07ea966faad5de93ee5dce6778367810.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 57

A Roadmap To World Class Forecasting February 22 -24, 2009 Stephen P. Crane, Wacker Chemical Corporation CREATING TOMORROW'S SOLUTIONSTo World Class Forecasting Accuracy, Januray 25, 2009 Roadmap Stephen Crane, Page 0

Content § § Wacker Company Overview Why Forecast? Forecasting Background and Challenges Six Keys to Improving Forecast Accuracy – Process, People, & Tools – Statistical Forecasting – Forecasting Segmentation – Data Aggregation – Utilizing Business Intelligence – Measurement & Exception Reporting § Forecasting Accuracy Results § Conclusions Roadmap To World Class Forecasting Accuracy, Januray 25, 2009 Stephen Crane, Page 1

Content § § Wacker Company Overview Why Forecast? Forecasting Background and Challenges Six Keys to Improving Forecast Accuracy – Process, People, & Tools – Statistical Forecasting – Forecasting Segmentation – Data Aggregation – Utilizing Business Intelligence – Measurement & Exception Reporting § Forecasting Accuracy Results § Conclusions Roadmap To World Class Forecasting Accuracy, Januray 25, 2009 Stephen Crane, Page 2

OVER 90 YEARS OF SUCCESS Wacker Chemie AG • Founded in 1914 by Dr. Alexander Wacker • Headquartered in Munich WACKER Group (2006) • Sales: € 3. 34 billion • EBITDA: € 786 million • Net income: € 311 million • Net cash flow: € 185 million • R&D: € 152 million • Capital expenditures: € 525 million • Employees: 14, 668 Roadmap To World Class Forecasting Accuracy, Januray 25, 2009 Stephen Crane, Page 3

WE ARE COMMITTED TO BENCHMARK-QUALITY PRODUCTS DESIGNED FOR OUR FOCUS INDUSTRIES Industries • Adhesives • Automotive and transport • Basic chemicals • Construction chemicals • Gumbase • Industrial coatings and printing inks • Paper and ceramics Products: • Polymer powders and dispersions for the construction industry • Polyvinyl acetate solid resins, polyvinyl alcohol solutions, polyvinyl butyral and vinyl chloride coand terpolymers Roadmap To World Class Forecasting Accuracy, Januray 25, 2009 Stephen Crane, Page 4

Content § § Wacker Company Overview Why Forecast? Forecasting Background and Challenges Six Keys to Improving Forecast Accuracy – Process, People, & Tools – Statistical Forecasting – Forecasting Segmentation – Data Aggregation – Utilizing Business Intelligence – Measurement & Exception Reporting § Forecasting Accuracy Results § Conclusions Roadmap To World Class Forecasting Accuracy, Januray 25, 2009 Stephen Crane, Page 5
Forecast Types § Most companies use three types of forecasts ü Sales or channel forecast ü Corporate planning forecasts ü Supplier forecasts § These forecasts are very different in their use, frequency, and definition § There needs to be a consistent demand single across these three forecasting processes, but most companies don’t know how to align them Roadmap To World Class Forecasting Accuracy, Januray 25, 2009 Stephen Crane, Page 6

Why Forecast? Businesses Need: § More than estimates and SWAGS § An accurate picture of the future § Understanding of marketplace factors § Ability to model/simulate forecast trends § Excellence in forecasting can boost a business’s financial health and gratify customers and employees § The forecast drives supply planning, production planning, inventory planning, raw material planning, and financial forecasting Roadmap To World Class Forecasting Accuracy, Januray 25, 2009 Stephen Crane, Page 7
Why Forecast? § High forecast accuracy cuts cost out of entire supply chain § Companies that are best at demand forecasting average; – 15% less inventory – 17% higher perfect order fulfillment – 35% shorter cash-to-cash cycle times – 1/10 the stockouts of their peers § 1% point improvement in forecast accuracy can yield a 2% point improvement in perfect order fulfillment § 3% increase in forecast accuracy increases profit margin 2% Source: AMR Research 2008 Roadmap To World Class Forecasting Accuracy, Januray 25, 2009 Stephen Crane, Page 8
Why Forecast? § Companies with higher forecast accuracy also achieve better delivery performance – Delivery performance to request date increased 2% for each 5% increase in forecast accuracy – Delivery performance to commit date increased 2. 5% for each 5% increase in forecast accuracy Source: PRTM 2008 Roadmap To World Class Forecasting Accuracy, Januray 25, 2009 Stephen Crane, Page 9
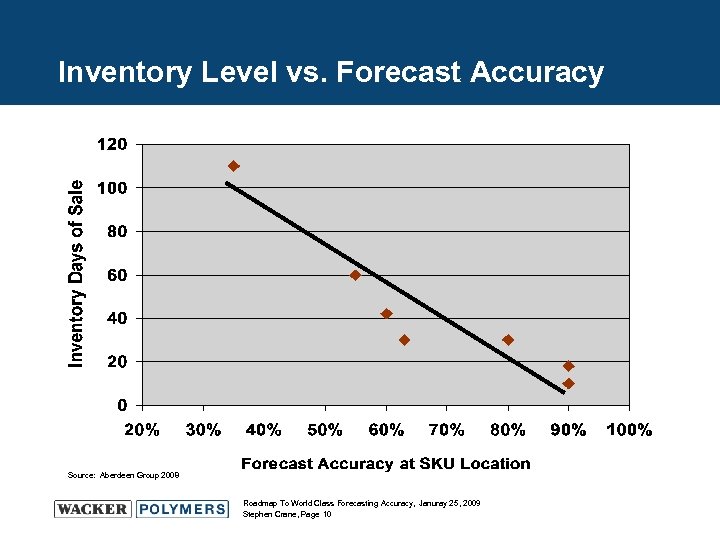
Inventory Level vs. Forecast Accuracy Source: Aberdeen Group 2008 Roadmap To World Class Forecasting Accuracy, Januray 25, 2009 Stephen Crane, Page 10

