9ad0b449df617135de91e11cdf0e849d.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 17

A Run-Time Reconfigurable 2 D Discrete Wavelet Transform using JBits Eric Keller Jonathan Ballagh Peter Athanas

Topics w Motivation w DWT Background w Design Overview w Interfacing w Results w Future Work/Conclusions www. xilinx. com
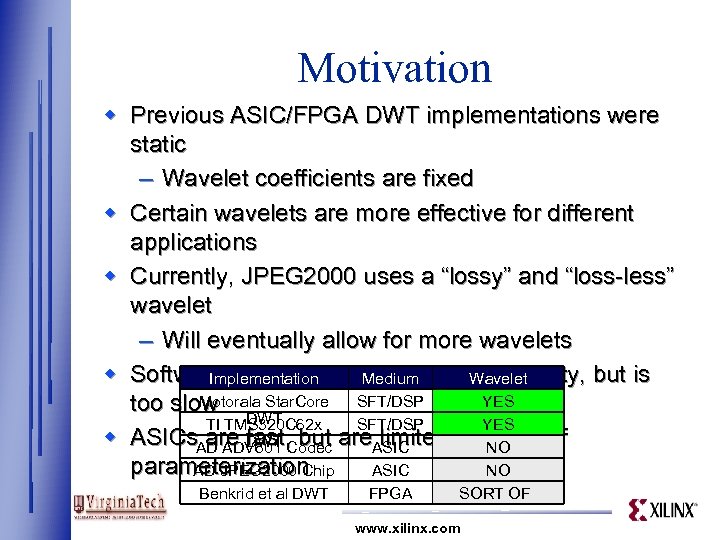
Motivation w Previous ASIC/FPGA DWT implementations were static – Wavelet coefficients are fixed w Certain wavelets are more effective for different applications w Currently, JPEG 2000 uses a “lossy” and “loss-less” wavelet – Will eventually allow for more wavelets w Software provides a great deal of flexibility, but is Implementation Medium Wavelet Selection Motorala Star. Core SFT/DSP YES too slow DWT TI TMS 320 C 62 x SFT/DSP YES w ASICs are fast, but are limited in terms of DWT AD ADV 601 Codec ASIC NO parameterization AD JPEG 2000 Chip ASIC NO Benkrid et al DWT FPGA SORT OF www. xilinx. com
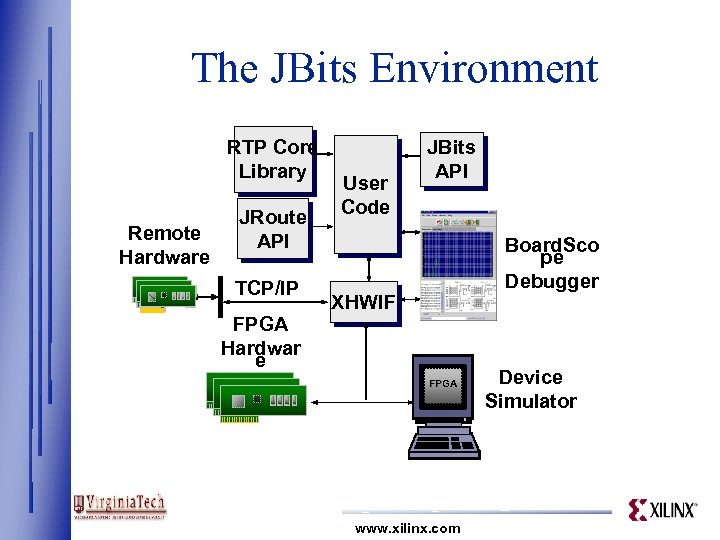
The JBits Environment RTP Core Library Remote Hardware JRoute API TCP/IP User Code JBits API Board. Sco pe Debugger XHWIF FPGA Hardwar e FPGA www. xilinx. com Device Simulator
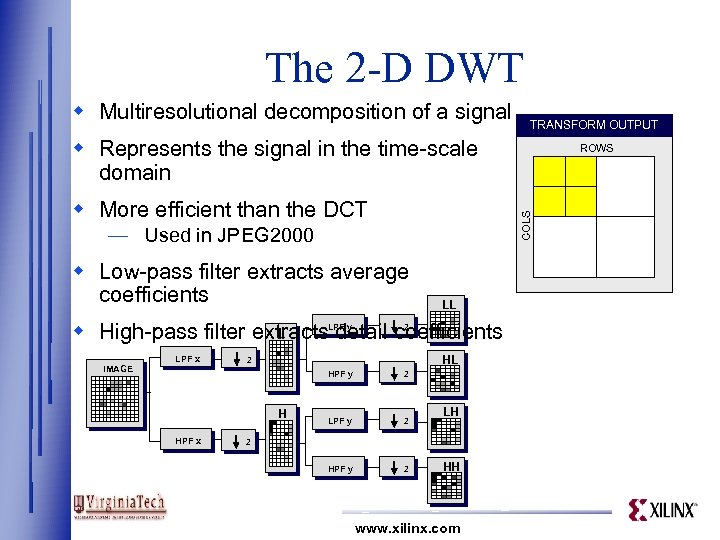
