281d96a3a03f38a0143e36c47ca1b114.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 20

A Taxonomy of Web Search by Andrei Broder Web Science I. Oelze 14. 12. 10 1

Overview Ø Motivation Ø Classic model for IR Ø Web-specific Needs Ø Taxonomy of Web Search Ø Evaluation Ø Evolution of Search Engines Ø Conclusions Web Science I. Oelze 14. 12. 10 2 1

Motivation Ø central tenet – information need But : show me url of the site where I can find a map of New York I want to buy a new computer intend behind web search not always informational web-specific needs should be taken into account Web Science I. Oelze 14. 12. 10 3 2

Aims of this Paper Aims : Ø point out the difference between classic IR and web search Ø introduce and analyze a taxonomy of web searches Ø show search engines deal with web-specific needs Web Science I. Oelze 14. 12. 10 4 3
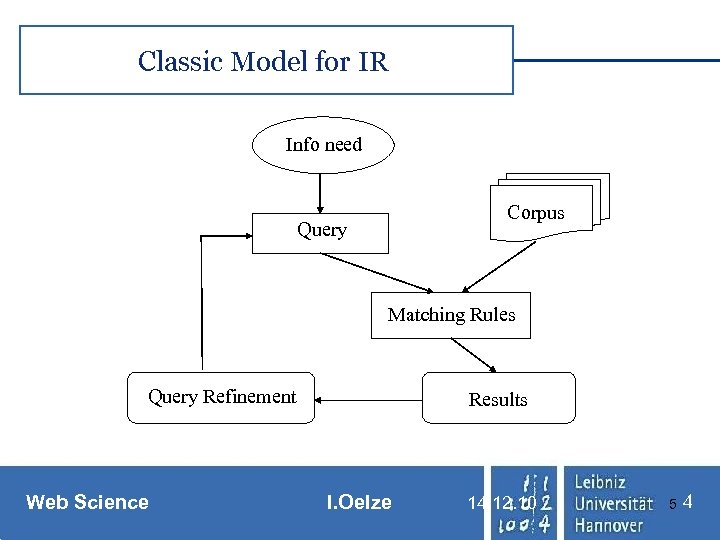
Classic Model for IR Info need Corpus Query Matching Rules Query Refinement Web Science Results I. Oelze 14. 12. 10 5 4
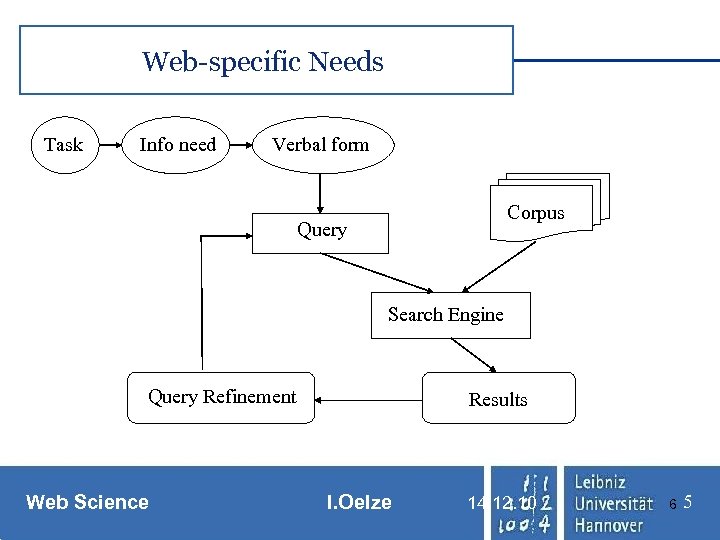
Web-specific Needs Task Info need Verbal form Corpus Query Search Engine Query Refinement Web Science Results I. Oelze 14. 12. 10 6 5
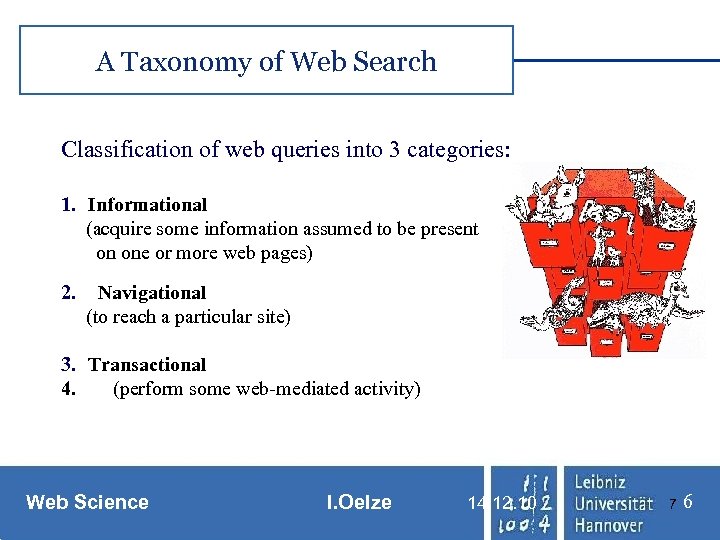
A Taxonomy of Web Search Classification of web queries into 3 categories: 1. Informational (acquire some information assumed to be present on one or more web pages) 2. Navigational (to reach a particular site) 3. Transactional 4. (perform some web-mediated activity) Web Science I. Oelze 14. 12. 10 7 6

