44c00f2dbd423497a2a8ef8e1b3ca49a.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 55
 A Services Oriented Architecture for Water Resources Data David R. Maidment Center for Research in Water Resources University of Texas at Austin
A Services Oriented Architecture for Water Resources Data David R. Maidment Center for Research in Water Resources University of Texas at Austin
 A Services Oriented Architecture for Water Resources Data • • CUAHSI and WATERS Water. ML and Water. One. Flow Hydrologic Information Server Modeling services
A Services Oriented Architecture for Water Resources Data • • CUAHSI and WATERS Water. ML and Water. One. Flow Hydrologic Information Server Modeling services
 A Services Oriented Architecture for Water Resources Data • • CUAHSI and WATERS Water. ML and Water. One. Flow Hydrologic Information Server Modeling services
A Services Oriented Architecture for Water Resources Data • • CUAHSI and WATERS Water. ML and Water. One. Flow Hydrologic Information Server Modeling services
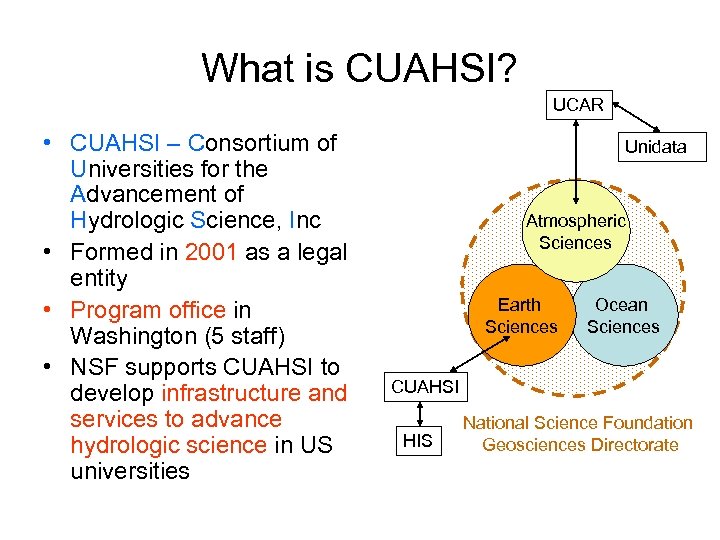 What is CUAHSI? UCAR • CUAHSI – Consortium of Universities for the Advancement of Hydrologic Science, Inc • Formed in 2001 as a legal entity • Program office in Washington (5 staff) • NSF supports CUAHSI to develop infrastructure and services to advance hydrologic science in US universities Unidata Atmospheric Sciences Earth Sciences Ocean Sciences CUAHSI HIS National Science Foundation Geosciences Directorate
What is CUAHSI? UCAR • CUAHSI – Consortium of Universities for the Advancement of Hydrologic Science, Inc • Formed in 2001 as a legal entity • Program office in Washington (5 staff) • NSF supports CUAHSI to develop infrastructure and services to advance hydrologic science in US universities Unidata Atmospheric Sciences Earth Sciences Ocean Sciences CUAHSI HIS National Science Foundation Geosciences Directorate
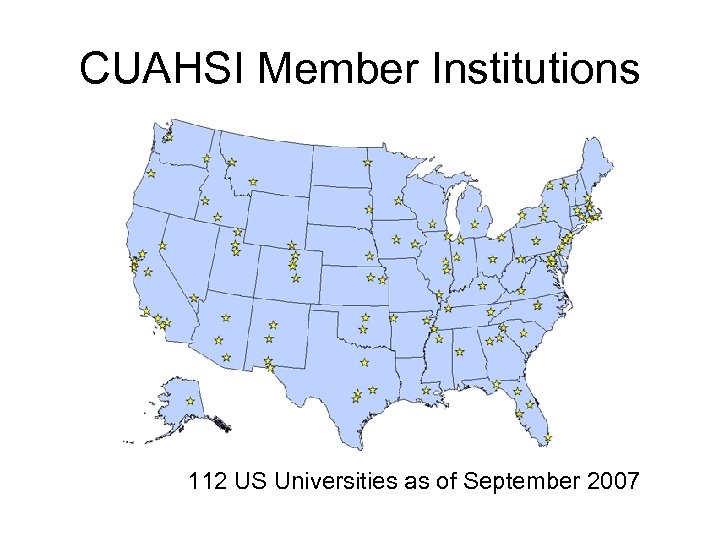 CUAHSI Member Institutions 112 US Universities as of September 2007
CUAHSI Member Institutions 112 US Universities as of September 2007
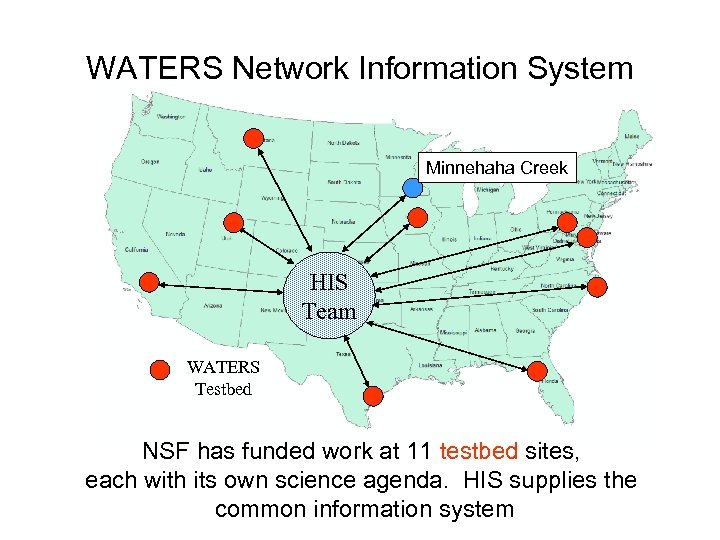 WATERS Network Information System Minnehaha Creek HIS Team WATERS Testbed NSF has funded work at 11 testbed sites, each with its own science agenda. HIS supplies the common information system
WATERS Network Information System Minnehaha Creek HIS Team WATERS Testbed NSF has funded work at 11 testbed sites, each with its own science agenda. HIS supplies the common information system
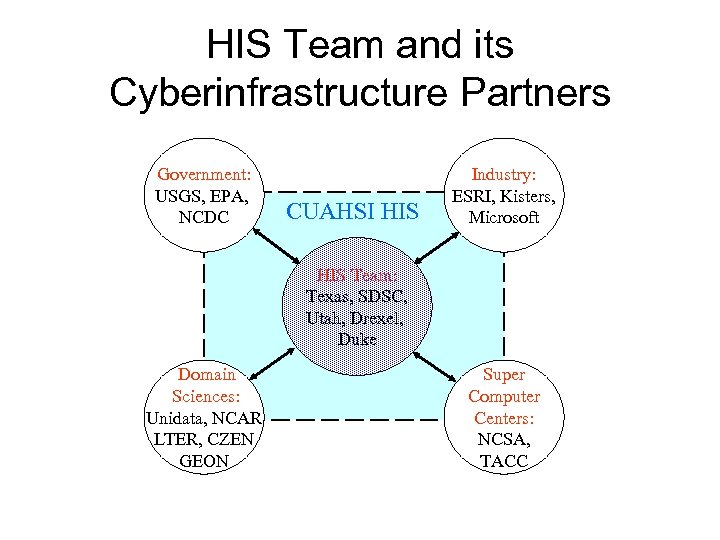 HIS Team and its Cyberinfrastructure Partners Government: USGS, EPA, NCDC CUAHSI HIS Industry: ESRI, Kisters, Microsoft HIS Team: Texas, SDSC, Utah, Drexel, Duke Domain Sciences: Unidata, NCAR LTER, CZEN GEON Super Computer Centers: NCSA, TACC
HIS Team and its Cyberinfrastructure Partners Government: USGS, EPA, NCDC CUAHSI HIS Industry: ESRI, Kisters, Microsoft HIS Team: Texas, SDSC, Utah, Drexel, Duke Domain Sciences: Unidata, NCAR LTER, CZEN GEON Super Computer Centers: NCSA, TACC
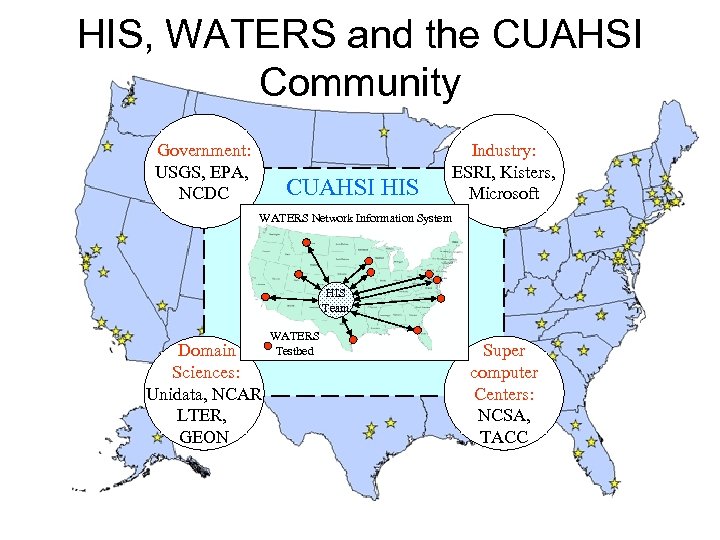 HIS, WATERS and the CUAHSI Community Government: USGS, EPA, NCDC CUAHSI HIS Industry: ESRI, Kisters, Microsoft WATERS Network Information System HIS Team Domain Sciences: Unidata, NCAR LTER, GEON WATERS Testbed Super computer Centers: NCSA, TACC
