4c0e3a1d3e98cb1fc2a3b170c30446ec.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 65
 A Revolution in Cell Analysis Image. Stream Operator Training 2005
A Revolution in Cell Analysis Image. Stream Operator Training 2005
 The Image. Stream® System • Image. Stream® Imaging Flow Cytometer Brightfield, darkfield, and 4 fluorescent images at >15, 000 cells/minute • IDEAS® Statistical Image Analysis Software Quantitative cellular image analysis and population statistics • Novel Applications Translocation, co-localization, cell classification, cell cycle, apoptosis, etc. Training 2005
The Image. Stream® System • Image. Stream® Imaging Flow Cytometer Brightfield, darkfield, and 4 fluorescent images at >15, 000 cells/minute • IDEAS® Statistical Image Analysis Software Quantitative cellular image analysis and population statistics • Novel Applications Translocation, co-localization, cell classification, cell cycle, apoptosis, etc. Training 2005
 Just in Case … AMNIS (Latin), Stream or Torrent INSPIRE INstrument Software Processor for Imaging Research Experiments IDEAS Image Data Exploration and Analysis Software ASSIST Automated Suite of Systemwide Image. Stream Tests Training 2005
Just in Case … AMNIS (Latin), Stream or Torrent INSPIRE INstrument Software Processor for Imaging Research Experiments IDEAS Image Data Exploration and Analysis Software ASSIST Automated Suite of Systemwide Image. Stream Tests Training 2005
 Image. Stream Workflow Experimental Design Instrument Calibration with Speed. Beads® Data acquisition Data analysis Training 2005
Image. Stream Workflow Experimental Design Instrument Calibration with Speed. Beads® Data acquisition Data analysis Training 2005
 A Revolution in Cell Analysis Experimental Design Training 2005
A Revolution in Cell Analysis Experimental Design Training 2005
 Image. Stream Experimental Design Considerations: 1. Selection of cell type 2. Selection of probes 3. Fluorescence control samples 4. Sample prep requirements Training 2005
Image. Stream Experimental Design Considerations: 1. Selection of cell type 2. Selection of probes 3. Fluorescence control samples 4. Sample prep requirements Training 2005
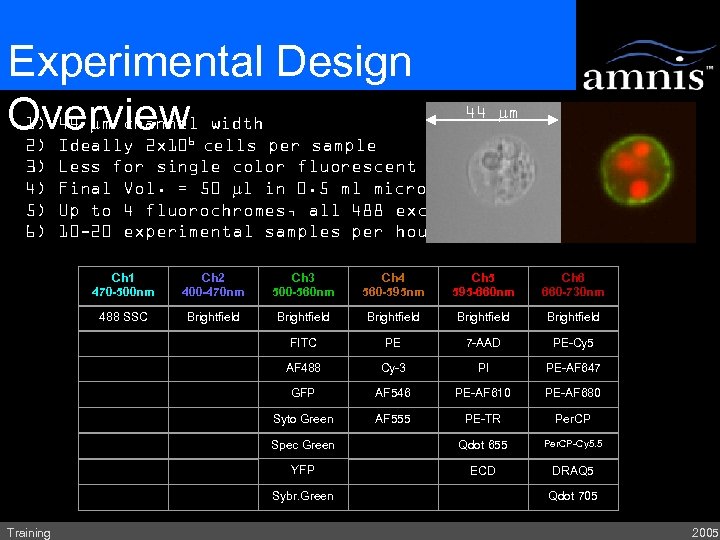 Experimental Design 1) 44 mm channel width Overview cells per sample 2) Ideally 2 x 10 44 mm 6 3) 4) 5) 6) Less for single color fluorescent controls Final Vol. = 50 ml in 0. 5 ml microcentrifuge tube Up to 4 fluorochromes, all 488 excitable 10 -20 experimental samples per hour Ch 1 470 -500 nm Ch 2 400 -470 nm Ch 3 500 -560 nm Ch 4 560 -595 nm Ch 5 595 -660 nm Ch 6 660 -730 nm 488 SSC Brightfield Brightfield FITC PE 7 -AAD PE-Cy 5 AF 488 Cy-3 PI PE-AF 647 GFP AF 546 PE-AF 610 PE-AF 680 Syto Green AF 555 PE-TR Per. CP Spec Green Qdot 655 Per. CP-Cy 5. 5 YFP ECD DRAQ 5 Sybr. Green Training Qdot 705 2005
Experimental Design 1) 44 mm channel width Overview cells per sample 2) Ideally 2 x 10 44 mm 6 3) 4) 5) 6) Less for single color fluorescent controls Final Vol. = 50 ml in 0. 5 ml microcentrifuge tube Up to 4 fluorochromes, all 488 excitable 10 -20 experimental samples per hour Ch 1 470 -500 nm Ch 2 400 -470 nm Ch 3 500 -560 nm Ch 4 560 -595 nm Ch 5 595 -660 nm Ch 6 660 -730 nm 488 SSC Brightfield Brightfield FITC PE 7 -AAD PE-Cy 5 AF 488 Cy-3 PI PE-AF 647 GFP AF 546 PE-AF 610 PE-AF 680 Syto Green AF 555 PE-TR Per. CP Spec Green Qdot 655 Per. CP-Cy 5. 5 YFP ECD DRAQ 5 Sybr. Green Training Qdot 705 2005
 Fluorescence Controls Fluorescence crosstalk control samples: • Unlabeled and single color-labeled cells • Cell type should be representative of experimental sample • Single color labels should be identical to those used in the experimental file: the fluorochrome MUST be identical • DNA control separate and run last • Collected with no brightfield • Used to guide automated crosstalk correction of experimental files Training 2005
Fluorescence Controls Fluorescence crosstalk control samples: • Unlabeled and single color-labeled cells • Cell type should be representative of experimental sample • Single color labels should be identical to those used in the experimental file: the fluorochrome MUST be identical • DNA control separate and run last • Collected with no brightfield • Used to guide automated crosstalk correction of experimental files Training 2005
 Sample Preparation • Sample Processing • Follow standard flow cytometric methods for cell harvesting, incubation, washing and staining (including reagent titration) • Final concentration of 4 x 107 cells per ml will run at approximately 75 cells per second • Take care to ‘balance’ fluorochrome staining intensities to avoid saturation of signal from bright stains at instrument setup conditions necessary for dim stains Training 2005
