bf68f6537dbf1651f7710fa1f056c348.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 67
 A Knowledge Level Software Engineering Methodology for Agent Oriented Programming The Tropos framework Fausto Giunchiglia Dept. of Information and Communication Technology University of Trento SRA Division ITC irst Trento fausto@itc. it - http: //sra. itc. it ATAL - Seattle, August 1 st, 2001 1
A Knowledge Level Software Engineering Methodology for Agent Oriented Programming The Tropos framework Fausto Giunchiglia Dept. of Information and Communication Technology University of Trento SRA Division ITC irst Trento fausto@itc. it - http: //sra. itc. it ATAL - Seattle, August 1 st, 2001 1
 Outline • • • – – – Key ideas Modeling language case study metamodel Transformational approach case study revisited tranformational operators composition of transformations: intuition Conclusion Future work Related work ATAL - Seattle, August 1 st, 2001 2
Outline • • • – – – Key ideas Modeling language case study metamodel Transformational approach case study revisited tranformational operators composition of transformations: intuition Conclusion Future work Related work ATAL - Seattle, August 1 st, 2001 2
 Key ideas ATAL - Seattle, August 1 st, 2001 3
Key ideas ATAL - Seattle, August 1 st, 2001 3
 Key ideas The Tropos framework is a novel approach in Agent Oriented Software Engineering, resting on the following 3 key ideas: 1. the Tropos approach framework spans the overall software development process, from early requirements down to implementation 2. we use the notion of agent and all the related mentalistic notions in all phases of software development 3. we adopt a transformational approach, i. e. , we perform refinement steps, inside one phase or between phases, using a set of transformation operators ATAL - Seattle, August 1 st, 2001 4
Key ideas The Tropos framework is a novel approach in Agent Oriented Software Engineering, resting on the following 3 key ideas: 1. the Tropos approach framework spans the overall software development process, from early requirements down to implementation 2. we use the notion of agent and all the related mentalistic notions in all phases of software development 3. we adopt a transformational approach, i. e. , we perform refinement steps, inside one phase or between phases, using a set of transformation operators ATAL - Seattle, August 1 st, 2001 4
 Key ideas (1. 1) The 5 phases of the Tropos framework: • Early requirements • Late requirements • Architectural design • Detailed design • Implementation ATAL - Seattle, August 1 st, 2001 5
Key ideas (1. 1) The 5 phases of the Tropos framework: • Early requirements • Late requirements • Architectural design • Detailed design • Implementation ATAL - Seattle, August 1 st, 2001 5
 Key ideas (1. 2) – we adopt a requirements drivensoftware development approach, exploiting goal analysis and actor dependencies analysis techniques (i* by E. Yu, NFR by Chung et al. , Kaos by Dardenne et al. ) Model the what, how and the why – the conceptual notions thus introduced are used along the whole development process ATAL - Seattle, August 1 st, 2001 6
Key ideas (1. 2) – we adopt a requirements drivensoftware development approach, exploiting goal analysis and actor dependencies analysis techniques (i* by E. Yu, NFR by Chung et al. , Kaos by Dardenne et al. ) Model the what, how and the why – the conceptual notions thus introduced are used along the whole development process ATAL - Seattle, August 1 st, 2001 6
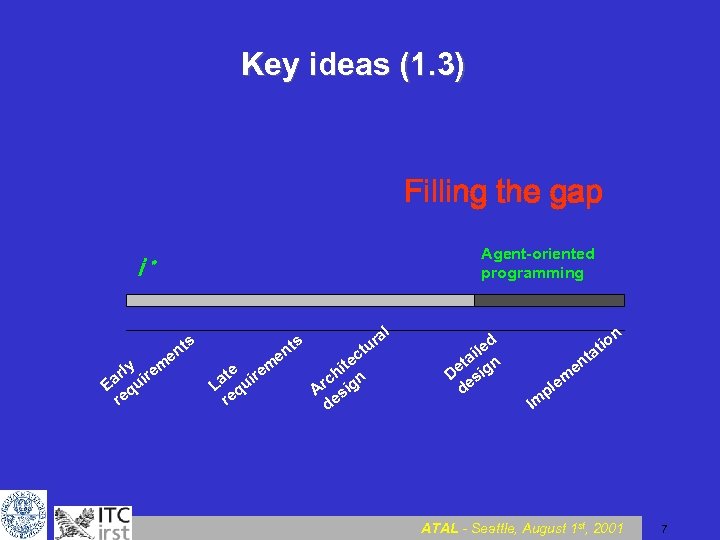 Key ideas (1. 3) Filling the gap i Agent oriented programming * ts ts en ly ar uir E q re em te r La qui re em en l ra tu c ite h rc ign A s de d ile a et ign D s de n io at t pl Im en m e ATAL - Seattle, August 1 st, 2001 7
Key ideas (1. 3) Filling the gap i Agent oriented programming * ts ts en ly ar uir E q re em te r La qui re em en l ra tu c ite h rc ign A s de d ile a et ign D s de n io at t pl Im en m e ATAL - Seattle, August 1 st, 2001 7
 Key ideas (2) • The notion of agent and goal is used along all the phases, therefore the key elements and dependencies describing the organizational setting can be used to justify and motivate each design and implementation choice. • Each artifact (including code) can be retraced back to the analysis performed during requirement phases. • There is a direct and natural correspondence between requirement analysis (social actors) and implemented code (software agents). System behaviour is easier to understand, explain, motivate. ATAL - Seattle, August 1 st, 2001 8