HIS, WATERS and the CUAHSI Community Government: USGS, EPA, NCDC CUAHSI HIS Industry: ESRI, Kisters, Microsoft WATERS Network Information System HIS Team Domain Sciences: Unidata, NCAR LTER, GEON WATERS Testbed Super computer Centers: NCSA, TACC
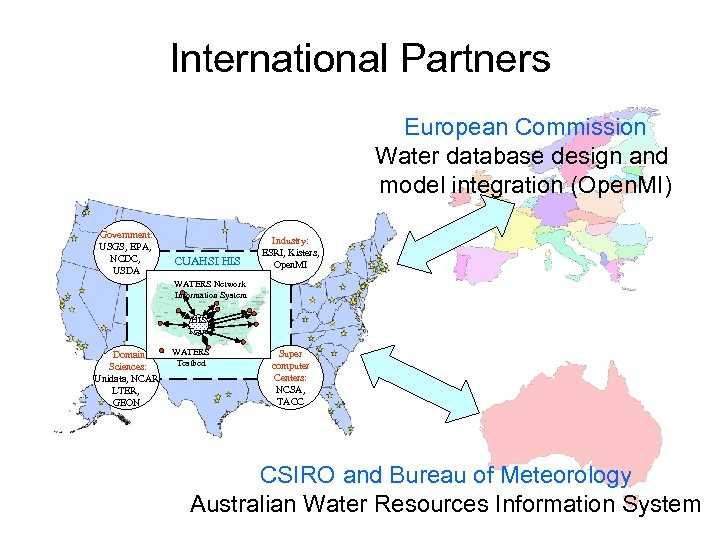 International Partners European Commission Water database design and model integration (Open. MI) Government: USGS, EPA, NCDC, USDA CUAHSI HIS Industry: ESRI, Kisters, Open. MI WATERS Network Information System HIS Team Domain Sciences: Unidata, NCAR LTER, GEON WATERS Testbed Super computer Centers: NCSA, TACC CSIRO and Bureau of Meteorology Australian Water Resources Information System
International Partners European Commission Water database design and model integration (Open. MI) Government: USGS, EPA, NCDC, USDA CUAHSI HIS Industry: ESRI, Kisters, Open. MI WATERS Network Information System HIS Team Domain Sciences: Unidata, NCAR LTER, GEON WATERS Testbed Super computer Centers: NCSA, TACC CSIRO and Bureau of Meteorology Australian Water Resources Information System
 HIS Goals • Hydrologic Data Access – providing better access to a large volume of high quality hydrologic data across the nation • Support for Observatories – integrating local observations by academic investigators with hydrologic data for a region • Advancement of Hydrologic Science – modeling and analysis of “hydrology in a dynamic earth” • Hydrologic Education – bringing more data into the classroom
HIS Goals • Hydrologic Data Access – providing better access to a large volume of high quality hydrologic data across the nation • Support for Observatories – integrating local observations by academic investigators with hydrologic data for a region • Advancement of Hydrologic Science – modeling and analysis of “hydrology in a dynamic earth” • Hydrologic Education – bringing more data into the classroom
 A Services Oriented Architecture for Water Resources Data • • CUAHSI and WATERS Water. ML and Water. One. Flow Hydrologic Information Server Modeling services
A Services Oriented Architecture for Water Resources Data • • CUAHSI and WATERS Water. ML and Water. One. Flow Hydrologic Information Server Modeling services
 Definition The CUAHSI Hydrologic Information System (HIS) is a geographically distributed network of data sources and functions that are integrated using web services so that they operate as a connected whole.
Definition The CUAHSI Hydrologic Information System (HIS) is a geographically distributed network of data sources and functions that are integrated using web services so that they operate as a connected whole.
 Services Oriented Architecture (from Wikipedia) • Service-oriented Architecture (SOA) is an architectural design pattern that concerns itself with defining loosely-coupled relationships between producers and consumers. • A major focus of Web services is to make functional building blocks accessible over standard Internet protocols that are independent from platforms and programming languages. • The Web Services Description Language (WSDL, pronounced 'wiz-dəl' or spelled out, 'WS-D-L') is an XML-based language that provides a model for describing Web services. Defined by the World Wide Web Consortium (W 3 C)
