e540b9e8460afcac367b5091c8be10c9.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 20

A perspective from beyond the ESS Alistair Hamilton Director – Statistical Information Standards Australian Bureau of Statistics

Overview • Frameworks for collaborations beyond the ESS • Towards a top down view on what’s required for industrialisation – Possible “top down” pre-requisites

ESS Strategy & “GSS” Aspirations • Legal framework – Different situation • Very little binding governance across GSS (Global Statistical System) • More diverse national contexts(? ) • Methodological Developments – Shared interest : Best practice & common tools – More heterogeneous, less well bound, context • Modernisation of IT Infrastructure – Shared challenge, broadly shared directions • Standardisation and industrialisation – Shared aspirations : eg HLG-BAS

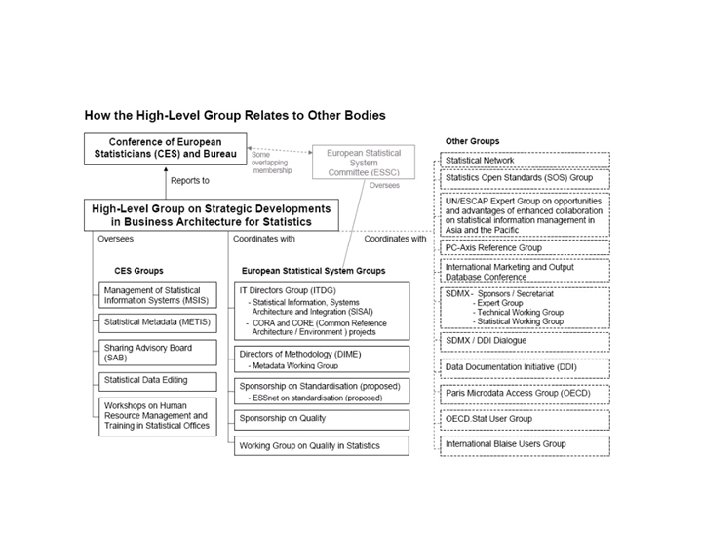
HLG-BAS • High Level Group for Strategic Directions in Business Architecture in Statistics – Created by Bureau of the Conference of European Statisticians (CES) in 2010 – Mission : Oversee and guide discussions on developments in the business architecture of the statistical production process, including methodology and information technology aspects – Strategic Vision endorsed by CES in June 2011 – Translating vision to strategy (and implementation) is theme for workshop next week


Some key points from the vision • We have to re-invent our products and processes and adapt to a changed world • We need to work together – The challenges are too big for statistical organisations to tackle on their own • Emphasis on related themes of Industrialisation and Standardisation
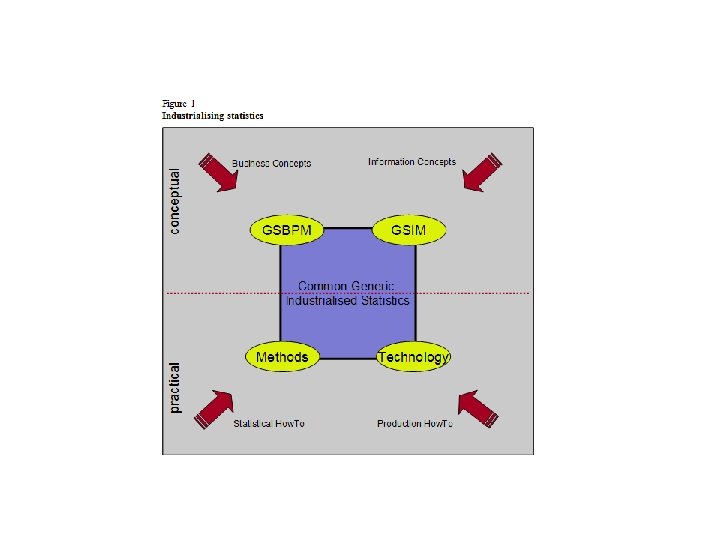