Order Fill Rate Increases 4. 5% for Each 5% Increase in Forecast Accuracy Source: Aberdeen Group 2008 Roadmap To World Class Forecasting Accuracy, Januray 25, 2009 Stephen Crane, Page 11
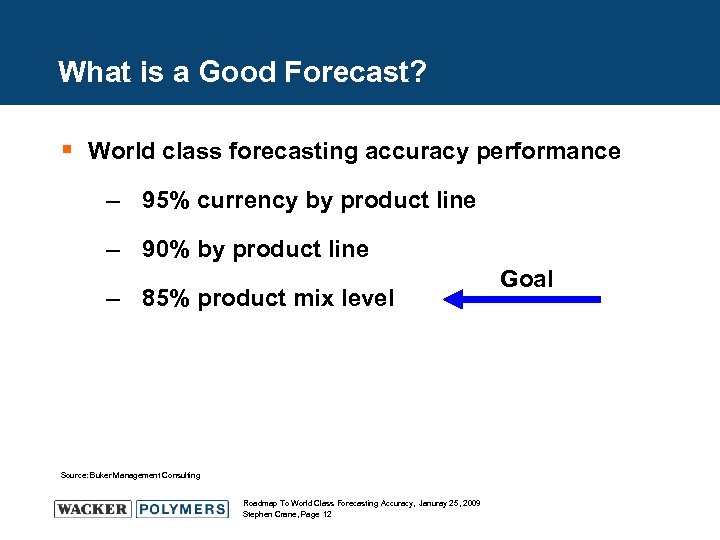
What is a Good Forecast? § World class forecasting accuracy performance – 95% currency by product line – 90% by product line – 85% product mix level Source: Buker Management Consulting Roadmap To World Class Forecasting Accuracy, Januray 25, 2009 Stephen Crane, Page 12 Goal

Content § § Wacker Company Overview Forecasting Benefits Forecasting Background and Challenges Six Keys to Improving Forecast Accuracy – Process, People, & Tools – Statistical Forecasting – Forecasting Segmentation – Data Aggregation – Utilizing Business Intelligence – Measurement & Exception Reporting § Forecasting Accuracy Results § Conclusions Roadmap To World Class Forecasting Accuracy, Januray 25, 2009 Stephen Crane, Page 13

Forecasting Background & Challenges § A typical forecasting process involves historical demand data loaded into a database using statistical software to generate forecasts § Statistical software is rarely allowed to operate on its own § Instead, a management team usually reviews and overrides the statistical forecast before giving the revised version its blessing as the official company projection of future demand § In reality, forecasting is often a difficult and thankless endeavor with accuracies fluctuating wildly § Companies tend to react to inaccuracies with significant investments in technology, processes, and people § However, new investments do not guarantee better forecasts § There are often fundamental issues that need to be recognized and addressed before positive results can be achieved Roadmap To World Class Forecasting Accuracy, Januray 25, 2009 Stephen Crane, Page 14

Forecasting Background & Challenges § Forecasting should really be the foundation for profitable operations § When businesses know their sales for next week, next month, and next year, they only invest in the facilities, equipment, materials, and staffing they need § Constraints can be proactively identified and eliminated, allowing the operations of the business to be prioritized to focus on the product lines that deliver the highest return § So there are huge opportunities to minimize costs and maximize profits if we know what tomorrow will bring – but we don’t. Therefore we forecast! Roadmap To World Class Forecasting Accuracy, Januray 25, 2009 Stephen Crane, Page 15

Content § § Wacker Company Overview Forecasting Benefits Forecasting Background and Challenges Six Keys to Improving Forecast Accuracy – Process, People, & Tools – Statistical Forecasting – Forecasting Segmentation – Data Aggregation – Utilizing Business Intelligence – Measurement & Exception Reporting § Forecasting Accuracy Results § Conclusions Roadmap To World Class Forecasting Accuracy, Januray 25, 2009 Stephen Crane, Page 16

Forecasting success requires making the right choices Roadmap To World Class Forecasting Accuracy, Januray 25, 2009 Stephen Crane, Page 17

Step 1: Defining the Process, People, & Tools Roadmap To World Class Forecasting Accuracy, Januray 25, 2009 Stephen Crane, Page 18