Services Oriented Architecture (from Wikipedia) • Service-oriented Architecture (SOA) is an architectural design pattern that concerns itself with defining loosely-coupled relationships between producers and consumers. • A major focus of Web services is to make functional building blocks accessible over standard Internet protocols that are independent from platforms and programming languages. • The Web Services Description Language (WSDL, pronounced 'wiz-dəl' or spelled out, 'WS-D-L') is an XML-based language that provides a model for describing Web services. Defined by the World Wide Web Consortium (W 3 C)
 Web Pages and Web Services http: //his. safl. umn. edu/SAFLMC/cuahsi_1_0. asmx? http: //www. safl. umn. edu/ Uses Hypertext Markup Language (HTML) Uses Water. ML (an e. Xtended Markup Language for water data)
Web Pages and Web Services http: //his. safl. umn. edu/SAFLMC/cuahsi_1_0. asmx? http: //www. safl. umn. edu/ Uses Hypertext Markup Language (HTML) Uses Water. ML (an e. Xtended Markup Language for water data)
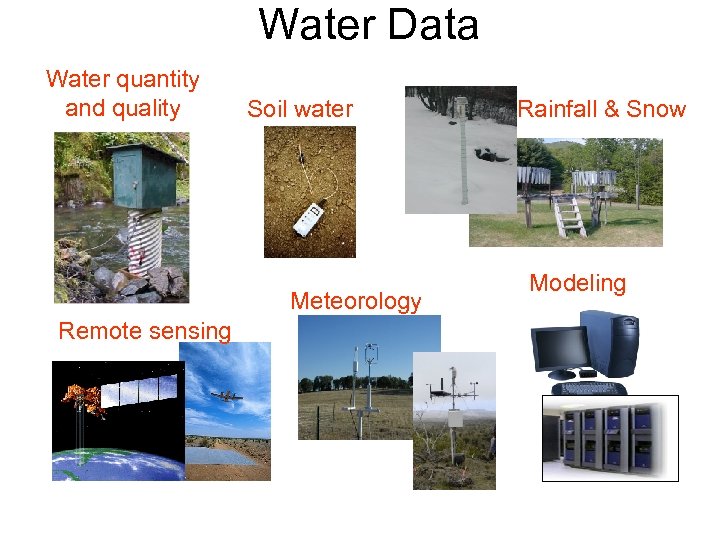 Water Data Water quantity and quality Soil water Meteorology Remote sensing Rainfall & Snow Modeling
Water Data Water quantity and quality Soil water Meteorology Remote sensing Rainfall & Snow Modeling
 Water Data Web Sites
Water Data Web Sites
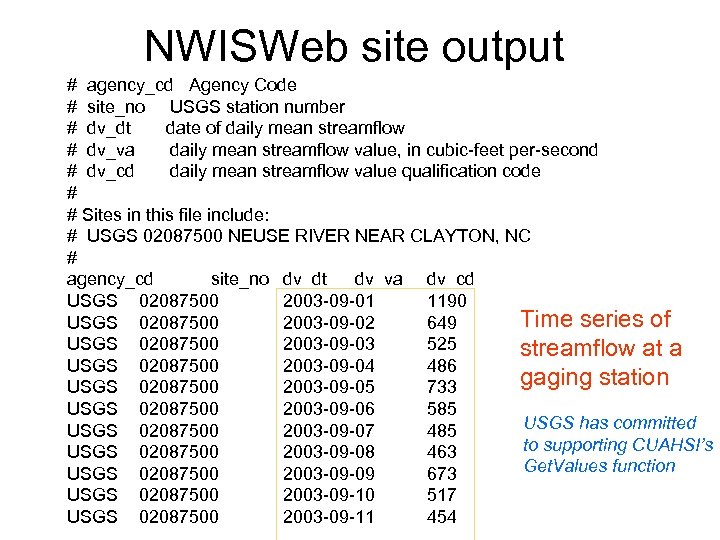 NWISWeb site output # agency_cd Agency Code # site_no USGS station number # dv_dt date of daily mean streamflow # dv_va daily mean streamflow value, in cubic-feet per-second # dv_cd daily mean streamflow value qualification code # # Sites in this file include: # USGS 02087500 NEUSE RIVER NEAR CLAYTON, NC # agency_cd site_no dv_dt dv_va dv_cd USGS 02087500 2003 -09 -01 1190 Time series of USGS 02087500 2003 -09 -02 649 USGS 02087500 2003 -09 -03 525 streamflow at a USGS 02087500 2003 -09 -04 486 gaging station USGS 02087500 2003 -09 -05 733 USGS 02087500 2003 -09 -06 585 USGS has committed USGS 02087500 2003 -09 -07 485 to supporting CUAHSI’s USGS 02087500 2003 -09 -08 463 Get. Values function USGS 02087500 2003 -09 -09 673 USGS 02087500 2003 -09 -10 517 USGS 02087500 2003 -09 -11 454
NWISWeb site output # agency_cd Agency Code # site_no USGS station number # dv_dt date of daily mean streamflow # dv_va daily mean streamflow value, in cubic-feet per-second # dv_cd daily mean streamflow value qualification code # # Sites in this file include: # USGS 02087500 NEUSE RIVER NEAR CLAYTON, NC # agency_cd site_no dv_dt dv_va dv_cd USGS 02087500 2003 -09 -01 1190 Time series of USGS 02087500 2003 -09 -02 649 USGS 02087500 2003 -09 -03 525 streamflow at a USGS 02087500 2003 -09 -04 486 gaging station USGS 02087500 2003 -09 -05 733 USGS 02087500 2003 -09 -06 585 USGS has committed USGS 02087500 2003 -09 -07 485 to supporting CUAHSI’s USGS 02087500 2003 -09 -08 463 Get. Values function USGS 02087500 2003 -09 -09 673 USGS 02087500 2003 -09 -10 517 USGS 02087500 2003 -09 -11 454
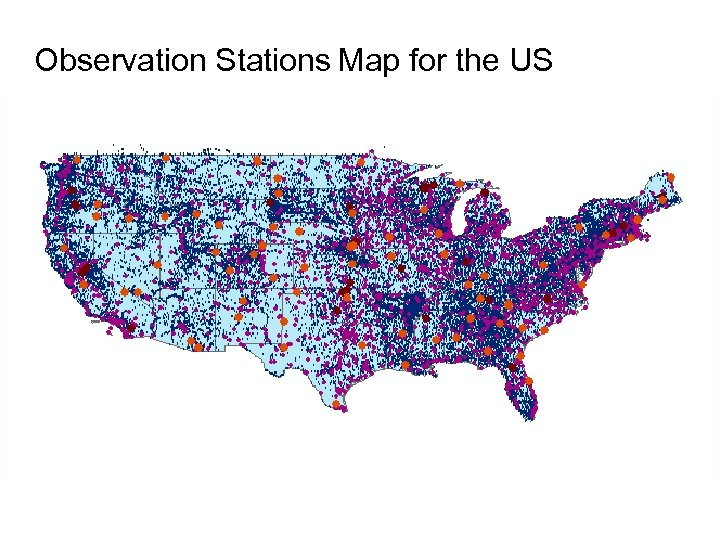 Observation Stations Map for the US Ameriflux Towers (NASA & DOE) NOAA Automated Surface Observing System USGS National Water Information System NOAA Climate Reference Network
