f1bf685dd293259fe1fb1cca2780a025.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 26

A strategy to create a revolution in Public Behaviour in Organ Donation TSS Forum – 30 th July 2014 Ceri Rose – Assistant Director – Marketing and Digital

The challenge • 2020 strategy Outcome 1 – increase consent/authorisation rates to over 80% • Little improvement since 2008

The approach • Research – Understanding current attitudes and behaviours
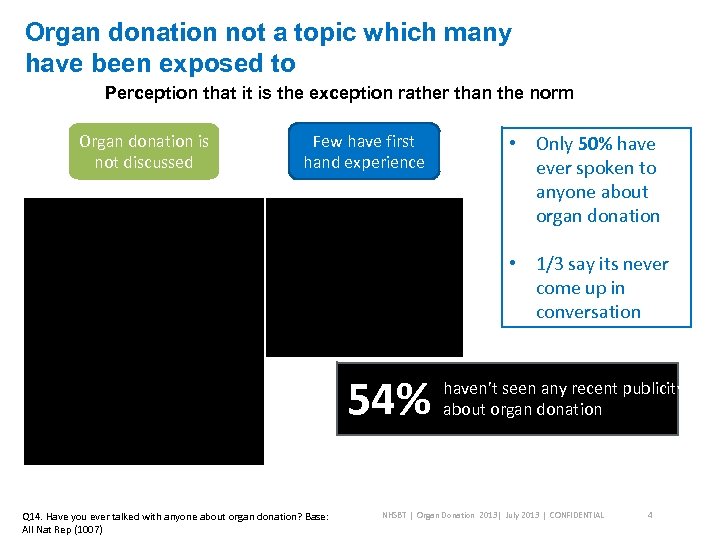
Organ donation not a topic which many have been exposed to Perception that it is the exception rather than the norm Organ donation is not discussed Few have first hand experience • Only 50% have ever spoken to anyone about organ donation • Many are uncomfortable • Lack of first hand confronting upsetting experience of organ emotions around their own donation (process/ • 1/3 say its never mortality giving consent) come up in • Death is considered too • Top of mind conversation personal and too sensitive association is living in conversations donation • Few are aware of wishes of those closest to them haven’t seen any recent publicity • Seen as not in the public about organ donation eye in comparison to other health campaigns 54% Q 14. Have you ever talked with anyone about organ donation? Base: All Nat Rep (1007) NHSBT | Organ Donation 2013| July 2013 | CONFIDENTIAL 4
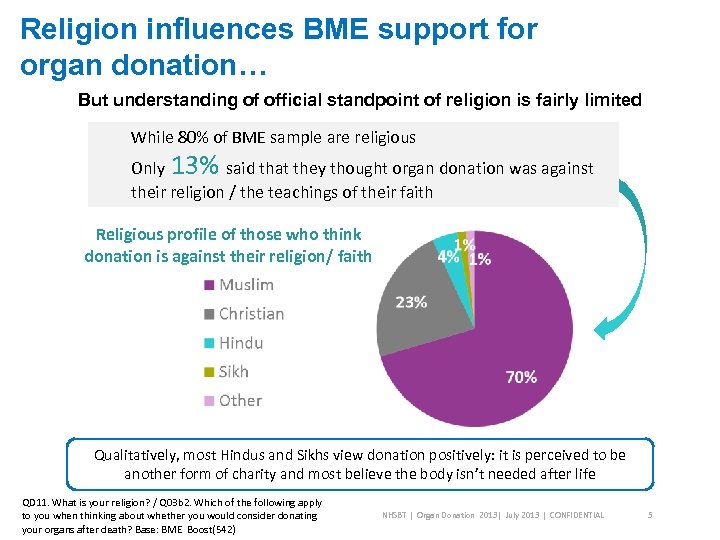
Religion influences BME support for organ donation… But understanding of official standpoint of religion is fairly limited While 80% of BME sample are religious Only 13% said that they thought organ donation was against their religion / the teachings of their faith Religious profile of those who think donation is against their religion/ faith Qualitatively, most Hindus and Sikhs view donation positively: it is perceived to be another form of charity and most believe the body isn’t needed after life QD 11. What is your religion? / Q 03 b 2. Which of the following apply to you when thinking about whether you would consider donating your organs after death? Base: BME Boost(542) NHSBT | Organ Donation 2013| July 2013 | CONFIDENTIAL 5
