Chapter 30.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 50
 A Macroeconomic Theory of the Open Economy Chapter 30 Copyright © 2001 by Harcourt, Inc. All rights reserved. Requests for permission to make copies of any part of the work should be mailed to: Permissions Department, Harcourt College Publishers, 6277 Sea Harbor Drive, Orlando, Florida 32887 -6777.
A Macroeconomic Theory of the Open Economy Chapter 30 Copyright © 2001 by Harcourt, Inc. All rights reserved. Requests for permission to make copies of any part of the work should be mailed to: Permissions Department, Harcourt College Publishers, 6277 Sea Harbor Drive, Orlando, Florida 32887 -6777.
 Key Macroeconomic Variables in an Open Economy u. The important macroeconomic variables of an open economy include: u net exports u net foreign investment u nominal exchange rates u real exchange rates Harcourt, Inc. items and derived items copyright © 2001 by Harcourt, Inc.
Key Macroeconomic Variables in an Open Economy u. The important macroeconomic variables of an open economy include: u net exports u net foreign investment u nominal exchange rates u real exchange rates Harcourt, Inc. items and derived items copyright © 2001 by Harcourt, Inc.
 Basic Assumptions of a Macroeconomic Model of an Open Economy u The model takes the economy’s GDP as given. u The model takes the economy’s price level as given. Harcourt, Inc. items and derived items copyright © 2001 by Harcourt, Inc.
Basic Assumptions of a Macroeconomic Model of an Open Economy u The model takes the economy’s GDP as given. u The model takes the economy’s price level as given. Harcourt, Inc. items and derived items copyright © 2001 by Harcourt, Inc.
 The Market for Loanable Funds S = I + NFI u At the equilibrium interest rate, the amount that people want to save exactly balances the desired quantities of investment and net foreign investment. Harcourt, Inc. items and derived items copyright © 2001 by Harcourt, Inc.
The Market for Loanable Funds S = I + NFI u At the equilibrium interest rate, the amount that people want to save exactly balances the desired quantities of investment and net foreign investment. Harcourt, Inc. items and derived items copyright © 2001 by Harcourt, Inc.
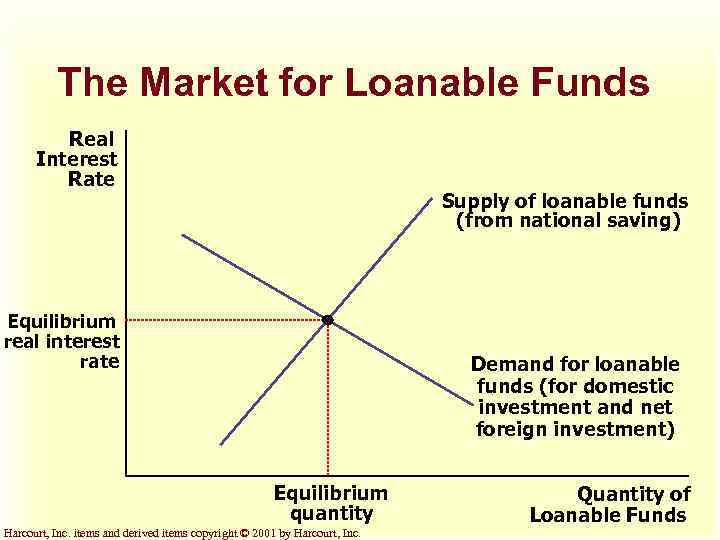
 The Market for Loanable Funds u The supply of loanable funds comes from national saving (S). u The demand for loanable funds comes from domestic investment (I) and net foreign investment (NFI). Harcourt, Inc. items and derived items copyright © 2001 by Harcourt, Inc.
The Market for Loanable Funds u The supply of loanable funds comes from national saving (S). u The demand for loanable funds comes from domestic investment (I) and net foreign investment (NFI). Harcourt, Inc. items and derived items copyright © 2001 by Harcourt, Inc.
 The Market for Loanable Funds u The supply and demand for loanable funds depend on the real interest rate. u A higher real interest rate encourages people to save and raises the quantity of loanable funds supplied. u The interest rate adjusts to bring the supply and demand for loanable funds into balance. Harcourt, Inc. items and derived items copyright © 2001 by Harcourt, Inc.
The Market for Loanable Funds u The supply and demand for loanable funds depend on the real interest rate. u A higher real interest rate encourages people to save and raises the quantity of loanable funds supplied. u The interest rate adjusts to bring the supply and demand for loanable funds into balance. Harcourt, Inc. items and derived items copyright © 2001 by Harcourt, Inc.
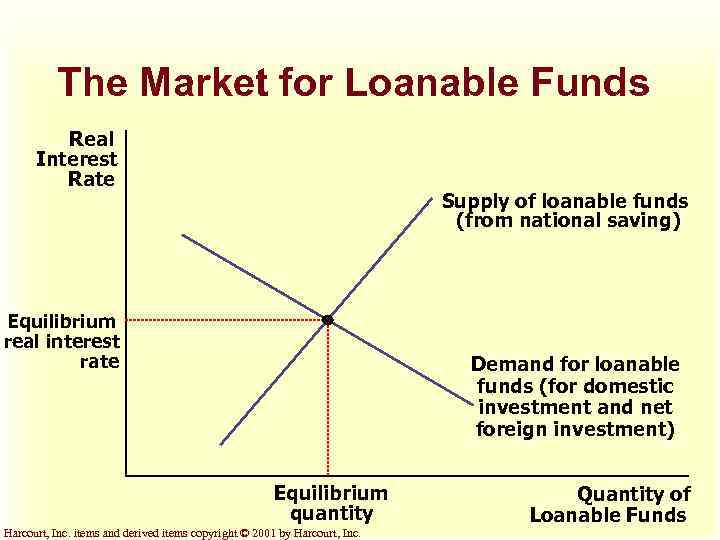 The Market for Loanable Funds Real Interest Rate Supply of loanable funds (from national saving) Equilibrium real interest rate Demand for loanable funds (for domestic investment and net foreign investment) Equilibrium quantity Harcourt, Inc. items and derived items copyright © 2001 by Harcourt, Inc. Quantity of Loanable Funds
The Market for Loanable Funds Real Interest Rate Supply of loanable funds (from national saving) Equilibrium real interest rate Demand for loanable funds (for domestic investment and net foreign investment) Equilibrium quantity Harcourt, Inc. items and derived items copyright © 2001 by Harcourt, Inc. Quantity of Loanable Funds
 The Market for Loanable Funds At the equilibrium interest rate, the amount that people want to save exactly balances the desired quantities of domestic investment and net foreign investment. Harcourt, Inc. items and derived items copyright © 2001 by Harcourt, Inc.
