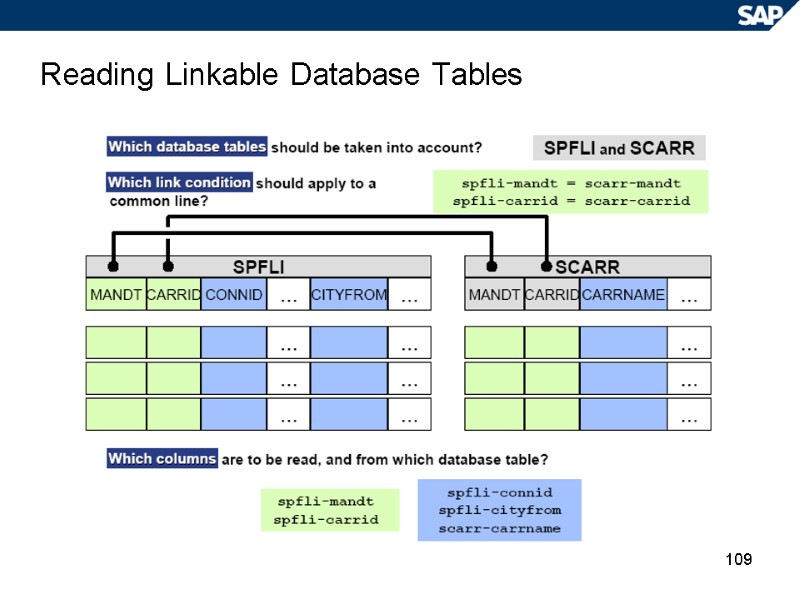
109 Reading Linkable Database Tables
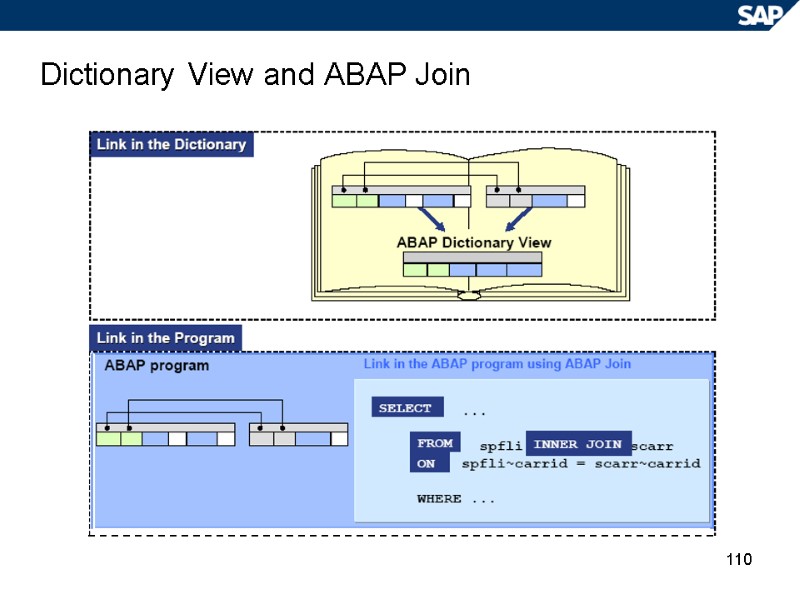
110 Dictionary View and ABAP Join
111 Preview: Reusable Components for Data Retrieval
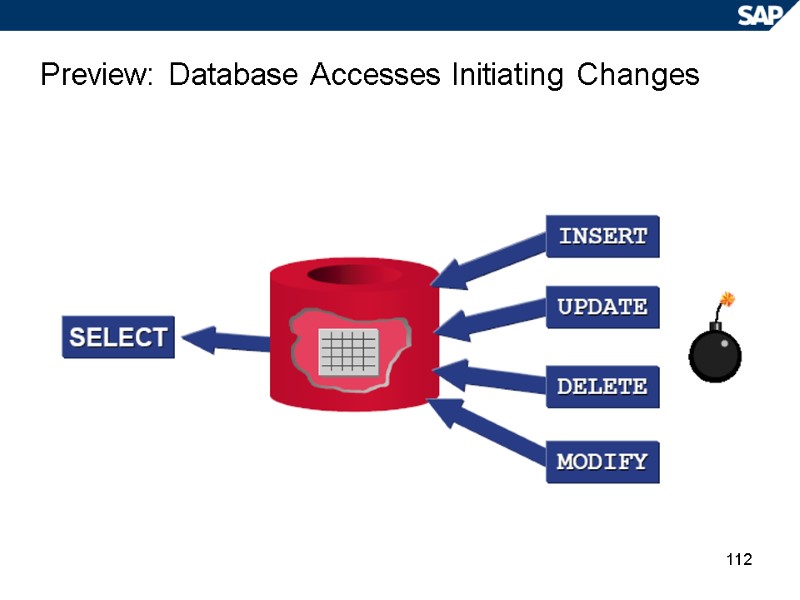
112 Preview: Database Accesses Initiating Changes

113 Data Retrieval: Summary Now you are able to: List various ways of finding database tables Program read access to specific columns and lines within a particular database table Implement authorization checks List the read access options for multiple database tables

114 EXERCISES!

115 Internal Program Modularization with Subroutines Contents: Defining Subroutines Interface Parameters Visibility Calling Subroutines Subroutines in Debugging Mode

116 Internal Program Modularization with Subroutines: Unit Objectives At the conclusion of this unit, you will be able to: Define subroutines Call subroutines Analyzes the execution subroutines in debugging mode
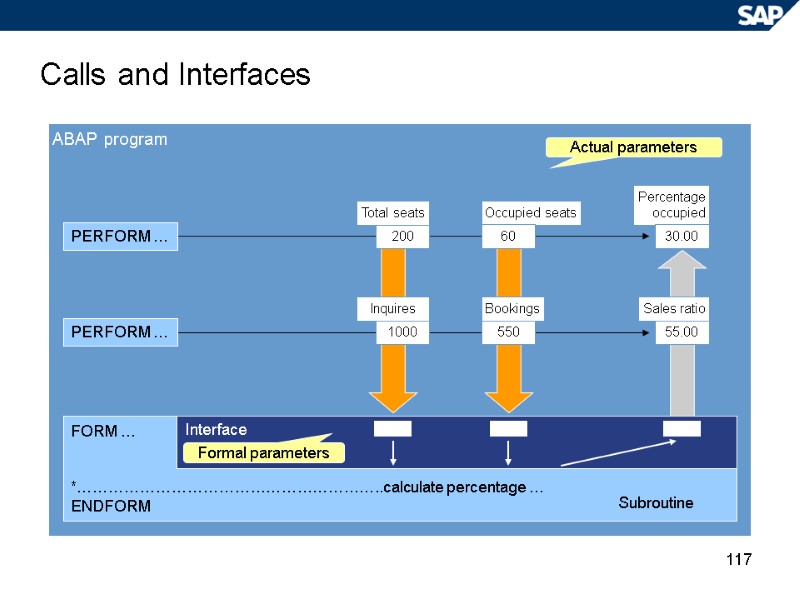
117 Calls and Interfaces ABAP program FORM … *…………………………………………………..calculate percentage … ENDFORM Subroutine Interface Formal parameters Actual parameters Percentage occupied Sales ratio 30.00 55.00 Inquires 1000 200 Total seats Occupied seats Bookings 60 550 PERFORM … PERFORM …
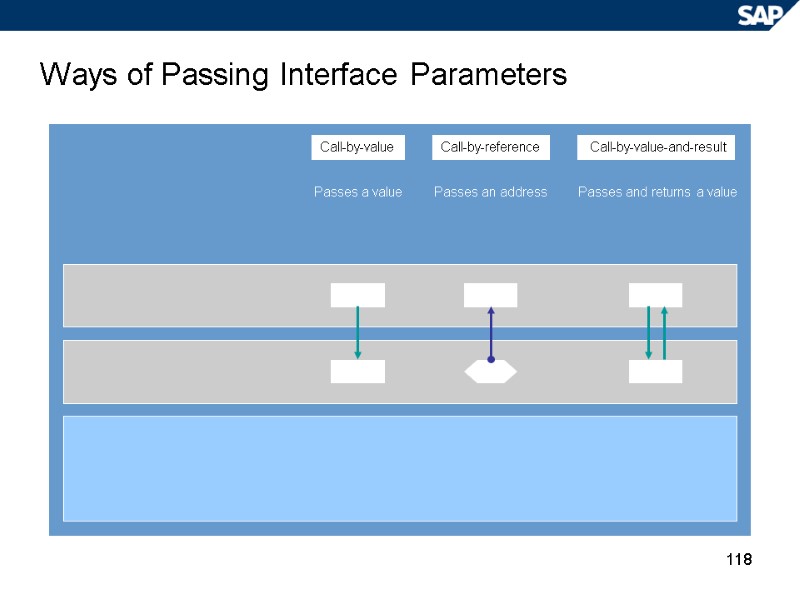
118 Ways of Passing Interface Parameters Call-by-value-and-result Call-by-value Call-by-reference Passes and returns a value Passes a value Passes an address
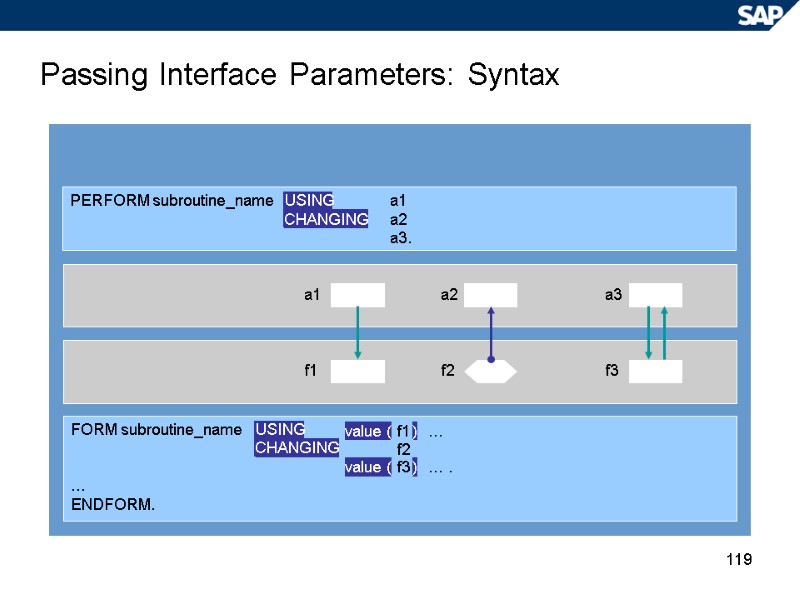
119 Passing Interface Parameters: Syntax FORM subroutine_name … ENDFORM. PERFORM subroutine_name a1 a2 a3. USING CHANGING a1 a2 a3 f1 f2 f3 USING CHANGING value ( value ( f1 f2 f3 ) ) … … .
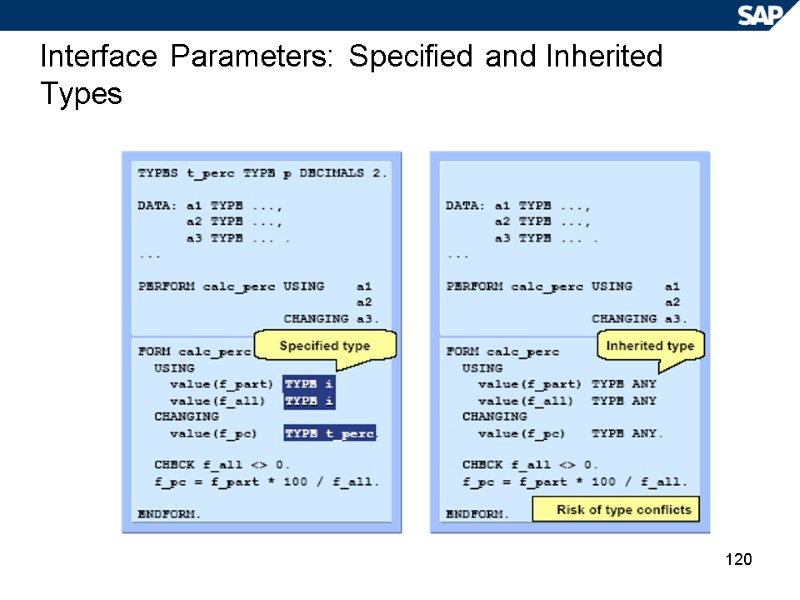
120 Interface Parameters: Specified and Inherited Types
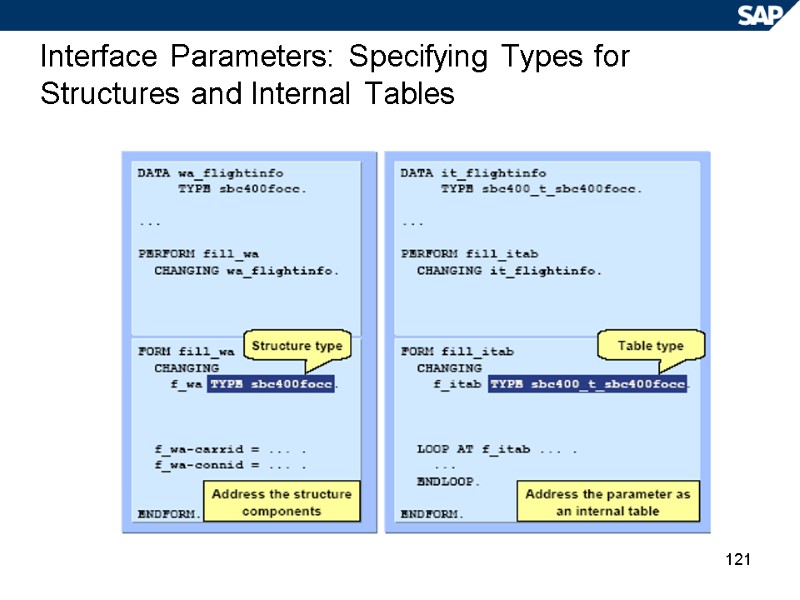
121 Interface Parameters: Specifying Types for Structures and Internal Tables

122 Visibility of Global and Local Data Objects

123 Syntax Example: Passing an Internal Table
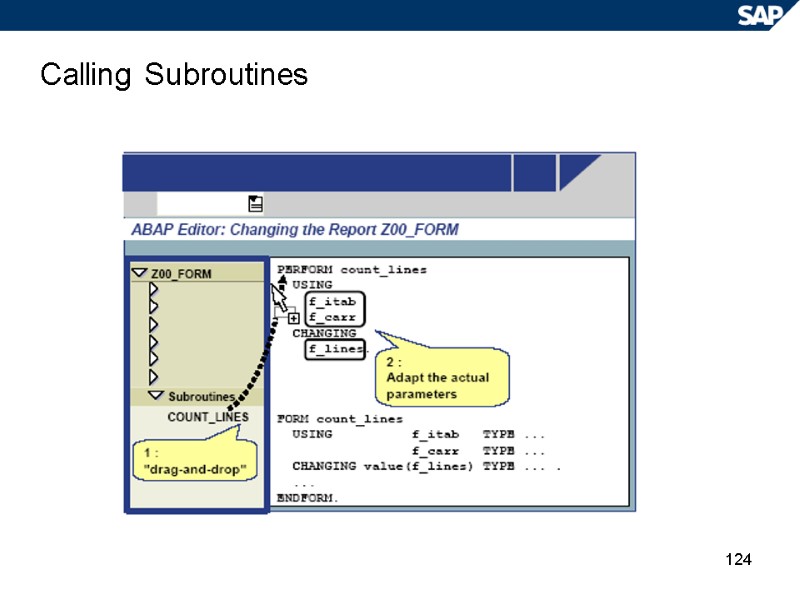
124 Calling Subroutines
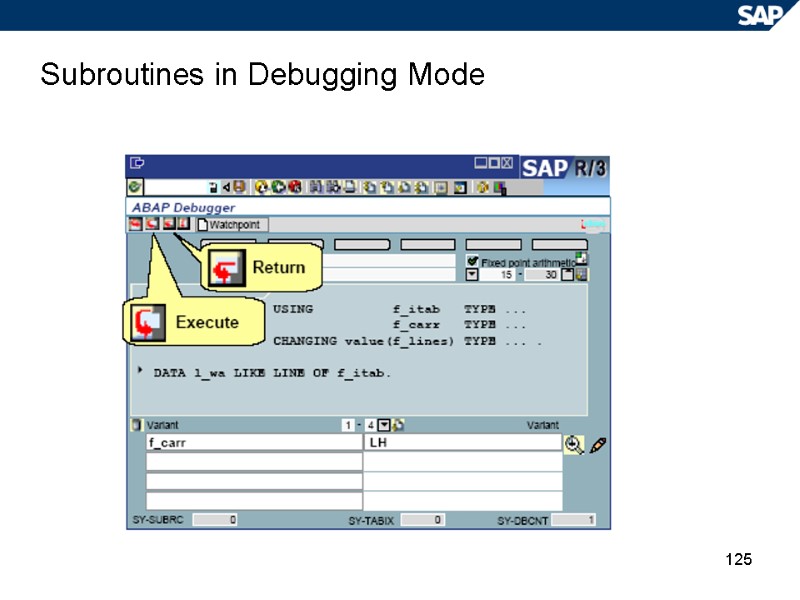
125 Subroutines in Debugging Mode

126 Internal Program Modularization with Subroutines: Unit Summary You are now able to: Define subroutines Call subroutines Analyzes the execution subroutines in debugging mode

127 EXERCISES!

128 The ABAP Runtime System Contents: Execution of Event Blocks by the ABAP Runtime System Event Block LOAD-OF-PROGRAM (INITIALIZATION) Event Block START-OF-SELECTION