Key ideas (2) • The notion of agent and goal is used along all the phases, therefore the key elements and dependencies describing the organizational setting can be used to justify and motivate each design and implementation choice. • Each artifact (including code) can be retraced back to the analysis performed during requirement phases. • There is a direct and natural correspondence between requirement analysis (social actors) and implemented code (software agents). System behaviour is easier to understand, explain, motivate. ATAL - Seattle, August 1 st, 2001 8
 Key ideas (3. 1) We adopt a transformational approach: (for early and late requirements, and partially for the architectural design) • start with a limited list of Tropos conceptual elements (actors, goals, softgoals, . . . ) • iteratively and incrementally: – add details – revise dependency relationships Each step corresponds to the introduction/deletion of relationships/elements in the model. ATAL - Seattle, August 1 st, 2001 9
Key ideas (3. 1) We adopt a transformational approach: (for early and late requirements, and partially for the architectural design) • start with a limited list of Tropos conceptual elements (actors, goals, softgoals, . . . ) • iteratively and incrementally: – add details – revise dependency relationships Each step corresponds to the introduction/deletion of relationships/elements in the model. ATAL - Seattle, August 1 st, 2001 9
 Key ideas (3. 2) Advantages of the (transformational) approach : • provides systematic description of the process • allows for process analysis • provides guidelines to the engineer • provides a sound basis for describing and evaluating requirement acquisition and design strategies ATAL - Seattle, August 1 st, 2001 10
Key ideas (3. 2) Advantages of the (transformational) approach : • provides systematic description of the process • allows for process analysis • provides guidelines to the engineer • provides a sound basis for describing and evaluating requirement acquisition and design strategies ATAL - Seattle, August 1 st, 2001 10
 Modeling language ATAL - Seattle, August 1 st, 2001 11
Modeling language ATAL - Seattle, August 1 st, 2001 11
 Modeling language case study ATAL - Seattle, August 1 st, 2001 12
Modeling language case study ATAL - Seattle, August 1 st, 2001 12
 The e. Culture system case study • a web-based broker of cultural information and services for the province of Trentino • usable by a variety of users (e. g. Trentinos, tourists, scholars and students). ATAL - Seattle, August 1 st, 2001 13
The e. Culture system case study • a web-based broker of cultural information and services for the province of Trentino • usable by a variety of users (e. g. Trentinos, tourists, scholars and students). ATAL - Seattle, August 1 st, 2001 13
 The e. Culture system case study Following the 5 phases of the Tropos framework down to the implementation • Early requirements • Late requirements • Architectural design • Detailed design • Implementation Tropos social actors Agents ATAL - Seattle, August 1 st, 2001 14
The e. Culture system case study Following the 5 phases of the Tropos framework down to the implementation • Early requirements • Late requirements • Architectural design • Detailed design • Implementation Tropos social actors Agents ATAL - Seattle, August 1 st, 2001 14
 Early requirements Main activities We analyze the environment (i. e. existing organizational setting) and model it in terms of relevant actors and their respective dependencies ATAL - Seattle, August 1 st, 2001 15
Early requirements Main activities We analyze the environment (i. e. existing organizational setting) and model it in terms of relevant actors and their respective dependencies ATAL - Seattle, August 1 st, 2001 15
 Early requirements The stakeholders of the e. Culture domain Citizen Museum PAT Visitor ATAL - Seattle, August 1 st, 2001 16
Early requirements The stakeholders of the e. Culture domain Citizen Museum PAT Visitor ATAL - Seattle, August 1 st, 2001 16
