1cdebb7970dd95181f32ecd8f3f2df41.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 18
 A Hyper-Heuristic Multi-Criteria Decision Support System for Ecoefficient Product life Cycle. John R. Woodward (Computer Science) and Nabil Gindy (Engineering) The University of Nottingham Ningbo China (UNNC)
A Hyper-Heuristic Multi-Criteria Decision Support System for Ecoefficient Product life Cycle. John R. Woodward (Computer Science) and Nabil Gindy (Engineering) The University of Nottingham Ningbo China (UNNC)
 OUTLINE • Problem of eco-friendly design. – Complex interacting systems – Missing data? – Ill defined problem – no overall measure. Decision Support – analytical hierarchical process. Machine Learning – Heuristics – Genetic Programming
OUTLINE • Problem of eco-friendly design. – Complex interacting systems – Missing data? – Ill defined problem – no overall measure. Decision Support – analytical hierarchical process. Machine Learning – Heuristics – Genetic Programming
 Key Points • To use decision support system to steer the designer away from eco-unfriendly designs at all stages in the design and manufacturing process, saving the designer time. Some problems 1. No agreed measure of environmental impact. 2. Concrete data may be unavailable. 3. Multi-dimensional Pareto design front. Ill defined problem by its very nature.
Key Points • To use decision support system to steer the designer away from eco-unfriendly designs at all stages in the design and manufacturing process, saving the designer time. Some problems 1. No agreed measure of environmental impact. 2. Concrete data may be unavailable. 3. Multi-dimensional Pareto design front. Ill defined problem by its very nature.
 Problems • An in-depth understanding of design. • And in-depth understanding of food-webs and ecological niches etc. • This is a complex system of interactions. • How do we manage unforeseen consequences. • Analytical hieratical processes is one way of combining different experts from the same field and different fields.
Problems • An in-depth understanding of design. • And in-depth understanding of food-webs and ecological niches etc. • This is a complex system of interactions. • How do we manage unforeseen consequences. • Analytical hieratical processes is one way of combining different experts from the same field and different fields.
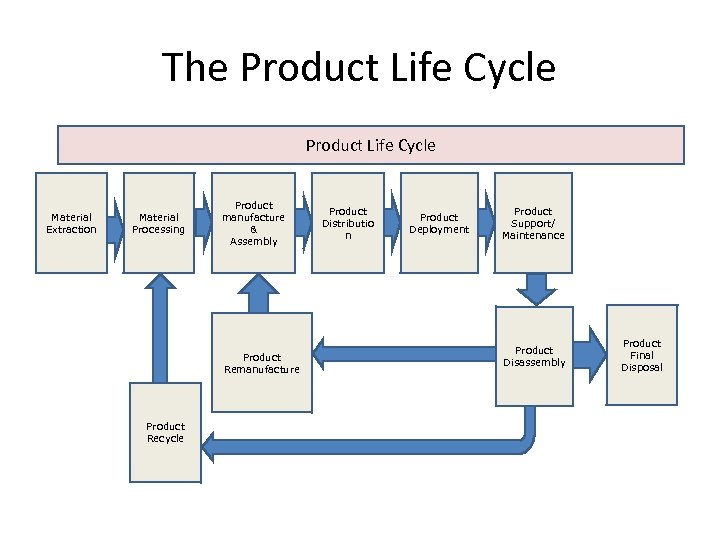 The Product Life Cycle Material Extraction Material Processing Product manufacture & Assembly Product Remanufacture Product Recycle Product Distributio n Product Deployment Product Support/ Maintenance Product Disassembly Product Final Disposal
The Product Life Cycle Material Extraction Material Processing Product manufacture & Assembly Product Remanufacture Product Recycle Product Distributio n Product Deployment Product Support/ Maintenance Product Disassembly Product Final Disposal
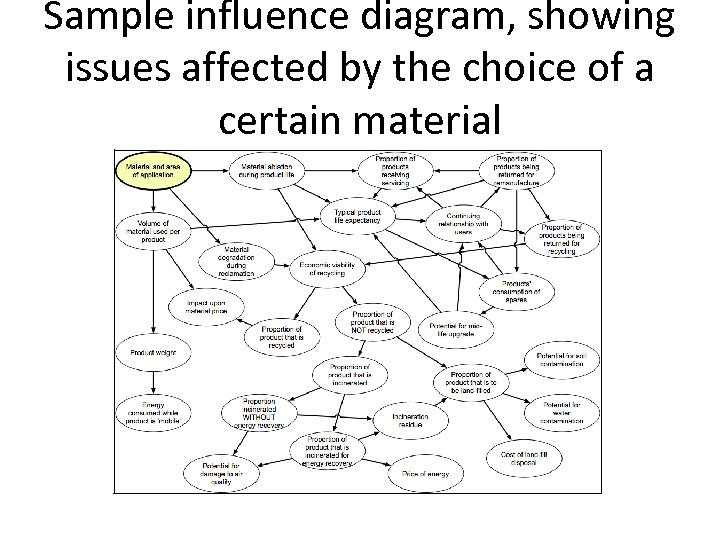 Sample influence diagram, showing issues affected by the choice of a certain material