129 The ABAP Runtime System: Unit Objectives At the conclusion of this unit, you will be able to: Describe the event-controlled processes for executing an ABAP program Use the event block LOAD-OF-PROGRAM (INITIALIZATION) Use the event block START-OF-SELECTION
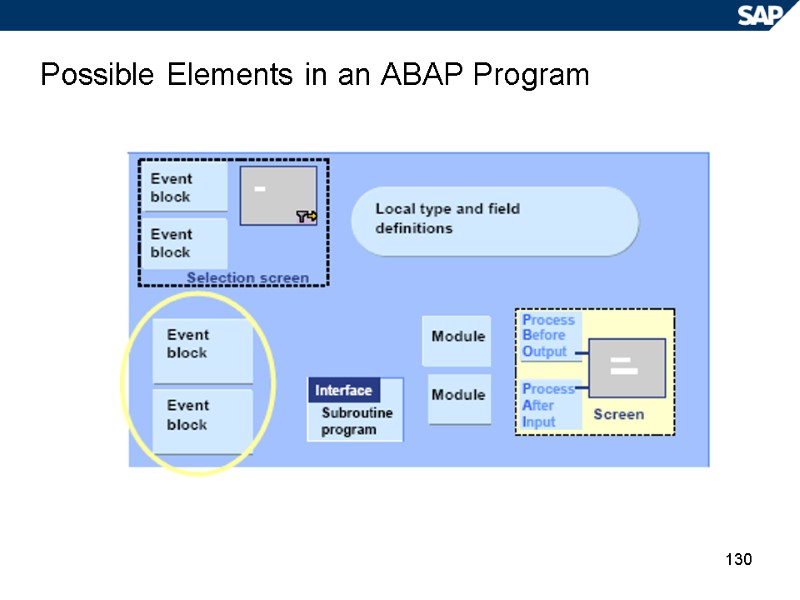
130 Possible Elements in an ABAP Program
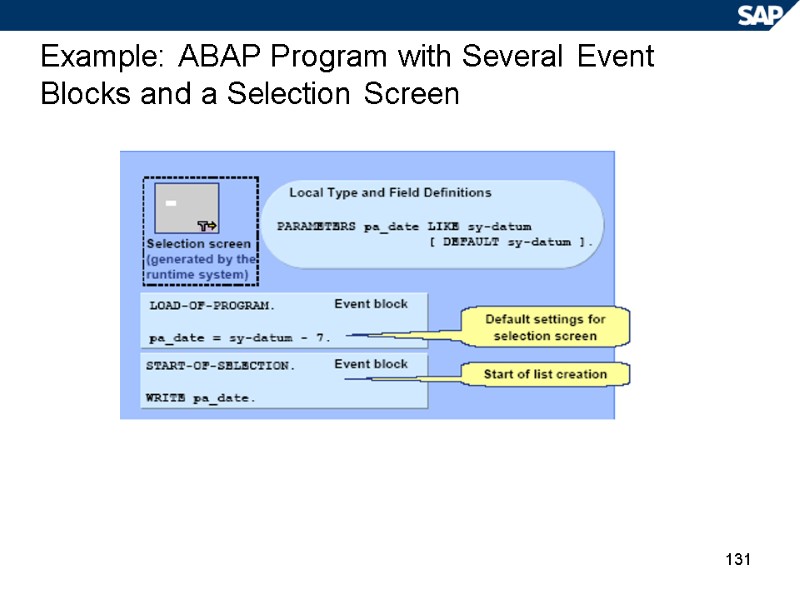
131 Example: ABAP Program with Several Event Blocks and a Selection Screen
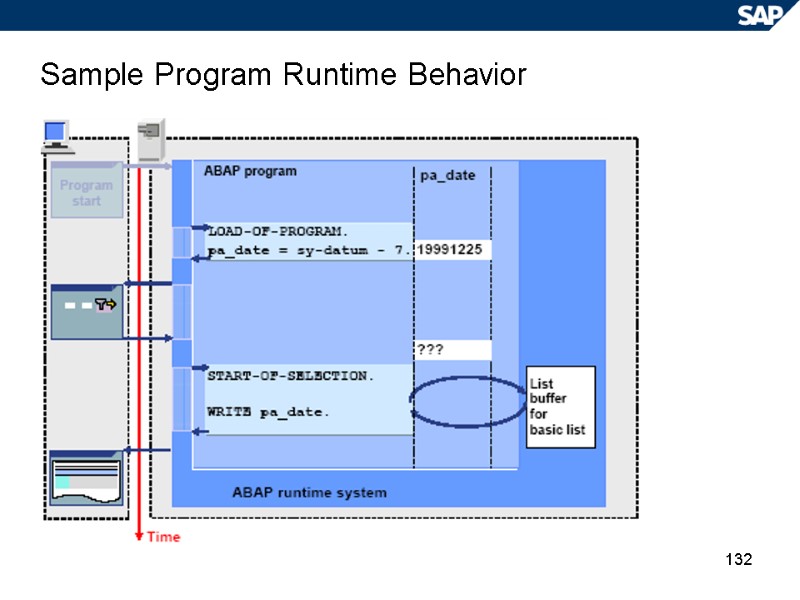
132 Sample Program Runtime Behavior
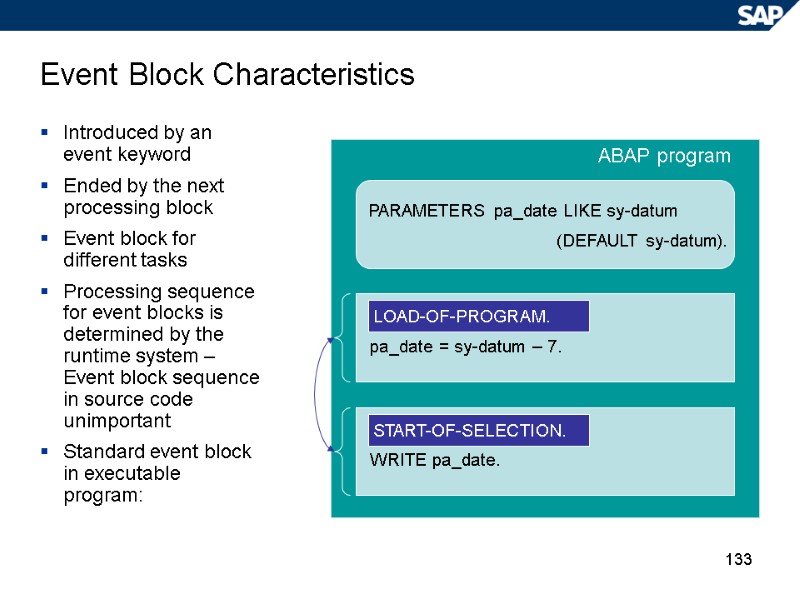
133 Event Block Characteristics Introduced by an event keyword Ended by the next processing block Event block for different tasks Processing sequence for event blocks is determined by the runtime system – Event block sequence in source code unimportant Standard event block in executable program: ABAP program PARAMETERS pa_date LIKE sy-datum (DEFAULT sy-datum). pa_date = sy-datum – 7. WRITE pa_date. LOAD-OF-PROGRAM. START-OF-SELECTION.

134 The ABAP Runtime System: Unit Summary You are now able to: Describe the event-controlled processes for executing an ABAP program Use the event block LOAD-OF-PROGRAM (INITIALIZATION) Use the event block START-OF-SELECTION

135 User Dialog List Contents: List attributes and strengths Basic list List events Interactive lists Example with syntax: Detail list

136 User Dialog List: Unit Objectives At the conclusion of this unit, you will be able to: Describe list attributes and strengths Write a program that displays the detail of a specific line from your basic list to an interactive list whenever the user double-clicks that particular line Explain the runtime behavior of your program during the AT LINE-SELECTION event
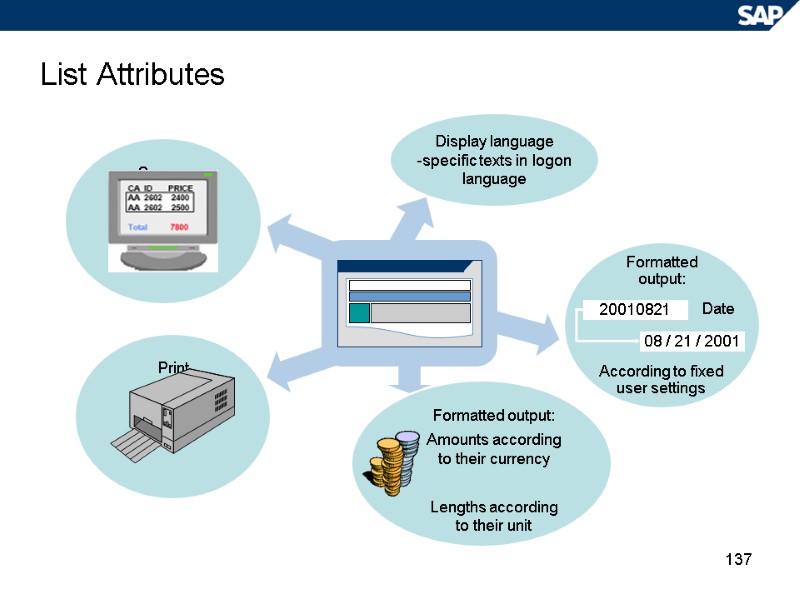
137 List Attributes Screen Display language -specific texts in logon language Print Formatted output: Amounts according to their currency Lengths according to their unit
138 Standard List Functions: Back / Exit / Cancel Scroll Print Find (in list) Save
139 List Headers in the Default Page Header From within the list: From the ABAP Editor:
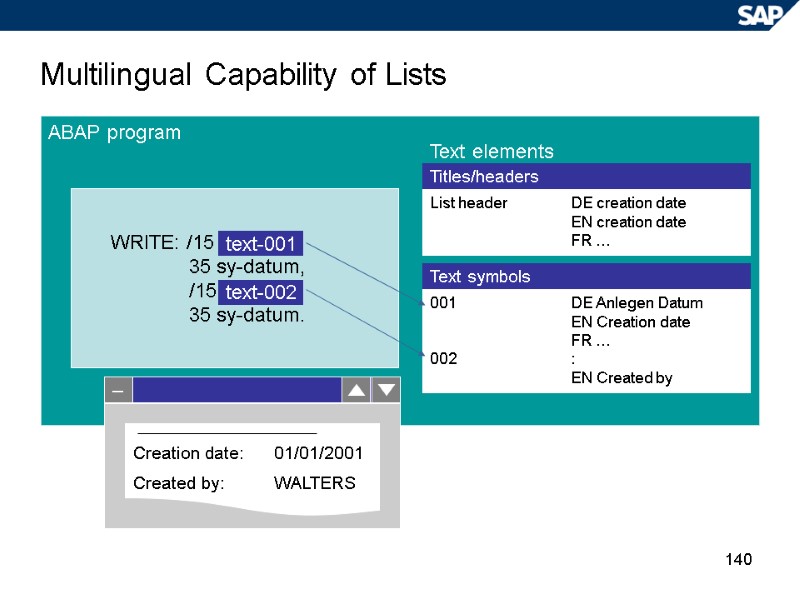
140 Multilingual Capability of Lists ABAP program WRITE: /15 35 sy-datum, /15 35 sy-datum. text-001 text-002 Text elements – Creation date: 01/01/2001 Created by: WALTERS
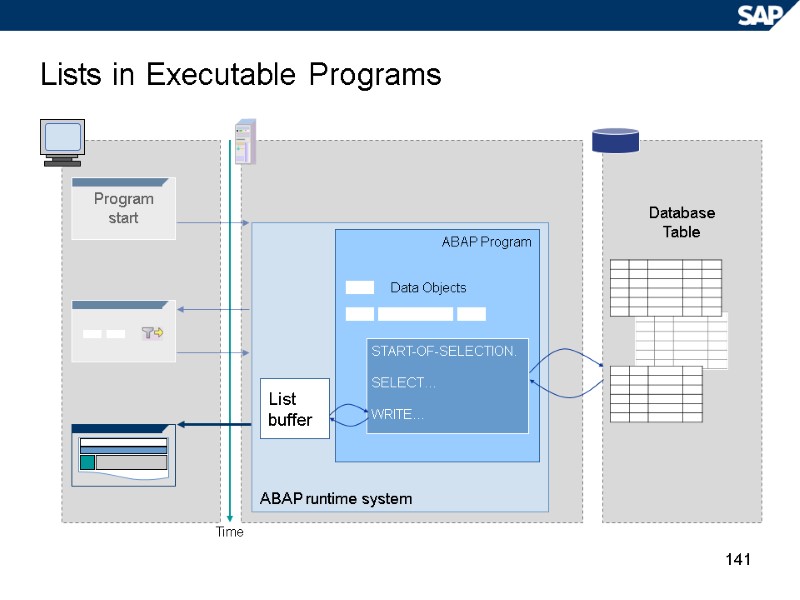
141 Lists in Executable Programs Database Table Time ABAP runtime system ABAP Program START-OF-SELECTION. SELECT… WRITE… Data Objects List buffer
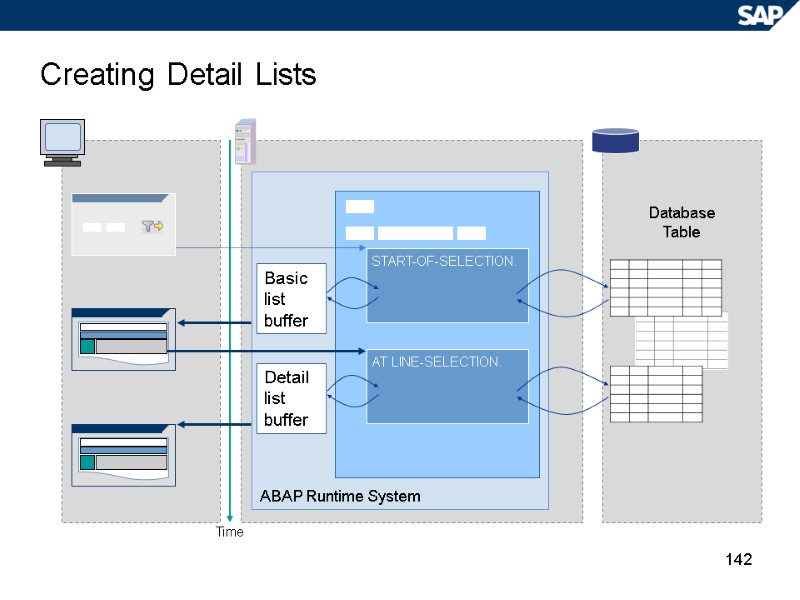
142 Creating Detail Lists Database Table Time ABAP Runtime System START-OF-SELECTION. Detail list buffer AT LINE-SELECTION. Basic list buffer
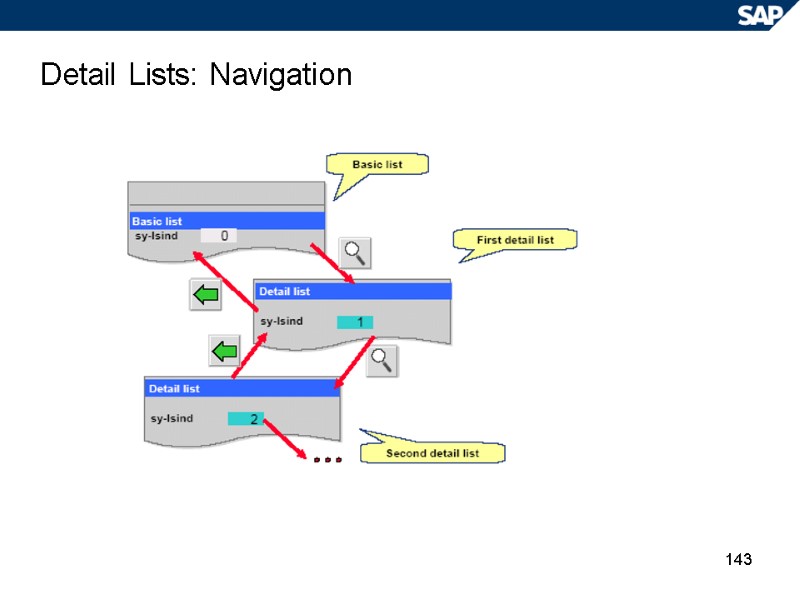
143 Detail Lists: Navigation
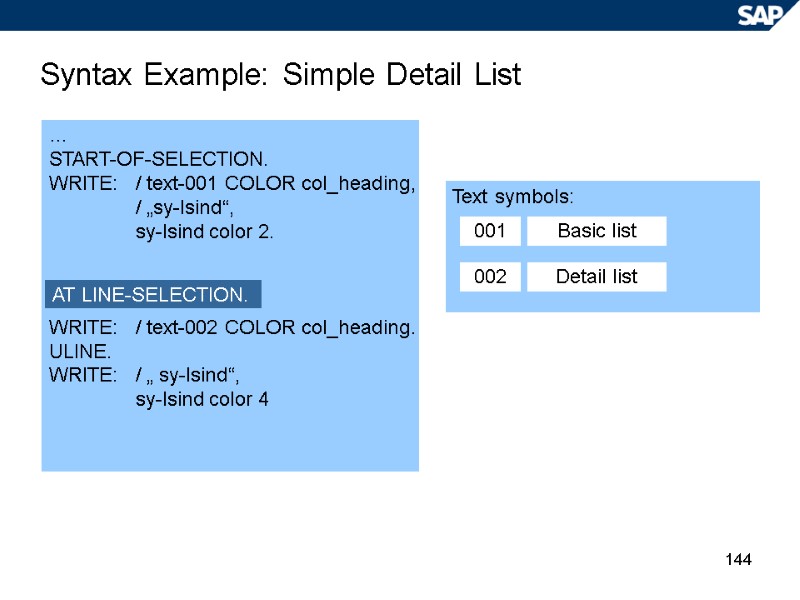
144 Syntax Example: Simple Detail List … START-OF-SELECTION. WRITE: / text-001 COLOR col_heading, / „sy-lsind“, sy-lsind color 2. WRITE: / text-002 COLOR col_heading. ULINE. WRITE: / „ sy-lsind“, sy-lsind color 4 AT LINE-SELECTION. Text symbols: 001 002 Basic list Detail list
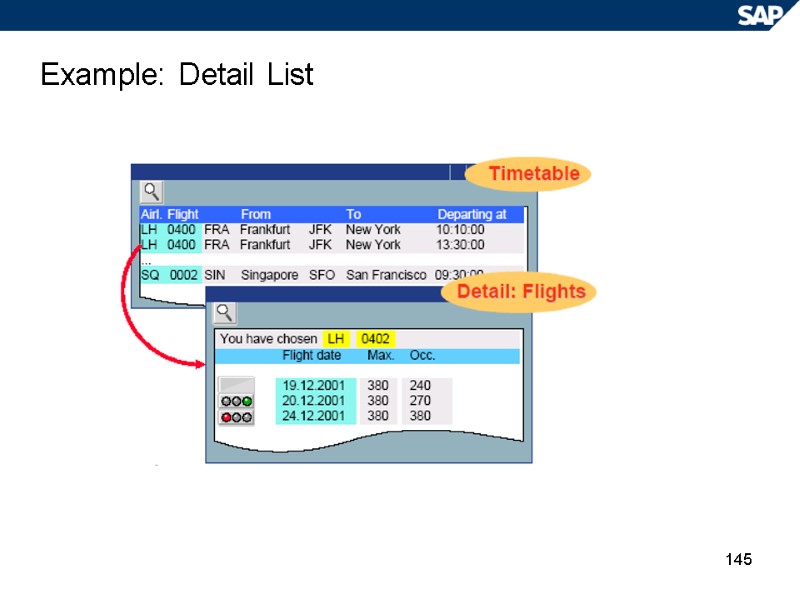
145 Example: Detail List
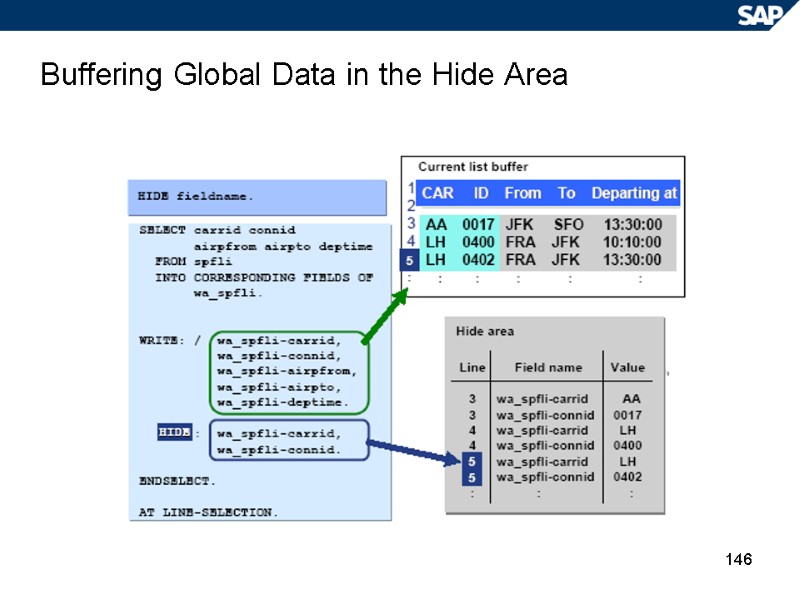
146 Buffering Global Data in the Hide Area
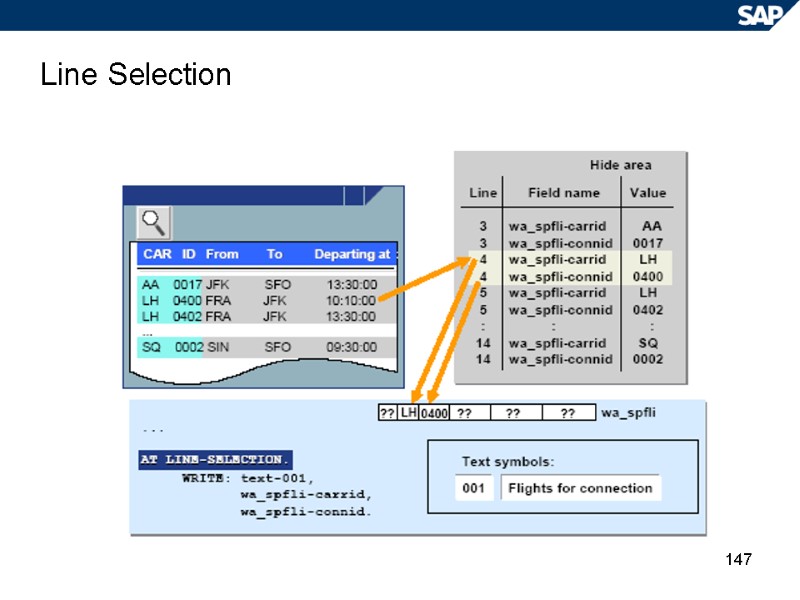
147 Line Selection
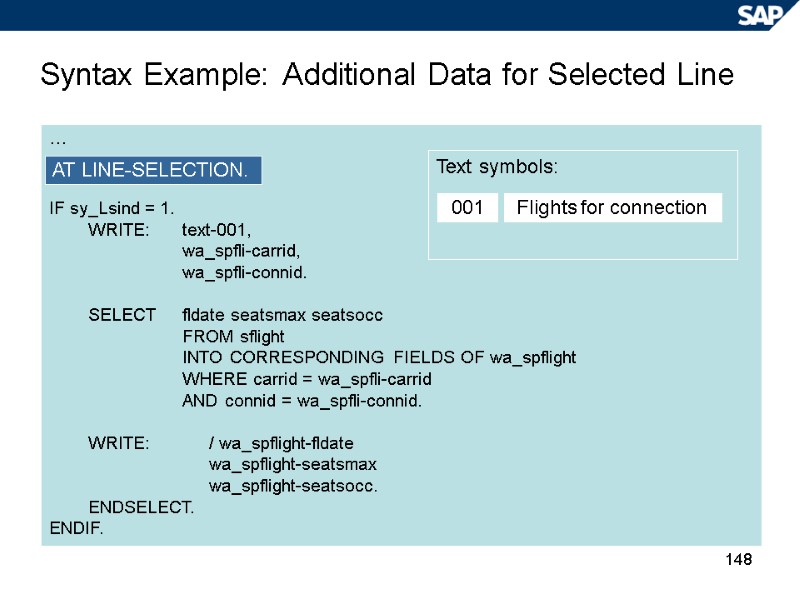
148 Syntax Example: Additional Data for Selected Line … IF sy_Lsind = 1. WRITE: text-001, wa_spfli-carrid, wa_spfli-connid. SELECT fldate seatsmax seatsocc FROM sflight INTO CORRESPONDING FIELDS OF wa_spflight WHERE carrid = wa_spfli-carrid AND connid = wa_spfli-connid. WRITE: / wa_spflight-fldate wa_spflight-seatsmax wa_spflight-seatsocc. ENDSELECT. ENDIF. AT LINE-SELECTION. Text symbols: 001 Flights for connection

