279bed36ff20b07c37f0c406e02c021c.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 53

A Power. Point Presentation By MD. ABDUR RAZZAK

Just-In-Time Manufacturing

Just-In-Time Manufacturing: A Definition • Uses a systems approach to develop and operate a manufacturing system • Organizes the production process so that parts are available when they are needed • A method for optimizing processes that involves continual reduction of waste

Central Themes Surrounding Just-In-Time • Simplicity • Quality • Elimination of Waste

Just-In-Time Techniques • Inventory Reduction as a Tool for Improvement • Supplier Relationships • Inventory “Pull” • Uniform Plant Loading

Goals of Just-In-Time Systems • Design for Optimum Quality and Cost • Minimize resources needed for Design and Manufacturing • Be Responsive to the Customers Needs • Develop Trust and Open Relationships with Suppliers and Customers • Develop a Commitment to Improve the Total Manufacturing System

Advantages of JIT Manufacturing • Materials Cost Savings • Manufacturing Cost Savings • Sales Cost Savings

Disadvantages of Just-In -Time Manufacturing • Implementing thorough JIT procedures can involve a major overhaul of your business systems - it may be difficult and expensive to introduce. • JIT manufacturing also opens businesses to a number of risks, notably those associated with your supply chain. With no stocks to fall back on, a minor disruption in supplies to your business from just one supplier could force production to cease at very short notice.

A Real World Example • PCs Just In Time Management: Del Computer Corporation has finally tuned its Just-in. Time system so that an order for a customized personal computer that comes in over the internet at 9 AM. can be on a delivery truck to the customer by 9 P. M. In addition, Dell's low cost production system allows it to under price its rivals by 10% to 15%. This combination has made Dell the envy of the personal computer industry and has enabled the company to grow at five times the industry rate. How does the company's just in time system deliver lower costs? "While machines from Compaq and IBM can languish on dealer shelves for two months Dell does not start ordering components and assembling computers until an order is booked. That may sound like no biggie, but the price of PC parts can fall rapidly in just a few months. By ordering right before assembly, Dell figures it s parts, on average, are 60 days newer than those in an IBM or Compaq machine sold at the same time. That can translate into a 6% profit advantage in components alone
Kanbans • Learn what Kanbans are and the different way the terminology is used in industry • Understand how to setup a kanban • Understand how to implement a kanban system
Kanban Definition What is Kanban? • Card system that controls production & inventory • Visual “pull” system vs. a “black box” push system (ie - MRP)
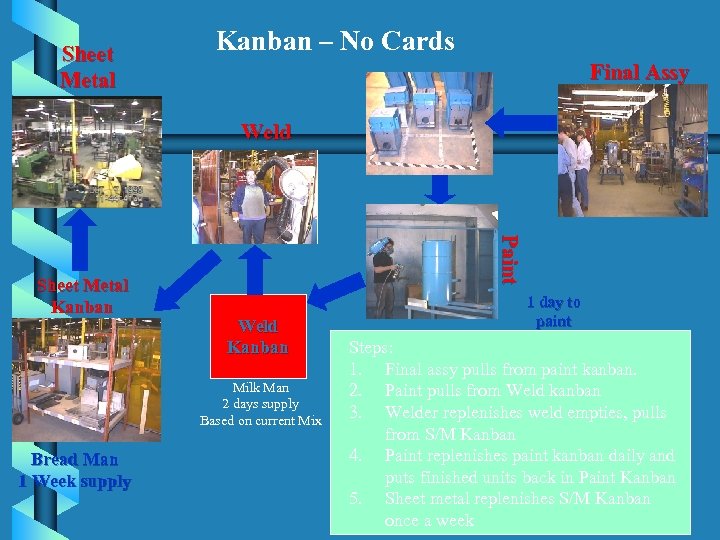
Sheet Metal Kanban – No Cards Final Assy Weld Paint Sheet Metal Kanban Weld Kanban Milk Man 2 days supply Based on current Mix Bread Man 1 Week supply 1 day to paint Steps: 1. Final assy pulls from paint kanban. 2. Paint pulls from Weld kanban 3. Welder replenishes weld empties, pulls from S/M Kanban 4. Paint replenishes paint kanban daily and puts finished units back in Paint Kanban 5. Sheet metal replenishes S/M Kanban once a week
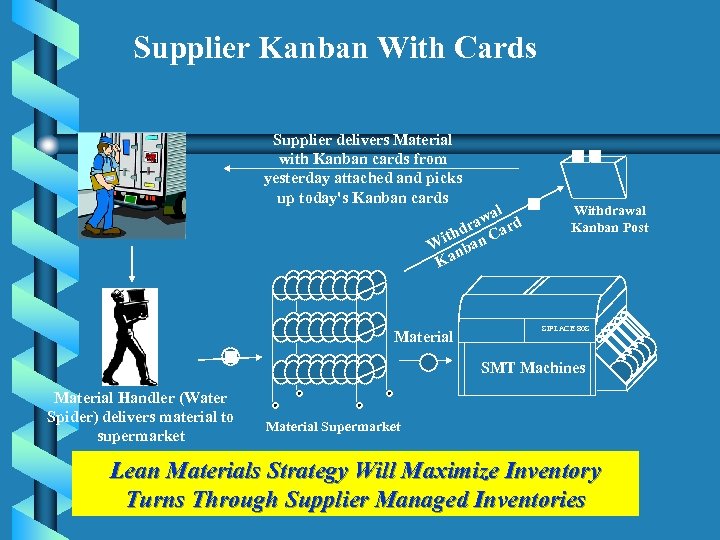
Supplier Kanban With Cards Supplier delivers Material with Kanban cards from yesterday attached and picks up today's Kanban cards al aw rd dr ith an Ca W nb Ka Material Withdrawal Kanban Post SIPLACE 80 S SMT Machines Material Handler (Water Spider) delivers material to supermarket Material Supermarket Lean Materials Strategy Will Maximize Inventory Turns Through Supplier Managed Inventories