The 2 -D DWT w Multiresolutional decomposition of a signal TRANSFORM OUTPUT w Represents the signal in the time-scale domain COLS w Low-pass filter extracts average coefficients LL L w High-pass filter extracts detail coefficients LPF x 2 HL 2 HPF y H HPF x 2 LPF y 2 HPF y 2 Low/High Output LH 2 HH www. xilinx. com Low-Pass High-Pass Output High/Low Output High/High Output — Used in JPEG 2000 IMAGE Low/Low Output w More efficient than the DCT LPF y ROWS Output
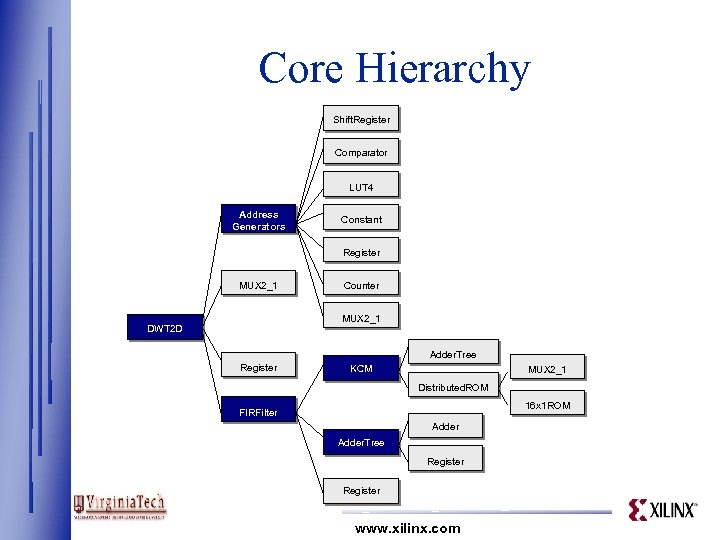
Core Hierarchy Shift. Register Comparator LUT 4 Address Generators Constant Register MUX 2_1 Counter MUX 2_1 DWT 2 D Adder. Tree Register KCM MUX 2_1 Distributed. ROM 16 x 1 ROM FIRFilter Adder. Tree Register www. xilinx. com
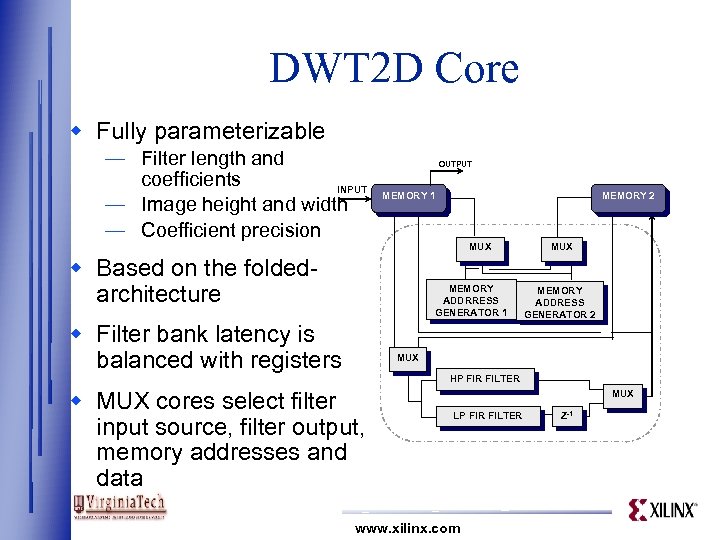
DWT 2 D Core w Fully parameterizable — Filter length and coefficients INPUT — Image height and width — Coefficient precision OUTPUT MEMORY 1 MEMORY 2 MUX w Based on the foldedarchitecture MEMORY ADDRRESS GENERATOR 1 w Filter bank latency is balanced with registers MUX MEMORY ADDRESS GENERATOR 2 MUX HP FIR FILTER w MUX cores select filter input source, filter output, memory addresses and data MUX LP FIR FILTER www. xilinx. com Z-1
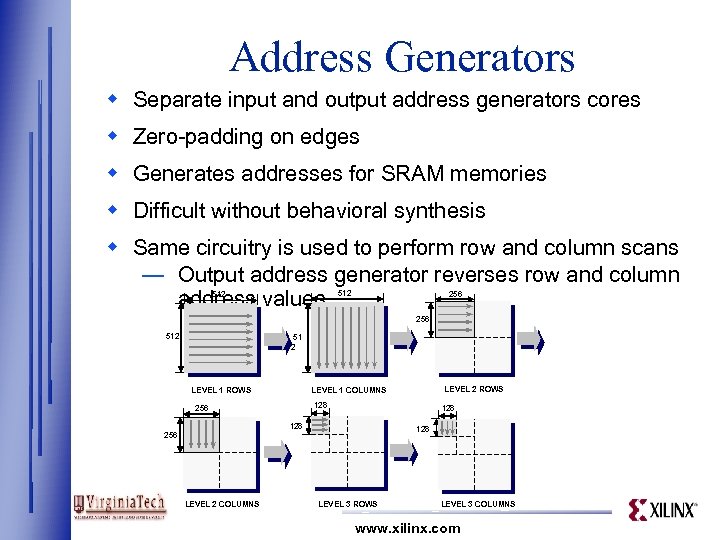
