fcdbf275bf40262279e55c6914b46e68.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 21
 A Validation Methodology for Graphics Processors Thesis Work Presentation 10. 2006 Author: Valtteri Rantala Supervisor: Prof. Raimo Kantola Instructor: M. Sc. Harri Syrjä
A Validation Methodology for Graphics Processors Thesis Work Presentation 10. 2006 Author: Valtteri Rantala Supervisor: Prof. Raimo Kantola Instructor: M. Sc. Harri Syrjä
 Content • Background • Objectives & methodology • Graphics processors & design process • Validation in general • Validation methodology • Validation of the Vector Graphics unit • Conclusions • Future study 2
Content • Background • Objectives & methodology • Graphics processors & design process • Validation in general • Validation methodology • Validation of the Vector Graphics unit • Conclusions • Future study 2
 Background • ATI technologies Finland (formerly Bitboys oy) designs IP cores for mobile devices • Quality is extremely important in processor design • Errors are extremely costly to repair after the design is implemented in silicon • Customer dissatisfaction • Company saw it necessary to reinforce the quality process • Validation was a part of the quality assurance that needed improvement 3
Background • ATI technologies Finland (formerly Bitboys oy) designs IP cores for mobile devices • Quality is extremely important in processor design • Errors are extremely costly to repair after the design is implemented in silicon • Customer dissatisfaction • Company saw it necessary to reinforce the quality process • Validation was a part of the quality assurance that needed improvement 3
 Objectives & methodology • Objectives · To develop the validation process for graphic processors · To specify documentation for the validation process • To find suitable testing techniques to be used in the validation process • Scope • Only validation aspect of quality assurance is inspected • Only validation of one unit is inspected in thesis • Individual test cases are not introduced • Methodology • Literature survey • Discussion with experts 4
Objectives & methodology • Objectives · To develop the validation process for graphic processors · To specify documentation for the validation process • To find suitable testing techniques to be used in the validation process • Scope • Only validation aspect of quality assurance is inspected • Only validation of one unit is inspected in thesis • Individual test cases are not introduced • Methodology • Literature survey • Discussion with experts 4
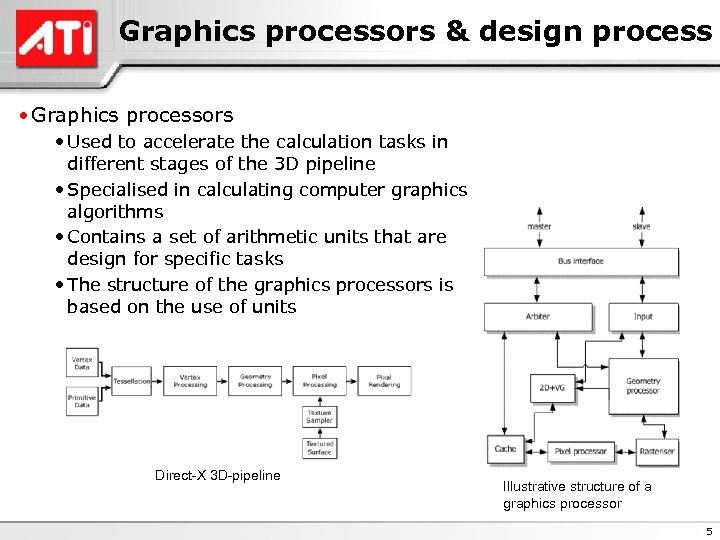 Graphics processors & design process • Graphics processors • Used to accelerate the calculation tasks in different stages of the 3 D pipeline • Specialised in calculating computer graphics algorithms • Contains a set of arithmetic units that are design for specific tasks • The structure of the graphics processors is based on the use of units Direct-X 3 D-pipeline Illustrative structure of a graphics processor 5
Graphics processors & design process • Graphics processors • Used to accelerate the calculation tasks in different stages of the 3 D pipeline • Specialised in calculating computer graphics algorithms • Contains a set of arithmetic units that are design for specific tasks • The structure of the graphics processors is based on the use of units Direct-X 3 D-pipeline Illustrative structure of a graphics processor 5