Sample Preparation • Sample Processing • Follow standard flow cytometric methods for cell harvesting, incubation, washing and staining (including reagent titration) • Final concentration of 4 x 107 cells per ml will run at approximately 75 cells per second • Take care to ‘balance’ fluorochrome staining intensities to avoid saturation of signal from bright stains at instrument setup conditions necessary for dim stains Training 2005
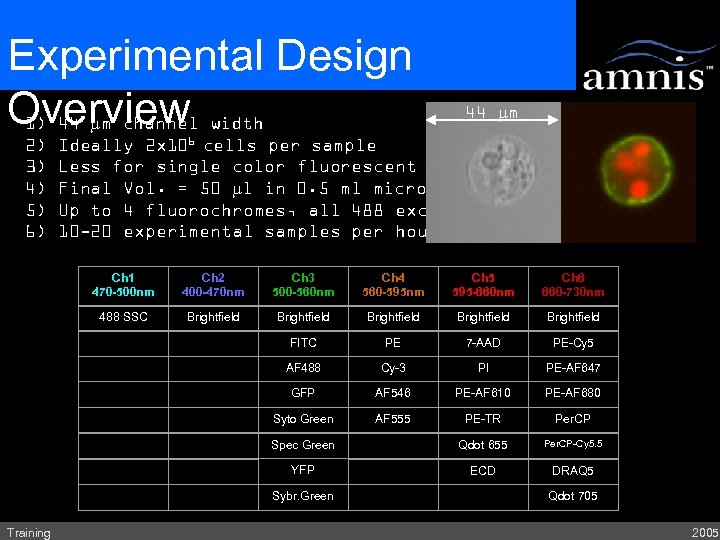 Experimental Design Overview width 1) 44 mm channel 2) 3) 4) 5) 6) 44 mm Ideally 2 x 106 cells per sample Less for single color fluorescent controls Final Vol. = 50 ml in 0. 5 ml microcentrifuge tube Up to 4 fluorochromes, all 488 excitable 10 -20 experimental samples per hour Ch 1 470 -500 nm Ch 2 400 -470 nm Ch 3 500 -560 nm Ch 4 560 -595 nm Ch 5 595 -660 nm Ch 6 660 -730 nm 488 SSC Brightfield Brightfield FITC PE 7 -AAD PE-Cy 5 AF 488 Cy-3 PI PE-AF 647 GFP AF 546 PE-AF 610 PE-AF 680 Syto Green AF 555 PE-TR Per. CP Spec Green Qdot 655 Per. CP-Cy 5. 5 YFP ECD DRAQ 5 Sybr. Green Training Qdot 705 2005
Experimental Design Overview width 1) 44 mm channel 2) 3) 4) 5) 6) 44 mm Ideally 2 x 106 cells per sample Less for single color fluorescent controls Final Vol. = 50 ml in 0. 5 ml microcentrifuge tube Up to 4 fluorochromes, all 488 excitable 10 -20 experimental samples per hour Ch 1 470 -500 nm Ch 2 400 -470 nm Ch 3 500 -560 nm Ch 4 560 -595 nm Ch 5 595 -660 nm Ch 6 660 -730 nm 488 SSC Brightfield Brightfield FITC PE 7 -AAD PE-Cy 5 AF 488 Cy-3 PI PE-AF 647 GFP AF 546 PE-AF 610 PE-AF 680 Syto Green AF 555 PE-TR Per. CP Spec Green Qdot 655 Per. CP-Cy 5. 5 YFP ECD DRAQ 5 Sybr. Green Training Qdot 705 2005
 A Revolution in Cell Analysis Calibration and Speed. Beads Training 2005
A Revolution in Cell Analysis Calibration and Speed. Beads Training 2005
 Speed. Beads - Instrument calibration and run-time system integrity – Run-time system integrity • Maintains continuous synchronization and autofocus independent of cell concentration or type – Automatic Instrument Calibrations and Tests • Optical, illumination, fluidic and camera systems – Loaded at the beginning of each day and run continuously until shut down – IR laser scattering characteristics monitored – Automatically classified and not included in sample file Training 2005
Speed. Beads - Instrument calibration and run-time system integrity – Run-time system integrity • Maintains continuous synchronization and autofocus independent of cell concentration or type – Automatic Instrument Calibrations and Tests • Optical, illumination, fluidic and camera systems – Loaded at the beginning of each day and run continuously until shut down – IR laser scattering characteristics monitored – Automatically classified and not included in sample file Training 2005
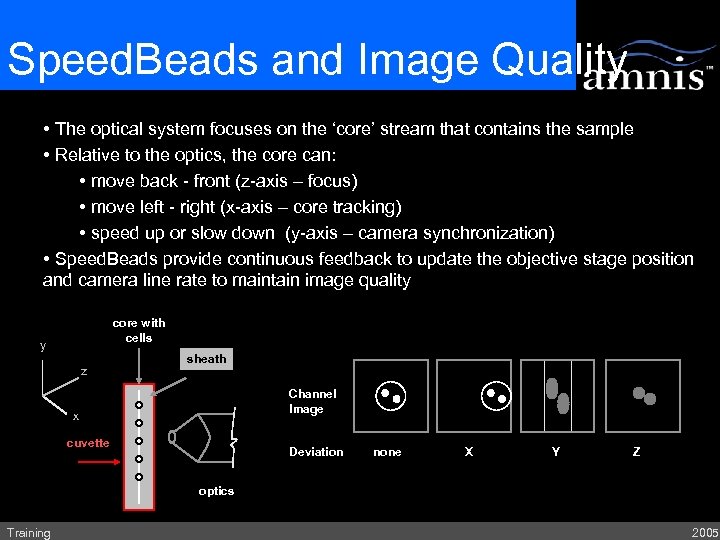 Speed. Beads and Image Quality • The optical system focuses on the ‘core’ stream that contains the sample • Relative to the optics, the core can: • move back - front (z-axis – focus) • move left - right (x-axis – core tracking) • speed up or slow down (y-axis – camera synchronization) • Speed. Beads provide continuous feedback to update the objective stage position and camera line rate to maintain image quality core with cells y z sheath Channel Image x cuvette Deviation none X Y Z optics Training 2005
Speed. Beads and Image Quality • The optical system focuses on the ‘core’ stream that contains the sample • Relative to the optics, the core can: • move back - front (z-axis – focus) • move left - right (x-axis – core tracking) • speed up or slow down (y-axis – camera synchronization) • Speed. Beads provide continuous feedback to update the objective stage position and camera line rate to maintain image quality core with cells y z sheath Channel Image x cuvette Deviation none X Y Z optics Training 2005
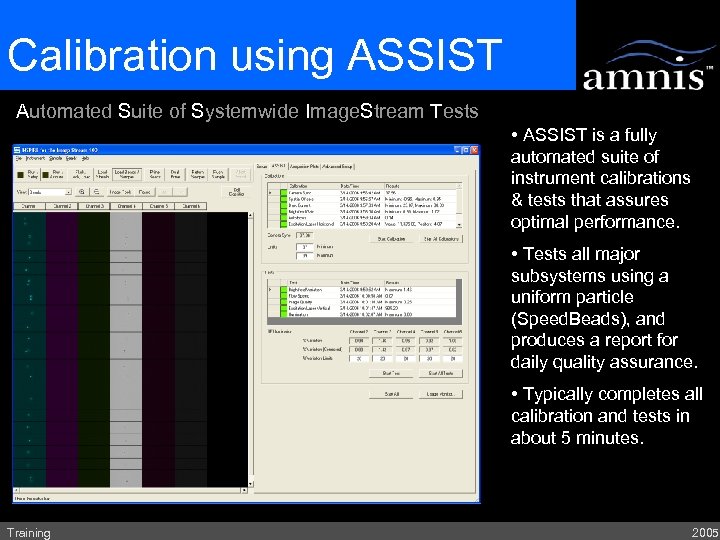 Calibration using ASSIST Automated Suite of Systemwide Image. Stream Tests • ASSIST is a fully automated suite of instrument calibrations & tests that assures optimal performance. • Tests all major subsystems using a uniform particle (Speed. Beads), and produces a report for daily quality assurance. • Typically completes all calibration and tests in about 5 minutes. Training 2005
Calibration using ASSIST Automated Suite of Systemwide Image. Stream Tests • ASSIST is a fully automated suite of instrument calibrations & tests that assures optimal performance. • Tests all major subsystems using a uniform particle (Speed. Beads), and produces a report for daily quality assurance. • Typically completes all calibration and tests in about 5 minutes. Training 2005