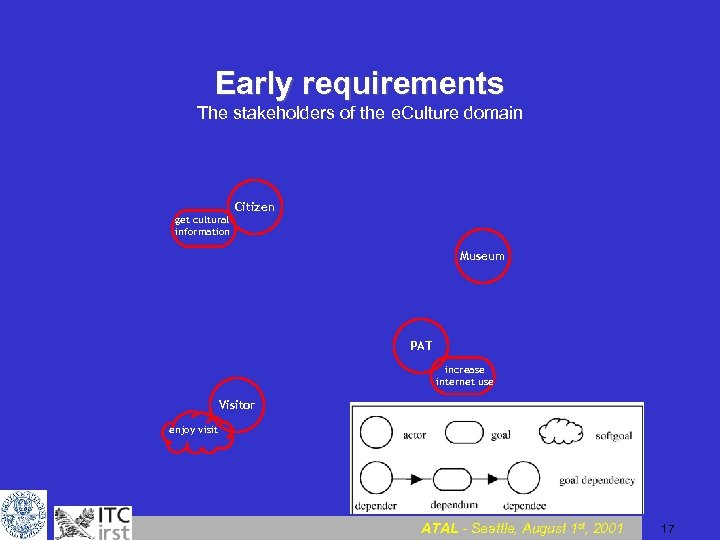 Early requirements The stakeholders of the e. Culture domain get cultural information Citizen Museum PAT increase internet use Visitor enjoy visit ATAL - Seattle, August 1 st, 2001 17
Early requirements The stakeholders of the e. Culture domain get cultural information Citizen Museum PAT increase internet use Visitor enjoy visit ATAL - Seattle, August 1 st, 2001 17
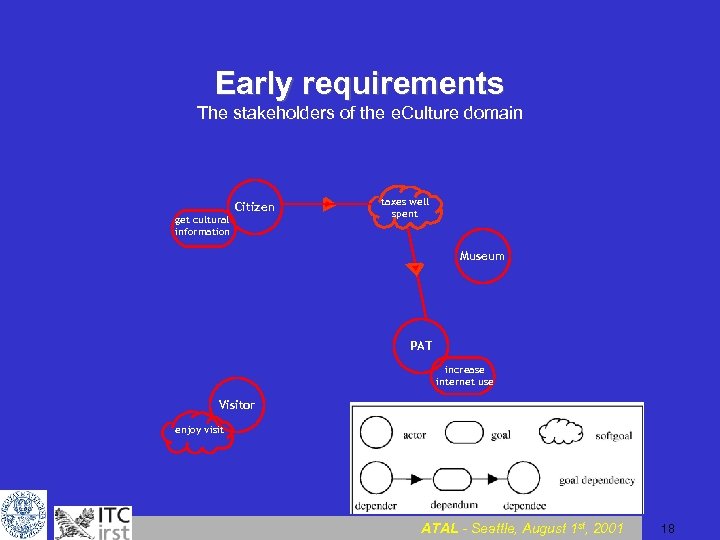 Early requirements The stakeholders of the e. Culture domain get cultural information Citizen taxes well spent Museum PAT increase internet use Visitor enjoy visit ATAL - Seattle, August 1 st, 2001 18
Early requirements The stakeholders of the e. Culture domain get cultural information Citizen taxes well spent Museum PAT increase internet use Visitor enjoy visit ATAL - Seattle, August 1 st, 2001 18
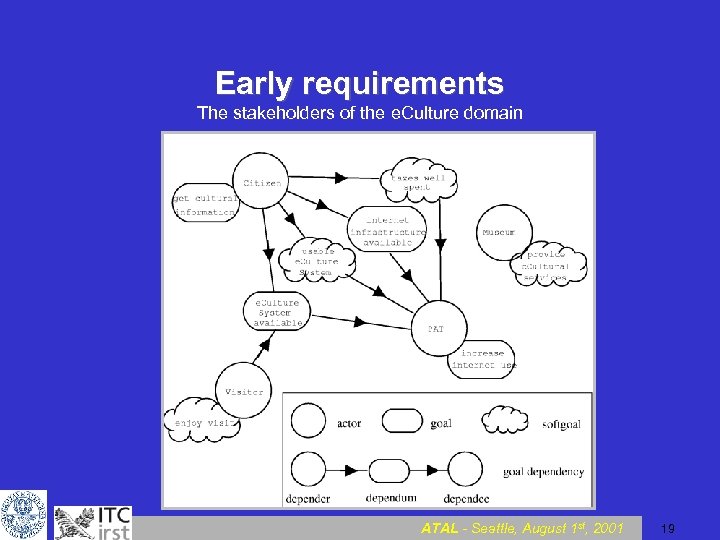 Early requirements The stakeholders of the e. Culture domain ATAL - Seattle, August 1 st, 2001 19
Early requirements The stakeholders of the e. Culture domain ATAL - Seattle, August 1 st, 2001 19
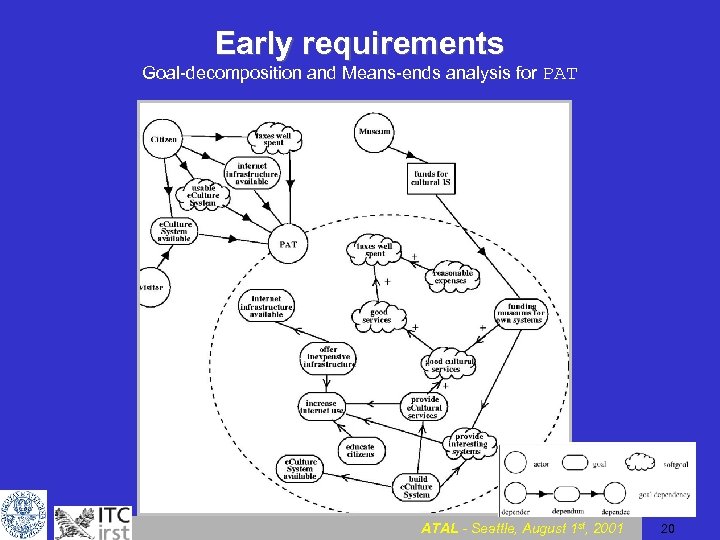 Early requirements Goal-decomposition and Means-ends analysis for PAT ATAL - Seattle, August 1 st, 2001 20
Early requirements Goal-decomposition and Means-ends analysis for PAT ATAL - Seattle, August 1 st, 2001 20
 Late requirements Main activities We introduce the system actor and analize its dependencies with actors in its environment identifying system’s functional and non-functional requirements ATAL - Seattle, August 1 st, 2001 21
Late requirements Main activities We introduce the system actor and analize its dependencies with actors in its environment identifying system’s functional and non-functional requirements ATAL - Seattle, August 1 st, 2001 21
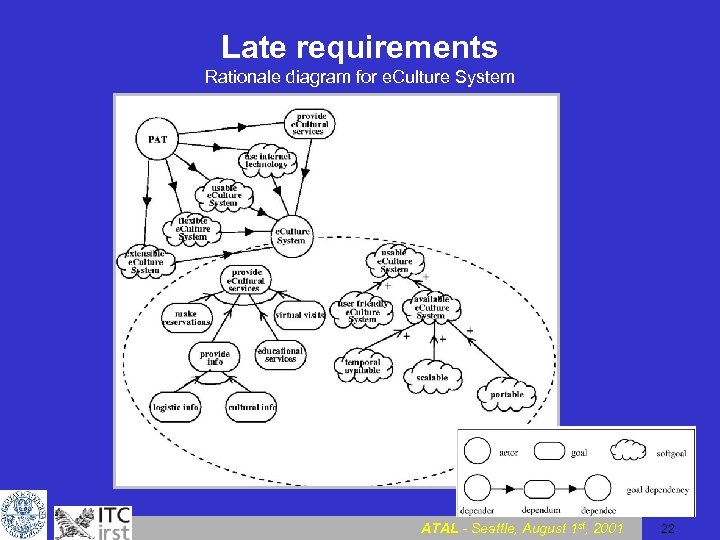 Late requirements Rationale diagram for e. Culture System ATAL - Seattle, August 1 st, 2001 22
Late requirements Rationale diagram for e. Culture System ATAL - Seattle, August 1 st, 2001 22
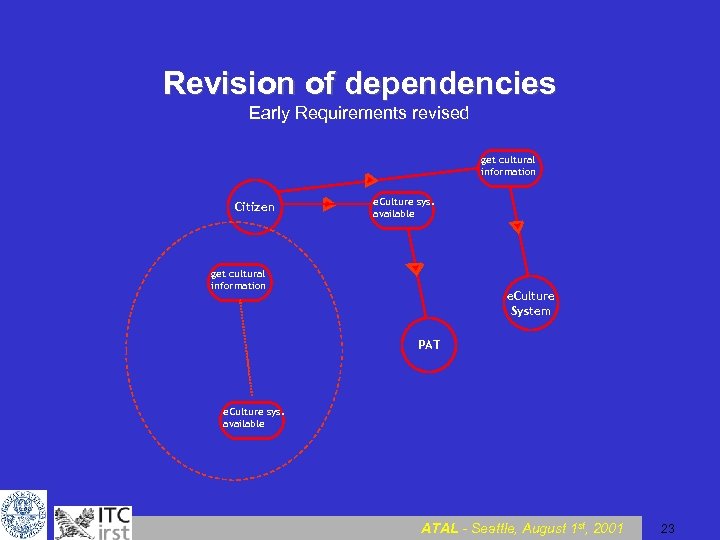 Revision of dependencies Early Requirements revised get cultural information Citizen e. Culture sys. available get cultural information e. Culture System PAT e. Culture sys. available ATAL - Seattle, August 1 st, 2001 23
Revision of dependencies Early Requirements revised get cultural information Citizen e. Culture sys. available get cultural information e. Culture System PAT e. Culture sys. available ATAL - Seattle, August 1 st, 2001 23
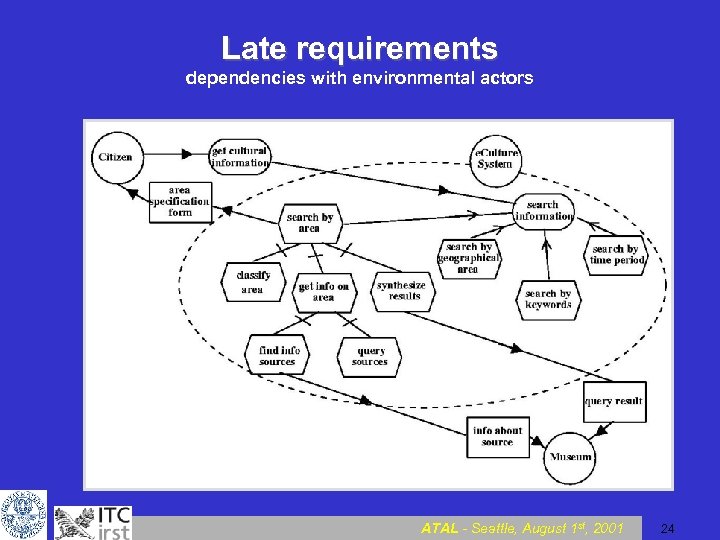 Late requirements dependencies with environmental actors ATAL - Seattle, August 1 st, 2001 24
Late requirements dependencies with environmental actors ATAL - Seattle, August 1 st, 2001 24
 Architectural design Main activities 3 steps: 1. decomposing and refining the system actor diagram … at three different levels of abstraction 2. identifying capabilities 3. from actors to agents ATAL - Seattle, August 1 st, 2001 25
Architectural design Main activities 3 steps: 1. decomposing and refining the system actor diagram … at three different levels of abstraction 2. identifying capabilities 3. from actors to agents ATAL - Seattle, August 1 st, 2001 25
 Architectural design: step 1 a: inclusion of new actors due to delegation of subgoals upon goal analysis of system's goals b: inclusion of new actors according to the choice of a specific architectural style (design patterns) c: inclusion of new actors contributing positively to the fulfillment of some Non Functional Requirements ATAL - Seattle, August 1 st, 2001 26
Architectural design: step 1 a: inclusion of new actors due to delegation of subgoals upon goal analysis of system's goals b: inclusion of new actors according to the choice of a specific architectural style (design patterns) c: inclusion of new actors contributing positively to the fulfillment of some Non Functional Requirements ATAL - Seattle, August 1 st, 2001 26
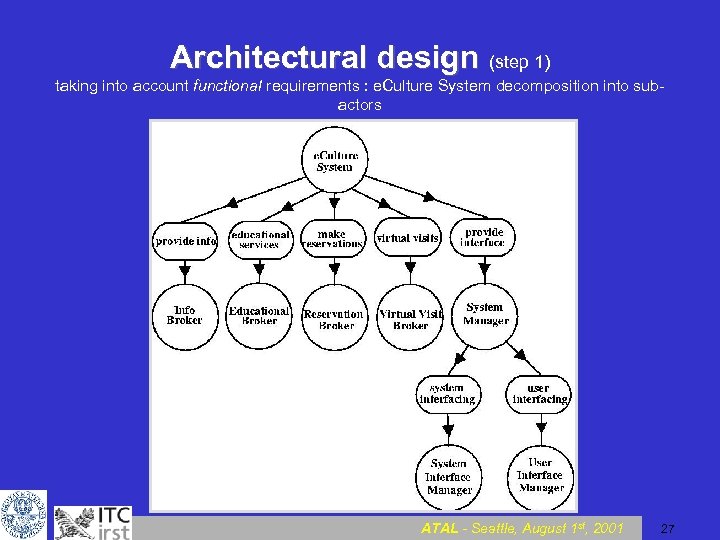 Architectural design (step 1) taking into account functional requirements : e. Culture System decomposition into subactors ATAL - Seattle, August 1 st, 2001 27
Architectural design (step 1) taking into account functional requirements : e. Culture System decomposition into subactors ATAL - Seattle, August 1 st, 2001 27
