d2610cfafd604aa708152f009fb389d5.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 31

 A Meta-Analysis of Research on Motivational Interviewing Treatment Effectiveness (MARMITE) Jennifer Hettema Julie Steele William R. Miller Annual Review of Clinical Psychology Vol 1, 2005 (in press)
A Meta-Analysis of Research on Motivational Interviewing Treatment Effectiveness (MARMITE) Jennifer Hettema Julie Steele William R. Miller Annual Review of Clinical Psychology Vol 1, 2005 (in press)
 funded by a grant from The Robert Wood Johnson Foundation
funded by a grant from The Robert Wood Johnson Foundation
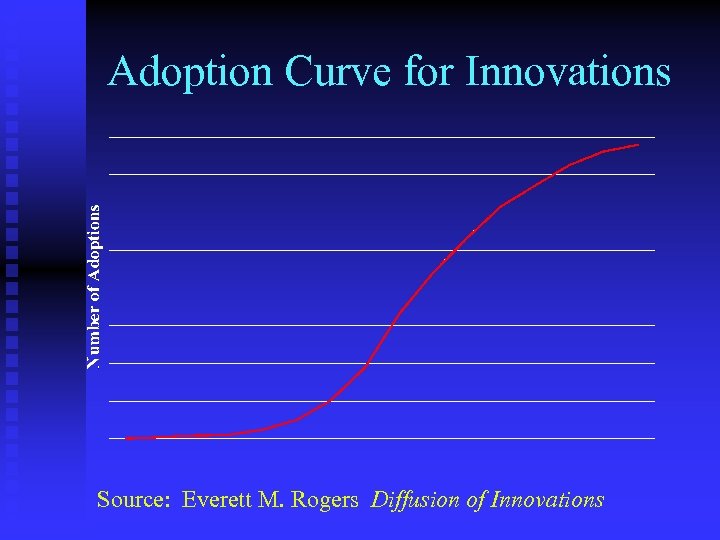 Adoption Curve for Innovations Source: Everett M. Rogers Diffusion of Innovations
Adoption Curve for Innovations Source: Everett M. Rogers Diffusion of Innovations
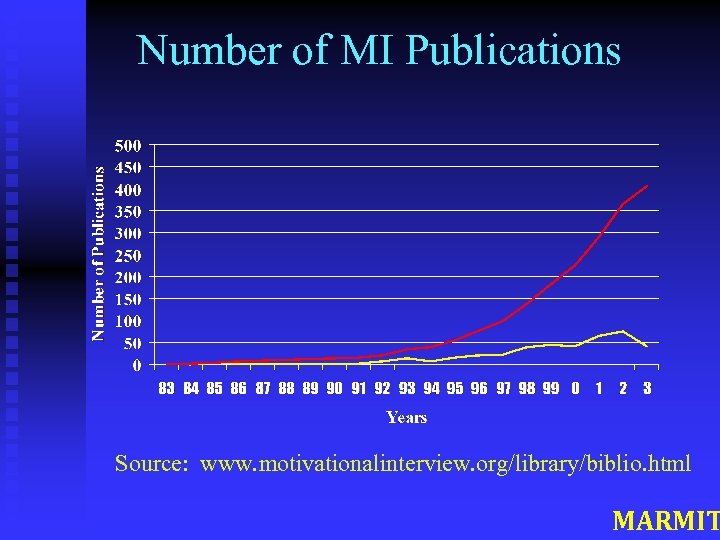 Number of MI Publications Source: www. motivationalinterview. org/library/biblio. html MARMIT
Number of MI Publications Source: www. motivationalinterview. org/library/biblio. html MARMIT
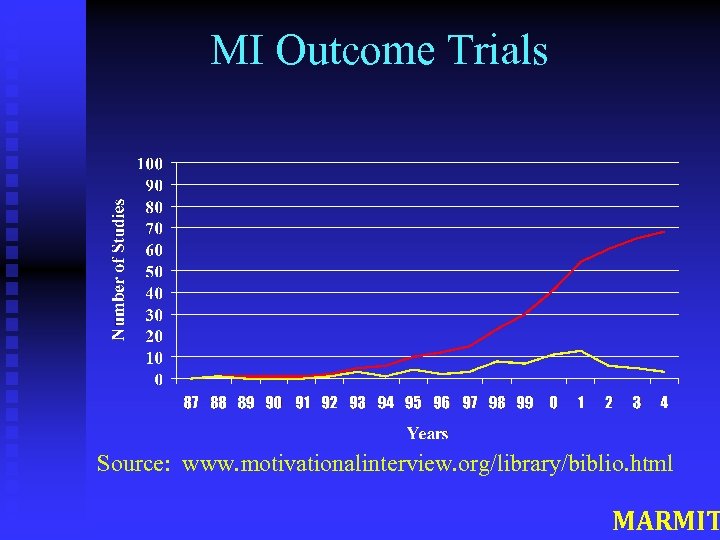 MI Outcome Trials Source: www. motivationalinterview. org/library/biblio. html MARMIT
MI Outcome Trials Source: www. motivationalinterview. org/library/biblio. html MARMIT
 Inclusion Criteria for MI Trials For within-group effect sizes: n At least one treatment group including MI n At least one post-treatment outcome measure For between-group effect sizes: n At least one control or comparison condition without MI components n Procedure for creating pre-treatment equivalence of groups MARMIT
Inclusion Criteria for MI Trials For within-group effect sizes: n At least one treatment group including MI n At least one post-treatment outcome measure For between-group effect sizes: n At least one control or comparison condition without MI components n Procedure for creating pre-treatment equivalence of groups MARMIT
 All studies double-coded for: Methodological quality on 12 dimensions n Other study characteristics n Attributes of the MI intervention(s) n Within-group effect sizes n Between-group effect sizes n MARMIT
All studies double-coded for: Methodological quality on 12 dimensions n Other study characteristics n Attributes of the MI intervention(s) n Within-group effect sizes n Between-group effect sizes n MARMIT
 Effect sizes were computed: For all reported outcome variables n At all reported follow-up points n For all between-group contrasts n With 95% confidence intervals n Correcting for small sample bias n MARMIT
