e79d196db3292c8565784a8f32207ff3.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 83
 A Logic of Diversity Scott E Page Complex Systems, Political Science, Economics and Institute for Social Research University of Michigan Santa Fe Institute Michigania 02005
A Logic of Diversity Scott E Page Complex Systems, Political Science, Economics and Institute for Social Research University of Michigan Santa Fe Institute Michigania 02005
 The dim boy claps because the others clap. - Richard Hugo Michigania 02005
The dim boy claps because the others clap. - Richard Hugo Michigania 02005
 A Logic of Diversity I am going to replace abstract concepts, metaphors, and mantras with formal frameworks to produce a logic of individual diversity and its aggregative implications. Michigania 02005
A Logic of Diversity I am going to replace abstract concepts, metaphors, and mantras with formal frameworks to produce a logic of individual diversity and its aggregative implications. Michigania 02005
 Co-Authors Lu Hong: Mathematics of Diversity Jenna Bednar: Cultural Diversity and Institutional Path Dependence Michigania 02005
Co-Authors Lu Hong: Mathematics of Diversity Jenna Bednar: Cultural Diversity and Institutional Path Dependence Michigania 02005
 The Diversity Mantra Identity Diverse Diversity Perspectives Michigania 02005
The Diversity Mantra Identity Diverse Diversity Perspectives Michigania 02005
 Extending The Mantra Identity Diverse Better Diversity Perspectives Outcomes Michigania 02005
Extending The Mantra Identity Diverse Better Diversity Perspectives Outcomes Michigania 02005
 Enlarging The Mantra Identity Diverse Better Diversity Perspectives Outcomes Michigania 02005
Enlarging The Mantra Identity Diverse Better Diversity Perspectives Outcomes Michigania 02005
 Identity Michigania 02005
Identity Michigania 02005
 Training Michigania 02005
Training Michigania 02005
 Experiential Michigania 02005
Experiential Michigania 02005
 Enlarging The Mantra Identity, Training, Diverse Better Experiential Perspectives Outcomes Diversity Michigania 02005
Enlarging The Mantra Identity, Training, Diverse Better Experiential Perspectives Outcomes Diversity Michigania 02005
 Today’s Talk: Unpacking The First Box Diverse Perspectives Michigania 02005
Today’s Talk: Unpacking The First Box Diverse Perspectives Michigania 02005
 Wednesday’s Talk: Demonstrating Causality Better Diverse Perspectives Michigania 02005 Outcomes
Wednesday’s Talk: Demonstrating Causality Better Diverse Perspectives Michigania 02005 Outcomes
 Today’s Talk Describing the differences inside of our heads - cognitive differences. Michigania 02005
Today’s Talk Describing the differences inside of our heads - cognitive differences. Michigania 02005
