f49896c0b785adc7aabcf65aea081861.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 21
 A Qualitative Selection Process for Advanced ALE Waveforms Chuck Tefer Rockwell Collins Government Systems (RCGS) Division Rockwell Collins, Inc. © 2002
A Qualitative Selection Process for Advanced ALE Waveforms Chuck Tefer Rockwell Collins Government Systems (RCGS) Division Rockwell Collins, Inc. © 2002
 Outline q q q q 2 Introduction Why ALE? – A Historical Perspective RCGS Experience With Existing 2 G ALE Networks What Are Customers Now Asking For? The Enhanced ALE Landscape Developing A Selection Process The Selection Matrix Conclusion Rockwell Collins, Inc. © 2002
Outline q q q q 2 Introduction Why ALE? – A Historical Perspective RCGS Experience With Existing 2 G ALE Networks What Are Customers Now Asking For? The Enhanced ALE Landscape Developing A Selection Process The Selection Matrix Conclusion Rockwell Collins, Inc. © 2002
 Introduction q q q 3 The purpose of this presentation is to assist HF communicators in deciding which advanced Automatic Link Establishment (ALE) waveform is right for their needs We will examine the many factors that should be considered when contemplating a major ALE waveform upgrade We will develop a process for evaluating those factors that is tailored to the individual customer’s existing capabilities Rockwell Collins, Inc. © 2002
Introduction q q q 3 The purpose of this presentation is to assist HF communicators in deciding which advanced Automatic Link Establishment (ALE) waveform is right for their needs We will examine the many factors that should be considered when contemplating a major ALE waveform upgrade We will develop a process for evaluating those factors that is tailored to the individual customer’s existing capabilities Rockwell Collins, Inc. © 2002
 Why ALE? q HF radio communication traditionally required the full-time services of a highly skilled radio operator – – – q Enter ALE – The goal was to make HF radio as easy to use as a telephone – – 4 Strict coordination of propagating frequency vs. time Knowledge of global geography Manual monitoring of one or more frequencies Automated monitoring of multiple channels (Scanning) Pseudo-real-time propagation update (Sounding) Unique user ID (Addresses) Simple connection (Automatic Linking) Rockwell Collins, Inc. © 2002
Why ALE? q HF radio communication traditionally required the full-time services of a highly skilled radio operator – – – q Enter ALE – The goal was to make HF radio as easy to use as a telephone – – 4 Strict coordination of propagating frequency vs. time Knowledge of global geography Manual monitoring of one or more frequencies Automated monitoring of multiple channels (Scanning) Pseudo-real-time propagation update (Sounding) Unique user ID (Addresses) Simple connection (Automatic Linking) Rockwell Collins, Inc. © 2002
 HF Before ALE PROPAGATION FORECAST OPERATIONS SCHEDULE MANUAL OPERATING PROCEDURES 12 9 AUTHORIZED FREQ LIST 3 HF COMM TRAINING MANUAL COMM PLAN PRIMARY Date Frequency Time ALTERNATE Date Frequency Time BACK-UP 6 CALENDAR JAN FEB Listening Skills MAR Making Voice Calls Following Comm Plan APR MAY Recovery From Comm Outages JUN PRIOR PLANNING AND COORDINATION REQUIRED 5 Tuning The Radio OPERATOR WORKLOAD INTENSIVE Rockwell Collins, Inc. © 2002
