3e9af6cc60e979819382c7ecfc519949.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 15

A Web-based Automatic Evaluation System Chittaranjan Mandal (School of IT, IIT Kharagpur, India) Chris Reade (Kingston Business School, Kingston University, UK) Vijay Luxmi Sinha (School of IT, IIT Kharagpur, India) ECEL 2004 Mandal, Reade, Sinha

Automated Evaluation • • • Motivation Other systems and choices Our design and choices Details of assignment set-up Conclusions and ‘The bigger picture’ ECEL 2004 Mandal, Reade, Sinha

Programming assignments (at IIT Kharagpur) 9600 to mark per semester – Setting assignment (5 hrs? ) – Distribution and collection (Automated by WBCM) – Marking (@20 m each) = 3200 hrs = 20 people * 20 working days each For sophisticated testing maybe 5 times this. ECEL 2004 Mandal, Reade, Sinha

Automated marking is a must Additional Benefits: – automated rapid feedback (resubmission possibilities) – consistency – plagiarism checking – rigorous testing (suite) ECEL 2004 Mandal, Reade, Sinha

Different to simple test and assessment What can be automatically assessed? • Program behavior (execution) – – – Correctness testing Performance testing Whole program and/or components Data (randomising + special test cases) Large numbers of runs • Analysis of structure and style (still very hard to do) ECEL 2004 Mandal, Reade, Sinha

Other Systems • Full Automation versus Assistance – examples: Try (1989) / ASSYST 1997 • Feedback Only versus Full Management – examples: Submit (2003) / Ceilidh (1993) • Eval of Design / Behavior / Components • Fixed / multiple programming language – Pascal, Ada, Scheme, C, C++, Java • Web-based? – examples: GAME (2004), Submit (2003) ECEL 2004 Mandal, Reade, Sinha

Our design choices and goals • Choose: – – Component testing (performance and behavior) Single language (for now) Full automation AND rapid feedback Integration with full management system WBCM • Security of the process – Potentially unsafe programs (malicious/accident) • Marking issues – Partly working programs – Feedback based on schema • Address Overheads for assignment setup ECEL 2004 Mandal, Reade, Sinha

Setting up an assignment • Design a programming problem – Sub-problem approach (white box) – Marking scheme • Implementation involves (formally) – Expressing assignment plan (components and strategy) – writing components for test harness – describe testing data and process – describe marking scheme with feedback example: mergesort …. ECEL 2004 Mandal, Reade, Sinha
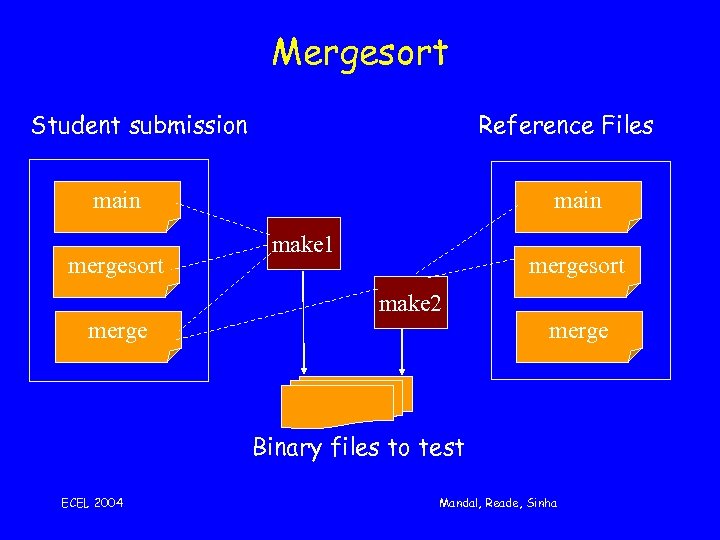
Mergesort Student submission Reference Files main mergesort main make 1 mergesort make 2 merge Binary files to test ECEL 2004 Mandal, Reade, Sinha
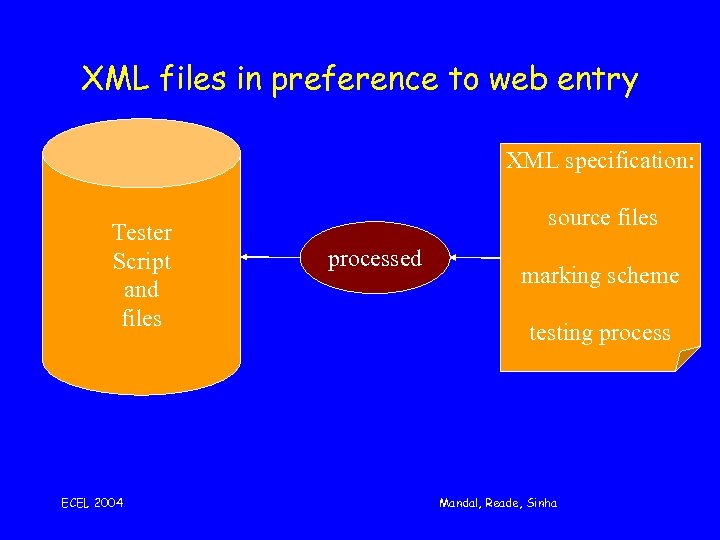
XML files in preference to web entry XML specification: Tester Script and files ECEL 2004 source files processed marking scheme testing process Mandal, Reade, Sinha
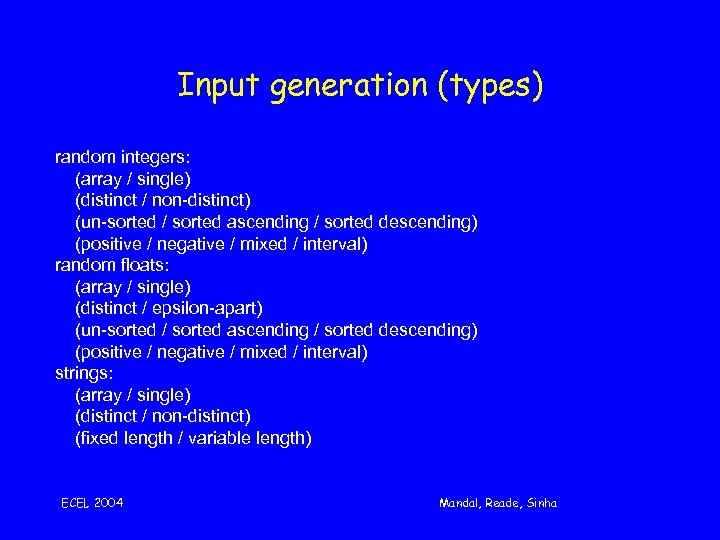
Input generation (types) random integers: (array / single) (distinct / non-distinct) (un-sorted / sorted ascending / sorted descending) (positive / negative / mixed / interval) random floats: (array / single) (distinct / epsilon-apart) (un-sorted / sorted ascending / sorted descending) (positive / negative / mixed / interval) strings: (array / single) (distinct / non-distinct) (fixed length / variable length) ECEL 2004 Mandal, Reade, Sinha