 Brief Intermission Link to training (calculus, physics, etc. . ) obvious. Link to experience (we reason based on past cases) also clear But what of identity and culture? Michigania 02005
Brief Intermission Link to training (calculus, physics, etc. . ) obvious. Link to experience (we reason based on past cases) also clear But what of identity and culture? Michigania 02005
 A Most Important Question Michigania 02005
A Most Important Question Michigania 02005
 A Most Important Question Where do you keep your ketchup? Fridge? Cupboard? Michigania 02005
A Most Important Question Where do you keep your ketchup? Fridge? Cupboard? Michigania 02005
 The Follow-up Questions Shoes on or off in your house? Cross street when the red hand is flashing but no cars are present? Read newspaper at breakfast table? When you greet friends do you hug? Michigania 02005
The Follow-up Questions Shoes on or off in your house? Cross street when the red hand is flashing but no cars are present? Read newspaper at breakfast table? When you greet friends do you hug? Michigania 02005
 The Diversity Mantra Identity Diverse Diversity Perspectives Michigania 02005
The Diversity Mantra Identity Diverse Diversity Perspectives Michigania 02005
 Diverse Perspectives? Perspectives Heuristics Interpretations Mental Models Michigania 02005
Diverse Perspectives? Perspectives Heuristics Interpretations Mental Models Michigania 02005
 Perspectives A perspective is a representation of the set of possible solutions. Michigania 02005
Perspectives A perspective is a representation of the set of possible solutions. Michigania 02005
 The Value of Perspectives Most great breakthroughs in science result from new perspectives. Newton: Planetary Motion Mendeleyev: Periodic Table Michigania 02005
The Value of Perspectives Most great breakthroughs in science result from new perspectives. Newton: Planetary Motion Mendeleyev: Periodic Table Michigania 02005
 Diverse Perspectives (x, y) (r, ) Cartesian Michigania 02005 Polar
Diverse Perspectives (x, y) (r, ) Cartesian Michigania 02005 Polar
 Ben and Jerry y chunk size x z number of chunks Michigania 02005
Ben and Jerry y chunk size x z number of chunks Michigania 02005
 Consultant 1 x z y caloric rank Michigania 02005
Consultant 1 x z y caloric rank Michigania 02005
 Consultant 2 z x masticity Michigania 02005 y
Consultant 2 z x masticity Michigania 02005 y
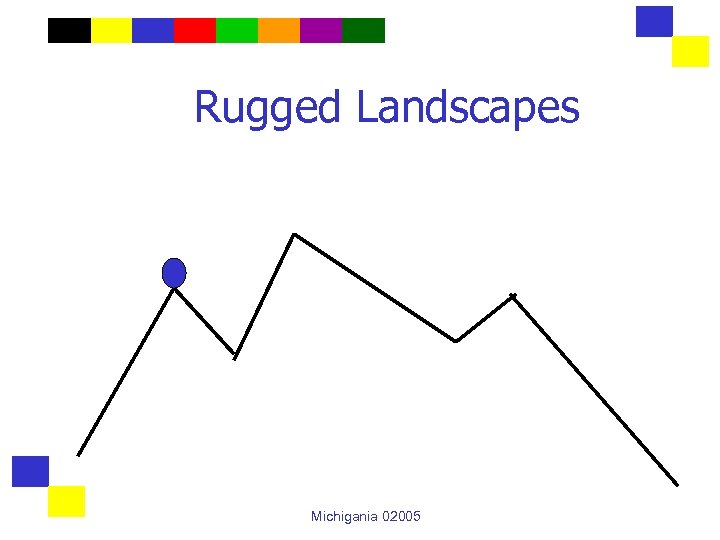 Rugged Landscapes Michigania 02005
Rugged Landscapes Michigania 02005
 Perspectives and Difficulty A perspective creates a landscape where the elevation of each solution equals its value. The better the perspective, the less rugged the landscape. Michigania 02005