Six Keys to Improving Forecast Accuracy Step 1: Defining the Process, People, & Tools Process § Forecast accuracy improvement and success rely on the proper blending of process, people, and IT tools § Overemphasis on any one leads to an imbalance that can defeat the desired result § The process should be defined first followed by roles and responsibilities and then IT applications § The more people that touch a forecast, the greater the bias and the greater the forecast error Roadmap To World Class Forecasting Accuracy, Januray 25, 2009 Stephen Crane, Page 19
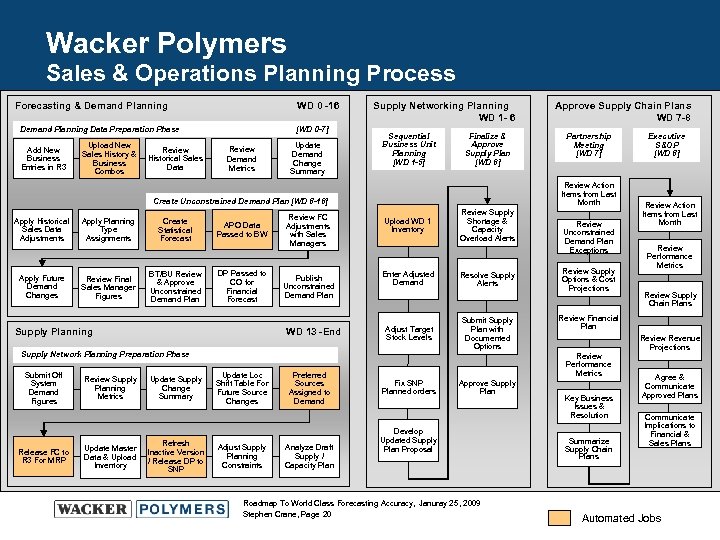
Wacker Polymers Sales & Operations Planning Process Forecasting & Demand Planning WD 0 -16 Demand Planning Data Preparation Phase Add New Business Entries in R 3 Upload New Sales History & Business Combos Review Historical Sales Data [WD 0 -7] Review Demand Metrics Update Demand Change Summary Supply Networking Planning WD 1 - 6 Sequential Business Unit Planning [WD 1 -5] Finalize & Approve Supply Plan [WD 6] Apply Future Demand Changes Apply Planning Type Assignments Review Final Sales Manager Figures Create Statistical Forecast BT/BU Review & Approve Unconstrained Demand Plan APO Data Passed to BW DP Passed to CO for Financial Forecast Supply Planning Review FC Adjustments with Sales Managers Publish Unconstrained Demand Plan WD 13 -End Upload WD 1 Inventory Enter Adjusted Demand Adjust Target Stock Levels Supply Network Planning Preparation Phase Submit Off System Demand Figures Release FC to R 3 For MRP Review Supply Planning Metrics Update Master Data & Upload Inventory Update Supply Change Summary Refresh Inactive Version / Release DP to SNP Update Loc Shift Table For Future Source Changes Adjust Supply Planning Constraints Preferred Sources Assigned to Demand Analyze Draft Supply / Capacity Plan Partnership Meeting [WD 7] Review Action Items from Last Month Create Unconstrained Demand Plan [WD 8 -16] Apply Historical Sales Data Adjustments Approve Supply Chain Plans WD 7 -8 Review Supply Shortage & Capacity Overload Alerts Resolve Supply Alerts Submit Supply Plan with Documented Options Review Unconstrained Demand Plan Exceptions Review Supply Options & Cost Projections Approve Supply Plan Develop Updated Supply Plan Proposal Roadmap To World Class Forecasting Accuracy, Januray 25, 2009 Stephen Crane, Page 20 Review Action Items from Last Month Review Performance Metrics Review Supply Chain Plans Review Financial Plan Review Performance Metrics Fix SNP Planned orders Executive S&OP [WD 8] Key Business Issues & Resolution Summarize Supply Chain Plans Review Revenue Projections Agree & Communicate Approved Plans Communicate Implications to Financial & Sales Plans Automated Jobs
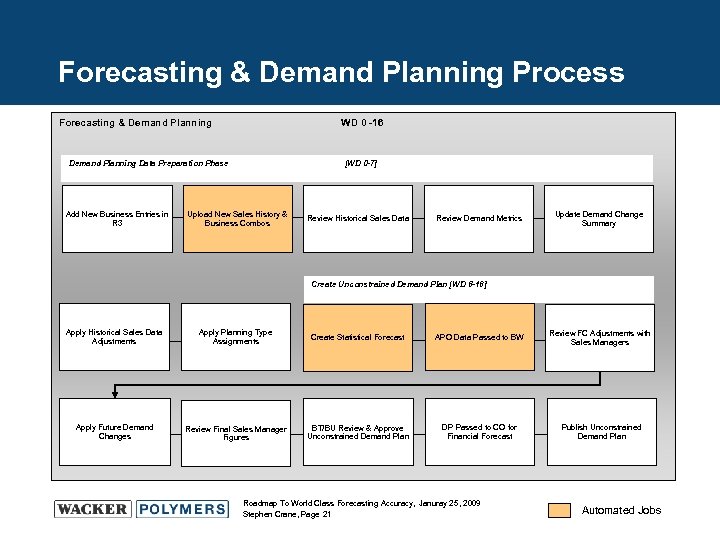
Forecasting & Demand Planning Process Forecasting & Demand Planning WD 0 -16 Demand Planning Data Preparation Phase Add New Business Entries in R 3 [WD 0 -7] Upload New Sales History & Business Combos Review Historical Sales Data Review Demand Metrics Update Demand Change Summary Create Unconstrained Demand Plan [WD 8 -16] Apply Historical Sales Data Adjustments Apply Planning Type Assignments Create Statistical Forecast APO Data Passed to BW Review FC Adjustments with Sales Managers Apply Future Demand Changes Review Final Sales Manager Figures BT/BU Review & Approve Unconstrained Demand Plan DP Passed to CO for Financial Forecast Publish Unconstrained Demand Plan Roadmap To World Class Forecasting Accuracy, Januray 25, 2009 Stephen Crane, Page 21 Automated Jobs

Six Keys to Improving Forecast Accuracy Step 1: Defining the Process, People, & Tools People § People make organizations, are critical to the forecasting process, and how it’s used within the organization § They need to understand how their role fits with the work process and how to make improvements § Position descriptions need to be defined with clear responsibilities that are accepted by the organization § Full time positions are essential § Limit the number of people involved with forecasting process Roadmap To World Class Forecasting Accuracy, Januray 25, 2009 Stephen Crane, Page 22

Six Keys to Improving Forecast Accuracy Step 1: Defining the Process, People, & Tools (Con’t) IT Tools § Forecasting software is sometimes “sold” as the answer to forecasting issues § Software does not solve forecasting problems. Processes and people solve the problems § Implementing forecasting software should never be considered an IT project, but a business process improvement project § Forecasting applications can eliminate much of the manual work associated with forecasting if configured properly Roadmap To World Class Forecasting Accuracy, Januray 25, 2009 Stephen Crane, Page 23