Observation Stations Map for the US Ameriflux Towers (NASA & DOE) NOAA Automated Surface Observing System USGS National Water Information System NOAA Climate Reference Network
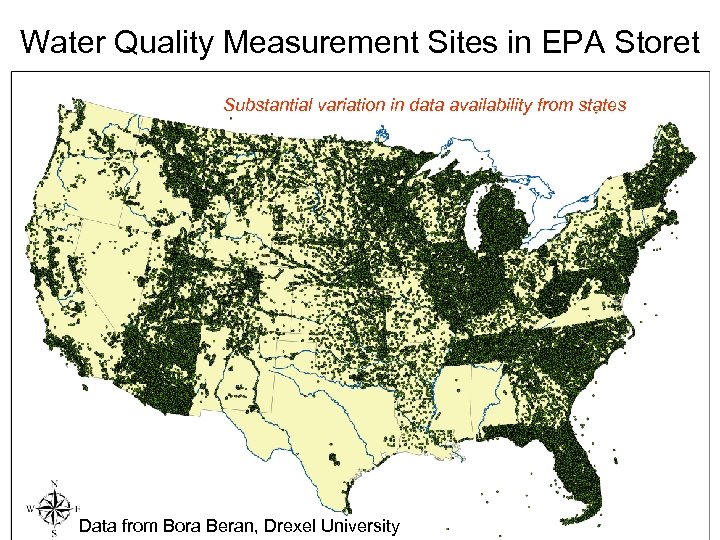 Water Quality Measurement Sites in EPA Storet Substantial variation in data availability from states Data from Bora Beran, Drexel University
Water Quality Measurement Sites in EPA Storet Substantial variation in data availability from states Data from Bora Beran, Drexel University
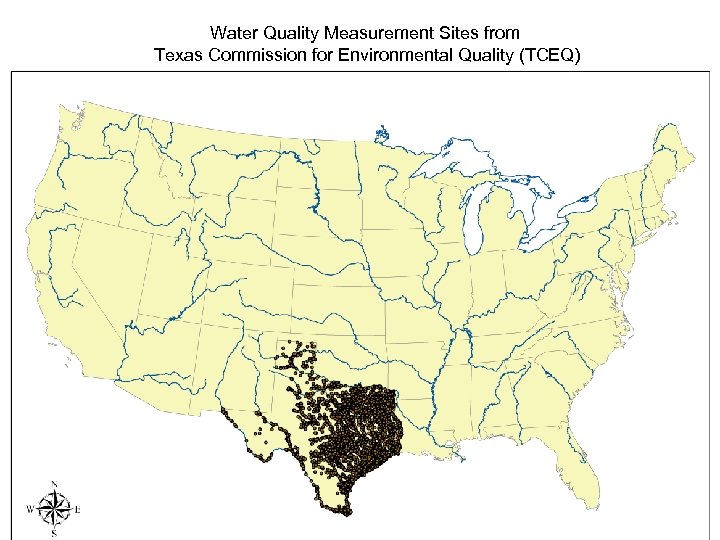 Water Quality Measurement Sites from Texas Commission for Environmental Quality (TCEQ)
Water Quality Measurement Sites from Texas Commission for Environmental Quality (TCEQ)
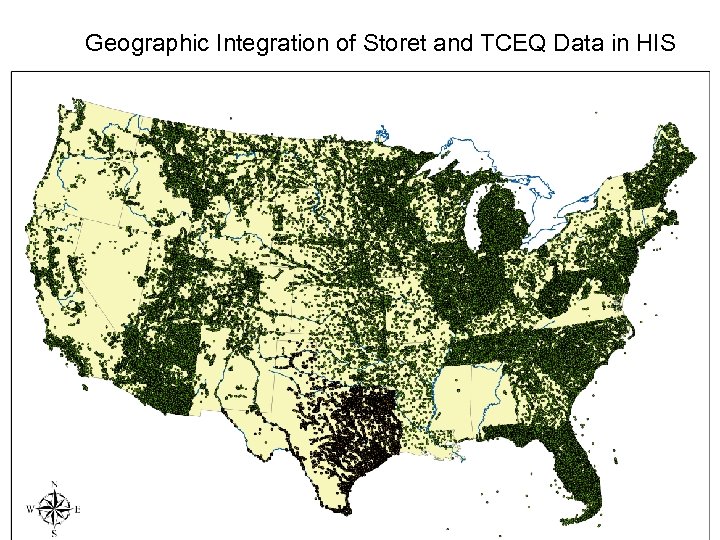 Geographic Integration of Storet and TCEQ Data in HIS
Geographic Integration of Storet and TCEQ Data in HIS
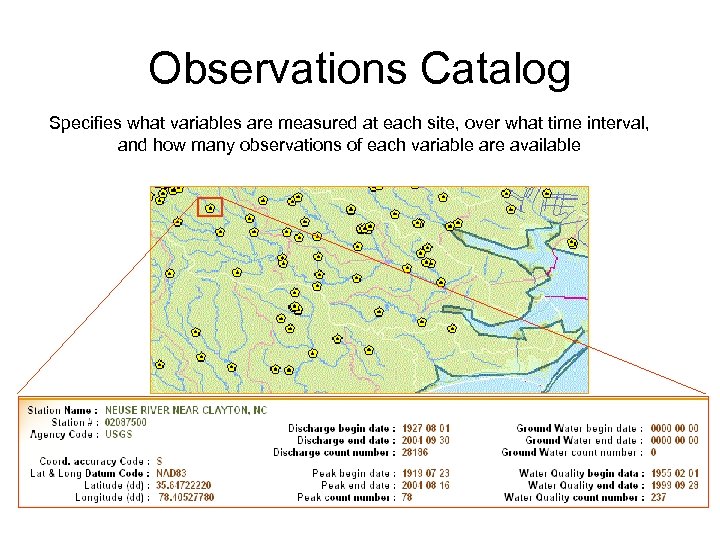 Observations Catalog Specifies what variables are measured at each site, over what time interval, and how many observations of each variable are available
Observations Catalog Specifies what variables are measured at each site, over what time interval, and how many observations of each variable are available
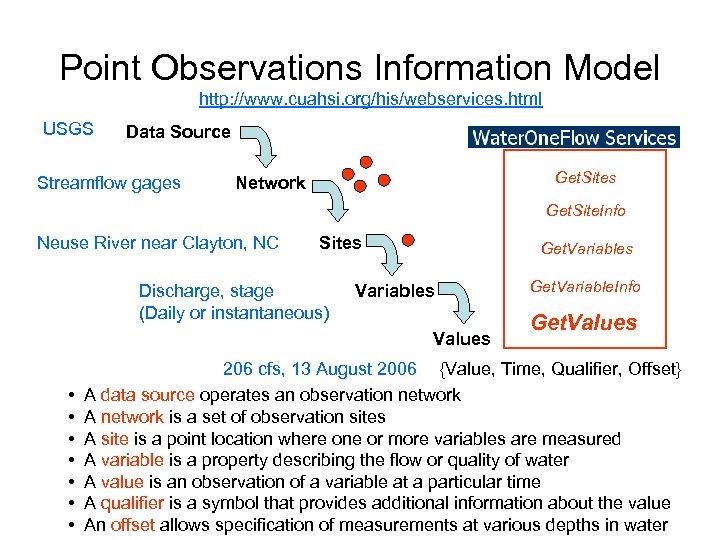 Point Observations Information Model http: //www. cuahsi. org/his/webservices. html USGS Data Source Streamflow gages Get. Sites Network Get. Site. Info Neuse River near Clayton, NC Sites Discharge, stage (Daily or instantaneous) Get. Variables Values • • Get. Variable. Info Get. Values 206 cfs, 13 August 2006 {Value, Time, Qualifier, Offset} A data source operates an observation network A network is a set of observation sites A site is a point location where one or more variables are measured A variable is a property describing the flow or quality of water A value is an observation of a variable at a particular time A qualifier is a symbol that provides additional information about the value An offset allows specification of measurements at various depths in water
Point Observations Information Model http: //www. cuahsi. org/his/webservices. html USGS Data Source Streamflow gages Get. Sites Network Get. Site. Info Neuse River near Clayton, NC Sites Discharge, stage (Daily or instantaneous) Get. Variables Values • • Get. Variable. Info Get. Values 206 cfs, 13 August 2006 {Value, Time, Qualifier, Offset} A data source operates an observation network A network is a set of observation sites A site is a point location where one or more variables are measured A variable is a property describing the flow or quality of water A value is an observation of a variable at a particular time A qualifier is a symbol that provides additional information about the value An offset allows specification of measurements at various depths in water
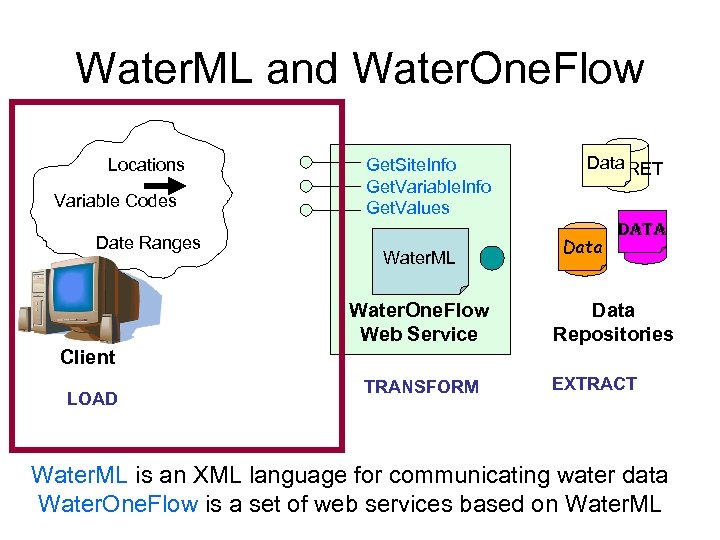 Water. ML and Water. One. Flow Locations Variable Codes Get. Site. Info Get. Variable. Info Get. Values Data STORET Water. ML Water. One. Flow Web Service Date Ranges Data NAM NWIS Data Repositories Client LOAD TRANSFORM EXTRACT Water. ML is an XML language for communicating water data Water. One. Flow is a set of web services based on Water. ML