The Market for Loanable Funds At the equilibrium interest rate, the amount that people want to save exactly balances the desired quantities of domestic investment and net foreign investment. Harcourt, Inc. items and derived items copyright © 2001 by Harcourt, Inc.
 The Market for Foreign. Currency Exchange u The two sides of the foreign-currency exchange market are represented by NFI and NX. u NFI represents the imbalance between the purchases and sales of capital assets. u NX represents the imbalance between exports and imports of goods and services. Harcourt, Inc. items and derived items copyright © 2001 by Harcourt, Inc.
The Market for Foreign. Currency Exchange u The two sides of the foreign-currency exchange market are represented by NFI and NX. u NFI represents the imbalance between the purchases and sales of capital assets. u NX represents the imbalance between exports and imports of goods and services. Harcourt, Inc. items and derived items copyright © 2001 by Harcourt, Inc.
 The Market for Foreign. Currency Exchange u In the market foreign-currency exchange, U. S. dollars are traded foreign currencies. u For an economy as a whole, NFI and NX must balance each other out, or: NFI = NX Harcourt, Inc. items and derived items copyright © 2001 by Harcourt, Inc.
The Market for Foreign. Currency Exchange u In the market foreign-currency exchange, U. S. dollars are traded foreign currencies. u For an economy as a whole, NFI and NX must balance each other out, or: NFI = NX Harcourt, Inc. items and derived items copyright © 2001 by Harcourt, Inc.
 The Market for Foreign. Currency Exchange The price that balances the supply and demand foreign-currency is the real exchange rate. Harcourt, Inc. items and derived items copyright © 2001 by Harcourt, Inc.
The Market for Foreign. Currency Exchange The price that balances the supply and demand foreign-currency is the real exchange rate. Harcourt, Inc. items and derived items copyright © 2001 by Harcourt, Inc.
 The Market for Foreign. Currency Exchange u The demand curve foreign currency is downward sloping because a higher exchange rate makes domestic goods more expensive. u The supply curve is vertical because the quantity of dollars supplied for net foreign investment is unrelated to the real exchange rate. Harcourt, Inc. items and derived items copyright © 2001 by Harcourt, Inc.
The Market for Foreign. Currency Exchange u The demand curve foreign currency is downward sloping because a higher exchange rate makes domestic goods more expensive. u The supply curve is vertical because the quantity of dollars supplied for net foreign investment is unrelated to the real exchange rate. Harcourt, Inc. items and derived items copyright © 2001 by Harcourt, Inc.
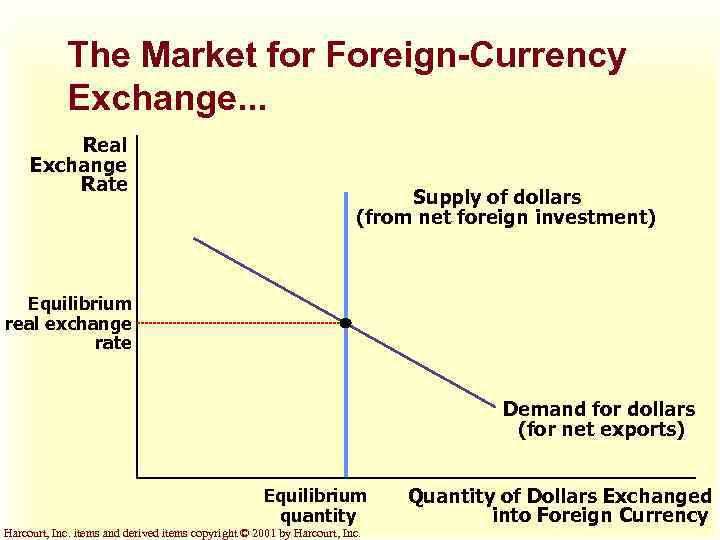
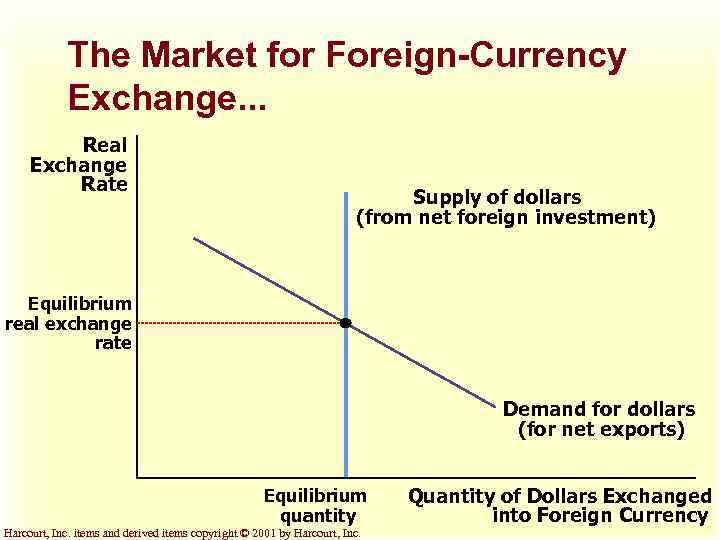 The Market for Foreign-Currency Exchange. . . Real Exchange Rate Supply of dollars (from net foreign investment) Equilibrium real exchange rate Demand for dollars (for net exports) Equilibrium quantity Harcourt, Inc. items and derived items copyright © 2001 by Harcourt, Inc. Quantity of Dollars Exchanged into Foreign Currency
The Market for Foreign-Currency Exchange. . . Real Exchange Rate Supply of dollars (from net foreign investment) Equilibrium real exchange rate Demand for dollars (for net exports) Equilibrium quantity Harcourt, Inc. items and derived items copyright © 2001 by Harcourt, Inc. Quantity of Dollars Exchanged into Foreign Currency
 The Market for Foreign. Currency Exchange u The real exchange rate adjusts to balance the supply and demand for dollars. u At the equilibrium real exchange rate, the demand for dollars to buy net exports exactly balances the supply of dollars to be exchanged into foreign currency to buy assets abroad. Harcourt, Inc. items and derived items copyright © 2001 by Harcourt, Inc.