Effect sizes were computed: For all reported outcome variables n At all reported follow-up points n For all between-group contrasts n With 95% confidence intervals n Correcting for small sample bias n MARMIT
 72 studies included so far: Alcohol (31) One study each: n Drug Abuse (14) Gambling n Smoking (6) Eating Disorders n HIV Risk (5) Relationships n Treatment Compliance (5) n Water purification (4) n Diet and exercise (4) n MARMIT
72 studies included so far: Alcohol (31) One study each: n Drug Abuse (14) Gambling n Smoking (6) Eating Disorders n HIV Risk (5) Relationships n Treatment Compliance (5) n Water purification (4) n Diet and exercise (4) n MARMIT
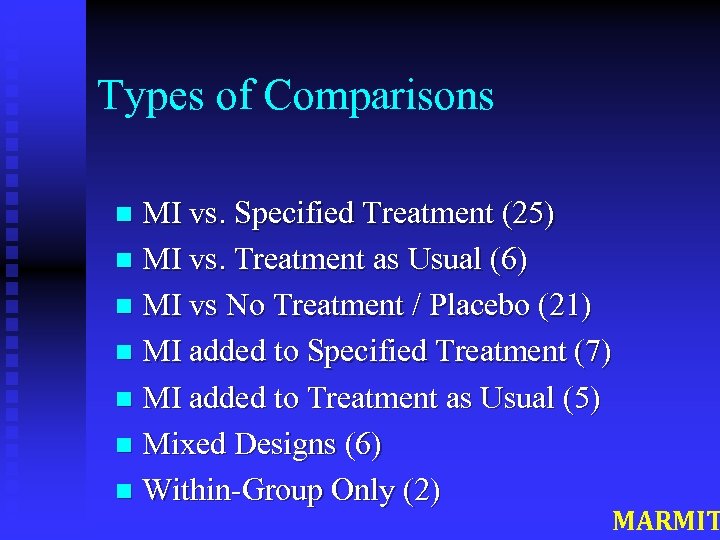 Types of Comparisons MI vs. Specified Treatment (25) n MI vs. Treatment as Usual (6) n MI vs No Treatment / Placebo (21) n MI added to Specified Treatment (7) n MI added to Treatment as Usual (5) n Mixed Designs (6) n Within-Group Only (2) n MARMIT
Types of Comparisons MI vs. Specified Treatment (25) n MI vs. Treatment as Usual (6) n MI vs No Treatment / Placebo (21) n MI added to Specified Treatment (7) n MI added to Treatment as Usual (5) n Mixed Designs (6) n Within-Group Only (2) n MARMIT
 Methodological Quality Compared to 361 alcohol treatment trials: n MQS Mean = 10. 76 vs. 10. 68 (ns) n Intervention quality control 78% vs 57% n Multisite trials: 28% vs. 5% n Follow-up > 12 months 18% vs. 51% n Follow-up completion > 70% 45% vs. 75% MARMIT
Methodological Quality Compared to 361 alcohol treatment trials: n MQS Mean = 10. 76 vs. 10. 68 (ns) n Intervention quality control 78% vs 57% n Multisite trials: 28% vs. 5% n Follow-up > 12 months 18% vs. 51% n Follow-up completion > 70% 45% vs. 75% MARMIT
 Outcome (Dependent) Measures Mean of 3. 3 outcome variables per study n Range: 1 to 12 n n To avoid capitalization on change, we computed a combined effect size (d) averaging across all reported outcome variables in each study MARMIT
Outcome (Dependent) Measures Mean of 3. 3 outcome variables per study n Range: 1 to 12 n n To avoid capitalization on change, we computed a combined effect size (d) averaging across all reported outcome variables in each study MARMIT
 Specified Characteristics of MI n n n Being collaborative Client centered Nonjudgmental Building trust Reducing resistance Increasing readiness n n n Increasing self-efficacy Reflective listening Increasing discrepancy Eliciting change talk Exploring ambivalence Expressing empathy MARMIT