HF Before ALE PROPAGATION FORECAST OPERATIONS SCHEDULE MANUAL OPERATING PROCEDURES 12 9 AUTHORIZED FREQ LIST 3 HF COMM TRAINING MANUAL COMM PLAN PRIMARY Date Frequency Time ALTERNATE Date Frequency Time BACK-UP 6 CALENDAR JAN FEB Listening Skills MAR Making Voice Calls Following Comm Plan APR MAY Recovery From Comm Outages JUN PRIOR PLANNING AND COORDINATION REQUIRED 5 Tuning The Radio OPERATOR WORKLOAD INTENSIVE Rockwell Collins, Inc. © 2002
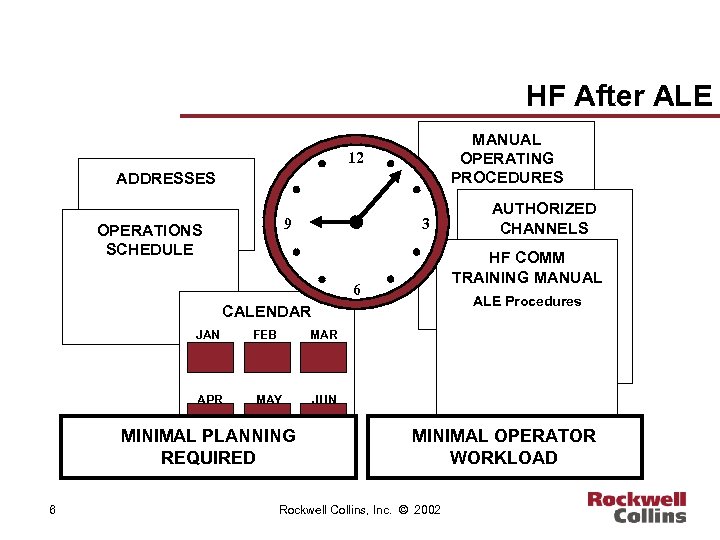 HF After ALE MANUAL OPERATING PROCEDURES 12 ADDRESSES 9 OPERATIONS SCHEDULE 3 HF COMM TRAINING MANUAL 6 ALE Procedures CALENDAR JAN FEB MAR APR MAY JUN MINIMAL PLANNING REQUIRED 6 AUTHORIZED CHANNELS MINIMAL OPERATOR WORKLOAD Rockwell Collins, Inc. © 2002
HF After ALE MANUAL OPERATING PROCEDURES 12 ADDRESSES 9 OPERATIONS SCHEDULE 3 HF COMM TRAINING MANUAL 6 ALE Procedures CALENDAR JAN FEB MAR APR MAY JUN MINIMAL PLANNING REQUIRED 6 AUTHORIZED CHANNELS MINIMAL OPERATOR WORKLOAD Rockwell Collins, Inc. © 2002
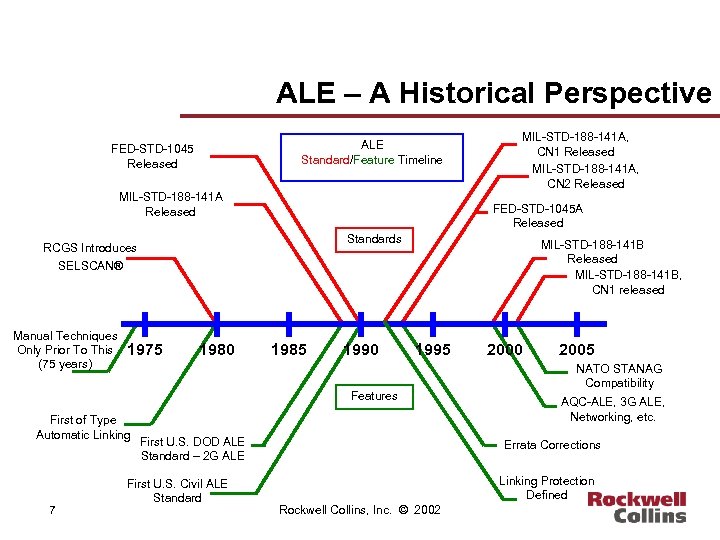 ALE – A Historical Perspective ALE Standard/Feature Timeline FED-STD-1045 Released MIL-STD-188 -141 A, CN 1 Released MIL-STD-188 -141 A, CN 2 Released FED-STD-1045 A Released Standards RCGS Introduces MIL-STD-188 -141 B Released MIL-STD-188 -141 B, CN 1 released SELSCAN® Manual Techniques Only Prior To This (75 years) 1975 1980 1985 1990 1995 Features First of Type Automatic Linking 7 First U. S. DOD ALE Standard – 2 G ALE First U. S. Civil ALE Standard 2000 2005 NATO STANAG Compatibility AQC-ALE, 3 G ALE, Networking, etc. Errata Corrections Linking Protection Defined Rockwell Collins, Inc. © 2002
ALE – A Historical Perspective ALE Standard/Feature Timeline FED-STD-1045 Released MIL-STD-188 -141 A, CN 1 Released MIL-STD-188 -141 A, CN 2 Released FED-STD-1045 A Released Standards RCGS Introduces MIL-STD-188 -141 B Released MIL-STD-188 -141 B, CN 1 released SELSCAN® Manual Techniques Only Prior To This (75 years) 1975 1980 1985 1990 1995 Features First of Type Automatic Linking 7 First U. S. DOD ALE Standard – 2 G ALE First U. S. Civil ALE Standard 2000 2005 NATO STANAG Compatibility AQC-ALE, 3 G ALE, Networking, etc. Errata Corrections Linking Protection Defined Rockwell Collins, Inc. © 2002
 RCGS Experience Rockwell Collins has gained extensive experience as supplier to some of the largest ALE networks now in operation q – – 8 Over 9000 ALE-equipped products fielded Standard HF supplier for USAF ground airborne platforms that comprise the largest operational, globalcoverage ALE network in the world ALE is currently supported in 7 RCGS HF product lines and ancillary equipments We provide network management tools, passive propagation forecasting tools, and extensive system engineering experience to our customers Rockwell Collins, Inc. © 2002
RCGS Experience Rockwell Collins has gained extensive experience as supplier to some of the largest ALE networks now in operation q – – 8 Over 9000 ALE-equipped products fielded Standard HF supplier for USAF ground airborne platforms that comprise the largest operational, globalcoverage ALE network in the world ALE is currently supported in 7 RCGS HF product lines and ancillary equipments We provide network management tools, passive propagation forecasting tools, and extensive system engineering experience to our customers Rockwell Collins, Inc. © 2002