Sample influence diagram, showing issues affected by the choice of a certain material
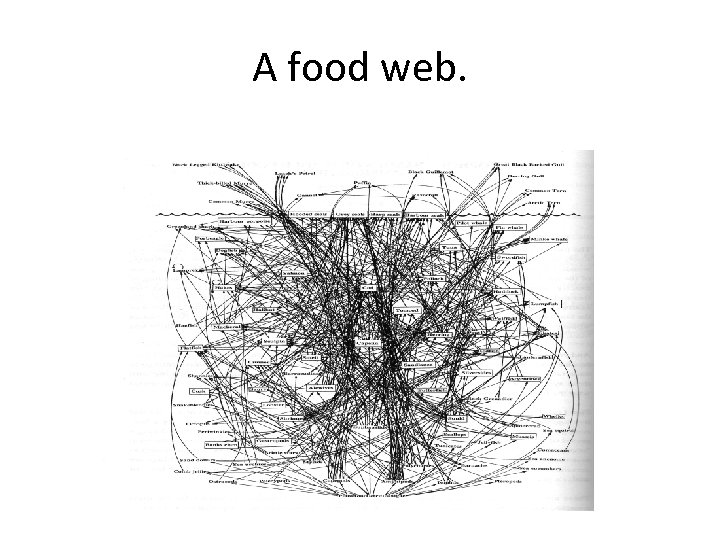 A food web.
A food web.
 Problem of choosing Nappies • Do I use reusable nappies or disposable? • The cost of each is easy to calculate – a simple linear programming decision making process. • But what is the environmental cost of each choice? • Financial cost is immediate and transparent. • Environmental cost is delayed and opaque.
Problem of choosing Nappies • Do I use reusable nappies or disposable? • The cost of each is easy to calculate – a simple linear programming decision making process. • But what is the environmental cost of each choice? • Financial cost is immediate and transparent. • Environmental cost is delayed and opaque.
 No agreed measures (energy? NO NO NO). • Carbon emissions, Oil points scale, energy (? ). • These are quantifiable. • How do we quantify the “loss of biodiversity” against the clean-up cost of a river. • Are we trying to compare apples and pairs. • We do not have a universal measure of environmental impact – and we never will! (too complicated and multi-dimensional).
No agreed measures (energy? NO NO NO). • Carbon emissions, Oil points scale, energy (? ). • These are quantifiable. • How do we quantify the “loss of biodiversity” against the clean-up cost of a river. • Are we trying to compare apples and pairs. • We do not have a universal measure of environmental impact – and we never will! (too complicated and multi-dimensional).
 Concrete data may be unavailable. • Even if we did have an agreed measure – sometimes we could not calculate it and data is not available. • Data may be unavailable so need to combine the opinions of experts. • Statistical methods of ranking ect could be employed to deal with these decisions.
Concrete data may be unavailable. • Even if we did have an agreed measure – sometimes we could not calculate it and data is not available. • Data may be unavailable so need to combine the opinions of experts. • Statistical methods of ranking ect could be employed to deal with these decisions.
 Decision Support 1 • • An algorithm or software. Does not make decisions for us. Supports human decision making. Not trying to model cognitive processes. Decision support is already used in many areas. Method – analytical hierarchical process. Example – university careers advisor – marriage guidance (? ).
Decision Support 1 • • An algorithm or software. Does not make decisions for us. Supports human decision making. Not trying to model cognitive processes. Decision support is already used in many areas. Method – analytical hierarchical process. Example – university careers advisor – marriage guidance (? ).
 Decision Support 2 • The knowledge does not exist in the mind of a single expert, but in the minds of a society of experts who may be distributed geographically and culturally and racially. • A decision support system is a way to overcome this, bringing together the collective knowledge.