Specified Characteristics of MI n n n Being collaborative Client centered Nonjudgmental Building trust Reducing resistance Increasing readiness n n n Increasing self-efficacy Reflective listening Increasing discrepancy Eliciting change talk Exploring ambivalence Expressing empathy MARMIT
 Specified Characteristics of MI Of 12 possible characteristics of MI, The average number mentioned was 3. 6 Range: 0 -12 MARMIT
Specified Characteristics of MI Of 12 possible characteristics of MI, The average number mentioned was 3. 6 Range: 0 -12 MARMIT
 Treatment “Dose” of MI Average “dose” of 2 sessions (2. 2 hours) The contrasts in dose varied from: Comparison group 25 hours longer than MI to MI 6 hours longer than no-treatment MARMIT
Treatment “Dose” of MI Average “dose” of 2 sessions (2. 2 hours) The contrasts in dose varied from: Comparison group 25 hours longer than MI to MI 6 hours longer than no-treatment MARMIT
 Quality Control of MI n Average training time: 10 hours (N=13) Manual-guided n Post-training supervision n Fidelity checks n 74% 29% 36% MARMIT
Quality Control of MI n Average training time: 10 hours (N=13) Manual-guided n Post-training supervision n Fidelity checks n 74% 29% 36% MARMIT
 Where was MI tested? n n n n Outpatient clinics (15) Inpatient facilities (11) Educational settings (6) Community organizations (5) G. P. offices (5) Prenatal clinics (3) Emergency rooms (2) n n n n Halfway house (2) EAP Telephone (3) In home (1) Jail (1) Mixed (7) Unspecified (8) MARMIT
Where was MI tested? n n n n Outpatient clinics (15) Inpatient facilities (11) Educational settings (6) Community organizations (5) G. P. offices (5) Prenatal clinics (3) Emergency rooms (2) n n n n Halfway house (2) EAP Telephone (3) In home (1) Jail (1) Mixed (7) Unspecified (8) MARMIT
 Who delivered MI? Paraprofessionals / students (8) n Master’s level (6) n Psychologists (6) n Nurses (3) n Physicians (2) n Dietician (1) n Mixed (22) n MARMIT
Who delivered MI? Paraprofessionals / students (8) n Master’s level (6) n Psychologists (6) n Nurses (3) n Physicians (2) n Dietician (1) n Mixed (22) n MARMIT
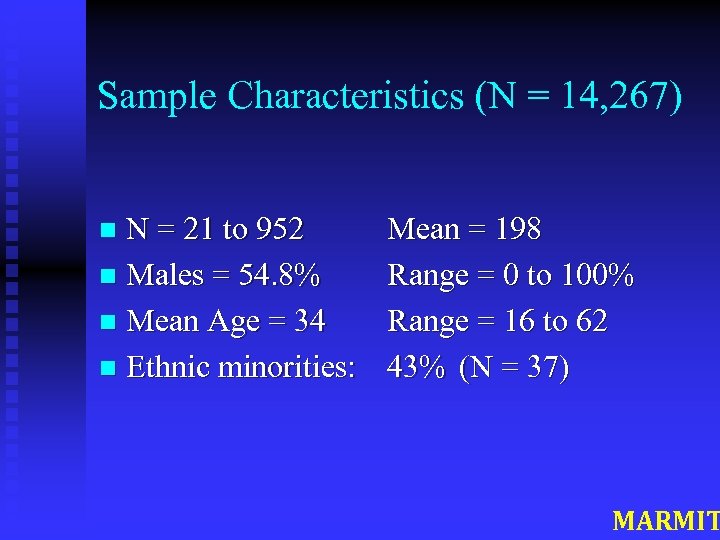 Sample Characteristics (N = 14, 267) N = 21 to 952 n Males = 54. 8% n Mean Age = 34 n Ethnic minorities: n Mean = 198 Range = 0 to 100% Range = 16 to 62 43% (N = 37) MARMIT