Benefits of Kanban • Primary – Eliminate over-production, the #1 waste – Produce only what is ordered, when ordered, & quantity ordered • Secondary – Increase flexibility to meet customer demand – Reduction in scheduling by Production Control & Manufacturing – Competitive advantage by sequencing shipments to customers (what they want, when they want it, in the order they want it!)

disadvantage of Kanban • A breakdown in the Kanban system can result in the entire line shutting down. • The throughput of a Kanban system is not managed but is instead a result of controlled WIP and known cycle times.

Toyota Kanban Timeframe • Took 12 years to flow down kanban within Toyota • It then took: – 8 years to have 60% of first tier suppliers on kanban – 20 years to get 98% of first tier suppliers on kanban – Only approximately 50% of Toyota suppliers are using kanban systems internally today

Total Quality Management (TQM) System: • It is the process of individual & organizational development the purpose of which is to increase the level of satisfaction of all the stakeholders • IS THE SET OF MANAGEMENT PROCESSES AND SYSTEMS THAT CREATE DELIGHTED CUSTOMERS THROUGH EMPOWERED EMPLOYEES, LEADING TO HIGHER REVENUES & LOWER COST

COMPONENTS OF TQM 1. 2. 3. 4. PRICE REDUCTION CUSTOMER SATISFACTION INVOLVEMENT OF EVERYONE CONTINUOUS QUALITY IMPROVEMENT 5. LEADERSHIP

The goal (1) • The main goal of developing TQM (Total Quality Management) culture in the company is to ensure the fulfilment of customer needs and expectations, even go beyond the expectations.

Advantages of Total Quality Management • • Improves reputation- faults and problems are spotted and sorted quicker (zero defects) Higher employee morale– workers motivated by extra responsibility, team work and involvement in decisions of TQM Lower costs – Decrease waste as fewer defective products and no need for separate Quality Control inspectors

Disadvantages of Total Quality Management initial introduction costs- training workers and disrupting current production whilst being implemented Benefits may not be seen for several years Workers may be resistant to change – may feel less secure in jobs

Real Business Example TQM is not just a big company phenomenon. Penril Data. Comm is a maryland designer and producer of data communications and equipment. Before embarking on TQM, defect rates were so high that the company was reworking or scrapping one third of everything it made. Applying TQM techniques resulted in an 81% decrease in defects, an 83% decrease in failures in the first three months of use, and a 73% decrease in first year warranty repairs. TQM was credited with taking the company "from the brink of financial disaster" to excellent financial

Practical work • Development of self-assessment method • Implementation of the method+ interviews • Problematic areas and analysis

Six Sigma Definitions • “Six Sigma is a business improvement approach that seeks to find and eliminate causes of mistakes or defects in business processes by focusing on process outputs that are of critical importance to customers. ” (Snee, 2004). • “Six Sigma is a useful management philosophy and problem-solving methodology but it is not a comprehensive management system.