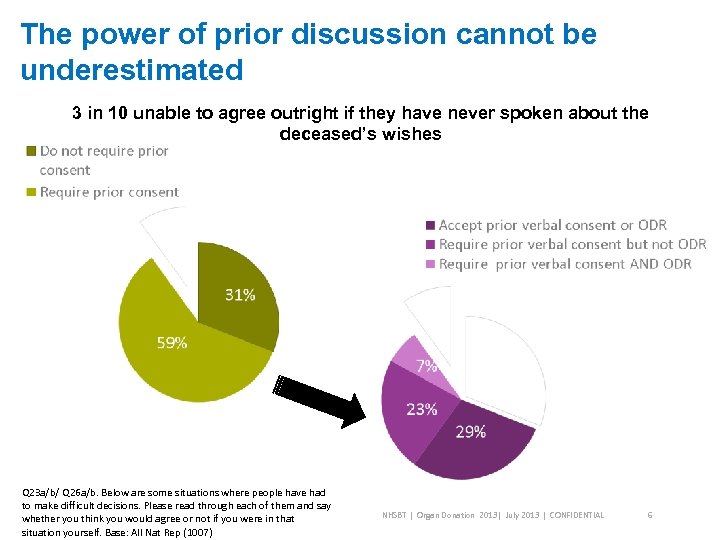
The power of prior discussion cannot be underestimated 3 in 10 unable to agree outright if they have never spoken about the deceased’s wishes Q 23 a/b/ Q 26 a/b. Below are some situations where people have had to make difficult decisions. Please read through each of them and say whether you think you would agree or not if you were in that situation yourself. Base: All Nat Rep (1007) NHSBT | Organ Donation 2013| July 2013 | CONFIDENTIAL 6
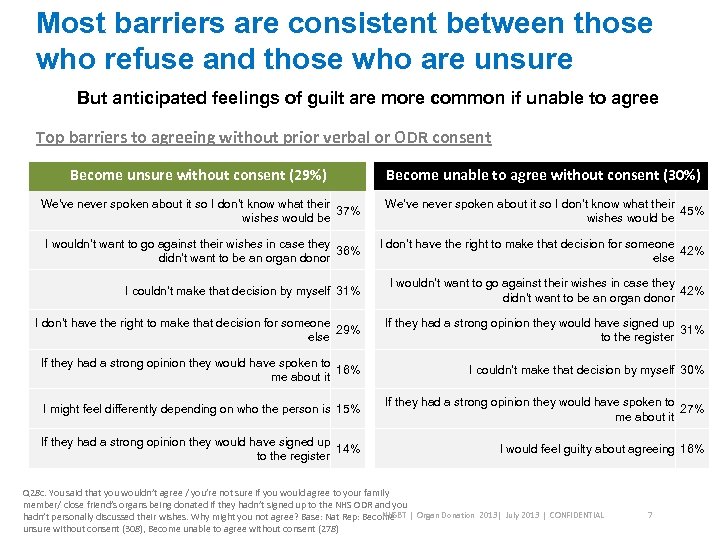
Most barriers are consistent between those who refuse and those who are unsure But anticipated feelings of guilt are more common if unable to agree Top barriers to agreeing without prior verbal or ODR consent Become unsure without consent (29%) Become unable to agree without consent (30%) We've never spoken about it so I don’t know what their 37% wishes would be We've never spoken about it so I don’t know what their 45% wishes would be I wouldn’t want to go against their wishes in case they 36% didn’t want to be an organ donor I don’t have the right to make that decision for someone 42% else I couldn’t make that decision by myself 31% I wouldn’t want to go against their wishes in case they 42% didn’t want to be an organ donor I don’t have the right to make that decision for someone 29% else If they had a strong opinion they would have signed up 31% to the register If they had a strong opinion they would have spoken to 16% me about it I couldn’t make that decision by myself 30% I might feel differently depending on who the person is 15% If they had a strong opinion they would have spoken to 27% me about it If they had a strong opinion they would have signed up 14% to the register I would feel guilty about agreeing 16% Q 28 c. You said that you wouldn’t agree / you’re not sure if you would agree to your family member/ close friend’s organs being donated if they hadn’t signed up to the NHS ODR and you NHSBT hadn’t personally discussed their wishes. Why might you not agree? Base: Nat Rep: Become | Organ Donation 2013| July 2013 | CONFIDENTIAL unsure without consent (308), Become unable to agree without consent (278) 7