Step 2: Establish Statistical Forecasting Capability Roadmap To World Class Forecasting Accuracy, Januray 25, 2009 Stephen Crane, Page 24
Six Keys to Improving Forecast Accuracy Step 2: Establish Statistical Forecasting Capability § Many supply chains just too complex to manually generate forecasts for all products and customers § Forecasting engines are widely used to improve forecast accuracy by generating statistical forecasts § Statistical forecasting uses sales history to predict the future by identifying trends and patterns within the data to develop a forecast while testing the results for reasonableness § Need to decide at what level the forecasting should be done – Product family – Individual product – Product/customer ship-to – Plant/product/customer ship-to Roadmap To World Class Forecasting Accuracy, Januray 25, 2009 Stephen Crane, Page 25
Six Keys to Improving Forecast Accuracy Step 2: Establish Statistical Forecasting Capability (Con’t) § Need to decide how often to forecast – – Quarterly Monthly Weekly Daily § Determine how much sales history is required for meaningful statistical forecast (minimum 2 years) § Migrate sales history from legacy systems. Very difficult to do correctly. Master data must be correct § Analyze the forecast error associated with using available forecasting algorithms to optimize accuracy of forecast Roadmap To World Class Forecasting Accuracy, Januray 25, 2009 Stephen Crane, Page 26

Six Keys to Improving Forecast Accuracy Step 2: Establish Statistical Forecasting Capability (Con’t) § Typical statistical forecasting methods include – – – – Multiple regression analysis Trend analysis Seasonal Simple moving average Weighted moving average Exponential smoothing Automatic selection Recommended Roadmap To World Class Forecasting Accuracy, Januray 25, 2009 LBU/LRU Sales Meeting October 28, 2008 Stephen Crane, Randy 27 Page Tomas LS, Page 27
Six Keys to Improving Forecast Accuracy Step 2: Establish Statistical Forecasting Capability (Con’t) § It is critical to make the appropriate forecast adjustments to generate an accurate statistical forecast Adjustments Necessary to History – – – Data errors Lost product volume Lost customers One time customer outages Discontinued products Non-optimal sourcing Roadmap To World Class Forecasting Accuracy, Januray 25, 2009 LBU/LRU Sales Meeting October 28, 2008 Stephen Crane, Randy 28 Page Tomas LS, Page 28

Step 3: Forecasting Segmentation 80/20 Analysis Roadmap To World Class Forecasting Accuracy, Januray 25, 2009 Stephen Crane, Page 29

Six Keys to Improving Forecast Accuracy Step 3: Forecasting Segmentation - 80/20 Analysis It is crucial to distinguish the “high-value” forecasts for special attention while automating the “not-as-valuable” forecasts High Statistical Forecastability (measured by 1/COV) Non-High Impact Items Use Data Aggregation in Statistical Model for all Non-HI Items Gather Business Intelligence for all HI items Manage by Exception using Exception Reports Collaborate with Customer (if possible) ~ 80% Total Volume Low Notes COV (Coefficient of Variation) = STD Deviation/Ave. Demand Low Sales Volume/Impact Roadmap To World Class Forecasting Accuracy, Januray 25, 2009 Stephen Crane, Page 30 High
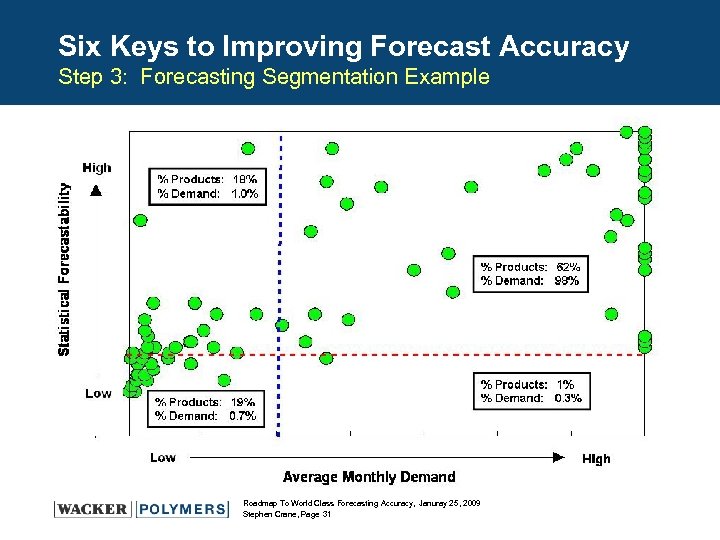
Six Keys to Improving Forecast Accuracy Step 3: Forecasting Segmentation Example Roadmap To World Class Forecasting Accuracy, Januray 25, 2009 Stephen Crane, Page 31

Step 4: Data Aggregation Roadmap To World Class Forecasting Accuracy, Januray 25, 2009 Stephen Crane, Page 32

Six Keys to Improving Forecast Accuracy Step 4: Data Aggregation § SAP APO 4. 1 used forecasting and demand planning § Forecasting done at product/customer ship-to level § Thousands of unique customer / product combinations exist to manage § Too much data for Planners to review monthly § Sales history for many combinations (78%) was sporadic and difficult to forecast, i. e. , high forecasting errors § So how do you get a good forecast for sporadic combinations? – Forecast at a more aggregate level Roadmap To World Class Forecasting Accuracy, Januray 25, 2009 Stephen Crane, Page 33
Six Keys to Improving Forecast Accuracy Step 4: Data Aggregation (Con’t) Getting a good forecast for sporadic combinations…. § Compile non-high impact items from segmentation analysis § Program forecast model to aggregate non-high impact items to logical planning source, will vary by business (plant, warehouse, production unit, etc. ) § Generate statistical forecast at aggregate logical planning source § Disaggregate statistical forecast to lowest forecast level in model based on past history (plant/product/customer ship-to) § Aggregation to the plant/product level reduced number of combinations to review by 80% Aggregation produces a more accurate forecast for sporadic combinations allowing more time to focus on high impact combinations Roadmap To World Class Forecasting Accuracy, Januray 25, 2009 Stephen Crane, Page 34