149 User Dialog List: Unit Summery You are now able to: Describe list attributes and strengths Write a program that displays the details of a specific line from your basic list to an interactive list whenever the user double-clicks that particular line Explain the runtime behavior of your program during the AT LINE-SELECTION event

150 EXERCISES!
151 User Dialog Selection Screen Contents: Selection screen attributes and strengths Defining selection screens Evaluating user input to restrict database selection Selection screen events Syntax examples: Additional input checks with error dialog

152 User Dialog List: Unit Objectives At the conclusion of this unit, you will be able to: Describe selection screen attributes and strengths Write a program that allows you to enter intervals on a selection screen and that can be used to restrict the number of data records retrieved from the database Write a program that contains additional input checks for the selection screen and returns to the selection if an error occurs
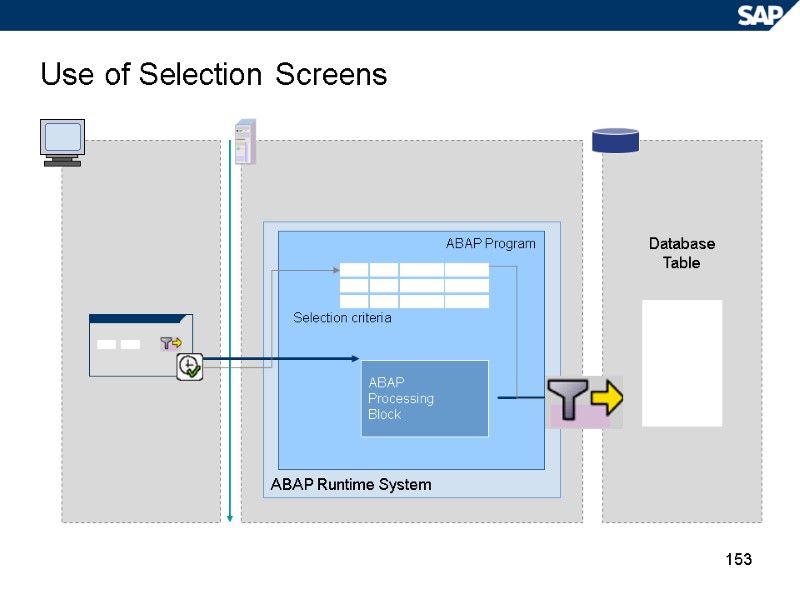
153 Database Table Use of Selection Screens ABAP Runtime System ABAP Program ABAP Processing Block Selection criteria
154 Overview: Selection Screen Attributes Selection Screen Attributes Single Fields (PARAMETERS) Value Sets (SELECT-OPTIONS) Selection Screen Events
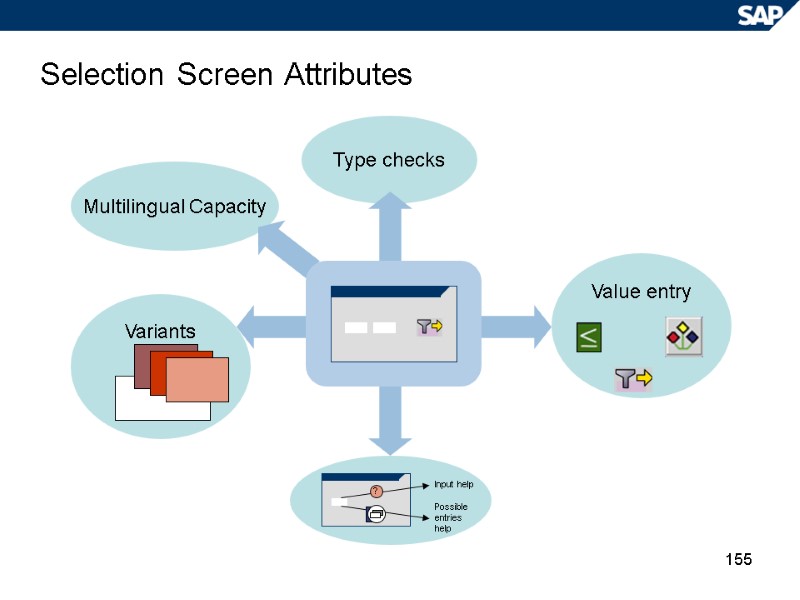
155 Variants Multilingual Capacity Type checks Selection Screen Attributes Value entry
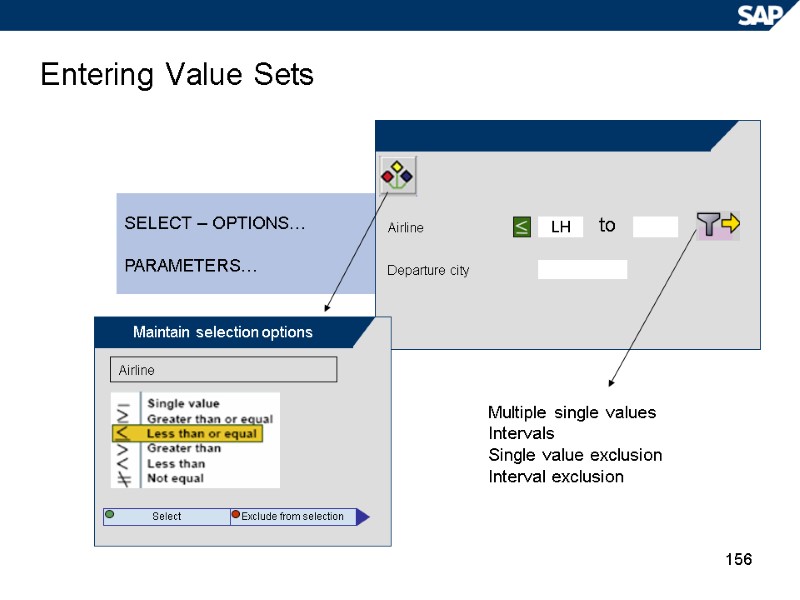
156 Entering Value Sets LH to Airline Departure city SELECT – OPTIONS… PARAMETERS… Maintain selection options Airline Select Exclude from selection Multiple single values Intervals Single value exclusion Interval exclusion
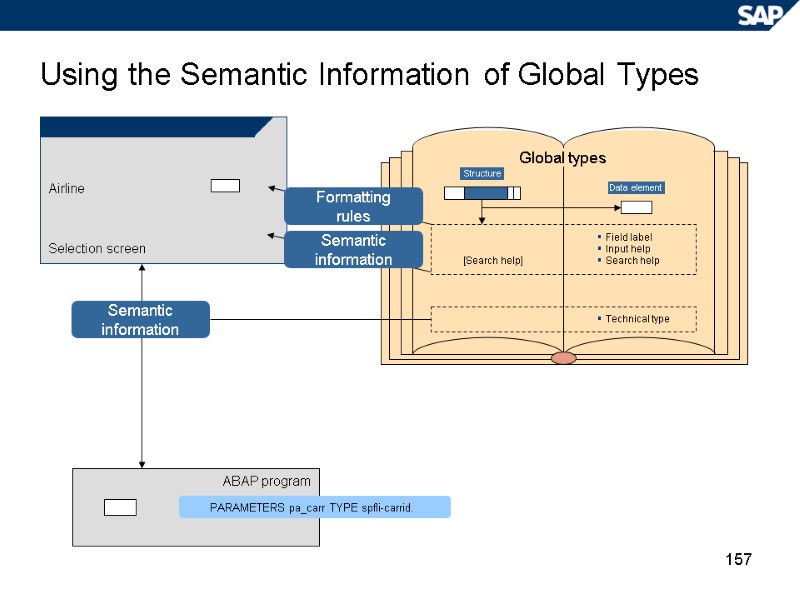
157 Using the Semantic Information of Global Types Airline Selection screen ABAP program PARAMETERS pa_carr TYPE spfli-carrid. Global types Data element Structure [Search help] Field label Input help Search help Technical type Formatting rules Semantic information Semantic information
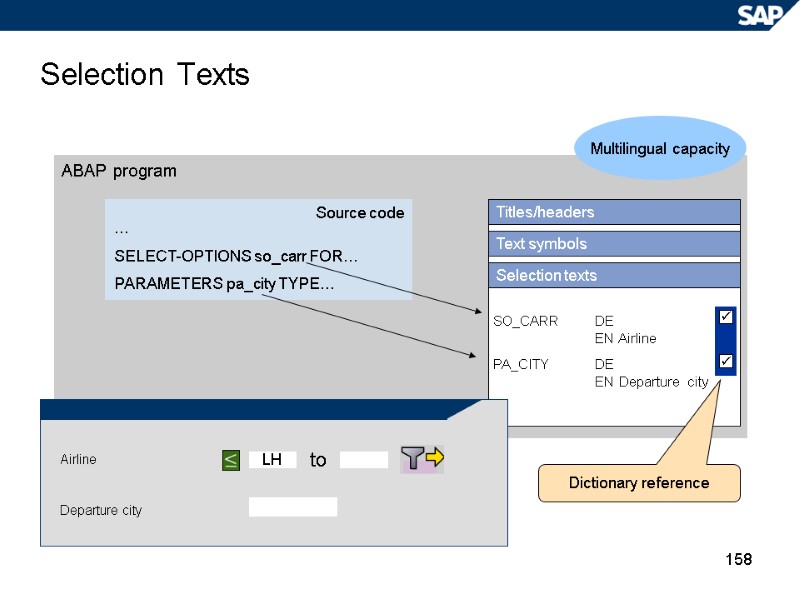
158 Selection Texts ABAP program Multilingual capacity Titles/headers Text symbols Selection texts SO_CARR DE EN Airline PA_CITY DE EN Departure city Dictionary reference
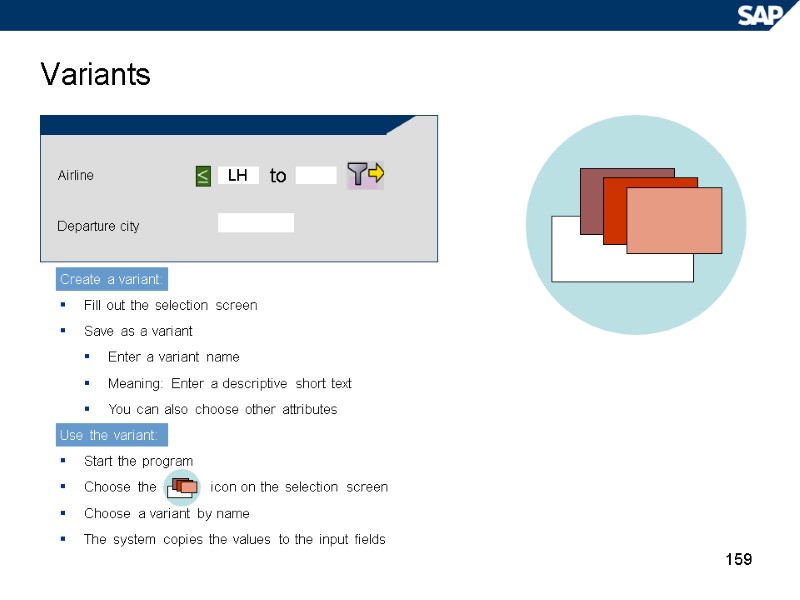
159 Variants LH Airline Departure city to Create a variant: Fill out the selection screen Save as a variant Enter a variant name Meaning: Enter a descriptive short text You can also choose other attributes Use the variant: Start the program Choose the icon on the selection screen Choose a variant by name The system copies the values to the input fields
160 Single Fields (PARAMETERS) Selection Screen Attributes Single Fields (PARAMETERS) Value Sets (SELECT-OPTIONS) Selection Screen Events
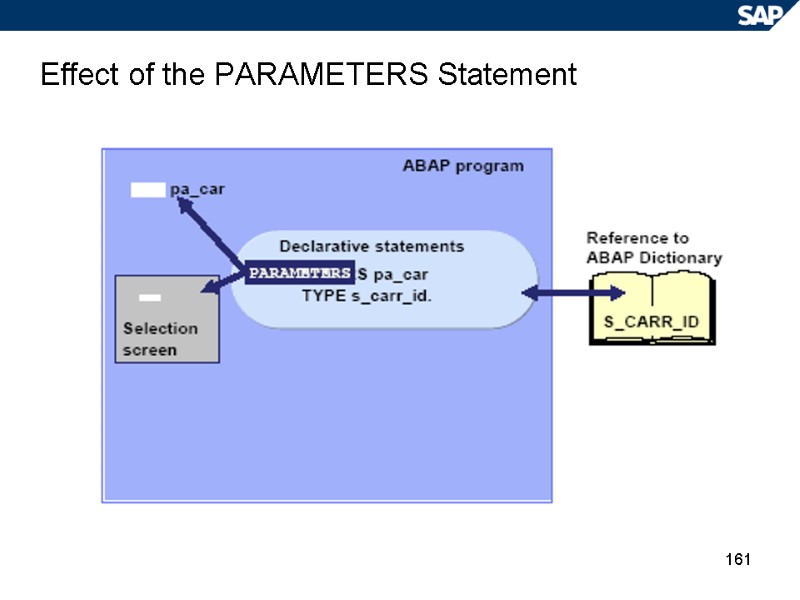
161 Effect of the PARAMETERS Statement
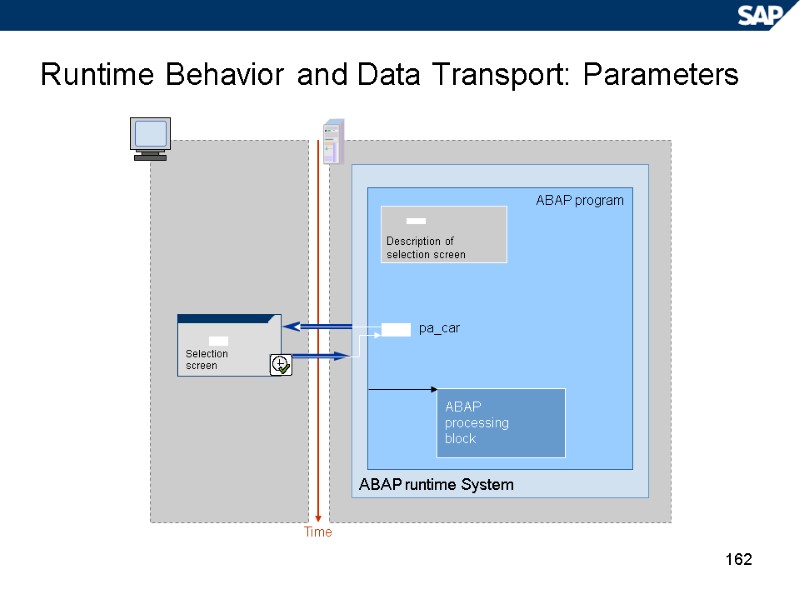
162 Runtime Behavior and Data Transport: Parameters