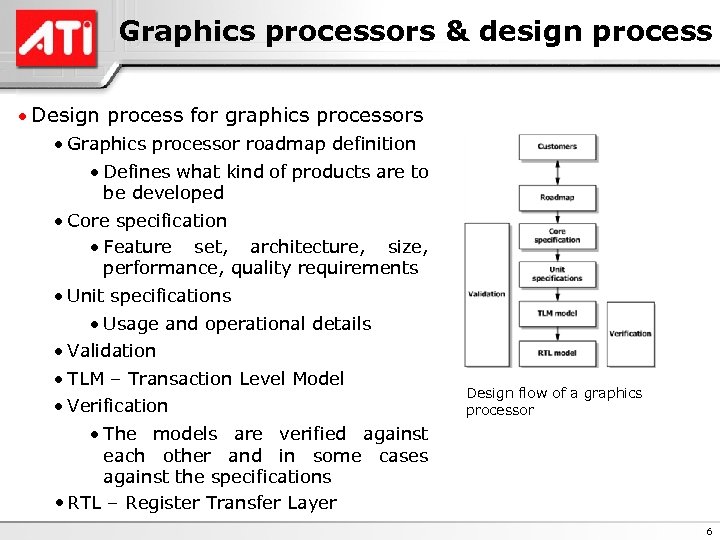 Graphics processors & design process · Design process for graphics processors · Graphics processor roadmap definition · Defines what kind of products are to be developed · Core specification · Feature set, architecture, size, performance, quality requirements · Unit specifications · Usage and operational details · Validation · TLM – Transaction Level Model · Verification · The models are verified against each other and in some cases against the specifications • RTL – Register Transfer Layer Design flow of a graphics processor 6
Graphics processors & design process · Design process for graphics processors · Graphics processor roadmap definition · Defines what kind of products are to be developed · Core specification · Feature set, architecture, size, performance, quality requirements · Unit specifications · Usage and operational details · Validation · TLM – Transaction Level Model · Verification · The models are verified against each other and in some cases against the specifications • RTL – Register Transfer Layer Design flow of a graphics processor 6
 Validation in general • Validation is a part of the quality assurance • The goal of the validation is to discover defects as early as possible • Validation is defined as “The process of evaluating a system or component during or at the end of the development process to determine whether it satisfies specified requirements”(IEEE 1012) • Consists of analysis, evaluation, review, inspection and testing of products • Different validation approaches • Walk-through • Formal methods • Test development • Prototyping 7
Validation in general • Validation is a part of the quality assurance • The goal of the validation is to discover defects as early as possible • Validation is defined as “The process of evaluating a system or component during or at the end of the development process to determine whether it satisfies specified requirements”(IEEE 1012) • Consists of analysis, evaluation, review, inspection and testing of products • Different validation approaches • Walk-through • Formal methods • Test development • Prototyping 7
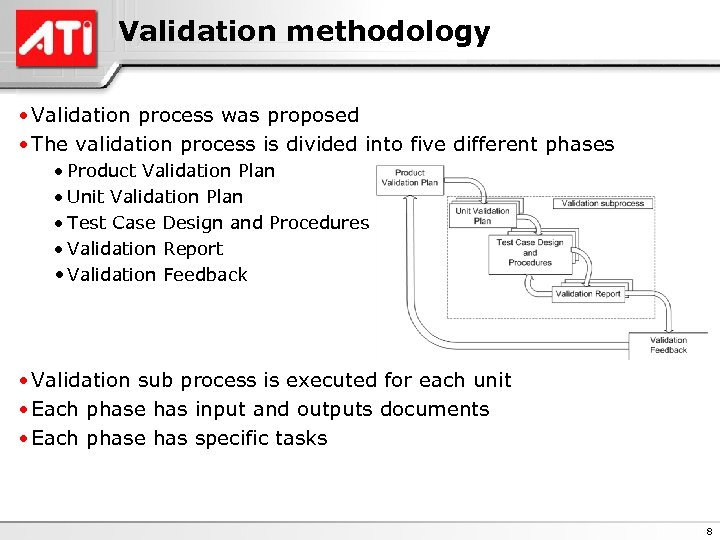 Validation methodology • Validation process was proposed • The validation process is divided into five different phases · Product Validation Plan · Unit Validation Plan · Test Case Design and Procedures · Validation Report • Validation Feedback • Validation sub process is executed for each unit • Each phase has input and outputs documents • Each phase has specific tasks 8
Validation methodology • Validation process was proposed • The validation process is divided into five different phases · Product Validation Plan · Unit Validation Plan · Test Case Design and Procedures · Validation Report • Validation Feedback • Validation sub process is executed for each unit • Each phase has input and outputs documents • Each phase has specific tasks 8
 Validation methodology • Product Validation Plan • To employ the validation resources efficiently, to monitor, to control, and to allow the identification of each participant’s role and responsibility • The purpose of this document is to describe the validation program for the product on a high level • Validation Program Management • Describes the program schedule, milestones and goals for each milestone, defect and reporting management, and staffing and risk management • Concept Level Validation • Describe on a system level what the system must be able to do • Performance, power consumption, acceptance use cases and APIs • Hardware Level Validation • Describes feature level validation • Hardware features are introduced on a high-level and the overall validation methodology for each feature group is described 9