Sample Characteristics (N = 14, 267) N = 21 to 952 n Males = 54. 8% n Mean Age = 34 n Ethnic minorities: n Mean = 198 Range = 0 to 100% Range = 16 to 62 43% (N = 37) MARMIT
 Some Generalizations n n n Wide variability in effect size across studies, within problem areas (e. g. , for alcohol problems, d varies from 0 to 3. 0) Effects of MI appear early Effects of MI diminish over time, except in additive studies u d =. 77 at post-treatment u d =. 31 at 4 -6 months u d =. 30 at 6 -12 months MARMIT
Some Generalizations n n n Wide variability in effect size across studies, within problem areas (e. g. , for alcohol problems, d varies from 0 to 3. 0) Effects of MI appear early Effects of MI diminish over time, except in additive studies u d =. 77 at post-treatment u d =. 31 at 4 -6 months u d =. 30 at 6 -12 months MARMIT
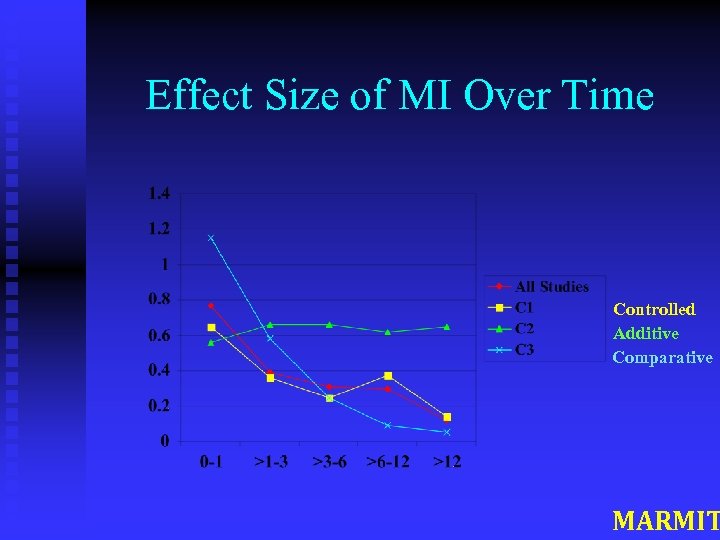 Effect Size of MI Over Time Controlled Additive Comparative MARMIT
Effect Size of MI Over Time Controlled Additive Comparative MARMIT
 Effect size was not predicted by: Number of MI attributes mentioned n Methodological quality of study, except Use of a manual to guide MI did predict effect size: u Studies not using a manual d =. 65 u Studies using a manual d =. 37 n Demographic characteristics, except: u Anglo/Caucasian samples d =. 39 u Minority samples d =. 79 n MARMIT
Effect size was not predicted by: Number of MI attributes mentioned n Methodological quality of study, except Use of a manual to guide MI did predict effect size: u Studies not using a manual d =. 65 u Studies using a manual d =. 37 n Demographic characteristics, except: u Anglo/Caucasian samples d =. 39 u Minority samples d =. 79 n MARMIT
 Effect size varied with outcome measures Alcohol: n Quantity of drinking n Frequency of drinking n BAC estimates n Negative consequences HIV Risk: n Knowledge n Behavioral Intentions n Sexual risk-taking d =. 30 d =. 31 d =. 22 d =. 08 d = 1. 46 d =. 88 d =. 07 MARMIT
Effect size varied with outcome measures Alcohol: n Quantity of drinking n Frequency of drinking n BAC estimates n Negative consequences HIV Risk: n Knowledge n Behavioral Intentions n Sexual risk-taking d =. 30 d =. 31 d =. 22 d =. 08 d = 1. 46 d =. 88 d =. 07 MARMIT
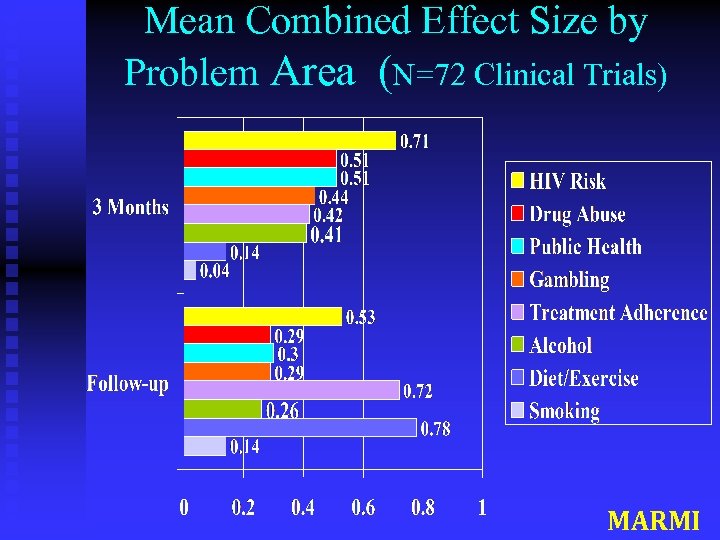 Mean Combined Effect Size by Problem Area (N=72 Clinical Trials) MARMI
Mean Combined Effect Size by Problem Area (N=72 Clinical Trials) MARMI