 Architectural design: step 1 a: inclusion of new actors due to delegation of subgoals upon goal analysis of system's goals b: inclusion of new actors according to the choice of a specific architectural style (design patterns) c: inclusion of new actors contributing positively to the fulfillment of some Non Functional Requirements ATAL - Seattle, August 1 st, 2001 28
Architectural design: step 1 a: inclusion of new actors due to delegation of subgoals upon goal analysis of system's goals b: inclusion of new actors according to the choice of a specific architectural style (design patterns) c: inclusion of new actors contributing positively to the fulfillment of some Non Functional Requirements ATAL - Seattle, August 1 st, 2001 28
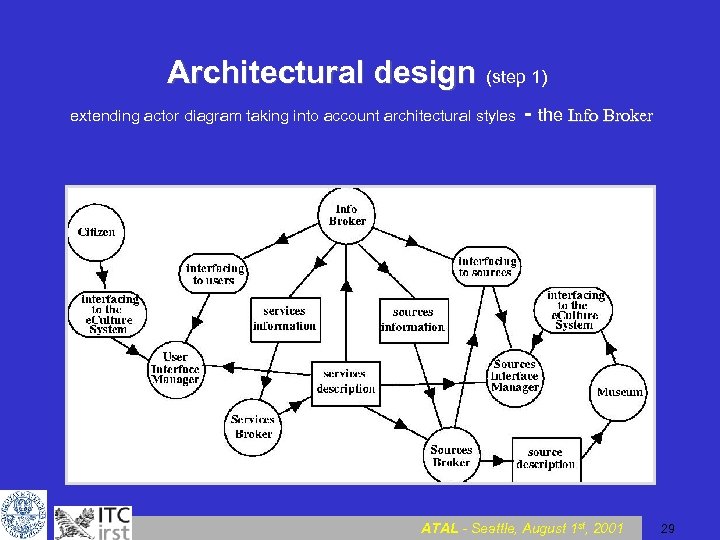 Architectural design (step 1) extending actor diagram taking into account architectural styles the Info Broker ATAL - Seattle, August 1 st, 2001 29
Architectural design (step 1) extending actor diagram taking into account architectural styles the Info Broker ATAL - Seattle, August 1 st, 2001 29
 Architectural design Step 2 identifying actor capabilities from the analysis of dependencies in the actor diagram …an intuitive idea of this process ATAL - Seattle, August 1 st, 2001 30
Architectural design Step 2 identifying actor capabilities from the analysis of dependencies in the actor diagram …an intuitive idea of this process ATAL - Seattle, August 1 st, 2001 30
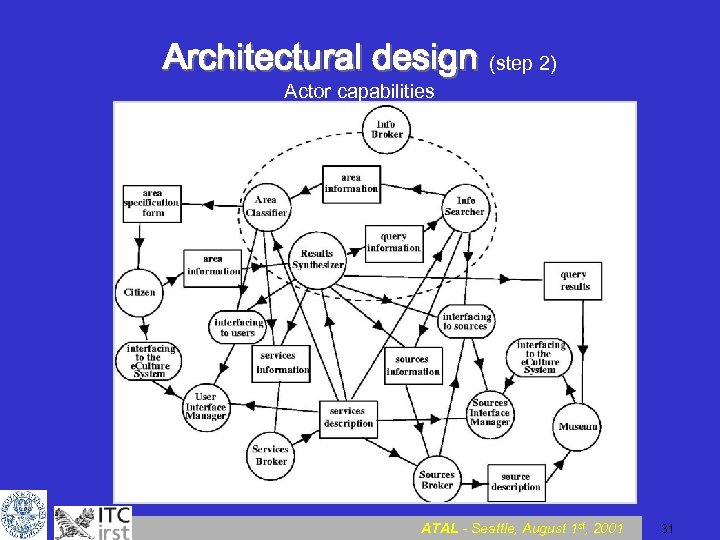 Architectural design (step 2) Actor capabilities ATAL - Seattle, August 1 st, 2001 31
Architectural design (step 2) Actor capabilities ATAL - Seattle, August 1 st, 2001 31
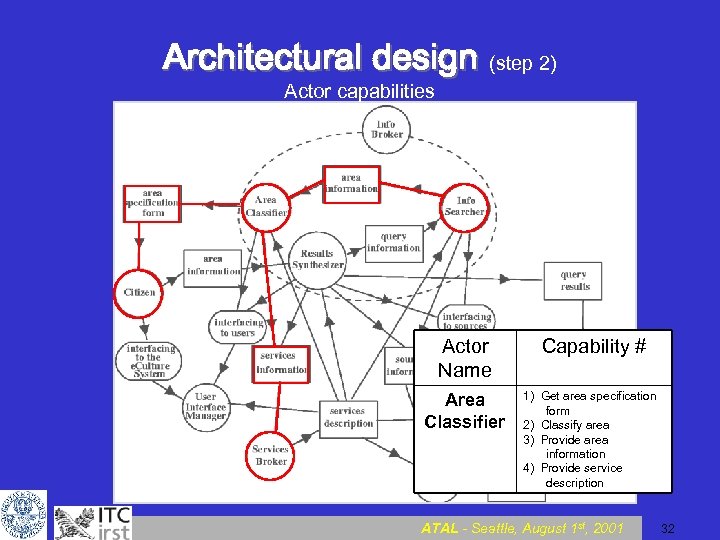 Architectural design (step 2) Actor capabilities Actor Name Area Classifier Capability # 1) Get area specification form 2) Classify area 3) Provide area information 4) Provide service description ATAL - Seattle, August 1 st, 2001 32
Architectural design (step 2) Actor capabilities Actor Name Area Classifier Capability # 1) Get area specification form 2) Classify area 3) Provide area information 4) Provide service description ATAL - Seattle, August 1 st, 2001 32
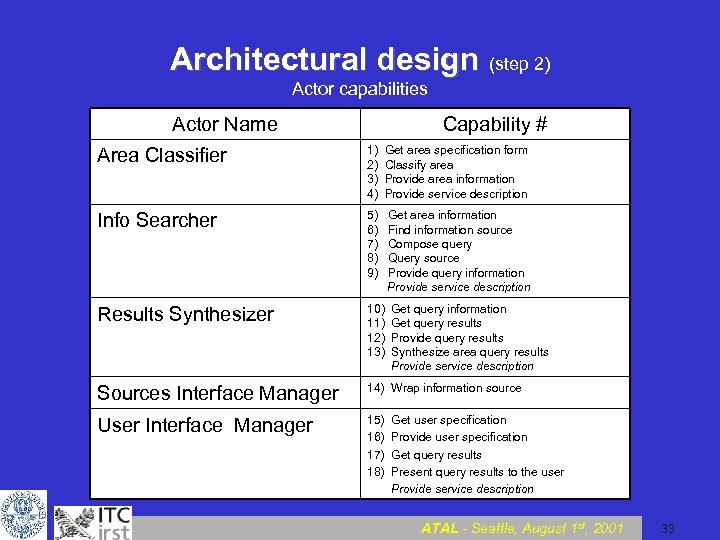 Architectural design (step 2) Actor capabilities Actor Name Capability # Area Classifier 1) 2) 3) 4) Get area specification form Classify area Provide area information Provide service description Info Searcher 5) 6) 7) 8) 9) Get area information Find information source Compose query Query source Provide query information Provide service description Results Synthesizer 10) 11) 12) 13) Get query information Get query results Provide query results Synthesize area query results Provide service description Sources Interface Manager 14) Wrap information source User Interface Manager 15) 16) 17) 18) Get user specification Provide user specification Get query results Present query results to the user Provide service description ATAL - Seattle, August 1 st, 2001 33
Architectural design (step 2) Actor capabilities Actor Name Capability # Area Classifier 1) 2) 3) 4) Get area specification form Classify area Provide area information Provide service description Info Searcher 5) 6) 7) 8) 9) Get area information Find information source Compose query Query source Provide query information Provide service description Results Synthesizer 10) 11) 12) 13) Get query information Get query results Provide query results Synthesize area query results Provide service description Sources Interface Manager 14) Wrap information source User Interface Manager 15) 16) 17) 18) Get user specification Provide user specification Get query results Present query results to the user Provide service description ATAL - Seattle, August 1 st, 2001 33
 Architectural design Step 3 from actors to agents …. ATAL - Seattle, August 1 st, 2001 34
Architectural design Step 3 from actors to agents …. ATAL - Seattle, August 1 st, 2001 34