Validation methodology • Product Validation Plan • To employ the validation resources efficiently, to monitor, to control, and to allow the identification of each participant’s role and responsibility • The purpose of this document is to describe the validation program for the product on a high level • Validation Program Management • Describes the program schedule, milestones and goals for each milestone, defect and reporting management, and staffing and risk management • Concept Level Validation • Describe on a system level what the system must be able to do • Performance, power consumption, acceptance use cases and APIs • Hardware Level Validation • Describes feature level validation • Hardware features are introduced on a high-level and the overall validation methodology for each feature group is described 9
 Validation methodology • Unit Validation Plan • For every unit • Describes how the specific unit will be validated • Contains to tasks: feature analysis and validation goal analysis • Feature analysis • All the features that are to be implemented are analysed • All features must be: clear, unambiguous, internally consistent and testable • Priority class is given for each feature • Validation goal analysis • features are analysed and the validation goals for each feature is presented · Feature spreadsheet is made · Target feature, validation items, methodology description, number of test cases 10
Validation methodology • Unit Validation Plan • For every unit • Describes how the specific unit will be validated • Contains to tasks: feature analysis and validation goal analysis • Feature analysis • All the features that are to be implemented are analysed • All features must be: clear, unambiguous, internally consistent and testable • Priority class is given for each feature • Validation goal analysis • features are analysed and the validation goals for each feature is presented · Feature spreadsheet is made · Target feature, validation items, methodology description, number of test cases 10
 Validation methodology · Test Case Design and Procedures · All testing work is done in this phase · Test case execution · Result analysis · Defect reporting · Test Case Design Principles • Test cases should uses the same coding standards as product developers • Only to test a feature • Size is 128 x 128 pixels or smaller, RTL is 100 to 1000 times slower to run than TLM designs. • Test Execution Framework • Test environment • Validation environment 11
Validation methodology · Test Case Design and Procedures · All testing work is done in this phase · Test case execution · Result analysis · Defect reporting · Test Case Design Principles • Test cases should uses the same coding standards as product developers • Only to test a feature • Size is 128 x 128 pixels or smaller, RTL is 100 to 1000 times slower to run than TLM designs. • Test Execution Framework • Test environment • Validation environment 11
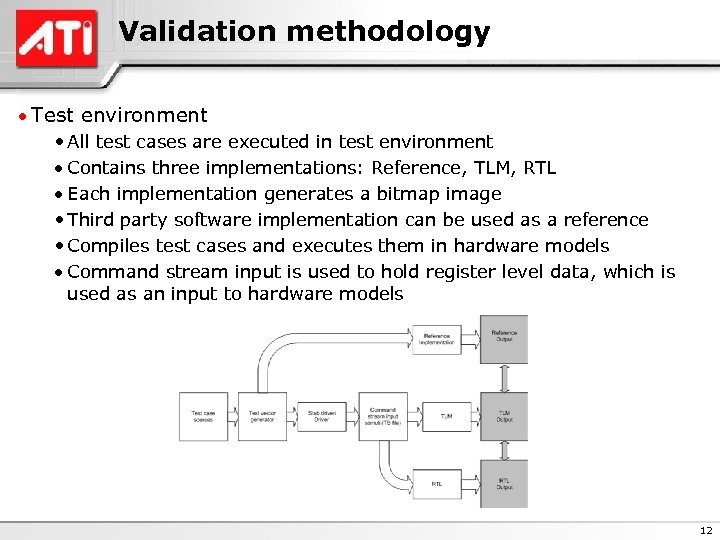 Validation methodology · Test environment • All test cases are executed in test environment · Contains three implementations: Reference, TLM, RTL · Each implementation generates a bitmap image • Third party software implementation can be used as a reference • Compiles test cases and executes them in hardware models · Command stream input is used to hold register level data, which is used as an input to hardware models 12