The approach • Research – Understanding current attitudes and behaviours – Understanding what we need to do
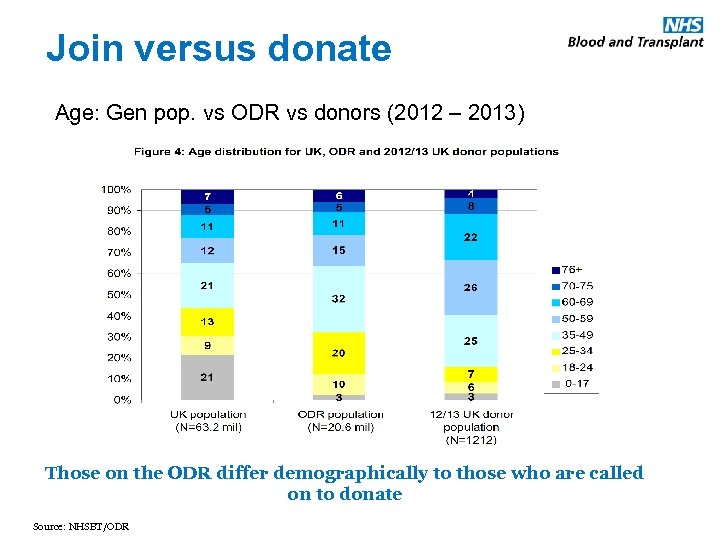
Join versus donate Age: Gen pop. vs ODR vs donors (2012 – 2013) Those on the ODR differ demographically to those who are called on to donate Source: NHSBT/ODR
Learnings from others
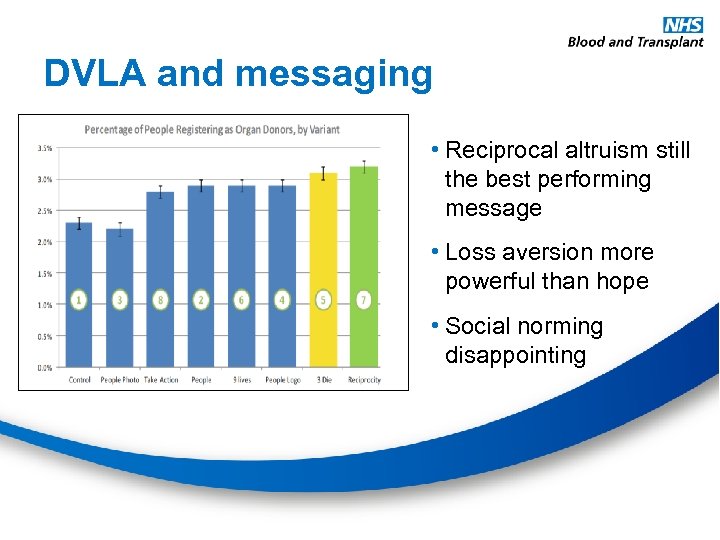
DVLA and messaging • Reciprocal altruism still the best performing message • Loss aversion more powerful than hope • Social norming disappointing

The approach • Research – Understanding current attitudes and behaviours – Understanding what we need to do – The strategy – a direction of travel http: //www. nhsbt. nhs. uk/to 2020/about-the-strategy/changing-behaviour/

