ce2564fd666214a21ea43fb1b0862999.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 84
 A New Nation The American Revolution and Creation of the United States
A New Nation The American Revolution and Creation of the United States
 Quiz • Describe the American values at the time of the Revolution in America. • IN your opinion did these values contribute to the revolution. Why or Why not? ?
Quiz • Describe the American values at the time of the Revolution in America. • IN your opinion did these values contribute to the revolution. Why or Why not? ?
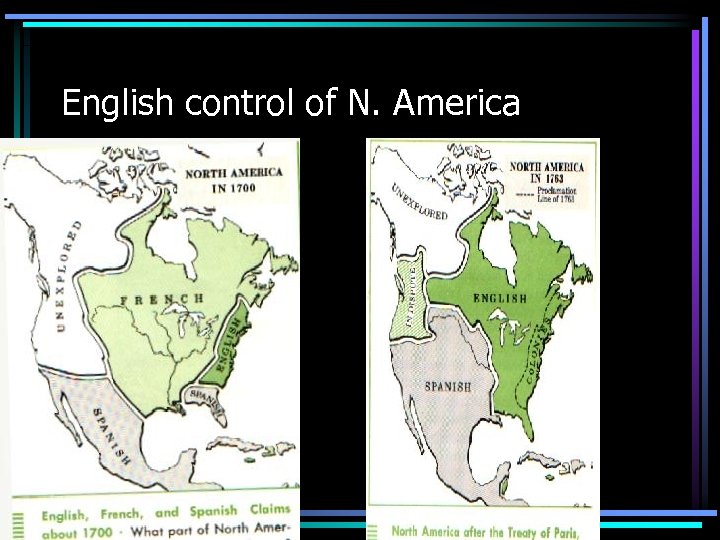 English control of N. America
English control of N. America
 American Mind • After England’s wars with the French were complete many problems existed. – Post-war debts – High Taxes – Need for money to finance acquired lands • Counted on colonies to help – Most accepted others rejected – Some wanted control of lives – American values- holders of destiny
American Mind • After England’s wars with the French were complete many problems existed. – Post-war debts – High Taxes – Need for money to finance acquired lands • Counted on colonies to help – Most accepted others rejected – Some wanted control of lives – American values- holders of destiny
 Proclamation of 1763 • French-Indian War creates need for British to raise money and control colonists • First regulation placed on colonies by England • Established a boundary between the Appalachian Mountains west into Indian lands • No one could trade past this line • Colonists seen this as a challenge to their rights to push west and find new markets
Proclamation of 1763 • French-Indian War creates need for British to raise money and control colonists • First regulation placed on colonies by England • Established a boundary between the Appalachian Mountains west into Indian lands • No one could trade past this line • Colonists seen this as a challenge to their rights to push west and find new markets
 Proclamation of 1763
Proclamation of 1763
 Sugar Act • Passed by parliament of 1764 -chief economic minister George Greenville • Also called the American Revenue Act • Raise revenues to pay debts and help keep the military in the colonies. • the Sugar Act imposed new or higher duties on sugar, textiles, coffee, indigo, and wine from non-British territories; • it also added to the list of "enumerated goods" that the colonies could ship only to English ports.
Sugar Act • Passed by parliament of 1764 -chief economic minister George Greenville • Also called the American Revenue Act • Raise revenues to pay debts and help keep the military in the colonies. • the Sugar Act imposed new or higher duties on sugar, textiles, coffee, indigo, and wine from non-British territories; • it also added to the list of "enumerated goods" that the colonies could ship only to English ports.
 Stamp Act • Required the use of specially marked paper or the affixing of stamps on all wills, contracts, other legal documents, and newspapers • Made a legal business transaction you had to pay the tax • First internal tax within colonies • Virtual representation vs. taxation without representation
Stamp Act • Required the use of specially marked paper or the affixing of stamps on all wills, contracts, other legal documents, and newspapers • Made a legal business transaction you had to pay the tax • First internal tax within colonies • Virtual representation vs. taxation without representation
 Colonial Reaction to Stamp Act • Taxation without representation • Massive protests occurred in the colonies • Stamp Act Congress- England had right to enforce laws but not direct taxes • Boycott ensued • Stamp Act was repealed • Declaratory Act- England had the right to legislate for the colonists
Colonial Reaction to Stamp Act • Taxation without representation • Massive protests occurred in the colonies • Stamp Act Congress- England had right to enforce laws but not direct taxes • Boycott ensued • Stamp Act was repealed • Declaratory Act- England had the right to legislate for the colonists
 Quiz • What was the Sugar Act? • What was the Stamp Act? • Explain the impact of the Stamp Act Congress on the Stamp Act. • Describe the importance of the Declaratory Act. • Explain the events leading up to the Boston Massacre • Bonus: Describe virtual representation
Quiz • What was the Sugar Act? • What was the Stamp Act? • Explain the impact of the Stamp Act Congress on the Stamp Act. • Describe the importance of the Declaratory Act. • Explain the events leading up to the Boston Massacre • Bonus: Describe virtual representation
 Charles Townshend • Prime Minister of Great Britain in 1767. Colonists believed he would be more favorable • Quartering Act – Required colonial legislatures to pay for supplies need by British Troops – Unless payments were made all laws passed by the colonies would be nullified • Revenue Act (Townshend Duties) – Taxed American imports of tea, glass, lead, paper, and paint – Thought that external tax would not be opposed
Charles Townshend • Prime Minister of Great Britain in 1767. Colonists believed he would be more favorable • Quartering Act – Required colonial legislatures to pay for supplies need by British Troops – Unless payments were made all laws passed by the colonies would be nullified • Revenue Act (Townshend Duties) – Taxed American imports of tea, glass, lead, paper, and paint – Thought that external tax would not be opposed
 Townshend • American Board of Customs Commissioners – Collected the taxes for Townshend – Became hated for dubious techniques of collection – Boston Massacre • Rioting over the actions of the Commissioners brought the British military to the city in 1768 • Troops fired on a protest in 1770 when troops fired on a rock throwing crowd. • Colonists used incident to stir up anti-British sentiments • Actually caused a relaxation in tensions.