Address Generators w Separate input and output address generators cores w Zero-padding on edges w Generates addresses for SRAM memories w Difficult without behavioral synthesis w Same circuitry is used to perform row and column scans — Output address generator reverses row and column address values 512 256 512 51 2 LEVEL 1 ROWS 128 256 LEVEL 2 COLUMNS LEVEL 2 ROWS LEVEL 1 COLUMNS 128 LEVEL 3 ROWS LEVEL 3 COLUMNS www. xilinx. com
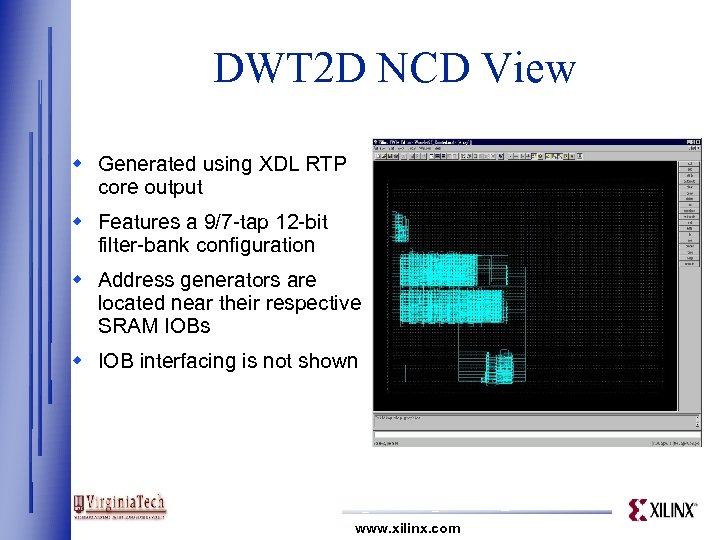
DWT 2 D NCD View w Generated using XDL RTP core output w Features a 9/7 -tap 12 -bit filter-bank configuration w Address generators are located near their respective SRAM IOBs w IOB interfacing is not shown www. xilinx. com
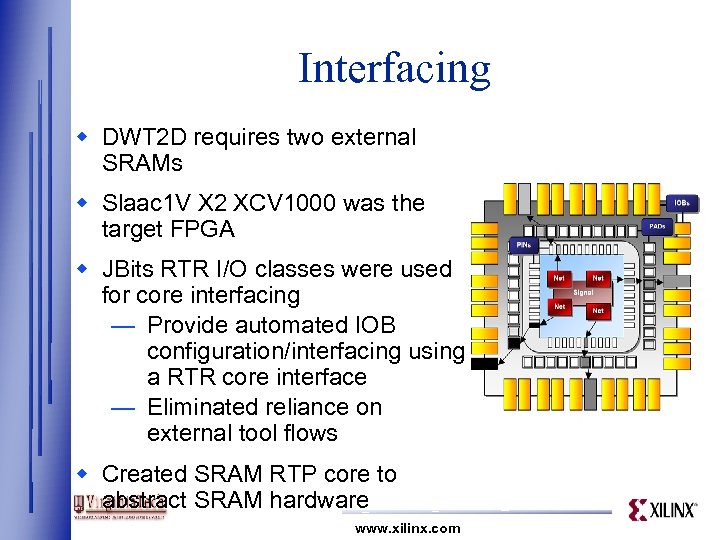
Interfacing w DWT 2 D requires two external SRAMs w Slaac 1 V X 2 XCV 1000 was the target FPGA w JBits RTR I/O classes were used for core interfacing — Provide automated IOB configuration/interfacing using a RTR core interface — Eliminated reliance on external tool flows w Created SRAM RTP core to abstract SRAM hardware www. xilinx. com
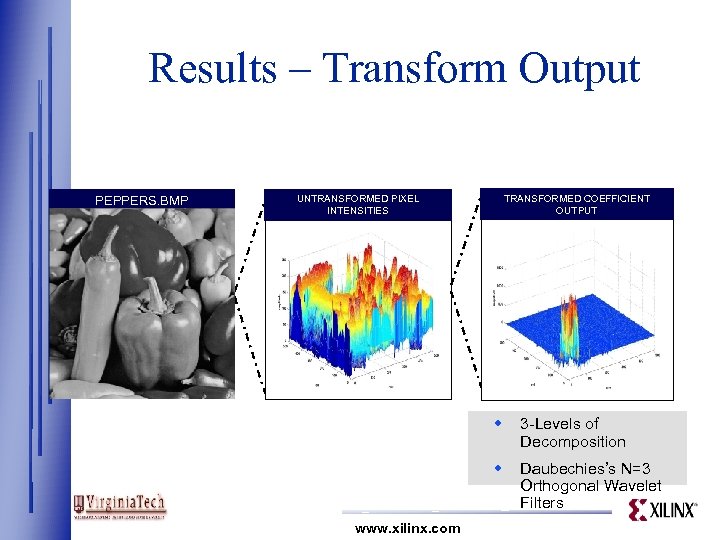
Results – Transform Output PEPPERS. BMP TRANSFORMED COEFFICIENT OUTPUT UNTRANSFORMED PIXEL INTENSITIES w w www. xilinx. com 3 -Levels of Decomposition Daubechies’s N=3 Orthogonal Wavelet Filters