What is the Six Sigma Philosophy? Science * We don’t know what we don’t know. Six Sigma * If we can’t measure it, we really don’t know much about it. Art * If we don’t know much about it, we can’t control it. Magic * If we can’t control it, we are at the mercy of chance. Focus on the Customer!
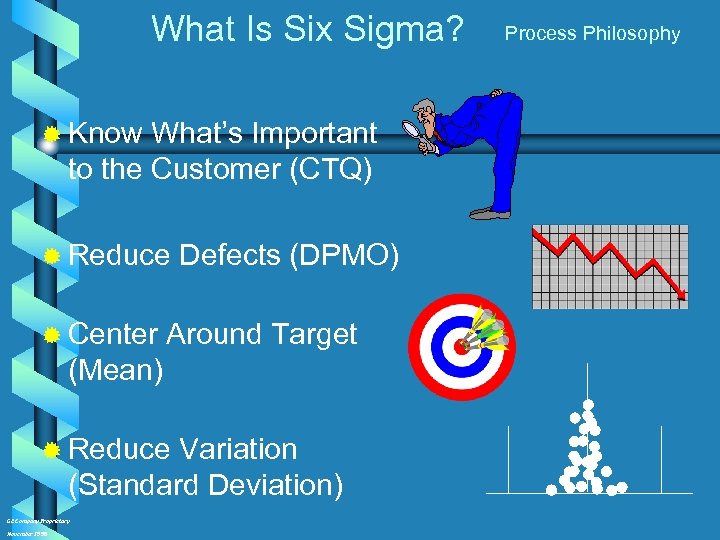
What Is Six Sigma? ® Know What’s Important to the Customer (CTQ) ® Reduce ® Center Defects (DPMO) Around Target (Mean) ® Reduce Variation (Standard Deviation) GE Company Proprietary November 1998 Process Philosophy ?
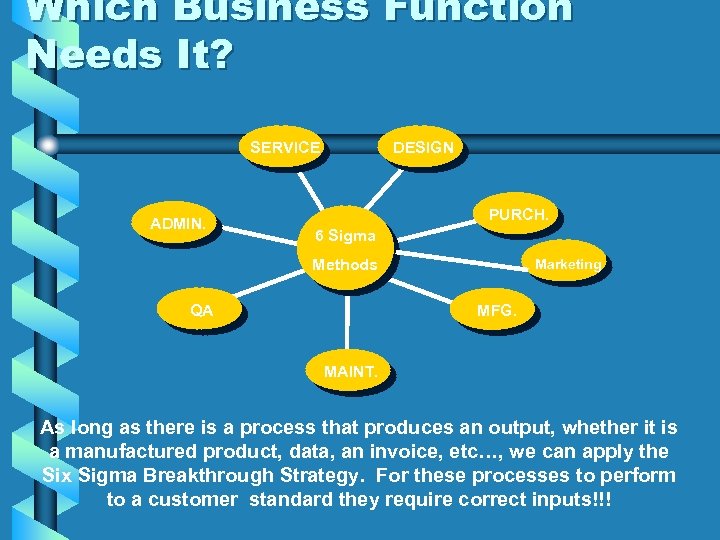
Which Business Function Needs It? SERVICE ADMIN. DESIGN PURCH. 6 Sigma Methods QA Marketing MFG. MAINT. As long as there is a process that produces an output, whether it is a manufactured product, data, an invoice, etc…, we can apply the Six Sigma Breakthrough Strategy. For these processes to perform to a customer standard they require correct inputs!!!

Advantages and Disadvantages of Six Sigma has its both advantages and disadvantages, Following are some points which we have examined: �Six Sigma aims to maximize customer satisfaction and minimize defects - Globalization and instant access to information, products and services continue to change the way our customers conduct business. Today's competitive environment leaves no room for error. We must delight our customers and relentlessly look for new ways to exceed their expectations. This is why Six Sigma Quality has become a part of our culture.