Townshend • American Board of Customs Commissioners – Collected the taxes for Townshend – Became hated for dubious techniques of collection – Boston Massacre • Rioting over the actions of the Commissioners brought the British military to the city in 1768 • Troops fired on a protest in 1770 when troops fired on a rock throwing crowd. • Colonists used incident to stir up anti-British sentiments • Actually caused a relaxation in tensions.
 Boston Massacre
Boston Massacre
 Massachusetts Circular Letter • Drafted by Samuel Adams • Raised the issue of “Taxation without representation” • Townshend ordered the Mass. House of Representatives dissolved • Boycott of British goods • Loss of revenues by Britain that exceeded profits made by Townshend Acts.
Massachusetts Circular Letter • Drafted by Samuel Adams • Raised the issue of “Taxation without representation” • Townshend ordered the Mass. House of Representatives dissolved • Boycott of British goods • Loss of revenues by Britain that exceeded profits made by Townshend Acts.
 The Road to Revolution Boston Harbor
The Road to Revolution Boston Harbor
 Quiz • Charles Townshend placed many acts upon the colonists during his time as prime minister. • Discuss the so-called Townshend Acts and explain colonists reaction to the acts.
Quiz • Charles Townshend placed many acts upon the colonists during his time as prime minister. • Discuss the so-called Townshend Acts and explain colonists reaction to the acts.
 1772 • Two events brought the period of calm to an end. – Rhode Island colonists burned the British ship The Gaspee – The salaries for the governor and judges of Mass would be paid for by the king. – Left many to believe that Britain was undermining colonial self-rule • Committee of Correspondence – Bring news of British abuses to town meetings – Stirred up Anti-British sentiment
1772 • Two events brought the period of calm to an end. – Rhode Island colonists burned the British ship The Gaspee – The salaries for the governor and judges of Mass would be paid for by the king. – Left many to believe that Britain was undermining colonial self-rule • Committee of Correspondence – Bring news of British abuses to town meetings – Stirred up Anti-British sentiment
 Tea Act • Lord North replaced Townshend as minister of Britain. • North wanted to bail out East India Company from bankruptcy – East India Co. got monopoly on sale and distribution of tea into colonies – Lowered the price of tea to an all time low price – Revenue from the tea tax even though it was low was unacceptable to the colonists – Cemented Parliament’s right to tax the colonists
Tea Act • Lord North replaced Townshend as minister of Britain. • North wanted to bail out East India Company from bankruptcy – East India Co. got monopoly on sale and distribution of tea into colonies – Lowered the price of tea to an all time low price – Revenue from the tea tax even though it was low was unacceptable to the colonists – Cemented Parliament’s right to tax the colonists
 Boston Tea Party • Colonists were led to believe that the king was trying to purchase loyalty with cheap tea • When tea shipments arrived Samuel Adams called for the tea to be sent back and no tax be paid • Dressed as Mohawk Indians and boarded the ship and threw the 342 chests of tea into the harbor
Boston Tea Party • Colonists were led to believe that the king was trying to purchase loyalty with cheap tea • When tea shipments arrived Samuel Adams called for the tea to be sent back and no tax be paid • Dressed as Mohawk Indians and boarded the ship and threw the 342 chests of tea into the harbor
 Boston Tea Party
Boston Tea Party
 Boston Tea Party
Boston Tea Party
 Indians dumping tea
Indians dumping tea
 Coercive Acts • In Response to the Boston Tea Party, Parliament hit the colonists The Coercive Acts (Intolerable Acts) • Boston Port Act- Closed the port of Boston • Until the cost of tea and duties were paid in full • A new Quartering Act would allow British soldiers to be housed by colonists • Quebec Act: Set up Catholic government in Quebec. Gave away some colonists lands to Quebec • Revoked the Ma. Charter – Town meetings could not be held – Act for Impartial Administration of Justice- British soldiers would not be tried in the colonies.
Coercive Acts • In Response to the Boston Tea Party, Parliament hit the colonists The Coercive Acts (Intolerable Acts) • Boston Port Act- Closed the port of Boston • Until the cost of tea and duties were paid in full • A new Quartering Act would allow British soldiers to be housed by colonists • Quebec Act: Set up Catholic government in Quebec. Gave away some colonists lands to Quebec • Revoked the Ma. Charter – Town meetings could not be held – Act for Impartial Administration of Justice- British soldiers would not be tried in the colonies.
 Quiz • Explain the provisions of the following acts against the colonists – Sugar Act – Stamp Act – Quartering Act • What goods had duties placed on them by the Townshend Acts? • Describe the provisions of the Tea Act. • Why were colonists so opposed to the Tea Act? • What were the provisions of the Coercive Acts- Hint 5 of them? • Bonus: What did the power of the purse refer to? • Bonus 2: How did the Sugar and Townshend Acts apply to mercantilism while the Stamp Act did not?
Quiz • Explain the provisions of the following acts against the colonists – Sugar Act – Stamp Act – Quartering Act • What goods had duties placed on them by the Townshend Acts? • Describe the provisions of the Tea Act. • Why were colonists so opposed to the Tea Act? • What were the provisions of the Coercive Acts- Hint 5 of them? • Bonus: What did the power of the purse refer to? • Bonus 2: How did the Sugar and Townshend Acts apply to mercantilism while the Stamp Act did not?
 Quiz • Discuss the impact the Townshend duties had on the colonies. • Explain the reasons behind the Boston Tea Party. • Why were the Coercive Acts intolerable to the colonists? • Describe the outcome of the First Continental Congress • List one of the two profound effects of the Battle at Bunker Hill. • Bonus: What was the one condition for George Washington to assume command of the American forces?