The Market for Foreign. Currency Exchange u The real exchange rate adjusts to balance the supply and demand for dollars. u At the equilibrium real exchange rate, the demand for dollars to buy net exports exactly balances the supply of dollars to be exchanged into foreign currency to buy assets abroad. Harcourt, Inc. items and derived items copyright © 2001 by Harcourt, Inc.
 Equilibrium in the Open Economy u In the market for loanable funds, supply comes from national saving and demand comes from domestic investment and net foreign investment. u In the market foreign-currency exchange, supply comes from net foreign investment and demand comes from net exports. Harcourt, Inc. items and derived items copyright © 2001 by Harcourt, Inc.
Equilibrium in the Open Economy u In the market for loanable funds, supply comes from national saving and demand comes from domestic investment and net foreign investment. u In the market foreign-currency exchange, supply comes from net foreign investment and demand comes from net exports. Harcourt, Inc. items and derived items copyright © 2001 by Harcourt, Inc.
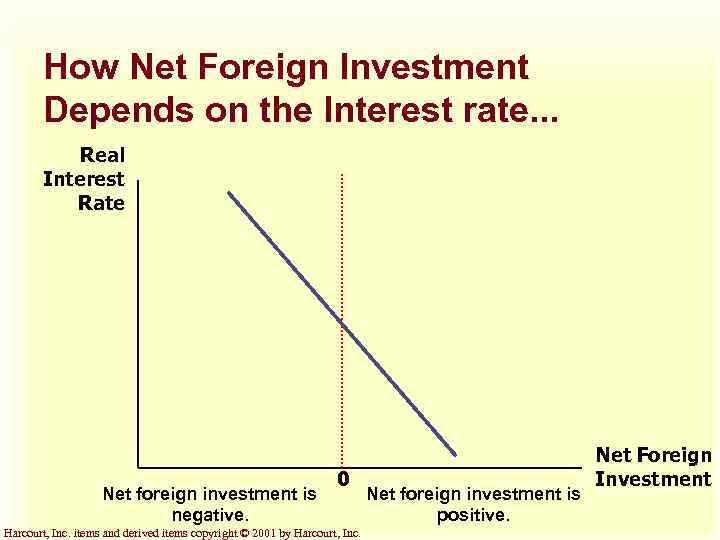
 Equilibrium in the Open Economy u. Net foreign investment links the loanable funds market and the foreign -currency exchange market. u The key determinant of net foreign investment is the real interest rate. Harcourt, Inc. items and derived items copyright © 2001 by Harcourt, Inc.
Equilibrium in the Open Economy u. Net foreign investment links the loanable funds market and the foreign -currency exchange market. u The key determinant of net foreign investment is the real interest rate. Harcourt, Inc. items and derived items copyright © 2001 by Harcourt, Inc.
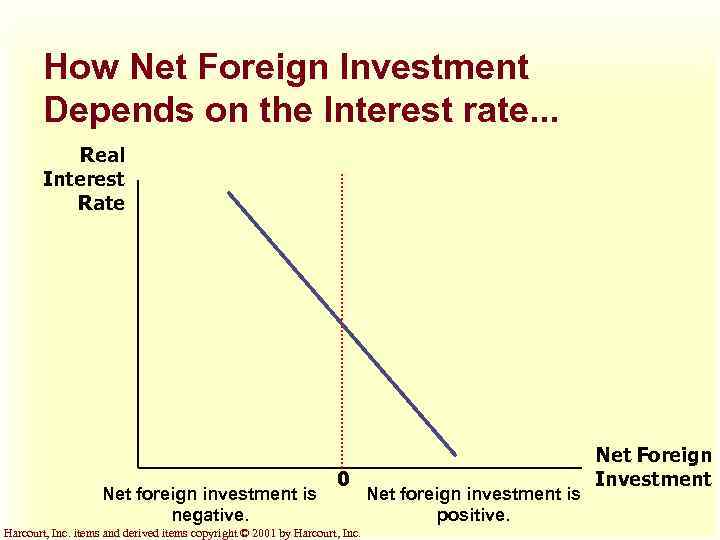 How Net Foreign Investment Depends on the Interest rate. . . Real Interest Rate Net foreign investment is negative. 0 Harcourt, Inc. items and derived items copyright © 2001 by Harcourt, Inc. Net foreign investment is positive. Net Foreign Investment
How Net Foreign Investment Depends on the Interest rate. . . Real Interest Rate Net foreign investment is negative. 0 Harcourt, Inc. items and derived items copyright © 2001 by Harcourt, Inc. Net foreign investment is positive. Net Foreign Investment
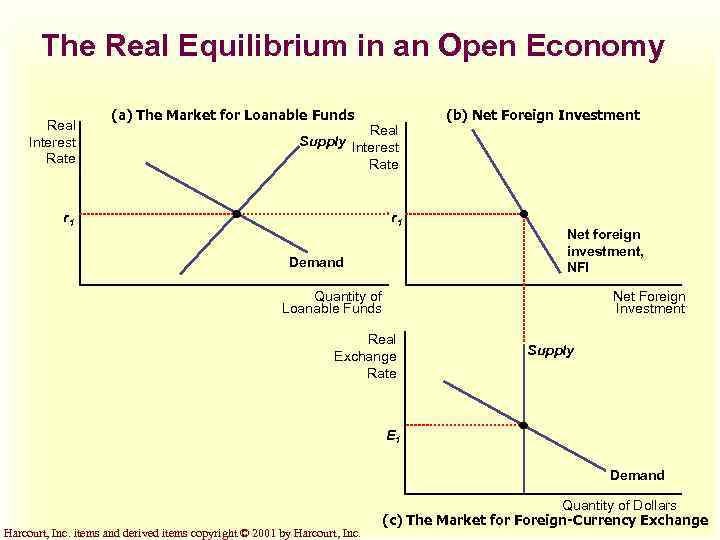
 Equilibrium in the Open Economy u Prices in the loanable funds market and the foreign-currency exchange market adjust simultaneously to balance supply and demand in these two markets. u As they do, they determine the macroeconomic variables of national saving, domestic investment, net foreign investment, and net exports. Harcourt, Inc. items and derived items copyright © 2001 by Harcourt, Inc.
Equilibrium in the Open Economy u Prices in the loanable funds market and the foreign-currency exchange market adjust simultaneously to balance supply and demand in these two markets. u As they do, they determine the macroeconomic variables of national saving, domestic investment, net foreign investment, and net exports. Harcourt, Inc. items and derived items copyright © 2001 by Harcourt, Inc.