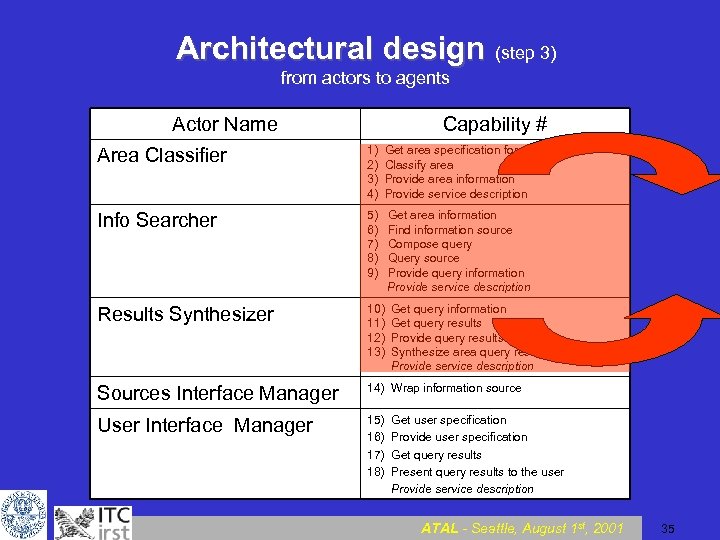 Architectural design (step 3) from actors to agents Actor Name Capability # Area Classifier 1) 2) 3) 4) Get area specification form Classify area Provide area information Provide service description Info Searcher 5) 6) 7) 8) 9) Get area information Find information source Compose query Query source Provide query information Provide service description Results Synthesizer 10) 11) 12) 13) Get query information Get query results Provide query results Synthesize area query results Provide service description Sources Interface Manager 14) Wrap information source User Interface Manager 15) 16) 17) 18) Get user specification Provide user specification Get query results Present query results to the user Provide service description ATAL - Seattle, August 1 st, 2001 35
Architectural design (step 3) from actors to agents Actor Name Capability # Area Classifier 1) 2) 3) 4) Get area specification form Classify area Provide area information Provide service description Info Searcher 5) 6) 7) 8) 9) Get area information Find information source Compose query Query source Provide query information Provide service description Results Synthesizer 10) 11) 12) 13) Get query information Get query results Provide query results Synthesize area query results Provide service description Sources Interface Manager 14) Wrap information source User Interface Manager 15) 16) 17) 18) Get user specification Provide user specification Get query results Present query results to the user Provide service description ATAL - Seattle, August 1 st, 2001 35
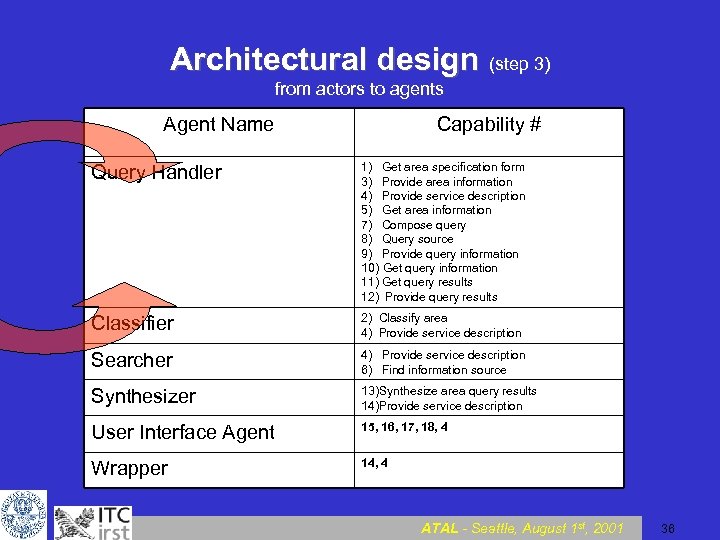 Architectural design (step 3) from actors to agents Agent Name Capability # Query Handler 1) Get area specification form 3) Provide area information 4) Provide service description 5) Get area information 7) Compose query 8) Query source 9) Provide query information 10) Get query information 11) Get query results 12) Provide query results Classifier 2) Classify area 4) Provide service description Searcher 4) Provide service description 6) Find information source Synthesizer 13)Synthesize area query results 14)Provide service description User Interface Agent 15, 16, 17, 18, 4 Wrapper 14, 4 ATAL - Seattle, August 1 st, 2001 36
Architectural design (step 3) from actors to agents Agent Name Capability # Query Handler 1) Get area specification form 3) Provide area information 4) Provide service description 5) Get area information 7) Compose query 8) Query source 9) Provide query information 10) Get query information 11) Get query results 12) Provide query results Classifier 2) Classify area 4) Provide service description Searcher 4) Provide service description 6) Find information source Synthesizer 13)Synthesize area query results 14)Provide service description User Interface Agent 15, 16, 17, 18, 4 Wrapper 14, 4 ATAL - Seattle, August 1 st, 2001 36
 Detailed design Main activities Specification of the agents’ micro level taking into account the implementation platform. Objective: to perform a design that will map directly to the code. We consider a BDI multiagent platform, so … ATAL - Seattle, August 1 st, 2001 37
Detailed design Main activities Specification of the agents’ micro level taking into account the implementation platform. Objective: to perform a design that will map directly to the code. We consider a BDI multiagent platform, so … ATAL - Seattle, August 1 st, 2001 37
 Detailed design BDI platform case We model: • capabilities – capability diagrams (currently AUML activity diagrams) ATAL - Seattle, August 1 st, 2001 38
Detailed design BDI platform case We model: • capabilities – capability diagrams (currently AUML activity diagrams) ATAL - Seattle, August 1 st, 2001 38
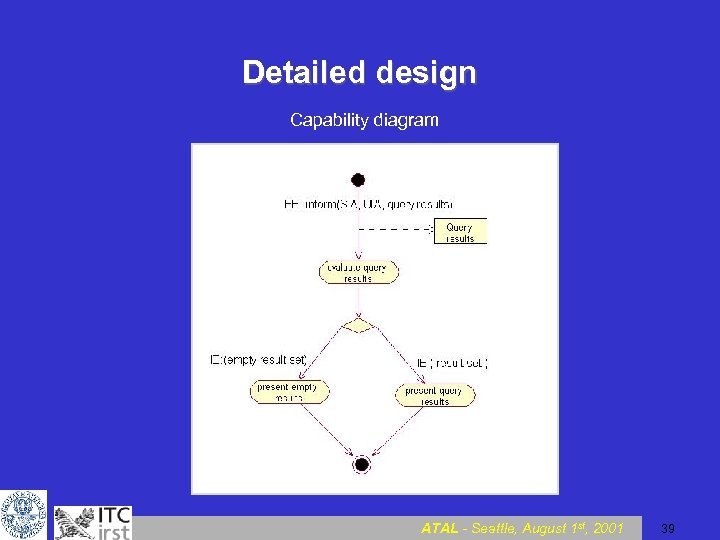 Detailed design Capability diagram ATAL - Seattle, August 1 st, 2001 39
Detailed design Capability diagram ATAL - Seattle, August 1 st, 2001 39
 Detailed design BDI platform case We model: • capabilities – capability diagrams (currently AUML activity diagrams) • plans – plan diagrams (currently AUML activity diagrams ATAL - Seattle, August 1 st, 2001 40
Detailed design BDI platform case We model: • capabilities – capability diagrams (currently AUML activity diagrams) • plans – plan diagrams (currently AUML activity diagrams ATAL - Seattle, August 1 st, 2001 40
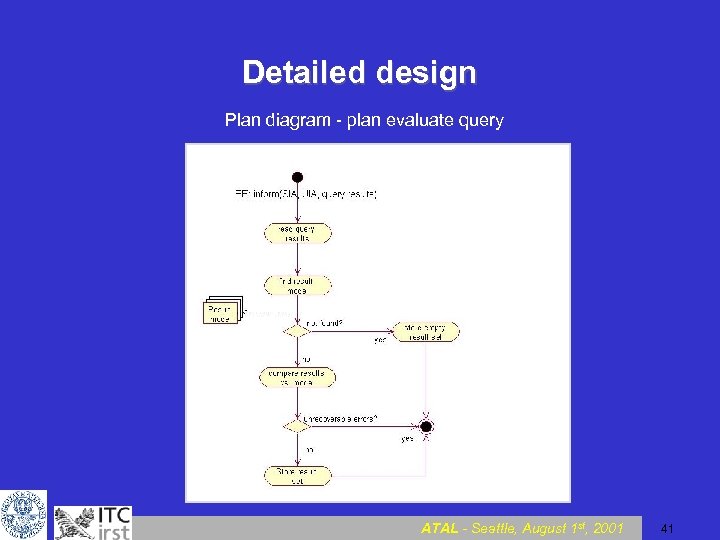 Detailed design Plan diagram - plan evaluate query ATAL - Seattle, August 1 st, 2001 41
Detailed design Plan diagram - plan evaluate query ATAL - Seattle, August 1 st, 2001 41