Water. ML and Water. One. Flow Locations Variable Codes Get. Site. Info Get. Variable. Info Get. Values Data STORET Water. ML Water. One. Flow Web Service Date Ranges Data NAM NWIS Data Repositories Client LOAD TRANSFORM EXTRACT Water. ML is an XML language for communicating water data Water. One. Flow is a set of web services based on Water. ML
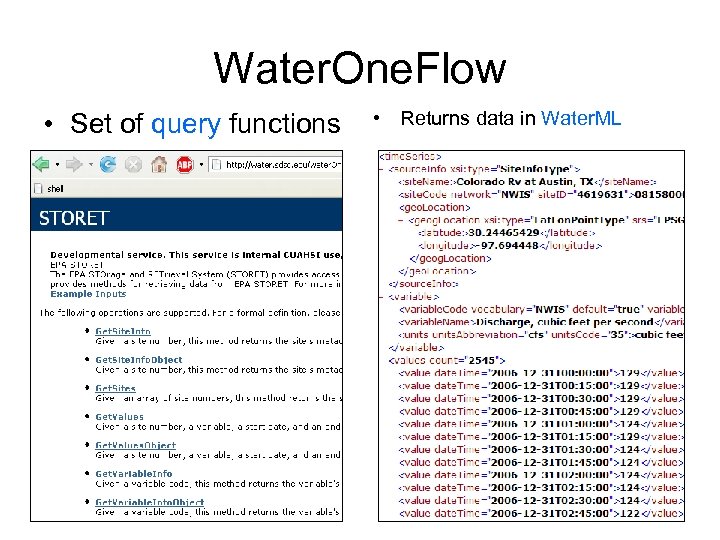 Water. One. Flow • Set of query functions • Returns data in Water. ML
Water. One. Flow • Set of query functions • Returns data in Water. ML
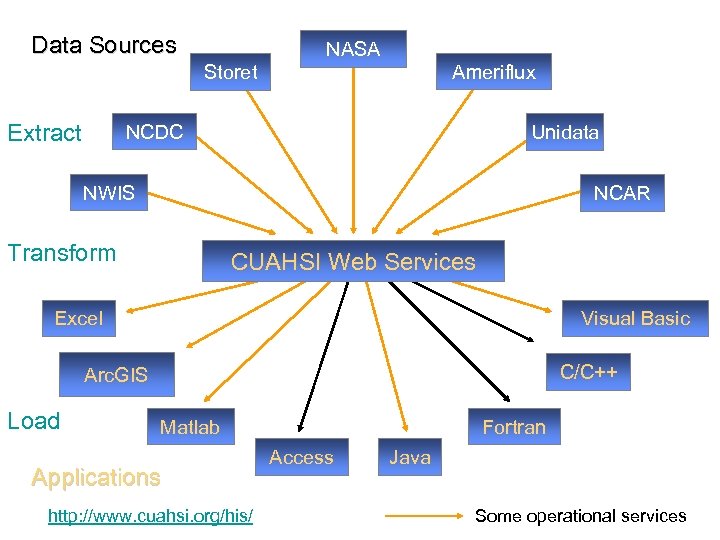 Data Sources Storet Extract NASA Ameriflux NCDC Unidata NWIS NCAR Transform CUAHSI Web Services Excel Visual Basic C/C++ Arc. GIS Load Matlab Applications http: //www. cuahsi. org/his/ Fortran Access Java Some operational services
Data Sources Storet Extract NASA Ameriflux NCDC Unidata NWIS NCAR Transform CUAHSI Web Services Excel Visual Basic C/C++ Arc. GIS Load Matlab Applications http: //www. cuahsi. org/his/ Fortran Access Java Some operational services
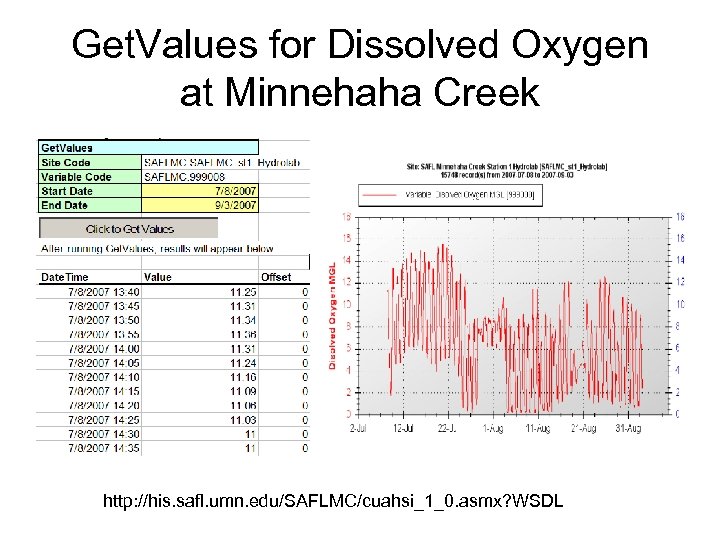 Get. Values for Dissolved Oxygen at Minnehaha Creek http: //his. safl. umn. edu/SAFLMC/cuahsi_1_0. asmx? WSDL
Get. Values for Dissolved Oxygen at Minnehaha Creek http: //his. safl. umn. edu/SAFLMC/cuahsi_1_0. asmx? WSDL
 A Services Oriented Architecture for Water Resources Data • • CUAHSI and WATERS Water. ML and Water. One. Flow Hydrologic Information Server Modeling services
A Services Oriented Architecture for Water Resources Data • • CUAHSI and WATERS Water. ML and Water. One. Flow Hydrologic Information Server Modeling services
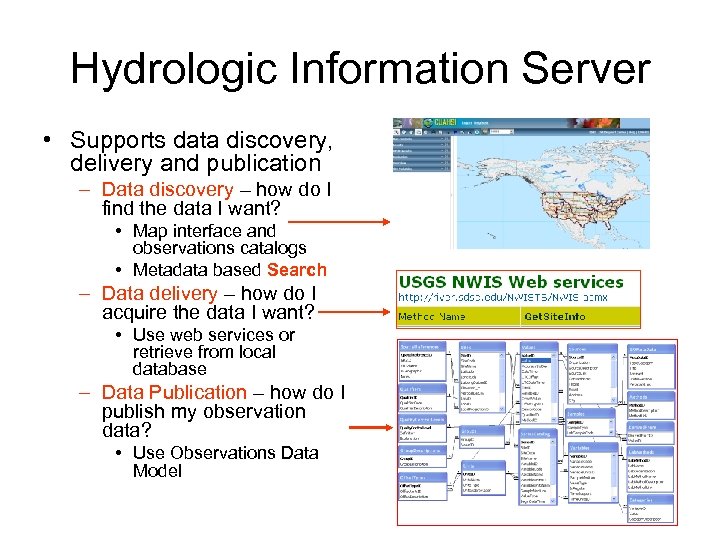 Hydrologic Information Server • Supports data discovery, delivery and publication – Data discovery – how do I find the data I want? • Map interface and observations catalogs • Metadata based Search – Data delivery – how do I acquire the data I want? • Use web services or retrieve from local database – Data Publication – how do I publish my observation data? • Use Observations Data Model
Hydrologic Information Server • Supports data discovery, delivery and publication – Data discovery – how do I find the data I want? • Map interface and observations catalogs • Metadata based Search – Data delivery – how do I acquire the data I want? • Use web services or retrieve from local database – Data Publication – how do I publish my observation data? • Use Observations Data Model
 Water Resource Regions and HUC’s
Water Resource Regions and HUC’s
 National Hydrography Dataset
National Hydrography Dataset
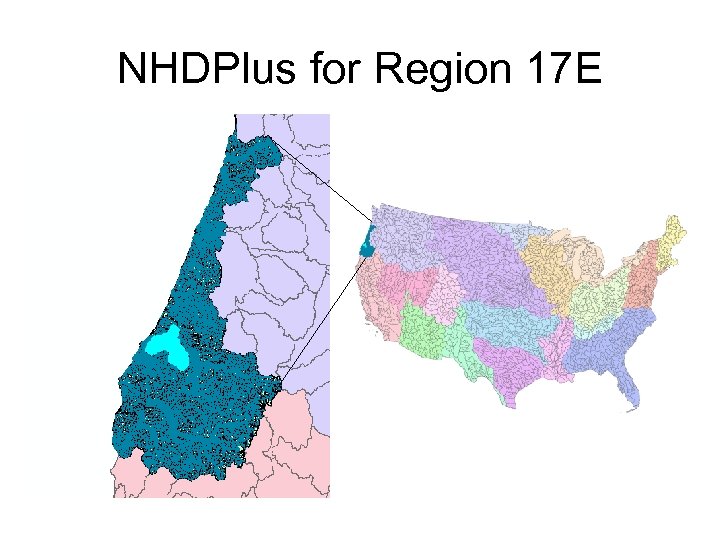 NHDPlus for Region 17 E
NHDPlus for Region 17 E
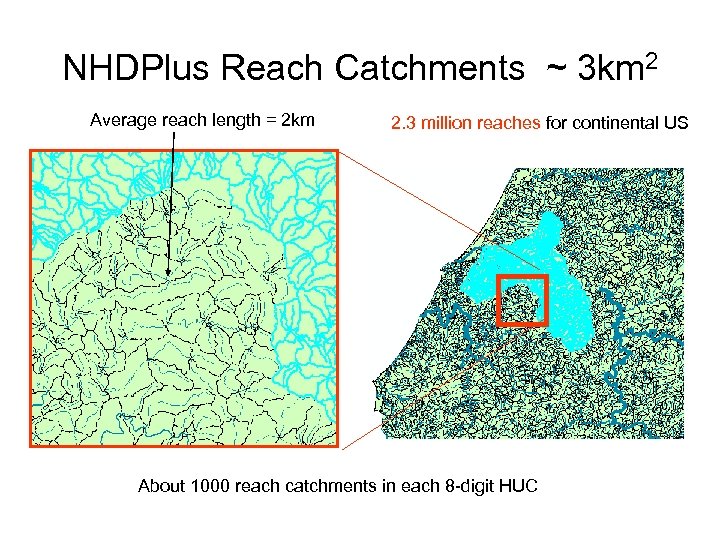 NHDPlus Reach Catchments ~ 3 km 2 Average reach length = 2 km 2. 3 million reaches for continental US About 1000 reach catchments in each 8 -digit HUC
NHDPlus Reach Catchments ~ 3 km 2 Average reach length = 2 km 2. 3 million reaches for continental US About 1000 reach catchments in each 8 -digit HUC
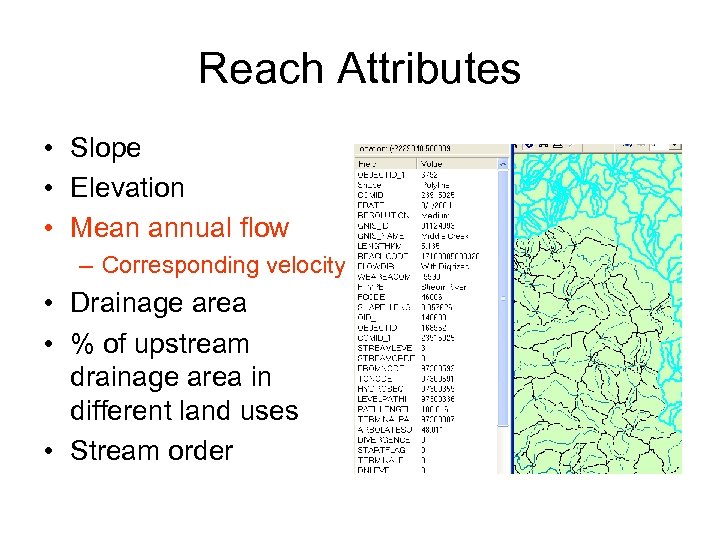 Reach Attributes • Slope • Elevation • Mean annual flow – Corresponding velocity • Drainage area • % of upstream drainage area in different land uses • Stream order