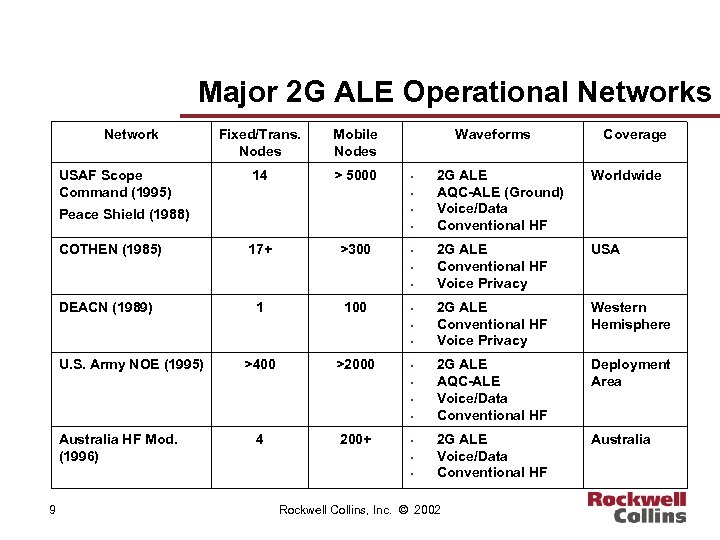 Major 2 G ALE Operational Networks Network USAF Scope Command (1995) Fixed/Trans. Nodes Mobile Nodes 14 > 5000 • • • Peace Shield (1988) COTHEN (1985) Waveforms • 17+ >300 • • • DEACN (1989) 1 100 • • • U. S. Army NOE (1995) >400 >2000 • • Australia HF Mod. (1996) 4 200+ • • • 9 Coverage 2 G ALE AQC-ALE (Ground) Voice/Data Conventional HF Worldwide 2 G ALE Conventional HF Voice Privacy USA 2 G ALE Conventional HF Voice Privacy Western Hemisphere 2 G ALE AQC-ALE Voice/Data Conventional HF Deployment Area 2 G ALE Voice/Data Conventional HF Australia Rockwell Collins, Inc. © 2002
Major 2 G ALE Operational Networks Network USAF Scope Command (1995) Fixed/Trans. Nodes Mobile Nodes 14 > 5000 • • • Peace Shield (1988) COTHEN (1985) Waveforms • 17+ >300 • • • DEACN (1989) 1 100 • • • U. S. Army NOE (1995) >400 >2000 • • Australia HF Mod. (1996) 4 200+ • • • 9 Coverage 2 G ALE AQC-ALE (Ground) Voice/Data Conventional HF Worldwide 2 G ALE Conventional HF Voice Privacy USA 2 G ALE Conventional HF Voice Privacy Western Hemisphere 2 G ALE AQC-ALE Voice/Data Conventional HF Deployment Area 2 G ALE Voice/Data Conventional HF Australia Rockwell Collins, Inc. © 2002
 What Are Customers Now Asking For? Affordable Enhancements q – – More Responsive Networks q – – Quicker links Reduced sounding overhead Better Security q – – 10 Military platform lifetimes being extended out of necessity JTRS mandate causing reluctance to perform major upgrades to legacy systems “A-kit” modifications drive cost Software-only upgrades very desirable Linking protection Physical security Rockwell Collins, Inc. © 2002
What Are Customers Now Asking For? Affordable Enhancements q – – More Responsive Networks q – – Quicker links Reduced sounding overhead Better Security q – – 10 Military platform lifetimes being extended out of necessity JTRS mandate causing reluctance to perform major upgrades to legacy systems “A-kit” modifications drive cost Software-only upgrades very desirable Linking protection Physical security Rockwell Collins, Inc. © 2002
 What Are Customers Now Asking For? Global Interoperability q – – Tailorable q – – Every customer has unique requirements not defined by a standard Waveforms must accommodate “bolt-on” capabilities Better Traffic Compatibility q – – 11 New waveforms must be backward compatible Lowest common denominator determines cross-network capabilities Link setup should facilitate traffic type of choice, e. g. MILSTD-188 -110 B App. C QAM @ 9. 6 kbps Transparent link setup for networking Rockwell Collins, Inc. © 2002
What Are Customers Now Asking For? Global Interoperability q – – Tailorable q – – Every customer has unique requirements not defined by a standard Waveforms must accommodate “bolt-on” capabilities Better Traffic Compatibility q – – 11 New waveforms must be backward compatible Lowest common denominator determines cross-network capabilities Link setup should facilitate traffic type of choice, e. g. MILSTD-188 -110 B App. C QAM @ 9. 6 kbps Transparent link setup for networking Rockwell Collins, Inc. © 2002