 Detailed design BDI platform case We model: • capabilities – capability diagrams (currently AUML activity diagrams) • plans – plan diagrams (currently AUML activity diagrams • agents interaction – agent interactions diagrams (currently AUML sequence diagrams ATAL - Seattle, August 1 st, 2001 42
Detailed design BDI platform case We model: • capabilities – capability diagrams (currently AUML activity diagrams) • plans – plan diagrams (currently AUML activity diagrams • agents interaction – agent interactions diagrams (currently AUML sequence diagrams ATAL - Seattle, August 1 st, 2001 42
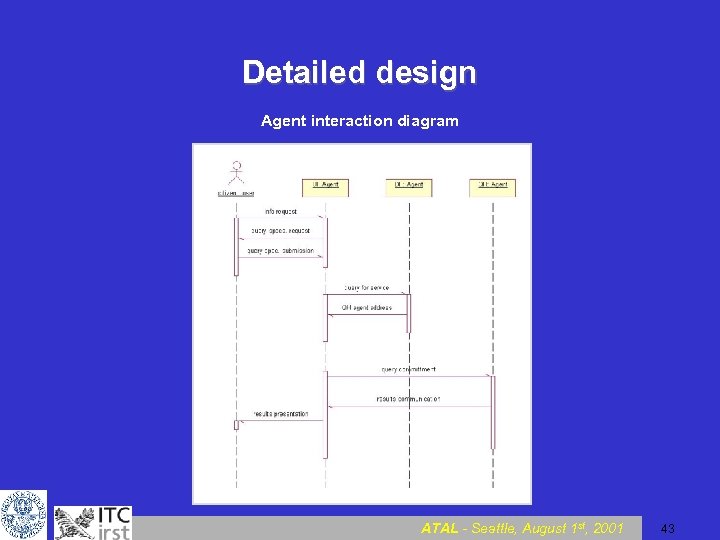 Detailed design Agent interaction diagram ATAL - Seattle, August 1 st, 2001 43
Detailed design Agent interaction diagram ATAL - Seattle, August 1 st, 2001 43
 Implementation Main activities … follow step by step the detailed design specification … In JACK (BDI multiagent platform) agents are autonomous software components that have explicit goals (desires) to achieve or events to handle, beliefs and capabilities. They are programmed with a set of plans that make them capable of achieving goals. ATAL - Seattle, August 1 st, 2001 44
Implementation Main activities … follow step by step the detailed design specification … In JACK (BDI multiagent platform) agents are autonomous software components that have explicit goals (desires) to achieve or events to handle, beliefs and capabilities. They are programmed with a set of plans that make them capable of achieving goals. ATAL - Seattle, August 1 st, 2001 44
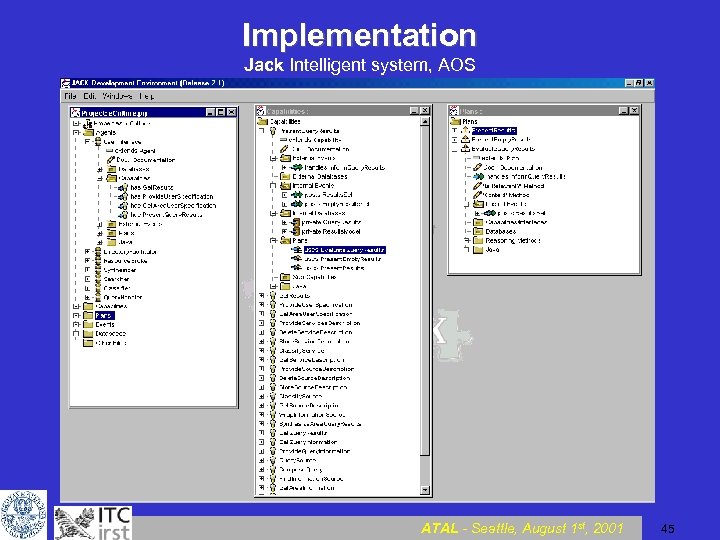 Implementation Jack Intelligent system, AOS ATAL - Seattle, August 1 st, 2001 45
Implementation Jack Intelligent system, AOS ATAL - Seattle, August 1 st, 2001 45
 Modeling language metamodel ATAL - Seattle, August 1 st, 2001 46
Modeling language metamodel ATAL - Seattle, August 1 st, 2001 46
 Metamodel A detailed definition is available for the early and late requiremet models. Tropos conceptual entities (actors, goals, softgoals, …) of a tropos model are seen as instances of classes in a metamodel described by UML class diagrams. ATAL - Seattle, August 1 st, 2001 47
Metamodel A detailed definition is available for the early and late requiremet models. Tropos conceptual entities (actors, goals, softgoals, …) of a tropos model are seen as instances of classes in a metamodel described by UML class diagrams. ATAL - Seattle, August 1 st, 2001 47
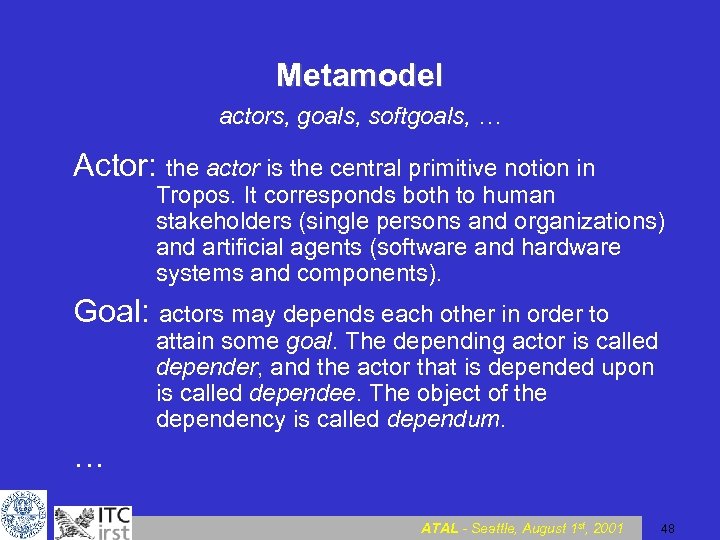 Metamodel actors, goals, softgoals, … Actor: the actor is the central primitive notion in Tropos. It corresponds both to human stakeholders (single persons and organizations) and artificial agents (software and hardware systems and components). Goal: actors may depends each other in order to attain some goal. The depending actor is called depender, and the actor that is depended upon is called dependee. The object of the dependency is called dependum. … ATAL - Seattle, August 1 st, 2001 48
Metamodel actors, goals, softgoals, … Actor: the actor is the central primitive notion in Tropos. It corresponds both to human stakeholders (single persons and organizations) and artificial agents (software and hardware systems and components). Goal: actors may depends each other in order to attain some goal. The depending actor is called depender, and the actor that is depended upon is called dependee. The object of the dependency is called dependum. … ATAL - Seattle, August 1 st, 2001 48
 Metamodel Entity ATAL - Seattle, August 1 st, 2001 49
Metamodel Entity ATAL - Seattle, August 1 st, 2001 49
 Metamodel N-ary Relatioship ATAL - Seattle, August 1 st, 2001 50
Metamodel N-ary Relatioship ATAL - Seattle, August 1 st, 2001 50
 Metamodel Actor ATAL - Seattle, August 1 st, 2001 51
Metamodel Actor ATAL - Seattle, August 1 st, 2001 51
 Metamodel Goal ATAL - Seattle, August 1 st, 2001 52
Metamodel Goal ATAL - Seattle, August 1 st, 2001 52
 Metamodel Plan ATAL - Seattle, August 1 st, 2001 53
Metamodel Plan ATAL - Seattle, August 1 st, 2001 53
 Transformational approach ATAL - Seattle, August 1 st, 2001 54
Transformational approach ATAL - Seattle, August 1 st, 2001 54
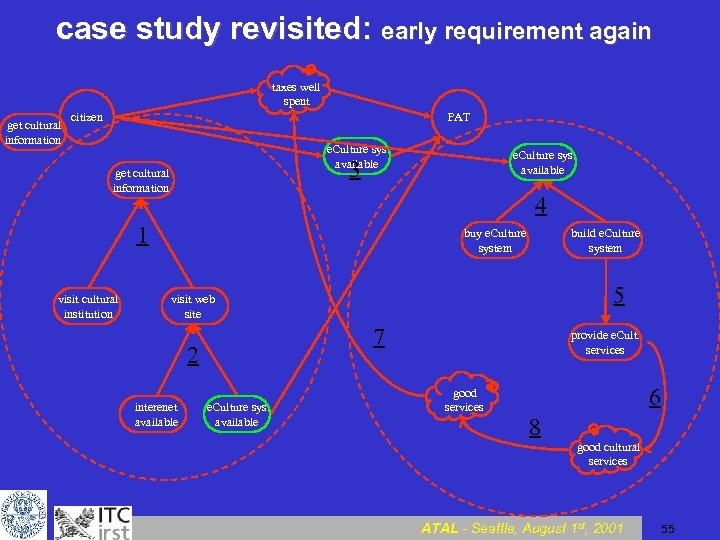 case study revisited: early requirement again taxes well spent get cultural information citizen PAT e. Culture sys. available 3 get cultural information 4 1 visit cultural institution e. Culture sys. available buy e. Culture system build e. Culture system 5 visit web site 7 2 interenet available e. Culture sys. available provide e. Cult. services good services 6 8 good cultural services ATAL - Seattle, August 1 st, 2001 55