 A Revolution in Cell Analysis Data Acquisition Training 2005
A Revolution in Cell Analysis Data Acquisition Training 2005
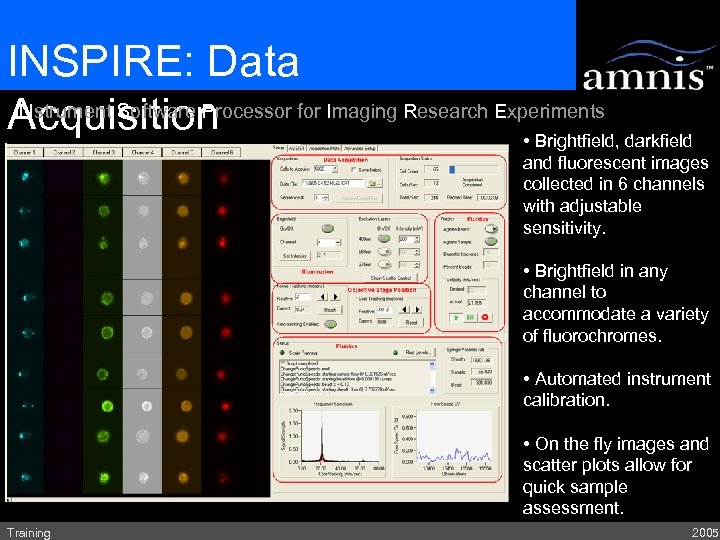 INSPIRE: Data INstrument Software Processor for Imaging Research Experiments Acquisition • Brightfield, darkfield and fluorescent images collected in 6 channels with adjustable sensitivity. • Brightfield in any channel to accommodate a variety of fluorochromes. • Automated instrument calibration. • On the fly images and scatter plots allow for quick sample assessment. Training 2005
INSPIRE: Data INstrument Software Processor for Imaging Research Experiments Acquisition • Brightfield, darkfield and fluorescent images collected in 6 channels with adjustable sensitivity. • Brightfield in any channel to accommodate a variety of fluorochromes. • Automated instrument calibration. • On the fly images and scatter plots allow for quick sample assessment. Training 2005
 Instrument Run Sequence 1. Load sample 2. Run cells with Speed. Beads 3. Establish stable core fluidics 4. Establish appropriate instrument settings 5. Choose classifiers to distinguish cells, from debris 6. Collect data 7. Return sample (optional) 8. Flush sample syringe and lines 9. Load next sample Training 2005
Instrument Run Sequence 1. Load sample 2. Run cells with Speed. Beads 3. Establish stable core fluidics 4. Establish appropriate instrument settings 5. Choose classifiers to distinguish cells, from debris 6. Collect data 7. Return sample (optional) 8. Flush sample syringe and lines 9. Load next sample Training 2005
 Instrument settings 1. Choose channel for Brightfield (blocked for fluorescent control) 2. Set laser power and/or camera stages to avoid camera pixel saturation by monitoring Peak Intensity plots 3. Adjust laser height to maximize dynamic range of 488 scatter intensity while still maintaining high fluorescence sensitivity 4. For samples that contain abundant debris, set squelch value to reduce sensitivity of object detection so that debris is ignored. 5. Note that the excitation & detection conditions selected for the control (laser power, camera staging) MUST be used for the experimental samples Training 2005
Instrument settings 1. Choose channel for Brightfield (blocked for fluorescent control) 2. Set laser power and/or camera stages to avoid camera pixel saturation by monitoring Peak Intensity plots 3. Adjust laser height to maximize dynamic range of 488 scatter intensity while still maintaining high fluorescence sensitivity 4. For samples that contain abundant debris, set squelch value to reduce sensitivity of object detection so that debris is ignored. 5. Note that the excitation & detection conditions selected for the control (laser power, camera staging) MUST be used for the experimental samples Training 2005
 Choose Classifiers Detected objects can be classified in three ways: 1. Cells 2. Beads 3. Debris Only the Cells make it into your primary data file. You can save the bead and debris into separate files if you wish. Beads are automatically classified Cells can be classified based on object feature thresholds. Objects that fall outside the boundaries of any of the thresholds are classified as debris. Training 2005
Choose Classifiers Detected objects can be classified in three ways: 1. Cells 2. Beads 3. Debris Only the Cells make it into your primary data file. You can save the bead and debris into separate files if you wish. Beads are automatically classified Cells can be classified based on object feature thresholds. Objects that fall outside the boundaries of any of the thresholds are classified as debris. Training 2005
 Instrument Shutdown 1. Optionally return experimental sample to tube 2. Change Sheath tank to Rinse 3. Run sterilize script: 1. Powers off illumination (all) 2. Flushes lines 3. Cleans instrument: automatically runs detergent, alcohol, bleach & water Training 2005
Instrument Shutdown 1. Optionally return experimental sample to tube 2. Change Sheath tank to Rinse 3. Run sterilize script: 1. Powers off illumination (all) 2. Flushes lines 3. Cleans instrument: automatically runs detergent, alcohol, bleach & water Training 2005
 A Revolution in Cell Analysis Data Analysis: Opening Files Training 2005
A Revolution in Cell Analysis Data Analysis: Opening Files Training 2005