Quiz • Discuss the impact the Townshend duties had on the colonies. • Explain the reasons behind the Boston Tea Party. • Why were the Coercive Acts intolerable to the colonists? • Describe the outcome of the First Continental Congress • List one of the two profound effects of the Battle at Bunker Hill. • Bonus: What was the one condition for George Washington to assume command of the American forces?
 QUIZ • What were the provisions and consequences of the following Acts? – Sugar – Stamp – Townshend – Tea – Intolerable (Coercive)
QUIZ • What were the provisions and consequences of the following Acts? – Sugar – Stamp – Townshend – Tea – Intolerable (Coercive)
 First Continental Congress • Philadelphia: September and October 1774 • Many called for the Suffolk Reserves – Condemn the Coercive acts – Called for colonists to form militias – Ban on imports , exports, and consumption – Would not pay tax until port of Boston was re-opened and Mass government was restored. – Enforced through the committee of correspondence • Plan was more moderate – Condemned Parliament for not allowing colonists the rights and privileges that they enjoy as English subjects – Colonists can chart on course on taxes and internal matters, subject to veto by the king – All acts since 1763 be repealed.
First Continental Congress • Philadelphia: September and October 1774 • Many called for the Suffolk Reserves – Condemn the Coercive acts – Called for colonists to form militias – Ban on imports , exports, and consumption – Would not pay tax until port of Boston was re-opened and Mass government was restored. – Enforced through the committee of correspondence • Plan was more moderate – Condemned Parliament for not allowing colonists the rights and privileges that they enjoy as English subjects – Colonists can chart on course on taxes and internal matters, subject to veto by the king – All acts since 1763 be repealed.
 First Continental Congress • Dominion Theory – Colonies not subject to parliament but to the Crown. • Lord North – Conciliatory Resolutions: Taxes only to regulate trade. – Colony could keep taxes generated if they would pay for the military in the colonies
First Continental Congress • Dominion Theory – Colonies not subject to parliament but to the Crown. • Lord North – Conciliatory Resolutions: Taxes only to regulate trade. – Colony could keep taxes generated if they would pay for the military in the colonies
 Militias • Colonists began to fortify towns with Minute Men. • Some organizers began to be arrested • April 19 1775: colonists and British faced off in Lexington – 8 colonists were killed • British went on to Concord where militias were supplied – Colonists fired upon the Brits wounding 273 in retreat • Fighting quickly spread – Boston, Vermont, Bunker Hill
Militias • Colonists began to fortify towns with Minute Men. • Some organizers began to be arrested • April 19 1775: colonists and British faced off in Lexington – 8 colonists were killed • British went on to Concord where militias were supplied – Colonists fired upon the Brits wounding 273 in retreat • Fighting quickly spread – Boston, Vermont, Bunker Hill
 Second Continental Congress • Olive Branch Petition- professing loyalty to the king and asking him to end the bloodshed • Declaration of the Causes and Necessity of Taking Up Arms– Denounced the Lexington bloodshed – Refused independence but said the colonists would resist becoming slaves to the Crown. • Continental Army was declared to support the rights of colonists – This Congress would assume governmental duties – George Washington declared in charge of the Army- Bunker Hill
Second Continental Congress • Olive Branch Petition- professing loyalty to the king and asking him to end the bloodshed • Declaration of the Causes and Necessity of Taking Up Arms– Denounced the Lexington bloodshed – Refused independence but said the colonists would resist becoming slaves to the Crown. • Continental Army was declared to support the rights of colonists – This Congress would assume governmental duties – George Washington declared in charge of the Army- Bunker Hill
 Choosing Sides • King rejects Olive Branch Petition • Colonists get French as ally • Loyalists – Those loyal to the king – 20% of the colonists • Patriots – Against England – Out numbered the loyalists 5 to 1 – Possible Civil War
Choosing Sides • King rejects Olive Branch Petition • Colonists get French as ally • Loyalists – Those loyal to the king – 20% of the colonists • Patriots – Against England – Out numbered the loyalists 5 to 1 – Possible Civil War
 Debate Reflections • Explain in your opinion who had the most to gain and who had the most to lose in the Revolutionary War. • Thomas Paine declared that it was Common Sense for America to break with England. Do you think he thought it would take a war if he was calling his article “common sense? ” • Explain what you think should happen to the Loyalists? To the French? Think of this as penalties or awards for their part in the war. • Explain the position of American slaves. Why is this interesting given your knowledge of the institution of slavery after the War?
Debate Reflections • Explain in your opinion who had the most to gain and who had the most to lose in the Revolutionary War. • Thomas Paine declared that it was Common Sense for America to break with England. Do you think he thought it would take a war if he was calling his article “common sense? ” • Explain what you think should happen to the Loyalists? To the French? Think of this as penalties or awards for their part in the war. • Explain the position of American slaves. Why is this interesting given your knowledge of the institution of slavery after the War?