Perspectives and Difficulty A perspective creates a landscape where the elevation of each solution equals its value. The better the perspective, the less rugged the landscape. Michigania 02005
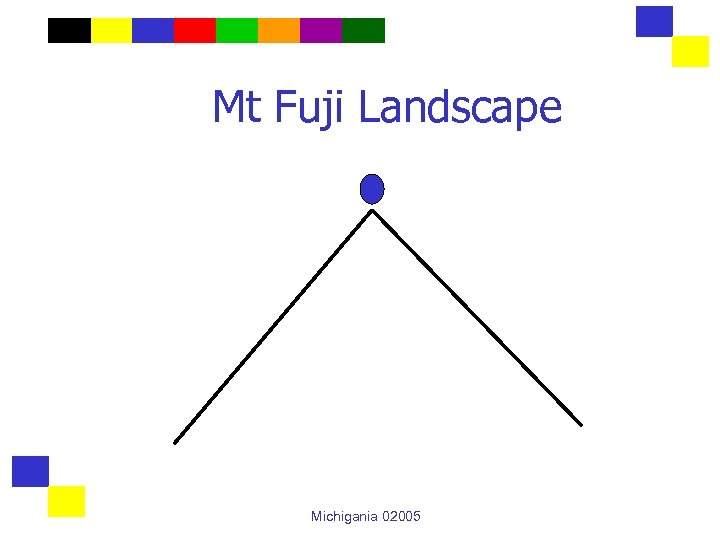 Mt Fuji Landscape Michigania 02005
Mt Fuji Landscape Michigania 02005
 Caloric Landscape Michigania 02005
Caloric Landscape Michigania 02005
 Chew Time Landscape Michigania 02005
Chew Time Landscape Michigania 02005
 Value of Consultants Michigania 02005
Value of Consultants Michigania 02005
 Perspectives in Strategic Contexts A perspective can also simplify a strategic context. What was hard can become easy. Michigania 02005
Perspectives in Strategic Contexts A perspective can also simplify a strategic context. What was hard can become easy. Michigania 02005
 Sum to Fifteen – Herb Simon Setup: Cards numbered 1 -9 face up on table Play: Players alternate selecting cards Object: To hold exactly three cards that add up to fifteen Michigania 02005
Sum to Fifteen – Herb Simon Setup: Cards numbered 1 -9 face up on table Play: Players alternate selecting cards Object: To hold exactly three cards that add up to fifteen Michigania 02005
 4/29/98 Page-De Marchi Match D: 7 P: 6 D: 5 P: 3 D: 1 P: 9 (12) (9) (6, 8, 12) (12, 9, 15) De Marchi offers Draw!! Michigania 02005
4/29/98 Page-De Marchi Match D: 7 P: 6 D: 5 P: 3 D: 1 P: 9 (12) (9) (6, 8, 12) (12, 9, 15) De Marchi offers Draw!! Michigania 02005
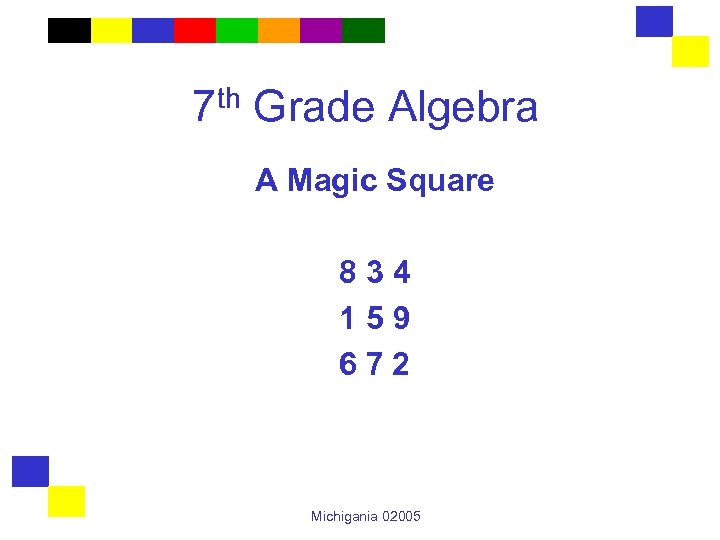 7 th Grade Algebra A Magic Square 834 159 672 Michigania 02005
7 th Grade Algebra A Magic Square 834 159 672 Michigania 02005
 Page-De Marchi Again _ __ _X_ Michigania 02005
Page-De Marchi Again _ __ _X_ Michigania 02005
 Page-De Marchi Again _ __ ___ 0 X_ Michigania 02005
Page-De Marchi Again _ __ ___ 0 X_ Michigania 02005
 Page-De Marchi Again _ __ _X_ 0 X_ Michigania 02005
Page-De Marchi Again _ __ _X_ 0 X_ Michigania 02005
 Page-De Marchi Again _ 0_ _X_ 0 X_ Michigania 02005
Page-De Marchi Again _ 0_ _X_ 0 X_ Michigania 02005
 Page-De Marchi Again _ 0_ XX_ 0 X_ Michigania 02005
Page-De Marchi Again _ 0_ XX_ 0 X_ Michigania 02005
 Page-De Marchi Again _ 0_ XX 0 0 X_ Michigania 02005
Page-De Marchi Again _ 0_ XX 0 0 X_ Michigania 02005
 An Equivalence It can be shown that tic tac toe on the magic square is equivalent to sum to fifteen. In one perspective the game is hard. In the other perspective, the game is easy. Michigania 02005
An Equivalence It can be shown that tic tac toe on the magic square is equivalent to sum to fifteen. In one perspective the game is hard. In the other perspective, the game is easy. Michigania 02005