Advantages and Disadvantages of Six Sigma In the sales field there is an old saying; "Eagles never fly with doves. But to find angles you go through lots of doves. " In today's world there is so much information on turnover based on specific industries so baseline the norm should be easy to come up with unless your industry is very special. Getting a sigma value is very easy as well with your current date on how your company is doing. Change however may not be from a process improvement unless management is willing to change as well. �Research proves that firms that successfully implement Six Sigma perform better in virtually every business category, including return on sales, return on investment, employment growth and stock value growth. The strategy that has to be applied in today's educational arena is a thoughtful concern on the part of the management to understand customer needs and strive to reduce defects throughout all educational processes.
Business Process Reengineering
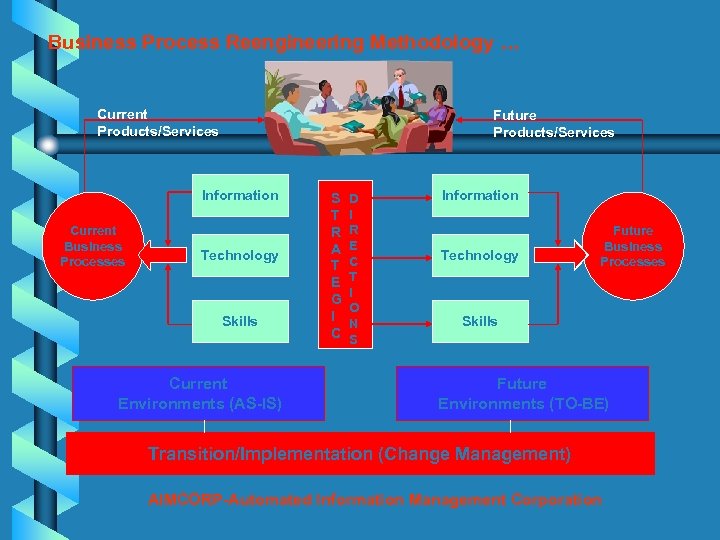
Business Process Reengineering Methodology … Current Products/Services Future Products/Services Information Current Business Processes Technology Skills Current Environments (AS-IS) S T R A T E G I C D I R E C T I O N S Information Technology Future Business Processes Skills Future Environments (TO-BE) Transition/Implementation (Change Management) AIMCORP-Automated Information Management Corporation

BUSINESS PROCESS REENGINEERING • The search for, and implementation of, radical change in business processes to achieve breakthrough results • Synonyms: business process redesign, business transformation, process innovation, business reinvention, change integration

BPR: LESSONS LEARNED • Get the strategy straight first • Lead from the top • Create a sense of urgency • Design from the outside in (customer)

BPR: STRATEGY* • Stakeholder Assessment shareholders, customers, employees • Determine which stakeholder expectations should be met to gain competitive advantage • Determine how to redesign to meet expectations • Map out IT solutions to support * Adapted from A. D. Little Inc.
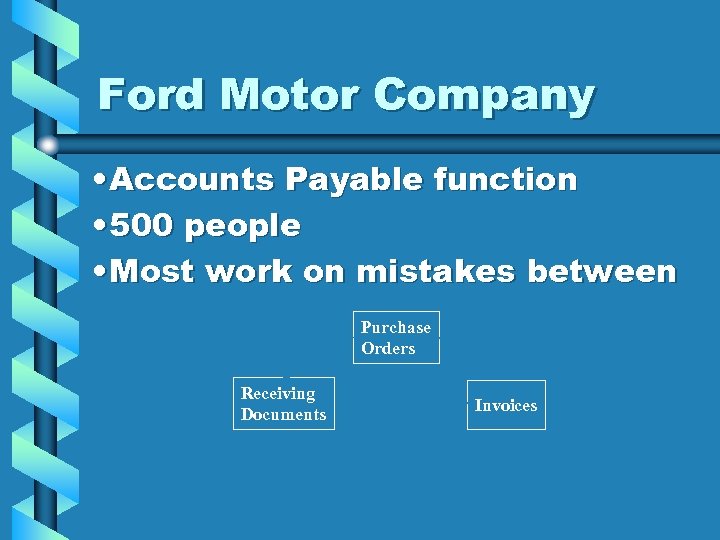
Ford Motor Company • Accounts Payable function • 500 people • Most work on mistakes between Purchase Orders Receiving Documents Invoices
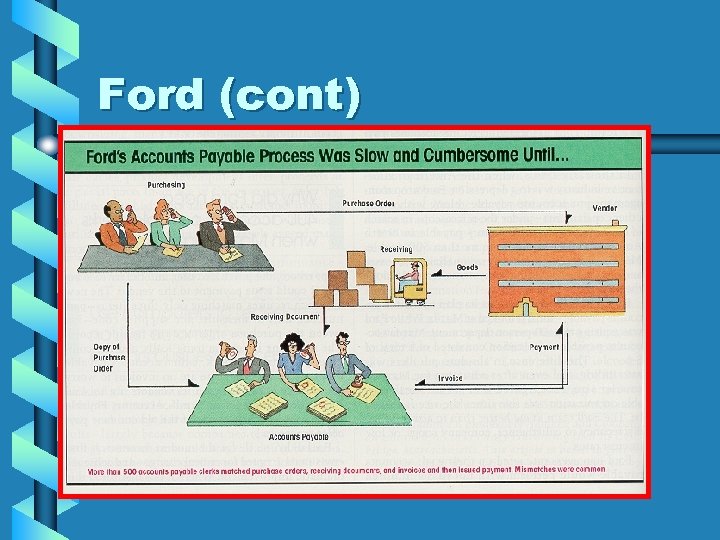
Ford (cont)
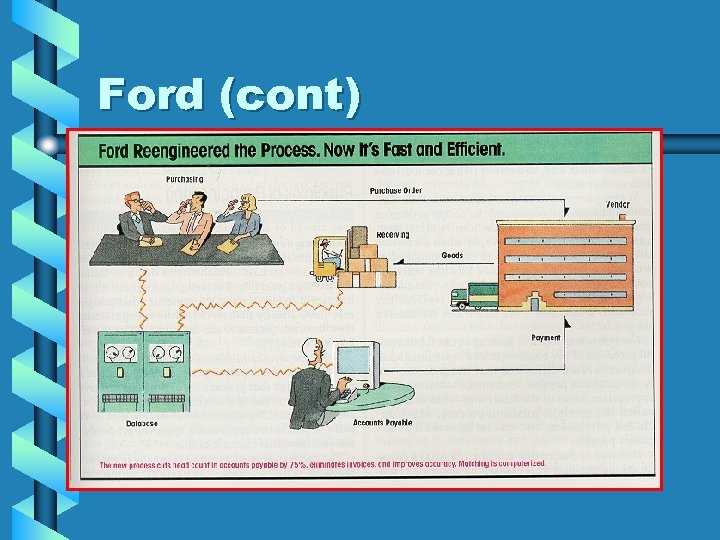
Ford (cont)