Step 5: Utilizing Business Intelligence Roadmap To World Class Forecasting Accuracy, Januray 25, 2009 Stephen Crane, Page 35
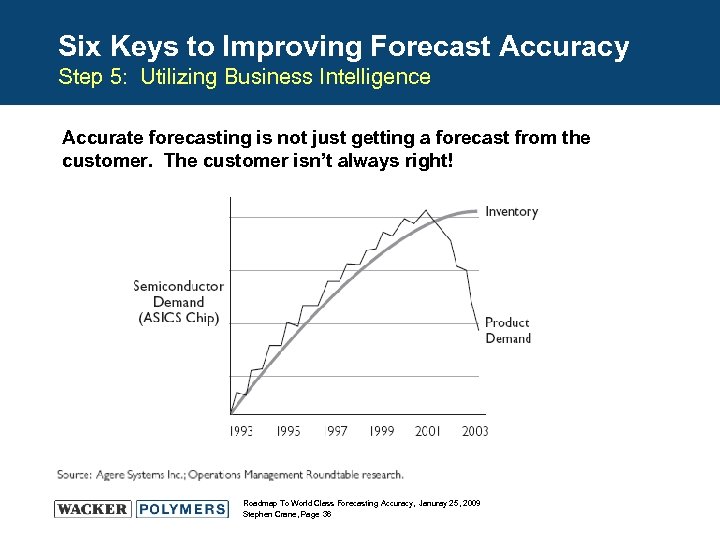
Six Keys to Improving Forecast Accuracy Step 5: Utilizing Business Intelligence Accurate forecasting is not just getting a forecast from the customer. The customer isn’t always right! Roadmap To World Class Forecasting Accuracy, Januray 25, 2009 Stephen Crane, Page 36

Six Keys to Improving Forecast Accuracy Step 5: Utilizing Business Intelligence § Since statistical forecasting is based on previous sales, it is necessary to take into account elements that can affect sales ü ü § Seasonality of the business State of the economy Competition and market position Product trends It’s also important to ask customers the right sales questions to validate forecast assumptions ü ü Where does this project rank today? When are you looking to make a purchasing decision? When will you be implementing? What would you like to see happen as a next step? Roadmap To World Class Forecasting Accuracy, Januray 25, 2009 Stephen Crane, Page 37

Six Keys to Improving Forecast Accuracy Step 5: Utilizing Business Intelligence Adjustments Made to Forecast § Pre-buying § Promotional impacts § Upside and downside volumes § Customer plants expected to be down § New business § New customers Decide where adjustments should be made Adjustments Made to History § Data errors § Lost product volume § One time customer outages § Packaging changes § Discontinued products Roadmap To World Class Forecasting Accuracy, Januray 25, 2009 Stephen Crane, Page 38

Step 6: Measurement & Exception Reporting Roadmap To World Class Forecasting Accuracy, Januray 25, 2009 Stephen Crane, Page 39
Six Keys to Improving Forecast Accuracy Step 6: Measurement & Exception Reporting § Systems are needed for measuring performance, tools for providing feedback, and targets that define what forecasting excellence is § Without ability to effectively measure and track forecasting performance, there is little opportunity to identify whether changes in the forecasting process are contributing to, or hindering business success § Effective measures should evaluate accuracy at different levels of aggregation, (plant, warehouse, sales region, etc. ) § Measuring and tracking forecast accuracy will help to build confidence in the forecasting process § Once users realize that mechanisms are in place to identify and eliminate sources of error, the organization will begin to use the forecast to support operations of the business Roadmap To World Class Forecasting Accuracy, Januray 25, 2009 Stephen Crane, Page 40