Reach Attributes • Slope • Elevation • Mean annual flow – Corresponding velocity • Drainage area • % of upstream drainage area in different land uses • Stream order
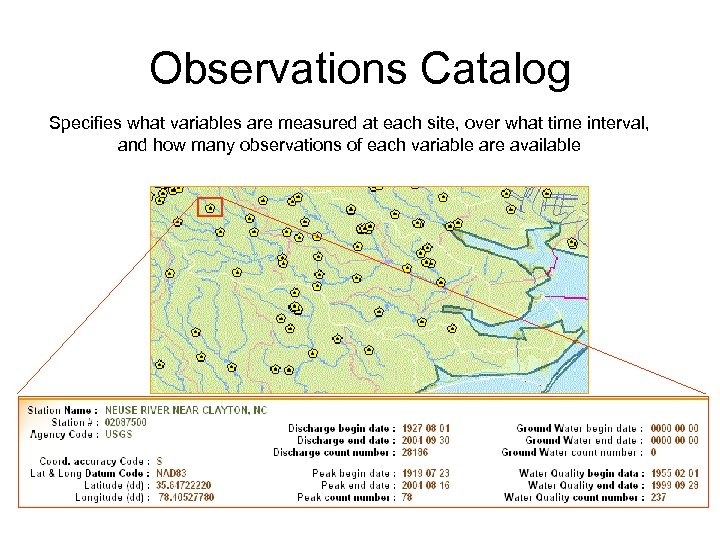 Observations Catalog Specifies what variables are measured at each site, over what time interval, and how many observations of each variable are available
Observations Catalog Specifies what variables are measured at each site, over what time interval, and how many observations of each variable are available
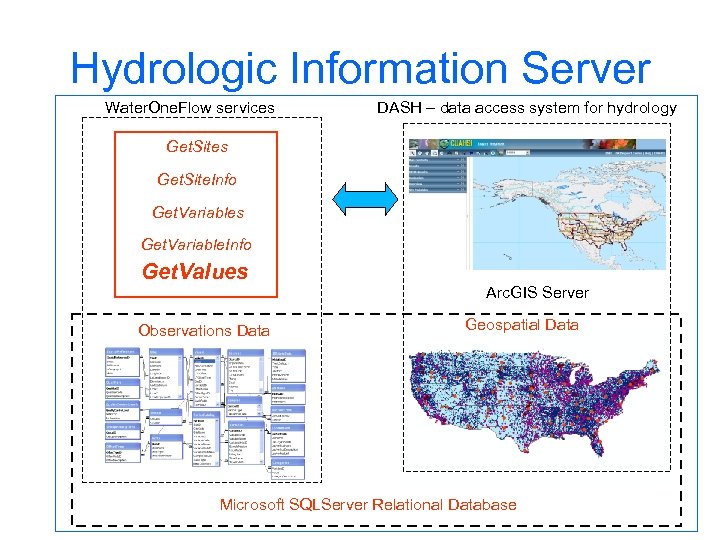 Hydrologic Information Server Water. One. Flow services DASH – data access system for hydrology Get. Sites Get. Site. Info Get. Variables Get. Variable. Info Get. Values Observations Data Arc. GIS Server Geospatial Data Microsoft SQLServer Relational Database
Hydrologic Information Server Water. One. Flow services DASH – data access system for hydrology Get. Sites Get. Site. Info Get. Variables Get. Variable. Info Get. Values Observations Data Arc. GIS Server Geospatial Data Microsoft SQLServer Relational Database
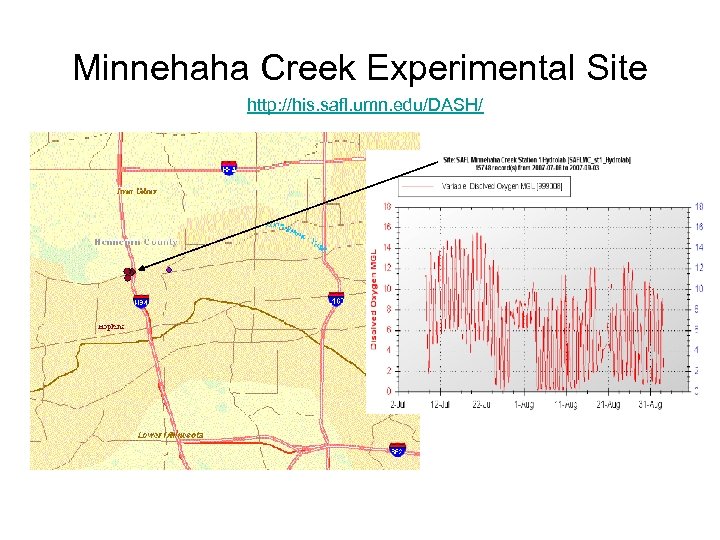 Minnehaha Creek Experimental Site http: //his. safl. umn. edu/DASH/
Minnehaha Creek Experimental Site http: //his. safl. umn. edu/DASH/
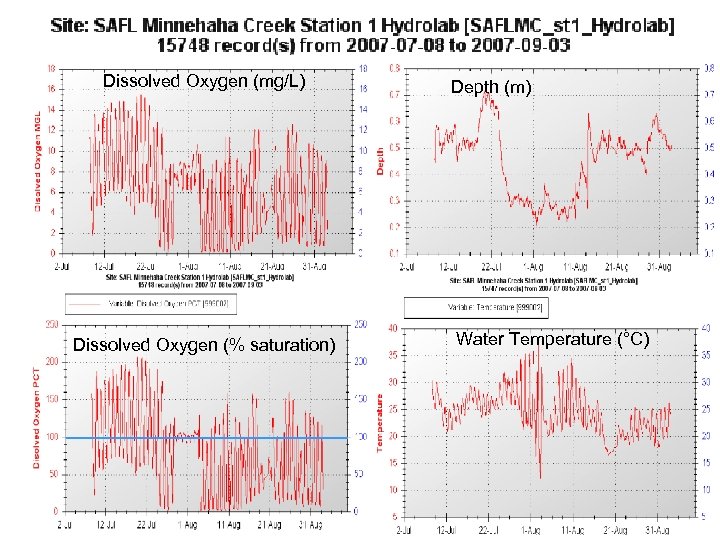 Dissolved Oxygen (mg/L) Dissolved Oxygen (% saturation) Depth (m) Water Temperature (°C)
Dissolved Oxygen (mg/L) Dissolved Oxygen (% saturation) Depth (m) Water Temperature (°C)
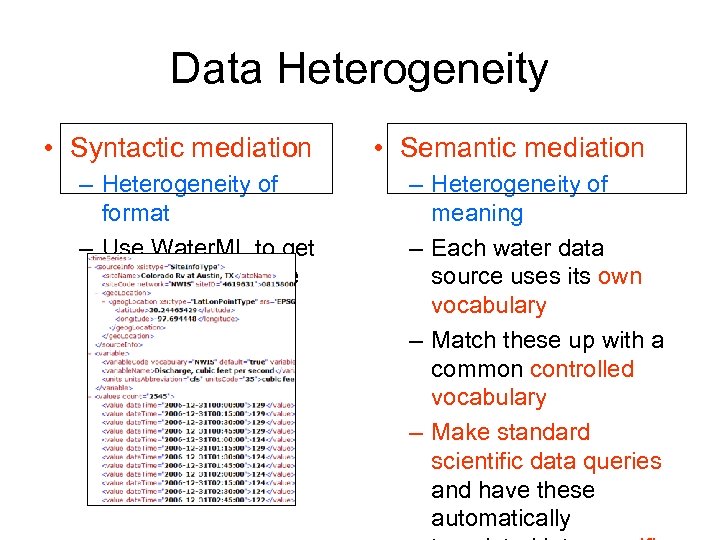 Data Heterogeneity • Syntactic mediation – Heterogeneity of format – Use Water. ML to get data into the same format • Semantic mediation – Heterogeneity of meaning – Each water data source uses its own vocabulary – Match these up with a common controlled vocabulary – Make standard scientific data queries and have these automatically
Data Heterogeneity • Syntactic mediation – Heterogeneity of format – Use Water. ML to get data into the same format • Semantic mediation – Heterogeneity of meaning – Each water data source uses its own vocabulary – Match these up with a common controlled vocabulary – Make standard scientific data queries and have these automatically
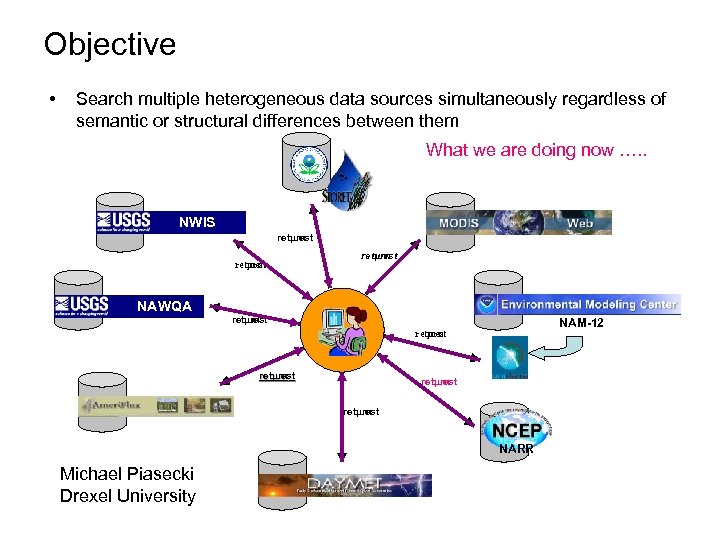 Objective • Search multiple heterogeneous data sources simultaneously regardless of semantic or structural differences between them What we are doing now …. . NWIS request return NAWQA request return request NAM-12 request return NARR Michael Piasecki Drexel University
Objective • Search multiple heterogeneous data sources simultaneously regardless of semantic or structural differences between them What we are doing now …. . NWIS request return NAWQA request return request NAM-12 request return NARR Michael Piasecki Drexel University
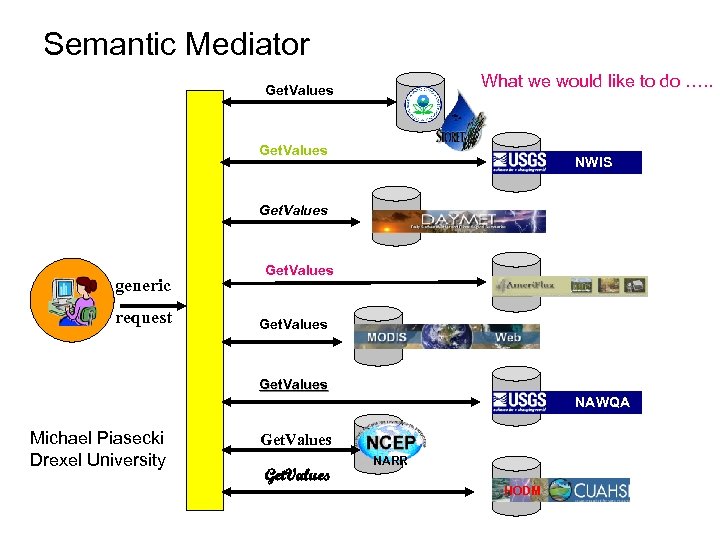 Semantic Mediator What we would like to do …. . Get. Values NWIS Get. Values generic request Get. Values NAWQA Michael Piasecki Drexel University Get. Values NARR HODM
Semantic Mediator What we would like to do …. . Get. Values NWIS Get. Values generic request Get. Values NAWQA Michael Piasecki Drexel University Get. Values NARR HODM