 What Is Hard Can Be Easy Theorem: For any problem there exists a representation such that the problem of finding an optimal solution is easy. Michigania 02005
What Is Hard Can Be Easy Theorem: For any problem there exists a representation such that the problem of finding an optimal solution is easy. Michigania 02005
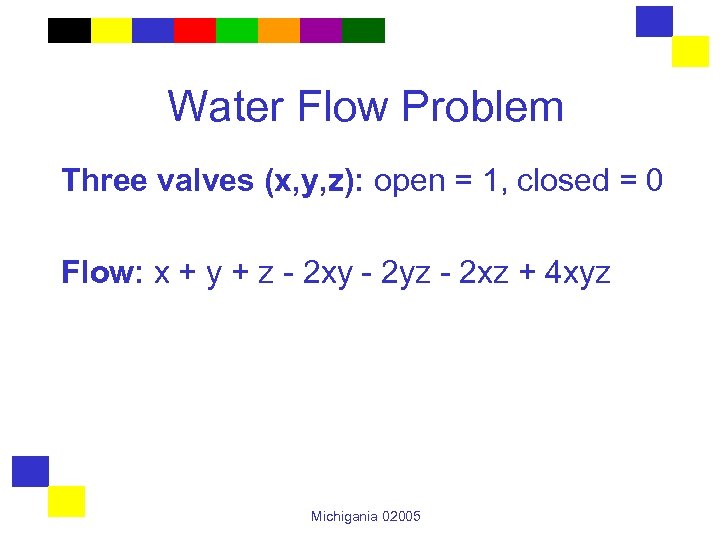 Water Flow Problem Three valves (x, y, z): open = 1, closed = 0 Flow: x + y + z - 2 xy - 2 yz - 2 xz + 4 xyz Michigania 02005
Water Flow Problem Three valves (x, y, z): open = 1, closed = 0 Flow: x + y + z - 2 xy - 2 yz - 2 xz + 4 xyz Michigania 02005
 Walsh Functions Walsh Function #3 W(x, y, z) = 0 if #1’s is even W(x, y, z) = 1 if #1’s is odd W(x, y, z) = x + y + z - 2 xy - 2 yz - 2 xz + 4 xyz Michigania 02005
Walsh Functions Walsh Function #3 W(x, y, z) = 0 if #1’s is even W(x, y, z) = 1 if #1’s is odd W(x, y, z) = x + y + z - 2 xy - 2 yz - 2 xz + 4 xyz Michigania 02005
 Caution Diverse perspectives create more adjacencies, and therefore more solutions. Those additional solutions include better solutions only if the perspectives are appropriate to the problem. More need not imply more better. Michigania 02005
Caution Diverse perspectives create more adjacencies, and therefore more solutions. Those additional solutions include better solutions only if the perspectives are appropriate to the problem. More need not imply more better. Michigania 02005
 Heuristics are techniques that we use for finding solutions. They can take many forms - simulated annealing algorithms - rule of 72 - do the opposite Michigania 02005
Heuristics are techniques that we use for finding solutions. They can take many forms - simulated annealing algorithms - rule of 72 - do the opposite Michigania 02005
 Heuristic Example Fill in the blank • 1 2 3 5 _ Michigania 02005 13
Heuristic Example Fill in the blank • 1 2 3 5 _ Michigania 02005 13
 Answer 1 2 3 5 8 Michigania 02005 13
Answer 1 2 3 5 8 Michigania 02005 13
 Heuristic 1 2 3 5 8 13 – xi+2 - xi+1 =xi Michigania 02005
Heuristic 1 2 3 5 8 13 – xi+2 - xi+1 =xi Michigania 02005
 Next Question 1 4 _ 16 25 Michigania 02005 36
Next Question 1 4 _ 16 25 Michigania 02005 36
 Answer 1 4 9 16 25 Michigania 02005 36
Answer 1 4 9 16 25 Michigania 02005 36
 Heuristic 1 4 9 16 25 – xi 2 Michigania 02005 36
Heuristic 1 4 9 16 25 – xi 2 Michigania 02005 36
 Last One! 1 2 6 _ 1806 Michigania 02005
Last One! 1 2 6 _ 1806 Michigania 02005
 Answer 1 2 6 42 1806 Michigania 02005
Answer 1 2 6 42 1806 Michigania 02005
 Heuristic 1 2 6 42 1806 – xi+1 – xi = xi 2 – 6 – 2 = 22 – 42 – 6 = 62 – 1806 – 42 = 422 Michigania 02005
Heuristic 1 2 6 42 1806 – xi+1 – xi = xi 2 – 6 – 2 = 22 – 42 – 6 = 62 – 1806 – 42 = 422 Michigania 02005