 Other Issues for Consideration q In addition to the perceived needs previously listed, customers need to consider things like: – – – 12 Is the new waveform easy to set up and use? Are the tools in place to allow me to manage my network effectively? Is the new waveform scalable to my needs? Does the new waveform increase the complexity of my communications system, potentially affecting reliability, maintenance, and cost? Does the new waveform require infrastructure changes to be effective, e. g. more authorized frequencies, higher RF power, time/key dissemination and coordination, etc. Is the new waveform mature? Has it been fielded and proven in real-world networks under real-world scenarios? Rockwell Collins, Inc. © 2002
Other Issues for Consideration q In addition to the perceived needs previously listed, customers need to consider things like: – – – 12 Is the new waveform easy to set up and use? Are the tools in place to allow me to manage my network effectively? Is the new waveform scalable to my needs? Does the new waveform increase the complexity of my communications system, potentially affecting reliability, maintenance, and cost? Does the new waveform require infrastructure changes to be effective, e. g. more authorized frequencies, higher RF power, time/key dissemination and coordination, etc. Is the new waveform mature? Has it been fielded and proven in real-world networks under real-world scenarios? Rockwell Collins, Inc. © 2002
 The Enhanced ALE Landscape q q q 13 MIL-STD-188 -141 B Appendix A, Alternative Quick Call Automatic Link Establishment (AQC-ALE) System MIL-STD-188 -141 B, Appendix C, Third Generation (3 G) HF Link Automation STANAG 4538 Technical Standard for an Automatic Radio Control System (ARCS) Rockwell Collins, Inc. © 2002
The Enhanced ALE Landscape q q q 13 MIL-STD-188 -141 B Appendix A, Alternative Quick Call Automatic Link Establishment (AQC-ALE) System MIL-STD-188 -141 B, Appendix C, Third Generation (3 G) HF Link Automation STANAG 4538 Technical Standard for an Automatic Radio Control System (ARCS) Rockwell Collins, Inc. © 2002
 The Enhanced ALE Landscape q MIL-STD-188 -141 B Appendix A, AQC-ALE – Variant of 2 G ALE primarily designed to reduce calling/sounding times – Asynchronous – 6 -character vs. 15 -character addresses – 14 Able to utilize most existing 2 G-equipped radios with minor (e. g. software upgrade) modifications Rockwell Collins, Inc. © 2002
The Enhanced ALE Landscape q MIL-STD-188 -141 B Appendix A, AQC-ALE – Variant of 2 G ALE primarily designed to reduce calling/sounding times – Asynchronous – 6 -character vs. 15 -character addresses – 14 Able to utilize most existing 2 G-equipped radios with minor (e. g. software upgrade) modifications Rockwell Collins, Inc. © 2002
 The Enhanced ALE Landscape q MIL-STD-188 -141 B, Appendix C, 3 G ALE – – q Totally new ALE technology Useful for faster linking, shorter/reduced sounding, more robust performance, and better networking Synchronous and asynchronous protocols Requires significant processing power and highly integrated modem, processor, and radio as well as accurate time STANAG 4538 ARCS – – 15 Essentially the same as 3 G with minor differences Implementation requirements are also comparable to 3 G Rockwell Collins, Inc. © 2002