Validation methodology · Test environment • All test cases are executed in test environment · Contains three implementations: Reference, TLM, RTL · Each implementation generates a bitmap image • Third party software implementation can be used as a reference • Compiles test cases and executes them in hardware models · Command stream input is used to hold register level data, which is used as an input to hardware models 12
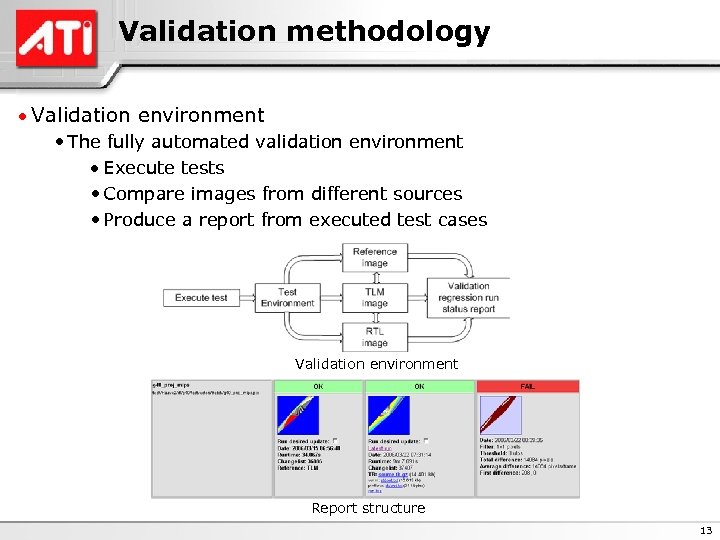 Validation methodology · Validation environment • The fully automated validation environment · Execute tests • Compare images from different sources • Produce a report from executed test cases Validation environment Report structure 13
Validation methodology · Validation environment • The fully automated validation environment · Execute tests • Compare images from different sources • Produce a report from executed test cases Validation environment Report structure 13
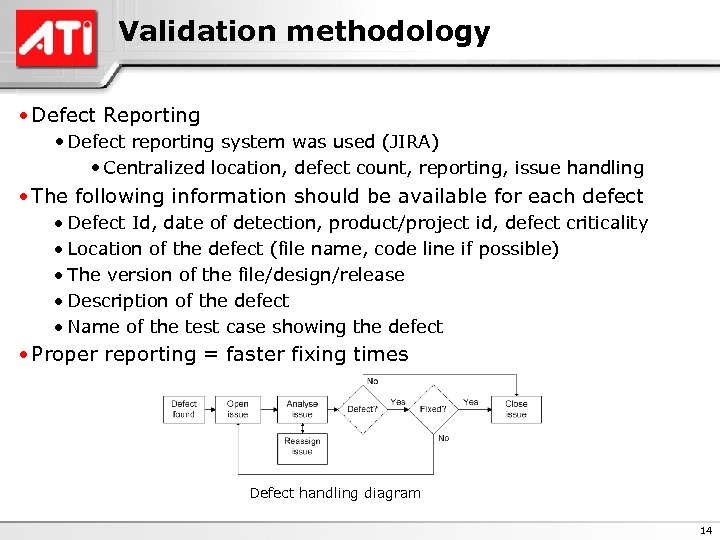 Validation methodology • Defect Reporting • Defect reporting system was used (JIRA) • Centralized location, defect count, reporting, issue handling • The following information should be available for each defect · Defect Id, date of detection, product/project id, defect criticality · Location of the defect (file name, code line if possible) · The version of the file/design/release · Description of the defect · Name of the test case showing the defect • Proper reporting = faster fixing times Defect handling diagram 14
Validation methodology • Defect Reporting • Defect reporting system was used (JIRA) • Centralized location, defect count, reporting, issue handling • The following information should be available for each defect · Defect Id, date of detection, product/project id, defect criticality · Location of the defect (file name, code line if possible) · The version of the file/design/release · Description of the defect · Name of the test case showing the defect • Proper reporting = faster fixing times Defect handling diagram 14
 Validation methodology • Validation Report • The purpose of this phase is to give a good understanding of the current validation status • Readership is all stakeholders • Generated weekly basis -> produces history data • Validation report contains the following information: · Status tracking of various variables · Test case implementation progress · Test cases passing rates for different design models • Defect tracking results · Test case coverage · The goal is to show that all the features are tested • Code coverage analysis • Statement coverage is used • Coverage for each file 15
Validation methodology • Validation Report • The purpose of this phase is to give a good understanding of the current validation status • Readership is all stakeholders • Generated weekly basis -> produces history data • Validation report contains the following information: · Status tracking of various variables · Test case implementation progress · Test cases passing rates for different design models • Defect tracking results · Test case coverage · The goal is to show that all the features are tested • Code coverage analysis • Statement coverage is used • Coverage for each file 15