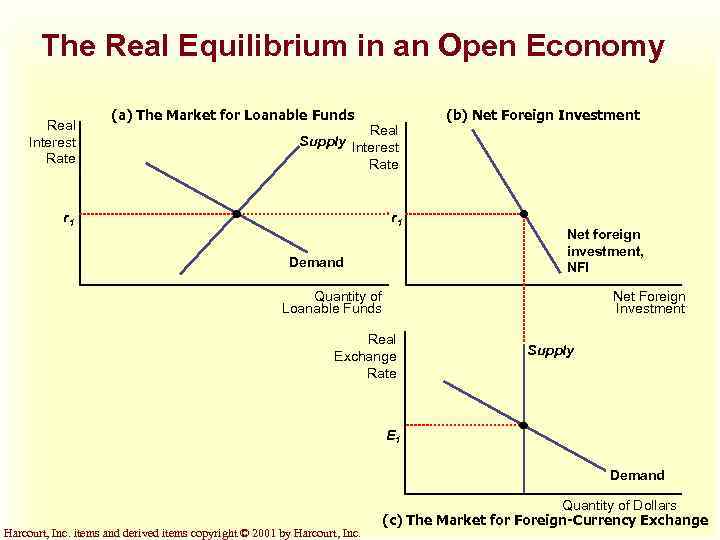 The Real Equilibrium in an Open Economy Real Interest Rate (a) The Market for Loanable Funds Real Supply Interest Rate r 1 Demand (b) Net Foreign Investment Net foreign investment, NFI Quantity of Loanable Funds Net Foreign Investment Real Exchange Rate Supply E 1 Demand Harcourt, Inc. items and derived items copyright © 2001 by Harcourt, Inc. Quantity of Dollars (c) The Market for Foreign-Currency Exchange
The Real Equilibrium in an Open Economy Real Interest Rate (a) The Market for Loanable Funds Real Supply Interest Rate r 1 Demand (b) Net Foreign Investment Net foreign investment, NFI Quantity of Loanable Funds Net Foreign Investment Real Exchange Rate Supply E 1 Demand Harcourt, Inc. items and derived items copyright © 2001 by Harcourt, Inc. Quantity of Dollars (c) The Market for Foreign-Currency Exchange
 How Changes in Policies and Events Affect an Open Economy u. The magnitude and variation in important macroeconomic variables depend on the following: u Government budget deficits u Trade policies u Political and economic stability Harcourt, Inc. items and derived items copyright © 2001 by Harcourt, Inc.
How Changes in Policies and Events Affect an Open Economy u. The magnitude and variation in important macroeconomic variables depend on the following: u Government budget deficits u Trade policies u Political and economic stability Harcourt, Inc. items and derived items copyright © 2001 by Harcourt, Inc.
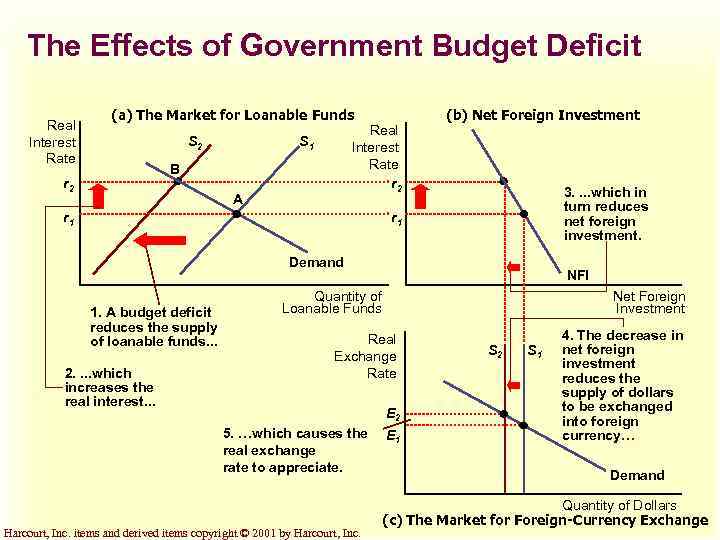
 Government Budget Deficits u. In an open economy, government budget deficits. . . ¼reduces the supply of loanable funds, ¼drives up the interest rate, ¼crowds out domestic investment, ¼cause net foreign investment to fall. Harcourt, Inc. items and derived items copyright © 2001 by Harcourt, Inc.
Government Budget Deficits u. In an open economy, government budget deficits. . . ¼reduces the supply of loanable funds, ¼drives up the interest rate, ¼crowds out domestic investment, ¼cause net foreign investment to fall. Harcourt, Inc. items and derived items copyright © 2001 by Harcourt, Inc.
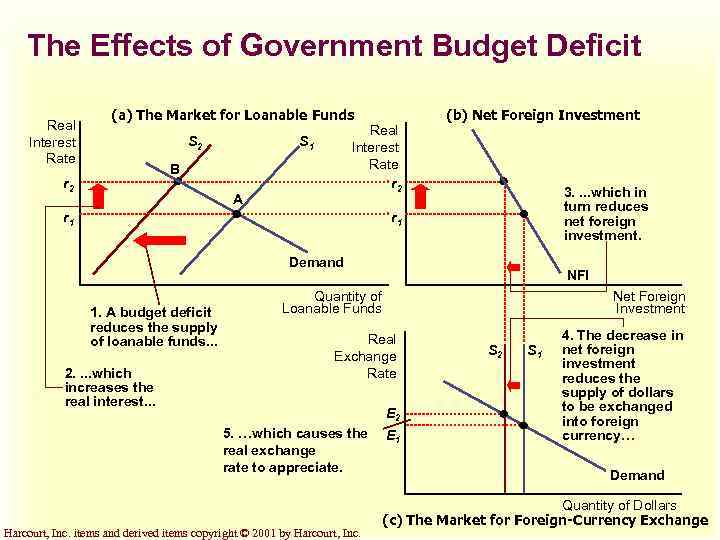 The Effects of Government Budget Deficit Real Interest Rate (a) The Market for Loanable Funds S 2 Real Interest Rate r 2 S 1 B r 2 A r 1 (b) Net Foreign Investment 3. . which in turn reduces net foreign investment. r 1 Demand 1. A budget deficit reduces the supply of loanable funds. . . 2. . which increases the real interest. . . NFI Quantity of Loanable Funds Net Foreign Investment Real Exchange Rate E 2 5. …which causes the real exchange rate to appreciate. Harcourt, Inc. items and derived items copyright © 2001 by Harcourt, Inc. E 1 S 2 S 1 4. The decrease in net foreign investment reduces the supply of dollars to be exchanged into foreign currency… Demand Quantity of Dollars (c) The Market for Foreign-Currency Exchange
The Effects of Government Budget Deficit Real Interest Rate (a) The Market for Loanable Funds S 2 Real Interest Rate r 2 S 1 B r 2 A r 1 (b) Net Foreign Investment 3. . which in turn reduces net foreign investment. r 1 Demand 1. A budget deficit reduces the supply of loanable funds. . . 2. . which increases the real interest. . . NFI Quantity of Loanable Funds Net Foreign Investment Real Exchange Rate E 2 5. …which causes the real exchange rate to appreciate. Harcourt, Inc. items and derived items copyright © 2001 by Harcourt, Inc. E 1 S 2 S 1 4. The decrease in net foreign investment reduces the supply of dollars to be exchanged into foreign currency… Demand Quantity of Dollars (c) The Market for Foreign-Currency Exchange
 Effect of Budget Deficits on the Loanable Funds Market u. A government budget deficit reduces national saving, which. . . shifts the supply curve for loanable funds to the left, which. . . raises interest rates. Harcourt, Inc. items and derived items copyright © 2001 by Harcourt, Inc.