 Independence • Common Sense: Thomas Paine – Tried to show Americans of the Inconsistency of British rule in the colonies • Declaration of Independence – – – Jefferson, Adams, and Franklin Jefferson is primary author Adopted on July 2, 1776 Slavery was at issue in the revisions Natural Rights– government should protect the rights of the people. Locke- Treatise on Government
Independence • Common Sense: Thomas Paine – Tried to show Americans of the Inconsistency of British rule in the colonies • Declaration of Independence – – – Jefferson, Adams, and Franklin Jefferson is primary author Adopted on July 2, 1776 Slavery was at issue in the revisions Natural Rights– government should protect the rights of the people. Locke- Treatise on Government
 War with England • The war shifted in geographical focus during the years – New England (1775 -1776) – Middle States (1776 -1778) – Southern States (1778 -1782) • Winter was a time in which the military would leave the battlefield and then return in the Spring – On Christmas 1776, Americans surprised a Hessian garrison by crossing the Delaware River at Trenton. – Raised the American morale
War with England • The war shifted in geographical focus during the years – New England (1775 -1776) – Middle States (1776 -1778) – Southern States (1778 -1782) • Winter was a time in which the military would leave the battlefield and then return in the Spring – On Christmas 1776, Americans surprised a Hessian garrison by crossing the Delaware River at Trenton. – Raised the American morale
 War with England • Saratoga – British found the terrain difficult – American forces led by Horatio Gates defeated the British – After the battle an alliance pact with the French was signed- Treaty of Alliance – French helped Americans with supplies for war • Valley Forge – Troops suffered through brutal winter with the promise of extra pay after the war – Battle(s) in the northern theater only proved to be stalemates at best
War with England • Saratoga – British found the terrain difficult – American forces led by Horatio Gates defeated the British – After the battle an alliance pact with the French was signed- Treaty of Alliance – French helped Americans with supplies for war • Valley Forge – Troops suffered through brutal winter with the promise of extra pay after the war – Battle(s) in the northern theater only proved to be stalemates at best
 End of the War • George Rogers Clark – TO end the “scalping” of Americans by the Indians. Clark and some other frontiersmen surrounded the British and Iroquois. Captured a British garrison • Yorktown – After the British had taken Savannah and Charleston they moved towards Yorktown, Va. – Yorktown was on a peninsula and when the French blocked the British from an ocean escape Yorktown was lost – British set down their arms led by Gen. Cornwallis
End of the War • George Rogers Clark – TO end the “scalping” of Americans by the Indians. Clark and some other frontiersmen surrounded the British and Iroquois. Captured a British garrison • Yorktown – After the British had taken Savannah and Charleston they moved towards Yorktown, Va. – Yorktown was on a peninsula and when the French blocked the British from an ocean escape Yorktown was lost – British set down their arms led by Gen. Cornwallis
 Treaty of Paris 1782 • Franklin, Adams, and John Jay • Great Britain recognized American independence with the Miss. River as its western boundary • Fishing rights off of Newfoundland • British troops would leave with all convenient speed • Americans had to compensate the Loyalists for property confiscated before British troops would leave
Treaty of Paris 1782 • Franklin, Adams, and John Jay • Great Britain recognized American independence with the Miss. River as its western boundary • Fishing rights off of Newfoundland • British troops would leave with all convenient speed • Americans had to compensate the Loyalists for property confiscated before British troops would leave
 Treaty of Paris • Native Americans would not recognize America • Slaves got nothing. Britain turned their back
Treaty of Paris • Native Americans would not recognize America • Slaves got nothing. Britain turned their back
 Quiz • Describe the Sugar Act and Townshend Duties and explain how they were similar. • What was the Stamp Act and discuss colonists reactions to this Act? • What was the Tea Act and describe what the Act led the colonists to do? • Discuss the Coercive Acts (all 5 of them)and the reaction made by colonists. • Describe the arguments in some publications about why the colonists should favor independence. • Bonus: Name one US negotiator in the Treaty of Paris