Risks in BPR • Advocates report failure rates of 50% to 70% • Sutcliffe [1999] reviewed difficulties –Employee resistance to change –Inadequate attention to employee concerns –Inappropriate staffing –Inadequate technologies

(Constrained) Reengineering Advantages (cont) • ERP provides the tool and structure to facilitate change • Proven and based on best practices • Forces change to happen • ERP bounds the design • Design is feasible and we know it works (it’s been proven – in other companies) • Cheaper than clean slate

Common Benefits of BPR • Enterprise integration – Departments are consolidated – Several jobs are combined into one job • Worker empowerment – There is both horizontal and vertical reorganization – Handoffs are eliminated – There are fewer rules and less coordination is required

Common Benefits of BPR, Cont’d • Number of steps in a process are reduced – This is simplification – Inspections, checks and controls are reduced or eliminated • The steps are performed in a more natural order

The Theory of Constraints (TOC) is a body of knowledge that has been developed over the past twenty years by Dr Eliyahu Goldratt. This body of knowledge challenges many of the assumptions about how we currently manage our businesses and organisations

The Theory of Constraints is based on the premise that: “Every real system, such as a business, must have within it at least one constraint. If this were not the case then the system could produce unlimited amounts of whatever it was striving for, profit in the case of a business. ………………. ”

Types of Constraint • • • THE MARKET CAPACITY RESOURCES SUPPLIERS FINANCE KNOWLEDGE OR COMPETENCE • POLICY

The Five Steps Step 1: Identify the system's constraint(s) Step 2: Decide how to exploit the system’s constraint(s) Step 3: Subordinate everything else to the above decision Step 4: Elevate the system’s constraint(s) Step 5: If in the previous step, a constraint has been broken go back to step 1, but do not allow inertia to become the system’s

‘TOC’ Applications 1. Production 2. Distribution and Supply Chain 3. Financial Management 4. Marketing 5. Strategic Planning 6. Project Management

Evaluation of TOC • Advantages – Improves capacity decisions in the short-run – Avoids build up of inventory – Aids in process understanding – Avoids local optimization – Improves communication between departments
Evaluation of TOC • Disadvantages – Negative impact on nonconstrained areas • Diverts attention from other areas that may be the next constraint • Temptation to reduce capacity

Evaluation of TOC • Ignores long-run considerations – Introduction of new products – Continuous improvement in nonconstrained areas • May lead organization away from strategy • Not a substitute for other accounting methods

Real Business Example The Lessons plant of Baxter International makes medical products such as sterile bags. Management of the plant is actually aware of the necessity to actively manage its constraints. For example, when materials are a constraint, management may go to a secondary vendor and purchase material at a higher cost than normal. When a machine is the constraint, a weekend shift is often added on the machine. If a particular machine is chronically the constraint and management has exhausted the possibilities of using it more effectively, then additional capacity is purchased. For example when the constraint was the plastic extruding machines, a new

extruding machine was ordered. However even before the machine arrived, management had determined that the constraint would shift to the blenders once the new extruding capacity was added. Therefore a new blender was already planned. By thinking ahead and focusing on the constraints, management is able to increase the plant's real capacity at the lowest possible cost.

Questions?

business is a Journey, not a Destination
279bed36ff20b07c37f0c406e02c021c.ppt