163 Using Parameters When Accessing the Database

164 Value sets (SELECT-OPTIONS) Selection Screen Attributes Single Fields (PARAMETERS) Value Sets (SELECT-OPTIONS) Selection Screen Events
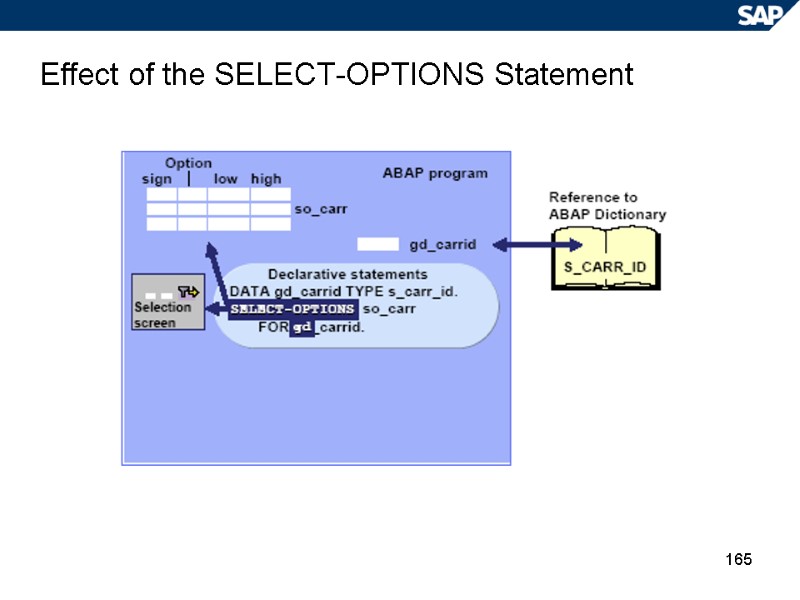
165 Effect of the SELECT-OPTIONS Statement
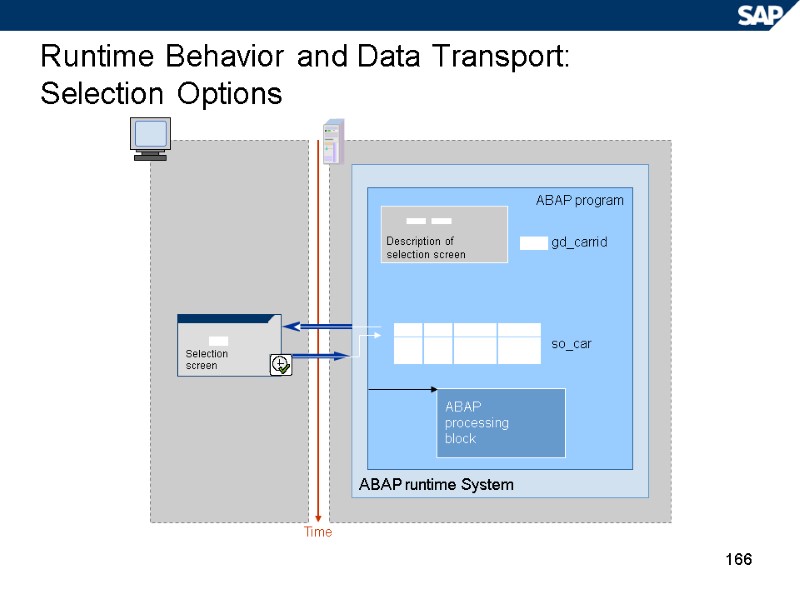
166 Runtime Behavior and Data Transport: Selection Options Time ABAP runtime System ABAP program so_car Selection screen Description of selection screen ABAP processing block gd_carrid
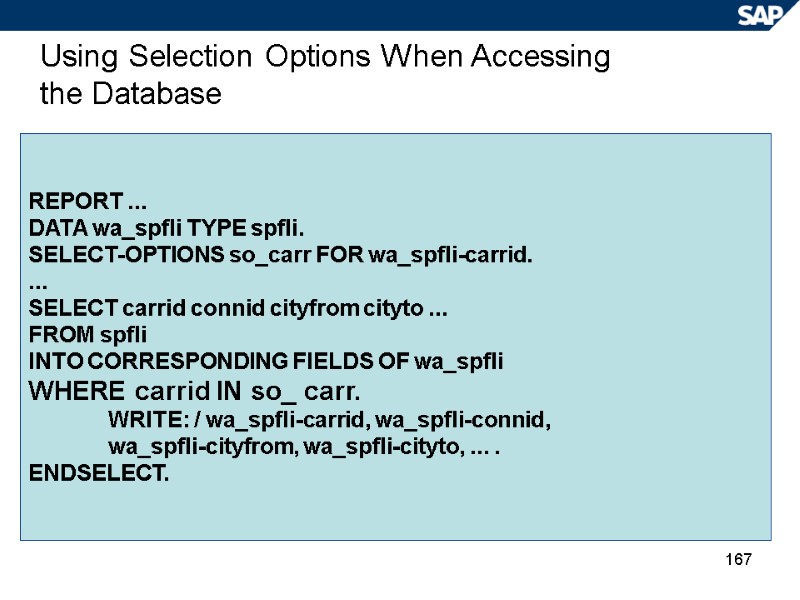
167 Using Selection Options When Accessing the Database REPORT ... DATA wa_spfli TYPE spfli. SELECT-OPTIONS so_carr FOR wa_spfli-carrid. ... SELECT carrid connid cityfrom cityto ... FROM spfli INTO CORRESPONDING FIELDS OF wa_spfli WHERE carrid IN so_ carr. WRITE: / wa_spfli-carrid, wa_spfli-connid, wa_spfli-cityfrom, wa_spfli-cityto, ... . ENDSELECT.
168 Selection Screen Events Selection Screen Attributes Single Fields (PARAMETERS) Value Sets (SELECT-OPTIONS) Selection Screen Events
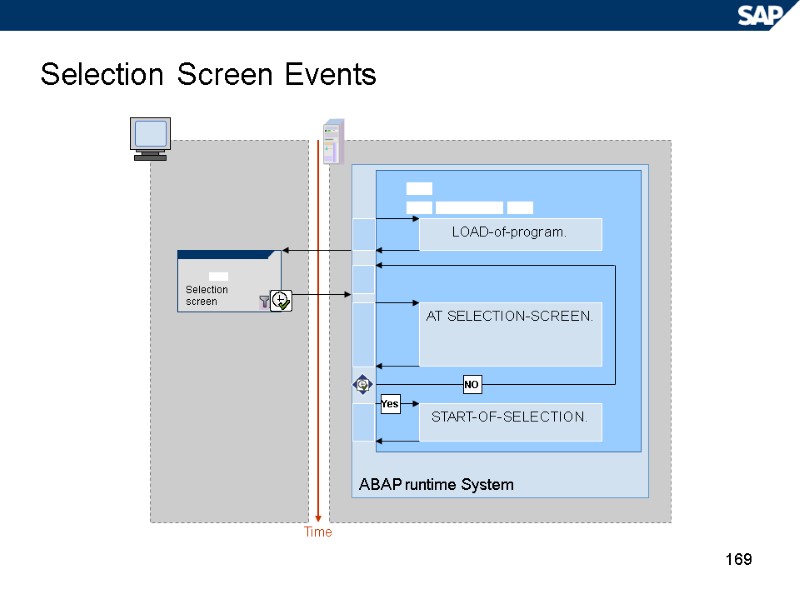
169 Selection Screen Events Time ABAP runtime System Selection screen LOAD-of-program. AT SELECTION-SCREEN. START-OF-SELECTION. NO Yes
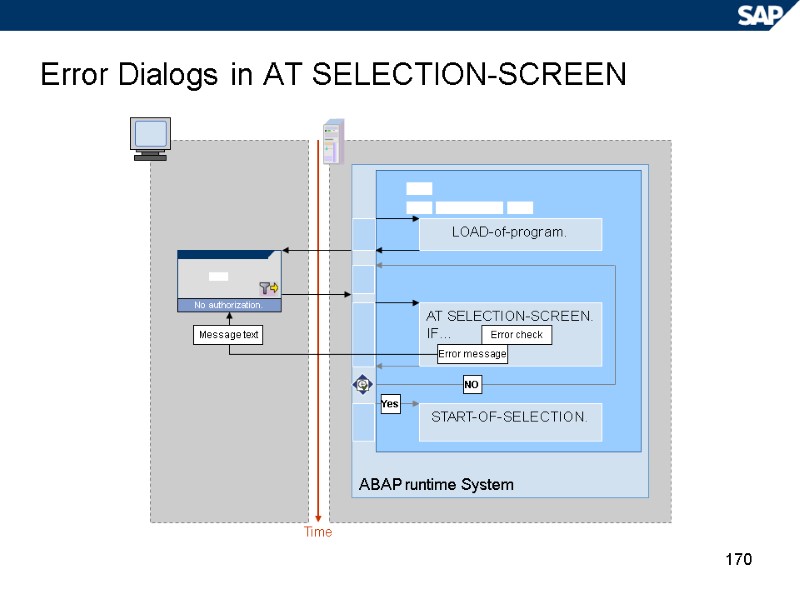
170 Error Dialogs in AT SELECTION-SCREEN Time ABAP runtime System LOAD-of-program. AT SELECTION-SCREEN. IF… START-OF-SELECTION. NO Yes No authorization. Error check Error message Message text
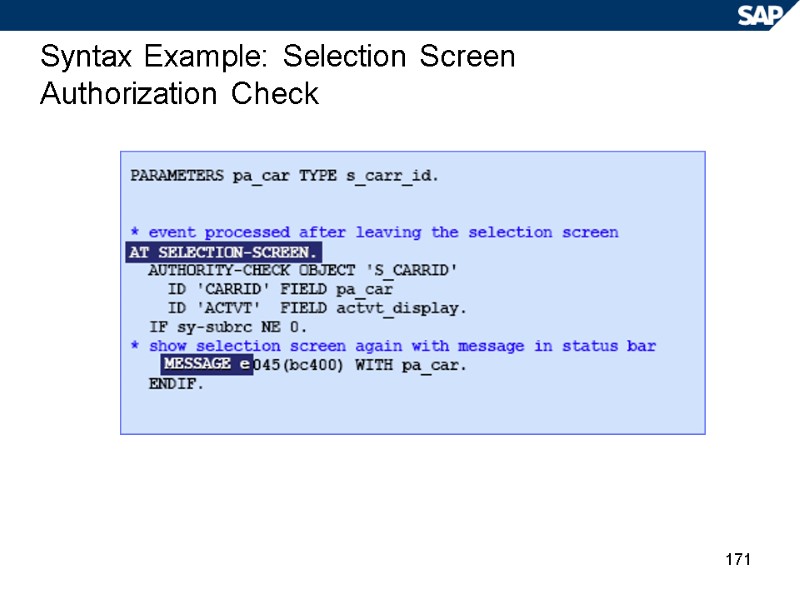
171 Syntax Example: Selection Screen Authorization Check

172 User Dialog List: Unit Summary You are now able to: Describe selection screen attributes and strengths Write a program that allows you to enter intervals on a selection screen and that can be used to restrict the number of data records retrieved from the database Write a program that contains additional input checks for the selection screen and returns to the selection screen if an error occurs

173 EXERCISES!

174 User Dialogs: Screens Contents: Screen Attributes and Strengths Creating Screens Layout Field Attributes Flow Logic Data Transport Using Pushbuttons and Evaluating User Actions

175 User Dialog Screen: Unit Objectives At the conclusion of this unit, you will be able to: Describe screen attributes and strengths Write a program that: Displays data on a screen Allows the user to change some of that data Allows the user to influence further program processing using pushbuttons
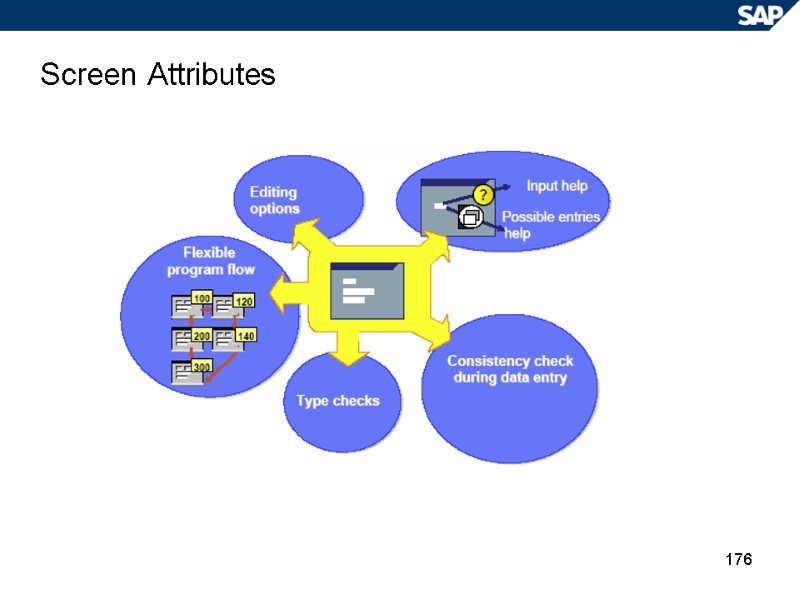
176 Screen Attributes
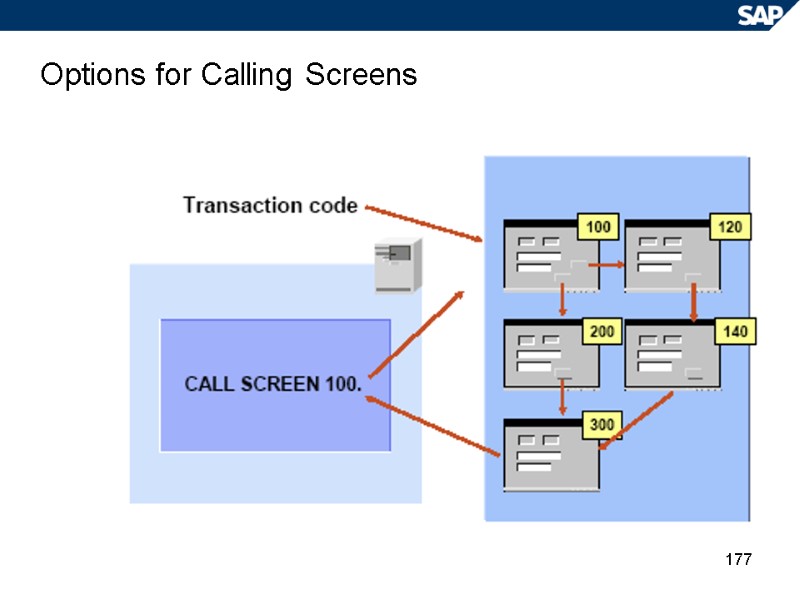
177 Options for Calling Screens
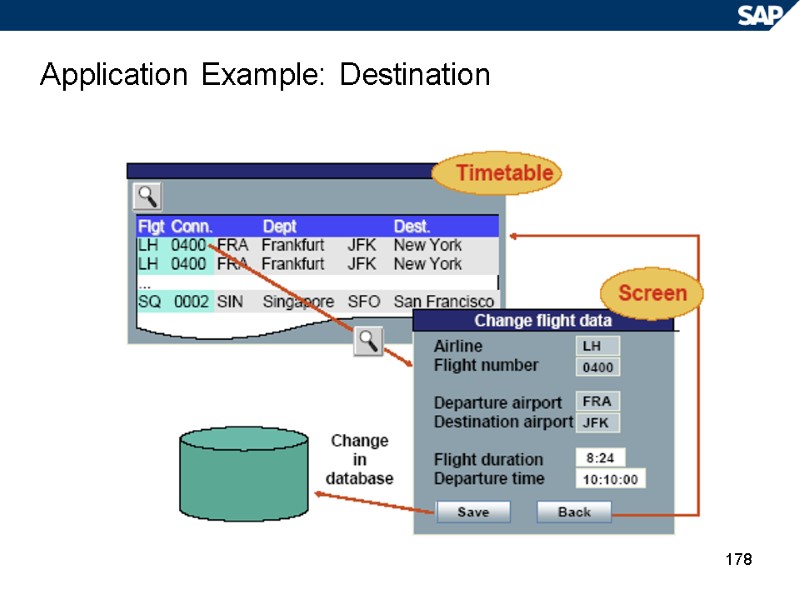
178 Application Example: Destination
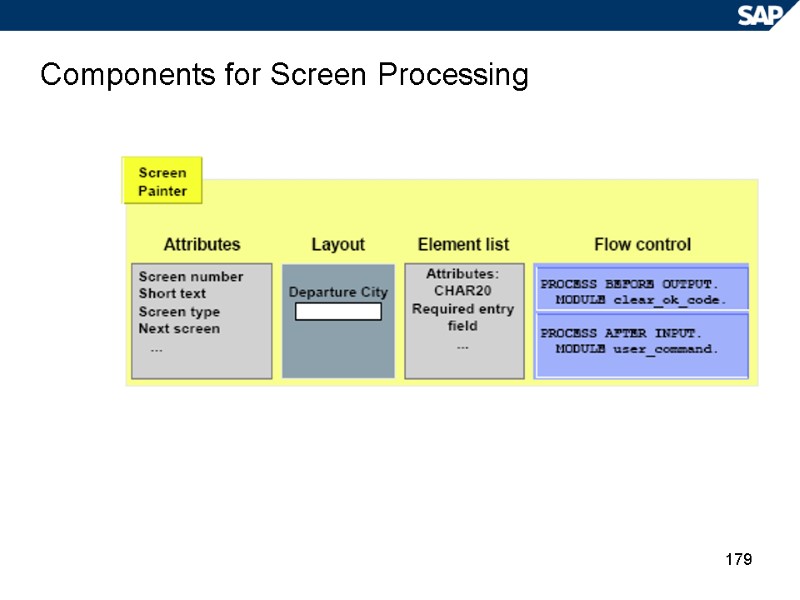
179 Components for Screen Processing
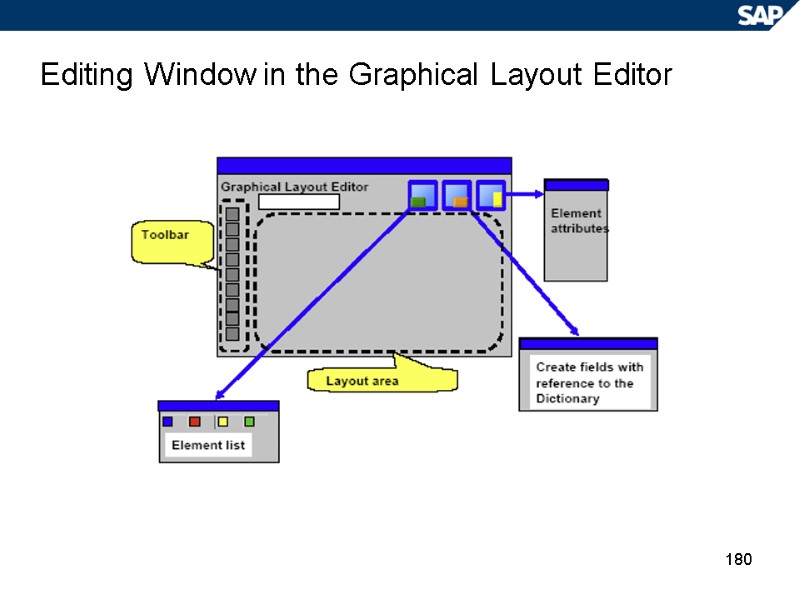
180 Editing Window in the Graphical Layout Editor
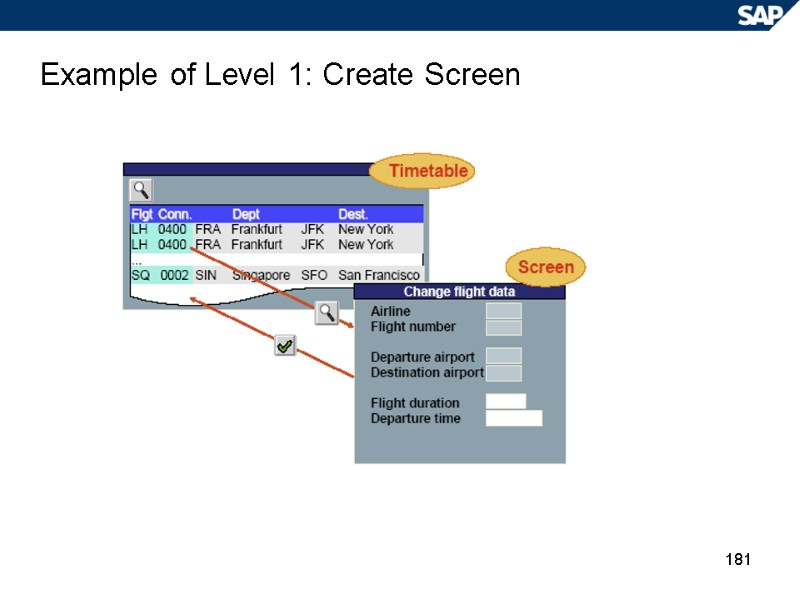
181 Example of Level 1: Create Screen
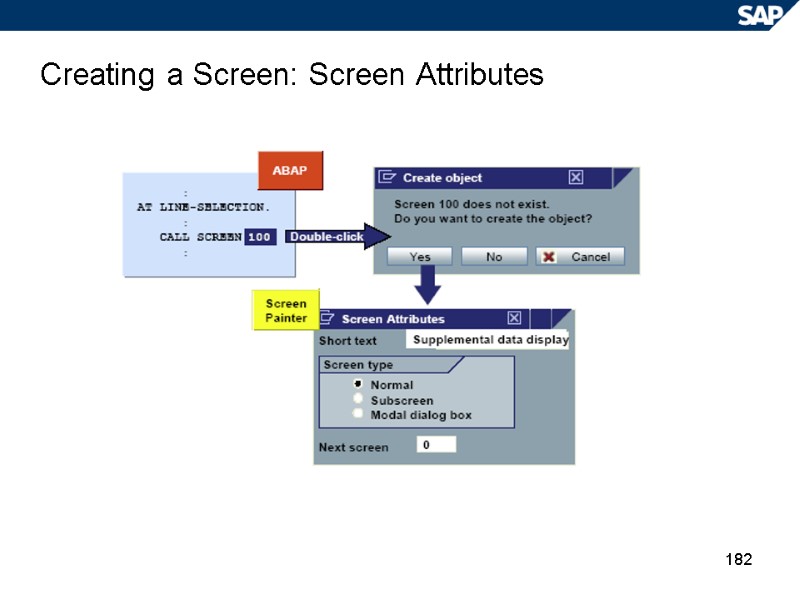
182 Creating a Screen: Screen Attributes
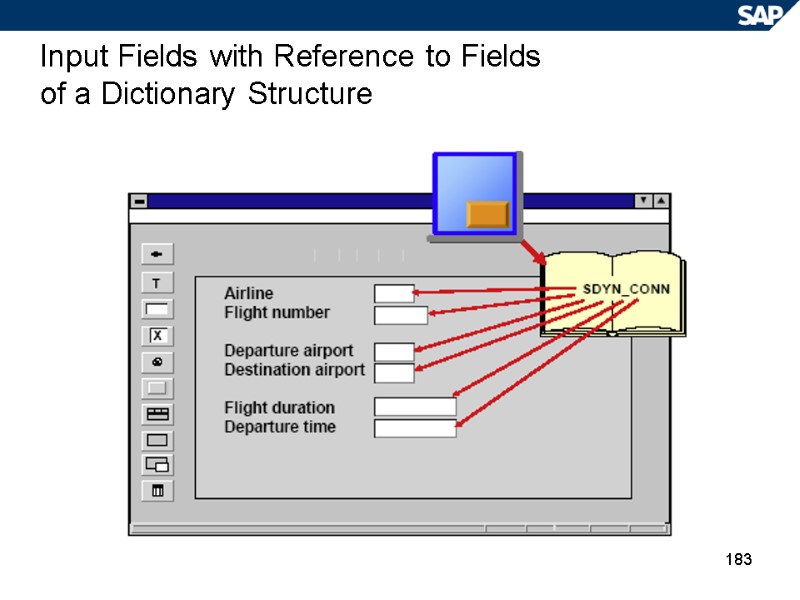
183 Input Fields with Reference to Fields of a Dictionary Structure
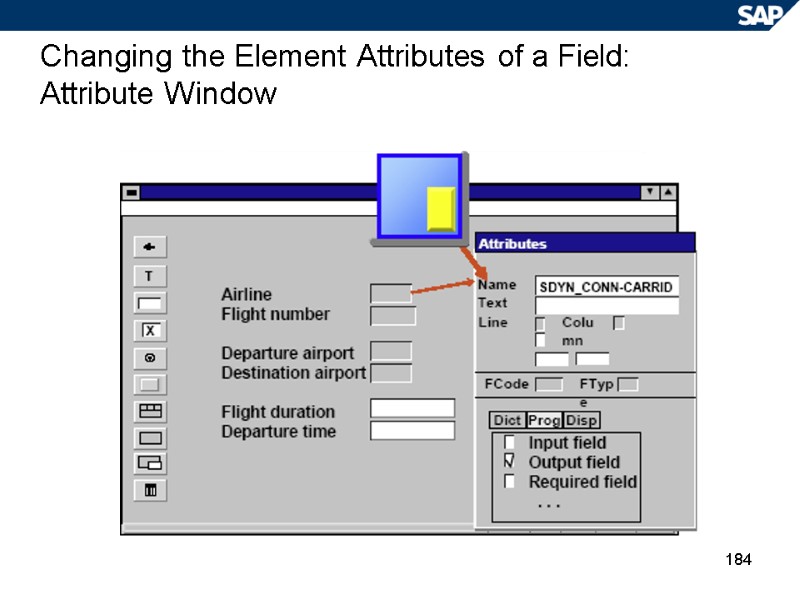
184 Changing the Element Attributes of a Field: Attribute Window
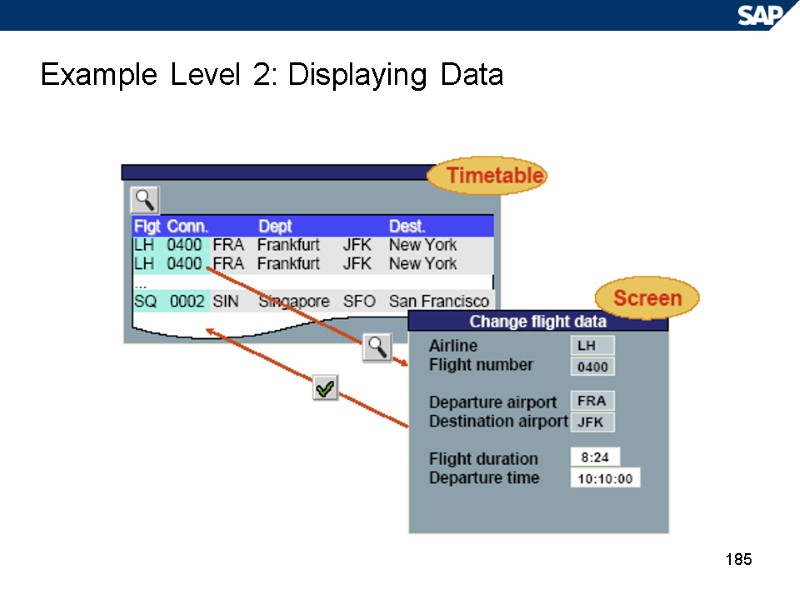
185 Example Level 2: Displaying Data
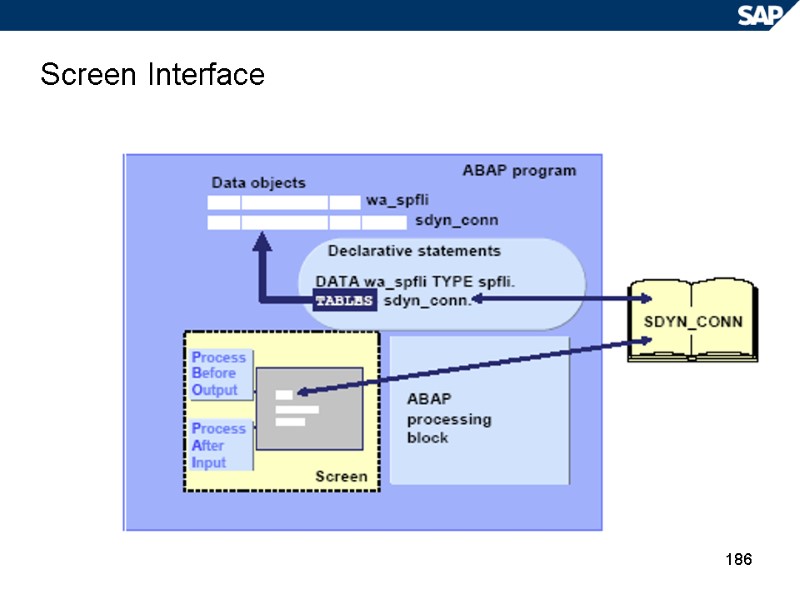
186 Screen Interface
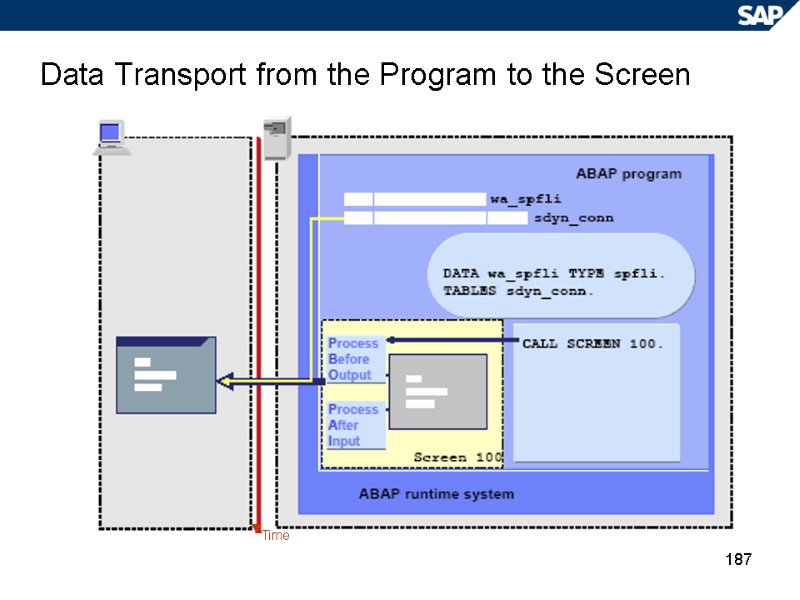
187 Data Transport from the Program to the Screen Time
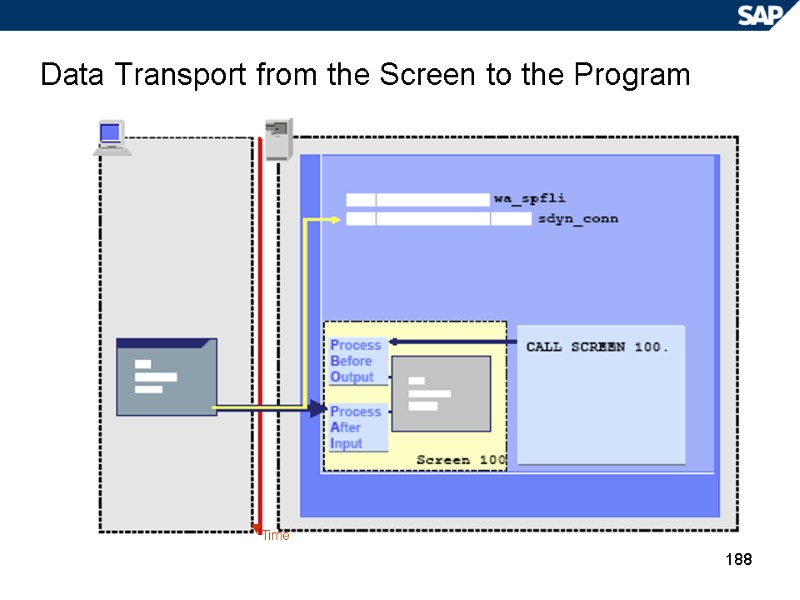
188 Data Transport from the Screen to the Program Time
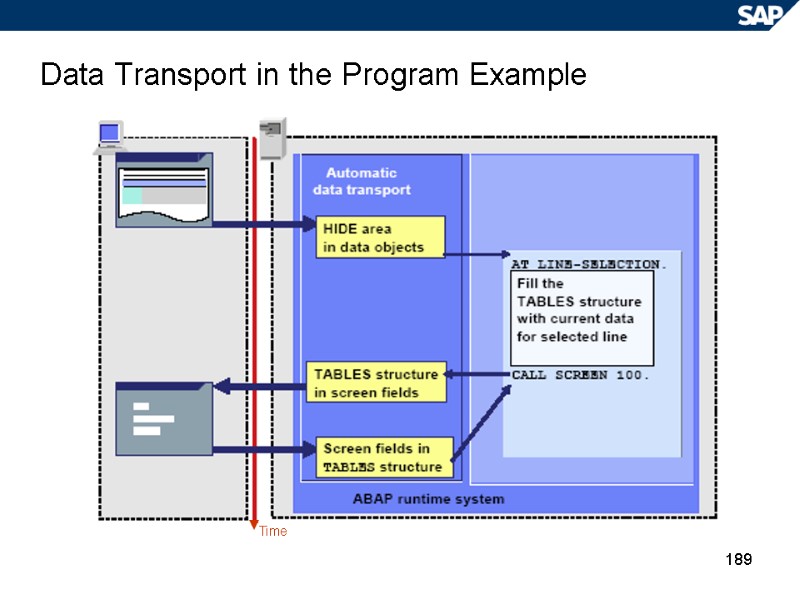
189 Data Transport in the Program Example Time
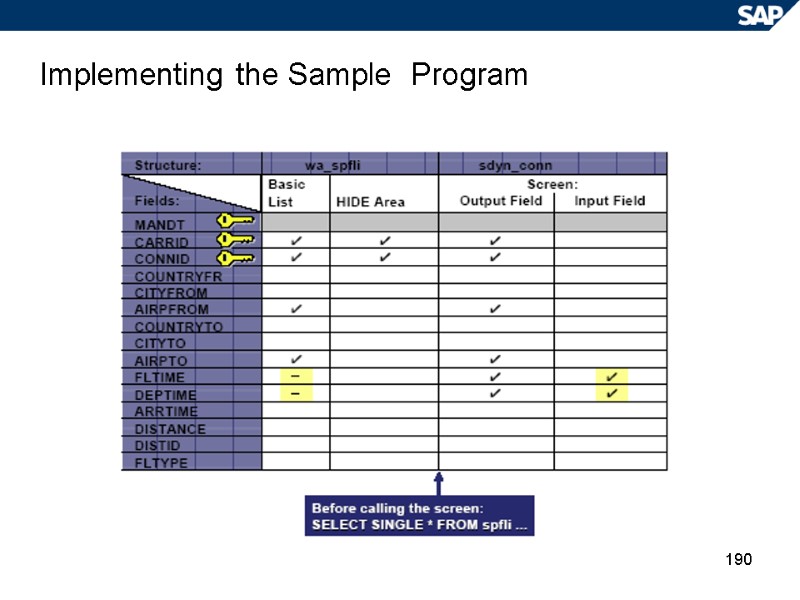
190 Implementing the Sample Program