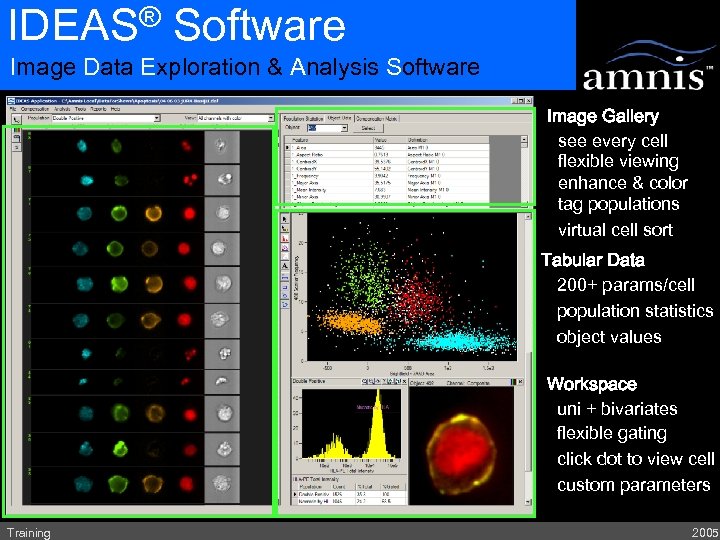 ® IDEAS Software Image Data Exploration & Analysis Software Image Gallery see every cell flexible viewing enhance & color tag populations virtual cell sort Tabular Data 200+ params/cell population statistics object values Workspace uni + bivariates flexible gating click dot to view cell custom parameters Training 2005
® IDEAS Software Image Data Exploration & Analysis Software Image Gallery see every cell flexible viewing enhance & color tag populations virtual cell sort Tabular Data 200+ params/cell population statistics object values Workspace uni + bivariates flexible gating click dot to view cell custom parameters Training 2005
 IDEAS Data Analysis Overview • The Image. Stream collects large numbers of digital images into a single file. • Using image processing algorithms, specific features can be quantified from these images. • IDEAS is the software tool used to analyze and report the image data acquired on the IS 100 instrument. Training 2005
IDEAS Data Analysis Overview • The Image. Stream collects large numbers of digital images into a single file. • Using image processing algorithms, specific features can be quantified from these images. • IDEAS is the software tool used to analyze and report the image data acquired on the IS 100 instrument. Training 2005
 IDEAS Data Analysis Overview • IDEAS: Cell image-based informatics • 6 images per cell, 30+ standard features per image • Customizable image display • User definable features • Features plotted on histograms or dot plots • Images linked to plotted data points • Populations can be created in many ways: • Standard region drawing tools • Tagged populations • Boolean combinations of multiple populations • Multiparametric filter-based • Full statistics repertoire • Reporting via copy to clipboard, export to stats program • Batch processing to apply analysis template to all files in an experiment Training 2005
IDEAS Data Analysis Overview • IDEAS: Cell image-based informatics • 6 images per cell, 30+ standard features per image • Customizable image display • User definable features • Features plotted on histograms or dot plots • Images linked to plotted data points • Populations can be created in many ways: • Standard region drawing tools • Tagged populations • Boolean combinations of multiple populations • Multiparametric filter-based • Full statistics repertoire • Reporting via copy to clipboard, export to stats program • Batch processing to apply analysis template to all files in an experiment Training 2005
 Files and their Structure Raw Image File (RIF)----------------200 MB/10, 000 events – raw instrument data – collection settings Compensated Image File (CIF)----------200 MB/10, 000 events – Corrected for spectral crosstalk – Corrected for offsets and gains from ASISST – Determination of object boundaries (segmentation) Data Analysis File (DAF)---------------10 MB/10, 000 events – – – Training Image Gallery Work Area (graphs and specific images) Calculated features and statistics Saved state of analysis Uses the CIF as a database: Keep track of where you store files! The DAF and related CIF must be in the same directory. 2005
Files and their Structure Raw Image File (RIF)----------------200 MB/10, 000 events – raw instrument data – collection settings Compensated Image File (CIF)----------200 MB/10, 000 events – Corrected for spectral crosstalk – Corrected for offsets and gains from ASISST – Determination of object boundaries (segmentation) Data Analysis File (DAF)---------------10 MB/10, 000 events – – – Training Image Gallery Work Area (graphs and specific images) Calculated features and statistics Saved state of analysis Uses the CIF as a database: Keep track of where you store files! The DAF and related CIF must be in the same directory. 2005
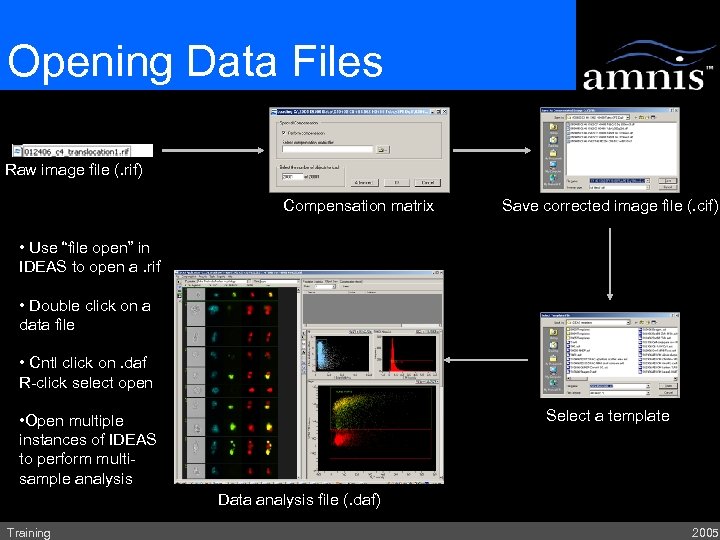 Opening Data Files Raw image file (. rif) Compensation matrix Save corrected image file (. cif) • Use “file open” in IDEAS to open a. rif • Double click on a data file • Cntl click on. daf R-click select open Select a template • Open multiple instances of IDEAS to perform multisample analysis Data analysis file (. daf) Training 2005
Opening Data Files Raw image file (. rif) Compensation matrix Save corrected image file (. cif) • Use “file open” in IDEAS to open a. rif • Double click on a data file • Cntl click on. daf R-click select open Select a template • Open multiple instances of IDEAS to perform multisample analysis Data analysis file (. daf) Training 2005
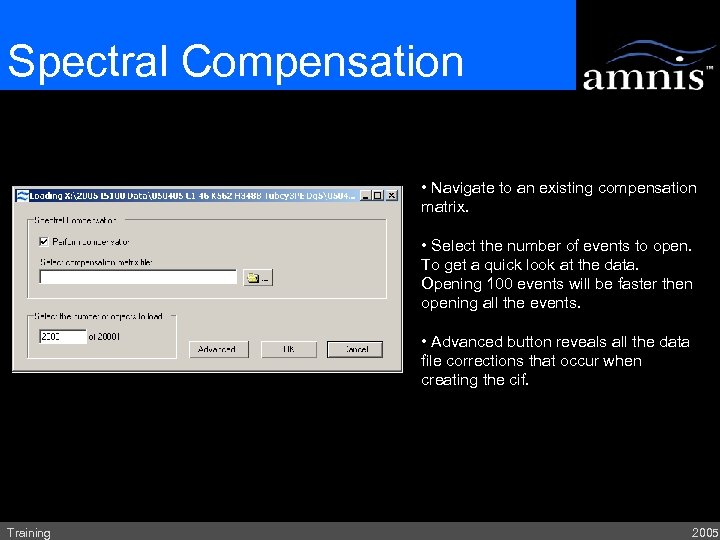 Spectral Compensation • Navigate to an existing compensation matrix. • Select the number of events to open. To get a quick look at the data. Opening 100 events will be faster then opening all the events. • Advanced button reveals all the data file corrections that occur when creating the cif. Training 2005