The strategy • Three objectives: – To increase the number of people on the ODR by at least 50% by 2020 (from a baseline of 20 m in 2014), rebalancing it towards people who are older (50+) and from DE socio-economic groups – To stimulate conversations and debate about donation, particularly through leveraging the ODR as a marketing tool – To present donation as a benefit to families in end-oflife and grieving process • Framework of 20 specific actions
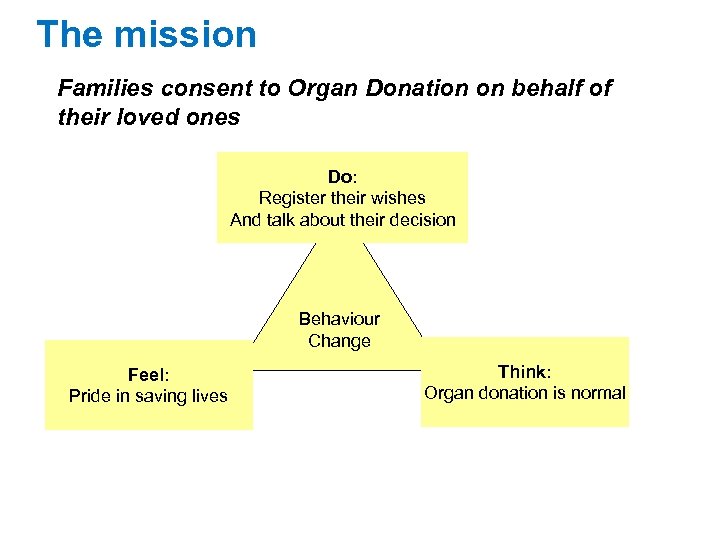
The mission Families consent to Organ Donation on behalf of their loved ones Do: Register their wishes And talk about their decision Behaviour Change Feel: Pride in saving lives Think: Organ donation is normal
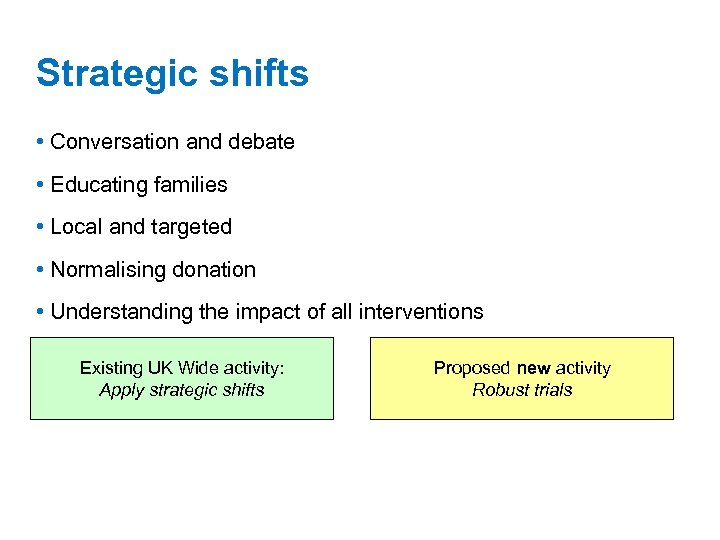
Strategic shifts • Conversation and debate • Educating families • Local and targeted • Normalising donation • Understanding the impact of all interventions Existing UK Wide activity: Apply strategic shifts Proposed new activity Robust trials