Effect of Budget Deficits on the Loanable Funds Market u. A government budget deficit reduces national saving, which. . . shifts the supply curve for loanable funds to the left, which. . . raises interest rates. Harcourt, Inc. items and derived items copyright © 2001 by Harcourt, Inc.
 Effect of Budget Deficits on Net Foreign Investment u Higher interest rates reduce net foreign investment. Harcourt, Inc. items and derived items copyright © 2001 by Harcourt, Inc.
Effect of Budget Deficits on Net Foreign Investment u Higher interest rates reduce net foreign investment. Harcourt, Inc. items and derived items copyright © 2001 by Harcourt, Inc.
 Effect on the Foreign-Currency Exchange Market u. A decrease in net foreign investment reduces the supply of dollars to be exchanged into foreign currency. u This causes the real exchange rate to appreciate. Harcourt, Inc. items and derived items copyright © 2001 by Harcourt, Inc.
Effect on the Foreign-Currency Exchange Market u. A decrease in net foreign investment reduces the supply of dollars to be exchanged into foreign currency. u This causes the real exchange rate to appreciate. Harcourt, Inc. items and derived items copyright © 2001 by Harcourt, Inc.
 Trade Policy u. A trade policy is a government policy that directly influences the quantity of goods and services that a country imports or exports. u Tariff: A tax on an imported good. u Import quota: A limit on the quantity of a good produced abroad and sold domestically. Harcourt, Inc. items and derived items copyright © 2001 by Harcourt, Inc.
Trade Policy u. A trade policy is a government policy that directly influences the quantity of goods and services that a country imports or exports. u Tariff: A tax on an imported good. u Import quota: A limit on the quantity of a good produced abroad and sold domestically. Harcourt, Inc. items and derived items copyright © 2001 by Harcourt, Inc.
 Trade Policy u Because they do not change national saving or domestic investment, trade policies do not affect the trade balance. u For a given level of national saving and domestic investment, the real exchange rate adjusts to keep the trade balance the same. u Trade policies have a greater effect on microeconomic than on macroeconomic markets. Harcourt, Inc. items and derived items copyright © 2001 by Harcourt, Inc.
Trade Policy u Because they do not change national saving or domestic investment, trade policies do not affect the trade balance. u For a given level of national saving and domestic investment, the real exchange rate adjusts to keep the trade balance the same. u Trade policies have a greater effect on microeconomic than on macroeconomic markets. Harcourt, Inc. items and derived items copyright © 2001 by Harcourt, Inc.
 Effect of an Import Quota u Because foreigners need dollars to buy U. S. net exports, there is an increased demand for dollars in the market foreign-currency. u This leads to an appreciation of the real exchange rate. Harcourt, Inc. items and derived items copyright © 2001 by Harcourt, Inc.
Effect of an Import Quota u Because foreigners need dollars to buy U. S. net exports, there is an increased demand for dollars in the market foreign-currency. u This leads to an appreciation of the real exchange rate. Harcourt, Inc. items and derived items copyright © 2001 by Harcourt, Inc.
 Effect of an Import Quota u There is no change in the interest rate because nothing happens in the loanable funds market. u There will be no change in net exports. u There is no change in net foreign investment even though an import quota reduces imports. Harcourt, Inc. items and derived items copyright © 2001 by Harcourt, Inc.
Effect of an Import Quota u There is no change in the interest rate because nothing happens in the loanable funds market. u There will be no change in net exports. u There is no change in net foreign investment even though an import quota reduces imports. Harcourt, Inc. items and derived items copyright © 2001 by Harcourt, Inc.
 Effect of an Import Quota u An appreciation of the dollar in the foreign exchange market encourages imports and discourages exports. u This offsets the initial increase in net exports due to import quota. Harcourt, Inc. items and derived items copyright © 2001 by Harcourt, Inc.
Effect of an Import Quota u An appreciation of the dollar in the foreign exchange market encourages imports and discourages exports. u This offsets the initial increase in net exports due to import quota. Harcourt, Inc. items and derived items copyright © 2001 by Harcourt, Inc.