Quiz • Describe the Sugar Act and Townshend Duties and explain how they were similar. • What was the Stamp Act and discuss colonists reactions to this Act? • What was the Tea Act and describe what the Act led the colonists to do? • Discuss the Coercive Acts (all 5 of them)and the reaction made by colonists. • Describe the arguments in some publications about why the colonists should favor independence. • Bonus: Name one US negotiator in the Treaty of Paris
 Creating A New Nation Governmental Structures of The United States of America
Creating A New Nation Governmental Structures of The United States of America
 Precursor of American Government • Ancient Greece and Rome- direct democracy • Magna Carta- listed rights the English monarch could not take away. • European Writers- natural rights- rights people are born with • Montesquieu- separation of powers
Precursor of American Government • Ancient Greece and Rome- direct democracy • Magna Carta- listed rights the English monarch could not take away. • European Writers- natural rights- rights people are born with • Montesquieu- separation of powers
 Articles of Confederation • • • Loose confederation of states National legislature Each state gets one vote No executive or judicial branches Unicameral Legislation- Confederation Congress • Legislature afraid power would be taken away
Articles of Confederation • • • Loose confederation of states National legislature Each state gets one vote No executive or judicial branches Unicameral Legislation- Confederation Congress • Legislature afraid power would be taken away
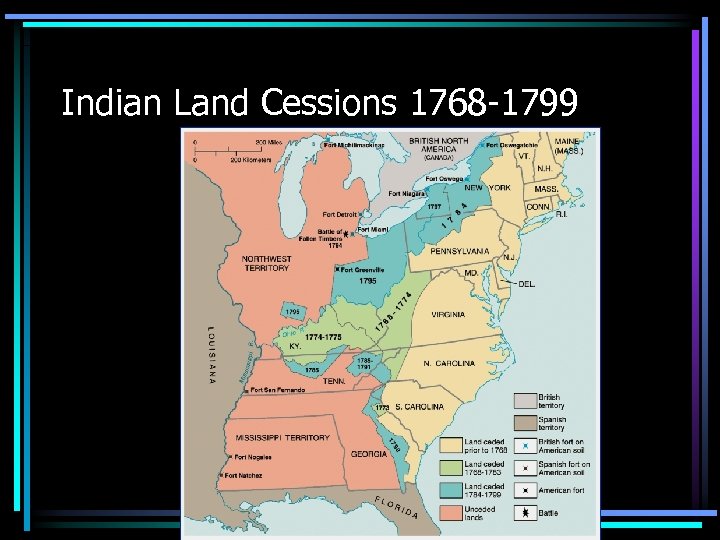 Indian Land Cessions 1768 -1799
Indian Land Cessions 1768 -1799
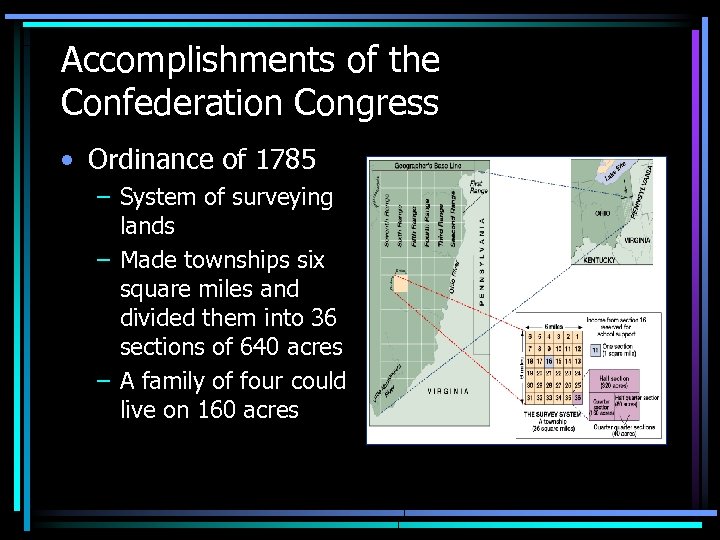 Accomplishments of the Confederation Congress • Ordinance of 1785 – System of surveying lands – Made townships six square miles and divided them into 36 sections of 640 acres – A family of four could live on 160 acres
Accomplishments of the Confederation Congress • Ordinance of 1785 – System of surveying lands – Made townships six square miles and divided them into 36 sections of 640 acres – A family of four could live on 160 acres
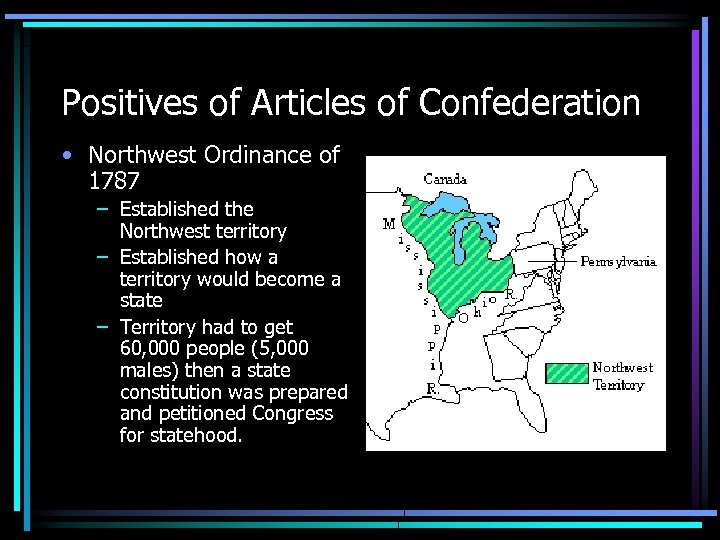 Positives of Articles of Confederation • Northwest Ordinance of 1787 – Established the Northwest territory – Established how a territory would become a state – Territory had to get 60, 000 people (5, 000 males) then a state constitution was prepared and petitioned Congress for statehood.
Positives of Articles of Confederation • Northwest Ordinance of 1787 – Established the Northwest territory – Established how a territory would become a state – Territory had to get 60, 000 people (5, 000 males) then a state constitution was prepared and petitioned Congress for statehood.
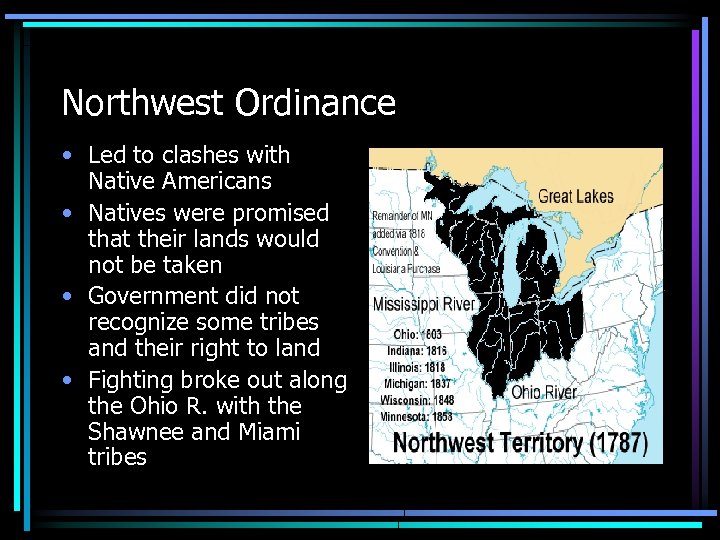 Northwest Ordinance • Led to clashes with Native Americans • Natives were promised that their lands would not be taken • Government did not recognize some tribes and their right to land • Fighting broke out along the Ohio R. with the Shawnee and Miami tribes
Northwest Ordinance • Led to clashes with Native Americans • Natives were promised that their lands would not be taken • Government did not recognize some tribes and their right to land • Fighting broke out along the Ohio R. with the Shawnee and Miami tribes
 Weakness of the Confederation Congress • • Needed nine votes to pass any law Could not tax states or people Could not regulate trade Congress could declare war but could not raise an army • Basically the New Government was State Rule
Weakness of the Confederation Congress • • Needed nine votes to pass any law Could not tax states or people Could not regulate trade Congress could declare war but could not raise an army • Basically the New Government was State Rule
 Writing Assignment • Analyze the effectiveness of the Articles of Confederation. – Strengths – Weaknesses – What should happen to it in the future? ? • With a partner create a plan for revisions of the Articles of Confederation to meet the needs of the people. • Combine into a group of 4 and mesh plans of revision into one working document
Writing Assignment • Analyze the effectiveness of the Articles of Confederation. – Strengths – Weaknesses – What should happen to it in the future? ? • With a partner create a plan for revisions of the Articles of Confederation to meet the needs of the people. • Combine into a group of 4 and mesh plans of revision into one working document
 Starter • Describe two weaknesses of the Articles of Confederation. • What was the Ordinance of 1785? • What was the Northwest Ordinance of 1787?