Spectral Compensation • Navigate to an existing compensation matrix. • Select the number of events to open. To get a quick look at the data. Opening 100 events will be faster then opening all the events. • Advanced button reveals all the data file corrections that occur when creating the cif. Training 2005
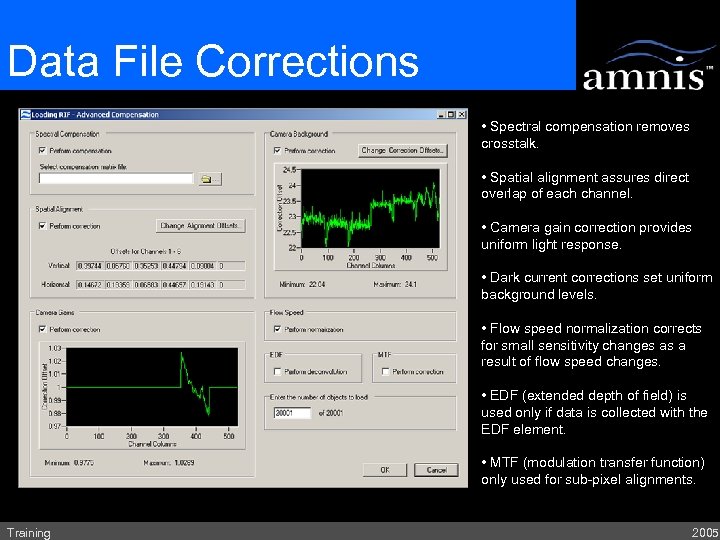 Data File Corrections • Spectral compensation removes crosstalk. • Spatial alignment assures direct overlap of each channel. • Camera gain correction provides uniform light response. • Dark current corrections set uniform background levels. • Flow speed normalization corrects for small sensitivity changes as a result of flow speed changes. • EDF (extended depth of field) is used only if data is collected with the EDF element. • MTF (modulation transfer function) only used for sub-pixel alignments. Training 2005
Data File Corrections • Spectral compensation removes crosstalk. • Spatial alignment assures direct overlap of each channel. • Camera gain correction provides uniform light response. • Dark current corrections set uniform background levels. • Flow speed normalization corrects for small sensitivity changes as a result of flow speed changes. • EDF (extended depth of field) is used only if data is collected with the EDF element. • MTF (modulation transfer function) only used for sub-pixel alignments. Training 2005
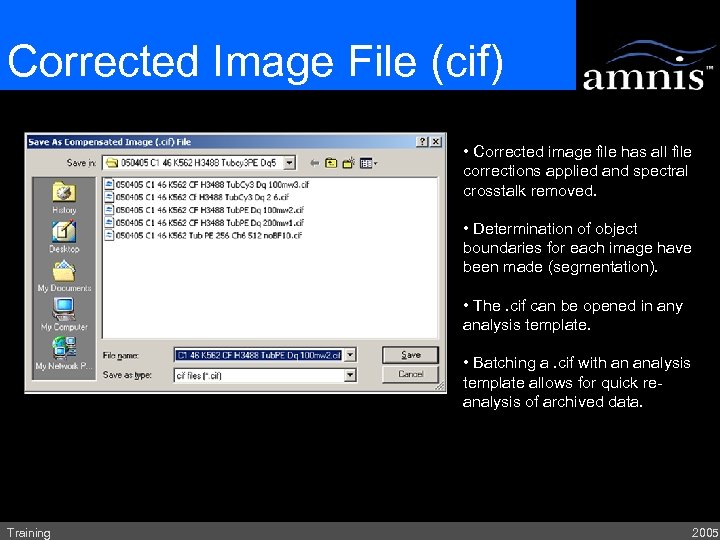 Corrected Image File (cif) • Corrected image file has all file corrections applied and spectral crosstalk removed. • Determination of object boundaries for each image have been made (segmentation). • The. cif can be opened in any analysis template. • Batching a. cif with an analysis template allows for quick reanalysis of archived data. Training 2005
Corrected Image File (cif) • Corrected image file has all file corrections applied and spectral crosstalk removed. • Determination of object boundaries for each image have been made (segmentation). • The. cif can be opened in any analysis template. • Batching a. cif with an analysis template allows for quick reanalysis of archived data. Training 2005
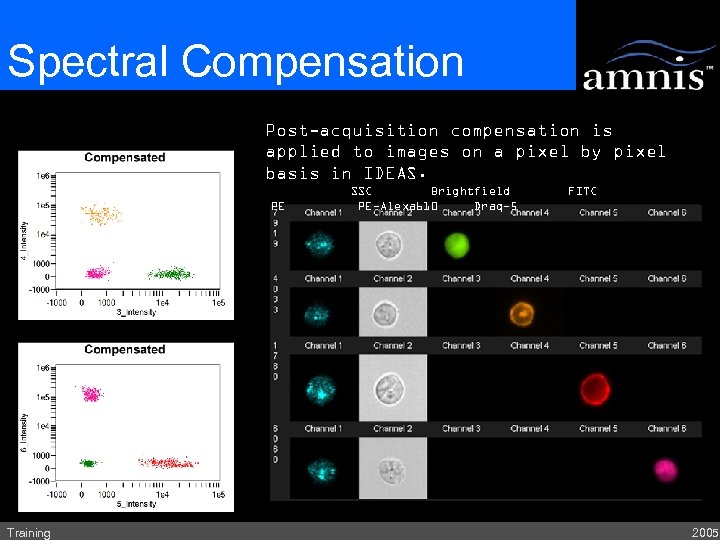 Spectral Compensation Post-acquisition compensationused to Single color control samples is applied toaimages on a pixel by pixel calculate 6 x 6 matrix. basis in IDEAS. PE Training SSC Brightfield PE-Alexa 610 Draq-5 FITC 2005
Spectral Compensation Post-acquisition compensationused to Single color control samples is applied toaimages on a pixel by pixel calculate 6 x 6 matrix. basis in IDEAS. PE Training SSC Brightfield PE-Alexa 610 Draq-5 FITC 2005
 IDEAS Templates • Templates contain • image display settings • workspace histograms • user defined and experiment specific feature calculations • Gating and population logic • Used in batch processing to provide uniform analysis for all experimental data files. Training 2005
IDEAS Templates • Templates contain • image display settings • workspace histograms • user defined and experiment specific feature calculations • Gating and population logic • Used in batch processing to provide uniform analysis for all experimental data files. Training 2005
 Data Analysis File (daf) • The daf presents the saved state of the analysis. • Uses the cif as its database for images and feature calculation. • Includes all information from the template. Training 2005
Data Analysis File (daf) • The daf presents the saved state of the analysis. • Uses the cif as its database for images and feature calculation. • Includes all information from the template. Training 2005
 IDEAS Files Review • Instrument creates Raw Image Files (rif) • Corrections and segmentation are applied when a rif is opened • Corrected images and segmentation masks are stored in a Corrected Image File (cif). • A cif is loaded into IDEAS using a template file. Defined features are calculated for each object. • Feature values and analysis results are saved in a Data Analysis File (daf). Training 2005
IDEAS Files Review • Instrument creates Raw Image Files (rif) • Corrections and segmentation are applied when a rif is opened • Corrected images and segmentation masks are stored in a Corrected Image File (cif). • A cif is loaded into IDEAS using a template file. Defined features are calculated for each object. • Feature values and analysis results are saved in a Data Analysis File (daf). Training 2005
 A Revolution in Cell Analysis Data Analysis: IDEAS Training 2005