The Enhanced ALE Landscape q MIL-STD-188 -141 B, Appendix C, 3 G ALE – – q Totally new ALE technology Useful for faster linking, shorter/reduced sounding, more robust performance, and better networking Synchronous and asynchronous protocols Requires significant processing power and highly integrated modem, processor, and radio as well as accurate time STANAG 4538 ARCS – – 15 Essentially the same as 3 G with minor differences Implementation requirements are also comparable to 3 G Rockwell Collins, Inc. © 2002
 Selection Process Strategy q Assumptions – Type of customer – We will define 3 types § Type 1 - No prior HF capability Type 2 - Currently using manual/channelized HF only § Type 3 - Currently using HF with 2 G ALE § – – 16 Assume no development cost for any of the waveforms Assume MIL-STD-188 -141 B 3 G ALE is equivalent to STANAG 4538 All waveforms are assumed to be available from the same source Comparative assessment is subjective and is based on the RCGS perspective Rockwell Collins, Inc. © 2002
Selection Process Strategy q Assumptions – Type of customer – We will define 3 types § Type 1 - No prior HF capability Type 2 - Currently using manual/channelized HF only § Type 3 - Currently using HF with 2 G ALE § – – 16 Assume no development cost for any of the waveforms Assume MIL-STD-188 -141 B 3 G ALE is equivalent to STANAG 4538 All waveforms are assumed to be available from the same source Comparative assessment is subjective and is based on the RCGS perspective Rockwell Collins, Inc. © 2002
 Selection Process Strategy q q 17 Using the previously identified needs, considerations, and customer types, a matrix was constructed The “best” waveform fit for each requirement was then established for each customer type, providing a generic assessment matrix Rockwell Collins, Inc. © 2002
Selection Process Strategy q q 17 Using the previously identified needs, considerations, and customer types, a matrix was constructed The “best” waveform fit for each requirement was then established for each customer type, providing a generic assessment matrix Rockwell Collins, Inc. © 2002
 Selection Process Strategy q 18 For a specific customer/program, the process is to: 1. Determine which customer type best fits the program 2. Delete any requirements that are not significant 3. Rank the remaining requirements from mostimportant to least-important based on the problem space or needs 4. Finally, count the number of times a waveform type appears under the applicable column 5. This, along with the ranked order of the need, should provide a strong indication of the waveform that should be considered Rockwell Collins, Inc. © 2002
Selection Process Strategy q 18 For a specific customer/program, the process is to: 1. Determine which customer type best fits the program 2. Delete any requirements that are not significant 3. Rank the remaining requirements from mostimportant to least-important based on the problem space or needs 4. Finally, count the number of times a waveform type appears under the applicable column 5. This, along with the ranked order of the need, should provide a strong indication of the waveform that should be considered Rockwell Collins, Inc. © 2002