 Combining Heuristics 1 2 6 42 1806 – xi+1 – xi = xi 2 This is a combination of the first two heuristics Michigania 02005
Combining Heuristics 1 2 6 42 1806 – xi+1 – xi = xi 2 This is a combination of the first two heuristics Michigania 02005
 One plus one equals THREE By knowing two heuristics, you know three heuristics: The two individual heuristic plus the combined heuristic. Michigania 02005
One plus one equals THREE By knowing two heuristics, you know three heuristics: The two individual heuristic plus the combined heuristic. Michigania 02005
 Interpretations Reality consists of many variables or attributes. People cannot include them all. Therefore, we either - consider only some attributes - lump things together Michigania 02005
Interpretations Reality consists of many variables or attributes. People cannot include them all. Therefore, we either - consider only some attributes - lump things together Michigania 02005
 “Lump to Live” If we did not lump various experiences, situations, and events into categories, we could not draw inferences, make generalities, or construct mental models. Michigania 02005
“Lump to Live” If we did not lump various experiences, situations, and events into categories, we could not draw inferences, make generalities, or construct mental models. Michigania 02005
 Real Life Examples “Kerry is a liberal” Soccer moms and NASCAR Dads Price Earnings Ratios Autism Modern Art SKA Michigania 02005
Real Life Examples “Kerry is a liberal” Soccer moms and NASCAR Dads Price Earnings Ratios Autism Modern Art SKA Michigania 02005
 An Example • Students and advisors can have one of four personality types: – – Obsessive Curious Ambitious Rule Following • Outcome function F maps each pair into an outcome which is either good or bad. Michigania 02005
An Example • Students and advisors can have one of four personality types: – – Obsessive Curious Ambitious Rule Following • Outcome function F maps each pair into an outcome which is either good or bad. Michigania 02005
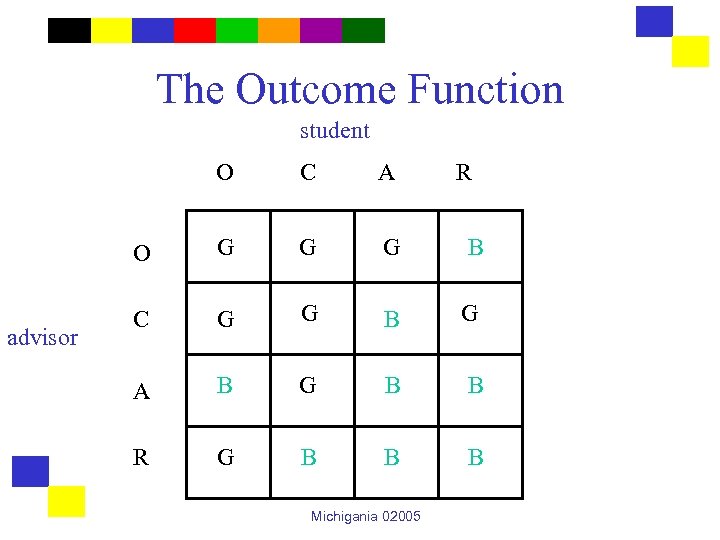 The Outcome Function student O A O advisor C G G G B C G G B G A B G B B R G B B B Michigania 02005 R
The Outcome Function student O A O advisor C G G G B C G G B G A B G B B R G B B B Michigania 02005 R
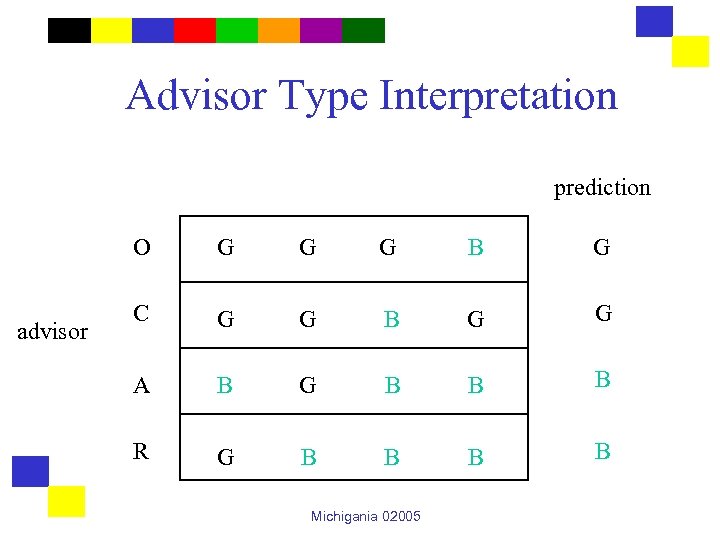 Advisor Type Interpretation prediction O advisor G G G B G C G G B G G A B G B B B R G B B Michigania 02005
Advisor Type Interpretation prediction O advisor G G G B G C G G B G G A B G B B B R G B B Michigania 02005
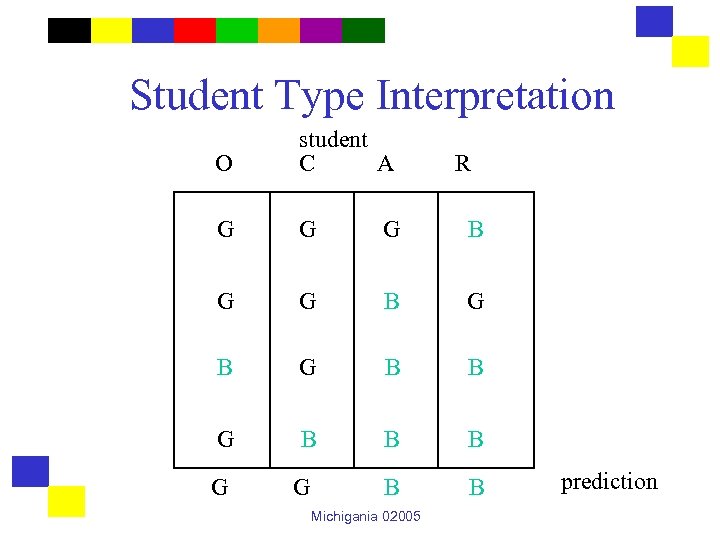 Student Type Interpretation O student C A G G G B G B B B G G B B Michigania 02005 R prediction