A Revolution in Cell Analysis Data Analysis: IDEAS Training 2005
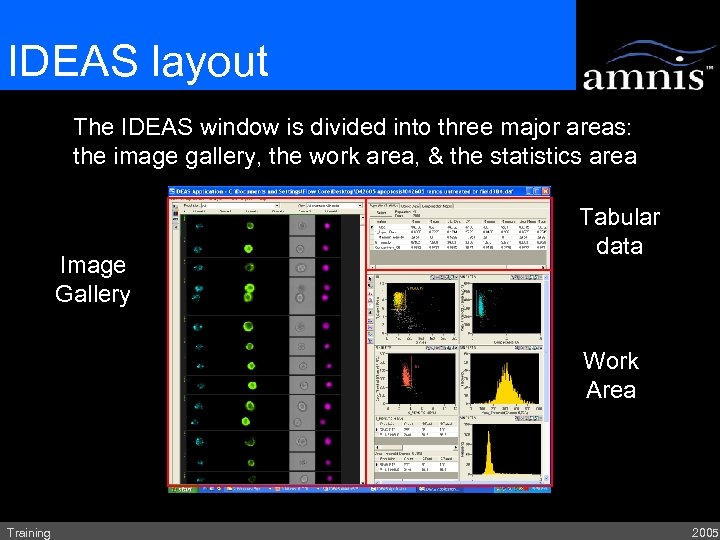 IDEAS layout The IDEAS window is divided into three major areas: the image gallery, the work area, & the statistics area Image Gallery Tabular data Work Area Training 2005
IDEAS layout The IDEAS window is divided into three major areas: the image gallery, the work area, & the statistics area Image Gallery Tabular data Work Area Training 2005
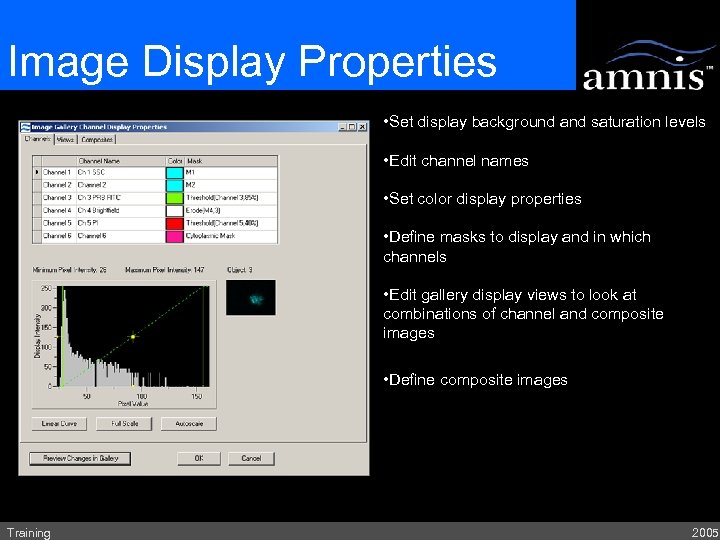 Image Display Properties • Set display background and saturation levels • Edit channel names • Set color display properties • Define masks to display and in which channels • Edit gallery display views to look at combinations of channel and composite images • Define composite images. Training 2005
Image Display Properties • Set display background and saturation levels • Edit channel names • Set color display properties • Define masks to display and in which channels • Edit gallery display views to look at combinations of channel and composite images • Define composite images. Training 2005
 IDEAS: Masks • Masks – Set of pixels that make up a ‘region of interest’ in an image – IDEAS automatically determines a sensitive mask for each channel of each object. This mask is best used for measuring the overall staining intensity detected in a given image. However, this mask may be less appropriate for other shape related features. IDEAS provides tools to create ‘featureappropriate’ custom masks – The user can create custom masks in two ways: • Functionalize an existing mask (erode, dilate, fill, threshold, morphology) • Make complex masks through boolean combinations – These masks can then be used to build features Training 2005
IDEAS: Masks • Masks – Set of pixels that make up a ‘region of interest’ in an image – IDEAS automatically determines a sensitive mask for each channel of each object. This mask is best used for measuring the overall staining intensity detected in a given image. However, this mask may be less appropriate for other shape related features. IDEAS provides tools to create ‘featureappropriate’ custom masks – The user can create custom masks in two ways: • Functionalize an existing mask (erode, dilate, fill, threshold, morphology) • Make complex masks through boolean combinations – These masks can then be used to build features Training 2005
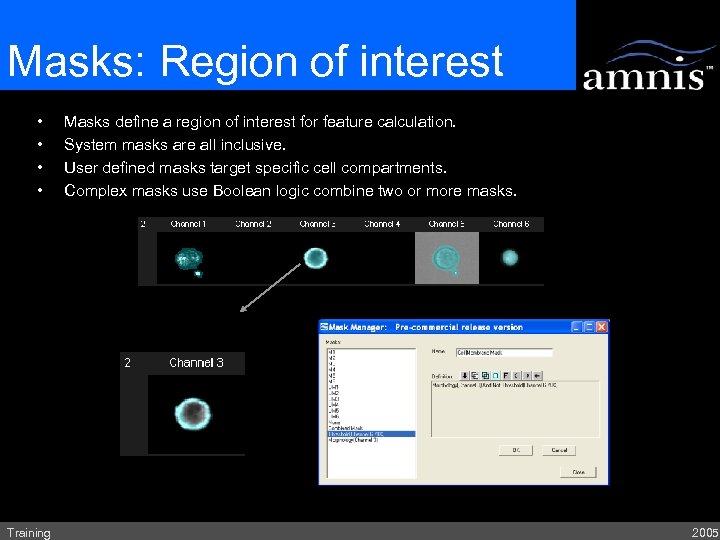 Masks: Region of interest • • Training Masks define a region of interest for feature calculation. System masks are all inclusive. User defined masks target specific cell compartments. Complex masks use Boolean logic combine two or more masks. 2005
Masks: Region of interest • • Training Masks define a region of interest for feature calculation. System masks are all inclusive. User defined masks target specific cell compartments. Complex masks use Boolean logic combine two or more masks. 2005
 IDEAS: Masks • Functionalize a mask: • Example = threshold the system mask for the channel 6 image (nuclear stain) to constrain the region of interest to the region of dominant nuclear dye signal. Training 2005
IDEAS: Masks • Functionalize a mask: • Example = threshold the system mask for the channel 6 image (nuclear stain) to constrain the region of interest to the region of dominant nuclear dye signal. Training 2005
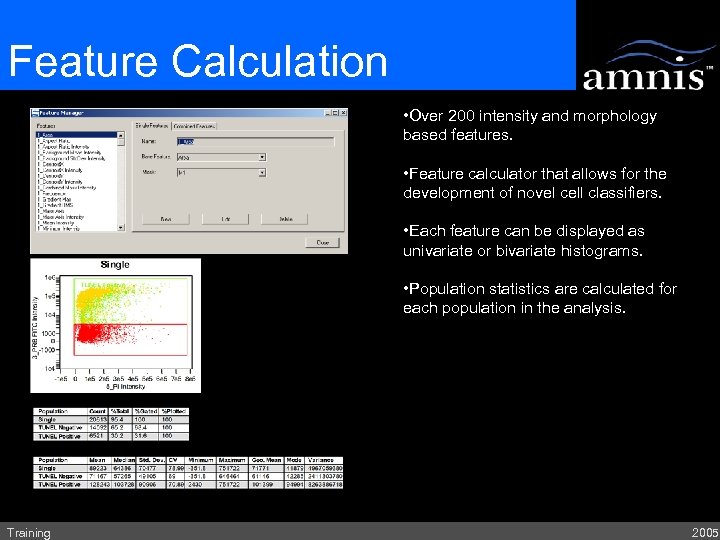 Feature Calculation • Over 200 intensity and morphology based features. • Feature calculator that allows for the development of novel cell classifiers. • Each feature can be displayed as univariate or bivariate histograms. • Population statistics are calculated for each population in the analysis. Training 2005
Feature Calculation • Over 200 intensity and morphology based features. • Feature calculator that allows for the development of novel cell classifiers. • Each feature can be displayed as univariate or bivariate histograms. • Population statistics are calculated for each population in the analysis. Training 2005
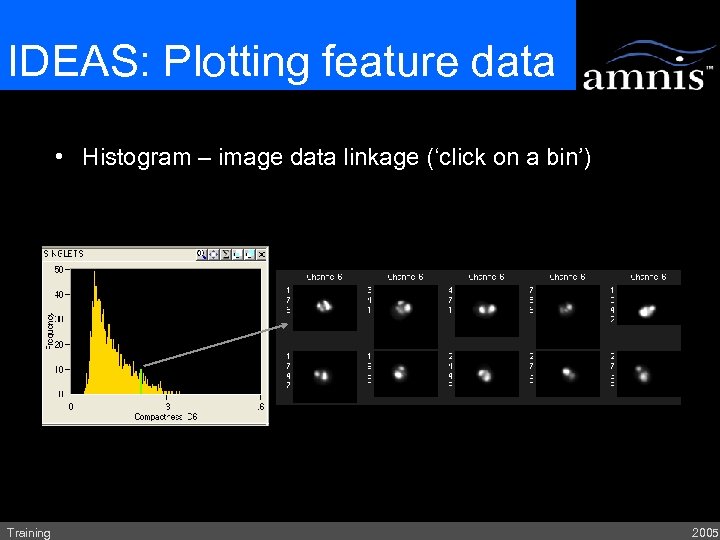 IDEAS: Plotting feature data • Histogram – image data linkage (‘click on a bin’) Training 2005
IDEAS: Plotting feature data • Histogram – image data linkage (‘click on a bin’) Training 2005
 IDEAS: Plotting feature data • Scatter plots – image data linkage (‘click on a dot’) Training 2005
IDEAS: Plotting feature data • Scatter plots – image data linkage (‘click on a dot’) Training 2005
 IDEAS: Populations • Population creation (4 ways) – – Regions physically drawn on plots Tagging cells Boolean combinations Filtering (‘find-like-cells’) • Population display – ‘Virtual sort’ in the Image Gallery – Show/Hide on existing scatter plots Training 2005