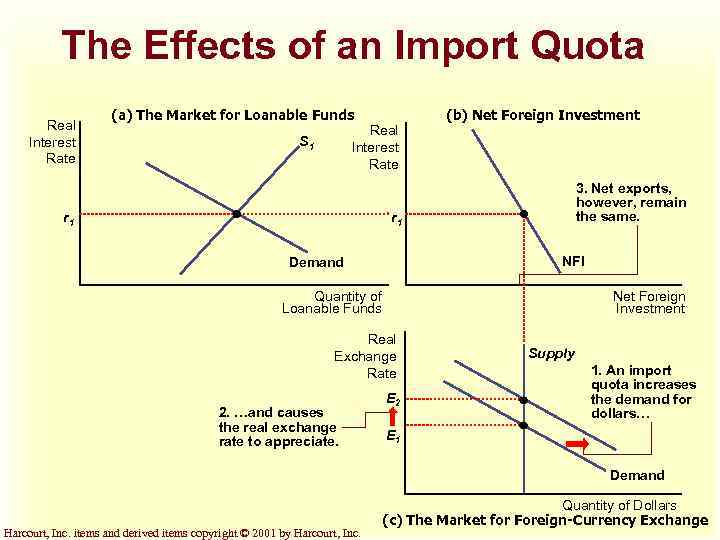 The Effects of an Import Quota Real Interest Rate (a) The Market for Loanable Funds Real Interest Rate S 1 r 1 (b) Net Foreign Investment 3. Net exports, however, remain the same. r 1 NFI Demand Quantity of Loanable Funds Net Foreign Investment Real Exchange Rate 2. …and causes the real exchange rate to appreciate. E 2 Supply 1. An import quota increases the demand for dollars… E 1 Demand Harcourt, Inc. items and derived items copyright © 2001 by Harcourt, Inc. Quantity of Dollars (c) The Market for Foreign-Currency Exchange
The Effects of an Import Quota Real Interest Rate (a) The Market for Loanable Funds Real Interest Rate S 1 r 1 (b) Net Foreign Investment 3. Net exports, however, remain the same. r 1 NFI Demand Quantity of Loanable Funds Net Foreign Investment Real Exchange Rate 2. …and causes the real exchange rate to appreciate. E 2 Supply 1. An import quota increases the demand for dollars… E 1 Demand Harcourt, Inc. items and derived items copyright © 2001 by Harcourt, Inc. Quantity of Dollars (c) The Market for Foreign-Currency Exchange
 Effect of an Import Quota Trade policies do not affect the trade balance. Harcourt, Inc. items and derived items copyright © 2001 by Harcourt, Inc.
Effect of an Import Quota Trade policies do not affect the trade balance. Harcourt, Inc. items and derived items copyright © 2001 by Harcourt, Inc.
 Political Instability and Capital Flight Capital flight is a large and sudden movement of funds out of a country, usually due to political instability. Harcourt, Inc. items and derived items copyright © 2001 by Harcourt, Inc.
Political Instability and Capital Flight Capital flight is a large and sudden movement of funds out of a country, usually due to political instability. Harcourt, Inc. items and derived items copyright © 2001 by Harcourt, Inc.
 Political Instability and Capital Flight u Capital flight has its largest impact on the country from which the capital is fleeing, but it also affects other countries. u If investors become concerned about the safety of their investments, capital can quickly leave an economy. u Interest rates increase and the domestic currency depreciates. Harcourt, Inc. items and derived items copyright © 2001 by Harcourt, Inc.
Political Instability and Capital Flight u Capital flight has its largest impact on the country from which the capital is fleeing, but it also affects other countries. u If investors become concerned about the safety of their investments, capital can quickly leave an economy. u Interest rates increase and the domestic currency depreciates. Harcourt, Inc. items and derived items copyright © 2001 by Harcourt, Inc.
 Political Instability in Mexico and Capital Flight u When investors around the world observed political problems in Mexico in 1994, they sold some of their Mexican assets and used the proceeds to buy assets of other countries. Harcourt, Inc. items and derived items copyright © 2001 by Harcourt, Inc.
Political Instability in Mexico and Capital Flight u When investors around the world observed political problems in Mexico in 1994, they sold some of their Mexican assets and used the proceeds to buy assets of other countries. Harcourt, Inc. items and derived items copyright © 2001 by Harcourt, Inc.
 Political Instability in Mexico and Capital Flight u This increased Mexican net foreign investment. u The demand for loanable funds in the loanable funds market increased, which increased the interest rate. u This increased the supply of pesos in the foreign-currency exchange market. Harcourt, Inc. items and derived items copyright © 2001 by Harcourt, Inc.
Political Instability in Mexico and Capital Flight u This increased Mexican net foreign investment. u The demand for loanable funds in the loanable funds market increased, which increased the interest rate. u This increased the supply of pesos in the foreign-currency exchange market. Harcourt, Inc. items and derived items copyright © 2001 by Harcourt, Inc.
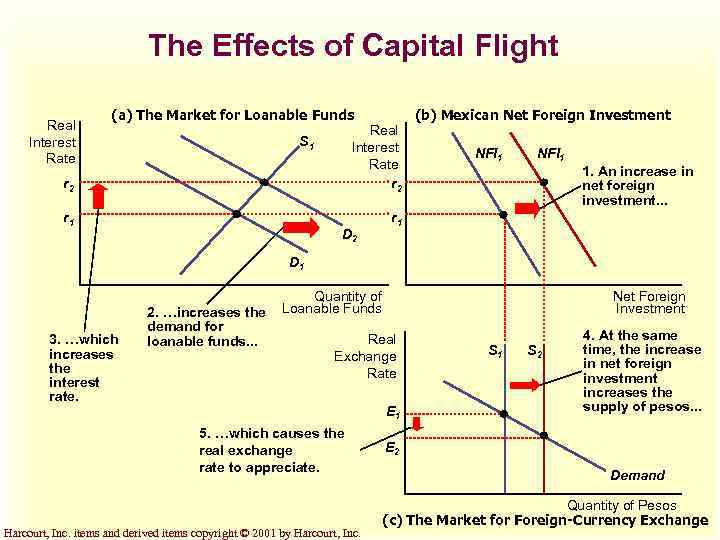 The Effects of Capital Flight Real Interest Rate (a) The Market for Loanable Funds r 2 Real Interest Rate r 2 r 1 (b) Mexican Net Foreign Investment r 1 S 1 D 2 NFI 1 1. An increase in net foreign investment. . . D 1 3. …which increases the interest rate. 2. …increases the demand for loanable funds. . . Quantity of Loanable Funds Net Foreign Investment Real Exchange Rate E 1 5. …which causes the real exchange rate to appreciate. Harcourt, Inc. items and derived items copyright © 2001 by Harcourt, Inc. S 1 S 2 4. At the same time, the increase in net foreign investment increases the supply of pesos. . . E 2 Demand Quantity of Pesos (c) The Market for Foreign-Currency Exchange
The Effects of Capital Flight Real Interest Rate (a) The Market for Loanable Funds r 2 Real Interest Rate r 2 r 1 (b) Mexican Net Foreign Investment r 1 S 1 D 2 NFI 1 1. An increase in net foreign investment. . . D 1 3. …which increases the interest rate. 2. …increases the demand for loanable funds. . . Quantity of Loanable Funds Net Foreign Investment Real Exchange Rate E 1 5. …which causes the real exchange rate to appreciate. Harcourt, Inc. items and derived items copyright © 2001 by Harcourt, Inc. S 1 S 2 4. At the same time, the increase in net foreign investment increases the supply of pesos. . . E 2 Demand Quantity of Pesos (c) The Market for Foreign-Currency Exchange
 Summary u To analyze the macroeconomics of open economies, two markets are central – the market for loanable funds and the market foreign-currency exchange. u In the market for loanable funds, the interest rate adjusts to balance supply for loanable funds (from national saving) and demand for loanable funds (from domestic investment and net foreign investment). Harcourt, Inc. items and derived items copyright © 2001 by Harcourt, Inc.