case study revisited: early requirement again taxes well spent get cultural information citizen PAT e. Culture sys. available 3 get cultural information 4 1 visit cultural institution e. Culture sys. available buy e. Culture system build e. Culture system 5 visit web site 7 2 interenet available e. Culture sys. available provide e. Cult. services good services 6 8 good cultural services ATAL - Seattle, August 1 st, 2001 55
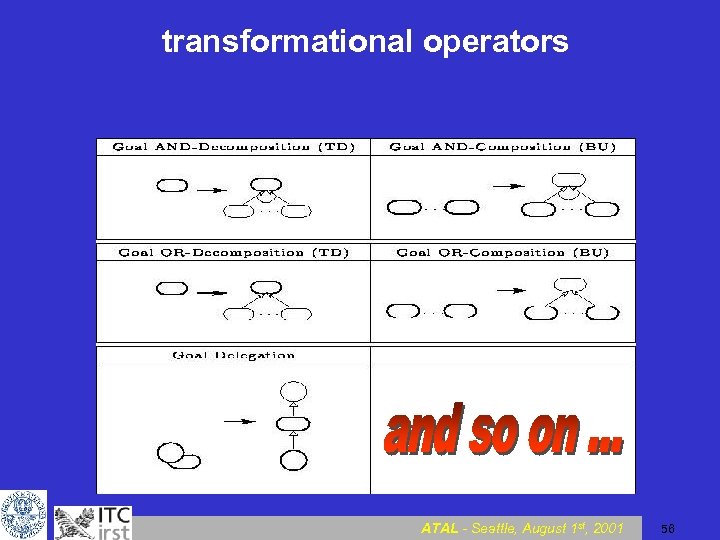 transformational operators ATAL - Seattle, August 1 st, 2001 56
transformational operators ATAL - Seattle, August 1 st, 2001 56
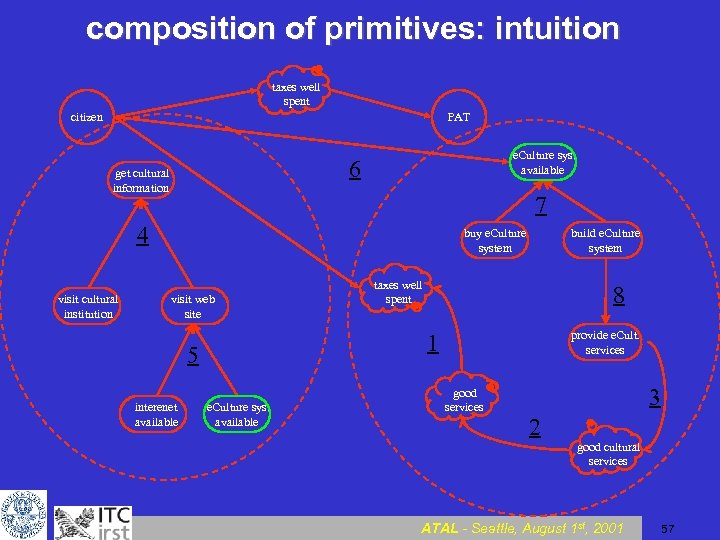 composition of primitives: intuition taxes well spent citizen PAT e. Culture sys. available 6 get cultural information 7 4 visit cultural institution buy e. Culture system visit web site taxes well spent 8 provide e. Cult. services 1 5 interenet available build e. Culture system e. Culture sys. available good services 3 2 good cultural services ATAL - Seattle, August 1 st, 2001 57
composition of primitives: intuition taxes well spent citizen PAT e. Culture sys. available 6 get cultural information 7 4 visit cultural institution buy e. Culture system visit web site taxes well spent 8 provide e. Cult. services 1 5 interenet available build e. Culture system e. Culture sys. available good services 3 2 good cultural services ATAL - Seattle, August 1 st, 2001 57
 composition of primitives: intuition • Different transformation sequences may have different chances to lead to a satisfactory design; • even when the same design is obtained, different transformation sequences in the design process may lead at discovering/facing/discarding relevant elements at different times; • different analyses may have different costs; • balancing analysis costs and good results is a hard (human) planning task. ATAL - Seattle, August 1 st, 2001 58
composition of primitives: intuition • Different transformation sequences may have different chances to lead to a satisfactory design; • even when the same design is obtained, different transformation sequences in the design process may lead at discovering/facing/discarding relevant elements at different times; • different analyses may have different costs; • balancing analysis costs and good results is a hard (human) planning task. ATAL - Seattle, August 1 st, 2001 58
 Conclusion ATAL - Seattle, August 1 st, 2001 59
Conclusion ATAL - Seattle, August 1 st, 2001 59
 Conclusion The Tropos framework is a novel approach in Agent Oriented Software Engineering, resting on the following 3 key ideas: – the Tropos approach framework spans the overall software development process, from early requirements down to implementation – we use the notion of agent and all the related mentalistic notions in all phases of software development – we adopt a transformational approach, i. e. , we perform refinement steps, inside one phase or between phases, using a set of transformation operators ATAL - Seattle, August 1 st, 2001 60
Conclusion The Tropos framework is a novel approach in Agent Oriented Software Engineering, resting on the following 3 key ideas: – the Tropos approach framework spans the overall software development process, from early requirements down to implementation – we use the notion of agent and all the related mentalistic notions in all phases of software development – we adopt a transformational approach, i. e. , we perform refinement steps, inside one phase or between phases, using a set of transformation operators ATAL - Seattle, August 1 st, 2001 60
 Related work ATAL - Seattle, August 1 st, 2001 61
Related work ATAL - Seattle, August 1 st, 2001 61
 Related work 1) 2) 3) AOSE OOP Requirement engineering ATAL - Seattle, August 1 st, 2001 62
Related work 1) 2) 3) AOSE OOP Requirement engineering ATAL - Seattle, August 1 st, 2001 62
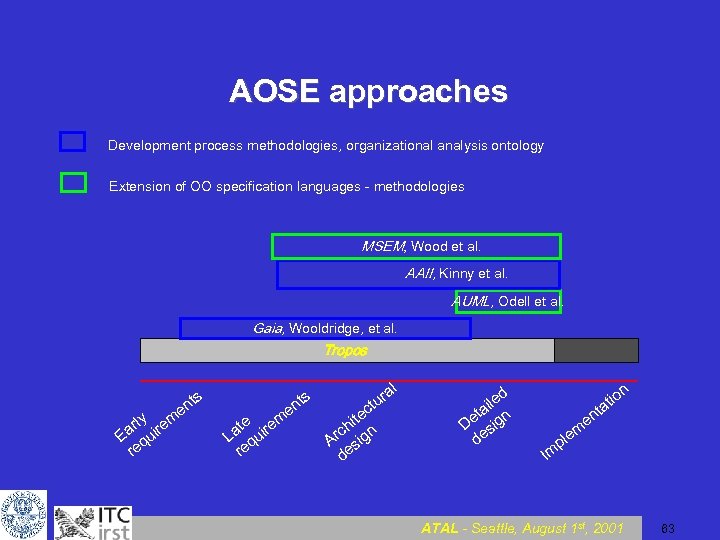 AOSE approaches Development process methodologies, organizational analysis ontology Extension of OO specification languages - methodologies MSEM, Wood et al. AAII, Kinny et al. AUML, Odell et al. Gaia, Wooldridge, et al. Tropos ly m ar uire E q re e s nt te r La qui re em e s nt al r ctu te hi n c Ar sig de d ile a et ign D s de n io at t en m e pl Im ATAL - Seattle, August 1 st, 2001 63