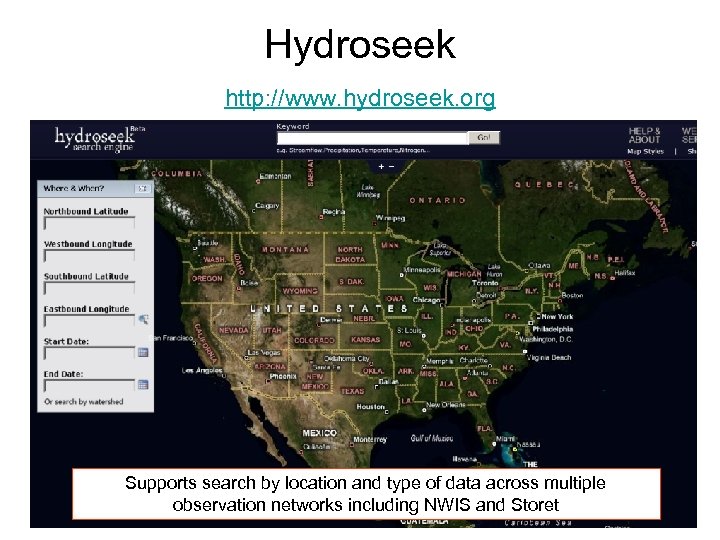 Hydroseek http: //www. hydroseek. org Supports search by location and type of data across multiple observation networks including NWIS and Storet
Hydroseek http: //www. hydroseek. org Supports search by location and type of data across multiple observation networks including NWIS and Storet
 A Services Oriented Architecture for Water Resources Data • • CUAHSI and WATERS Water. ML and Water. One. Flow Hydrologic Information Server Modeling services
A Services Oriented Architecture for Water Resources Data • • CUAHSI and WATERS Water. ML and Water. One. Flow Hydrologic Information Server Modeling services
 • Project sponsored by the European Commission to promote integration of water models within the Water Framework Directive • Software standards for model linking • Uses model core as an “engine” • http: //www. open. MI. org
• Project sponsored by the European Commission to promote integration of water models within the Water Framework Directive • Software standards for model linking • Uses model core as an “engine” • http: //www. open. MI. org
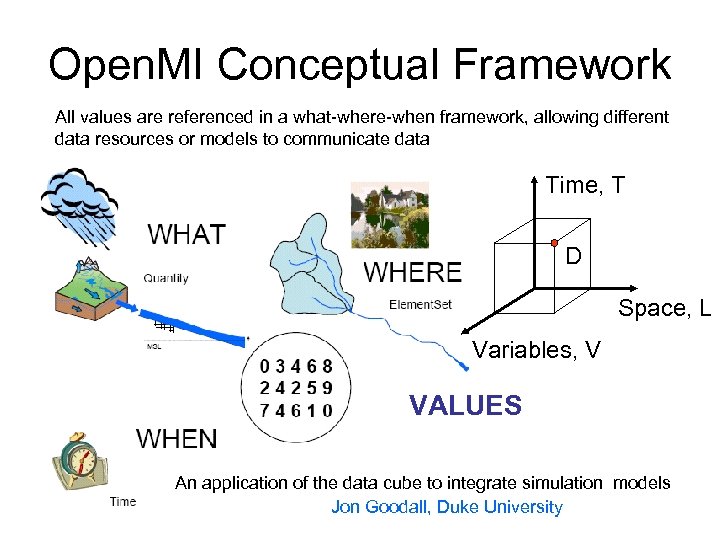 Open. MI Conceptual Framework All values are referenced in a what-where-when framework, allowing different data resources or models to communicate data Time, T D Space, L Variables, V VALUES An application of the data cube to integrate simulation models Jon Goodall, Duke University
Open. MI Conceptual Framework All values are referenced in a what-where-when framework, allowing different data resources or models to communicate data Time, T D Space, L Variables, V VALUES An application of the data cube to integrate simulation models Jon Goodall, Duke University
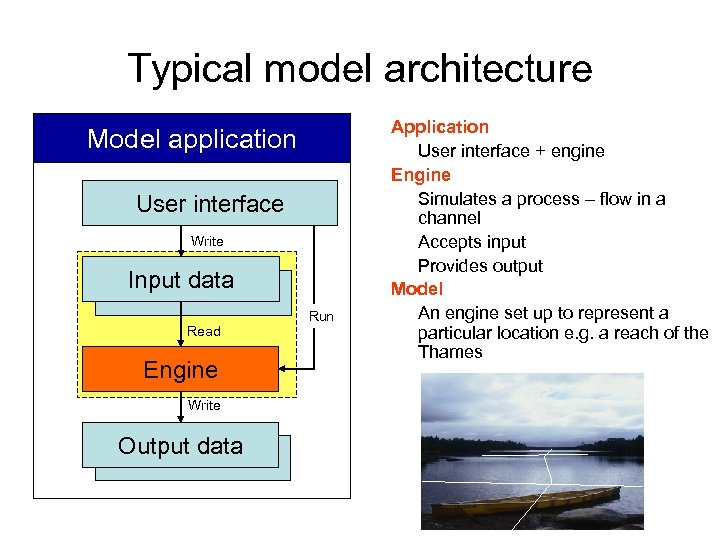 Typical model architecture Model application User interface Write Input data Read Engine Write Output data Run Application User interface + engine Engine Simulates a process – flow in a channel Accepts input Provides output Model An engine set up to represent a particular location e. g. a reach of the Thames
Typical model architecture Model application User interface Write Input data Read Engine Write Output data Run Application User interface + engine Engine Simulates a process – flow in a channel Accepts input Provides output Model An engine set up to represent a particular location e. g. a reach of the Thames
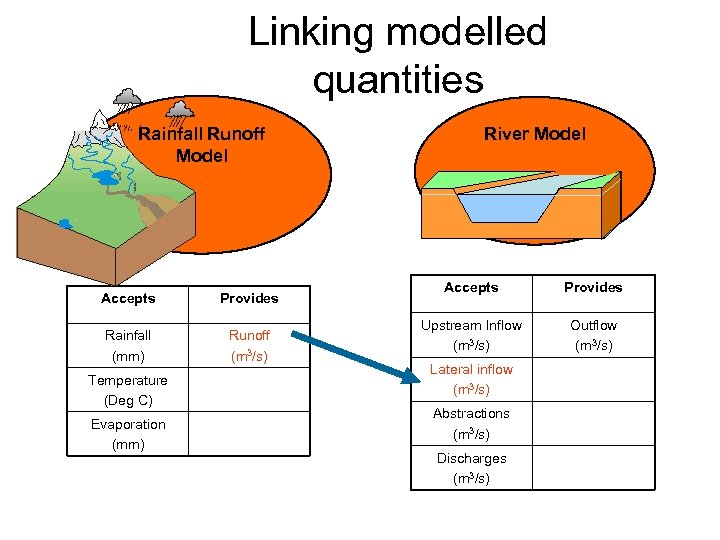 Linking modelled quantities Rainfall Runoff Model Accepts Provides Rainfall (mm) Runoff (m 3/s) Temperature (Deg C) Evaporation (mm) River Model Accepts Provides Upstream Inflow (m 3/s) Outflow (m 3/s) Lateral inflow (m 3/s) Abstractions (m 3/s) Discharges (m 3/s)
Linking modelled quantities Rainfall Runoff Model Accepts Provides Rainfall (mm) Runoff (m 3/s) Temperature (Deg C) Evaporation (mm) River Model Accepts Provides Upstream Inflow (m 3/s) Outflow (m 3/s) Lateral inflow (m 3/s) Abstractions (m 3/s) Discharges (m 3/s)
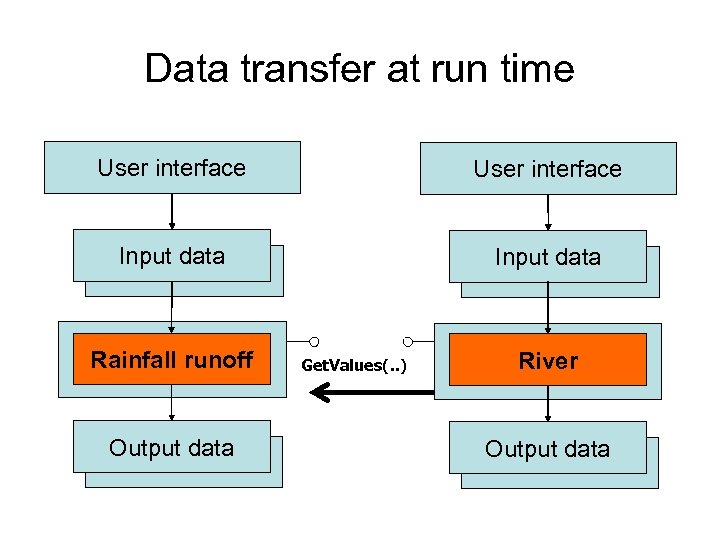 Data transfer at run time User interface Input data Rainfall runoff Output data Get. Values(. . ) River Output data
Data transfer at run time User interface Input data Rainfall runoff Output data Get. Values(. . ) River Output data
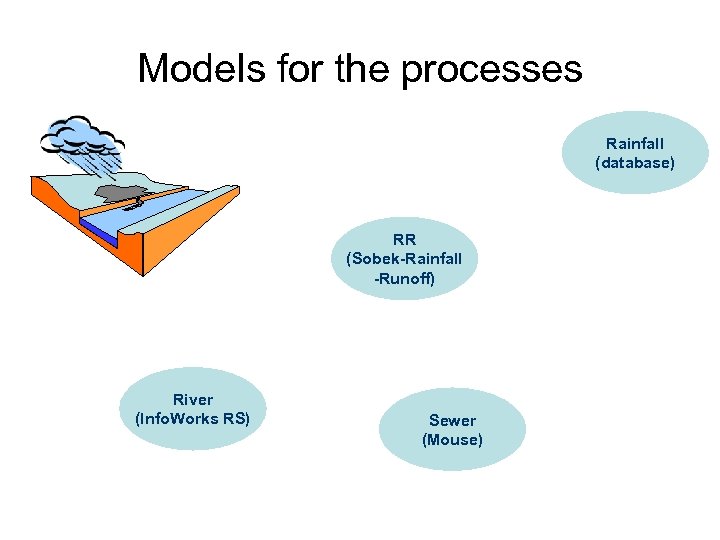 Models for the processes Rainfall (database) RR (Sobek-Rainfall -Runoff) River (Info. Works RS) Sewer (Mouse)