191 Syntax: Sample Program with Data Transport
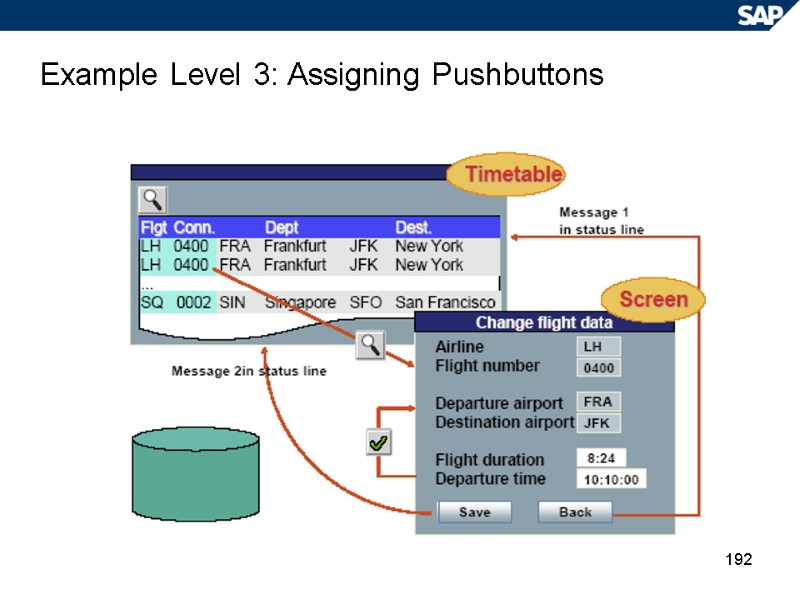
192 Example Level 3: Assigning Pushbuttons
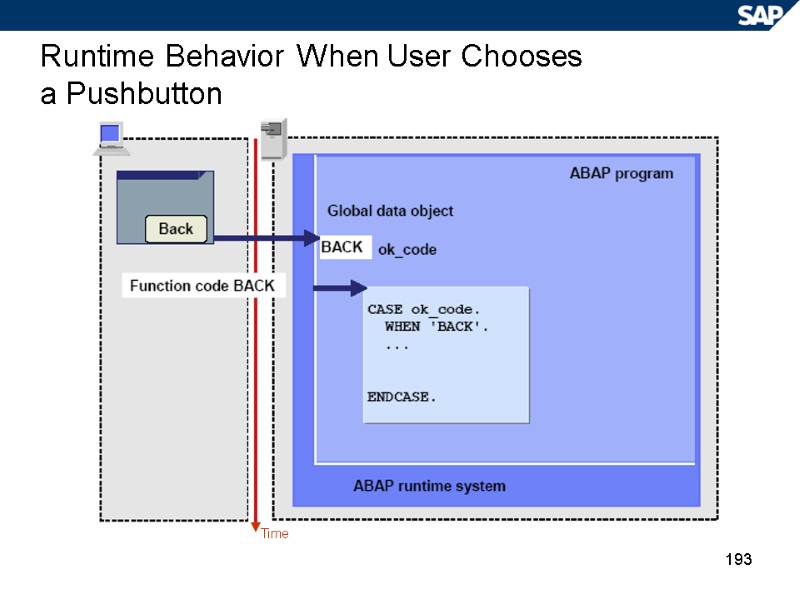
193 Runtime Behavior When User Chooses a Pushbutton Time
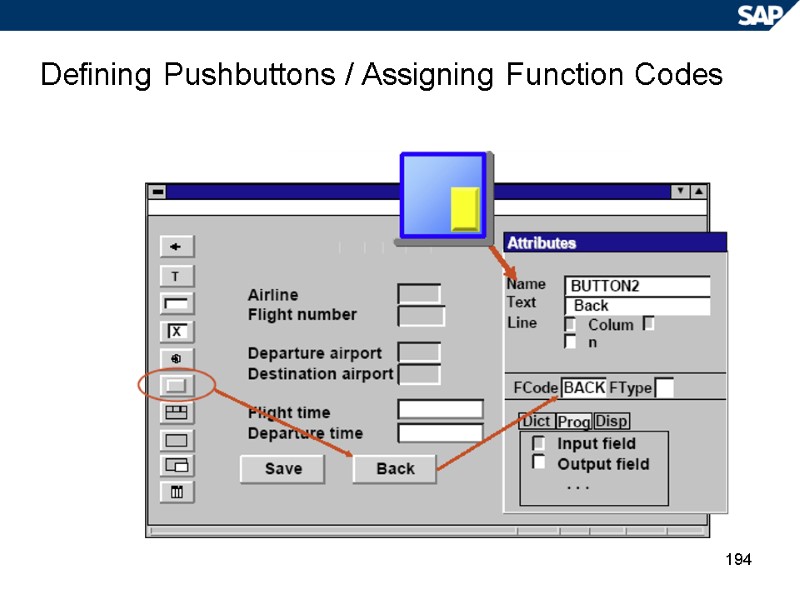
194 Defining Pushbuttons / Assigning Function Codes
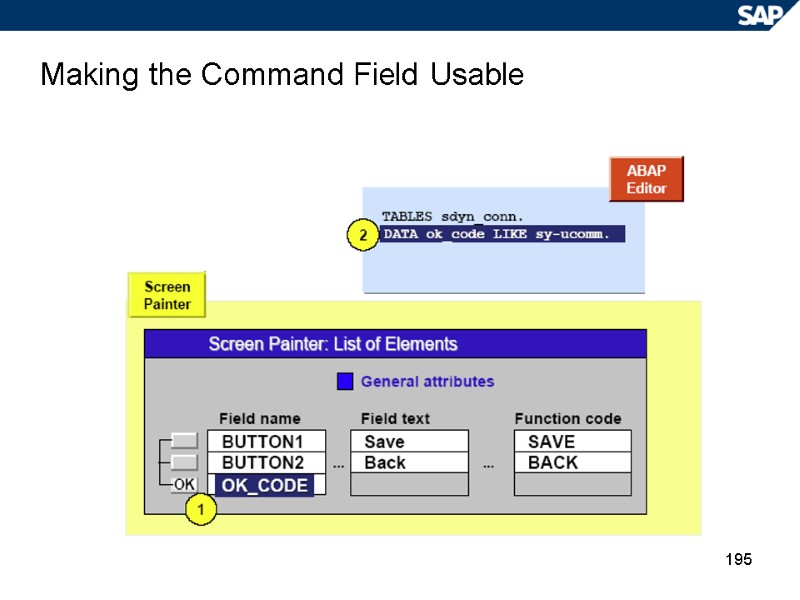
195 Making the Command Field Usable
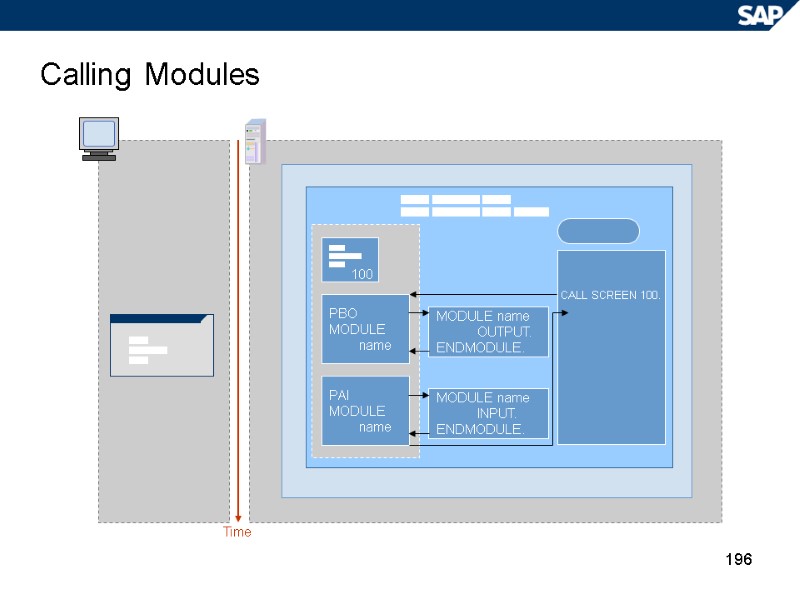
196 Calling Modules Time CALL SCREEN 100. PBO MODULE name 100 PAI MODULE name MODULE name OUTPUT. ENDMODULE. MODULE name INPUT. ENDMODULE.
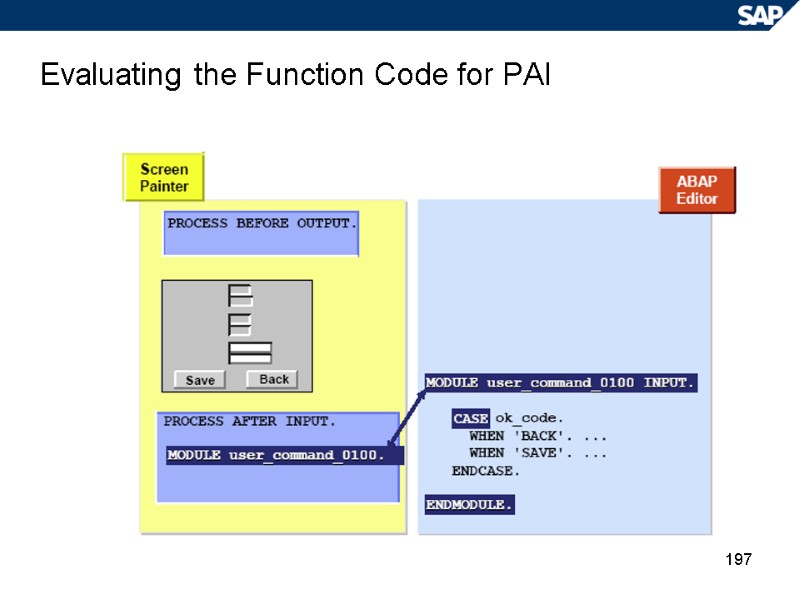
197 Evaluating the Function Code for PAI
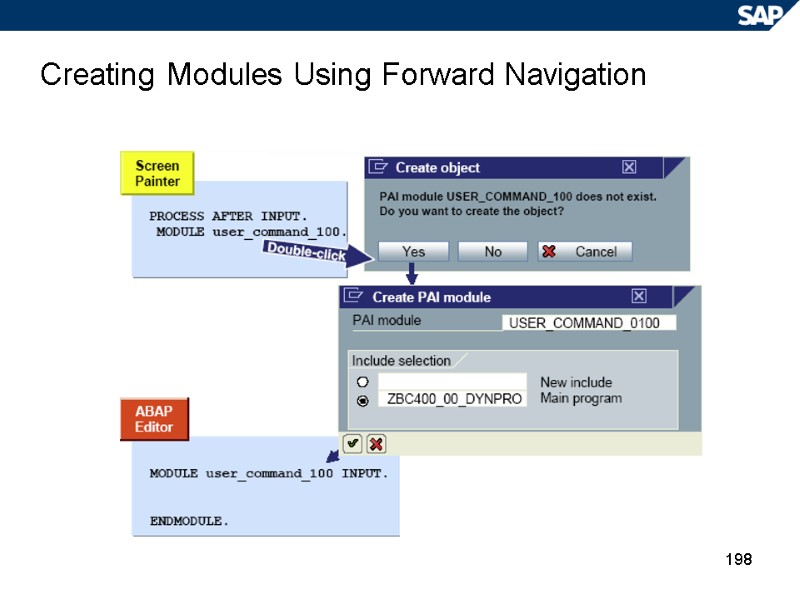
198 Creating Modules Using Forward Navigation
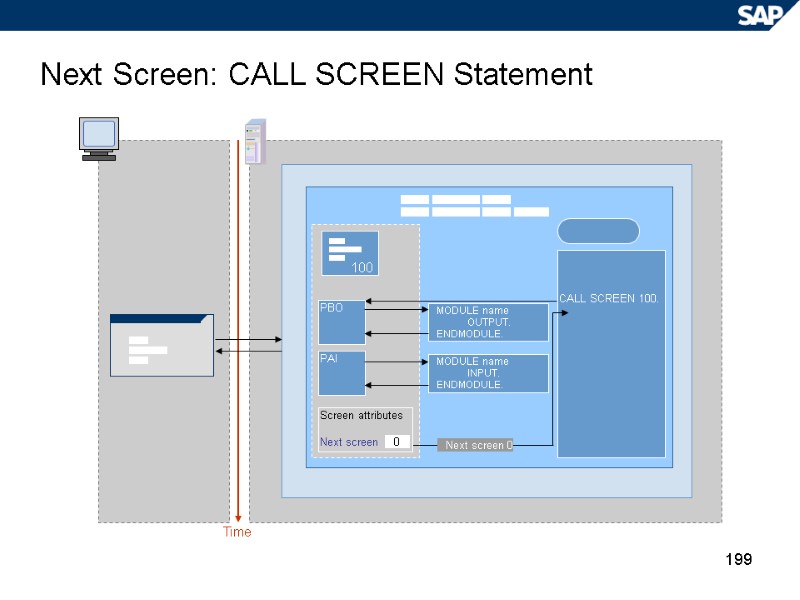
199 Next Screen: CALL SCREEN Statement Time CALL SCREEN 100. PAI MODULE name OUTPUT. ENDMODULE. MODULE name INPUT. ENDMODULE. Screen attributes Next screen 0 Next screen 0 PBO
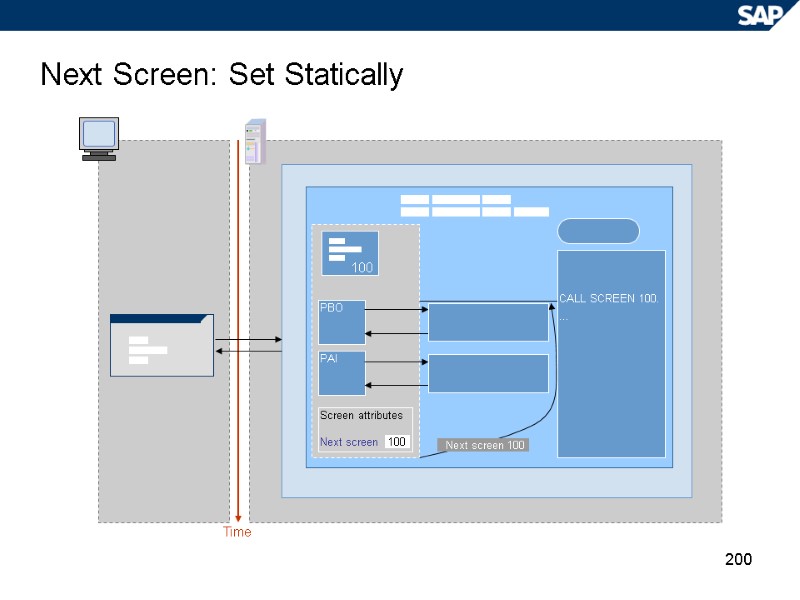
200 Next Screen: Set Statically Time PBO PAI Screen attributes Next screen 100 Next screen 100 CALL SCREEN 100. …
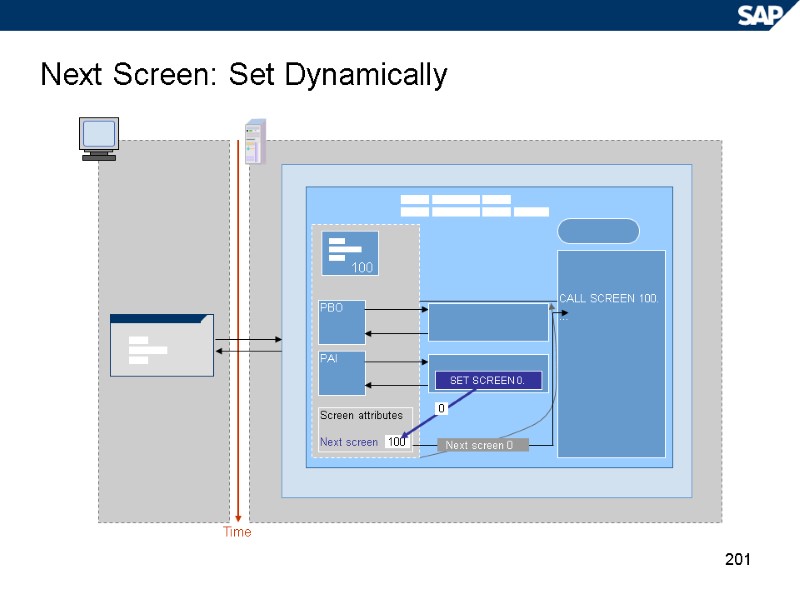
201 Next Screen: Set Dynamically Time PBO PAI Screen attributes Next screen 100 CALL SCREEN 100. … SET SCREEN 0. 0 Next screen 0