Starter • Describe two weaknesses of the Articles of Confederation. • What was the Ordinance of 1785? • What was the Northwest Ordinance of 1787?
![Annapolis Convention (1786) 12 representatives from 5 states [NY, NJ, PA, DE, VA] GOAL Annapolis Convention (1786) 12 representatives from 5 states [NY, NJ, PA, DE, VA] GOAL](https://present5.com/presentation/ce2564fd666214a21ea43fb1b0862999/image-52.jpg) Annapolis Convention (1786) 12 representatives from 5 states [NY, NJ, PA, DE, VA] GOAL address barriers that limited trade and commerce between the states. Not enough states were represented to make any real progress. Sent a report to the Congress to call a meeting of all the states to meet in Philadelphia to examine areas broader than just trade and commerce.
Annapolis Convention (1786) 12 representatives from 5 states [NY, NJ, PA, DE, VA] GOAL address barriers that limited trade and commerce between the states. Not enough states were represented to make any real progress. Sent a report to the Congress to call a meeting of all the states to meet in Philadelphia to examine areas broader than just trade and commerce.
 Shay’s Rebellion • America was in debt of 160 million after the war • Printed more money on European loans • Inflation skyrocketed • Daniel Shays – – Led 2, 000 men to shutdown courthouses Men were slaughtered by Mass. Militia Did get the Ma. Legislature to lower taxes Calls for a stronger national government to help states began.
Shay’s Rebellion • America was in debt of 160 million after the war • Printed more money on European loans • Inflation skyrocketed • Daniel Shays – – Led 2, 000 men to shutdown courthouses Men were slaughtered by Mass. Militia Did get the Ma. Legislature to lower taxes Calls for a stronger national government to help states began.
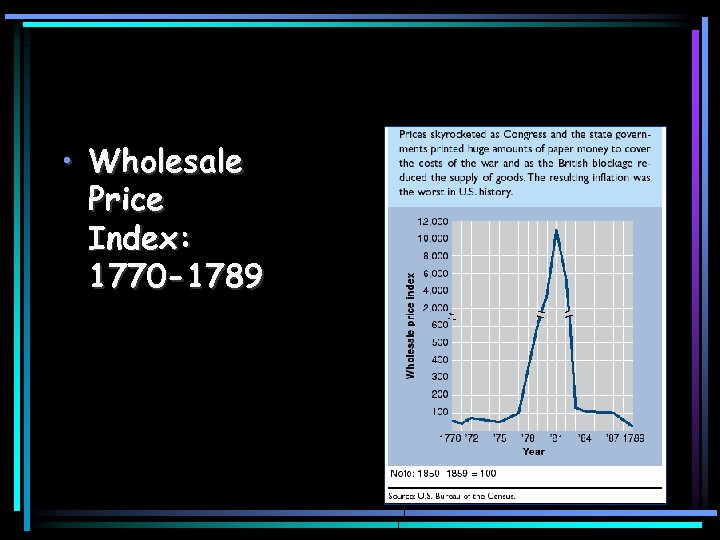 • Wholesale Price Index: 1770 -1789
• Wholesale Price Index: 1770 -1789
 Constitutional Convention • May 1787, 55 delegates from twelve states arrived in Philadelphia • Purpose was to revise the Articles of Confederation • As the convention continued in September of 1787 a new Constitution was in the works • New structure of government
Constitutional Convention • May 1787, 55 delegates from twelve states arrived in Philadelphia • Purpose was to revise the Articles of Confederation • As the convention continued in September of 1787 a new Constitution was in the works • New structure of government
 Virginia Plan • James Madison was main author • Called for a bicameral legislature to make laws, treaties, and levy taxes – Representation in both houses based on population – Member of lower house voted by the people – Members of the upper house would be chosen by member of the lower house. Selection would come from nominations from state • No plan for electing an executive – President chosen by Legislature- One term – Execute all laws
Virginia Plan • James Madison was main author • Called for a bicameral legislature to make laws, treaties, and levy taxes – Representation in both houses based on population – Member of lower house voted by the people – Members of the upper house would be chosen by member of the lower house. Selection would come from nominations from state • No plan for electing an executive – President chosen by Legislature- One term – Execute all laws
 New Jersey Plan • William Patterson main author • Large state plan would give power to states. Virginia and New York • Unicameral house of legislature • Power to levy taxes and regulate trade • Members chosen by state legislators and each state gets one vote • Multi-person executive would be elected by the legislature • Laws passed were binding to the states
New Jersey Plan • William Patterson main author • Large state plan would give power to states. Virginia and New York • Unicameral house of legislature • Power to levy taxes and regulate trade • Members chosen by state legislators and each state gets one vote • Multi-person executive would be elected by the legislature • Laws passed were binding to the states
 Connecticut (Great) Compromise • Authored by Roger Sherman • Large states wanted representation based on population • Small states wanted equal representation • Compromise – House of Rep: based on population of a state – Senate: 2 members with equal vote from each state
Connecticut (Great) Compromise • Authored by Roger Sherman • Large states wanted representation based on population • Small states wanted equal representation • Compromise – House of Rep: based on population of a state – Senate: 2 members with equal vote from each state
 3/5 ths Compromise • How would slaves be counted in terms of population to send Representatives to the Congress? • Count a slave as 3/5 ths a person for representation and direct tax purpose
3/5 ths Compromise • How would slaves be counted in terms of population to send Representatives to the Congress? • Count a slave as 3/5 ths a person for representation and direct tax purpose
 Quiz • What were the Articles of Confederation? • Explain the strengths and weaknesses of the Articles. • Explain the difference of the Virginia and New Jersey Plans. • Discuss the Great Compromise. • Explain the 3/5 ths compromise as well as the Northern and Southern response to this compromise.