IDEAS: Populations • Population creation (4 ways) – – Regions physically drawn on plots Tagging cells Boolean combinations Filtering (‘find-like-cells’) • Population display – ‘Virtual sort’ in the Image Gallery – Show/Hide on existing scatter plots Training 2005
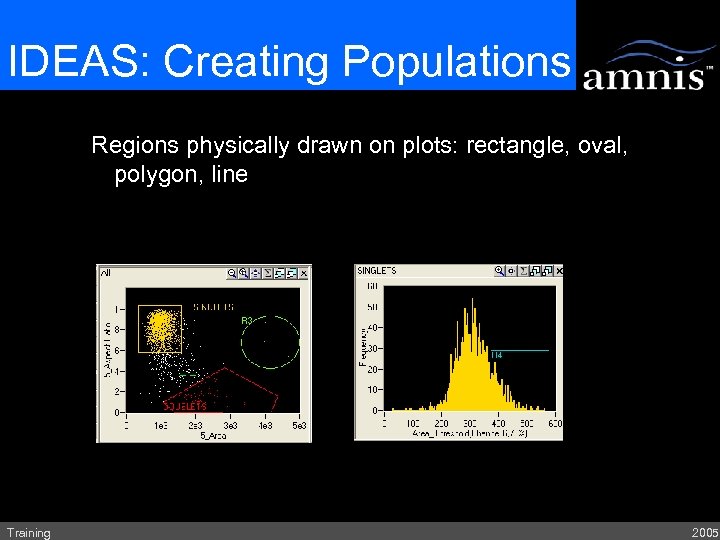 IDEAS: Creating Populations Regions physically drawn on plots: rectangle, oval, polygon, line Training 2005
IDEAS: Creating Populations Regions physically drawn on plots: rectangle, oval, polygon, line Training 2005
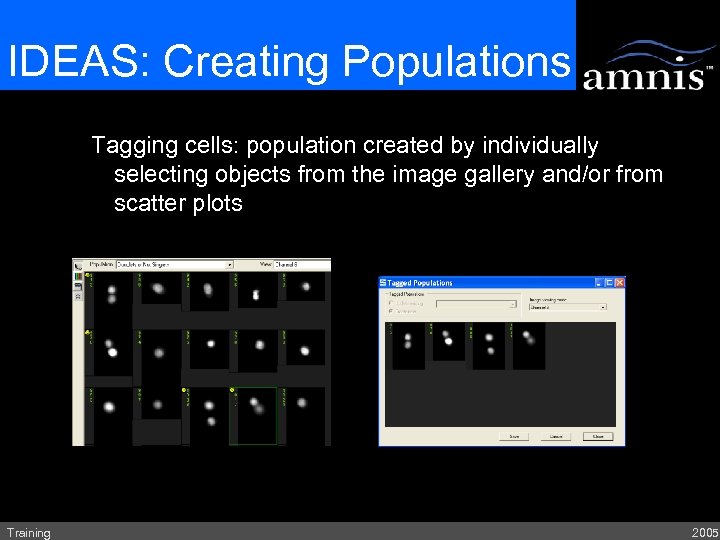 IDEAS: Creating Populations Tagging cells: population created by individually selecting objects from the image gallery and/or from scatter plots Training 2005
IDEAS: Creating Populations Tagging cells: population created by individually selecting objects from the image gallery and/or from scatter plots Training 2005
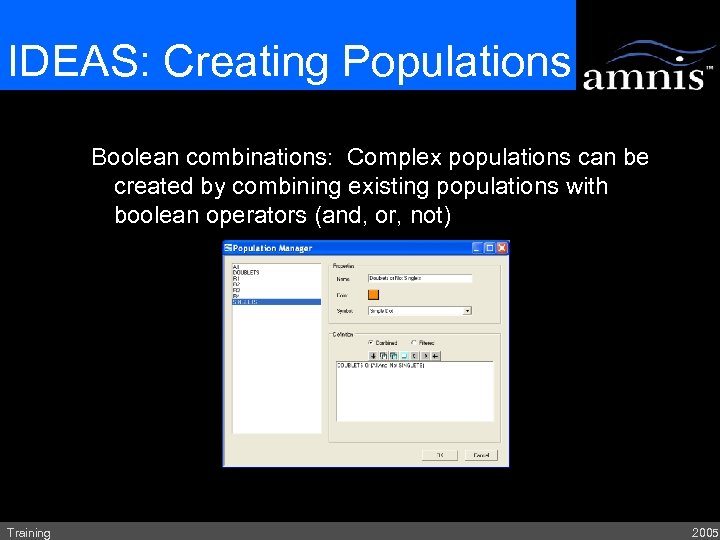 IDEAS: Creating Populations Boolean combinations: Complex populations can be created by combining existing populations with boolean operators (and, or, not) Training 2005
IDEAS: Creating Populations Boolean combinations: Complex populations can be created by combining existing populations with boolean operators (and, or, not) Training 2005
 IDEAS: Creating Populations Filtering (‘find-like-cells’): Populations can be created by instructing IDEAS to find all the objects that have similar features to a given cell or existing population. Training 2005
IDEAS: Creating Populations Filtering (‘find-like-cells’): Populations can be created by instructing IDEAS to find all the objects that have similar features to a given cell or existing population. Training 2005
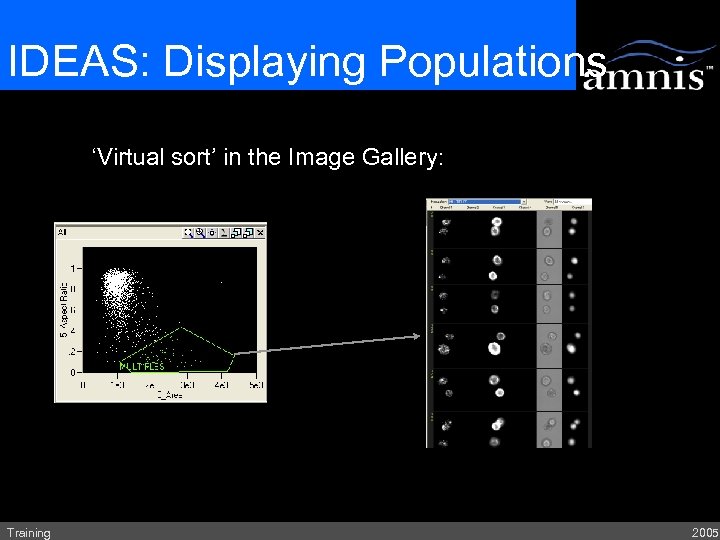 IDEAS: Displaying Populations ‘Virtual sort’ in the Image Gallery: Training 2005
IDEAS: Displaying Populations ‘Virtual sort’ in the Image Gallery: Training 2005
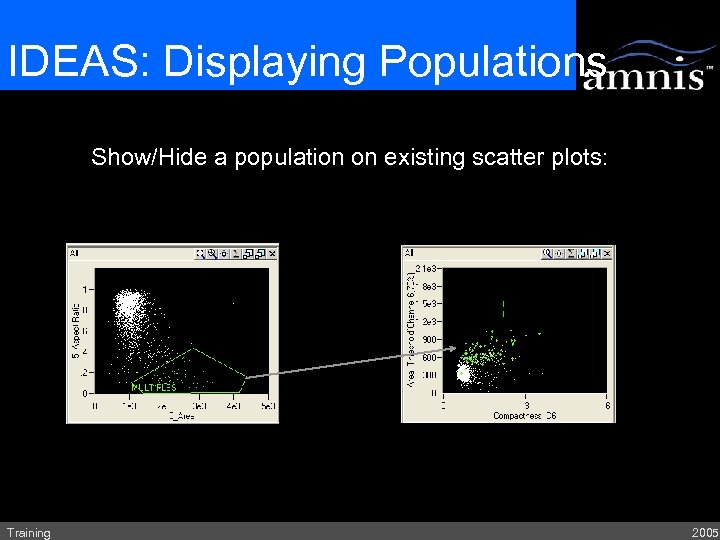 IDEAS: Displaying Populations Show/Hide a population on existing scatter plots: Training 2005
IDEAS: Displaying Populations Show/Hide a population on existing scatter plots: Training 2005
 IDEAS: Statistics • Statistics automatically calculated for each feature – Population stats: Count, % Total, % Gated, % Plotted – Feature stats: Mean, Median, Mode, Geometric Mean, Standard Deviation, CV, Variance • Displayed under each plot and/or in the Statistics Area Training 2005
IDEAS: Statistics • Statistics automatically calculated for each feature – Population stats: Count, % Total, % Gated, % Plotted – Feature stats: Mean, Median, Mode, Geometric Mean, Standard Deviation, CV, Variance • Displayed under each plot and/or in the Statistics Area Training 2005
 IDEAS: Data Reporting • Reporting – Copy image or image gallery to clipboard – Copy graph and/or stats to clipboard – Export stats to spreadsheet Training 2005
IDEAS: Data Reporting • Reporting – Copy image or image gallery to clipboard – Copy graph and/or stats to clipboard – Export stats to spreadsheet Training 2005
 IDEAS: Data Reporting • Copy image or image gallery to clipboard Single image Image Gallery (composite mode) Training 2005
IDEAS: Data Reporting • Copy image or image gallery to clipboard Single image Image Gallery (composite mode) Training 2005
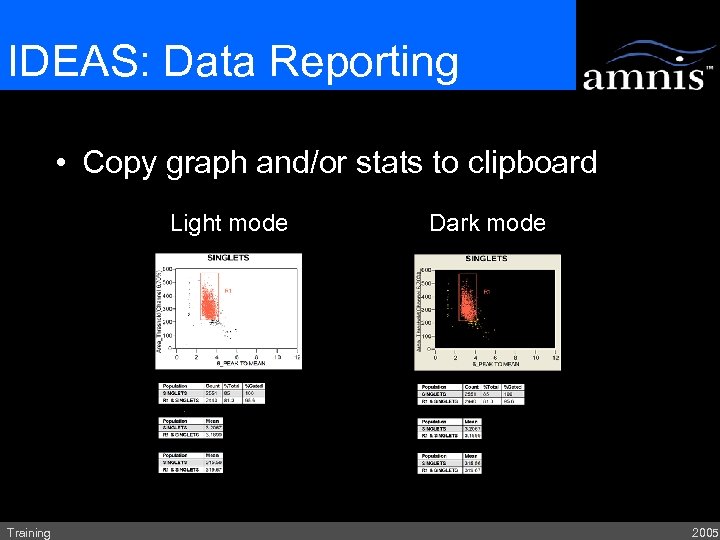 IDEAS: Data Reporting • Copy graph and/or stats to clipboard Light mode Training Dark mode 2005
IDEAS: Data Reporting • Copy graph and/or stats to clipboard Light mode Training Dark mode 2005
 IDEAS: Data Reporting • Export stats or feature data to spreadsheet • Export single image data to spreadsheet Training 2005
IDEAS: Data Reporting • Export stats or feature data to spreadsheet • Export single image data to spreadsheet Training 2005
 IDEAS: File tools • File tools – Batch processing • Apply a compensation matrix and a saved analysis template to all files within a given experiment – Merge files into one file – Create smaller files from sub-populations – Save data in. fcs format Training 2005
IDEAS: File tools • File tools – Batch processing • Apply a compensation matrix and a saved analysis template to all files within a given experiment – Merge files into one file – Create smaller files from sub-populations – Save data in. fcs format Training 2005
 IDEAS Data Analysis Review IDEAS is the software tool used to analyze and report the image data acquired on the Image. Stream. IDEAS allows the user to mine existing features, create new features, plot data, perform population statistical analysis and customize image display. Training 2005