 Validation methodology • Validation Feedback • The purpose is to get information about how well the process has worked • The Feedback is analysed and recommendations for improving the validation process are done based on the feedback • Collecting Feedback • From the process results · Low failure rate/high pass rate, defect density, inconsistent results • To make questionnaires and interview different stakeholders • Change Management • To have a planned approach to change implementation • Major/minor changes 16
Validation methodology • Validation Feedback • The purpose is to get information about how well the process has worked • The Feedback is analysed and recommendations for improving the validation process are done based on the feedback • Collecting Feedback • From the process results · Low failure rate/high pass rate, defect density, inconsistent results • To make questionnaires and interview different stakeholders • Change Management • To have a planned approach to change implementation • Major/minor changes 16
 Validation of the Vector Graphics unit • Validation process was used to validate the Vector Graphics unit • All validation process phases and tasks were executed • The feature analysis revealed a few errors in specification documentation • Test case design based on the unit specification • The test case principles guide the designing of the test cases • Code coverage analysis revealed unspecified features • Quality issues: what is accurate enough? 17
Validation of the Vector Graphics unit • Validation process was used to validate the Vector Graphics unit • All validation process phases and tasks were executed • The feature analysis revealed a few errors in specification documentation • Test case design based on the unit specification • The test case principles guide the designing of the test cases • Code coverage analysis revealed unspecified features • Quality issues: what is accurate enough? 17
 Conclusions • Importance of the validation was realised • Written process for the validation of the graphics processor with documentation templates • Predictability of the validation process was improved due the validation reporting and proper planning • No major rework was made in the project • Defects found in TLM after validation dropped from 30% -> 5% • There is now real history data to be used in the future projects • The documented progress increased confidence towards the product 18
Conclusions • Importance of the validation was realised • Written process for the validation of the graphics processor with documentation templates • Predictability of the validation process was improved due the validation reporting and proper planning • No major rework was made in the project • Defects found in TLM after validation dropped from 30% -> 5% • There is now real history data to be used in the future projects • The documented progress increased confidence towards the product 18
 Future study • The work for improving the validation process will continue after this thesis • The areas for future work are the areas that received most negative feedback • The use of validation metrics and the use of history data must be stressed in future projects • The quality of test vectors will be stressed in future projects 19
Future study • The work for improving the validation process will continue after this thesis • The areas for future work are the areas that received most negative feedback • The use of validation metrics and the use of history data must be stressed in future projects • The quality of test vectors will be stressed in future projects 19
 Any questions? 20
Any questions? 20
 Thank you! 21
Thank you! 21