XML specification for input generation <!----- input generation and test invocation ------> <loop. Var="x" start="1" end="50"> <input. Var="a 1" type="integer” var. Type="array" sequence="ascend” range="positive" duplication="distinct"> <array_size>50</array_size> </input> <input. Var="a 2" type="integer” var. Type="array" sequence="ascend” range="positive" duplication="distinct"> <array_size>50</array_size> </input> <distinction_class> a 1 a 2 </distinction_class> <test_function> test_merge_to_k (a 1, 50, a 2, 50) </test_function> </loop> <!------------------------------> ECEL 2004 Mandal, Reade, Sinha

XML specification for a test <auto_eval> <source_files>. . . </source_files> <test marks="10" abort_on_fail="true"> <text> Evaluation of merge_function </text>. . . <testing> <!--- input generation and test invocation ------> </testing> </test> <test marks="10" abort_on_fail="true"> <!--- similar specification for testing mergesort ----> </test> </auto_eval> ECEL 2004 Mandal, Reade, Sinha
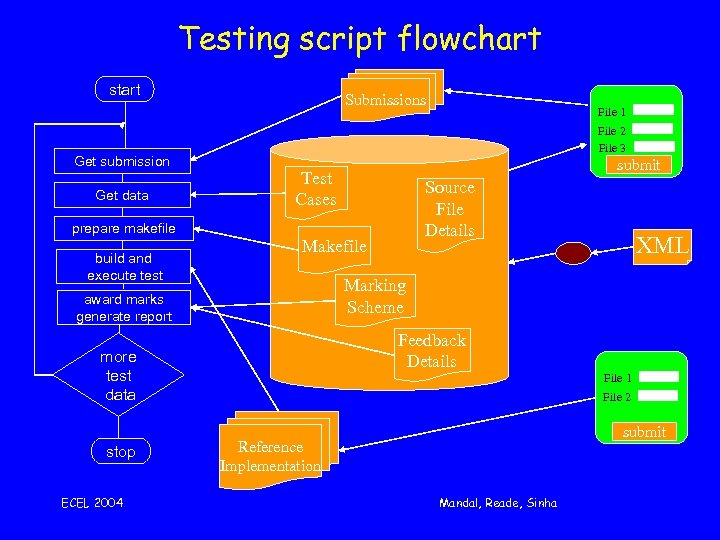
Testing script flowchart start Get submission Get data prepare makefile build and execute test Submissions File 2 File 3 Source File Details Makefile XML Marking Scheme Feedback Details more test data ECEL 2004 submit Test Cases award marks generate report stop File 1 File 2 submit Reference Implementation Mandal, Reade, Sinha

Conclusions This system is designed to support complex assessments. For automated assessment, the assessment set-up becomes the hardest part for designers – Our tool directly supports implementation of • Assessment strategy, marking sceme, feedback and testing harness – Key features • XML specs to generate testing script… • Re-use of assignment designs – Future Work • Generalising • Assessing effectiveness with more examples ECEL 2004 Mandal, Reade, Sinha
3e9af6cc60e979819382c7ecfc519949.ppt