IDEAS Data Analysis Review IDEAS is the software tool used to analyze and report the image data acquired on the Image. Stream. IDEAS allows the user to mine existing features, create new features, plot data, perform population statistical analysis and customize image display. Training 2005
 A Revolution in Cell Analysis Image. Stream Operator Training 2005
A Revolution in Cell Analysis Image. Stream Operator Training 2005
 IDEAS: Images • Up to 6 images per object • Displayed in the Image Gallery or Work Area • Customizable Image display: • Linear and non-linear display transformation • False color • Composites • Image Line and Region data Training 2005
IDEAS: Images • Up to 6 images per object • Displayed in the Image Gallery or Work Area • Customizable Image display: • Linear and non-linear display transformation • False color • Composites • Image Line and Region data Training 2005
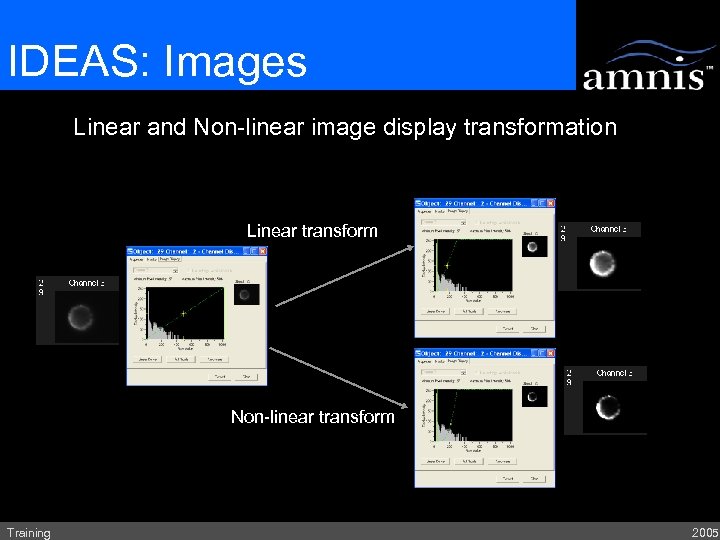 IDEAS: Images Linear and Non-linear image display transformation Linear transform Non-linear transform Training 2005
IDEAS: Images Linear and Non-linear image display transformation Linear transform Non-linear transform Training 2005
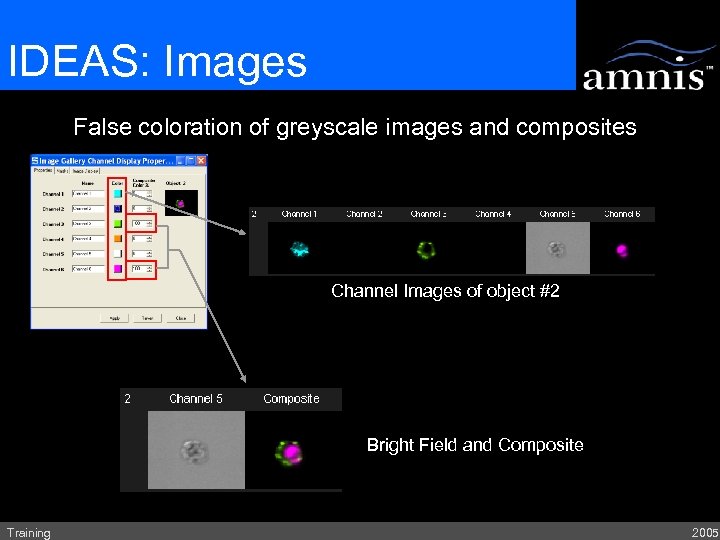 IDEAS: Images False coloration of greyscale images and composites Channel Images of object #2 Bright Field and Composite Training 2005
IDEAS: Images False coloration of greyscale images and composites Channel Images of object #2 Bright Field and Composite Training 2005
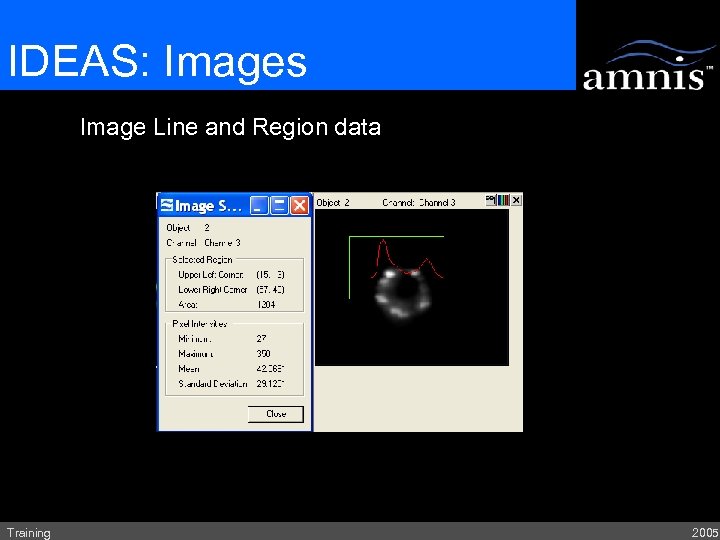 IDEAS: Images Image Line and Region data Training 2005
IDEAS: Images Image Line and Region data Training 2005
 IDEAS: Features – Features • Are attributes related to each object image. • Most of these features are derived from image processing algorithms, and most quantify morphologic aspects of the image. • A large set of features is automatically calculated by IDEAS • The user can create their own features through Boolean combinations and/or arithmetic operators • Some feature rely on a ‘mask’ or region of interest (discussed next). The user can calculate standard features based on customized masks Training 2005
IDEAS: Features – Features • Are attributes related to each object image. • Most of these features are derived from image processing algorithms, and most quantify morphologic aspects of the image. • A large set of features is automatically calculated by IDEAS • The user can create their own features through Boolean combinations and/or arithmetic operators • Some feature rely on a ‘mask’ or region of interest (discussed next). The user can calculate standard features based on customized masks Training 2005
 IDEAS: Plotting feature data • Plots – images linked to plotted data – Histograms and histogram overlays – Scatter plots – Linear, log, and Linear/Log transform plotting Training 2005
IDEAS: Plotting feature data • Plots – images linked to plotted data – Histograms and histogram overlays – Scatter plots – Linear, log, and Linear/Log transform plotting Training 2005
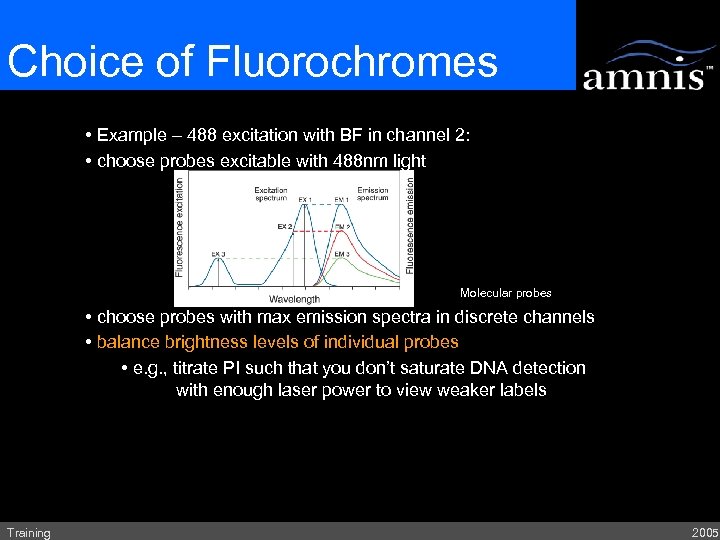 Choice of Fluorochromes • Example – 488 excitation with BF in channel 2: • choose probes excitable with 488 nm light Molecular probes • choose probes with max emission spectra in discrete channels • balance brightness levels of individual probes • e. g. , titrate PI such that you don’t saturate DNA detection with enough laser power to view weaker labels Training 2005
Choice of Fluorochromes • Example – 488 excitation with BF in channel 2: • choose probes excitable with 488 nm light Molecular probes • choose probes with max emission spectra in discrete channels • balance brightness levels of individual probes • e. g. , titrate PI such that you don’t saturate DNA detection with enough laser power to view weaker labels Training 2005
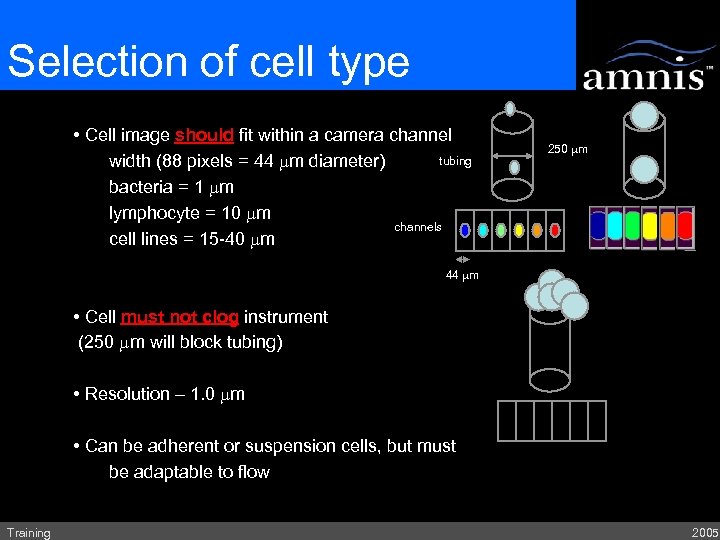 Selection of cell type • Cell image should fit within a camera channel tubing width (88 pixels = 44 mm diameter) bacteria = 1 mm lymphocyte = 10 mm channels cell lines = 15 -40 mm 250 mm 44 mm • Cell must not clog instrument (250 mm will block tubing) • Resolution – 1. 0 mm • Can be adherent or suspension cells, but must be adaptable to flow Training 2005
Selection of cell type • Cell image should fit within a camera channel tubing width (88 pixels = 44 mm diameter) bacteria = 1 mm lymphocyte = 10 mm channels cell lines = 15 -40 mm 250 mm 44 mm • Cell must not clog instrument (250 mm will block tubing) • Resolution – 1. 0 mm • Can be adherent or suspension cells, but must be adaptable to flow Training 2005