202 Syntax Example: Evaluating the Function Codes
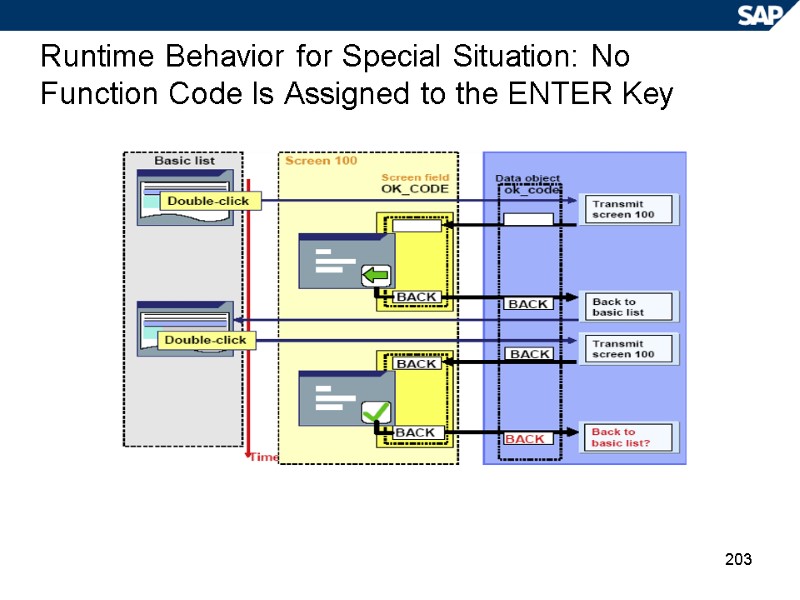
203 Runtime Behavior for Special Situation: No Function Code Is Assigned to the ENTER Key
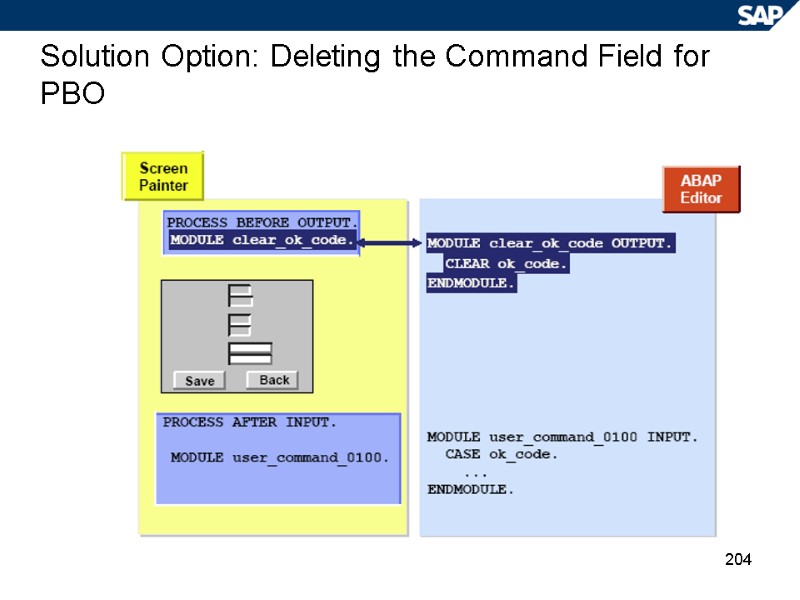
204 Solution Option: Deleting the Command Field for PBO
205 User Dialog Screen: Unit Summary You are now able to: Describe screen attributes and strengths Write a program that: Displays data on a screen Allows the user to change some of that data Allows the user to influence further program processing using pushbuttons

206 EXERCISES!

207 Interfaces Contents: Creating interfaces using the Menu Painter with the subobjects: Title Menu bar Standard toolbar Application toolbar Function key assignment

208 Interfaces: Unit Objectives At the conclusion of this unit, you will be able to: Create a GUI title Create a GUI status for a list and a screen that contains the following subobjects: Menu bar Standard toolbar Application toolbar Function key assignment
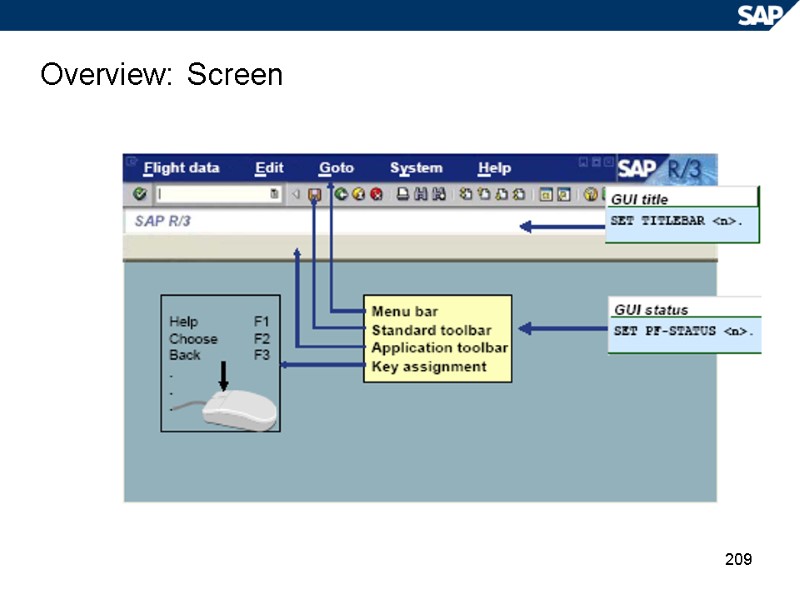
209 Overview: Screen
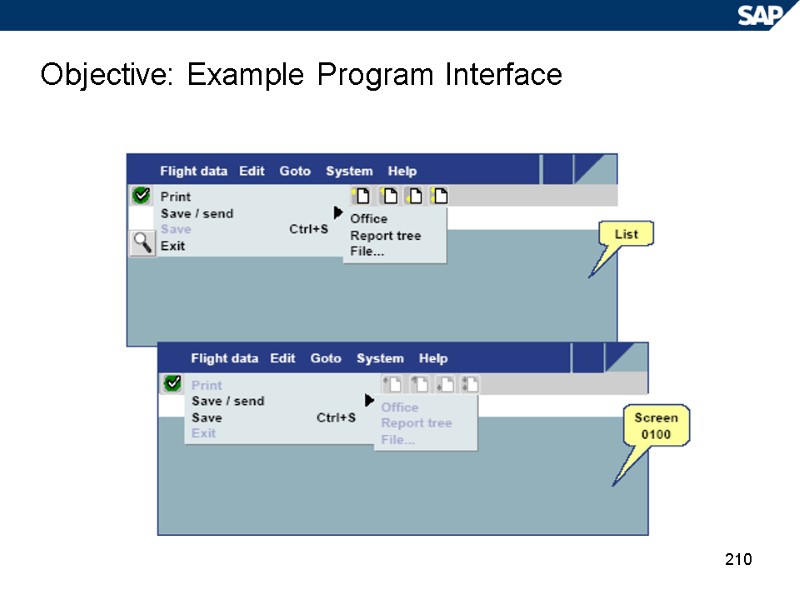
210 Objective: Example Program Interface
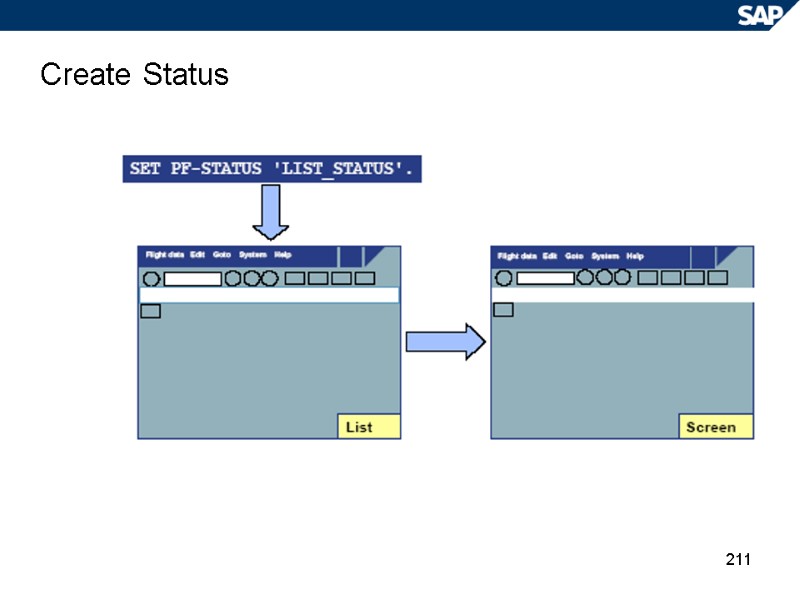
211 Create Status
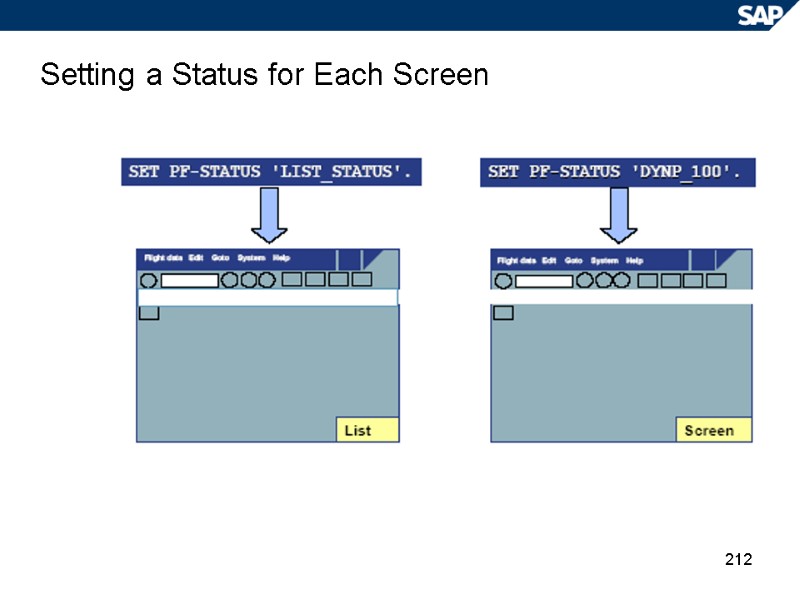
212 Setting a Status for Each Screen
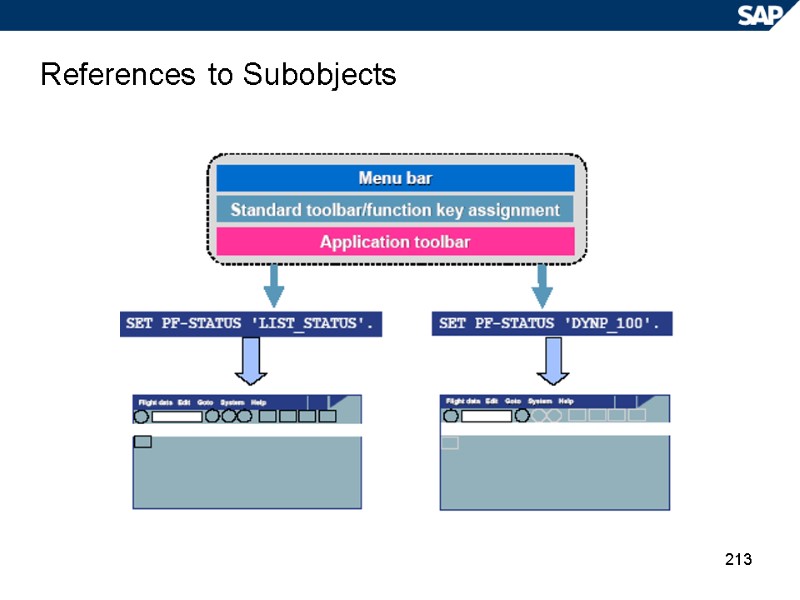
213 References to Subobjects
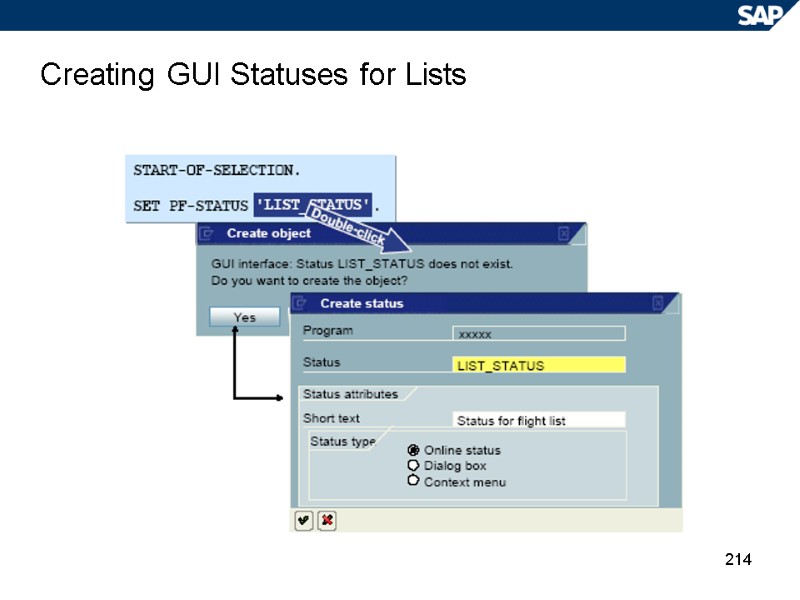
214 Creating GUI Statuses for Lists
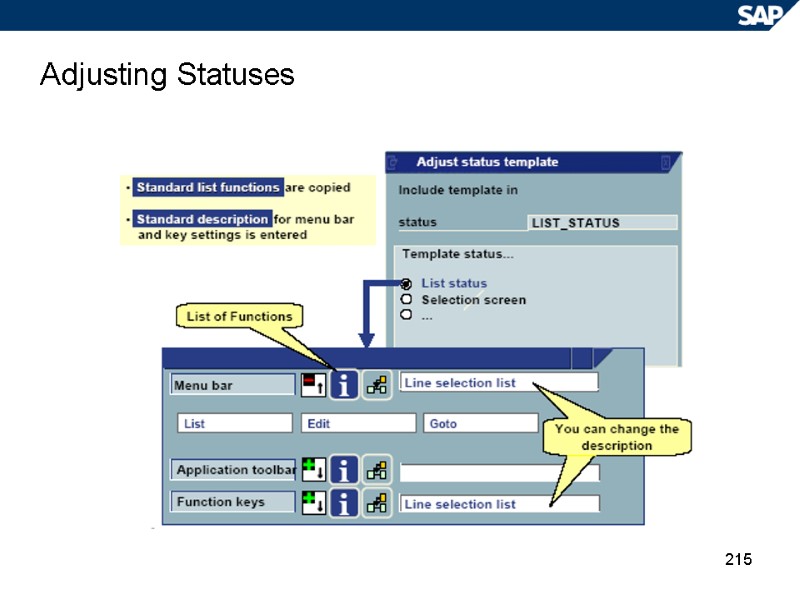
215 Adjusting Statuses
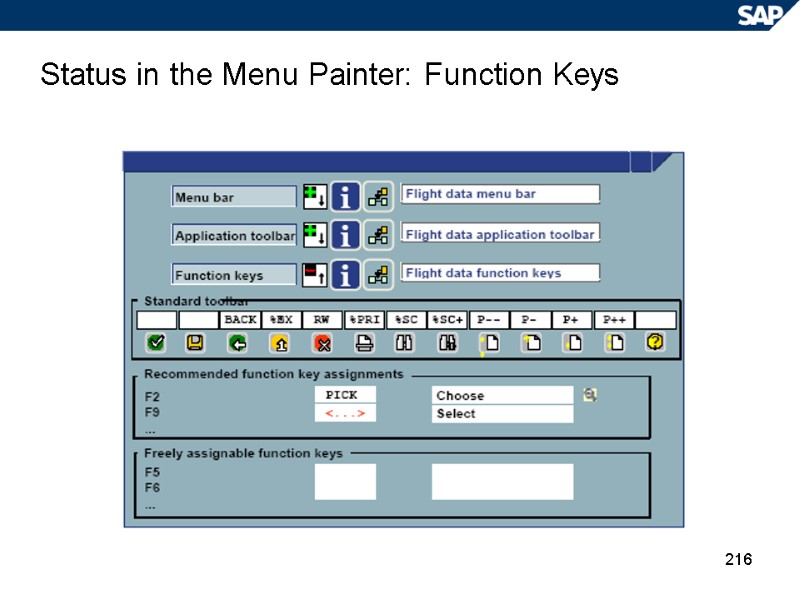
216 Status in the Menu Painter: Function Keys
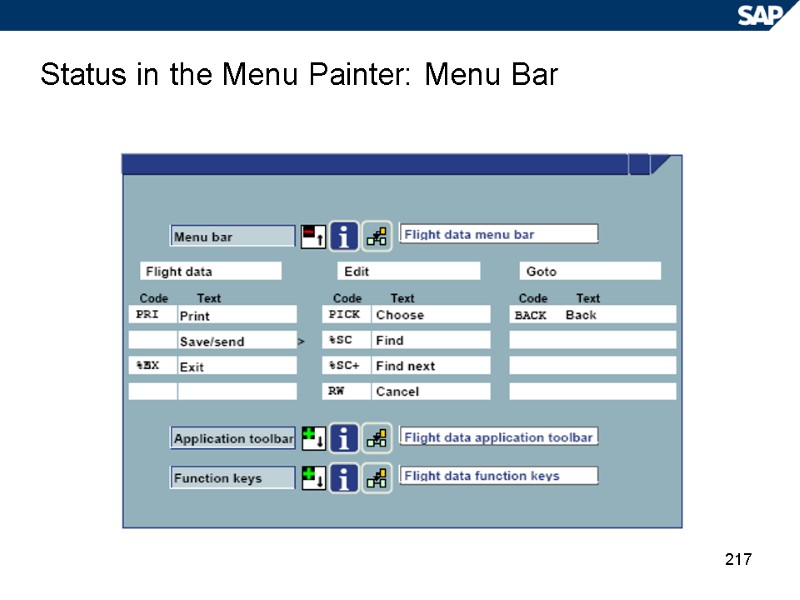
217 Status in the Menu Painter: Menu Bar
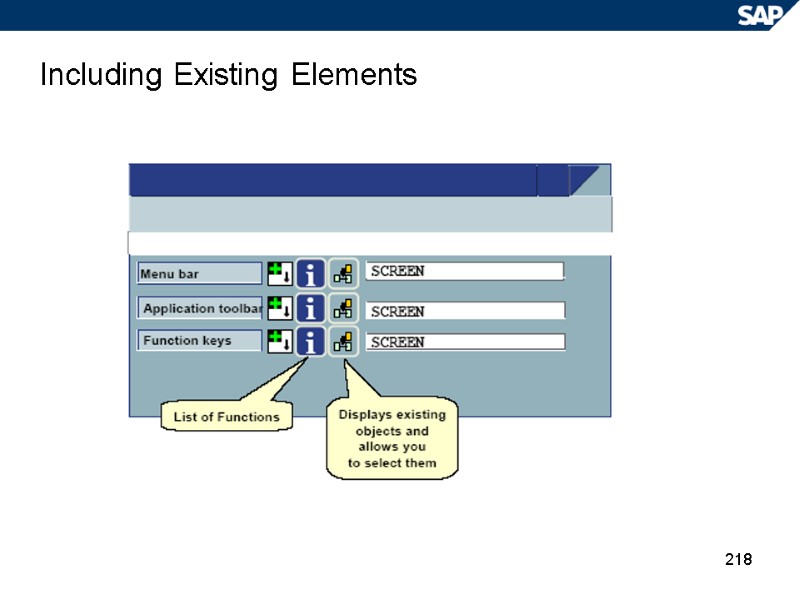
218 Including Existing Elements
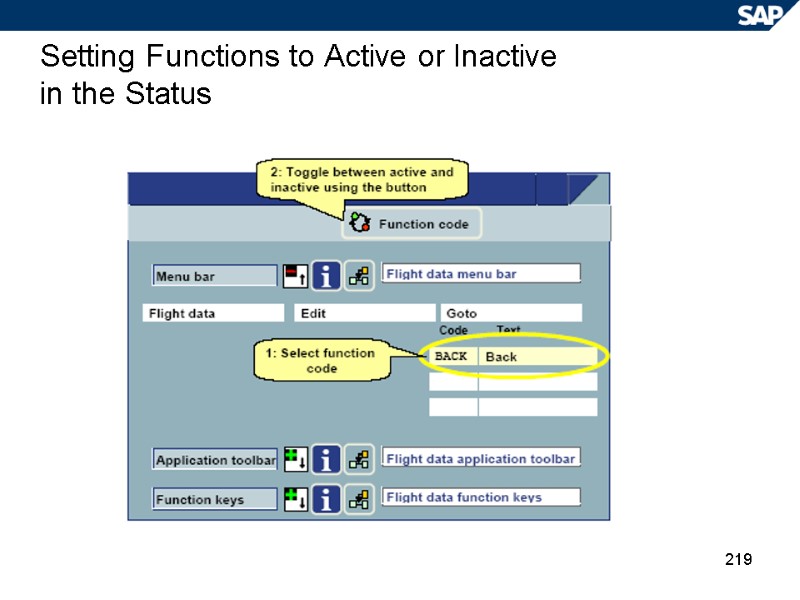
219 Setting Functions to Active or Inactive in the Status
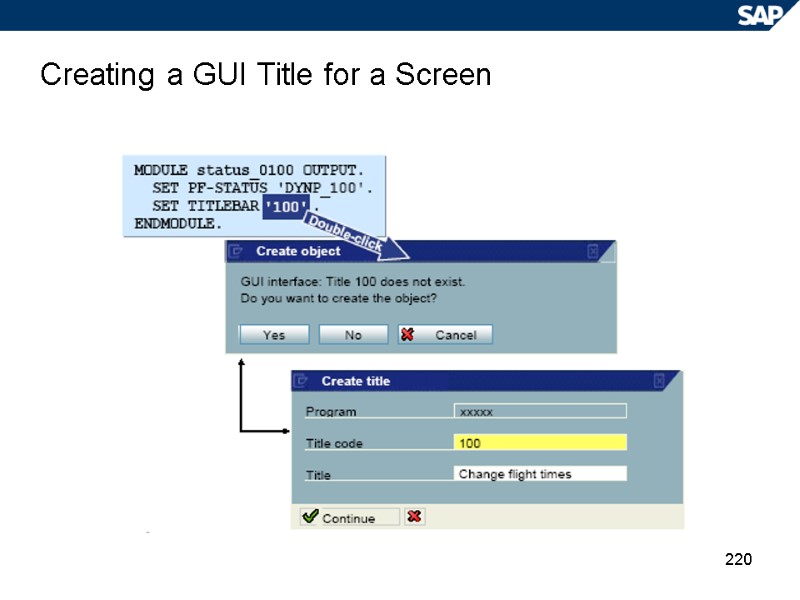
220 Creating a GUI Title for a Screen