Examples of other joint efforts : Statistical Network • Idea discussed at CSTAT (OECD Committee on Statistics) in 2009 – Trial a collaboration approach in striving for improvement in Statistical Information Management • Initial members : SE, NO, NZ, GB, CA, AU • Critical goal : "Harmonising statistical methods, systems and capabilities across statistical agencies". • Practical small steps to industrialise methods and processes to quickly and effectively benefit all participating NSIs • Building with sharing and re-use across the whole community, in mind • 5 specific collaborations in 1 st round

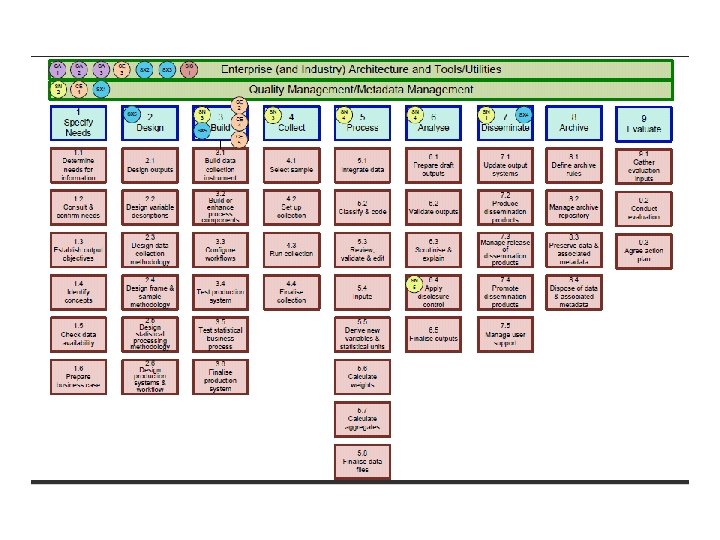
Example project • Generic Statistical Information Model (GSIM) – developing & operationalising GSIM agreed as highest priority strategic enabler of efficient & effective collaboration in the development & sharing of statistical information management systems. – progress through to associating GSIM with, eg, commonly agreed representation in XML – harness existing standards based representations wherever fit for purpose • SDMX & DDI-L agreed as key starting points – Co-ordinate & collaborate with other “networks” & groups • Eg METIS, ESSnets – GSIM focuses on all information objects used and/or produced in the course of various sub processes within a statistical business process.
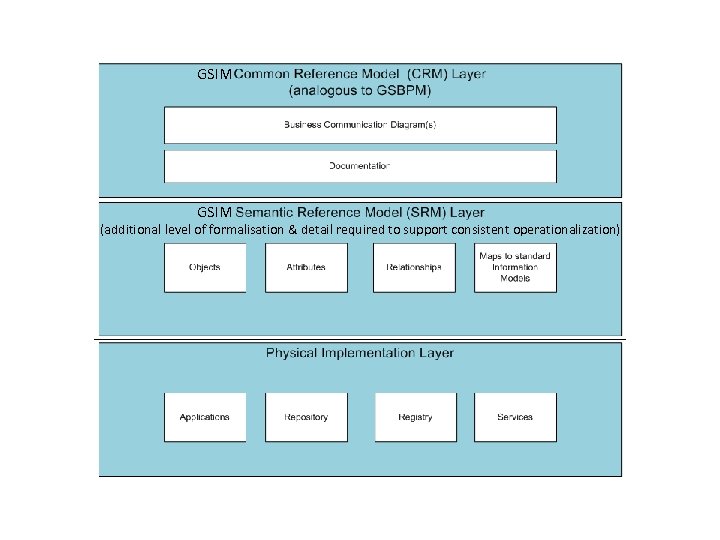
GSIM (additional level of formalisation & detail required to support consistent operationalization)

Other examples • Statistical Open Standards (SOS) Group – Members : IS, NO, SE, FI, DK, NL • OECD. Stat User Group – Members : OECD, IMF, IT, AU, NZ • Paris Microdata Access Group • Groups associated with PC-Axis & Blaise Many, many cases of individual NSIs undertaking R&D on topics covered by ESSnets!