Summary u To analyze the macroeconomics of open economies, two markets are central – the market for loanable funds and the market foreign-currency exchange. u In the market for loanable funds, the interest rate adjusts to balance supply for loanable funds (from national saving) and demand for loanable funds (from domestic investment and net foreign investment). Harcourt, Inc. items and derived items copyright © 2001 by Harcourt, Inc.
 Summary u In the market foreign-currency exchange, the real exchange rate adjusts to balance the supply of dollars (for net foreign investment) and the demand for dollars (for net exports). u Net foreign investment is the variable that connects the two markets. Harcourt, Inc. items and derived items copyright © 2001 by Harcourt, Inc.
Summary u In the market foreign-currency exchange, the real exchange rate adjusts to balance the supply of dollars (for net foreign investment) and the demand for dollars (for net exports). u Net foreign investment is the variable that connects the two markets. Harcourt, Inc. items and derived items copyright © 2001 by Harcourt, Inc.
 Summary u. A policy that reduces national saving, such as a government budget deficit, reduces the supply of loanable funds and drives up the interest rate. u The higher interest rate reduces net foreign investment, reducing the supply of dollars. u The dollar appreciates, and net exports fall. Harcourt, Inc. items and derived items copyright © 2001 by Harcourt, Inc.
Summary u. A policy that reduces national saving, such as a government budget deficit, reduces the supply of loanable funds and drives up the interest rate. u The higher interest rate reduces net foreign investment, reducing the supply of dollars. u The dollar appreciates, and net exports fall. Harcourt, Inc. items and derived items copyright © 2001 by Harcourt, Inc.
 Summary u. A trade restriction increases net exports and increases the demand for dollars in the market foreign-currency exchange. u As a result, the dollar appreciates in value, making domestic goods more expensive relative to foreign goods. u This appreciation offsets the initial impact of the trade restrictions on net exports. Harcourt, Inc. items and derived items copyright © 2001 by Harcourt, Inc.
Summary u. A trade restriction increases net exports and increases the demand for dollars in the market foreign-currency exchange. u As a result, the dollar appreciates in value, making domestic goods more expensive relative to foreign goods. u This appreciation offsets the initial impact of the trade restrictions on net exports. Harcourt, Inc. items and derived items copyright © 2001 by Harcourt, Inc.
 Summary u When investors change their attitudes about holding assets of a country, the ramifications for the country’s economy can be profound. u Political instability in a country can lead to capital flight. u Capital flight tends to increase interest rates and cause the country’s currency to depreciate. Harcourt, Inc. items and derived items copyright © 2001 by Harcourt, Inc.
Summary u When investors change their attitudes about holding assets of a country, the ramifications for the country’s economy can be profound. u Political instability in a country can lead to capital flight. u Capital flight tends to increase interest rates and cause the country’s currency to depreciate. Harcourt, Inc. items and derived items copyright © 2001 by Harcourt, Inc.
 Graphical Review Harcourt, Inc. items and derived items copyright © 2001 by Harcourt, Inc.
Graphical Review Harcourt, Inc. items and derived items copyright © 2001 by Harcourt, Inc.
 The Market for Loanable Funds Real Interest Rate Supply of loanable funds (from national saving) Equilibrium real interest rate Demand for loanable funds (for domestic investment and net foreign investment) Equilibrium quantity Harcourt, Inc. items and derived items copyright © 2001 by Harcourt, Inc. Quantity of Loanable Funds
The Market for Loanable Funds Real Interest Rate Supply of loanable funds (from national saving) Equilibrium real interest rate Demand for loanable funds (for domestic investment and net foreign investment) Equilibrium quantity Harcourt, Inc. items and derived items copyright © 2001 by Harcourt, Inc. Quantity of Loanable Funds
 The Market for Foreign-Currency Exchange. . . Real Exchange Rate Supply of dollars (from net foreign investment) Equilibrium real exchange rate Demand for dollars (for net exports) Equilibrium quantity Harcourt, Inc. items and derived items copyright © 2001 by Harcourt, Inc. Quantity of Dollars Exchanged into Foreign Currency
The Market for Foreign-Currency Exchange. . . Real Exchange Rate Supply of dollars (from net foreign investment) Equilibrium real exchange rate Demand for dollars (for net exports) Equilibrium quantity Harcourt, Inc. items and derived items copyright © 2001 by Harcourt, Inc. Quantity of Dollars Exchanged into Foreign Currency
 How Net Foreign Investment Depends on the Interest rate. . . Real Interest Rate Net foreign investment is negative. 0 Harcourt, Inc. items and derived items copyright © 2001 by Harcourt, Inc. Net foreign investment is positive. Net Foreign Investment