Decision Support 2 • The knowledge does not exist in the mind of a single expert, but in the minds of a society of experts who may be distributed geographically and culturally and racially. • A decision support system is a way to overcome this, bringing together the collective knowledge.
 Machine Learning • Machine Learning offers a number of techniques to assist decision support. • E. g. fuzzy data, missing values, unknown values. • statistical underpinning. • GP as HH can construct and decompose human designed heuristics.
Machine Learning • Machine Learning offers a number of techniques to assist decision support. • E. g. fuzzy data, missing values, unknown values. • statistical underpinning. • GP as HH can construct and decompose human designed heuristics.
 Heuristics and Hyper-Heristics • Heuristic is a rule of thumb, e. g. don’t buy the cheapest wine on a restaurant menu. • Heuristic has a strict computational definition. • A heuristic can be thought of as an approximation. • Hyper-heuristics is a machine learning methodology of combining atomic heuristics. • Collections of heuristics can outperform single heuristics. (an AHP is just a heuristic!!!)
Heuristics and Hyper-Heristics • Heuristic is a rule of thumb, e. g. don’t buy the cheapest wine on a restaurant menu. • Heuristic has a strict computational definition. • A heuristic can be thought of as an approximation. • Hyper-heuristics is a machine learning methodology of combining atomic heuristics. • Collections of heuristics can outperform single heuristics. (an AHP is just a heuristic!!!)
 Genetic Programming • Genetic Programming generates programs at random and uses “survival of the fittest” to produce programs for a purpose. • Like selective breeding of dogs, cattle etc. • The representation is understandable by humans (so some extent), unlike say artificial neural nets. • Human competitive solutions are now being produced. • We can evolve heuristics
Genetic Programming • Genetic Programming generates programs at random and uses “survival of the fittest” to produce programs for a purpose. • Like selective breeding of dogs, cattle etc. • The representation is understandable by humans (so some extent), unlike say artificial neural nets. • Human competitive solutions are now being produced. • We can evolve heuristics
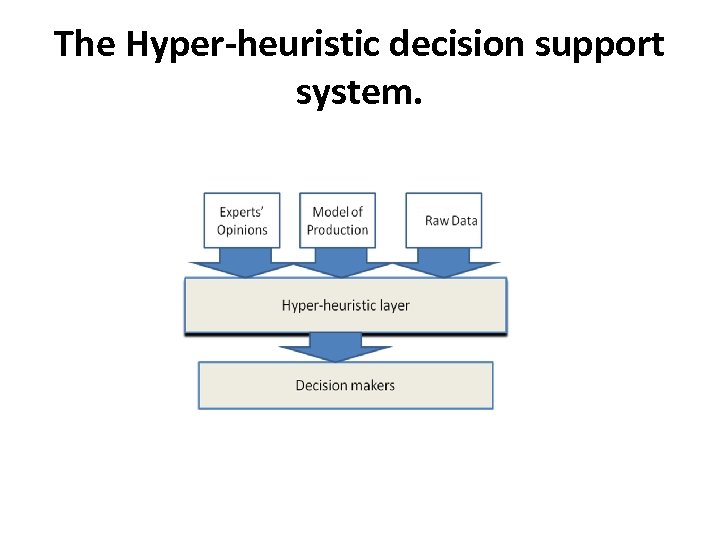 The Hyper-heuristic decision support system.
The Hyper-heuristic decision support system.
 Issues • Pareto front of design solutions. • Weighting criteria leads to ‘holes’ in the design front. • Clustering algorithms may decide what are important exemplars at the Pareto front. • Dealing with different levels of measurement (Discrete, Categorical, Nominal, and Ordinal) • Validation of the model? • On-line learning and unsupervised learning.
Issues • Pareto front of design solutions. • Weighting criteria leads to ‘holes’ in the design front. • Clustering algorithms may decide what are important exemplars at the Pareto front. • Dealing with different levels of measurement (Discrete, Categorical, Nominal, and Ordinal) • Validation of the model? • On-line learning and unsupervised learning.
 Summary • Eco-friendly design is difficult and requires some sort of decision support. • AHP is just one decision heuristic. • Genetic Programming can supplement human designed heuristics – an already established framework. • There are interesting issues machine learning can assist the design process.
Summary • Eco-friendly design is difficult and requires some sort of decision support. • AHP is just one decision heuristic. • Genetic Programming can supplement human designed heuristics – an already established framework. • There are interesting issues machine learning can assist the design process.