Student Type Interpretation O student C A G G G B G B B B G G B B Michigania 02005 R prediction
 Making Horse Races This is why we differ on our predictions of what will happen with stock prices, who will win sporting events, and who is a likely terrorist -- we look at the world differently. Michigania 02005
Making Horse Races This is why we differ on our predictions of what will happen with stock prices, who will win sporting events, and who is a likely terrorist -- we look at the world differently. Michigania 02005
 Miles Davis Experts parse the world more finely than the rest of. Michigania 02005
Miles Davis Experts parse the world more finely than the rest of. Michigania 02005
 Chicago El 1992 red line max 70 K riders blue line max 80 K riders Michigania 02005
Chicago El 1992 red line max 70 K riders blue line max 80 K riders Michigania 02005
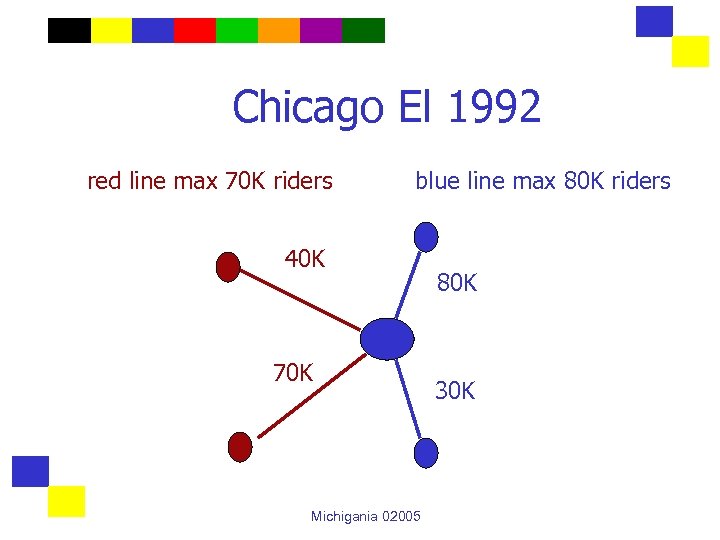 Chicago El 1992 red line max 70 K riders blue line max 80 K riders 40 K 70 K Michigania 02005 80 K 30 K
Chicago El 1992 red line max 70 K riders blue line max 80 K riders 40 K 70 K Michigania 02005 80 K 30 K
 Chicago El 1992 red line max 70 K riders blue line max 80 K riders 40 K 80 K 70 K 30 K Michigania 02005
Chicago El 1992 red line max 70 K riders blue line max 80 K riders 40 K 80 K 70 K 30 K Michigania 02005
 Chicago El 1992 yellow line max 40 K riders purple line max 80 K riders 40 K 70 K Michigania 02005 80 K 30 K
Chicago El 1992 yellow line max 40 K riders purple line max 80 K riders 40 K 70 K Michigania 02005 80 K 30 K
 Toolboxes vs Measuring Sticks We can think of a person’s ability as her collection of tools -- her perspectives, her heuristics, and her mental models -and not as an IQ score. Michigania 02005
Toolboxes vs Measuring Sticks We can think of a person’s ability as her collection of tools -- her perspectives, her heuristics, and her mental models -and not as an IQ score. Michigania 02005
 More Toolbox Combinatorics With one hundred tools, the number of collections of ten tools equals 17, 310, 309, 456, 440 Compare this to the number of I. Q. s! Michigania 02005
More Toolbox Combinatorics With one hundred tools, the number of collections of ten tools equals 17, 310, 309, 456, 440 Compare this to the number of I. Q. s! Michigania 02005
 Toolboxes and IQs Suppose 50 possible tools Sarah knows 20 Frank knows 12 What are odds that Sarah knows all that Frank knows? Michigania 02005
Toolboxes and IQs Suppose 50 possible tools Sarah knows 20 Frank knows 12 What are odds that Sarah knows all that Frank knows? Michigania 02005
 Toolboxes and IQs Suppose 50 possible tools Sarah knows 20 Frank knows 12 What are odds that Sarah knows all that Frank knows? About 4 in a billion Michigania 02005