Six Keys to Improving Forecast Accuracy Step 6: Measurement & Exception Reporting (Con’t) § A variety of analysis and measurements are needed to achieve significant improvement in forecast accuracy – Identifying High Impact exceptions for Sales review – Accuracy of adjustments made to statistical forecast – Identifying non-High Impact exceptions – Identify current month variances (Forecast – Actual) – Sales but no forecast exceptions – Forecast but no sales exceptions – No sales in last 12 months Roadmap To World Class Forecasting Accuracy, Januray 25, 2009 Stephen Crane, Page 41
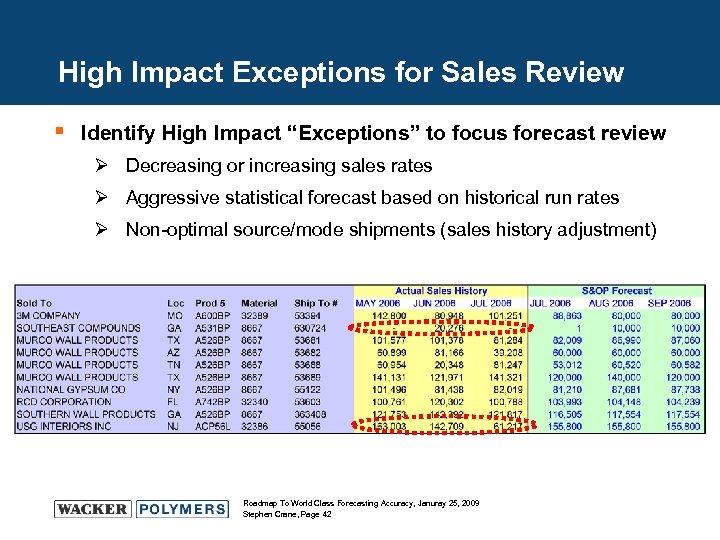
High Impact Exceptions for Sales Review § Identify High Impact “Exceptions” to focus forecast review Ø Decreasing or increasing sales rates Ø Aggressive statistical forecast based on historical run rates Ø Non-optimal source/mode shipments (sales history adjustment) Roadmap To World Class Forecasting Accuracy, Januray 25, 2009 Stephen Crane, Page 42
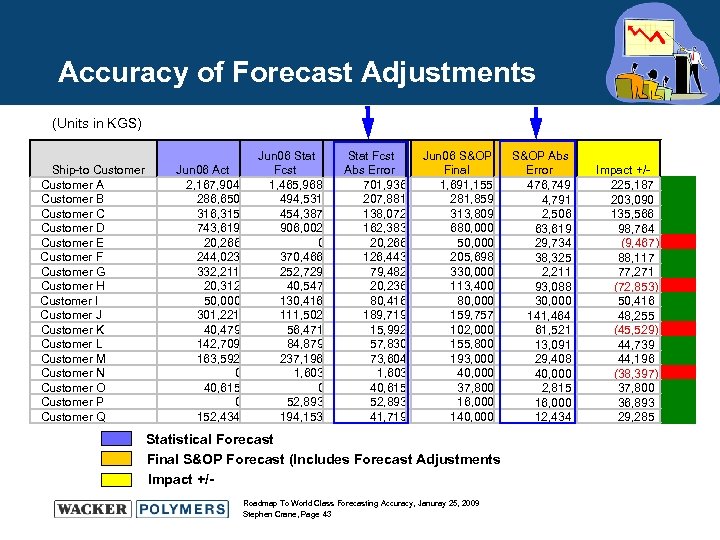
Accuracy of Forecast Adjustments (Units in KGS) Ship-to Customer A Customer B Customer C Customer D Customer E Customer F Customer G Customer H Customer I Customer J Customer K Customer L Customer M Customer N Customer O Customer P Customer Q Jun 06 Act 2, 167, 904 286, 650 316, 315 743, 619 20, 266 244, 023 332, 211 20, 312 50, 000 301, 221 40, 479 142, 709 163, 592 0 40, 615 0 152, 434 Jun 06 Stat Fcst 1, 465, 968 494, 531 454, 387 906, 002 0 370, 466 252, 729 40, 547 130, 416 111, 502 56, 471 84, 879 237, 196 1, 603 0 52, 893 194, 153 Stat Fcst Abs Error 701, 936 207, 881 138, 072 162, 383 20, 266 126, 443 79, 482 20, 236 80, 416 189, 719 15, 992 57, 830 73, 604 1, 603 40, 615 52, 893 41, 719 Jun 06 S&OP Final 1, 691, 155 281, 859 313, 809 680, 000 50, 000 205, 698 330, 000 113, 400 80, 000 159, 757 102, 000 155, 800 193, 000 40, 000 37, 800 16, 000 140, 000 Statistical Forecast Final S&OP Forecast (Includes Forecast Adjustments Impact +/Roadmap To World Class Forecasting