Top Down Pre-requisites (1) • Industry definition – Value propositions – Scope – Relationship with allied industries • comparisons with other information industries that have industrialised – More detail on what industrialisation means • Implications for future roles of NSIs, for staff

Top Down Pre-requisites (2) • Ways and means – Effective industry bodies • Role of international agencies – Additional industry frameworks/guides • Includes collaboration frameworks covering legal/IP/whole of life considerations – Agility (financial resources, projects, staff) – Confidence in delivery – Cultural change – Easier matching of costs & benefits

Top Down Pre-requisites (3) • Industry standards – Reference architecture – Service/component (particularly interface) – Information • GSIM + operationalisation – Process • GSBPM + operationalisation via CORE IM etc – Method • Combine service/component and information in plug and play and connectivity
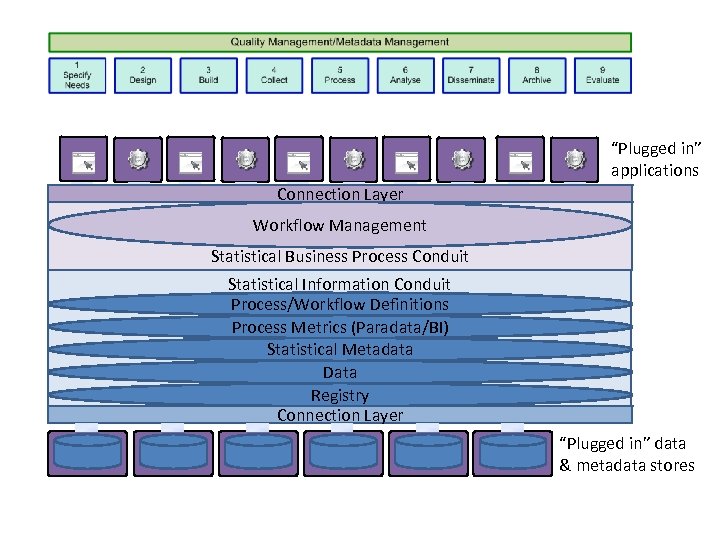
“Plugged in” applications Connection Layer Workflow Management Statistical Business Process Conduit Statistical Information Conduit Process/Workflow Definitions Process Metrics (Paradata/BI) Statistical Metadata Data Registry Connection Layer “Plugged in” data & metadata stores

Challenges • What are the other pre-requisites? • What is the critical path? – What are the first steps on it? – What is the role & path for connecting concept & practice? • How quickly can we progress it? • How best to organise to progress it? • What is the best interim strategy for agencies already undertaking major developments? • The local vs global “industrialisation” approach • Product vs Process

External observations on ESSnets • A lot of current interest beyond the ESS in regard to various ESSnets – Wider awareness (at a summary level) would generate even more interest • ESSnet processes are commendably open, eg – external participants as observers – dissemination of results & sharing of experiences • Admire resources and frameworks available to facilitate collaborative R&D within ESS and produced shared outputs • Agreed common directions across member states potentially represents a critical mass of “aligned” NSIs in a global context – ESS decisions influence broader GSS • ESSnet outputs, however, are not always put into practice consistently across member states? • Can be difficult to determine actual focus of an ESSnet and relationships with other work

Possibilities • Mapping is useful (of ESSnets & other work) – Network analysis of activities? • May also help identify gaps and overlaps? • Top down priorities may be clarified by – HLG-BAS Strategy for industrialisation & standardisation, and – Sponsorship on Standardisation – Architectural framework for ESS • Continue to consider going beyond ESS in “state of the art” studies • Seek to identify national & multi-national initiatives beyond ESS which strongly intersect with proposed ESSnets (or specific work packages within them) – via “community knowledge within the ESS” – via “advertising” to parties beyond the ESS self identify • possible use of UNECE, OECD etc channels?
e540b9e8460afcac367b5091c8be10c9.ppt