Toolboxes and IQs Suppose 50 possible tools Sarah knows 20 Frank knows 12 What are odds that Sarah knows all that Frank knows? About 4 in a billion Michigania 02005
 An Implicit Cheat I assumed that any tool can be acquired. (“I think I’ll learn string theory. ”) That may not be true. It could be that tools have an ordering - to learn one tool you must first learn another. Michigania 02005
An Implicit Cheat I assumed that any tool can be acquired. (“I think I’ll learn string theory. ”) That may not be true. It could be that tools have an ordering - to learn one tool you must first learn another. Michigania 02005
 Ladder Model Suppose the tools are arranged in a ladder, so that to learn tool nine you must first learn tools 1 -8. Sarah now knows tools 1 -20 Frank now knows tools 1 -15 Sarah is “smarter” than Frank. Michigania 02005
Ladder Model Suppose the tools are arranged in a ladder, so that to learn tool nine you must first learn tools 1 -8. Sarah now knows tools 1 -20 Frank now knows tools 1 -15 Sarah is “smarter” than Frank. Michigania 02005
 Many Ladders Model # of Ladders 1 2 3 4 5 Probability Sarah > Frank 100% 29% 9% 1% 0. 005% Michigania 02005
Many Ladders Model # of Ladders 1 2 3 4 5 Probability Sarah > Frank 100% 29% 9% 1% 0. 005% Michigania 02005
 A Puzzle Why do people in the humanities and the arts believe in the value of diversity and why do people in the sciences not? Michigania 02005
A Puzzle Why do people in the humanities and the arts believe in the value of diversity and why do people in the sciences not? Michigania 02005
 We Believe What We Know Discipline Math Physics Economics Political Science Literature # of Ladders Very Few Few Several Many Michigania 02005
We Believe What We Know Discipline Math Physics Economics Political Science Literature # of Ladders Very Few Few Several Many Michigania 02005
 Summary - We don’t apply our IQ directly - We apply tools - Perspectives, heuristics, interpretations, mental models - Tools are superadditive (42) - Cannot universally compare intelligences - Can compare domain specific intelligence Michigania 02005
Summary - We don’t apply our IQ directly - We apply tools - Perspectives, heuristics, interpretations, mental models - Tools are superadditive (42) - Cannot universally compare intelligences - Can compare domain specific intelligence Michigania 02005
 What’s Next - Individual diversity influences collective performance. - Explain``Wisdom of Crowds” - See that diversity and ability merit equal standing Michigania 02005
What’s Next - Individual diversity influences collective performance. - Explain``Wisdom of Crowds” - See that diversity and ability merit equal standing Michigania 02005