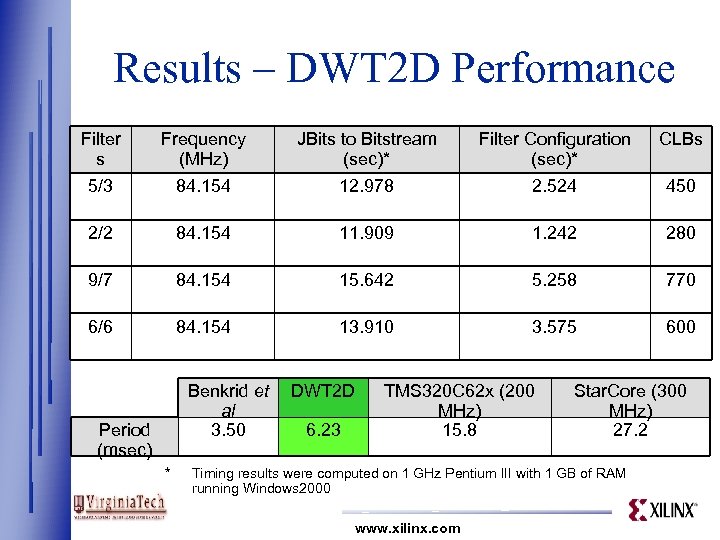
Results – DWT 2 D Performance Filter s Frequency (MHz) JBits to Bitstream (sec)* Filter Configuration (sec)* CLBs 5/3 84. 154 12. 978 2. 524 450 2/2 84. 154 11. 909 1. 242 280 9/7 84. 154 15. 642 5. 258 770 6/6 84. 154 13. 910 3. 575 600 Benkrid et al 3. 50 Period (msec) * DWT 2 D 6. 23 TMS 320 C 62 x (200 MHz) 15. 8 Star. Core (300 MHz) 27. 2 Timing results were computed on 1 GHz Pentium III with 1 GB of RAM running Windows 2000 www. xilinx. com
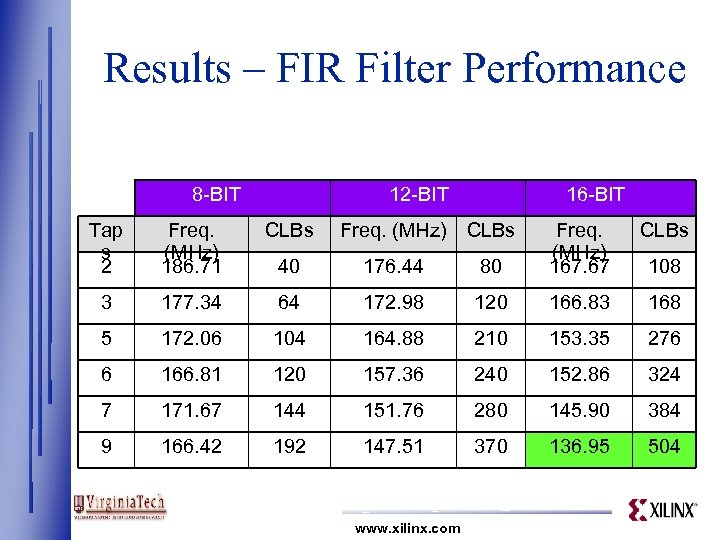
Results – FIR Filter Performance 8 -BIT 12 -BIT 16 -BIT Tap s 2 Freq. (MHz) 186. 71 CLBs Freq. (MHz) CLBs 80 Freq. (MHz) 167. 67 40 176. 44 3 177. 34 64 172. 98 120 166. 83 168 5 172. 06 104 164. 88 210 153. 35 276 6 166. 81 120 157. 36 240 152. 86 324 7 171. 67 144 151. 76 280 145. 90 384 9 166. 42 192 147. 51 370 136. 95 504 www. xilinx. com 108
Results - Partial Reconfiguration w Reconfiguration times are still too lengthy! w In most cases, only the filters are dynamic w Use existing DWT 2 D bitstream — Leave FIR filter circuitry in place — Use constant-folding to modify LUTs w Use JRTR to keep track of bitstream changes — Write only modified portion of bitstream www. xilinx. com
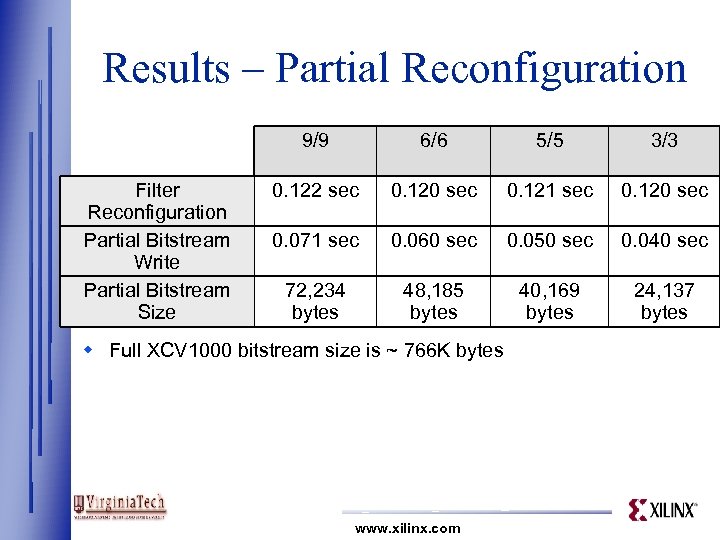