221 Cross-Program Modularization Contents: Working with Function Modules Working with Methods Working with BAPIs

222 Cross-Program Modularization: Unit Objectives At the conclusion of this unit, you will be able to: Acquire information on function modules Include function module calls in your program Include object instances and method calls in your program Include the ALV grid control for displaying data in a fixed screen area Acquire information BAPIs Include BAPI calls in your program
223 Working with Function Modules Working with Function Modules Working with Methods Working with BAPIs
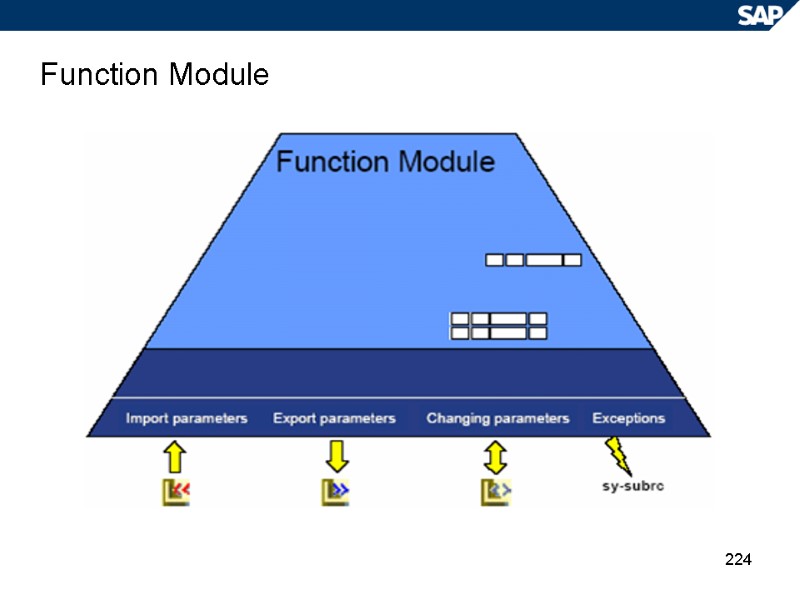
224 Function Module
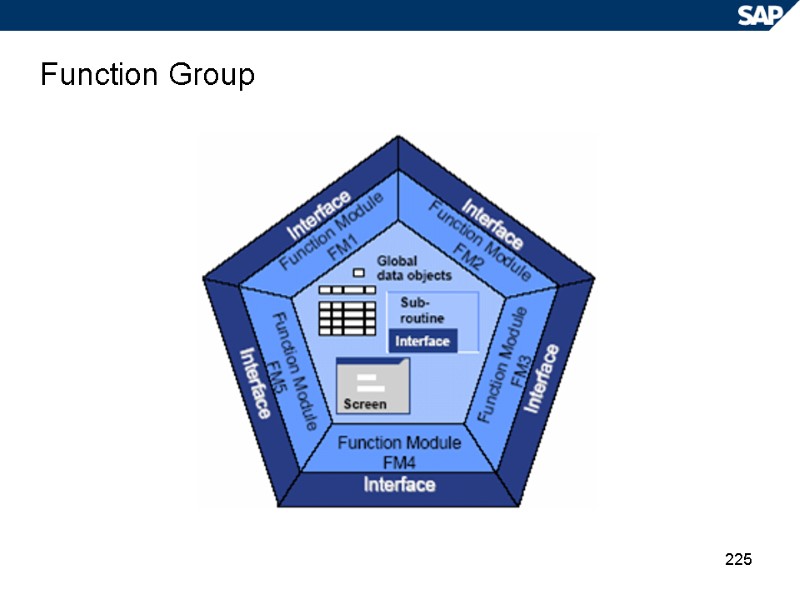
225 Function Group
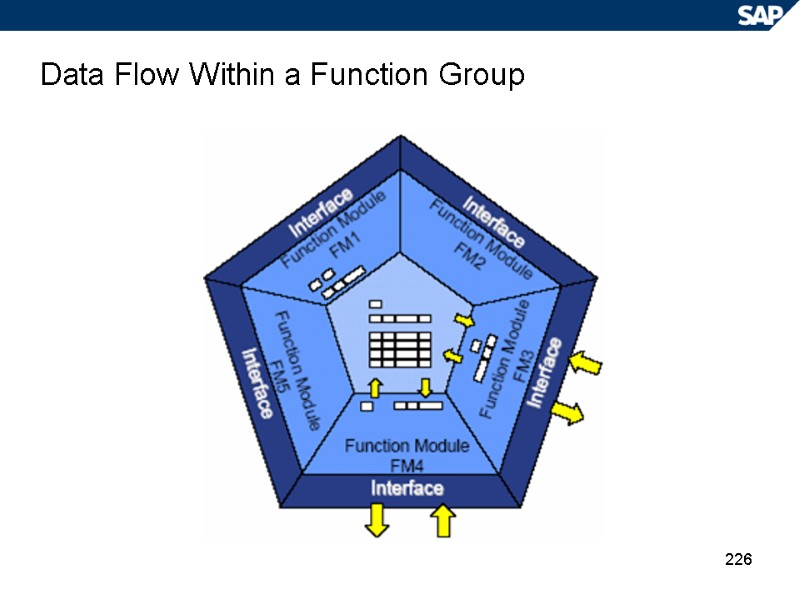
226 Data Flow Within a Function Group
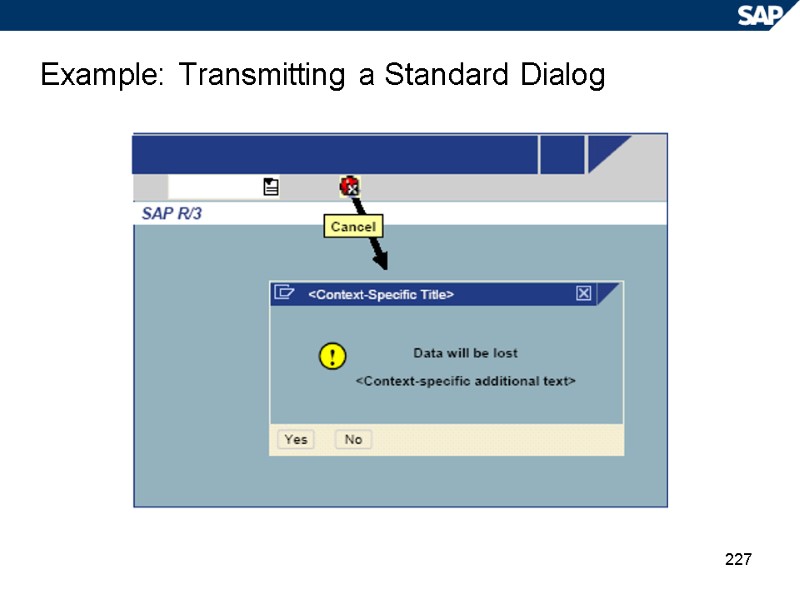
227 Example: Transmitting a Standard Dialog
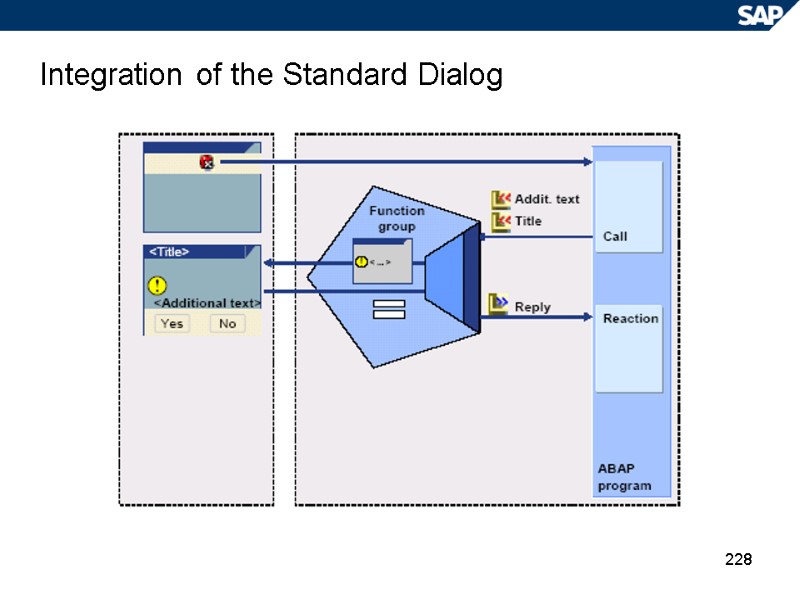
228 Integration of the Standard Dialog
229 Searching for Function Modules Searching within a particular application component: Application hierarchy Searching with the help of a program that uses the function module being searched for: Search in the ABAP Editor for the CALL FUNCTION statement Change to debugging mode during program execution and set breakpoint in the CALL FUNCTION statement If the function module transmits a screen, display the program name and the screen number using F1 and technical information or navigate directly
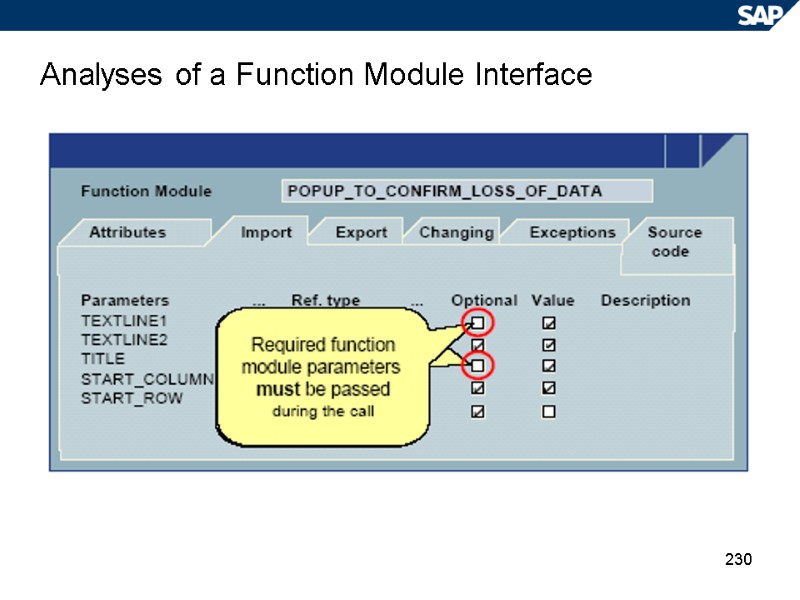
230 Analyses of a Function Module Interface
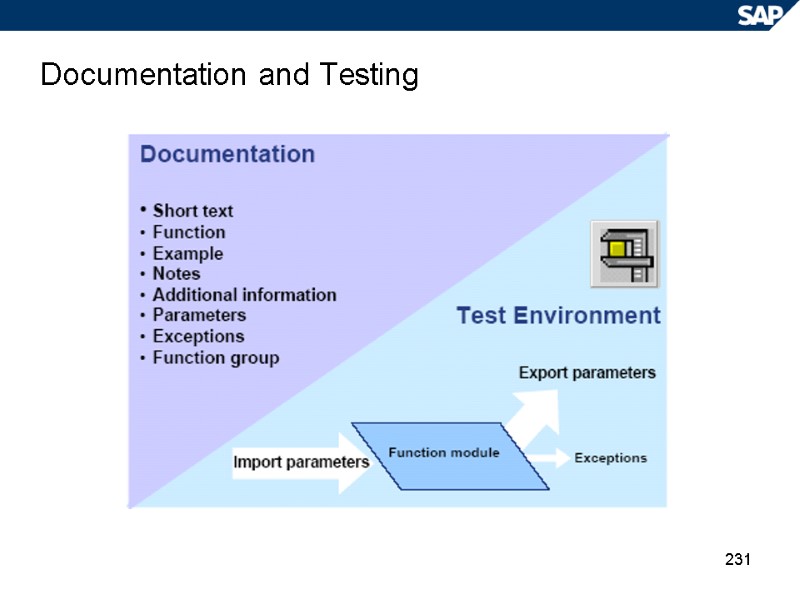
231 Documentation and Testing
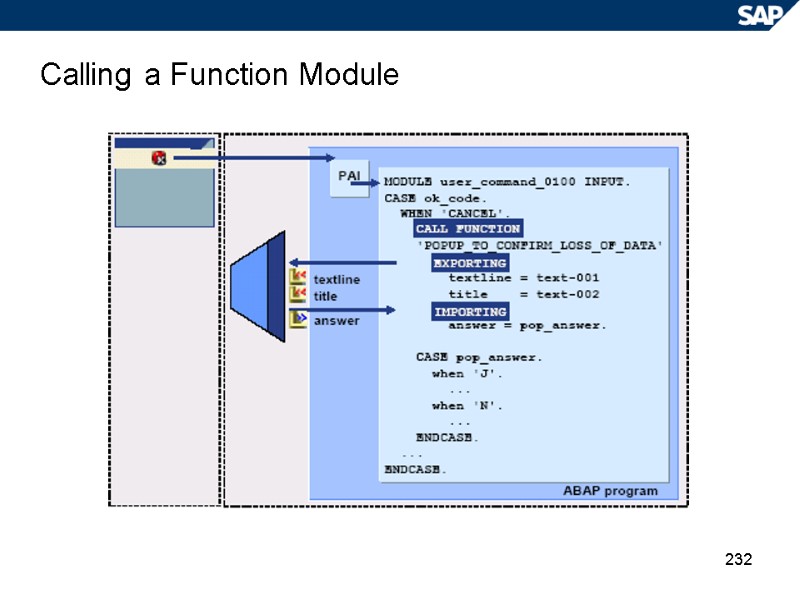
232 Calling a Function Module
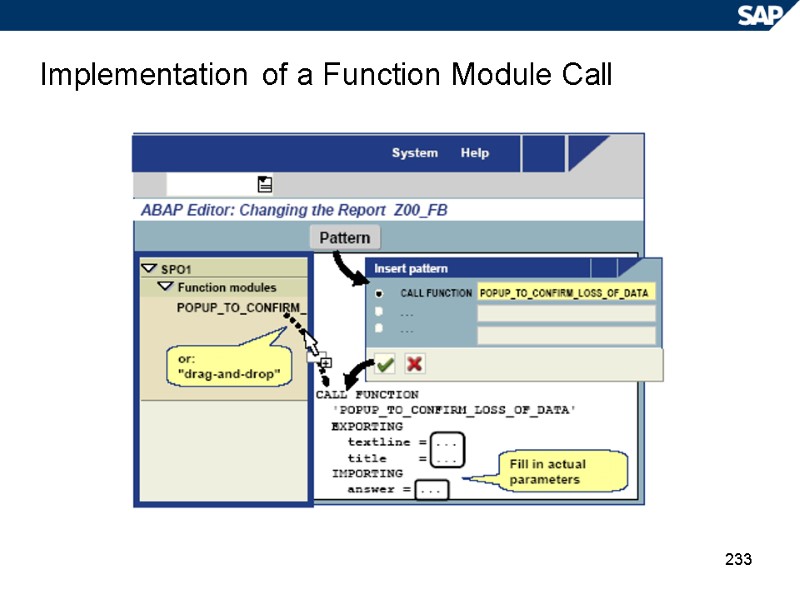
233 Implementation of a Function Module Call
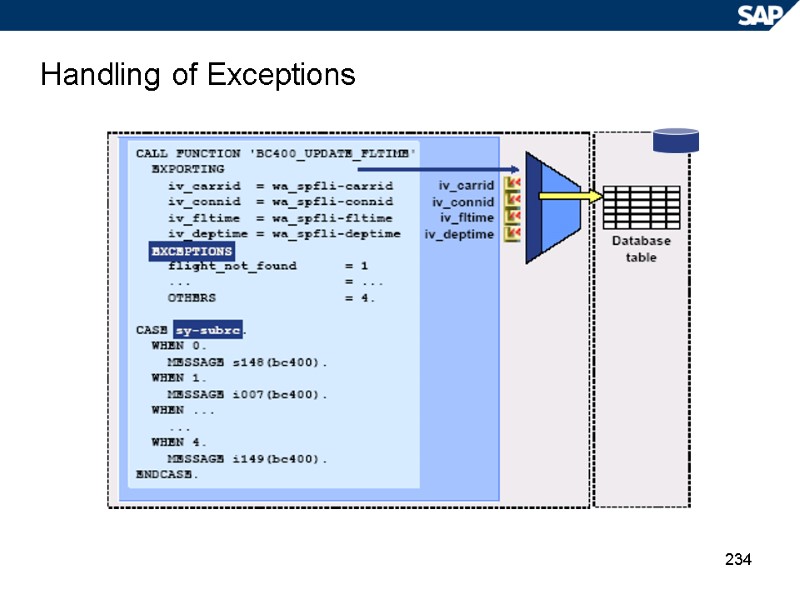
234 Handling of Exceptions