 Selection Matrix Customer Categorization Type 1 Type 2 Type 3 (No Prior HF) (Manual HF Only) (Using 2 G ALE) AQC-ALE Upgradeable 3 G ALE AQC-ALE Responsiveness 3 G ALE Backward Compatibility 3 G ALE AQC-ALE Security 3 G ALE Traffic Compatibility 3 G ALE AQC-ALE Tailorable 3 G ALE AQC-ALE Long-Term Affordability 3 G ALE AQC-ALE Network Management Tools 3 G ALE AQC-ALE Scalable AQC-ALE Maturity AQC-ALE Complexity AQC-ALE Need Acquisition Cost Interoperability 19 Rockwell Collins, Inc. © 2002
Selection Matrix Customer Categorization Type 1 Type 2 Type 3 (No Prior HF) (Manual HF Only) (Using 2 G ALE) AQC-ALE Upgradeable 3 G ALE AQC-ALE Responsiveness 3 G ALE Backward Compatibility 3 G ALE AQC-ALE Security 3 G ALE Traffic Compatibility 3 G ALE AQC-ALE Tailorable 3 G ALE AQC-ALE Long-Term Affordability 3 G ALE AQC-ALE Network Management Tools 3 G ALE AQC-ALE Scalable AQC-ALE Maturity AQC-ALE Complexity AQC-ALE Need Acquisition Cost Interoperability 19 Rockwell Collins, Inc. © 2002
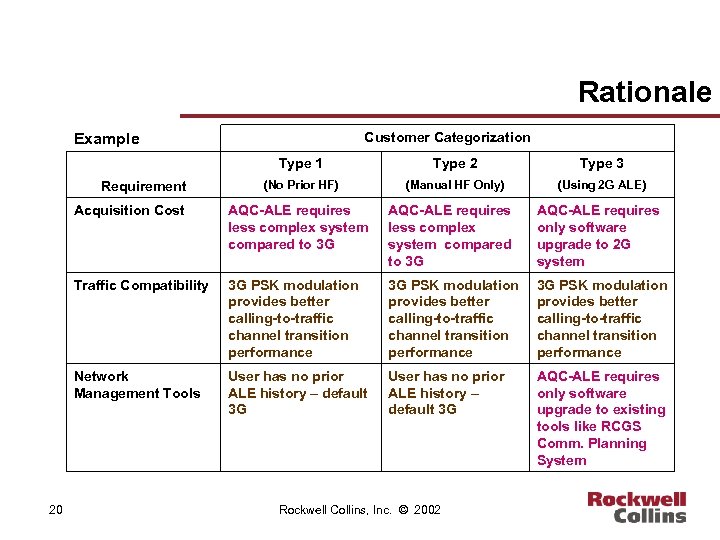 Rationale Customer Categorization Example Type 1 Requirement Type 2 Type 3 (No Prior HF) (Manual HF Only) (Using 2 G ALE) Acquisition Cost AQC-ALE requires less complex system compared to 3 G AQC-ALE requires only software upgrade to 2 G system Traffic Compatibility 3 G PSK modulation provides better calling-to-traffic channel transition performance Network Management Tools 20 AQC-ALE requires less complex system compared to 3 G User has no prior ALE history – default 3 G AQC-ALE requires only software upgrade to existing tools like RCGS Comm. Planning System Rockwell Collins, Inc. © 2002
Rationale Customer Categorization Example Type 1 Requirement Type 2 Type 3 (No Prior HF) (Manual HF Only) (Using 2 G ALE) Acquisition Cost AQC-ALE requires less complex system compared to 3 G AQC-ALE requires only software upgrade to 2 G system Traffic Compatibility 3 G PSK modulation provides better calling-to-traffic channel transition performance Network Management Tools 20 AQC-ALE requires less complex system compared to 3 G User has no prior ALE history – default 3 G AQC-ALE requires only software upgrade to existing tools like RCGS Comm. Planning System Rockwell Collins, Inc. © 2002
 Conclusion q q q We have shown that there are many factors to consider when evaluating advanced ALE waveforms A customer’s current state of HF/ALE operational capability will weigh heavily in the decision process We have offered an approach to assist decision makers in selecting an advanced ALE waveform A paper that greatly expands on this presentation will be posted on the HFIA website in the near future. 21 Rockwell Collins, Inc. © 2002
Conclusion q q q We have shown that there are many factors to consider when evaluating advanced ALE waveforms A customer’s current state of HF/ALE operational capability will weigh heavily in the decision process We have offered an approach to assist decision makers in selecting an advanced ALE waveform A paper that greatly expands on this presentation will be posted on the HFIA website in the near future. 21 Rockwell Collins, Inc. © 2002