1. Informational Queries Intent: acquire some information assumed to be present on one or more web pages Ø information is in static form Ø no further interaction is predicted 1. Where will WC 2018 be held? WC 2018 2. What is the current rank of Hannover 96? table Hannover 96 Web Science I. Oelze 14. 12. 10 8 7
2. Navigational Queries Intent : to reach a particular site Ø user visited it in the past or assumes that it exists Ø “known item” search or “home page finding task” Ø only one right result 1. What is the official website of IBM? official website IBM 2. HP Store in Germany HP Germany Web Science I. Oelze 14. 12. 10 9 8

3. Transactional Queries Intent : perform some web-mediated activity Ø further interaction is expected Ø main categories: shopping, finding servers, downloading various types of files 1. I need an accommodation in Rome hotel Rome 2. I want to buy a new bed Ikea Web Science I. Oelze 14. 12. 10 10 9

Scenario Alice wants to buy a printer. – Transactional Query Alice found 3 printers that she likes. She wants more information about them. – Infomational Query Alice wants some information about firma Lexmark. She assumes that it has a site in Germany. – Navigational Query Alice wants to download a document with a printer test. – Transactional Query Web Science I. Oelze 14. 12. 10 11 10

Evaluation 2 Methods : Ø a survey of Alta. Vista users Ø presented to random users Ø users are self selected Ø a pop-up window with the questions Ø analysis of the query log at Alta. Vista Web Science I. Oelze 14. 12. 10 12 11

Survey Queries Ø to distinguish between navigational and non-navigational queries: Which of the following describes best what you are trying to do? 24, 53 o I want to get to a specific website that I already have in mind % 68, 41 o I want a good site on this topic, but I don’t have a specific site in mind % Web Science I. Oelze 14. 12. 10 13 12

Survey Queries Ø to distinguish between transactional and non-transactional queries: Which of the following best describes why you conducted this search? 8, 16 % I am shopping for something to buy on the Internet o 5, 46 % I am shopping for something to buy elsewhere than on the Internet o 22, 55 % I want to download a file (e. g. music, images, programs, etc. ) o 57, 19 % None of these reasons o Web Science I. Oelze 14. 12. 10 14 13

Survey Queries Ø to distinguish between informational and non-informational queries: Which of the following describes best what you are looking for? 14, 83 o A site which is a collection of links to other sites regarding this topic % 76, 62 o The best site regarding this topic % Web Science I. Oelze 14. 12. 10 15 14
Log Analysis Ø a random set of 1000 queries from the daily Alta. Vista log Ø only English queries Ø sexually oriented queries are removed Ø queries that are neither navigational, nor transactional are assumed to be informational Web Science I. Oelze 14. 12. 10 16 15
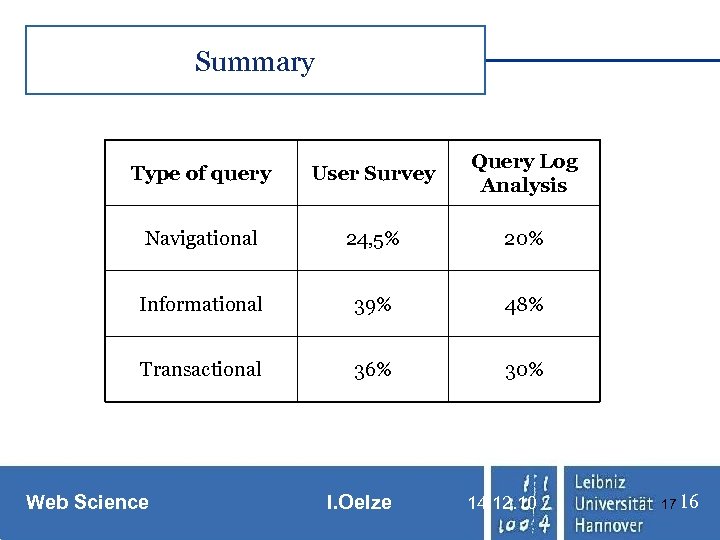
Summary Type of query User Survey Query Log Analysis Navigational 24, 5% 20% Informational 39% 48% Transactional 36% 30% Web Science I. Oelze 14. 12. 10 17 16
Evolution of Search Engines First generation (1995 -1997) Ø on-page data, close to classic IR, mostly informational queries Ø Alta. Vista, Excite, Web. Crawler, etc Second generation (1998 -1999) Ø off-page, use of web-specific data such as link analysis, anchor-text, and click-through data, informational and navigational queries Ø Google, Direct. Hit Third generation (2000 -now) Ø attempt to ask the “need behind a query”, data from multiple sources, support for informational, navigational, transactional queries Web Science I. Oelze 14. 12. 10 18 17

Conclusion and Comments Ø web search is task-driven Ø search engines need to deal with different types of queries Ø subtle difference between the navigational and informational queries Ø some misleading in the evaluation part Web Science I. Oelze 14. 12. 10 19 18

Questions ? ? ? Thanx! Web Science I. Oelze 14. 12. 10 20 19
281d96a3a03f38a0143e36c47ca1b114.ppt