Results – Partial Reconfiguration 9/9 Filter Reconfiguration Partial Bitstream Write Partial Bitstream Size 6/6 5/5 3/3 0. 122 sec 0. 120 sec 0. 121 sec 0. 120 sec 0. 071 sec 0. 060 sec 0. 050 sec 0. 040 sec 72, 234 bytes 48, 185 bytes 40, 169 bytes 24, 137 bytes w Full XCV 1000 bitstream size is ~ 766 K bytes www. xilinx. com
Future Work w Use a more efficient architecture (non-folded) — Recursive Pyramid Algorithm – Uses a systolic-parallel architecture – Transform period of N 2 cycles/level – Requires less memory w Use on-chip BRAM to store intermediate results w Reduce critical path delay — Bring DWT speed up to filter speeds w Add row-extension support — Symmetric reflection w Integrate core into a compression system — Add quantizer and entropy encoder cores www. xilinx. com

Conclusions w Designed a RTR/RTP 2 -D DWT core using JBits — Also created several smaller cores for the DWT core library — FIR Filter / Adder Tree / KCM / Adder / Comparator w No reliance on traditional vendor tools — Generated completely from a XCV 1000 NULL bitstream w Implemented an RTR I/O interfacing methodology — Used RTR I/O classes to connect the DWT 2 D core to the Slaac 1 V SRAMs w Showed that reasonable DWT 2 D reconfiguration www. xilinx. com
9ad0b449df617135de91e11cdf0e849d.ppt