Quiz • What were the Articles of Confederation? • Explain the strengths and weaknesses of the Articles. • Explain the difference of the Virginia and New Jersey Plans. • Discuss the Great Compromise. • Explain the 3/5 ths compromise as well as the Northern and Southern response to this compromise.
 Quiz • • • Discuss the Virginia Plan Discuss the NJ Plan Explain the Great Compromise Explain the 3/5 ths Compromise How were the Northern and Southern viewpoints of the 3/5 ths compromise different.
Quiz • • • Discuss the Virginia Plan Discuss the NJ Plan Explain the Great Compromise Explain the 3/5 ths Compromise How were the Northern and Southern viewpoints of the 3/5 ths compromise different.
 Branches of Government • Executive – Election by Congress or people – Electoral college: states choose electors to equal their number of reps in Congress. – Electors would vote for two presidential candidates – Whoever got the most votes was Pres. 2 nd most was VP. • Legislative – Congress with two houses
Branches of Government • Executive – Election by Congress or people – Electoral college: states choose electors to equal their number of reps in Congress. – Electors would vote for two presidential candidates – Whoever got the most votes was Pres. 2 nd most was VP. • Legislative – Congress with two houses
 Branches of Government • Judicial – Supreme Court • Separation of Powers – Government is in the hands of the three branches. – All have different duties • Checks and Balances – Makes sure that one branch does not dominate the others
Branches of Government • Judicial – Supreme Court • Separation of Powers – Government is in the hands of the three branches. – All have different duties • Checks and Balances – Makes sure that one branch does not dominate the others
 Federalist • Supporters of the Constitution • Supported a strong federal government • A strong federal government would provide protection, maintain order, regulate trade, and guarantee the rights of citizens. • Ensure the nation’s debt were paid.
Federalist • Supporters of the Constitution • Supported a strong federal government • A strong federal government would provide protection, maintain order, regulate trade, and guarantee the rights of citizens. • Ensure the nation’s debt were paid.
 Anti-Federalist • Feared that strong central government would endanger the people’s liberties and freedoms • Government was too far from the people. • Fearful of abuse of power
Anti-Federalist • Feared that strong central government would endanger the people’s liberties and freedoms • Government was too far from the people. • Fearful of abuse of power
 Ratification • Smaller states ratified the Constitution first • New Hampshire became the ninth state to ratify the Constitution however Virginia and New York had not ratified by 1788 • Both ratified after staunch debates in summer of 1788 • Rhode Island was last to ratify in 1790.
Ratification • Smaller states ratified the Constitution first • New Hampshire became the ninth state to ratify the Constitution however Virginia and New York had not ratified by 1788 • Both ratified after staunch debates in summer of 1788 • Rhode Island was last to ratify in 1790.
 US Constitution • First three articles give powers to the branches of government • Article IV gives relations of the states to one another • Article V- Process of Amendment • Article VI- General Provisions • Article VII- Ratification
US Constitution • First three articles give powers to the branches of government • Article IV gives relations of the states to one another • Article V- Process of Amendment • Article VI- General Provisions • Article VII- Ratification
 Essay • Compare and contrast the Articles of Confederation with the US Constitution. • You may refer to the Constitution of the United States of America on p. A 4 in your textbook • Create a chart with comparison criteria to help organize your response • Remember Writing Format for this class – Introduction – Body – Conclusion
Essay • Compare and contrast the Articles of Confederation with the US Constitution. • You may refer to the Constitution of the United States of America on p. A 4 in your textbook • Create a chart with comparison criteria to help organize your response • Remember Writing Format for this class – Introduction – Body – Conclusion
 Review • Describe – Virginia Plan – New Jersey Plan – Great Compromise – 3/5 th Compromise • Explain the difference between the Federalist and Anti-Federalist
Review • Describe – Virginia Plan – New Jersey Plan – Great Compromise – 3/5 th Compromise • Explain the difference between the Federalist and Anti-Federalist
 Organizing the New Government The New Nation
Organizing the New Government The New Nation
 George Washington • George Washington sworn in as 1 st President of US April 30, 1789 • First capital was New York City • Bill of Rights – James Madison led committee to add rights for people that had been guaranteed by the states – Most concern was the 1 st Amendment – Part of Anti-Federalist agenda – North Carolina and Rhode Island failed to ratify the Constitution until Bill of Rights was submitted to Congress
George Washington • George Washington sworn in as 1 st President of US April 30, 1789 • First capital was New York City • Bill of Rights – James Madison led committee to add rights for people that had been guaranteed by the states – Most concern was the 1 st Amendment – Part of Anti-Federalist agenda – North Carolina and Rhode Island failed to ratify the Constitution until Bill of Rights was submitted to Congress
 Alexander Hamilton
Alexander Hamilton
 Alexander Hamilton • Secretary of Treasury • Report on Public Credit (1790) – National debt was high after war – Pay the debt by printing new securities and honoring at face value the certificates issued by the Continental Congress – Federal government assume state debts. Assumption – Just pay off interest of debt was sufficient