235 Working with Methods Working with Function Modules Working with Methods Working with BAPIs
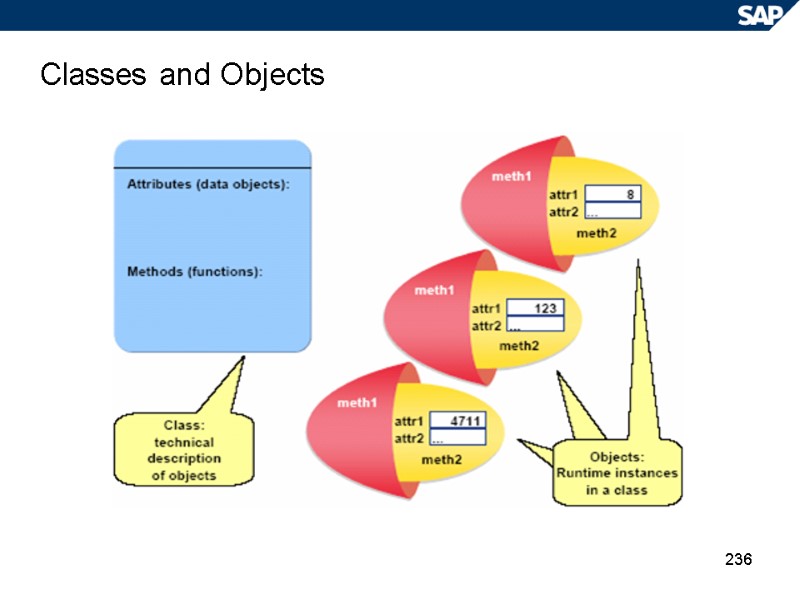
236 Classes and Objects
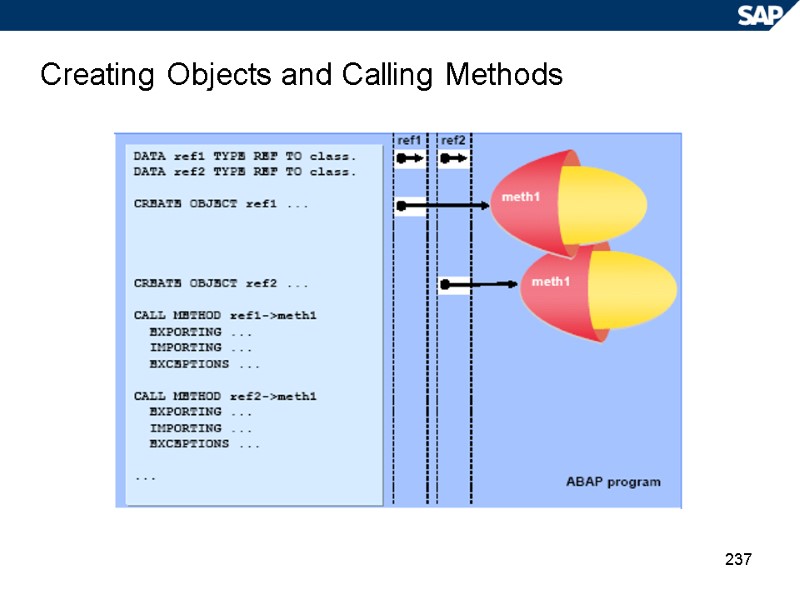
237 Creating Objects and Calling Methods
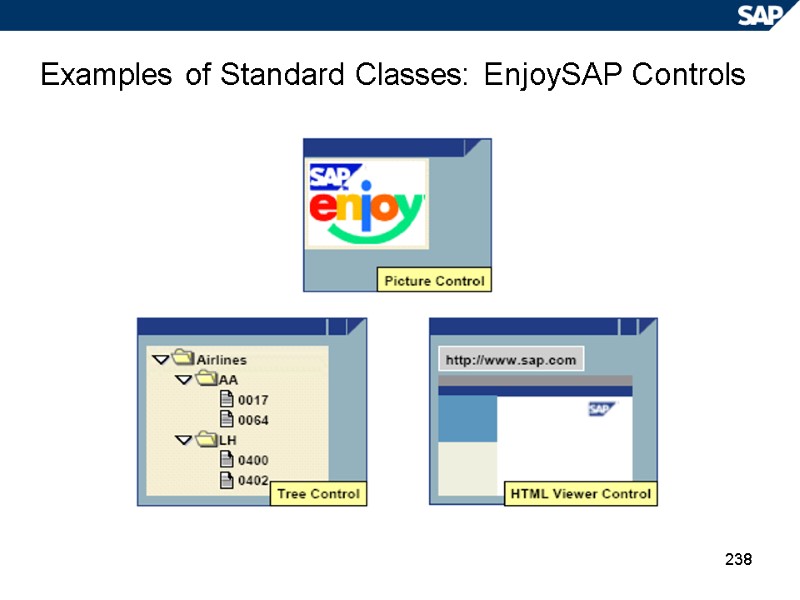
238 Examples of Standard Classes: EnjoySAP Controls
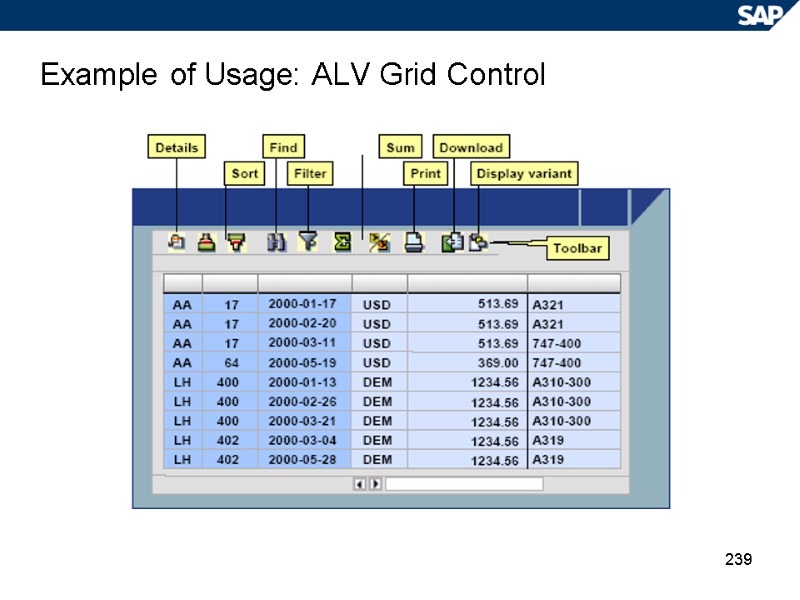
239 Example of Usage: ALV Grid Control
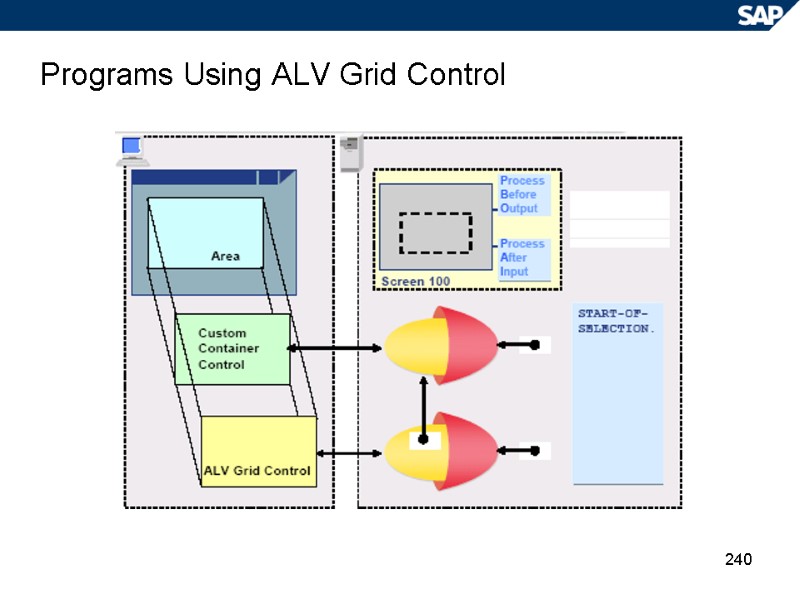
240 Programs Using ALV Grid Control
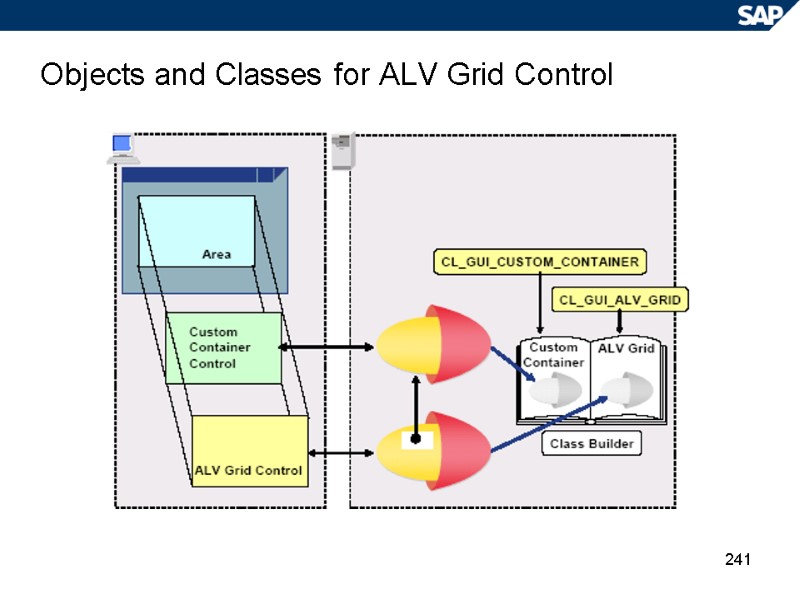
241 Objects and Classes for ALV Grid Control
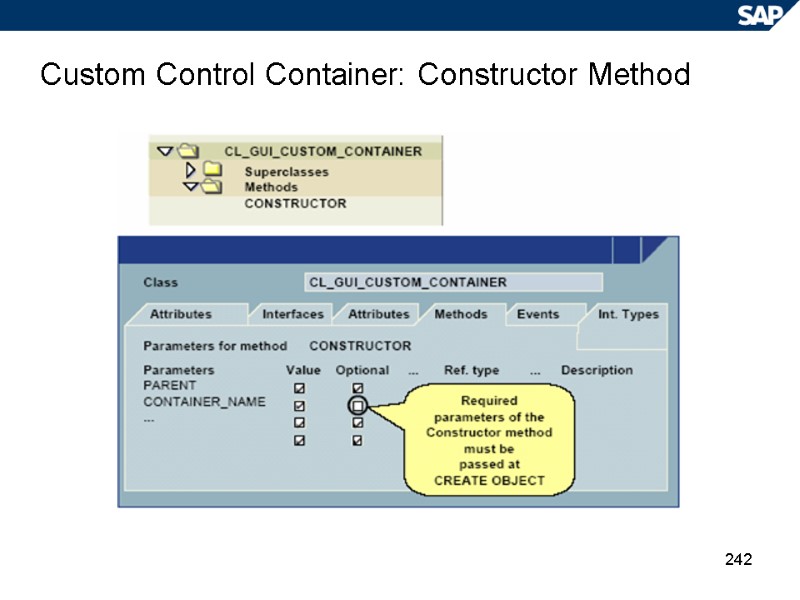
242 Custom Control Container: Constructor Method
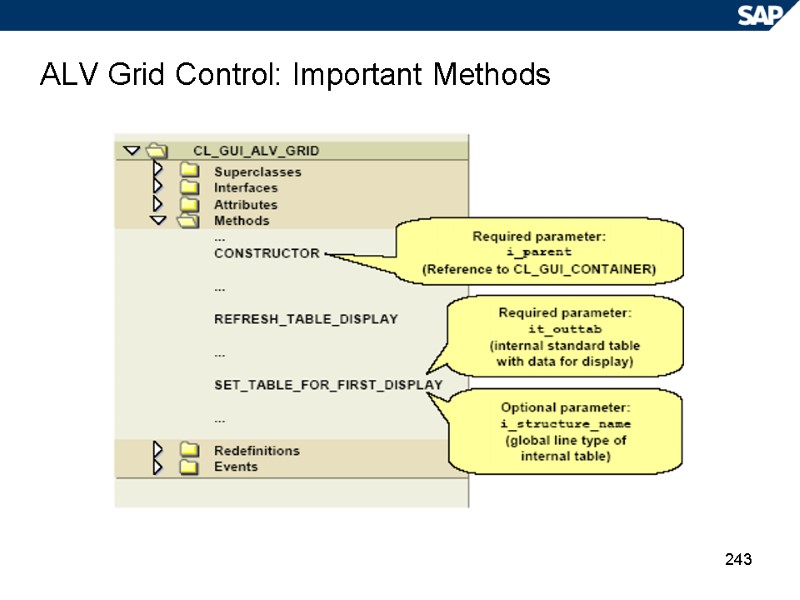
243 ALV Grid Control: Important Methods
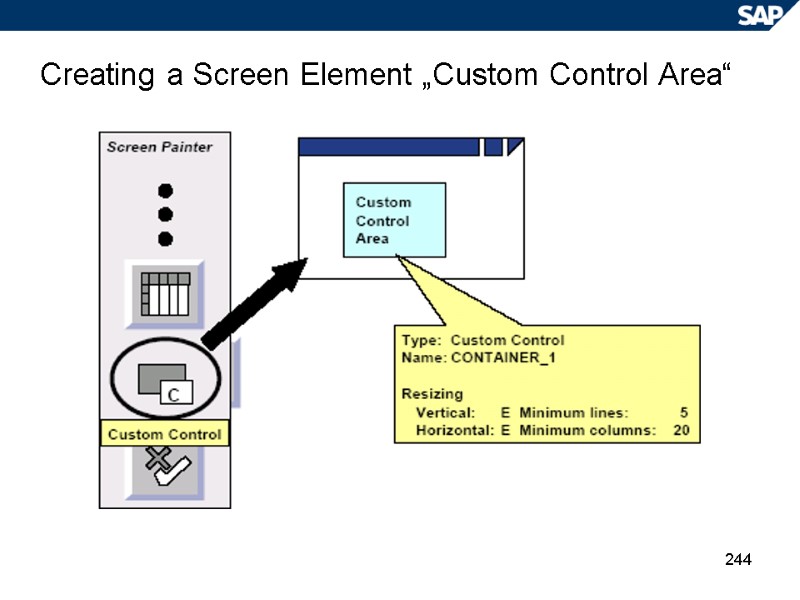
244 Creating a Screen Element „Custom Control Area“

245 Defining Reference Variables
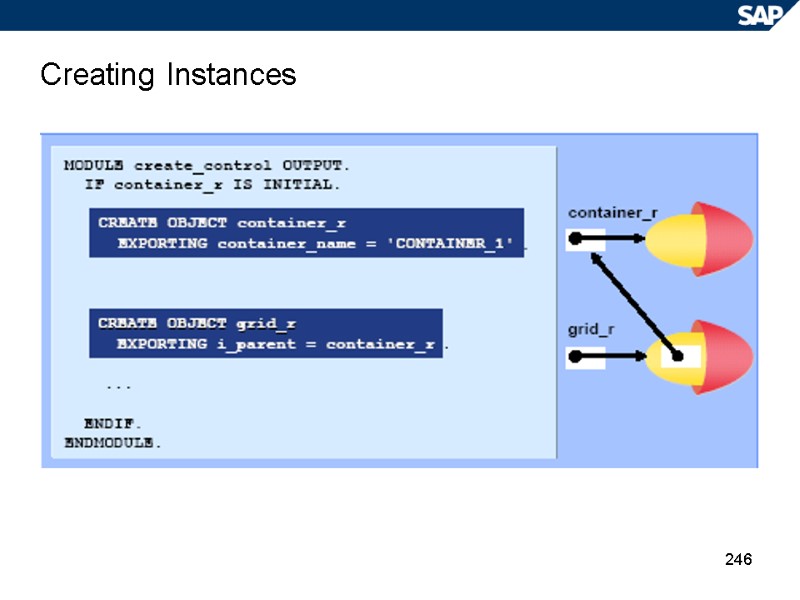
246 Creating Instances
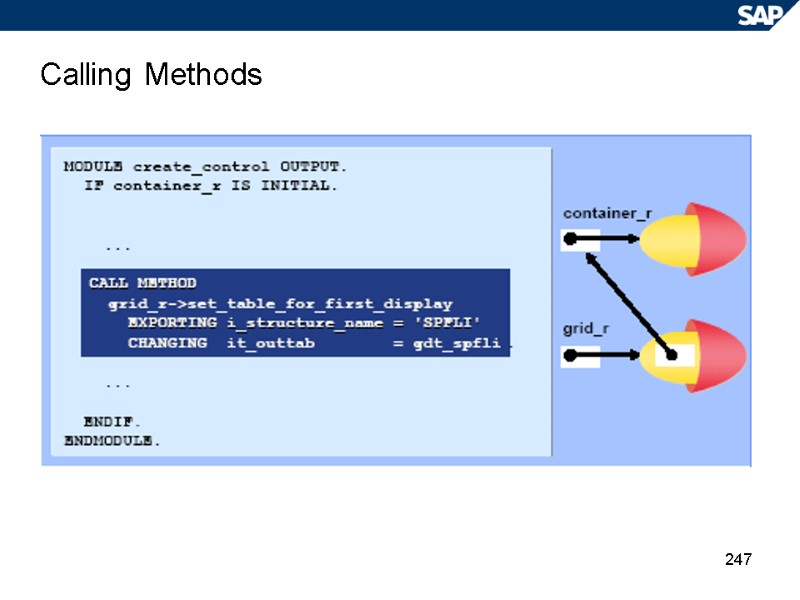
247 Calling Methods
248 Working with Function Modules Working with Function Modules Working with Methods Working with BAPIs

249 Business Application Programming Interface A BAPI is a well-defined interface to processes and data of a business application system, implemented as a business object method in the Business Object Repository (BOR).
16460-univ_abap_workbench_bc400.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 249