AOSE approaches Development process methodologies, organizational analysis ontology Extension of OO specification languages - methodologies MSEM, Wood et al. AAII, Kinny et al. AUML, Odell et al. Gaia, Wooldridge, et al. Tropos ly m ar uire E q re e s nt te r La qui re em e s nt al r ctu te hi n c Ar sig de d ile a et ign D s de n io at t en m e pl Im ATAL - Seattle, August 1 st, 2001 63
 Future work ATAL - Seattle, August 1 st, 2001 64
Future work ATAL - Seattle, August 1 st, 2001 64
 Future work • Formal Tropos • Architectural patterns • Formalization of the transformational approach (primitives and strategies) ATAL - Seattle, August 1 st, 2001 65
Future work • Formal Tropos • Architectural patterns • Formalization of the transformational approach (primitives and strategies) ATAL - Seattle, August 1 st, 2001 65
 The Tropos group Fausto Giunchiglia, Paolo Giorgini, Fabrizio Sannicoló University of Trento - Dept. of information and communication technology Paolo Bresciani, Anna Perini, Marco Pistore, Paolo Traverso SRA Division at ITC-IRST John Mylopoulos, Eric Yu, Manuel Kolp, Luiz Cysneiros, Ariel D. Fuxman Computer Science Dept. - University of Toronto Yves Lespérance York University, Toronto Jaelson Castro Universidade Federale de Pernambuco, Recife, Brazil Daniel Gross, Linda Lin Faculty of information Studies, University of Toronto ATAL - Seattle, August 1 st, 2001 66
The Tropos group Fausto Giunchiglia, Paolo Giorgini, Fabrizio Sannicoló University of Trento - Dept. of information and communication technology Paolo Bresciani, Anna Perini, Marco Pistore, Paolo Traverso SRA Division at ITC-IRST John Mylopoulos, Eric Yu, Manuel Kolp, Luiz Cysneiros, Ariel D. Fuxman Computer Science Dept. - University of Toronto Yves Lespérance York University, Toronto Jaelson Castro Universidade Federale de Pernambuco, Recife, Brazil Daniel Gross, Linda Lin Faculty of information Studies, University of Toronto ATAL - Seattle, August 1 st, 2001 66
![The Tropos framework where to find what I talked about [1] A. Perini, P. The Tropos framework where to find what I talked about [1] A. Perini, P.](https://present5.com/presentation/bf68f6537dbf1651f7710fa1f056c348/image-67.jpg) The Tropos framework where to find what I talked about [1] A. Perini, P. Bresciani, F. Giunchiglia, P. Giorgini and J. Mylopoulos, A Knowledge Level Software Engineering Methodology for Agent Oriented Programming. Proc. Int. Conf. Agents 2001 [2] P. Bresciani, A. Perini, P. Giorgini, F. Giunchiglia, J. Mylopoulos, Modeling early requirements in Tropos: a transformation based approach. AOSE workshop at Conf. Agents 2001 [3] P. Giorgini, A. Perini, J. Mylopoulos, F. Giunchiglia, P. Bresciani. Agent Oriented Software Development: A Case Study. Proc. Int. Conf. on Software Engineering & Knowledge Engineering (SEKE 01), 2001 [4] A. Fuxman, M. Pistore, J. Mylopoulos, P. Traverso. Model Checking Early Requirements Specifications in Tropos. IEEE Int. Symp. on Requirements Engineering, 2001 [5] M. Kolp, P. Giorgini, J. Mylopoulos. A Goal Based Organizational Perspective on Multi Agent Architectures. Proc. Int. Workshop ATAL-2001 ATAL - Seattle, August 1 st, 2001 67
The Tropos framework where to find what I talked about [1] A. Perini, P. Bresciani, F. Giunchiglia, P. Giorgini and J. Mylopoulos, A Knowledge Level Software Engineering Methodology for Agent Oriented Programming. Proc. Int. Conf. Agents 2001 [2] P. Bresciani, A. Perini, P. Giorgini, F. Giunchiglia, J. Mylopoulos, Modeling early requirements in Tropos: a transformation based approach. AOSE workshop at Conf. Agents 2001 [3] P. Giorgini, A. Perini, J. Mylopoulos, F. Giunchiglia, P. Bresciani. Agent Oriented Software Development: A Case Study. Proc. Int. Conf. on Software Engineering & Knowledge Engineering (SEKE 01), 2001 [4] A. Fuxman, M. Pistore, J. Mylopoulos, P. Traverso. Model Checking Early Requirements Specifications in Tropos. IEEE Int. Symp. on Requirements Engineering, 2001 [5] M. Kolp, P. Giorgini, J. Mylopoulos. A Goal Based Organizational Perspective on Multi Agent Architectures. Proc. Int. Workshop ATAL-2001 ATAL - Seattle, August 1 st, 2001 67