Accuracy, Januray 25, 2009 Stephen Crane, Page 43 S&OP Abs Error 476, 749 4, 791 2, 506 63, 619 29, 734 38, 325 2, 211 93, 088 30, 000 141, 464 61, 521 13, 091 29, 408 40, 000 2, 815 16, 000 12, 434 Impact +/225, 187 203, 090 135, 566 98, 764 (9, 467) 88, 117 77, 271 (72, 853) 50, 416 48, 255 (45, 529) 44, 739 44, 196 (38, 397) 37, 800 36, 893 29, 285
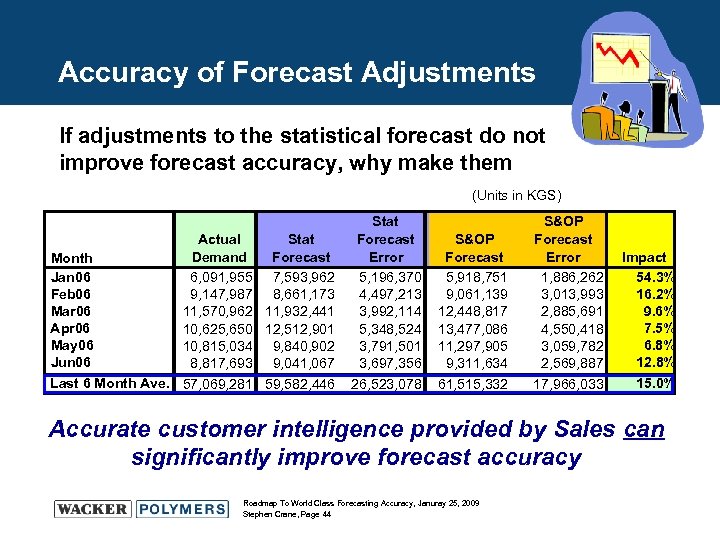
Accuracy of Forecast Adjustments If adjustments to the statistical forecast do not improve forecast accuracy, why make them (Units in KGS) Actual Stat Demand Forecast Month Jan 06 6, 091, 955 7, 593, 962 Feb 06 9, 147, 987 8, 661, 173 Mar 06 11, 570, 962 11, 932, 441 Apr 06 10, 625, 650 12, 512, 901 May 06 10, 815, 034 9, 840, 902 Jun 06 8, 817, 693 9, 041, 067 Last 6 Month Ave. 57, 069, 281 59, 582, 446 Stat Forecast Error 5, 196, 370 4, 497, 213 3, 992, 114 5, 348, 524 3, 791, 501 3, 697, 356 26, 523, 078 S&OP Forecast 5, 918, 751 9, 061, 139 12, 448, 817 13, 477, 086 11, 297, 905 9, 311, 634 61, 515, 332 S&OP Forecast Error 1, 886, 262 3, 013, 993 2, 885, 691 4, 550, 418 3, 059, 782 2, 569, 887 17, 966, 033 Impact 54. 3% 16. 2% 9. 6% 7. 5% 6. 8% 12. 8% 15. 0% Accurate customer intelligence provided by Sales can significantly improve forecast accuracy Roadmap To World Class Forecasting Accuracy, Januray 25, 2009 Stephen Crane, Page 44
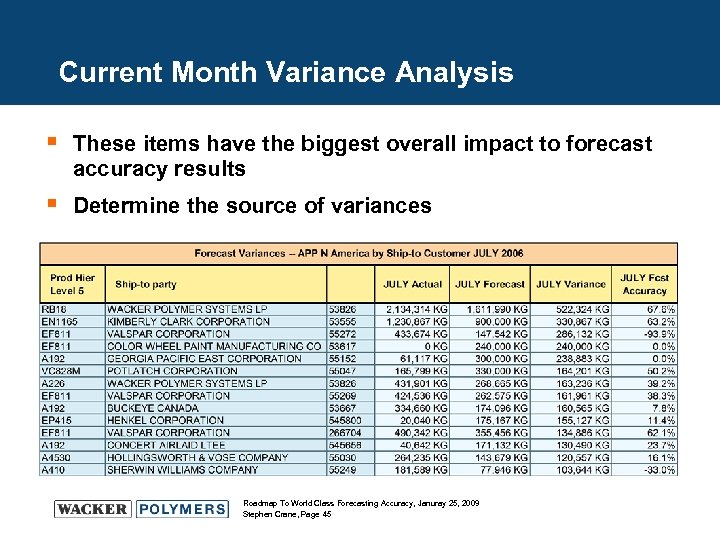
Current Month Variance Analysis § These items have the biggest overall impact to forecast accuracy results § Determine the source of variances Roadmap To World Class Forecasting Accuracy, Januray 25, 2009 Stephen Crane, Page 45
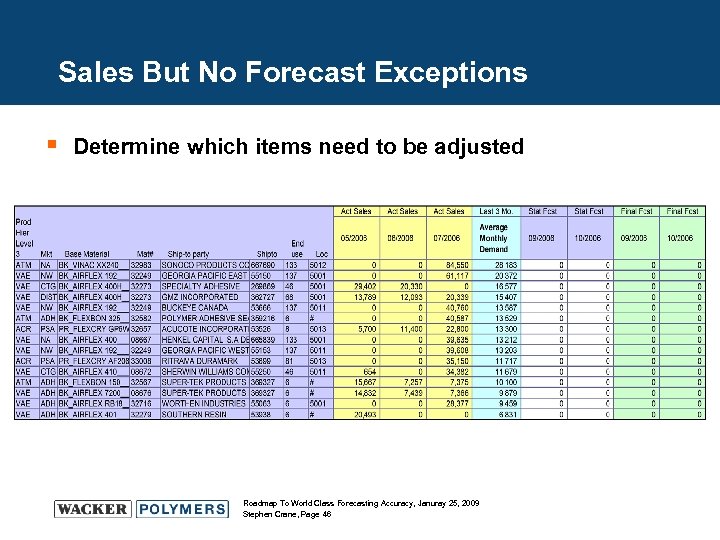
Sales But No Forecast Exceptions § Determine which items need to be adjusted Roadmap To World Class Forecasting Accuracy, Januray 25, 2009 Stephen Crane, Page 46
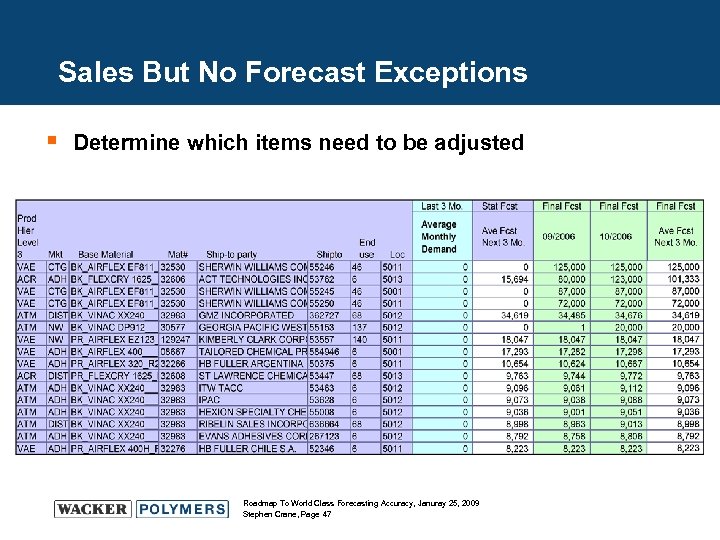
Sales But No Forecast Exceptions § Determine which items need to be adjusted Roadmap To World Class Forecasting Accuracy, Januray 25, 2009 Stephen Crane, Page 47