Alexander Hamilton • Secretary of Treasury • Report on Public Credit (1790) – National debt was high after war – Pay the debt by printing new securities and honoring at face value the certificates issued by the Continental Congress – Federal government assume state debts. Assumption – Just pay off interest of debt was sufficient
 Hamilton’s Critics • Critics claimed that many had sold their certificates at cheap prices • Current holders would make huge profits • States consented because they would lose debt • Congress passed the report • Report was huge financial success
Hamilton’s Critics • Critics claimed that many had sold their certificates at cheap prices • Current holders would make huge profits • States consented because they would lose debt • Congress passed the report • Report was huge financial success
 Hamilton (con’t) • Report on a National Bank – Federally chartered Bank – Handle Federal deposits, make loans to the gov’t and issue paper notes when cash was scarce – Funded by shareholders who could make profit
Hamilton (con’t) • Report on a National Bank – Federally chartered Bank – Handle Federal deposits, make loans to the gov’t and issue paper notes when cash was scarce – Funded by shareholders who could make profit
 Hamilton (con’t) • Report on Manufactures – Called for protective tariffs on imports to encourage domestic manufacturing – Congress did not support high tariff – Hamilton got same result by charging duties on goods imported on non. American ships than on American ships
Hamilton (con’t) • Report on Manufactures – Called for protective tariffs on imports to encourage domestic manufacturing – Congress did not support high tariff – Hamilton got same result by charging duties on goods imported on non. American ships than on American ships
 Whiskey Rebellion • Western Pennsylvania farmers movement • Distilled grains into liquor • Excise tax- levied by Hamilton- 25% of value of product • Farmers declared defiance against tax and rioted against tax officials • Militias set out to disperse rebellion • Federal law would be obeyed • Violent protest would not be allowed
Whiskey Rebellion • Western Pennsylvania farmers movement • Distilled grains into liquor • Excise tax- levied by Hamilton- 25% of value of product • Farmers declared defiance against tax and rioted against tax officials • Militias set out to disperse rebellion • Federal law would be obeyed • Violent protest would not be allowed
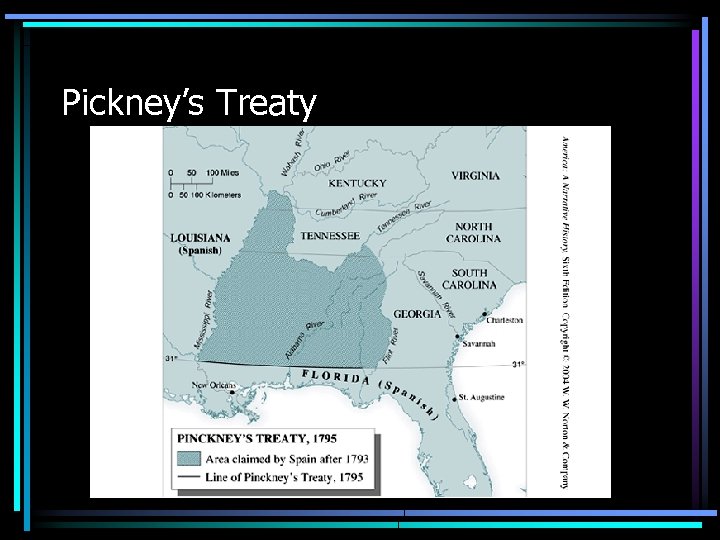
 Foreign Policy of Washington • Washington’s Neutrality – Isolationist point of view – Would not take sides between France and Great Britain – Britain took American vessels after it was thought US sided with France • Jay’s Treaty – British withdrew from Northwest and allowed for trade in the West Indies • Pinckney's Treaty or San Lorenzo – 31 st parallel as southern boundary of US – Free use of Miss River all the way to New Orleans to avoid duties on products
Foreign Policy of Washington • Washington’s Neutrality – Isolationist point of view – Would not take sides between France and Great Britain – Britain took American vessels after it was thought US sided with France • Jay’s Treaty – British withdrew from Northwest and allowed for trade in the West Indies • Pinckney's Treaty or San Lorenzo – 31 st parallel as southern boundary of US – Free use of Miss River all the way to New Orleans to avoid duties on products
 Pickney’s Treaty
Pickney’s Treaty
 John Adams
John Adams
 Foreign Policy • XYZ affair – Treaty with France not as easy – Election of Adams led the French to fire upon American ships – Americans went to meet with French minister Talleyrand – Refused to meet with them and referred them to unknown agents X, Y, Z – Talleyrand would negotiate with them when he got 250, 000 and France got 12 million – Led to greater hostilities between France and US – Fighting in the Caribbean Ocean.
Foreign Policy • XYZ affair – Treaty with France not as easy – Election of Adams led the French to fire upon American ships – Americans went to meet with French minister Talleyrand – Refused to meet with them and referred them to unknown agents X, Y, Z – Talleyrand would negotiate with them when he got 250, 000 and France got 12 million – Led to greater hostilities between France and US – Fighting in the Caribbean Ocean.
 Domestic Policy • Alien and Sedition Acts – A crime to “combine or conspire to oppose any policy of the United States or to intimidate public officials – Illegal to write, print, utter, or publish anything against the government – Zenger Affair: Colonial era case that materials may be published if are proven true
Domestic Policy • Alien and Sedition Acts – A crime to “combine or conspire to oppose any policy of the United States or to intimidate public officials – Illegal to write, print, utter, or publish anything against the government – Zenger Affair: Colonial era case that materials may be published if are proven true
 Domestic Policy • Kentucky and Virginia Resolutions – Jefferson wrote the KY resolution; Madison wrote the VA resolution – Doctrine of Interposition: states had the right to protect citizens by taking a stand against the unconstitutional federal laws – Nullification: right to cancel federal laws that state thought were unacceptable
Domestic Policy • Kentucky and Virginia Resolutions – Jefferson wrote the KY resolution; Madison wrote the VA resolution – Doctrine of Interposition: states had the right to protect citizens by taking a stand against the unconstitutional federal laws – Nullification: right to cancel federal laws that state thought were unacceptable
 Exit Pass • Explain assumption bill and why it was controversial. • What is neutrality and why did Washington think we should follow that policy? • Why were the KY and VA resolutions seen as important to the states?
Exit Pass • Explain assumption bill and why it was controversial. • What is neutrality and why did Washington think we should follow that policy? • Why were the KY and VA resolutions seen as important to the states?