How Net Foreign Investment Depends on the Interest rate. . . Real Interest Rate Net foreign investment is negative. 0 Harcourt, Inc. items and derived items copyright © 2001 by Harcourt, Inc. Net foreign investment is positive. Net Foreign Investment
 The Real Equilibrium in an Open Economy Real Interest Rate (a) The Market for Loanable Funds Real Supply Interest Rate r 1 Demand (b) Net Foreign Investment Net foreign investment, NFI Quantity of Loanable Funds Net Foreign Investment Real Exchange Rate Supply E 1 Demand Harcourt, Inc. items and derived items copyright © 2001 by Harcourt, Inc. Quantity of Dollars (c) The Market for Foreign-Currency Exchange
The Real Equilibrium in an Open Economy Real Interest Rate (a) The Market for Loanable Funds Real Supply Interest Rate r 1 Demand (b) Net Foreign Investment Net foreign investment, NFI Quantity of Loanable Funds Net Foreign Investment Real Exchange Rate Supply E 1 Demand Harcourt, Inc. items and derived items copyright © 2001 by Harcourt, Inc. Quantity of Dollars (c) The Market for Foreign-Currency Exchange
 The Effects of Government Budget Deficit Real Interest Rate (a) The Market for Loanable Funds Real Interest Rate r 2 S 1 S 2 B r 2 A r 1 (b) Net Foreign Investment 3. . which in turn reduces net foreign investment. r 1 Demand 1. A budget deficit reduces the supply of loanable funds. . . 2. . which increases the real interest. . . NFI Quantity of Loanable Funds Net Foreign Investment Real Exchange Rate E 2 5. …which causes the real exchange rate to appreciate. Harcourt, Inc. items and derived items copyright © 2001 by Harcourt, Inc. E 1 S 2 S 1 4. The decrease in net foreign investment reduces the supply of dollars to be exchanged into foreign currency… Demand Quantity of Dollars (c) The Market for Foreign-Currency Exchange
The Effects of Government Budget Deficit Real Interest Rate (a) The Market for Loanable Funds Real Interest Rate r 2 S 1 S 2 B r 2 A r 1 (b) Net Foreign Investment 3. . which in turn reduces net foreign investment. r 1 Demand 1. A budget deficit reduces the supply of loanable funds. . . 2. . which increases the real interest. . . NFI Quantity of Loanable Funds Net Foreign Investment Real Exchange Rate E 2 5. …which causes the real exchange rate to appreciate. Harcourt, Inc. items and derived items copyright © 2001 by Harcourt, Inc. E 1 S 2 S 1 4. The decrease in net foreign investment reduces the supply of dollars to be exchanged into foreign currency… Demand Quantity of Dollars (c) The Market for Foreign-Currency Exchange
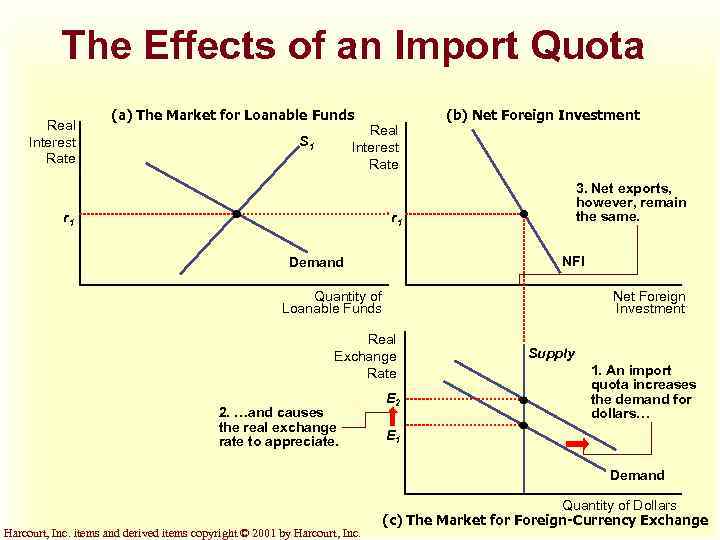 The Effects of an Import Quota Real Interest Rate (a) The Market for Loanable Funds Real Interest Rate S 1 r 1 (b) Net Foreign Investment 3. Net exports, however, remain the same. r 1 NFI Demand Quantity of Loanable Funds Net Foreign Investment Real Exchange Rate 2. …and causes the real exchange rate to appreciate. E 2 Supply 1. An import quota increases the demand for dollars… E 1 Demand Harcourt, Inc. items and derived items copyright © 2001 by Harcourt, Inc. Quantity of Dollars (c) The Market for Foreign-Currency Exchange
The Effects of an Import Quota Real Interest Rate (a) The Market for Loanable Funds Real Interest Rate S 1 r 1 (b) Net Foreign Investment 3. Net exports, however, remain the same. r 1 NFI Demand Quantity of Loanable Funds Net Foreign Investment Real Exchange Rate 2. …and causes the real exchange rate to appreciate. E 2 Supply 1. An import quota increases the demand for dollars… E 1 Demand Harcourt, Inc. items and derived items copyright © 2001 by Harcourt, Inc. Quantity of Dollars (c) The Market for Foreign-Currency Exchange
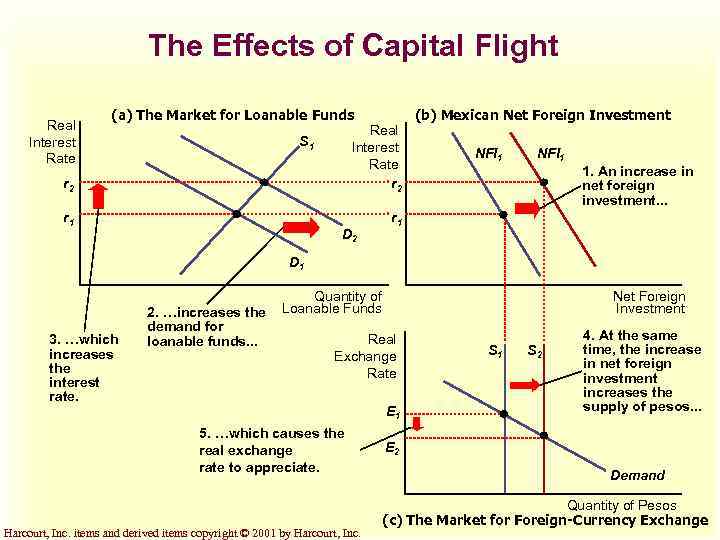 The Effects of Capital Flight Real Interest Rate (a) The Market for Loanable Funds r 2 Real Interest Rate r 2 r 1 (b) Mexican Net Foreign Investment r 1 S 1 D 2 NFI 1 1. An increase in net foreign investment. . . D 1 3. …which increases the interest rate. 2. …increases the demand for loanable funds. . . Quantity of Loanable Funds Net Foreign Investment Real Exchange Rate E 1 5. …which causes the real exchange rate to appreciate. Harcourt, Inc. items and derived items copyright © 2001 by Harcourt, Inc. S 1 S 2 4. At the same time, the increase in net foreign investment increases the supply of pesos. . . E 2 Demand Quantity of Pesos (c) The Market for Foreign-Currency Exchange
The Effects of Capital Flight Real Interest Rate (a) The Market for Loanable Funds r 2 Real Interest Rate r 2 r 1 (b) Mexican Net Foreign Investment r 1 S 1 D 2 NFI 1 1. An increase in net foreign investment. . . D 1 3. …which increases the interest rate. 2. …increases the demand for loanable funds. . . Quantity of Loanable Funds Net Foreign Investment Real Exchange Rate E 1 5. …which causes the real exchange rate to appreciate. Harcourt, Inc. items and derived items copyright © 2001 by Harcourt, Inc. S 1 S 2 4. At the same time, the increase in net foreign investment increases the supply of pesos. . . E 2 Demand Quantity of Pesos (c) The Market for Foreign-Currency Exchange