No Sales in Last 12 Months § Determine which items need to be deleted from forecast model Exception Report - No Sales Last 12 Months Roadmap To World Class Forecasting Accuracy, Januray 25, 2009 Stephen Crane, Page 48

Content § § Wacker Company Overview Why Forecast? Forecasting Background and Challenges Six Keys to Improving Forecast Accuracy – Process, People, & Tools – Statistical Forecasting – Forecasting Segmentation – Data Aggregation – Utilizing Business Intelligence – Measurement & Exception Reporting § Forecasting Accuracy Results § Conclusions Roadmap To World Class Forecasting Accuracy, Januray 25, 2009 Stephen Crane, Page 49
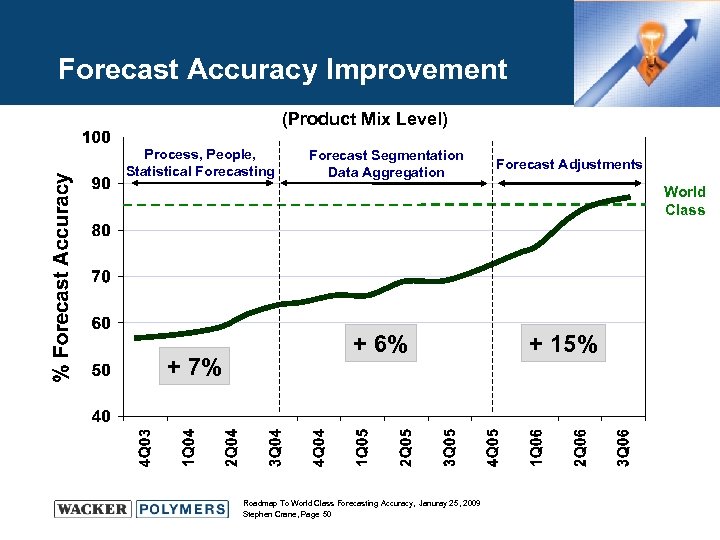
Forecast Accuracy Improvement (Product Mix Level) Process, People, Statistical Forecasting Forecast Segmentation Data Aggregation Forecast Adjustments World Class + 7% + 6% Roadmap To World Class Forecasting Accuracy, Januray 25, 2009 Stephen Crane, Page 50 + 15%

Production Plan Adherence Supply Planning Accuracy 38% Improvement 2004 2007 Roadmap To World Class Forecasting Accuracy, Januray 25, 2009 Stephen Crane, Page 51
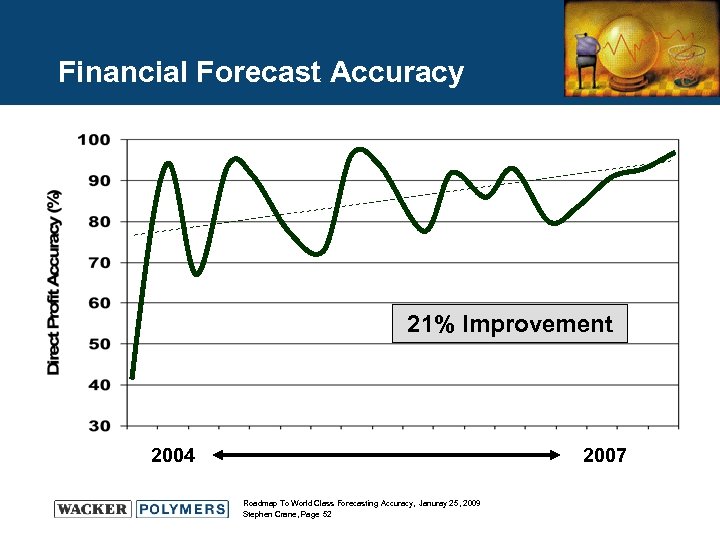
Financial Forecast Accuracy 21% Improvement 2004 2007 Roadmap To World Class Forecasting Accuracy, Januray 25, 2009 Stephen Crane, Page 52

Content § § Wacker Company Overview Why Forecast? Forecasting Background and Challenges Six Keys to Improving Forecast Accuracy – Process, People, & Tools – Statistical Forecasting – Forecasting Segmentation – Data Aggregation – Utilizing Business Intelligence – Measurement & Exception Reporting § Forecasting Accuracy Results § Conclusions Roadmap To World Class Forecasting Accuracy, Januray 25, 2009 Stephen Crane, Page 53

Conclusions As companies improve on their sales forecasting practices, they experience reductions in costs and increases in customer and employee satisfaction. Costs decline in inventory levels, raw materials, production, and logistics. But the first step any company must take before realizing these kind of benefits, is to recognize the importance of sales forecasting as a management function, and be willing to commit the necessary resources to becoming world class. Roadmap To World Class Forecasting Accuracy, Januray 25, 2009 Stephen Crane, Page 54

The Wacker Group Stephen P. Crane Director Strategic Supply Chain Management stephen. crane@wacker. com CREATING TOMORROW'S SOLUTIONS THANK YOU FOR YOUR ATTENTION Roadmap To World Class Forecasting Accuracy, Januray 25, 2009 Stephen Crane, Page 55

Age Old Question: Is Forecasting an Art or Science? • Science means statistically derived from information/data, where as • Art is more Judgmental, but derived from industry/market domain experience and knowledge • Unfortunately, the “Art” is always miss-interpreted as pure judgment (or gut feeling), rather than a true understanding of the dynamics surrounding the marketplace § In my 20 years of experience, I’ve found two truths to hold true: • The more people who touch the forecast, the more inaccurate the forecast, and • The more fact-based (informationdata supported) and mathematically derived the forecast, the more accurate the forecast… § Judgment almost always introduces political bias, based on the purpose or needs of the forecast exercise at hand. . . • Whenever bias is introduced into the equation error escalates • In other words, the more touch points your have in the forecasting process, the more bias (error)Class Forecasting Accuracy, Januray 25, 2009 forecast Roadmap To World you introduce into the Stephen Crane, Page 56
07ea966faad5de93ee5dce6778367810.ppt