Models for the processes Rainfall (database) RR (Sobek-Rainfall -Runoff) River (Info. Works RS) Sewer (Mouse)
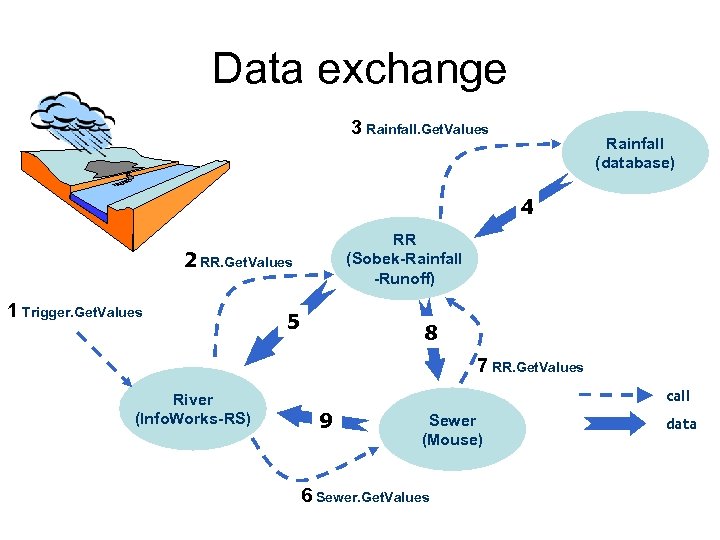 Data exchange 3 Rainfall. Get. Values Rainfall (database) 4 RR (Sobek-Rainfall -Runoff) 2 RR. Get. Values 1 Trigger. Get. Values 5 8 7 RR. Get. Values River (Info. Works-RS) call 9 Sewer (Mouse) 6 Sewer. Get. Values data
Data exchange 3 Rainfall. Get. Values Rainfall (database) 4 RR (Sobek-Rainfall -Runoff) 2 RR. Get. Values 1 Trigger. Get. Values 5 8 7 RR. Get. Values River (Info. Works-RS) call 9 Sewer (Mouse) 6 Sewer. Get. Values data
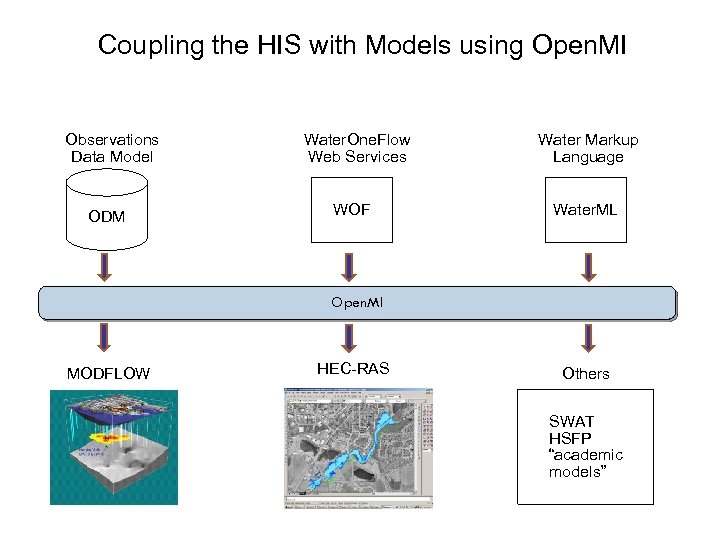 Coupling the HIS with Models using Open. MI Observations Data Model ODM Water. One. Flow Web Services WOF Water Markup Language Water. ML Open. MI MODFLOW HEC-RAS Others SWAT HSFP “academic models”
Coupling the HIS with Models using Open. MI Observations Data Model ODM Water. One. Flow Web Services WOF Water Markup Language Water. ML Open. MI MODFLOW HEC-RAS Others SWAT HSFP “academic models”
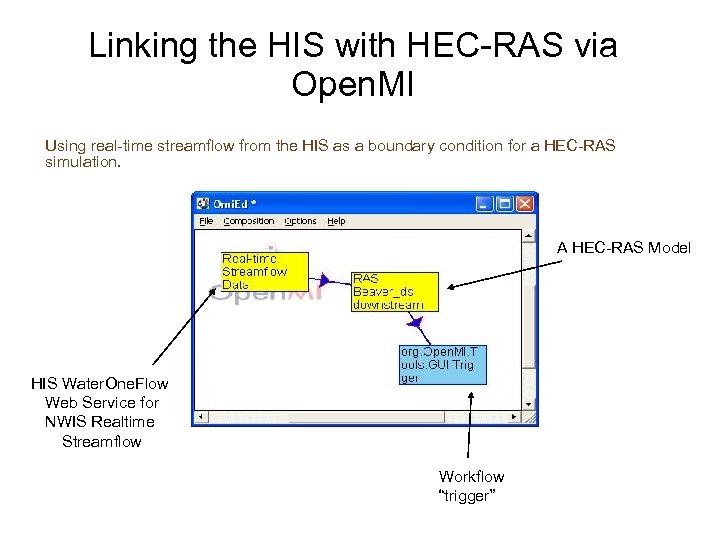 Linking the HIS with HEC-RAS via Open. MI Using real-time streamflow from the HIS as a boundary condition for a HEC-RAS simulation. A HEC-RAS Model HIS Water. One. Flow Web Service for NWIS Realtime Streamflow Workflow “trigger”
Linking the HIS with HEC-RAS via Open. MI Using real-time streamflow from the HIS as a boundary condition for a HEC-RAS simulation. A HEC-RAS Model HIS Water. One. Flow Web Service for NWIS Realtime Streamflow Workflow “trigger”
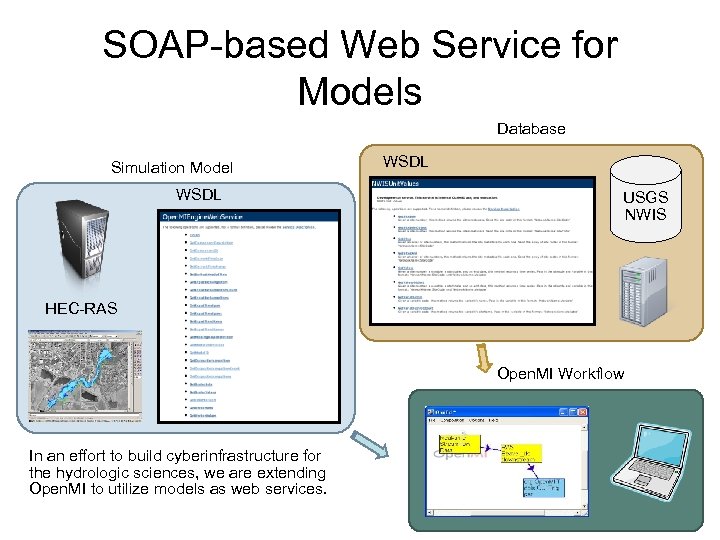 SOAP-based Web Service for Models Database Simulation Model WSDL USGS NWIS HEC-RAS Open. MI Workflow In an effort to build cyberinfrastructure for the hydrologic sciences, we are extending Open. MI to utilize models as web services.
SOAP-based Web Service for Models Database Simulation Model WSDL USGS NWIS HEC-RAS Open. MI Workflow In an effort to build cyberinfrastructure for the hydrologic sciences, we are extending Open. MI to utilize models as web services.
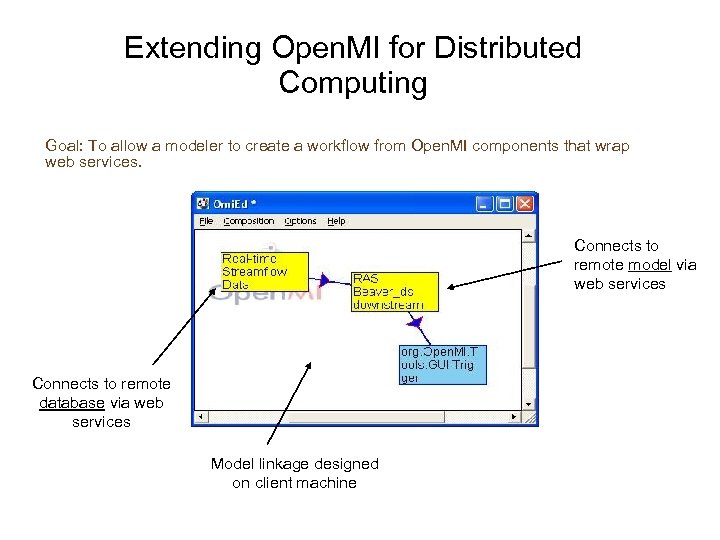 Extending Open. MI for Distributed Computing Goal: To allow a modeler to create a workflow from Open. MI components that wrap web services. Connects to remote model via web services Connects to remote database via web services Model linkage designed on client machine
Extending Open. MI for Distributed Computing Goal: To allow a modeler to create a workflow from Open. MI components that wrap web services. Connects to remote model via web services Connects to remote database via web services Model linkage designed on client machine
 Conclusion The CUAHSI Hydrologic Information System (HIS) is a geographically distributed network of hydrologic data sources and functions that are integrated using web services so that they function as a connected whole. For more information: http: //www. cuahsi. org/his. html
Conclusion The CUAHSI Hydrologic Information System (HIS) is a geographically distributed network of hydrologic data sources and functions that are integrated using web services so that they function as a connected whole. For more information: http: //www. cuahsi. org/his. html