 Conclusions 1. Robust and enduring effects when MI is added at the beginning of treatment MI increases treatment retention u MI increases treatment adherence u MI increases staff-perceived motivation u MARMIT
Conclusions 1. Robust and enduring effects when MI is added at the beginning of treatment MI increases treatment retention u MI increases treatment adherence u MI increases staff-perceived motivation u MARMIT
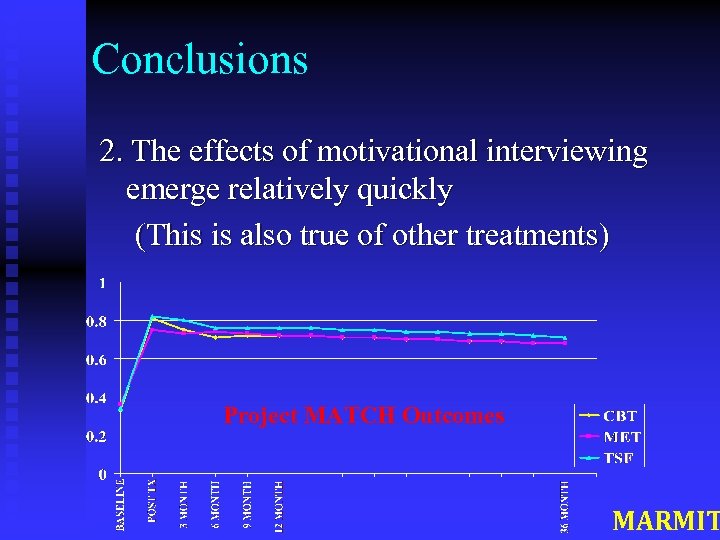 Conclusions 2. The effects of motivational interviewing emerge relatively quickly (This is also true of other treatments) Project MATCH Outcomes MARMIT
Conclusions 2. The effects of motivational interviewing emerge relatively quickly (This is also true of other treatments) Project MATCH Outcomes MARMIT
 Conclusions 2 a. The effects of motivational interviewing emerge relatively quickly q This may not be true for certain problem areas or dependent measures where “sleeper” effects occur (e. g. , effects of diet and exercise) MARMIT
Conclusions 2 a. The effects of motivational interviewing emerge relatively quickly q This may not be true for certain problem areas or dependent measures where “sleeper” effects occur (e. g. , effects of diet and exercise) MARMIT
 Conclusions 3. The between-group effects of motivational interviewing tend to diminish over 12 months This is also true of other treatments u Between-group differences diminish in part because control/comparison groups “catch up” over time u This may not be true of MI’s additive effects with other treatment u MARMIT
Conclusions 3. The between-group effects of motivational interviewing tend to diminish over 12 months This is also true of other treatments u Between-group differences diminish in part because control/comparison groups “catch up” over time u This may not be true of MI’s additive effects with other treatment u MARMIT
 Conclusions 4. The effects of MI are highly variable across sites and providers This is also true of other treatments, but may be more true with MI u Provider baseline characteristics do not predict effectiveness with MI u Treatment process variables do u Manuals may not be a good idea u MARMIT
Conclusions 4. The effects of MI are highly variable across sites and providers This is also true of other treatments, but may be more true with MI u Provider baseline characteristics do not predict effectiveness with MI u Treatment process variables do u Manuals may not be a good idea u MARMIT