Campaign plan > UK-wide activity Existing and funded activity: • Digital – websites, social media, • Content strategy addressing motivations and barriers • National partnerships • Faith Action Plan • National Transplant week • Materials - leaflets, banners, stands, promotional items • Donor card to first time registrants (85 k per month)
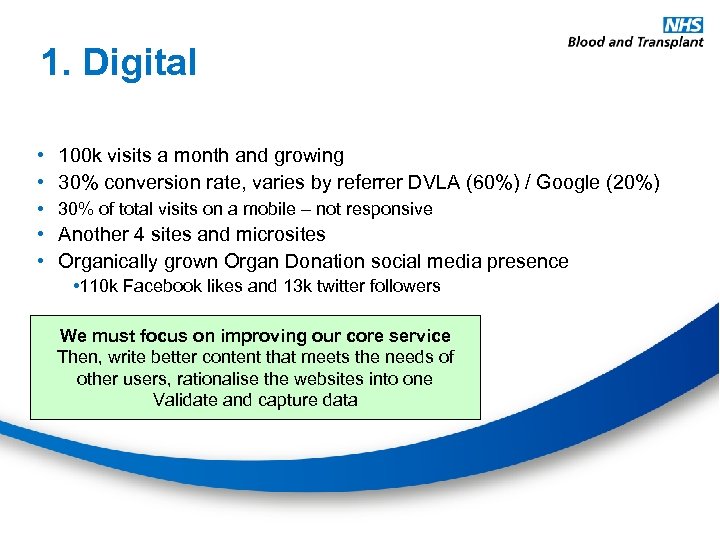
1. Digital • 100 k visits a month and growing • 30% conversion rate, varies by referrer DVLA (60%) / Google (20%) • 30% of total visits on a mobile – not responsive • Another 4 sites and microsites • Organically grown Organ Donation social media presence • 110 k Facebook likes and 13 k twitter followers We must focus on improving our core service Then, write better content that meets the needs of other users, rationalise the websites into one Validate and capture data
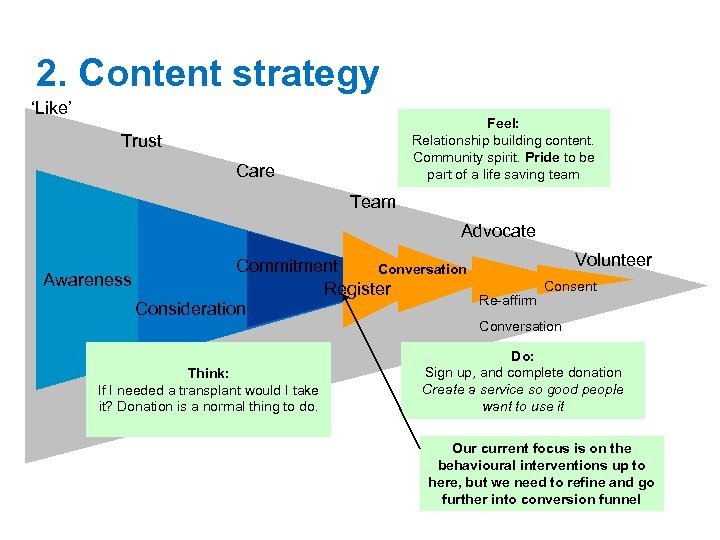
2. Content strategy ‘Like’ Feel: Relationship building content. Community spirit. Pride to be part of a life saving team Trust Care Team Advocate Commitment Conversation Awareness Register Consideration Think: If I needed a transplant would I take it? Donation is a normal thing to do. Volunteer Re-affirm Consent Conversation Do: Sign up, and complete donation Create a service so good people want to use it Our current focus is on the behavioural interventions up to here, but we need to refine and go further into conversion funnel
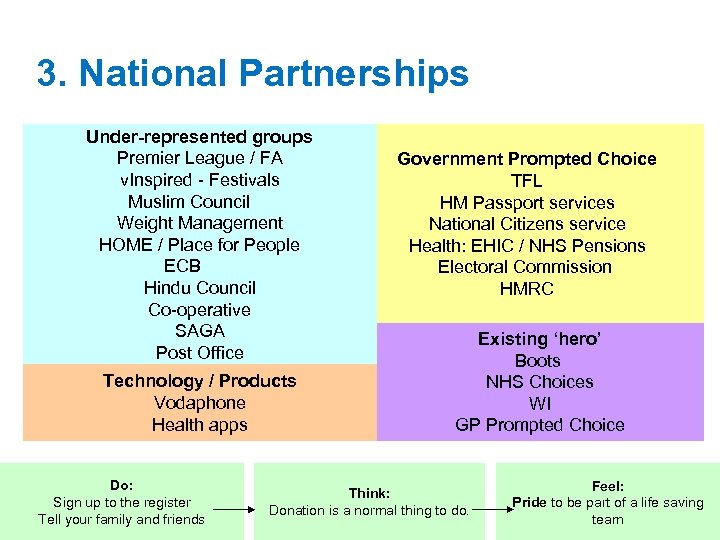
3. National Partnerships Under-represented groups Premier League / FA v. Inspired - Festivals Muslim Council Weight Management HOME / Place for People ECB Hindu Council Co-operative SAGA Post Office Technology / Products Vodaphone Health apps Do: Sign up to the register Tell your family and friends Government Prompted Choice TFL HM Passport services National Citizens service Health: EHIC / NHS Pensions Electoral Commission HMRC Existing ‘hero’ Boots NHS Choices WI GP Prompted Choice Think: Donation is a normal thing to do. Feel: Pride to be part of a life saving team

Campaign plan > UK-wide activity Existing and funded activity: 4. Faith Action Plan 5. National Transplant week 6. Materials - leaflets, banners, stands, promotional items 7. Donor card to first time registrants (85 k per month)

Campaign plan – trial approach • Areas of activity: – Current level as a baseline – Isolated, one intervention only – Dec – Hot house, all interventions – Jan onwards


Campaign plan – new activity • Developing a relationship management programme – Trialling re-carding re-registrants & supporting new channels • Targeted acquisition of new registrants • Targeted digital media • Expanded use of the organ donation card • Local partnerships • Education materials

Campaign plan – March onwards • Religious text on organ donor card • Donor card equivalents – apps • Order of St John Award – national ceremony • Donor cards for re-registrants
Proposed evaluation framework Quarterly and by DBD/DCD: • Consent rate • Referral rate • Approach with SNOD • % on the ODR • Family interest rate (from PDA) Example

Funding • Reduced campaign spend to fund increased operational activity • £ 800 k for UK wide activity • National approach to campaigning, 2014/15 budgets – – England - £ 500 k £ 0. 01 pp (proposed) Northern Ireland - £ 250 k £ 0. 14 pp Scotland - £ 250 k £ 0. 05 pp Wales - £ 808 k £ 0. 26 pp
f1bf685dd293259fe1fb1cca2780a025.ppt